9231b04dca6f09f35349f3aa0c397064.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 59
 REGULATORY MECHANISMS, GUIDELINES AND PROTOCOLS FOR TRANSGENIC CROPS; FOOD AND FEED SENARIO Dr. T. V. Ramanaiah Scientist-F Department of Biotechnology, Ministry of Science & Technology CGO Complex, Lodi Road, New Delhi - 110 003 Short-Term Orientation Course on Biosafety and Biotech Regulations 6 th -11 th Feb, 2006 at TERI 1
REGULATORY MECHANISMS, GUIDELINES AND PROTOCOLS FOR TRANSGENIC CROPS; FOOD AND FEED SENARIO Dr. T. V. Ramanaiah Scientist-F Department of Biotechnology, Ministry of Science & Technology CGO Complex, Lodi Road, New Delhi - 110 003 Short-Term Orientation Course on Biosafety and Biotech Regulations 6 th -11 th Feb, 2006 at TERI 1
 Biosafety Protecting human & animal health and environment from the possible adverse effects of the products of modern biotechnology Precautionary Approach is adopted for assessment of Biosafety 2
Biosafety Protecting human & animal health and environment from the possible adverse effects of the products of modern biotechnology Precautionary Approach is adopted for assessment of Biosafety 2
 Objectives of Regulations To facilitate & regulate Modern biotechnology work at different stages to achieve the objectives of biosafety. 3
Objectives of Regulations To facilitate & regulate Modern biotechnology work at different stages to achieve the objectives of biosafety. 3
 BIOSAFETY REGULATIONS & GUIDELINES * International: Cartagena Protocol on Biosafety OECD Guidelines * Country specific: USA, EU, Canada, Australia, Egypt, Japan, China, Philippines, Thailand, India, Pakistan, etc. 4
BIOSAFETY REGULATIONS & GUIDELINES * International: Cartagena Protocol on Biosafety OECD Guidelines * Country specific: USA, EU, Canada, Australia, Egypt, Japan, China, Philippines, Thailand, India, Pakistan, etc. 4
 GENETICALLY MODIFIED ORGANISMS (GMOs) AND r-DNA PRODUCTS GOVERNED BY Environment (Protection) Act, 1986 Came into force from 23. 05. 1986 Rules, 1989 on GMOs Notified on 05. 12. 1989 Came into force from 01. 10. 1993 5
GENETICALLY MODIFIED ORGANISMS (GMOs) AND r-DNA PRODUCTS GOVERNED BY Environment (Protection) Act, 1986 Came into force from 23. 05. 1986 Rules, 1989 on GMOs Notified on 05. 12. 1989 Came into force from 01. 10. 1993 5
 TRANSGENIC CROPS ARE ALSO GOVERNED BY ØIndustries (Development & Regulation) Act, 1951 - New Industrial Policy & Procedures, 1991 Ø Seeds Act, 1966 Ø Seeds Rules, 1968 Ø Seeds (Control) Order, 1983 Ø Seeds Policy, 1988, 2002 Ø Protection of Plant Varieties and Farmers’ Rights Act, 2001 6
TRANSGENIC CROPS ARE ALSO GOVERNED BY ØIndustries (Development & Regulation) Act, 1951 - New Industrial Policy & Procedures, 1991 Ø Seeds Act, 1966 Ø Seeds Rules, 1968 Ø Seeds (Control) Order, 1983 Ø Seeds Policy, 1988, 2002 Ø Protection of Plant Varieties and Farmers’ Rights Act, 2001 6
 The Indian Environment (Protection) Act (EPA), 1986 Ø Came into force from 23. 5. 1986. Ø Provides protection and improvement of Environment. Ø “Environment” includes water, air and land the interrelationship , which exists among and between water, air and land, and human beings, other living creatures, plants, microorganism and property Ø “Environmental pollutant” means any solid, liquid or gaseous substance present in such concentration as may be, or tend to be, injurious to environment. Ø “Environmental pollution” means the presence in the environment of any environmental pollutant. contd. . . 7
The Indian Environment (Protection) Act (EPA), 1986 Ø Came into force from 23. 5. 1986. Ø Provides protection and improvement of Environment. Ø “Environment” includes water, air and land the interrelationship , which exists among and between water, air and land, and human beings, other living creatures, plants, microorganism and property Ø “Environmental pollutant” means any solid, liquid or gaseous substance present in such concentration as may be, or tend to be, injurious to environment. Ø “Environmental pollution” means the presence in the environment of any environmental pollutant. contd. . . 7
 Some Important Sections of EPA Section -15 Ø Whoever fails to comply with or contravenes the act or any rules can be punished with imprisonment for a term up to 5 years, or with a fine up to Rs. 100, 000 or with both. Ø If failure or contravention continues beyond one year, the offender may be punishable with imprisonment which may extend up to 7 years. 8
Some Important Sections of EPA Section -15 Ø Whoever fails to comply with or contravenes the act or any rules can be punished with imprisonment for a term up to 5 years, or with a fine up to Rs. 100, 000 or with both. Ø If failure or contravention continues beyond one year, the offender may be punishable with imprisonment which may extend up to 7 years. 8
 Rules for the Manufacture, Use / Import / Export and Storage of Hazardous Microorganisms, Genetically Engineered Organisms or Cells (Rules 1989) * Notified in exercise of powers under sections 6, 8 & 25 of the EPA, 1986 on 5 th. Dec’ 89. * Rules are came into force from 01. 10. 1993. Application of Rules : * Manufacture, import and storage of microorganisms and Gene-technological products. * Genetically engineered organisms, microorganisms and cells and correspondingly to any substances and products and food stuffs, etc. * Sale, any kind of handling, exportation, importation, production, manufacture, processing, storage, drawing off, packaging, repackaging of GMOs and drugs & pharmaceuticals, food stuffs etc. from GMOs and Gene technology products. 9
Rules for the Manufacture, Use / Import / Export and Storage of Hazardous Microorganisms, Genetically Engineered Organisms or Cells (Rules 1989) * Notified in exercise of powers under sections 6, 8 & 25 of the EPA, 1986 on 5 th. Dec’ 89. * Rules are came into force from 01. 10. 1993. Application of Rules : * Manufacture, import and storage of microorganisms and Gene-technological products. * Genetically engineered organisms, microorganisms and cells and correspondingly to any substances and products and food stuffs, etc. * Sale, any kind of handling, exportation, importation, production, manufacture, processing, storage, drawing off, packaging, repackaging of GMOs and drugs & pharmaceuticals, food stuffs etc. from GMOs and Gene technology products. 9
 Approval and prohibitions, etc. under Rules, 1989 • No person shall import, export, transport, manufacture, process, use or sell any GMOs, substances or cells except with the approval of the GEAC. • Use of pathogenic organisms or GMOs or cells for research purpose shall be allowed under the Notification, 1989 of the EPA, 1986. • Any person operating or using GMOs for scale up or pilot operations shall have to obtain permission from GEAC. • Deliberate or unintentional release of GMOs not allowed. • Production in which GMOs are generated or used shall not be commenced except with the approval of GEAC. 10
Approval and prohibitions, etc. under Rules, 1989 • No person shall import, export, transport, manufacture, process, use or sell any GMOs, substances or cells except with the approval of the GEAC. • Use of pathogenic organisms or GMOs or cells for research purpose shall be allowed under the Notification, 1989 of the EPA, 1986. • Any person operating or using GMOs for scale up or pilot operations shall have to obtain permission from GEAC. • Deliberate or unintentional release of GMOs not allowed. • Production in which GMOs are generated or used shall not be commenced except with the approval of GEAC. 10
 Approval and prohibitions, etc. under Rules 1989 * GEAC supervises the implementation of rules and guidelines. * GEAC carries out supervision through SBCC, DLC or any authorized person. * If orders are not complied, SBCC/DLC may take suitable measures at the expenses of the person who is responsible. * In case of immediate interventions to prevent any damage, SBCC and DLC can take suitable measures and the expenses incurred will be recovered from the person responsible. 11
Approval and prohibitions, etc. under Rules 1989 * GEAC supervises the implementation of rules and guidelines. * GEAC carries out supervision through SBCC, DLC or any authorized person. * If orders are not complied, SBCC/DLC may take suitable measures at the expenses of the person who is responsible. * In case of immediate interventions to prevent any damage, SBCC and DLC can take suitable measures and the expenses incurred will be recovered from the person responsible. 11
 Approval and prohibitions, etc. under Rules 1989 * All approvals shall be for a period of 4 years at first instance renewable for 2 years at a time. * GEAC shall have powers to revoke approvals in case of: a) any new information on harmful effects of GMOs. b) GMOs cause such damage to the environment as could not be envisaged when approval was given. c) Non compliance of any conditions stipulated by GEAC. 12
Approval and prohibitions, etc. under Rules 1989 * All approvals shall be for a period of 4 years at first instance renewable for 2 years at a time. * GEAC shall have powers to revoke approvals in case of: a) any new information on harmful effects of GMOs. b) GMOs cause such damage to the environment as could not be envisaged when approval was given. c) Non compliance of any conditions stipulated by GEAC. 12
 COMPETENT AUTHORITIES 1. Recombinant DNA Advisory Committee (RDAC) 2. Review Committee on Genetic Manipulation (RCGM) 3. Institutional Biosafety Committee (IBSC) 4. Genetic Engineering Approval Committee (GEAC) 5. State Biotechnology Co-ordination Committee (SBCC) 6. District Level Committee (DLC) 13
COMPETENT AUTHORITIES 1. Recombinant DNA Advisory Committee (RDAC) 2. Review Committee on Genetic Manipulation (RCGM) 3. Institutional Biosafety Committee (IBSC) 4. Genetic Engineering Approval Committee (GEAC) 5. State Biotechnology Co-ordination Committee (SBCC) 6. District Level Committee (DLC) 13
 Recombinant DNA Advisory Committee (RDAC) Main functions • Review developments in Biotechnology at National and International level. • Recommend suitable and appropriate safety regulations for India in r-DNA research, use and applications. 14
Recombinant DNA Advisory Committee (RDAC) Main functions • Review developments in Biotechnology at National and International level. • Recommend suitable and appropriate safety regulations for India in r-DNA research, use and applications. 14
 Review Committee on Genetic Manipulation Main functions • To bring out manuals of guidelines specifying procedures for regulatory process on GMOs in research, use and applications including industry with a view to ensure environmental safety. • To review all on going r-DNA projects involving high risk category and controlled field experiments. • To lay down procedures for restriction or prohibition, production, sale, import & use of GMOs both for research and applications. • To permit experiments with category III risks and above with appropriate containment. • To authorize imports of GMOs/ transgenes for research purposes. • To authorize field experiments in 20 acres in multi-locations in one crop season with up to one acre at one site. • To generate relevant data on transgenic materials in appropriate systems. 15
Review Committee on Genetic Manipulation Main functions • To bring out manuals of guidelines specifying procedures for regulatory process on GMOs in research, use and applications including industry with a view to ensure environmental safety. • To review all on going r-DNA projects involving high risk category and controlled field experiments. • To lay down procedures for restriction or prohibition, production, sale, import & use of GMOs both for research and applications. • To permit experiments with category III risks and above with appropriate containment. • To authorize imports of GMOs/ transgenes for research purposes. • To authorize field experiments in 20 acres in multi-locations in one crop season with up to one acre at one site. • To generate relevant data on transgenic materials in appropriate systems. 15
 Institutional Bio-Safety Committee (IBSC) Main functions • To note and to approve r-DNA work. • To ensure adherence of r-DNA safety guidelines of government. • To prepare emergency plan according to guidelines. • To recommend to RCGM about category III risk or above experiments and to seek RCGM’s approval. • To inform DLC and SBCC as well as GEAC about the experiments where ever needed. • To act as nodal point for interaction with statutory bodies. • To ensure experimentation at designated location, taking into account approved protocols. 16
Institutional Bio-Safety Committee (IBSC) Main functions • To note and to approve r-DNA work. • To ensure adherence of r-DNA safety guidelines of government. • To prepare emergency plan according to guidelines. • To recommend to RCGM about category III risk or above experiments and to seek RCGM’s approval. • To inform DLC and SBCC as well as GEAC about the experiments where ever needed. • To act as nodal point for interaction with statutory bodies. • To ensure experimentation at designated location, taking into account approved protocols. 16
 Genetic Engineering Approval Committee (GEAC) Main functions • To permit the use of GMOs and products thereof for commercial applications. • To adopt procedures for restriction or prohibition, production, sale, import & use of GMOs both for research and applications under EPA. • To authorize large scale production and release of GMOs and products thereof into the environment. • To authorize agencies or persons to have powers to take punitive actions under the EPA. 17
Genetic Engineering Approval Committee (GEAC) Main functions • To permit the use of GMOs and products thereof for commercial applications. • To adopt procedures for restriction or prohibition, production, sale, import & use of GMOs both for research and applications under EPA. • To authorize large scale production and release of GMOs and products thereof into the environment. • To authorize agencies or persons to have powers to take punitive actions under the EPA. 17
 State Biotechnology Co-Ordination Committee (SBCC) Main functions • Powers to inspect, investigate and to take punitive action in case of violations of statutory provisions through the State Pollution Control Board or the Directorate of Health etc. • To review periodically the safety and control measures in various institutions handling GMOs. • To act as nodal agency at State level to assess the damage, if any, due to release of GMOs and to take on site control measures. 18
State Biotechnology Co-Ordination Committee (SBCC) Main functions • Powers to inspect, investigate and to take punitive action in case of violations of statutory provisions through the State Pollution Control Board or the Directorate of Health etc. • To review periodically the safety and control measures in various institutions handling GMOs. • To act as nodal agency at State level to assess the damage, if any, due to release of GMOs and to take on site control measures. 18
 District Level Committee (DLC) Main functions • To monitor the safety regulations in installations. • Have powers to inspect, investigate and report to the SBCC or the GEAC about compliance or non compliance of r-DNA guidelines or violations under EPA. • To act as nodal agency at District level to assess the damage, if any, due to release of GMOs and to take on site control measures. 19
District Level Committee (DLC) Main functions • To monitor the safety regulations in installations. • Have powers to inspect, investigate and report to the SBCC or the GEAC about compliance or non compliance of r-DNA guidelines or violations under EPA. • To act as nodal agency at District level to assess the damage, if any, due to release of GMOs and to take on site control measures. 19
 r-DNA GUIDELINES 1990 “ Recombinant DNA Safety Guidelines” 1994 “ Revised Guidelines for Safety in Biotechnology” 1998 “ Revised Guidelines for Research in Transgenic Plants & Guidelines for Toxicity and Allergenicity Evaluation of Transgenic Seeds, Plants and Plant Parts ” 1999 “Guidelines for Generating pre-clinical and Clinical data for r-DNA based Vaccines, Diagnostics and other Biologicals 20
r-DNA GUIDELINES 1990 “ Recombinant DNA Safety Guidelines” 1994 “ Revised Guidelines for Safety in Biotechnology” 1998 “ Revised Guidelines for Research in Transgenic Plants & Guidelines for Toxicity and Allergenicity Evaluation of Transgenic Seeds, Plants and Plant Parts ” 1999 “Guidelines for Generating pre-clinical and Clinical data for r-DNA based Vaccines, Diagnostics and other Biologicals 20
 COVERAGE OF REVISED GUIDELINES- 1998 * Recombinant DNA Research on plants and statutory bodies dealing with r- DNA work. * Classification of Genetic Engineering Experiments on plants a. Category - I b. Category - II c. Category - III * Containment measures followed in above categories. * Green House / Design for Field evaluation of transgenic plants. * Monitoring - cum - Evaluation Committee. * Biosafety aspects of the transgenic plants. * Import and shipment of genetically modified plants for research use only. * Toxicity guidelines for testing transgenic plants and plant parts. * Application for seeking approval under EPA for transgenic crops. 21
COVERAGE OF REVISED GUIDELINES- 1998 * Recombinant DNA Research on plants and statutory bodies dealing with r- DNA work. * Classification of Genetic Engineering Experiments on plants a. Category - I b. Category - II c. Category - III * Containment measures followed in above categories. * Green House / Design for Field evaluation of transgenic plants. * Monitoring - cum - Evaluation Committee. * Biosafety aspects of the transgenic plants. * Import and shipment of genetically modified plants for research use only. * Toxicity guidelines for testing transgenic plants and plant parts. * Application for seeking approval under EPA for transgenic crops. 21
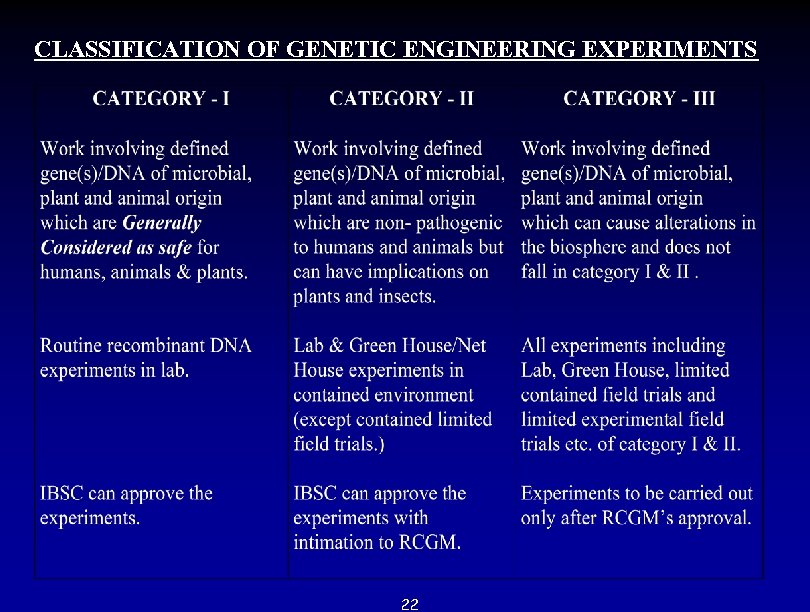 CLASSIFICATION OF GENETIC ENGINEERING EXPERIMENTS 22
CLASSIFICATION OF GENETIC ENGINEERING EXPERIMENTS 22
 Monitoring - cum - Evaluation Committee (MEC) Main functions • To undertake field visits at the experimental site (s). • To review the design of experiments / trials and collection of data during limited open field trials. • To collect information on the comparative agronomic advantages of transgenic crop. • To assess and advise on the risks and benefits from the use of transgenic plants. • To assist in collecting, consolidating and analyzing field data for evaluating environmental risks emanating from transgenic plants. • To recommend those transgenic crops which would be found to be environmentally safe and economically viable to RCGM and to GEAC for consideration to release into the environment. 23
Monitoring - cum - Evaluation Committee (MEC) Main functions • To undertake field visits at the experimental site (s). • To review the design of experiments / trials and collection of data during limited open field trials. • To collect information on the comparative agronomic advantages of transgenic crop. • To assess and advise on the risks and benefits from the use of transgenic plants. • To assist in collecting, consolidating and analyzing field data for evaluating environmental risks emanating from transgenic plants. • To recommend those transgenic crops which would be found to be environmentally safe and economically viable to RCGM and to GEAC for consideration to release into the environment. 23
 Amendments in the Guidelines Defining small experimental field trials: Small experimental field trials should be limited to a total of 20 acres in multi-locations in one crop season. In one location, where the experiment is conducted with transgenic plants, the land used should not be more than one acre. Any experiment beyond these limits in one crop season would require the approval of GEAC. Large scale experiments: Experiments using fermentors beyond 20 ltrs capacities exclusively for research purposes only to produce sufficient material/ products of GMOs required for generating pre-clinical and other relevant data required to establish the product for commercial use would not be included in the category of large scale experimentation/ operations. 24
Amendments in the Guidelines Defining small experimental field trials: Small experimental field trials should be limited to a total of 20 acres in multi-locations in one crop season. In one location, where the experiment is conducted with transgenic plants, the land used should not be more than one acre. Any experiment beyond these limits in one crop season would require the approval of GEAC. Large scale experiments: Experiments using fermentors beyond 20 ltrs capacities exclusively for research purposes only to produce sufficient material/ products of GMOs required for generating pre-clinical and other relevant data required to establish the product for commercial use would not be included in the category of large scale experimentation/ operations. 24
 Protocol for development Transgenic crops Institutional Biosafety Committee (IBSC) Examination & forwarding applications for approval of RCGM Review Committee on Genetic Manipulation (RCGM) Green house experiments, contained field trials, toxicity and allergenicity studies Farmer’s Field trials by Company ICAR trials Monitoring-cum- Evaluation Committee (MEC) Review Committee on Genetic Manipulation (RCGM) Genetic Engineering Approval Committee (GEAC) Evaluation of data and Environmental clearance of the event/ gene 25
Protocol for development Transgenic crops Institutional Biosafety Committee (IBSC) Examination & forwarding applications for approval of RCGM Review Committee on Genetic Manipulation (RCGM) Green house experiments, contained field trials, toxicity and allergenicity studies Farmer’s Field trials by Company ICAR trials Monitoring-cum- Evaluation Committee (MEC) Review Committee on Genetic Manipulation (RCGM) Genetic Engineering Approval Committee (GEAC) Evaluation of data and Environmental clearance of the event/ gene 25
 CONSTITUTION OF TASK FORCES ON BIOSAFETY REGULATIONS Ministry of Agriculture constituted a Task Force on ‘Applications of Agricultural Biotechnology’ Ministry of Environment & Forests constituted a Task Force on ‘Recombinant Pharma Sector’ 26
CONSTITUTION OF TASK FORCES ON BIOSAFETY REGULATIONS Ministry of Agriculture constituted a Task Force on ‘Applications of Agricultural Biotechnology’ Ministry of Environment & Forests constituted a Task Force on ‘Recombinant Pharma Sector’ 26
 Protocol-I For New Transgenic Event Institutional Biosafety Committee (IBSC) Preparation and/submission of application data Review Committee on Genetic Manipulation (RCGM) Evaluation of application data from IBSC* Approval for Laboratory and Green House Trials & contained field trials. For generation of environmental, toxicity and allergenicity data. Evaluation/monitoring of contained field trials through Monitoring-cum- Evaluation Committee (MEC) Genetic Engineering Approval Committee (GEAC) Approval for large scale Field Trials and Evaluation Protocol** Concurrent Farmer’s Field trials by Company ICAR trials for VCU involving SAUs and other appropriate State Agencies Genetic Engineering Approval Committee (GEAC) Evaluation of data and Environmental clearance of the event/ gene Ministry of Agriculture Approval for commercial release/notification/registration of variety(ies) / hybrid(s) by DAC/ICAR Ministry of Agriculture & State Governments Post-release monitoring and vigilance 27
Protocol-I For New Transgenic Event Institutional Biosafety Committee (IBSC) Preparation and/submission of application data Review Committee on Genetic Manipulation (RCGM) Evaluation of application data from IBSC* Approval for Laboratory and Green House Trials & contained field trials. For generation of environmental, toxicity and allergenicity data. Evaluation/monitoring of contained field trials through Monitoring-cum- Evaluation Committee (MEC) Genetic Engineering Approval Committee (GEAC) Approval for large scale Field Trials and Evaluation Protocol** Concurrent Farmer’s Field trials by Company ICAR trials for VCU involving SAUs and other appropriate State Agencies Genetic Engineering Approval Committee (GEAC) Evaluation of data and Environmental clearance of the event/ gene Ministry of Agriculture Approval for commercial release/notification/registration of variety(ies) / hybrid(s) by DAC/ICAR Ministry of Agriculture & State Governments Post-release monitoring and vigilance 27
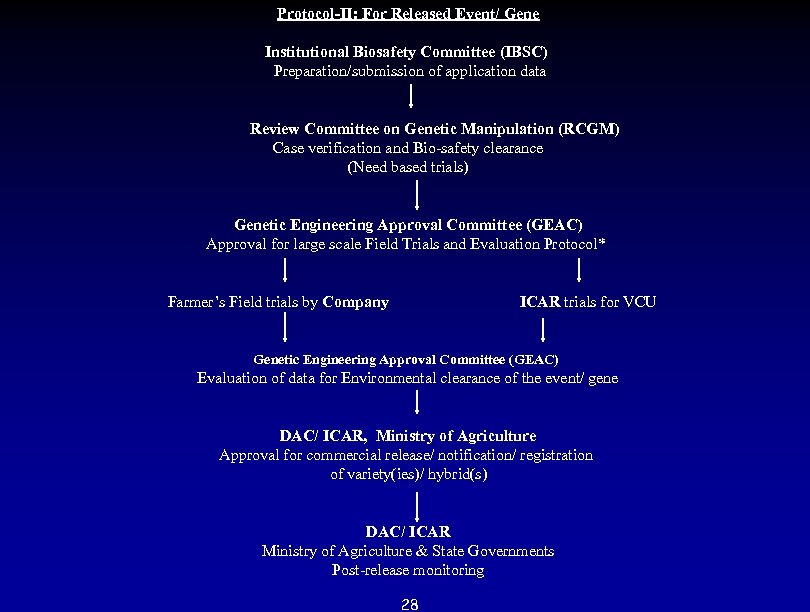 Protocol-II: For Released Event/ Gene Institutional Biosafety Committee (IBSC) Preparation/submission of application data Review Committee on Genetic Manipulation (RCGM) Case verification and Bio-safety clearance (Need based trials) Genetic Engineering Approval Committee (GEAC) Approval for large scale Field Trials and Evaluation Protocol* Farmer’s Field trials by Company ICAR trials for VCU Genetic Engineering Approval Committee (GEAC) Evaluation of data for Environmental clearance of the event/ gene DAC/ ICAR, Ministry of Agriculture Approval for commercial release/ notification/ registration of variety(ies)/ hybrid(s) DAC/ ICAR Ministry of Agriculture & State Governments Post-release monitoring 28
Protocol-II: For Released Event/ Gene Institutional Biosafety Committee (IBSC) Preparation/submission of application data Review Committee on Genetic Manipulation (RCGM) Case verification and Bio-safety clearance (Need based trials) Genetic Engineering Approval Committee (GEAC) Approval for large scale Field Trials and Evaluation Protocol* Farmer’s Field trials by Company ICAR trials for VCU Genetic Engineering Approval Committee (GEAC) Evaluation of data for Environmental clearance of the event/ gene DAC/ ICAR, Ministry of Agriculture Approval for commercial release/ notification/ registration of variety(ies)/ hybrid(s) DAC/ ICAR Ministry of Agriculture & State Governments Post-release monitoring 28
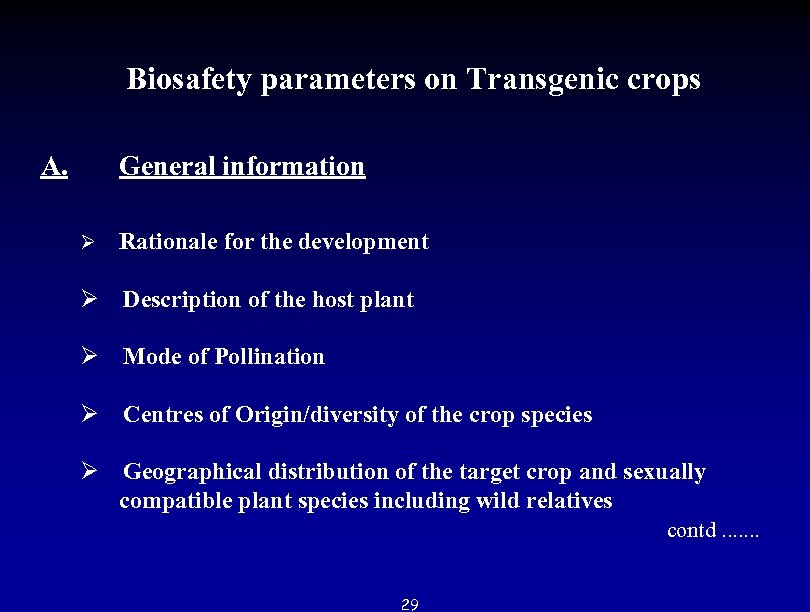 Biosafety parameters on Transgenic crops A. General information Ø Rationale for the development Ø Description of the host plant Ø Mode of Pollination Ø Centres of Origin/diversity of the crop species Ø Geographical distribution of the target crop and sexually compatible plant species including wild relatives contd. . . . 29
Biosafety parameters on Transgenic crops A. General information Ø Rationale for the development Ø Description of the host plant Ø Mode of Pollination Ø Centres of Origin/diversity of the crop species Ø Geographical distribution of the target crop and sexually compatible plant species including wild relatives contd. . . . 29
 Biosafety parameters on Transgenic crops B. Biosafety Parameters: 1. Genetic and Molecular parameters Ø Genetic analysis including copy number of inserts Ø Stability of the gene, Ø Level, site(s) and duration of expression of transgene Ø Characterization of expressed gene product Ø Efficacy/utility of gene product Ø Compositional analysis contd. . 30
Biosafety parameters on Transgenic crops B. Biosafety Parameters: 1. Genetic and Molecular parameters Ø Genetic analysis including copy number of inserts Ø Stability of the gene, Ø Level, site(s) and duration of expression of transgene Ø Characterization of expressed gene product Ø Efficacy/utility of gene product Ø Compositional analysis contd. . 30
 Biosafety parameters on Transgenic crops 2. Environmental parameters Ø Gene flow Ø Implications of out-crossing Ø Effect on target and non-target organisms Ø Effect on soil biota Contd…. 31
Biosafety parameters on Transgenic crops 2. Environmental parameters Ø Gene flow Ø Implications of out-crossing Ø Effect on target and non-target organisms Ø Effect on soil biota Contd…. 31
 Biosafety parameters on Transgenic crops 3. Toxicity parameters including histo-pathological studies (need based) Ø Food/feed safety evaluation in animals such as: * Effect on small laboratory animals * Effect on livestock animals (representative goat studies of large animals) * Effect on birds/ avian species * Effect on fish Contd…. 32
Biosafety parameters on Transgenic crops 3. Toxicity parameters including histo-pathological studies (need based) Ø Food/feed safety evaluation in animals such as: * Effect on small laboratory animals * Effect on livestock animals (representative goat studies of large animals) * Effect on birds/ avian species * Effect on fish Contd…. 32
 Biosafety parameters on Transgenic crops 4. Allergenicity parameters (need based) Ø Primary skin irritation test in rabbit/ guinea pigs Ø Irritation to mucous membrane test in rabbit/ guinea pig Ø Immunological responses in suitable animal system Contd…. 33
Biosafety parameters on Transgenic crops 4. Allergenicity parameters (need based) Ø Primary skin irritation test in rabbit/ guinea pigs Ø Irritation to mucous membrane test in rabbit/ guinea pig Ø Immunological responses in suitable animal system Contd…. 33
 Biosafety parameters on Transgenic crops C. Agronomic parameters Ø Efficacy of the gene at phenotypic level Ø Yield Ø Growth and developmental parameters Ø Responses to major diseases and insect-pests Ø Quality parameters Ø Economic evaluation/ cost: benefit ratio 34
Biosafety parameters on Transgenic crops C. Agronomic parameters Ø Efficacy of the gene at phenotypic level Ø Yield Ø Growth and developmental parameters Ø Responses to major diseases and insect-pests Ø Quality parameters Ø Economic evaluation/ cost: benefit ratio 34
 GUIDELINES FOR TOXICICTY AND ALLERGENICITY EVALUATION OF TRANSGENIC SEEDS, PLANTS AND PLANT PARTS Guidelines for Toxicity evaluation of transgenic seeds v Acute oral toxicity test of transgenic seeds in Rat v Sub-chronic (90 days) oral toxicity test of transgenic seeds in Rat v Sub-chronic oral toxicity – Goats – 90 days study v Feeding studies of transgenic plants/plant parts in Lactating Crossbred Dairy Cows v Feeding studies of transgenic plants/plant parts in Chicken. v Feeding studies of transgenic plants/plant parts in Catfish v Primary skin irritation test of transgenic seeds in Rabbit v Irritation to mucous membrane test of transgenic sees in female Rabbit v Skin sensitization test of transgenic seeds in Guinea pigs 35
GUIDELINES FOR TOXICICTY AND ALLERGENICITY EVALUATION OF TRANSGENIC SEEDS, PLANTS AND PLANT PARTS Guidelines for Toxicity evaluation of transgenic seeds v Acute oral toxicity test of transgenic seeds in Rat v Sub-chronic (90 days) oral toxicity test of transgenic seeds in Rat v Sub-chronic oral toxicity – Goats – 90 days study v Feeding studies of transgenic plants/plant parts in Lactating Crossbred Dairy Cows v Feeding studies of transgenic plants/plant parts in Chicken. v Feeding studies of transgenic plants/plant parts in Catfish v Primary skin irritation test of transgenic seeds in Rabbit v Irritation to mucous membrane test of transgenic sees in female Rabbit v Skin sensitization test of transgenic seeds in Guinea pigs 35
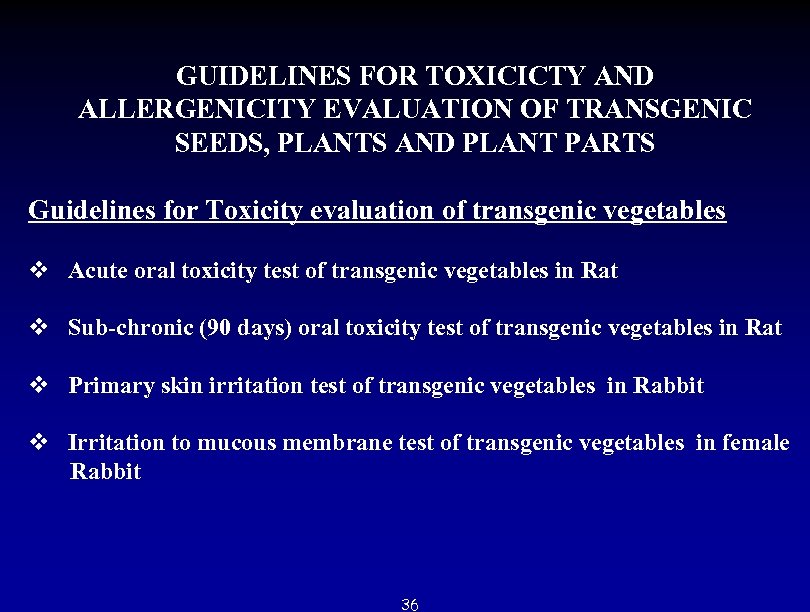 GUIDELINES FOR TOXICICTY AND ALLERGENICITY EVALUATION OF TRANSGENIC SEEDS, PLANTS AND PLANT PARTS Guidelines for Toxicity evaluation of transgenic vegetables v Acute oral toxicity test of transgenic vegetables in Rat v Sub-chronic (90 days) oral toxicity test of transgenic vegetables in Rat v Primary skin irritation test of transgenic vegetables in Rabbit v Irritation to mucous membrane test of transgenic vegetables in female Rabbit 36
GUIDELINES FOR TOXICICTY AND ALLERGENICITY EVALUATION OF TRANSGENIC SEEDS, PLANTS AND PLANT PARTS Guidelines for Toxicity evaluation of transgenic vegetables v Acute oral toxicity test of transgenic vegetables in Rat v Sub-chronic (90 days) oral toxicity test of transgenic vegetables in Rat v Primary skin irritation test of transgenic vegetables in Rabbit v Irritation to mucous membrane test of transgenic vegetables in female Rabbit 36
 GUIDELINES FOR TOXICICTY AND ALLERGENICITY EVALUATION OF TRANSGENIC SEEDS, PLANTS AND PLANT PARTS Guidelines for Toxicity evaluation of transgenic leaves v Sub-chronic (90 days) oral toxicity test of transgenic leaves in male Rabbit Protocol for Allergenicity testing of genetically transformed products in Animal Model v Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis (PCA) test v Pransnitz-Kustner (PK) test v Radioallergosorbent (RAST)/RAST inhibition test v Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) 37
GUIDELINES FOR TOXICICTY AND ALLERGENICITY EVALUATION OF TRANSGENIC SEEDS, PLANTS AND PLANT PARTS Guidelines for Toxicity evaluation of transgenic leaves v Sub-chronic (90 days) oral toxicity test of transgenic leaves in male Rabbit Protocol for Allergenicity testing of genetically transformed products in Animal Model v Passive Cutaneous Anaphylaxis (PCA) test v Pransnitz-Kustner (PK) test v Radioallergosorbent (RAST)/RAST inhibition test v Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) 37
 Agencies Involved in Environmental release of transgenic crops/ food products by imports Mo. A/ICAR, Mo. H&FW, DBT Applicant GEAC Commercial Release 38 Mo. E&F
Agencies Involved in Environmental release of transgenic crops/ food products by imports Mo. A/ICAR, Mo. H&FW, DBT Applicant GEAC Commercial Release 38 Mo. E&F
 GM Food & Feed Scenario • No GM Food / Feed approved so far in India • GM Food crops are being developed by several applicants • Policies on labeling, traceability etc are yet to be finalized 39
GM Food & Feed Scenario • No GM Food / Feed approved so far in India • GM Food crops are being developed by several applicants • Policies on labeling, traceability etc are yet to be finalized 39
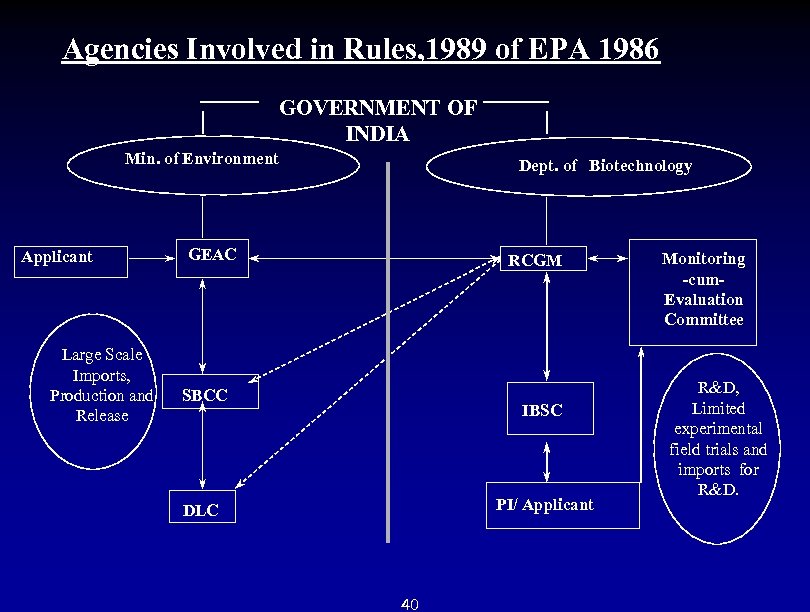 Agencies Involved in Rules, 1989 of EPA 1986 GOVERNMENT OF INDIA Min. of Environment Applicant Large Scale Imports, Production and Release Dept. of Biotechnology GEAC RCGM SBCC IBSC PI/ Applicant DLC 40 Monitoring -cum- Evaluation Committee R&D, Limited experimental field trials and imports for R&D.
Agencies Involved in Rules, 1989 of EPA 1986 GOVERNMENT OF INDIA Min. of Environment Applicant Large Scale Imports, Production and Release Dept. of Biotechnology GEAC RCGM SBCC IBSC PI/ Applicant DLC 40 Monitoring -cum- Evaluation Committee R&D, Limited experimental field trials and imports for R&D.
 Summary of r-DNA Research in India Number of Institutions engaged ~ 240 Number of Institutions engaged in ~ 95 transgenic research (60+35) Number of Private Institutions ~ 50 engaged in r-DNA therapeutics Other Institutions engaged in basic work ~ 95 41
Summary of r-DNA Research in India Number of Institutions engaged ~ 240 Number of Institutions engaged in ~ 95 transgenic research (60+35) Number of Private Institutions ~ 50 engaged in r-DNA therapeutics Other Institutions engaged in basic work ~ 95 41
 TRANSGENIC CROPS APPROVED GOBALLY Sl. No. CROP TRAIT 1. COUNTRY YEAR Canola Herbicide Tolerance (CP 4 EPSPS) Canada US Japan 1995 1999 1996 Canada US Japan Australia 1995 1996 2003 Herbicide Tolerance (PAT) Herbicide Tolerance (bxn) Canada Japan 1997 1998 Canada 1995 Herbicide Tolerance (ALS) contd… 42
TRANSGENIC CROPS APPROVED GOBALLY Sl. No. CROP TRAIT 1. COUNTRY YEAR Canola Herbicide Tolerance (CP 4 EPSPS) Canada US Japan 1995 1999 1996 Canada US Japan Australia 1995 1996 2003 Herbicide Tolerance (PAT) Herbicide Tolerance (bxn) Canada Japan 1997 1998 Canada 1995 Herbicide Tolerance (ALS) contd… 42
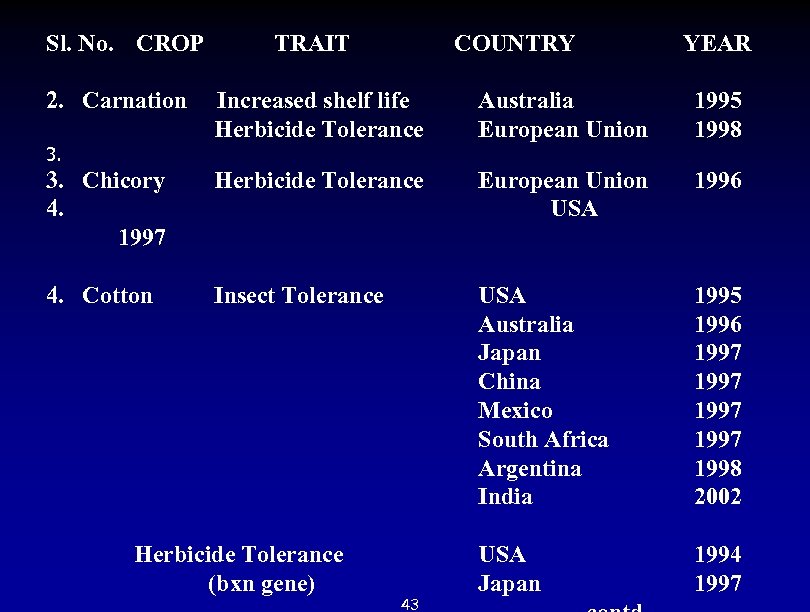 Sl. No. CROP TRAIT COUNTRY YEAR 2. Carnation Increased shelf life Australia 1995 Herbicide Tolerance European Union 1998 3. Chicory Herbicide Tolerance European Union 1996 4. USA 1997 4. Cotton Insect Tolerance USA Australia Japan China Mexico South Africa Argentina India 1995 1996 1997 1998 2002 Herbicide Tolerance USA 1994 (bxn gene) Japan 1997 43
Sl. No. CROP TRAIT COUNTRY YEAR 2. Carnation Increased shelf life Australia 1995 Herbicide Tolerance European Union 1998 3. Chicory Herbicide Tolerance European Union 1996 4. USA 1997 4. Cotton Insect Tolerance USA Australia Japan China Mexico South Africa Argentina India 1995 1996 1997 1998 2002 Herbicide Tolerance USA 1994 (bxn gene) Japan 1997 43
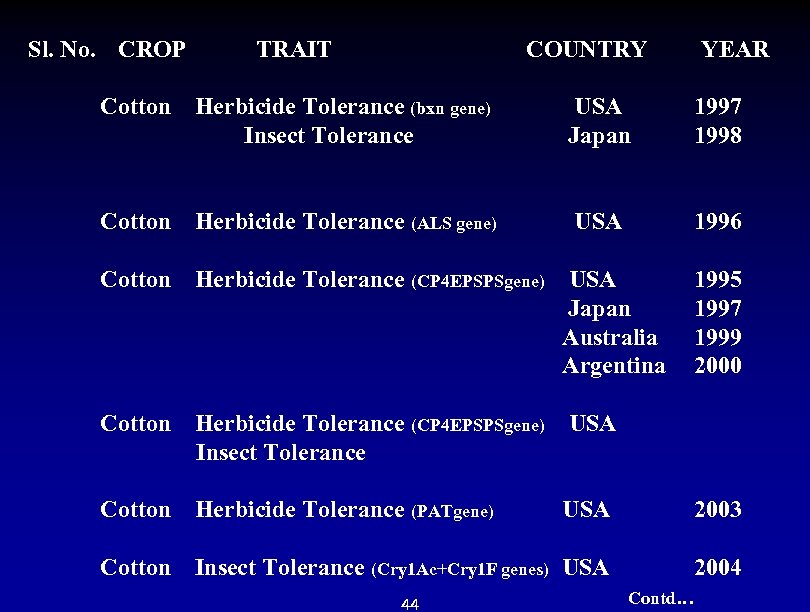 Sl. No. CROP TRAIT COUNTRY YEAR Cotton Herbicide Tolerance (bxn gene) USA 1997 Insect Tolerance Japan 1998 Cotton Herbicide Tolerance (ALS gene) USA Cotton Herbicide Tolerance (CP 4 EPSPSgene) USA Japan Australia Argentina 1996 1995 1997 1999 2000 Cotton Herbicide Tolerance (CP 4 EPSPSgene) USA Insect Tolerance Cotton Herbicide Tolerance (PATgene) USA 2003 Cotton Insect Tolerance (Cry 1 Ac+Cry 1 F genes) USA 2004 Contd… 44
Sl. No. CROP TRAIT COUNTRY YEAR Cotton Herbicide Tolerance (bxn gene) USA 1997 Insect Tolerance Japan 1998 Cotton Herbicide Tolerance (ALS gene) USA Cotton Herbicide Tolerance (CP 4 EPSPSgene) USA Japan Australia Argentina 1996 1995 1997 1999 2000 Cotton Herbicide Tolerance (CP 4 EPSPSgene) USA Insect Tolerance Cotton Herbicide Tolerance (PATgene) USA 2003 Cotton Insect Tolerance (Cry 1 Ac+Cry 1 F genes) USA 2004 Contd… 44
 Sl. No. CROP TRAIT COUNTRY YEAR 5. Linseed Herbicide Tolerance (ALS gene) Canada 1996 USA 1999 6. Maize Insect Tolerance USA Herbicide Tolerance(CP 4 EPSPS gene) Canada Japan 1996 1997 Maize Herbicide Tolerance (PAT gene) USA Canada Japan Argentina 1995 1996 1997 1998 Maize Herbicide Tolerance (PAT gene) USA 1995 Insect Tolerance Canada 1996 Japan 1996 Argentina 1996 EU 1997 Contd… 45
Sl. No. CROP TRAIT COUNTRY YEAR 5. Linseed Herbicide Tolerance (ALS gene) Canada 1996 USA 1999 6. Maize Insect Tolerance USA Herbicide Tolerance(CP 4 EPSPS gene) Canada Japan 1996 1997 Maize Herbicide Tolerance (PAT gene) USA Canada Japan Argentina 1995 1996 1997 1998 Maize Herbicide Tolerance (PAT gene) USA 1995 Insect Tolerance Canada 1996 Japan 1996 Argentina 1996 EU 1997 Contd… 45
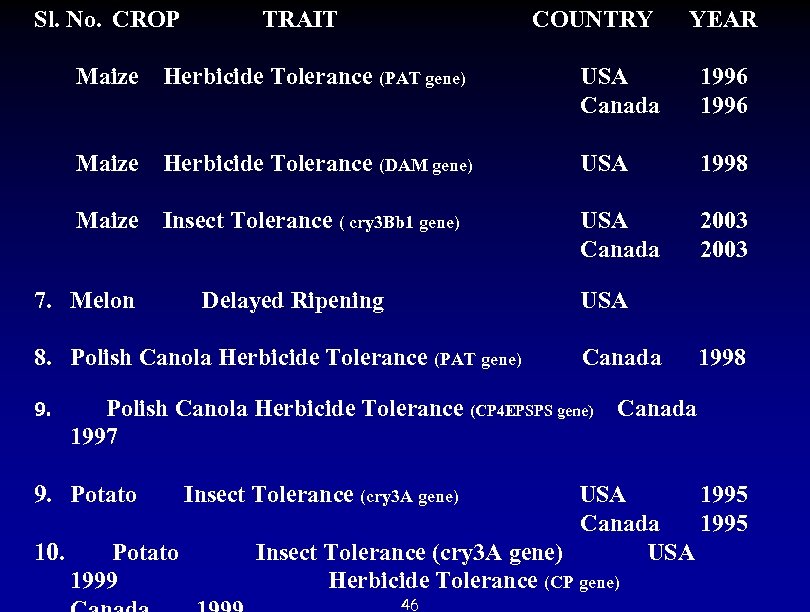 Sl. No. CROP TRAIT COUNTRY YEAR Maize Herbicide Tolerance (PAT gene) USA 1996 Canada 1996 Maize Herbicide Tolerance (DAM gene) USA 1998 Maize Insect Tolerance ( cry 3 Bb 1 gene) USA 2003 Canada 2003 7. Melon Delayed Ripening USA 8. Polish Canola Herbicide Tolerance (PAT gene) Canada 1998 9. Polish Canola Herbicide Tolerance (CP 4 EPSPS gene) Canada 1997 9. Potato Insect Tolerance (cry 3 A gene) USA 1995 Canada 1995 10. Potato Insect Tolerance (cry 3 A gene) USA 1999 Herbicide Tolerance (CP gene) 46
Sl. No. CROP TRAIT COUNTRY YEAR Maize Herbicide Tolerance (PAT gene) USA 1996 Canada 1996 Maize Herbicide Tolerance (DAM gene) USA 1998 Maize Insect Tolerance ( cry 3 Bb 1 gene) USA 2003 Canada 2003 7. Melon Delayed Ripening USA 8. Polish Canola Herbicide Tolerance (PAT gene) Canada 1998 9. Polish Canola Herbicide Tolerance (CP 4 EPSPS gene) Canada 1997 9. Potato Insect Tolerance (cry 3 A gene) USA 1995 Canada 1995 10. Potato Insect Tolerance (cry 3 A gene) USA 1999 Herbicide Tolerance (CP gene) 46
 Sl. No. CROP TRAIT 10. Rice COUNTRY YEAR Herbicide Tolerance (PAT gene) USA 1999 11. Soybean Herbicide Tolerance (CP 4 EPSPS gene) USA 1994 Argentina 1996 12. Japan 1996 Canada 1995 13. Uruguay 1997 14. Mexico 1998 15. Brazil 1998 16. South Africa 2001 Soybean Herbicide Tolerance ( PATgene) USA 1996 Canada 1999 47
Sl. No. CROP TRAIT 10. Rice COUNTRY YEAR Herbicide Tolerance (PAT gene) USA 1999 11. Soybean Herbicide Tolerance (CP 4 EPSPS gene) USA 1994 Argentina 1996 12. Japan 1996 Canada 1995 13. Uruguay 1997 14. Mexico 1998 15. Brazil 1998 16. South Africa 2001 Soybean Herbicide Tolerance ( PATgene) USA 1996 Canada 1999 47
 Sl. No. CROP TRAIT COUNTRY YEAR 12. Squash Resistance to viral infection (cp gene) USA 1994 13. Sugarbeet Herbicide Tolerance (CP 4 EPSPS gene) USA 1998 Sugarbeet Herbicide Tolerance (PAT gene) USA 1998 Canada 2001 14. Tomato Increased Shelf life (ACC gene) USA 1995 Tomato Insect Tolerance Tomato Delayed ripening (SAMase gene) USA 1998 USA 1996 Tomato Delayed ripening (ACCD gene) USA 1995 Tomato Delayed ripening (PG gene) USA 1992 Mexico 1995, Japan 1996 48
Sl. No. CROP TRAIT COUNTRY YEAR 12. Squash Resistance to viral infection (cp gene) USA 1994 13. Sugarbeet Herbicide Tolerance (CP 4 EPSPS gene) USA 1998 Sugarbeet Herbicide Tolerance (PAT gene) USA 1998 Canada 2001 14. Tomato Increased Shelf life (ACC gene) USA 1995 Tomato Insect Tolerance Tomato Delayed ripening (SAMase gene) USA 1998 USA 1996 Tomato Delayed ripening (ACCD gene) USA 1995 Tomato Delayed ripening (PG gene) USA 1992 Mexico 1995, Japan 1996 48
 Transgenic crops approved for conducting contained limited field trials including multi-location field trials during 2005 Sl. No Crop Institute 1. Brinjal Transgene Mahyco, Mumbai Sungro Seeds, N. Delhi IARI, N. Delhi cry 1 Ac cry 1 F 2. Cabbage Sungro Seeds, N. Delhi cry 1 Ac 3. Cauliflower Sungro Seeds, N. Delhi cry 1 Ab 4. Corn cry 1 Ab Turbo-Mu Monsanto, Mumbai Metahelix, Bangalore 49
Transgenic crops approved for conducting contained limited field trials including multi-location field trials during 2005 Sl. No Crop Institute 1. Brinjal Transgene Mahyco, Mumbai Sungro Seeds, N. Delhi IARI, N. Delhi cry 1 Ac cry 1 F 2. Cabbage Sungro Seeds, N. Delhi cry 1 Ac 3. Cauliflower Sungro Seeds, N. Delhi cry 1 Ab 4. Corn cry 1 Ab Turbo-Mu Monsanto, Mumbai Metahelix, Bangalore 49
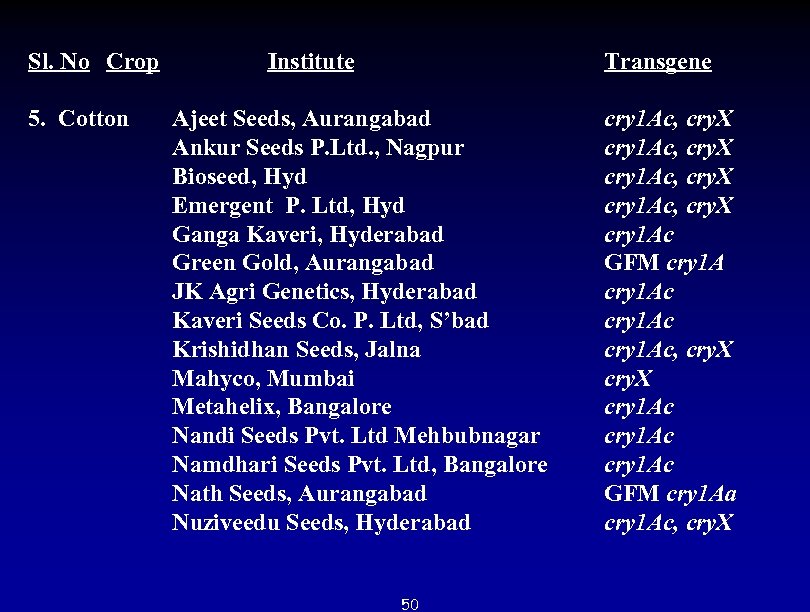 Sl. No Crop Institute 5. Cotton Ajeet Seeds, Aurangabad Ankur Seeds P. Ltd. , Nagpur Bioseed, Hyd Emergent P. Ltd, Hyd Ganga Kaveri, Hyderabad Green Gold, Aurangabad JK Agri Genetics, Hyderabad Kaveri Seeds Co. P. Ltd, S’bad Krishidhan Seeds, Jalna Mahyco, Mumbai Metahelix, Bangalore Nandi Seeds Pvt. Ltd Mehbubnagar Namdhari Seeds Pvt. Ltd, Bangalore Nath Seeds, Aurangabad Nuziveedu Seeds, Hyderabad 50 Transgene cry 1 Ac, cry. X cry 1 Ac GFM cry 1 Ac, cry. X cry 1 Ac GFM cry 1 Aa cry 1 Ac, cry. X
Sl. No Crop Institute 5. Cotton Ajeet Seeds, Aurangabad Ankur Seeds P. Ltd. , Nagpur Bioseed, Hyd Emergent P. Ltd, Hyd Ganga Kaveri, Hyderabad Green Gold, Aurangabad JK Agri Genetics, Hyderabad Kaveri Seeds Co. P. Ltd, S’bad Krishidhan Seeds, Jalna Mahyco, Mumbai Metahelix, Bangalore Nandi Seeds Pvt. Ltd Mehbubnagar Namdhari Seeds Pvt. Ltd, Bangalore Nath Seeds, Aurangabad Nuziveedu Seeds, Hyderabad 50 Transgene cry 1 Ac, cry. X cry 1 Ac GFM cry 1 Ac, cry. X cry 1 Ac GFM cry 1 Aa cry 1 Ac, cry. X
 Sl. No. Crop Institute Transgene Cotton Prabhat. Hyderabad cry 1 Ac Pravardhan, Hyderabad cry 1 Ac Proagro, Hyderabad cry 1 Ac Rasi Seeds Ltd. , Attur cry. X Syngenta India Ltd. , Pune Vip-3 A Tulsi Seeds, Guntur cry 1 Ac, cry. X UAS, Dharwad cry 1 Ac Vibha Agrotech Ltd. Hyderabad cry 1 Ac Vikki’s Agrotech, Hyderabad cry 1 Ac Vikram Seeds Ltd, Ahmedabad cry 1 Ac Zuari Seeds Ltd. Bangalore GFM cry 1 A 6. Groundnut ICRISAT, Hyderabad 7. Mustard UDSC, New Delhi 51 coat protein of IPCV barnase & barstar
Sl. No. Crop Institute Transgene Cotton Prabhat. Hyderabad cry 1 Ac Pravardhan, Hyderabad cry 1 Ac Proagro, Hyderabad cry 1 Ac Rasi Seeds Ltd. , Attur cry. X Syngenta India Ltd. , Pune Vip-3 A Tulsi Seeds, Guntur cry 1 Ac, cry. X UAS, Dharwad cry 1 Ac Vibha Agrotech Ltd. Hyderabad cry 1 Ac Vikki’s Agrotech, Hyderabad cry 1 Ac Vikram Seeds Ltd, Ahmedabad cry 1 Ac Zuari Seeds Ltd. Bangalore GFM cry 1 A 6. Groundnut ICRISAT, Hyderabad 7. Mustard UDSC, New Delhi 51 coat protein of IPCV barnase & barstar
 Sl. No Crop Institute 8. Okra Mahyco, Mumbai 9. Pigeonpea ICARISAT, Hyderbad Transgene cry 1 Ac 10. Rice IARI, N. Delhi Mahyco, Mumbai Metahelix, Bangalore cry 1 Ac, cry 1 Aa +cry 1 B cry 1 Ac NHX gene 11. Tomato IARI, New Delhi antisense replicase gene of tomato LCV cry 1 Ac Mahyco, Mumbai 52
Sl. No Crop Institute 8. Okra Mahyco, Mumbai 9. Pigeonpea ICARISAT, Hyderbad Transgene cry 1 Ac 10. Rice IARI, N. Delhi Mahyco, Mumbai Metahelix, Bangalore cry 1 Ac, cry 1 Aa +cry 1 B cry 1 Ac NHX gene 11. Tomato IARI, New Delhi antisense replicase gene of tomato LCV cry 1 Ac Mahyco, Mumbai 52
 CROPS UNDER FIELDTRIALS v 13 crops under various stages of contained field trials v Include brinjal, cotton, cabbage, groundnut, pigeon pea, mustard, potato, sorghum, tomato, tobacco, rice, okra and cauliflower v Traits include insect resistance, herbicide tolerance, virus resistance, nutritional enhancement, salt tolerance, fungal resistance, etc 53
CROPS UNDER FIELDTRIALS v 13 crops under various stages of contained field trials v Include brinjal, cotton, cabbage, groundnut, pigeon pea, mustard, potato, sorghum, tomato, tobacco, rice, okra and cauliflower v Traits include insect resistance, herbicide tolerance, virus resistance, nutritional enhancement, salt tolerance, fungal resistance, etc 53
 COMMERCIAL USE IN INDIA Ø Only one crop approved i. e. Bt. cotton containing Cry 1 Ac gene Ø Three hybrids approved in 2002, one in 2004 and 16 hybrids in 2005 Ø More hybrids under large scale trials Ø Large scale trials underway for Bt cotton containing Cry 1 Ac & Cry 2 Ab genes 54
COMMERCIAL USE IN INDIA Ø Only one crop approved i. e. Bt. cotton containing Cry 1 Ac gene Ø Three hybrids approved in 2002, one in 2004 and 16 hybrids in 2005 Ø More hybrids under large scale trials Ø Large scale trials underway for Bt cotton containing Cry 1 Ac & Cry 2 Ab genes 54
 Bt. COTTON AREA UNDER CULTIVATION v 2002 – 72, 000 acres v 2003 – 2, 30, 000 acres v 2004 – 13, 10, 000 acres v 2005 – 31, 02, 067 acres 55
Bt. COTTON AREA UNDER CULTIVATION v 2002 – 72, 000 acres v 2003 – 2, 30, 000 acres v 2004 – 13, 10, 000 acres v 2005 – 31, 02, 067 acres 55
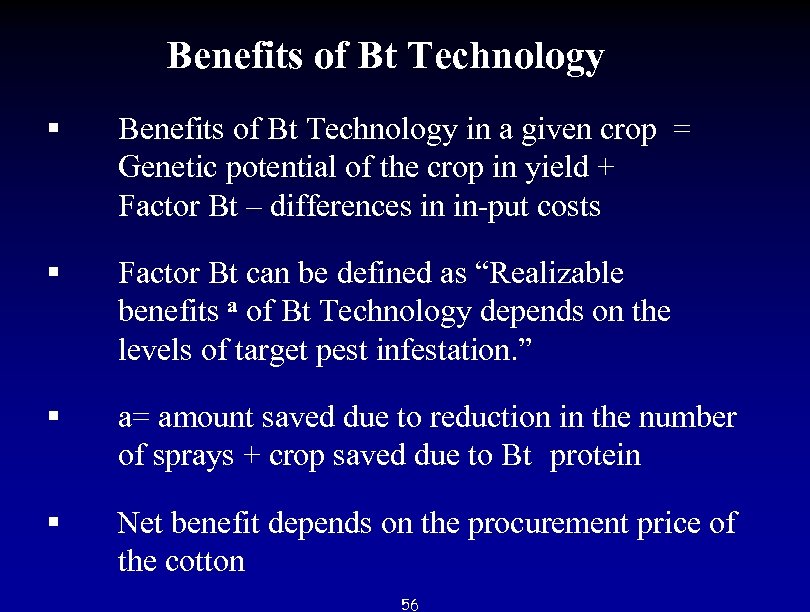 Benefits of Bt Technology § Benefits of Bt Technology in a given crop = Genetic potential of the crop in yield + Factor Bt – differences in in-put costs § Factor Bt can be defined as “Realizable benefits a of Bt Technology depends on the levels of target pest infestation. ” § a= amount saved due to reduction in the number of sprays + crop saved due to Bt protein § Net benefit depends on the procurement price of the cotton 56
Benefits of Bt Technology § Benefits of Bt Technology in a given crop = Genetic potential of the crop in yield + Factor Bt – differences in in-put costs § Factor Bt can be defined as “Realizable benefits a of Bt Technology depends on the levels of target pest infestation. ” § a= amount saved due to reduction in the number of sprays + crop saved due to Bt protein § Net benefit depends on the procurement price of the cotton 56
 CONCLUSIONS v All GMOs and r-DNA products are controlled commodities under the Rules- 1989 OF EPA- 1986. v The Rules & Procedures under EPA are compliance friendly. v The Competent Authorities and their roles are well defined. v Familiarity with the Rules & Procedures is essential for compliance. v The EPA to provide safe products to the society on existing scientific knowledge. 57
CONCLUSIONS v All GMOs and r-DNA products are controlled commodities under the Rules- 1989 OF EPA- 1986. v The Rules & Procedures under EPA are compliance friendly. v The Competent Authorities and their roles are well defined. v Familiarity with the Rules & Procedures is essential for compliance. v The EPA to provide safe products to the society on existing scientific knowledge. 57
 CONCLUSIONS Ø Biosafety is real concern Ø Biosafety regulations required to assess the safety of transgenic crops before its release in to environment Ø Biosafety concerns need to be addressed in a scientific manner Ø Continuous evolution of Biosafety Regulations are required 58
CONCLUSIONS Ø Biosafety is real concern Ø Biosafety regulations required to assess the safety of transgenic crops before its release in to environment Ø Biosafety concerns need to be addressed in a scientific manner Ø Continuous evolution of Biosafety Regulations are required 58
 THANK YOU 59
THANK YOU 59


