f4ae5e50542492c10dc2229bba8d3cc3.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24

Relativistic hydrodynamics – stability and causality P. Ván 1, 2 and T. S. Bíró 1 RMKI, Budapest 1 and University of Bergen 2 – Introduction – Causality – parabolic equations – Stability – Eckart problem – Separation of dissipative and nondissipative parts – Conclusions Zimányi 75 Memorial Workshop’ 07, Budapest
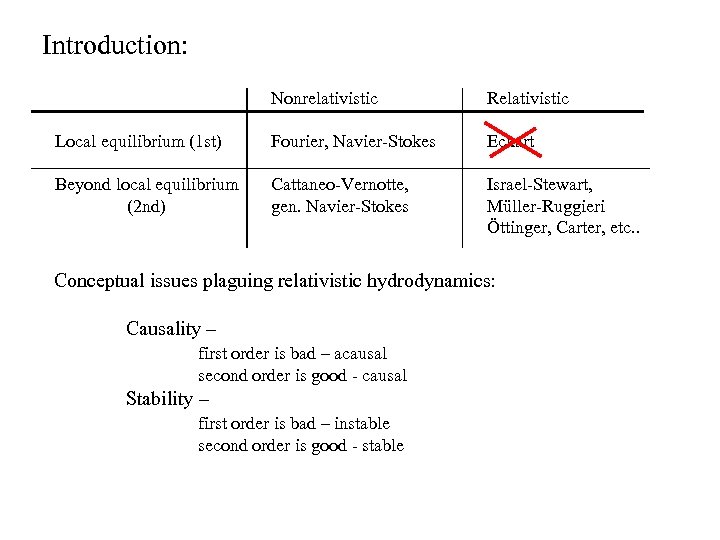
Introduction: Nonrelativistic Relativistic Local equilibrium (1 st) Fourier, Navier-Stokes Eckart Beyond local equilibrium (2 nd) Cattaneo-Vernotte, gen. Navier-Stokes Israel-Stewart, Müller-Ruggieri Öttinger, Carter, etc. . Conceptual issues plaguing relativistic hydrodynamics: Causality – first order is bad – acausal second order is good - causal Stability – first order is bad – instable second order is good - stable
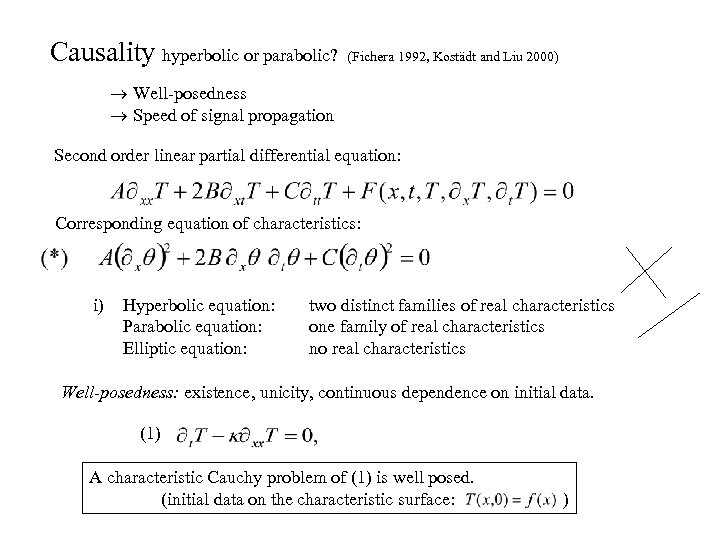
Causality hyperbolic or parabolic? (Fichera 1992, Kostädt and Liu 2000) Well-posedness Speed of signal propagation Second order linear partial differential equation: Corresponding equation of characteristics: i) Hyperbolic equation: Parabolic equation: Elliptic equation: two distinct families of real characteristics one family of real characteristics no real characteristics Well-posedness: existence, unicity, continuous dependence on initial data. (1) A characteristic Cauchy problem of (1) is well posed. (initial data on the characteristic surface: )
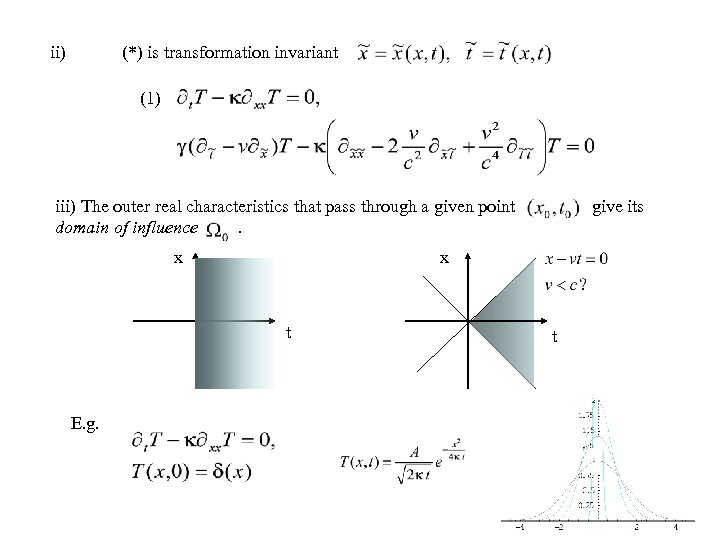
ii) (*) is transformation invariant (1) iii) The outer real characteristics that pass through a given point domain of influence. x x t E. g. give its t
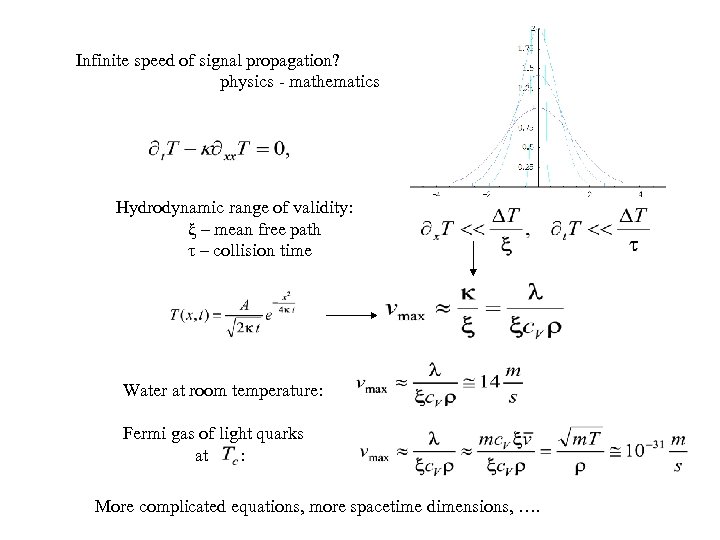
Infinite speed of signal propagation? physics - mathematics Hydrodynamic range of validity: ξ – mean free path τ – collision time Water at room temperature: Fermi gas of light quarks at : More complicated equations, more spacetime dimensions, ….
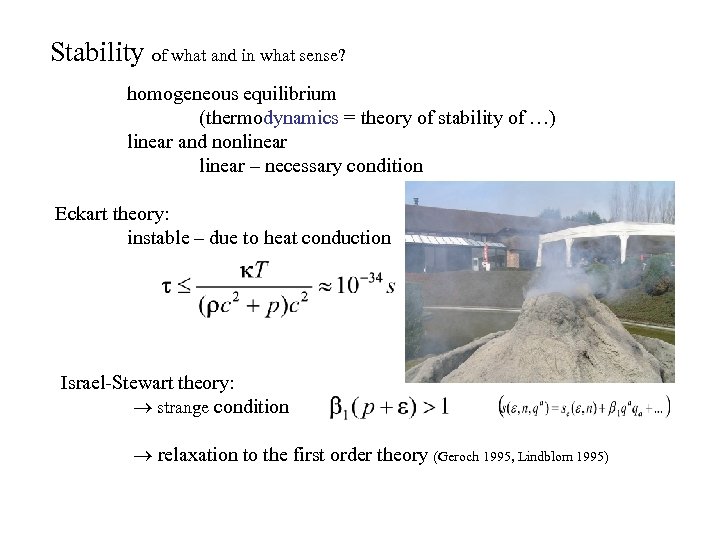
Stability of what and in what sense? homogeneous equilibrium (thermodynamics = theory of stability of …) linear and nonlinear – necessary condition Eckart theory: instable – due to heat conduction water Israel-Stewart theory: strange condition relaxation to the first order theory (Geroch 1995, Lindblom 1995)
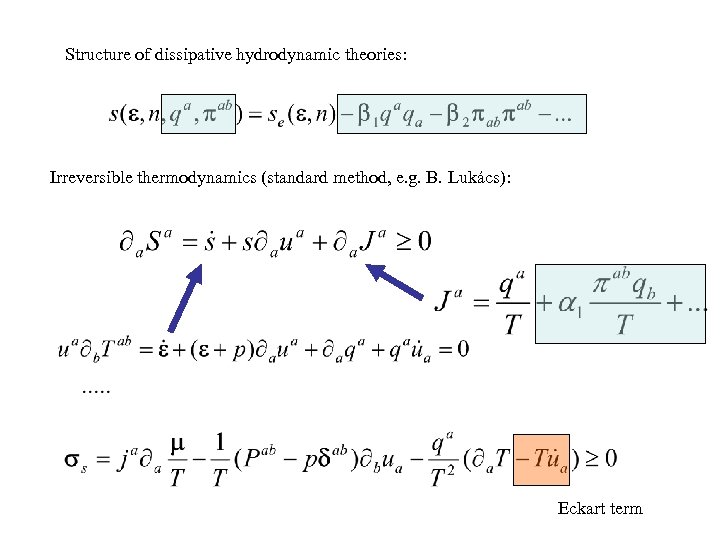
Structure of dissipative hydrodynamic theories: Irreversible thermodynamics (standard method, e. g. B. Lukács): Eckart term
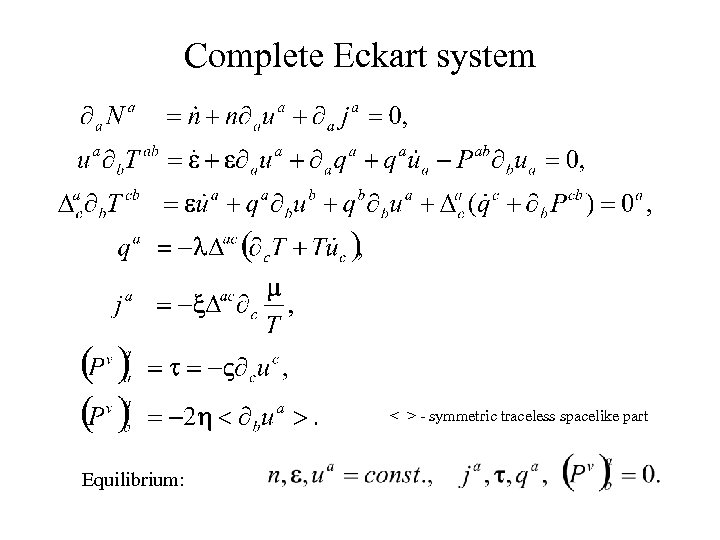
Complete Eckart system < > - symmetric traceless spacelike part Equilibrium:
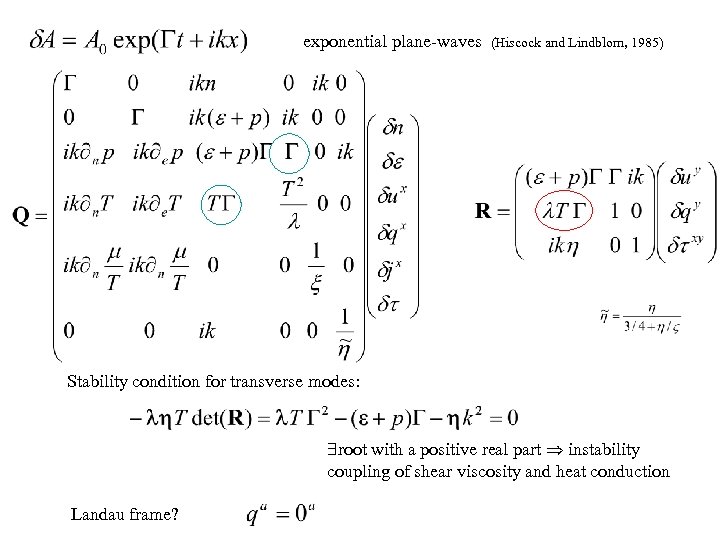
exponential plane-waves (Hiscock and Lindblom, 1985) Stability condition for transverse modes: $root with a positive real part instability coupling of shear viscosity and heat conduction Landau frame?

First or second (or higher) order theory? Causality: speed of the VALIDITY < speed of light both for first and second order Stability: Landau choice (q=0) is a temporary escape - entropy production, multicomponent fluids both for first and second order Origin of stability problem: wrong separation of dissipative and non dissipative terms and effects e. g. the choice of velocity field is not free (e. g. entropy production)

Separation of dissipation (PV and TSB ar. Xiv: 0704. 2039) flow energy Separation condition:

Something more… (a) energies: total= internal+ flow (mass? ) (b) velocity – momentum (heat) flow energy – heat flux
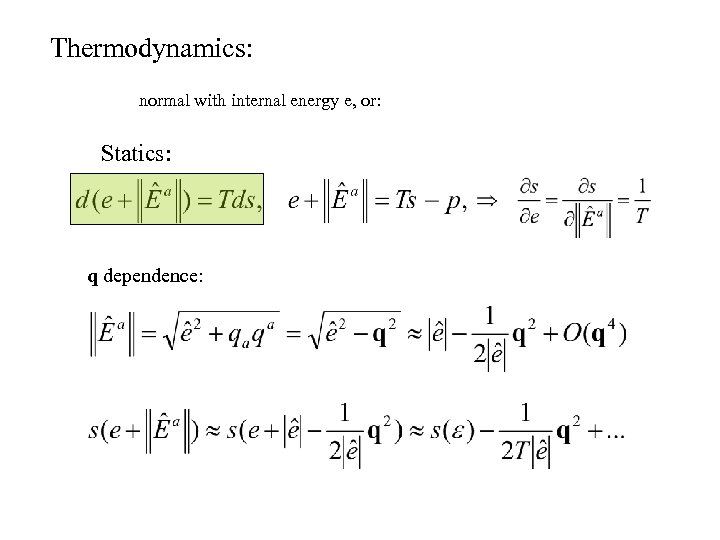
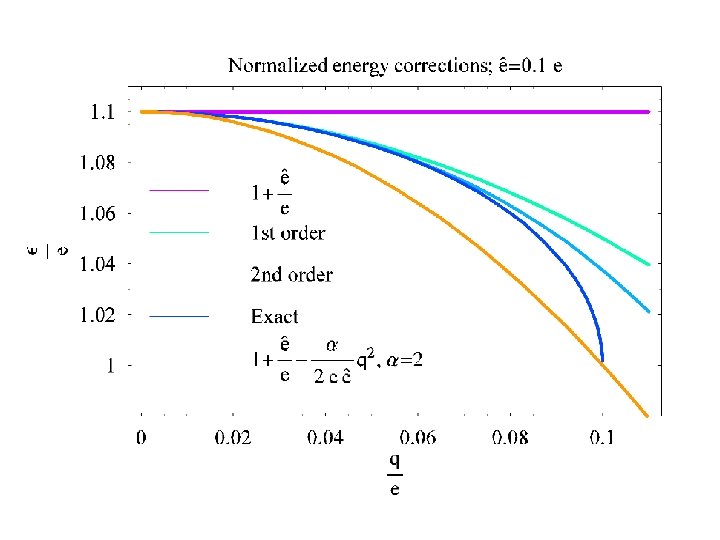
Thermodynamics: normal with internal energy e, or: Statics: q dependence:
Summary momentum density = but ≡ heat flow – energy = internal energy + flow energy – ADDS: – entropy flux and can ben justified (thermodynamic theory construction – Liu procedure) – linear stability of homogeneous equilibrium Thermodynamics stability of matter

Thank you for your attention!
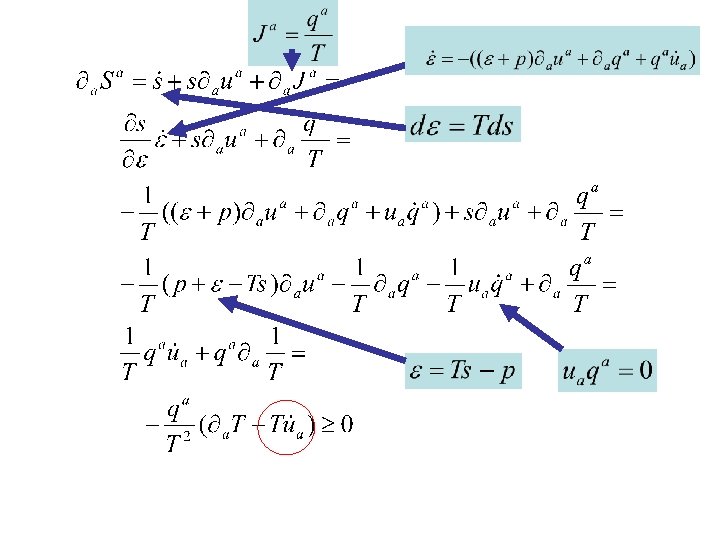
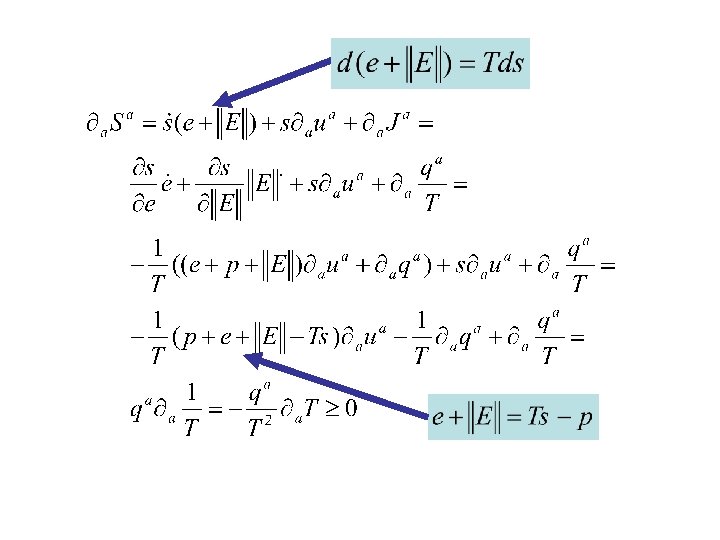
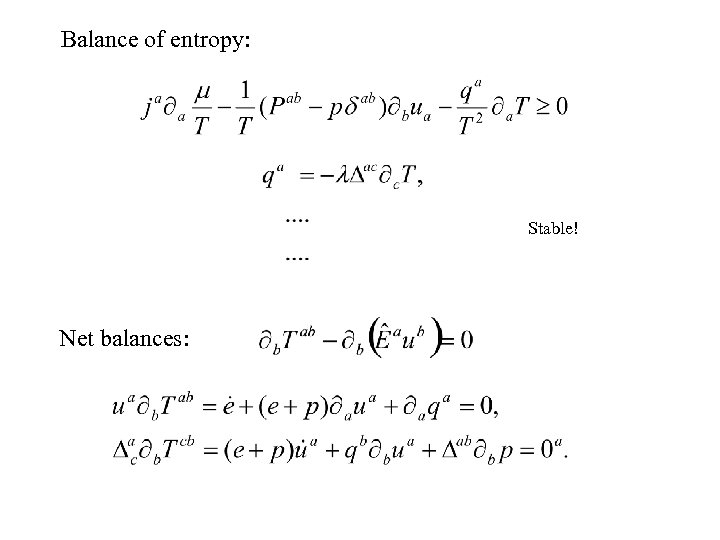
Balance of entropy: Stable! Net balances:
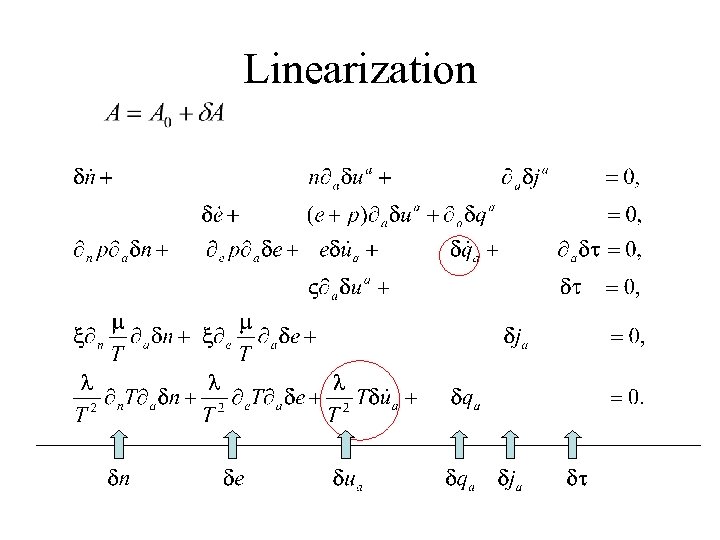
Linearization

Routh-Hurwitz: thermodynamic stability hydrodynamic stability
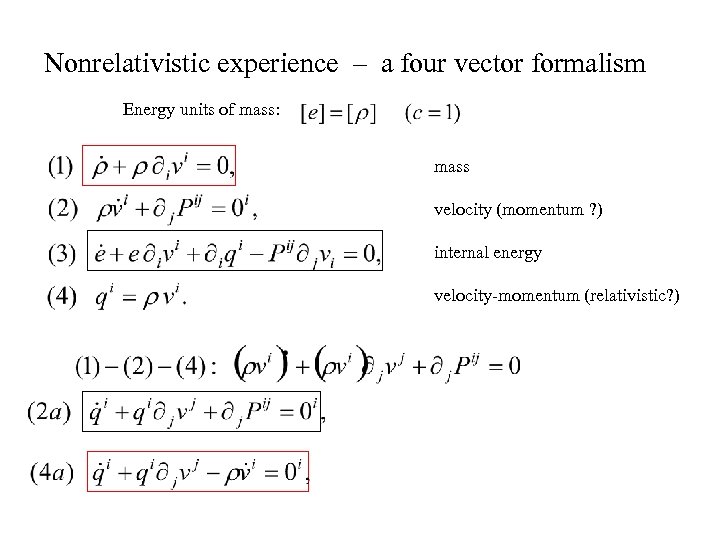
Nonrelativistic experience – a four vector formalism Energy units of mass: mass velocity (momentum ? ) internal energy velocity-momentum (relativistic? )
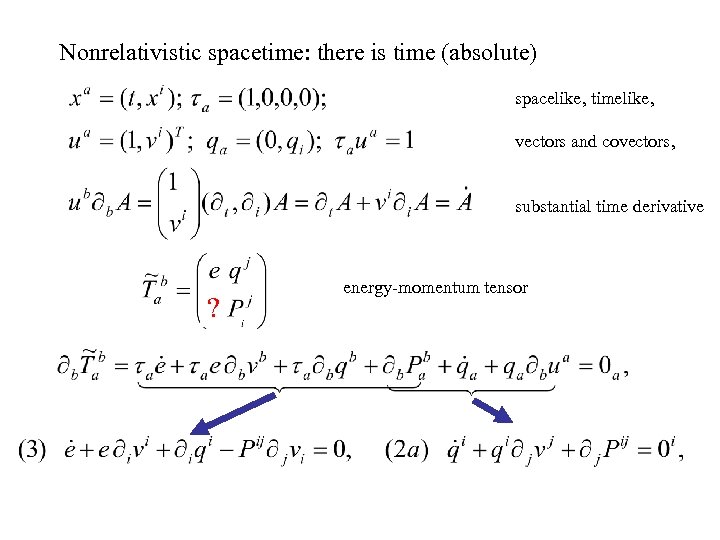
Nonrelativistic spacetime: there is time (absolute) spacelike, timelike, vectors and covectors, substantial time derivative ? energy-momentum tensor
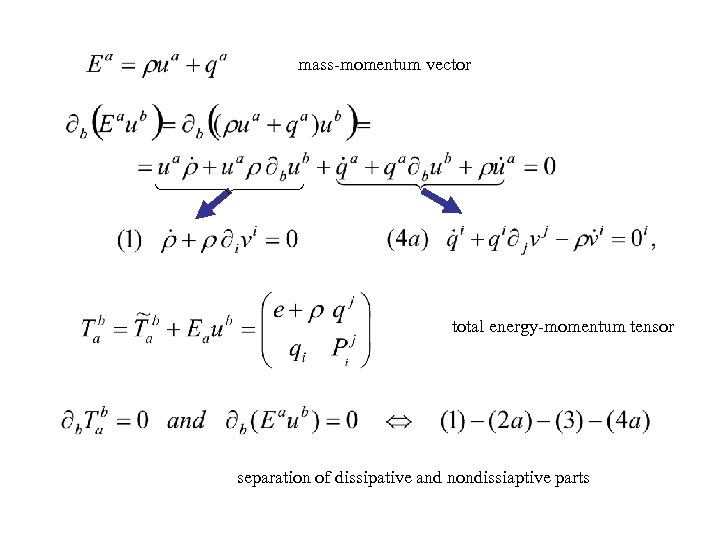
mass-momentum vector 14 244 4 3 total energy-momentum tensor separation of dissipative and nondissiaptive parts
f4ae5e50542492c10dc2229bba8d3cc3.ppt