ef5216ec9a2c847fbefb78f470375c09.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 23

Reliable Data Delivery Protocol (RDDP) William Anderson MEI Technologies Inc. 2006 MAPLD International Conference Washington, D. C. September 25, 2006 MAPLD International Conference 1 Space. Wire 101 Seminar
Reliable Data Delivery Protocol (RDDP) Introduction • Purpose – Provide a means of ensuring correct packet delivery from source to destination by • Acknowledgement from receiver • Selective Retransmit based on ACK timeout – Used over Space. Wire (Sp. W) – Minimize packet overhead – Be generic in nature • Developed to use Protocol ID (PID) standardized by ECSS-E-50 -11 – Permanent Protocol ID request pending • Developed by Geostationary Environmental Satellite (GOES) -R series project – Protocol developed to meet project data loss requirement 2006 MAPLD International Conference 2 Space. Wire 101 Seminar
RDDP Modes • Nominal Mode – Reliable Delivery – Acknowledge (ACK) every good packet • Urgent Message Mode – No ACKS & No Retransmits, fire and forget 2006 MAPLD International Conference 3 Space. Wire 101 Seminar

How It Works • The protocol provides multiple virtual channels multiplexed over a single Space. Wire connection. • Each virtual channel is independent of all other channels. • Channels should have allocated buffer space, and parameters set for each channel. • After ACK timeout, selective retransmit can occur. 2006 MAPLD International Conference 4 Space. Wire 101 Seminar
How It Works Transmitter • XMTR establishes link by sending a RESET to the receiver – RCVR never sends RESET, XMTR never receives RESET • XMTR may send up to Window Size packets ahead of last ACK • After ACK timeout, retransmit up to Max Retries number of times • After Max Retries is exhausted, notify host and quit. Host may issue RESET 2006 MAPLD International Conference 5 Space. Wire 101 Seminar

How It Works Receiver • Receiver sends ACK for every error free packet – No EOP, no CRC error, valid header • Receiver orders Reliable Delivery packets and eliminates duplicates • Receiver does not close or RESET a channel • Receiver may wait forever to receive opening RESET or next valid packet 2006 MAPLD International Conference 6 Space. Wire 101 Seminar

RDDP Features • 2 -Dword header. • Programmable parameters – sliding window size, timeouts, and retries. • 8 Bit CRC. 2006 MAPLD International Conference 7 Space. Wire 101 Seminar
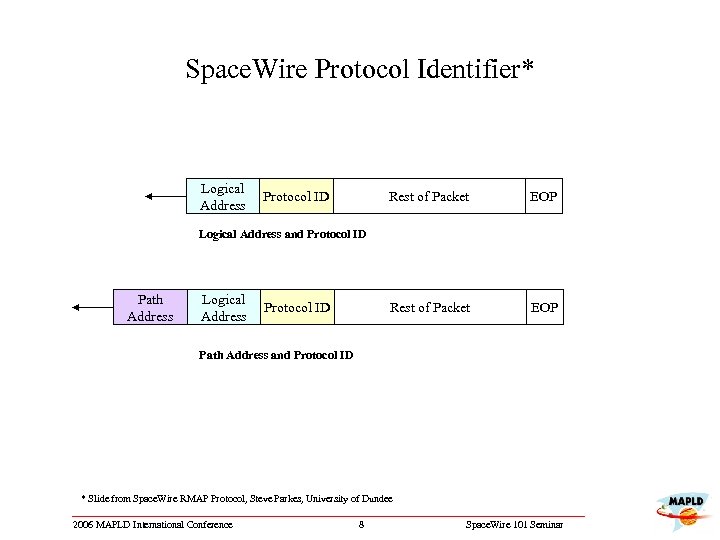
Space. Wire Protocol Identifier* Logical Address Protocol ID Rest of Packet EOP Logical Address and Protocol ID Path Address Logical Address Protocol ID Path Address and Protocol ID * Slide from Space. Wire RMAP Protocol, Steve Parkes, University of Dundee 2006 MAPLD International Conference 8 Space. Wire 101 Seminar
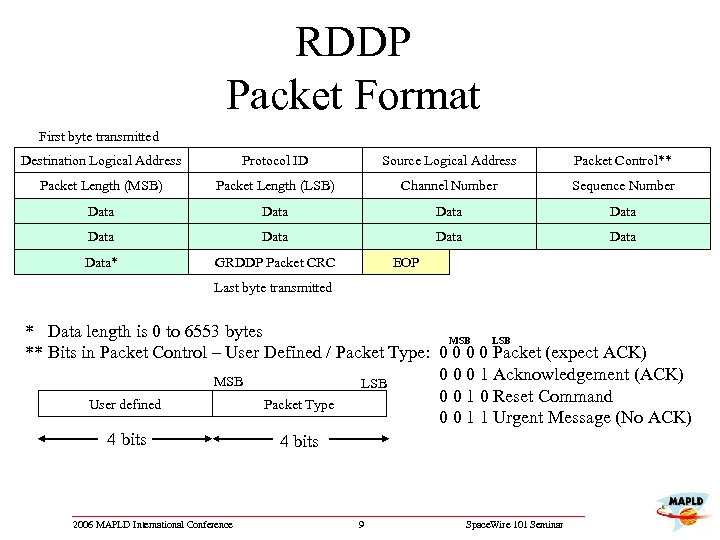
RDDP Packet Format First byte transmitted Destination Logical Address Protocol ID Source Logical Address Packet Control** Packet Length (MSB) Packet Length (LSB) Channel Number Sequence Number Data Data Data* GRDDP Packet CRC EOP Last byte transmitted * Data length is 0 to 6553 bytes MSB LSB ** Bits in Packet Control – User Defined / Packet Type: 0 0 Packet (expect ACK) 0 0 0 1 Acknowledgement (ACK) MSB LSB 0 0 1 0 Reset Command User defined Packet Type 0 0 1 1 Urgent Message (No ACK) 4 bits 2006 MAPLD International Conference 9 Space. Wire 101 Seminar
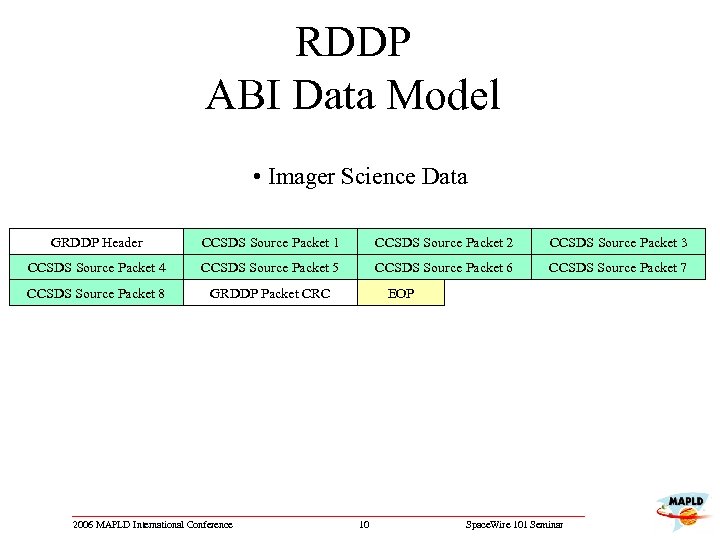
RDDP ABI Data Model • Imager Science Data GRDDP Header CCSDS Source Packet 1 CCSDS Source Packet 2 CCSDS Source Packet 3 CCSDS Source Packet 4 CCSDS Source Packet 5 CCSDS Source Packet 6 CCSDS Source Packet 7 CCSDS Source Packet 8 GRDDP Packet CRC 2006 MAPLD International Conference EOP 10 Space. Wire 101 Seminar
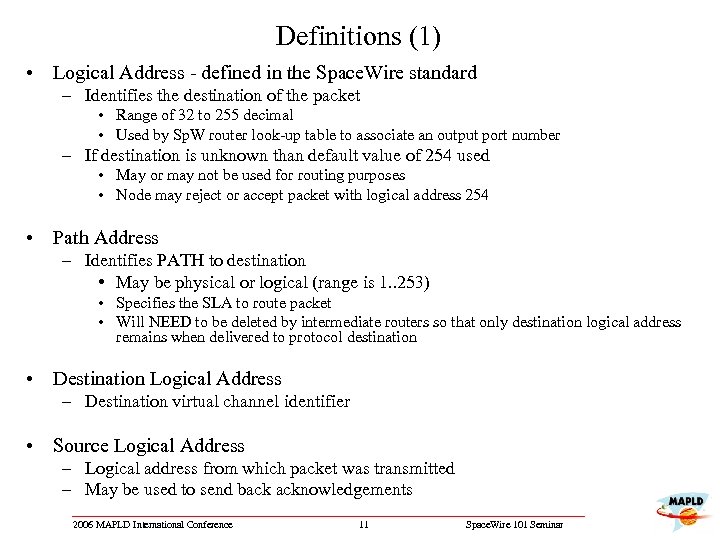
Definitions (1) • Logical Address - defined in the Space. Wire standard – Identifies the destination of the packet • Range of 32 to 255 decimal • Used by Sp. W router look-up table to associate an output port number – If destination is unknown than default value of 254 used • May or may not be used for routing purposes • Node may reject or accept packet with logical address 254 • Path Address – Identifies PATH to destination • May be physical or logical (range is 1. . 253) • Specifies the SLA to route packet • Will NEED to be deleted by intermediate routers so that only destination logical address remains when delivered to protocol destination • Destination Logical Address – Destination virtual channel identifier • Source Logical Address – Logical address from which packet was transmitted – May be used to send back acknowledgements 2006 MAPLD International Conference 11 Space. Wire 101 Seminar
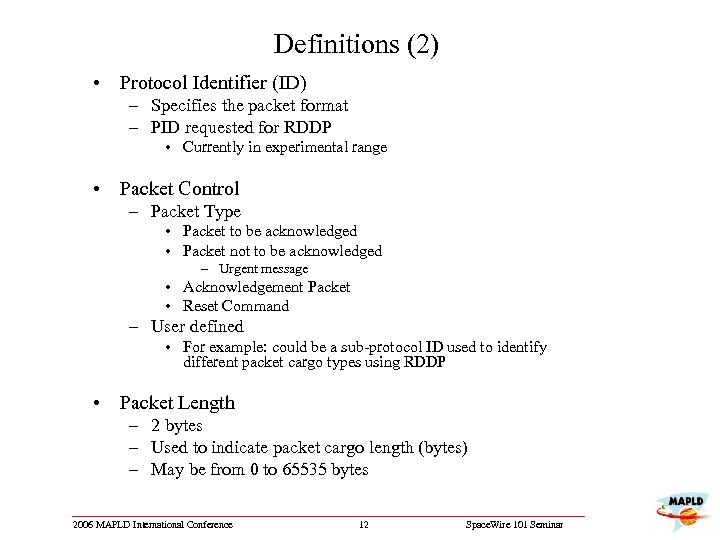
Definitions (2) • Protocol Identifier (ID) – Specifies the packet format – PID requested for RDDP • Currently in experimental range • Packet Control – Packet Type • Packet to be acknowledged • Packet not to be acknowledged – Urgent message • Acknowledgement Packet • Reset Command – User defined • For example: could be a sub-protocol ID used to identify different packet cargo types using RDDP • Packet Length – 2 bytes – Used to indicate packet cargo length (bytes) – May be from 0 to 65535 bytes 2006 MAPLD International Conference 12 Space. Wire 101 Seminar
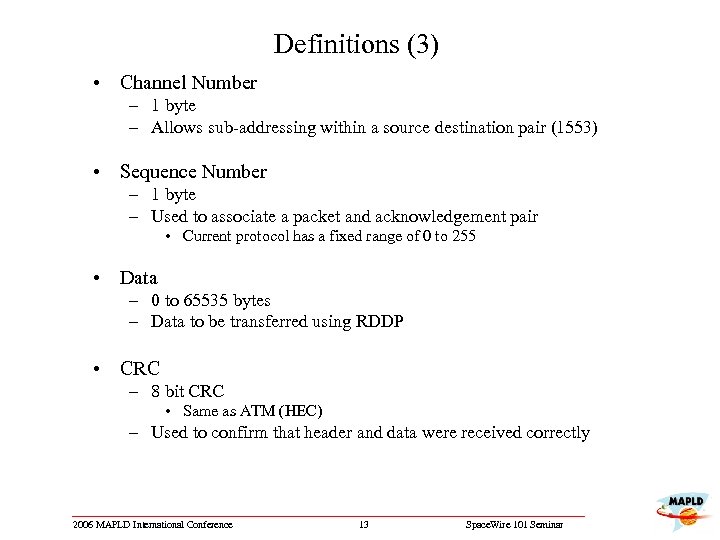
Definitions (3) • Channel Number – 1 byte – Allows sub-addressing within a source destination pair (1553) • Sequence Number – 1 byte – Used to associate a packet and acknowledgement pair • Current protocol has a fixed range of 0 to 255 • Data – 0 to 65535 bytes – Data to be transferred using RDDP • CRC – 8 bit CRC • Same as ATM (HEC) – Used to confirm that header and data were received correctly 2006 MAPLD International Conference 13 Space. Wire 101 Seminar

Sliding Window The RDDP Utilizes Selective Retransmit • The sliding window allows users to improve bandwidth efficiency. -- Gets around send and wait for ACK. -- Window size, timeouts, and number of retries can be tuned for maximum efficiency --- Window size should be half sequence number. • Allows reordering packets if received out of sequence. • Detects duplicate packets. 2006 MAPLD International Conference 14 Space. Wire 101 Seminar
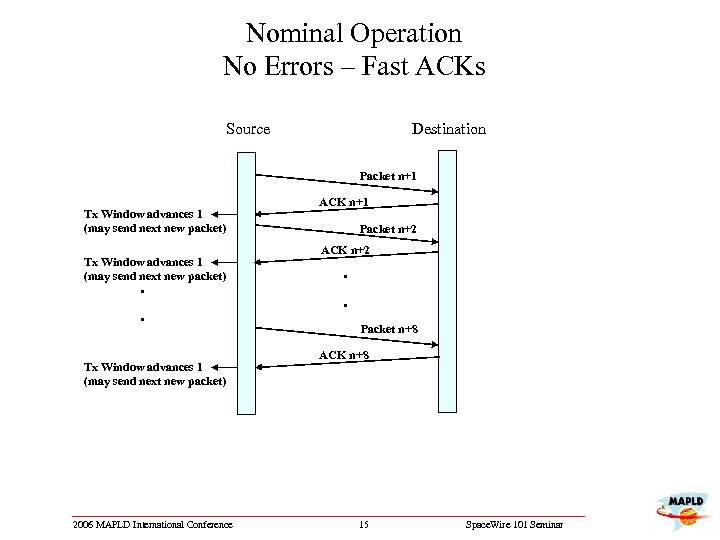
Nominal Operation No Errors – Fast ACKs Source Destination Packet n+1 Tx Window advances 1 (may send next new packet) . . Tx Window advances 1 (may send next new packet) 2006 MAPLD International Conference ACK n+1 Packet n+2 ACK n+2 . . Packet n+8 ACK n+8 15 Space. Wire 101 Seminar
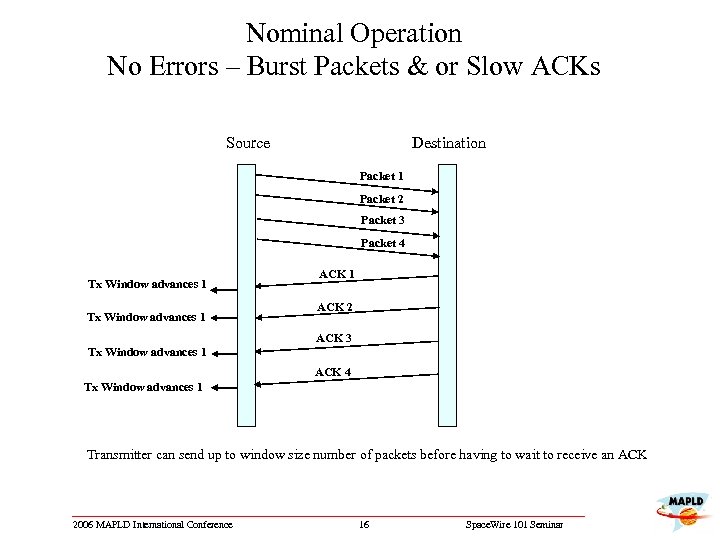
Nominal Operation No Errors – Burst Packets & or Slow ACKs Source Destination Packet 1 Packet 2 Packet 3 Packet 4 Tx Window advances 1 ACK 2 ACK 3 Tx Window advances 1 ACK 4 Tx Window advances 1 Transmitter can send up to window size number of packets before having to wait to receive an ACK 2006 MAPLD International Conference 16 Space. Wire 101 Seminar
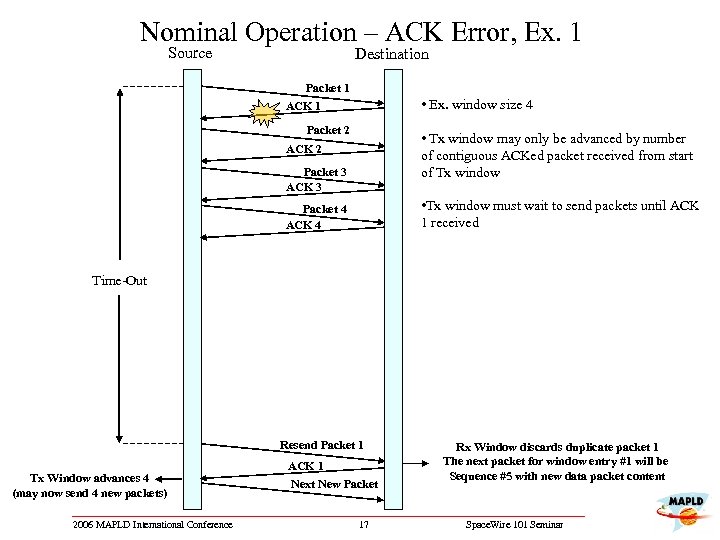
Nominal Operation – ACK Error, Ex. 1 Source Destination Packet 1 ACK 1 • Ex. window size 4 Packet 2 • Tx window may only be advanced by number of contiguous ACKed packet received from start of Tx window ACK 2 Packet 3 ACK 3 • Tx window must wait to send packets until ACK 1 received Packet 4 ACK 4 Time-Out Resend Packet 1 Tx Window advances 4 (may now send 4 new packets) 2006 MAPLD International Conference ACK 1 Next New Packet 17 Rx Window discards duplicate packet 1 The next packet for window entry #1 will be Sequence #5 with new data packet content Space. Wire 101 Seminar
GOES-R Reliable Data Delivery Protocol - Platforms • The GOES-R RDDP is now running on 3 hardware configurations • Development and testing has been SWTS to SWTS and SWTS to BAE ASIC – FPGA based Space. Wire Test Set (SWTS) • NASA Sp. W core • Windows PCI workstation – BAE Systems Sp. W ASIC integrated onto commercial PC board • NASA Sp. W core • PCI Windows workstation – BAE Systems Sp. W ASIC integrated onto flight board (ITT/ABI Rev A. ) • c. PCI form factor • Uses RAD 750 over c. PCI • Vx. Works 2006 MAPLD International Conference 18 Space. Wire 101 Seminar
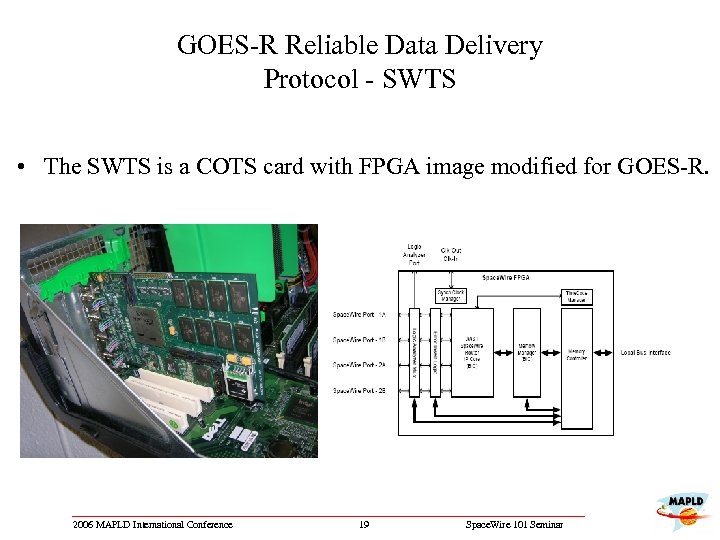
GOES-R Reliable Data Delivery Protocol - SWTS • The SWTS is a COTS card with FPGA image modified for GOES-R. 2006 MAPLD International Conference 19 Space. Wire 101 Seminar
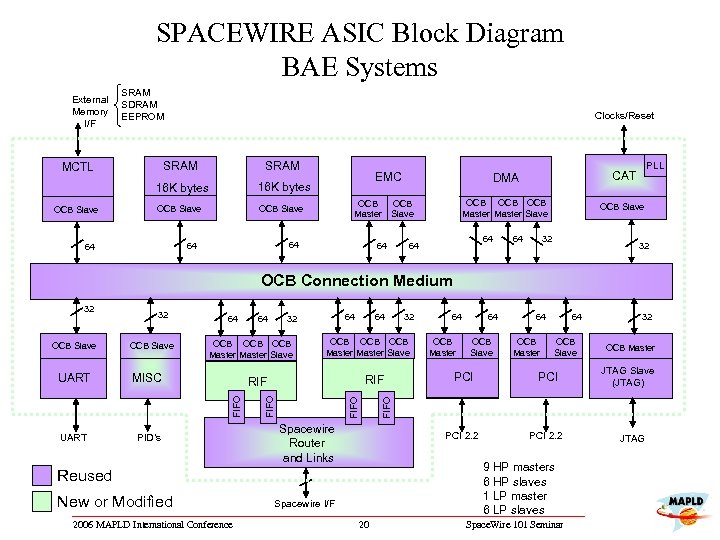
SPACEWIRE ASIC Block Diagram BAE Systems External Memory I/F SRAM SDRAM EEPROM Clocks/Reset SRAM 16 K bytes OCB Slave MCTL OCB Slave 64 64 64 OCB Master CAT OCB OCB Master Slave OCB Slave 64 PLL DMA OCB Slave EMC 64 64 64 32 32 OCB Connection Medium MISC UART PID’s 64 32 OCB OCB Master Slave 64 2006 MAPLD International Conference 64 OCB Master 64 OCB Slave Spacewire Router and Links PCI PCI 2. 2 RIF PCI 2. 2 9 HP masters 6 HP slaves 1 LP master 6 LP slaves Reused New or Modified 32 OCB OCB Master Slave RIF FIFO UART 64 Spacewire I/F 20 32 OCB Master JTAG Slave (JTAG) FIFO OCB Slave 64 FIFO OCB Slave 32 FIFO 32 Space. Wire 101 Seminar JTAG

GOES-R Reliable Data Delivery Protocol – ASIC Test Card 2006 MAPLD International Conference 21 Space. Wire 101 Seminar
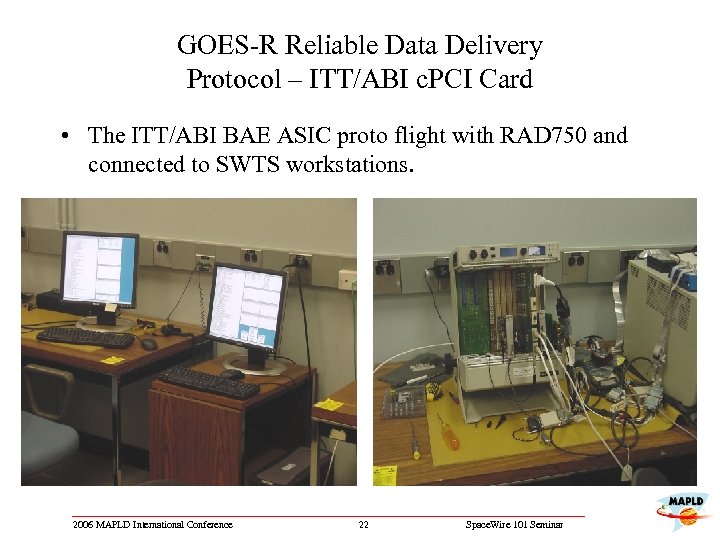
GOES-R Reliable Data Delivery Protocol – ITT/ABI c. PCI Card • The ITT/ABI BAE ASIC proto flight with RAD 750 and connected to SWTS workstations. 2006 MAPLD International Conference 22 Space. Wire 101 Seminar

RDDP Team Bill Anderson – GOES-R C&DH Lead Engineer Craig Bearer – GOES-R C&DH Engineer – Software Marco Figueiredo – GOES-R Senior Hardware Engineer Eric Lynum – GOES-R Electrical Design Engineer Dan May – GOES-R Test Engineer Glenn Rakow – GSFC Space. Wire Consultant Jeffrey A. Kronenwetter– GOES-R ABI System Engineer Alexander Krimchansky – GOES-R Systems Manager 2006 MAPLD International Conference 23 Space. Wire 101 Seminar
ef5216ec9a2c847fbefb78f470375c09.ppt