b966254d45da7a0d033be7dbf47c4f62.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 16
 Relevant Revenues, Relevant Costs, and the Decision Process
Relevant Revenues, Relevant Costs, and the Decision Process
 Relevant Costs and Relevant Revenues Relevant Costs Expected future costs that differ among alternative courses of action Relevant Revenues Expected future revenues that differ among alternative courses of action * Differential or Net Relevant Costs 2
Relevant Costs and Relevant Revenues Relevant Costs Expected future costs that differ among alternative courses of action Relevant Revenues Expected future revenues that differ among alternative courses of action * Differential or Net Relevant Costs 2
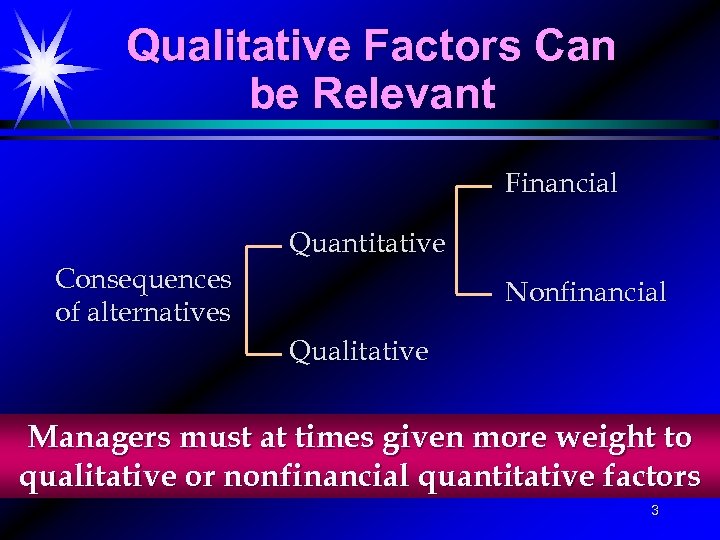 Qualitative Factors Can be Relevant Financial Consequences of alternatives Quantitative Nonfinancial Qualitative Managers must at times given more weight to qualitative or nonfinancial quantitative factors 3
Qualitative Factors Can be Relevant Financial Consequences of alternatives Quantitative Nonfinancial Qualitative Managers must at times given more weight to qualitative or nonfinancial quantitative factors 3
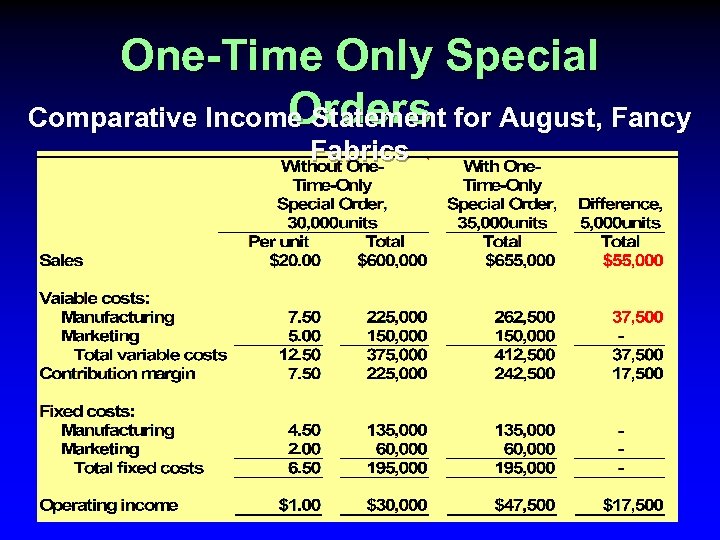 One-Time Only Special Orders Comparative Income Statement for August, Fancy Fabrics
One-Time Only Special Orders Comparative Income Statement for August, Fancy Fabrics
 How Unit Costs Can Mislead 1. When irrelevant costs are included. 2. When unit costs at different output levels are compared. Pitfalls in Relevant-Cost Analysis 1. To assume that all variable costs are relevant. 2. To assume that all fixed costs are irrelevant.
How Unit Costs Can Mislead 1. When irrelevant costs are included. 2. When unit costs at different output levels are compared. Pitfalls in Relevant-Cost Analysis 1. To assume that all variable costs are relevant. 2. To assume that all fixed costs are irrelevant.
 Outsourcing and Make-or-Buy Decisions Outsourcing is the process of purchasing goods or services from outside vendors rather than producing the same goods and providing the same services within the organization Make-or-buy decision : Decisions about whether a producer of goods or services will insource or oursource Sometimes qualitative factors dictate management’s make-or-buy decision. The most important factors in the make-or-buy decision : quality, dependability of supplies, cost. 6
Outsourcing and Make-or-Buy Decisions Outsourcing is the process of purchasing goods or services from outside vendors rather than producing the same goods and providing the same services within the organization Make-or-buy decision : Decisions about whether a producer of goods or services will insource or oursource Sometimes qualitative factors dictate management’s make-or-buy decision. The most important factors in the make-or-buy decision : quality, dependability of supplies, cost. 6
 Relevant Items for Make-or-Buy Decision for HDS at the El Cerrito Company
Relevant Items for Make-or-Buy Decision for HDS at the El Cerrito Company
 Opportunity Costs, Outsourcing, and Capacity Constraint Deciding to use a resource in a particular way causes a manager to give up the opportunity to use the resource in alternative ways. The lost opportunity is a cost that manager must take into account when making a decision. v Opportunity cost is the contribution to income that is foregone(rejected) by not using a limited resource in its next-best alternative use. v Opportunity costs are seldom incorporated into formal financial accounting reports because these 8 costs do not entail cash receipts or disbursements. v
Opportunity Costs, Outsourcing, and Capacity Constraint Deciding to use a resource in a particular way causes a manager to give up the opportunity to use the resource in alternative ways. The lost opportunity is a cost that manager must take into account when making a decision. v Opportunity cost is the contribution to income that is foregone(rejected) by not using a limited resource in its next-best alternative use. v Opportunity costs are seldom incorporated into formal financial accounting reports because these 8 costs do not entail cash receipts or disbursements. v
 Total-Alternatives Approach and Opportunity. Costs Approach to Make-or-Buy Decisions for El Cerrito
Total-Alternatives Approach and Opportunity. Costs Approach to Make-or-Buy Decisions for El Cerrito
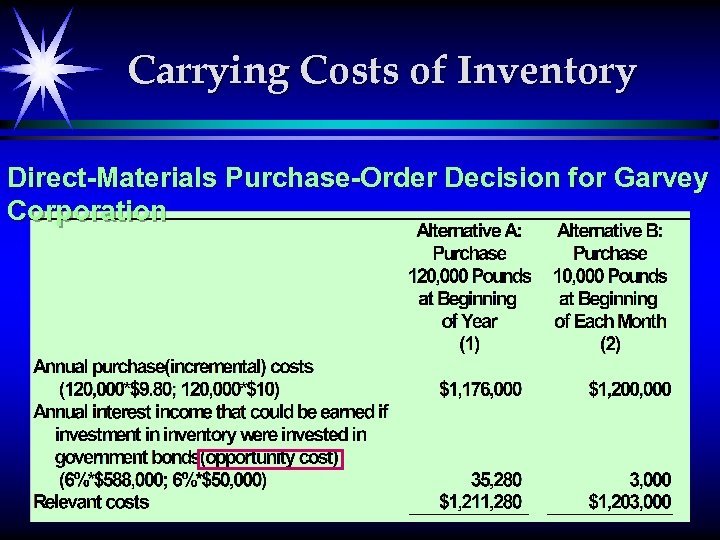 Carrying Costs of Inventory Direct-Materials Purchase-Order Decision for Garvey Corporation 10
Carrying Costs of Inventory Direct-Materials Purchase-Order Decision for Garvey Corporation 10
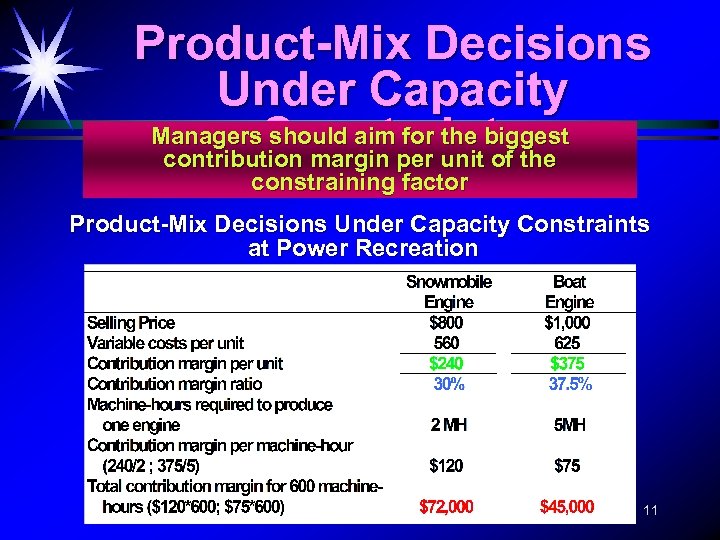 Product-Mix Decisions Under Capacity Managers. Constraints should aim for the biggest contribution margin per unit of the constraining factor Product-Mix Decisions Under Capacity Constraints at Power Recreation 11
Product-Mix Decisions Under Capacity Managers. Constraints should aim for the biggest contribution margin per unit of the constraining factor Product-Mix Decisions Under Capacity Constraints at Power Recreation 11
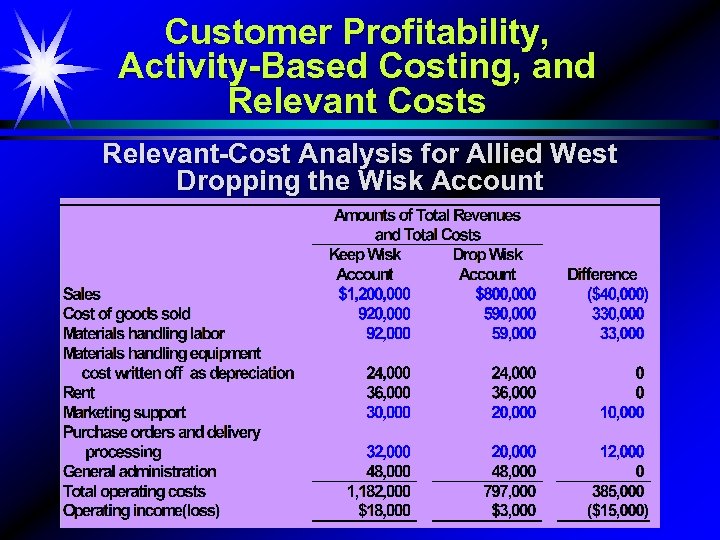 Customer Profitability, Activity-Based Costing, and Relevant Costs Relevant-Cost Analysis for Allied West Dropping the Wisk Account 12
Customer Profitability, Activity-Based Costing, and Relevant Costs Relevant-Cost Analysis for Allied West Dropping the Wisk Account 12
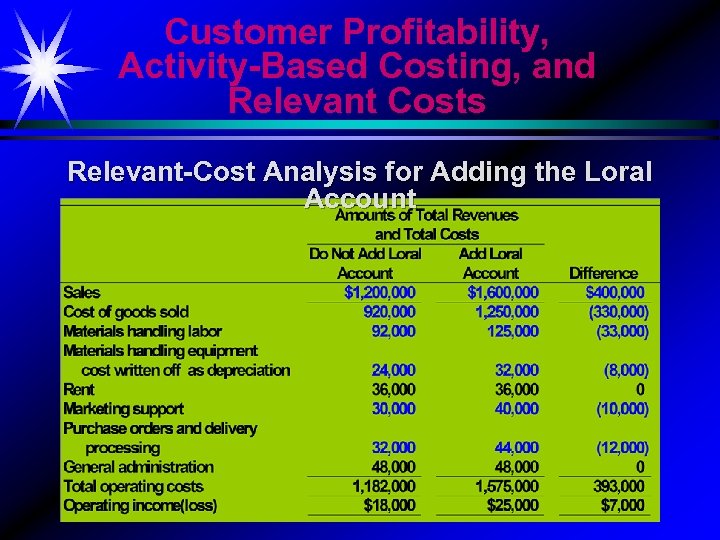 Customer Profitability, Activity-Based Costing, and Relevant Costs Relevant-Cost Analysis for Adding the Loral Account 13
Customer Profitability, Activity-Based Costing, and Relevant Costs Relevant-Cost Analysis for Adding the Loral Account 13
 Irrelevance of Past Costs and Equipment-Replacement Decisions Past costs(sunk costs) are unavoidable because they cannot be changed, no matter what action is taken Relevance of four commonly encountered items in equipment-replacement decisions 1. Book value of old machine: Irrelevant, machine because it is a past cost. 2. Current disposal price of old machine: machine Relevant, because it is an expected future cash inflow that differs between alternatives. 3. Gain or loss on disposal : A meaningless combination of two items. 14 4. Cost of new machine: Relevant. machine
Irrelevance of Past Costs and Equipment-Replacement Decisions Past costs(sunk costs) are unavoidable because they cannot be changed, no matter what action is taken Relevance of four commonly encountered items in equipment-replacement decisions 1. Book value of old machine: Irrelevant, machine because it is a past cost. 2. Current disposal price of old machine: machine Relevant, because it is an expected future cash inflow that differs between alternatives. 3. Gain or loss on disposal : A meaningless combination of two items. 14 4. Cost of new machine: Relevant. machine
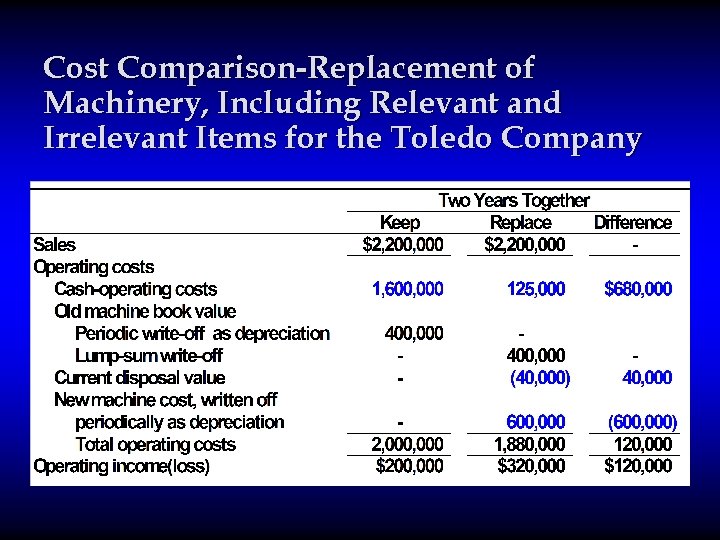 Cost Comparison-Replacement of Machinery, Including Relevant and Irrelevant Items for the Toledo Company
Cost Comparison-Replacement of Machinery, Including Relevant and Irrelevant Items for the Toledo Company
 Decisions and Performance Evaluation If the performance-evaluation model conflicts with the decision model, the performance-evaluation model often prevails in influencing a manager’s behavior. Even if top management’s goals are long-run (and consistent with the decision model), the subordinate manager’s concern is more likely to be short-run if his or her evaluation is based on short-run measures such as operating income. Resolving the conflict between the decision model and the performance-evaluation model is frequently a baffling problem in practice. In theory, resolving the difficulty seems obvious - merely design consistent models. 16
Decisions and Performance Evaluation If the performance-evaluation model conflicts with the decision model, the performance-evaluation model often prevails in influencing a manager’s behavior. Even if top management’s goals are long-run (and consistent with the decision model), the subordinate manager’s concern is more likely to be short-run if his or her evaluation is based on short-run measures such as operating income. Resolving the conflict between the decision model and the performance-evaluation model is frequently a baffling problem in practice. In theory, resolving the difficulty seems obvious - merely design consistent models. 16


