Metabolism regulation 2016.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 50
REGULATION OF METABOLISM
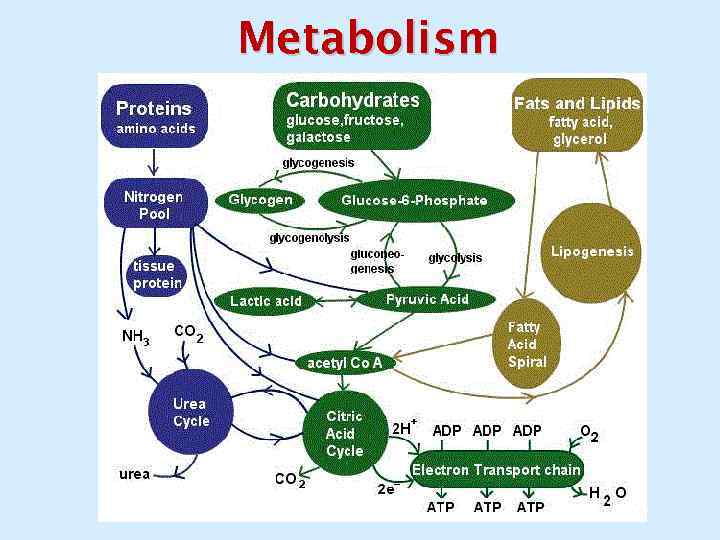
Metabolism
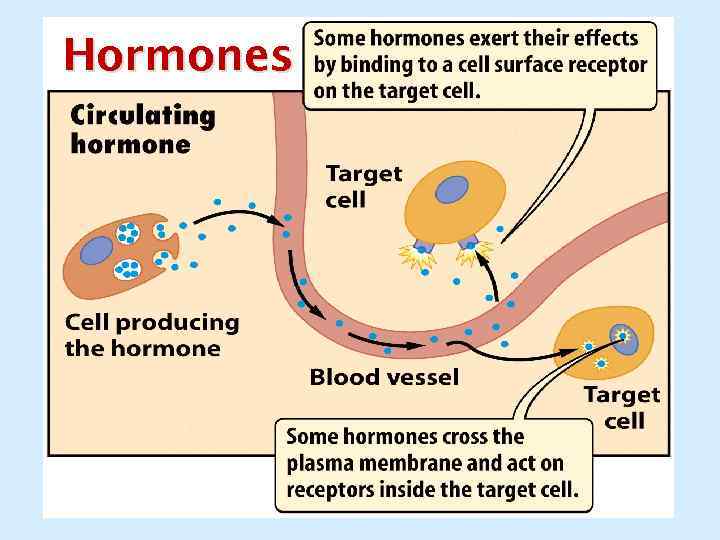
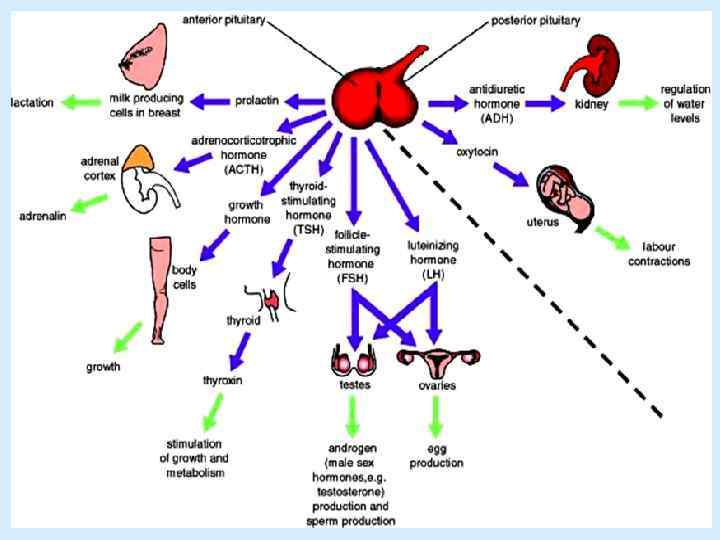
Hormones
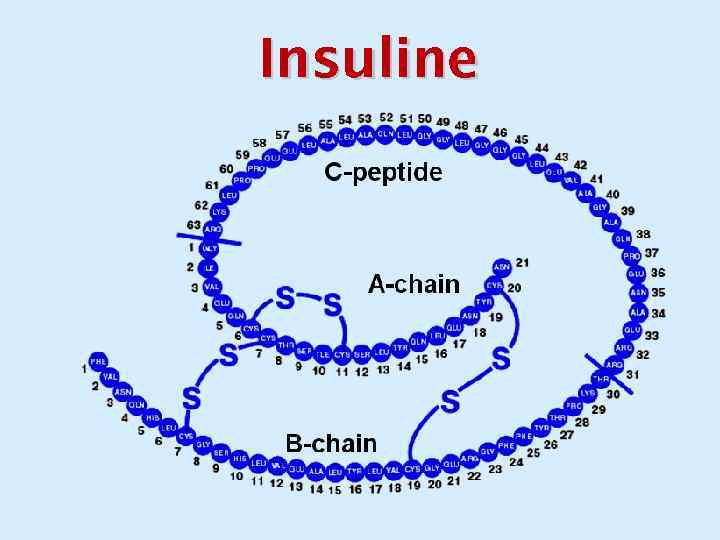
Insuline
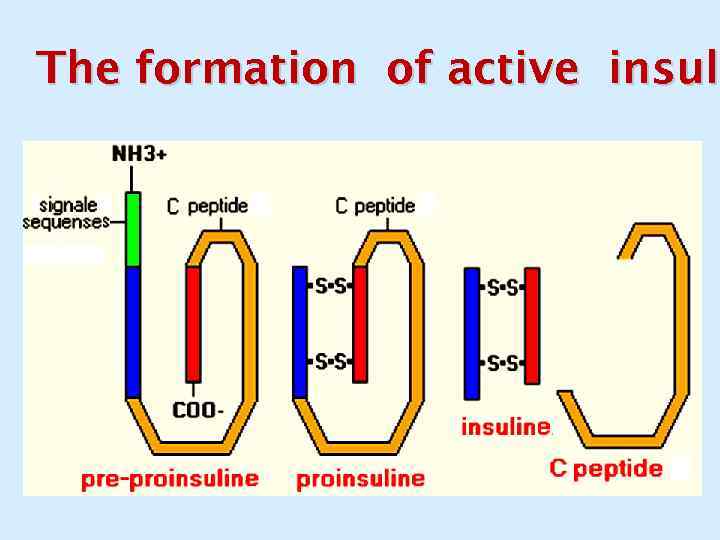
The formation of active insuli active insul
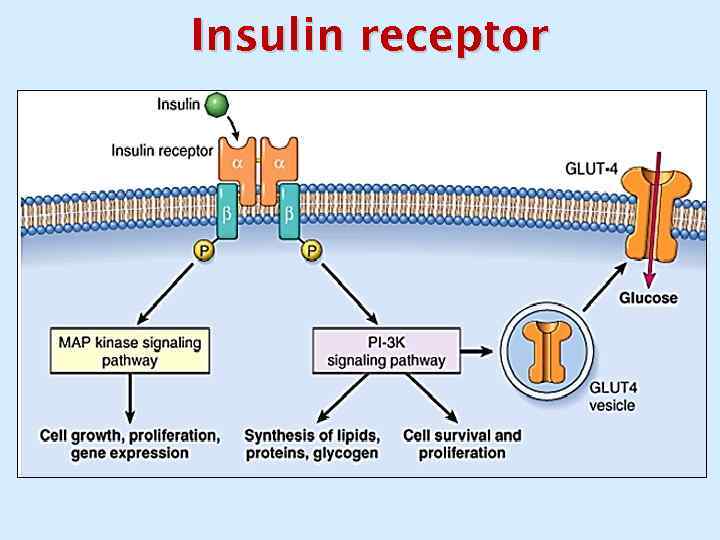
Insulin receptor
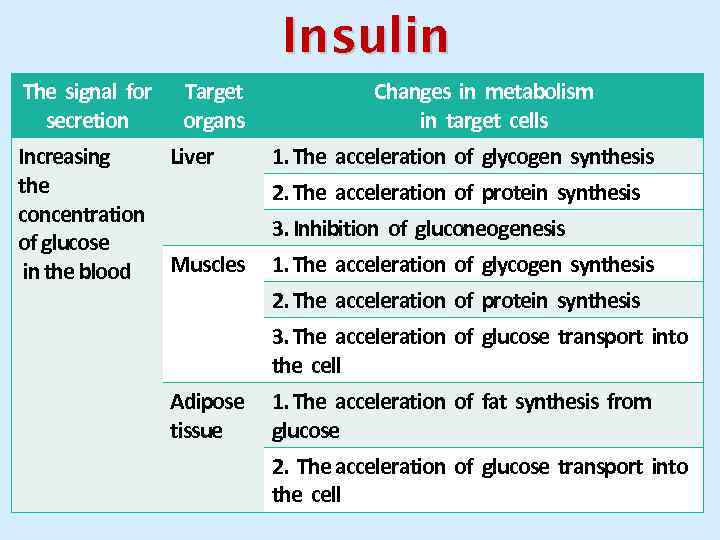
Insulin The signal for Target secretion organs Increasing Liver the concentration of glucose Muscles in the blood Changes in metabolism in target cells 1. The acceleration of glycogen synthesis 2. The acceleration of protein synthesis 3. Inhibition of gluconeogenesis 1. The acceleration of glycogen synthesis 2. The acceleration of protein synthesis 3. The acceleration of glucose transport into the cell Adipose 1. The acceleration of fat synthesis from tissue glucose 2. The acceleration of glucose transport into the cell
Glucagon
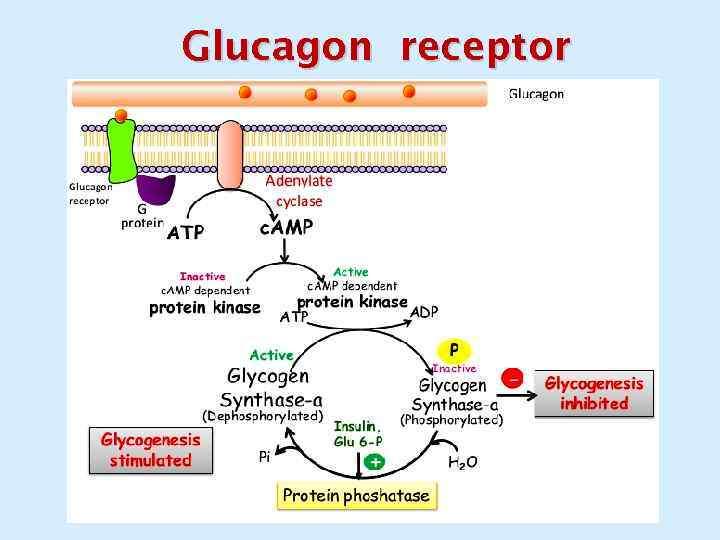
Glucagon receptor
Glucagon The signal Target Changes in Сигнал для секреции Органы-мишени Изменения for secretion organs metabolism in target метаболизма в клетках-мишенях cells Понижение Печень 1. Ускорение Lowering 1. The acceleration концентрации Liver распада blood glucose of glycogen breakdown глюкозы в крови гликогена 2. Ускорение levels 2. The acceleration глюконеогенеза of gluconeogenesis Жировая Ускорение Adipose The acceleration ткань липолиза tissue of lipolysis
Adrenaline
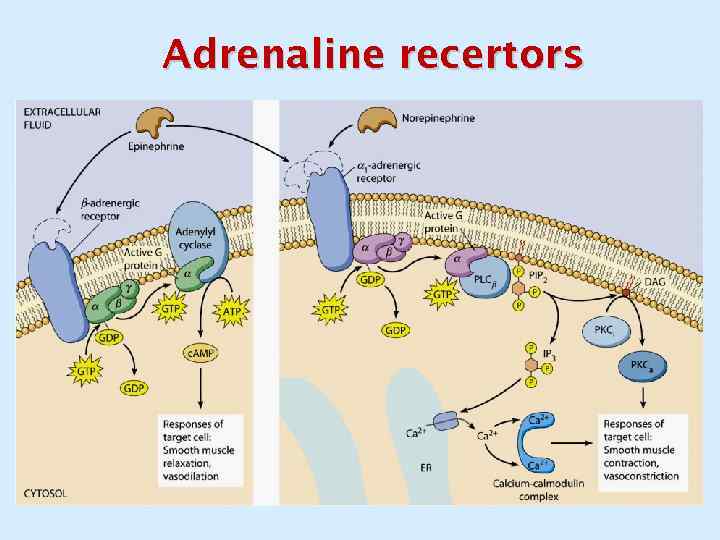
Adrenaline recertors
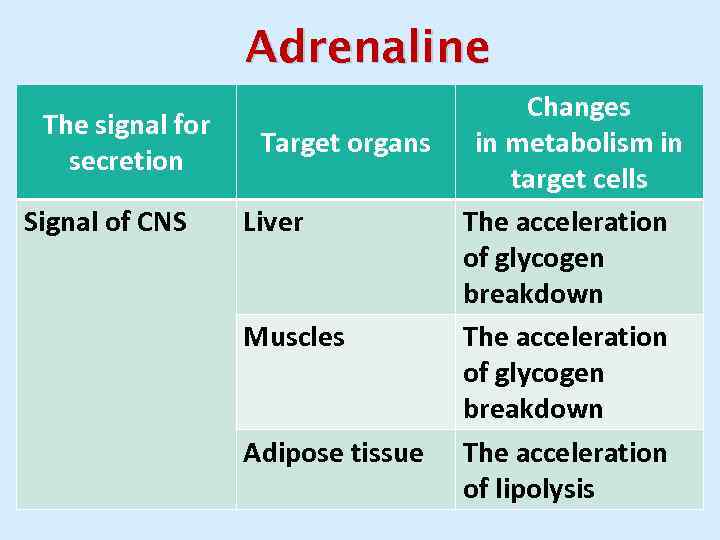
Adrenaline The signal for secretion Signal of CNS Target organs Liver Muscles Adipose tissue Changes in metabolism in target cells The acceleration of glycogen breakdown The acceleration of lipolysis
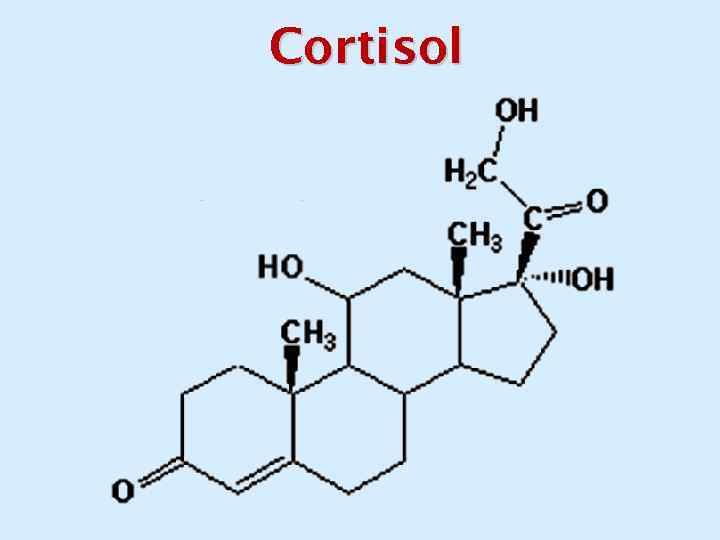
Cortisol
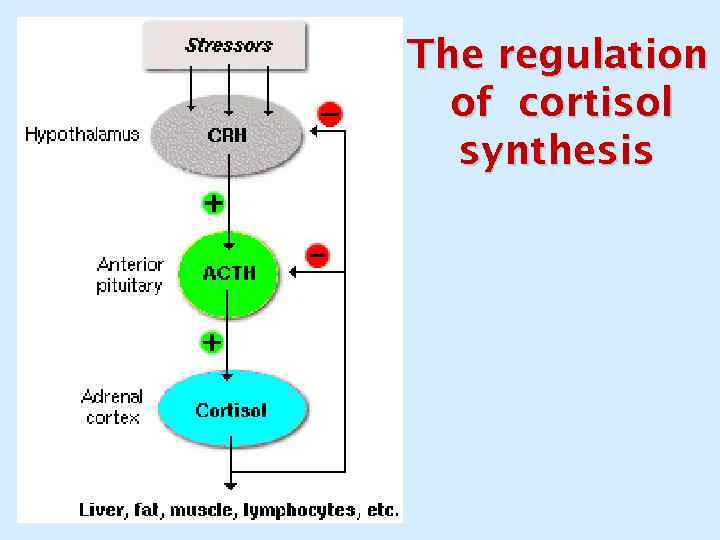
The regulation of cortisol synthesis
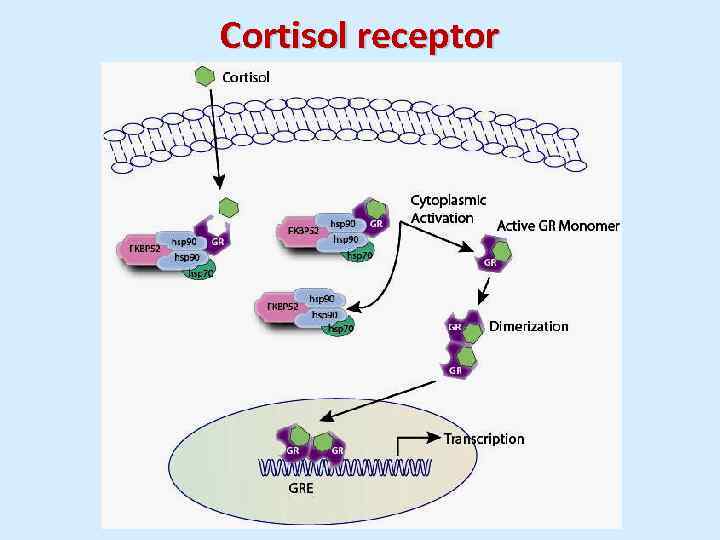
Cortisol receptor
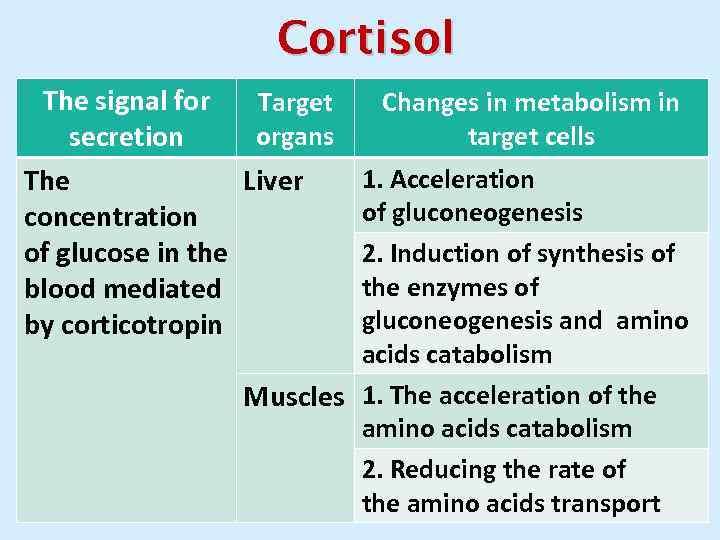
Cortisol The signal for Target organs secretion The Liver concentration of glucose in the blood mediated by corticotropin Changes in metabolism in target cells 1. Acceleration of gluconeogenesis 2. Induction of synthesis of the enzymes of gluconeogenesis and amino acids catabolism Muscles 1. The acceleration of the amino acids catabolism 2. Reducing the rate of the amino acids transport
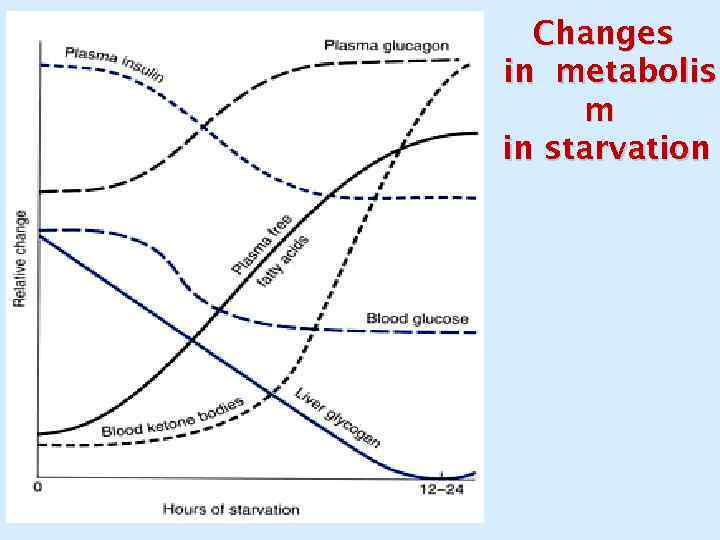
Changes in metabolis m in starvation
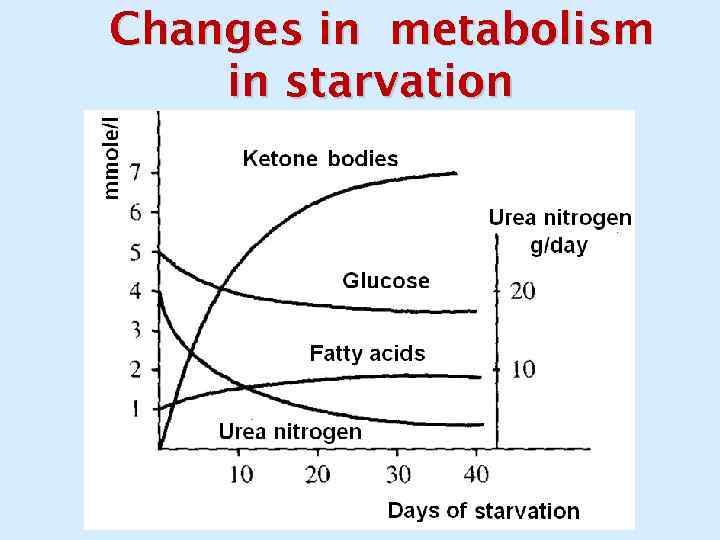
Changes in metabolism in starvation

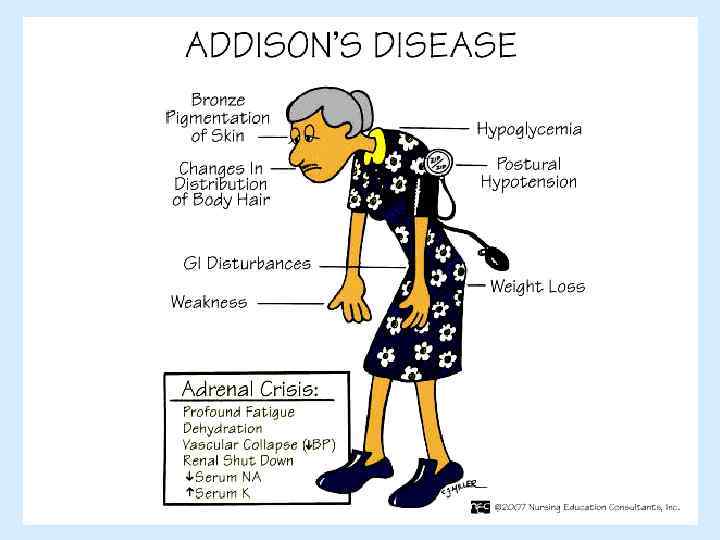
The main manifestations of diabetes Decreased synthesis and deposition of glycogen and fat Hyperglycemia Hyperlipoproteinemia Ketonemia Azotemia and azoturia Polyuria and polydipsia
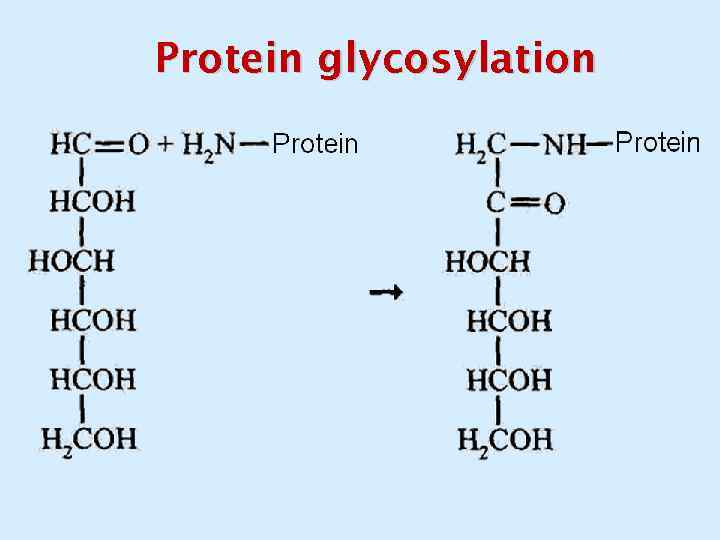
Protein glycosylation
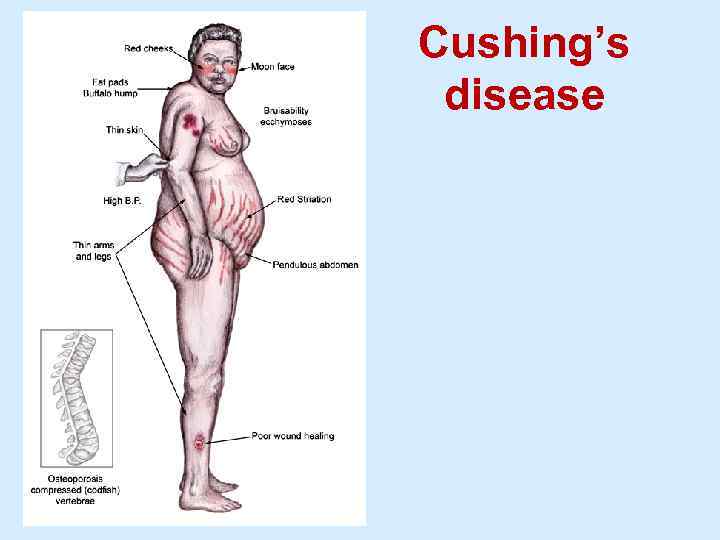
Cushing’s disease

REGULATION OF PHOSPHORUS AND CALCIUM METABOLISM
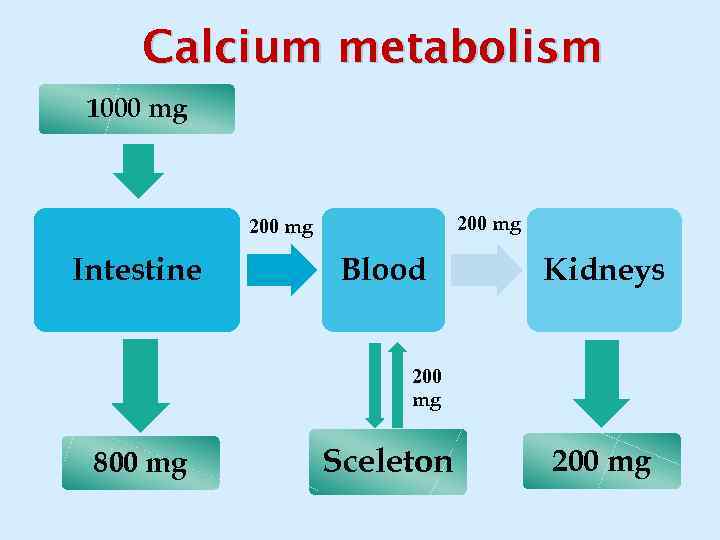
Calcium metabolism 1000 mg 200 mg Intestine Blood Kidneys 200 mg 800 mg Sceleton 200 mg
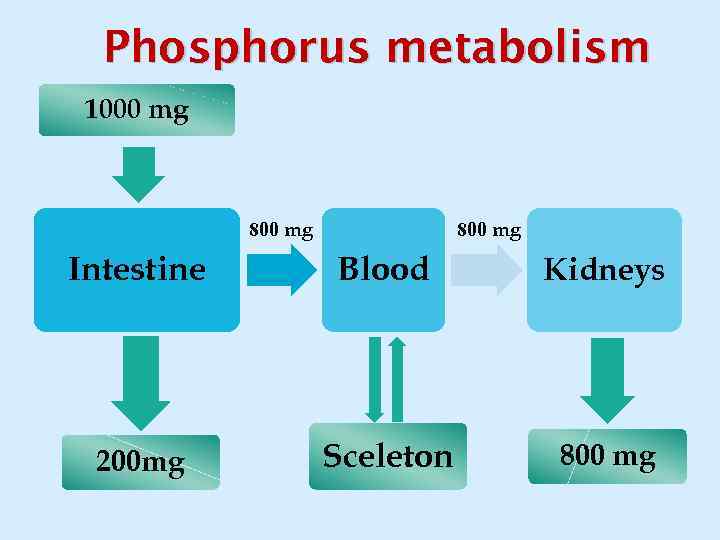
Phosphorus metabolism 1000 mg 800 mg Intestine Blood Kidneys 200 mg Sceleton 800 mg
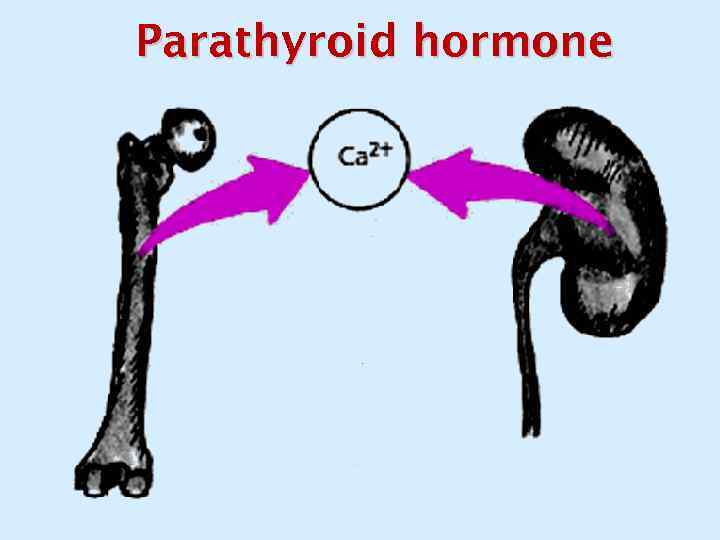
Parathyroid hormone
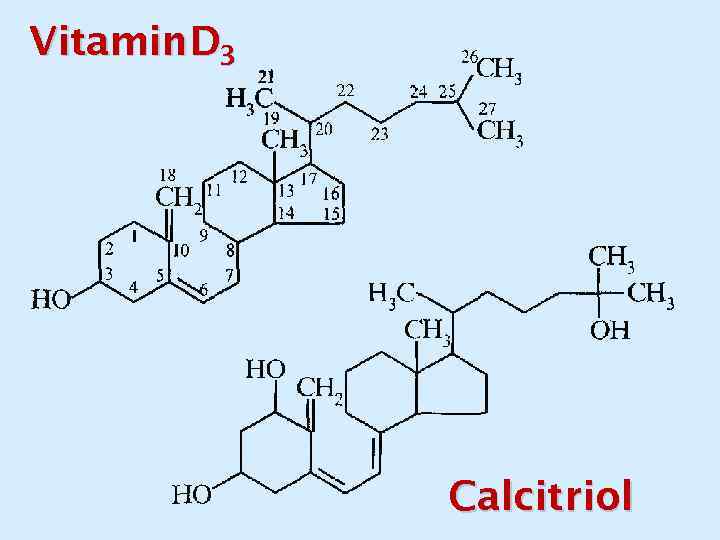
Vitamin. D 3 Calcitriol
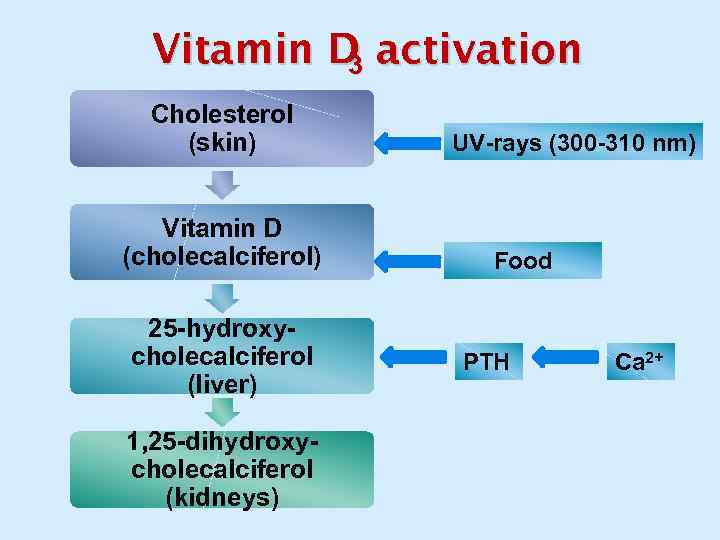
Vitamin D activation 3 Cholesterol (skin) Vitamin D (cholecalciferol) 25 -hydroxycholecalciferol (liver) 1, 25 -dihydroxycholecalciferol (kidneys) UV-rays (300 -310 nm) Food PTH Са 2+
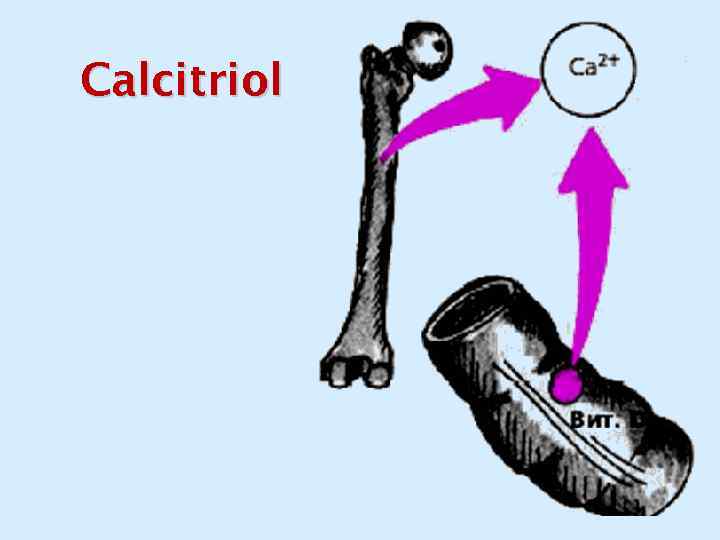
Calcitriol
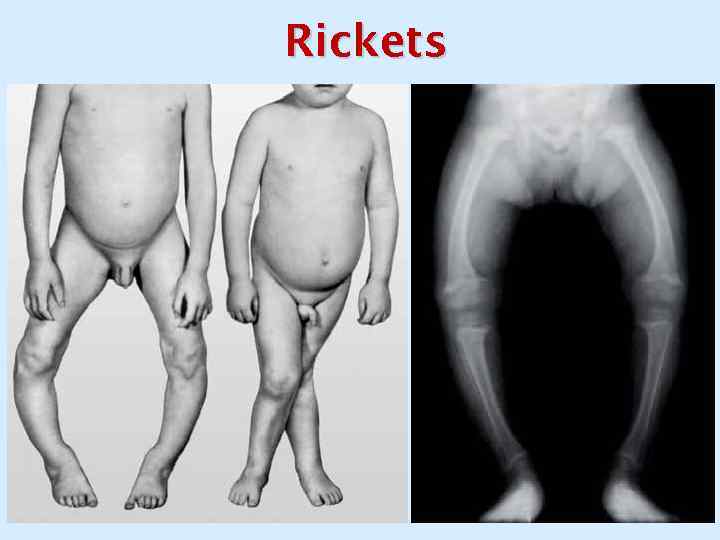
Rickets
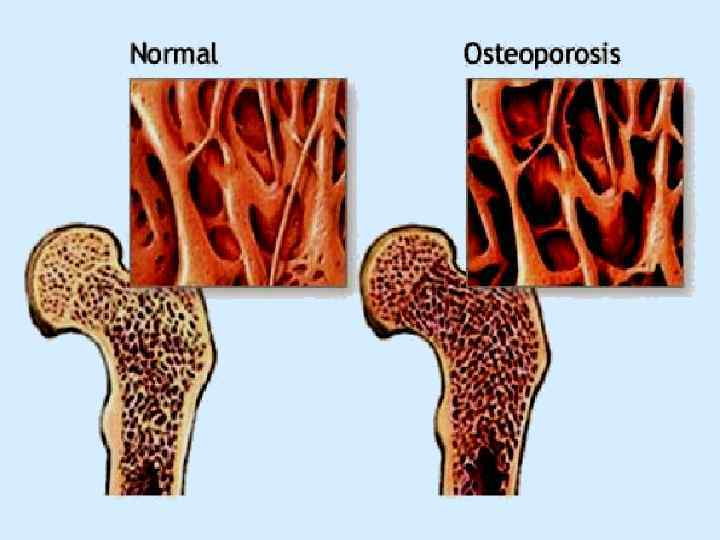
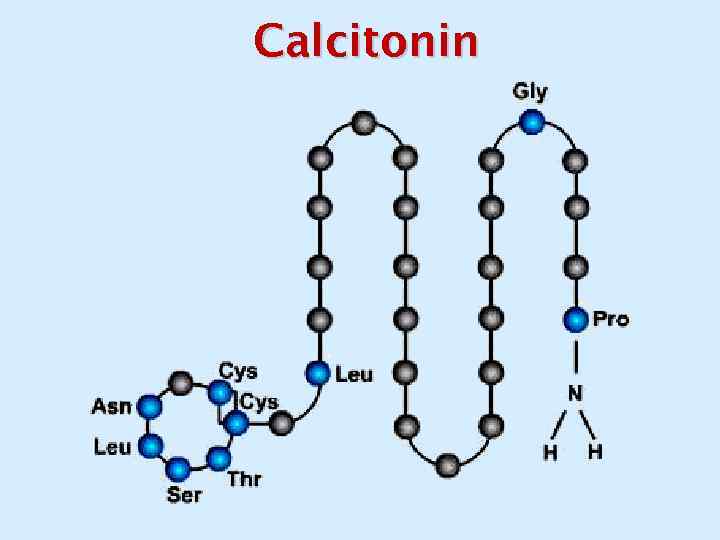
Calcitonin
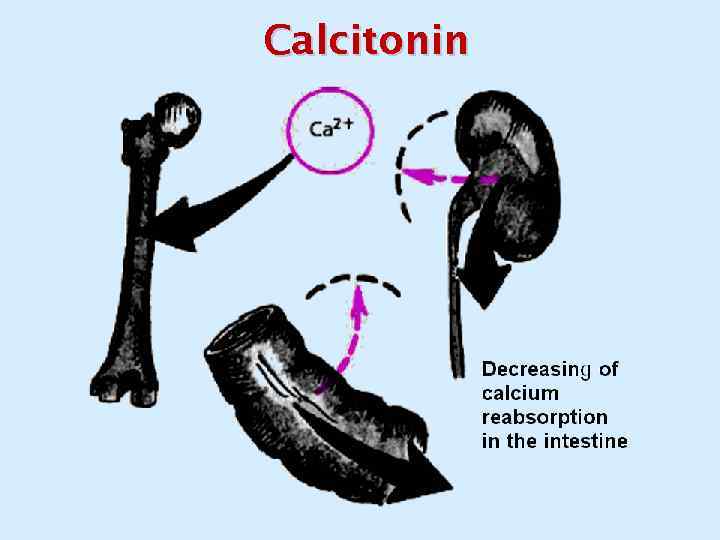
Calcitonin
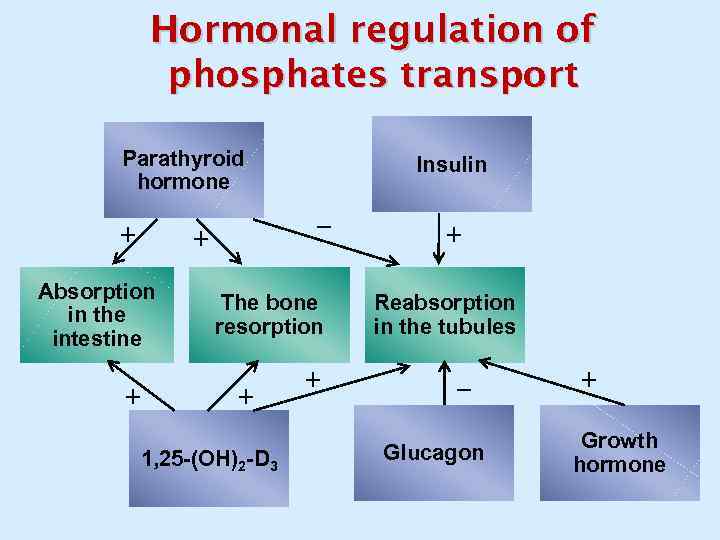
Hormonal regulation of phosphates transport Parathyroid hormone + _ + Absorption in the intestine + Insulin The bone resorption + 1, 25 -(ОН)2 -D 3 + + Reabsorption in the tubules _ Glucagon + Growth hormone
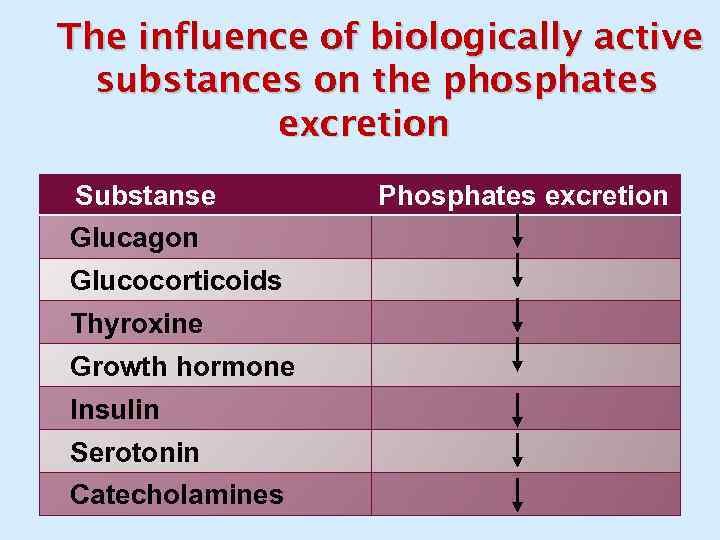
The influence of biologically active substances on the phosphates excretion Substanse Glucagon Glucocorticoids Thyroxine Growth hormone Insulin Serotonin Catecholamines Phosphates excretion

WATER AND SALT METABOLISM RENAL BIOCHEMISTRY
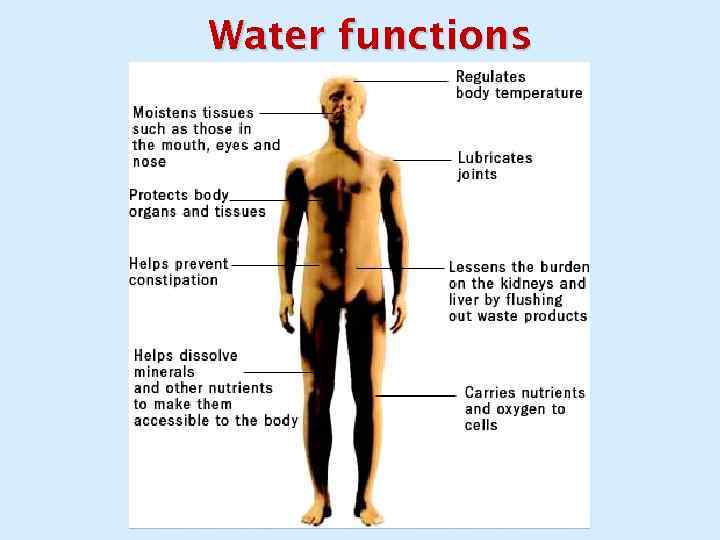
Water functions

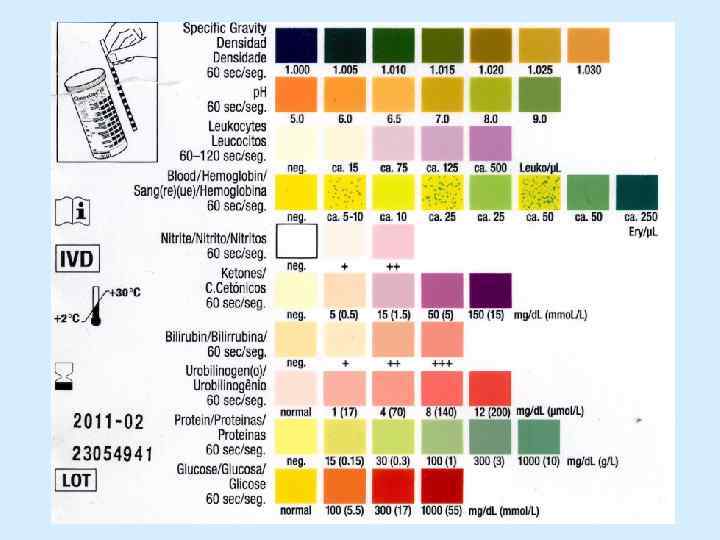
Urinalysis
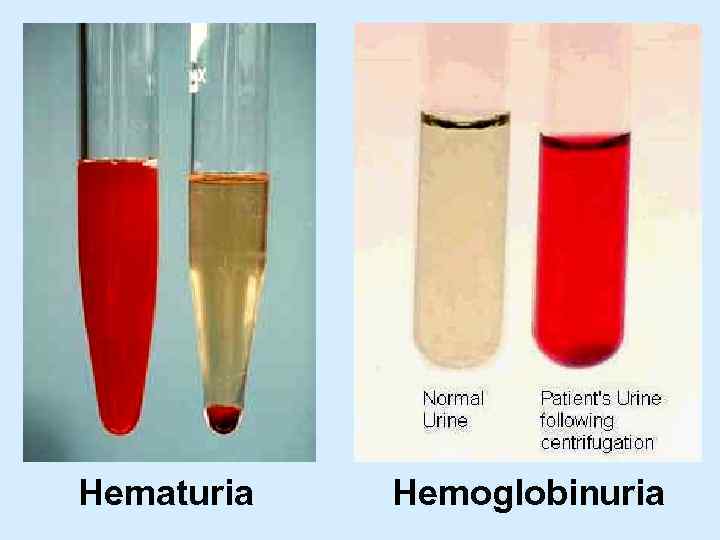
Hematuria Hemoglobinuria
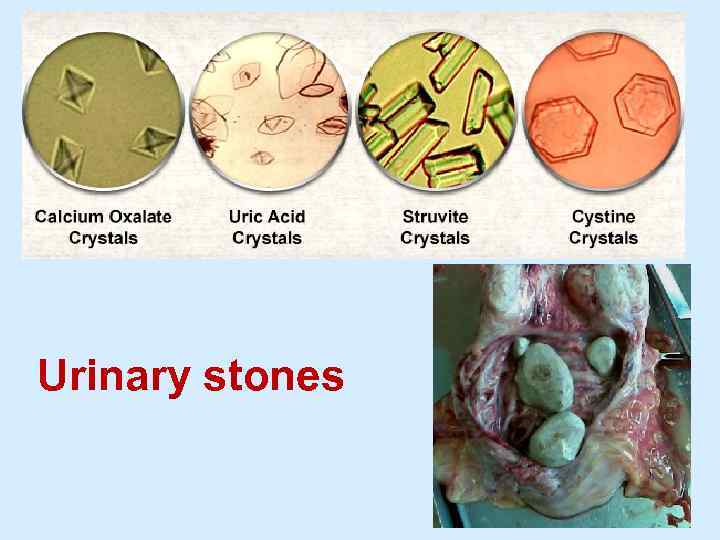
Urinary stones

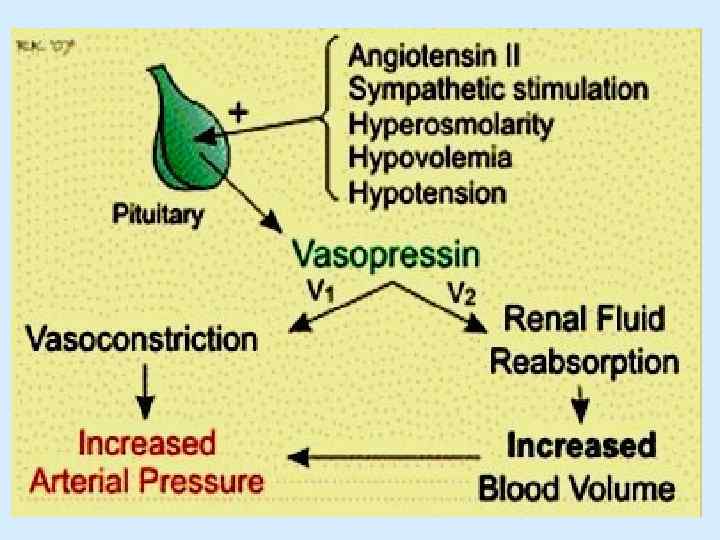
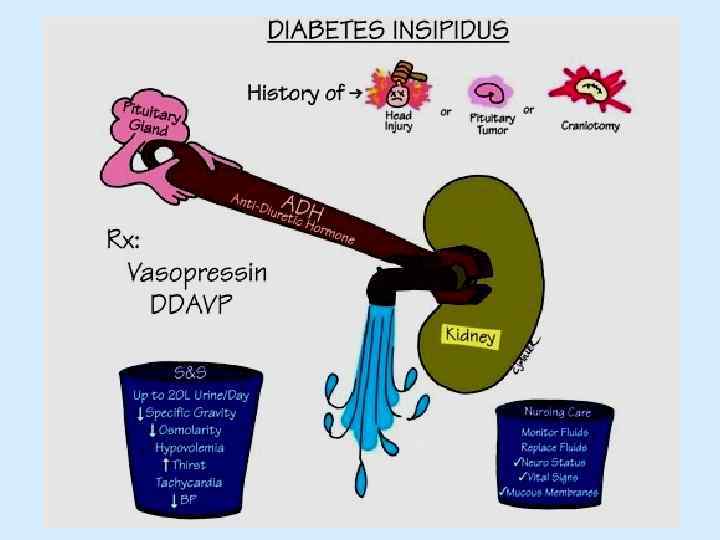
Vasopressin
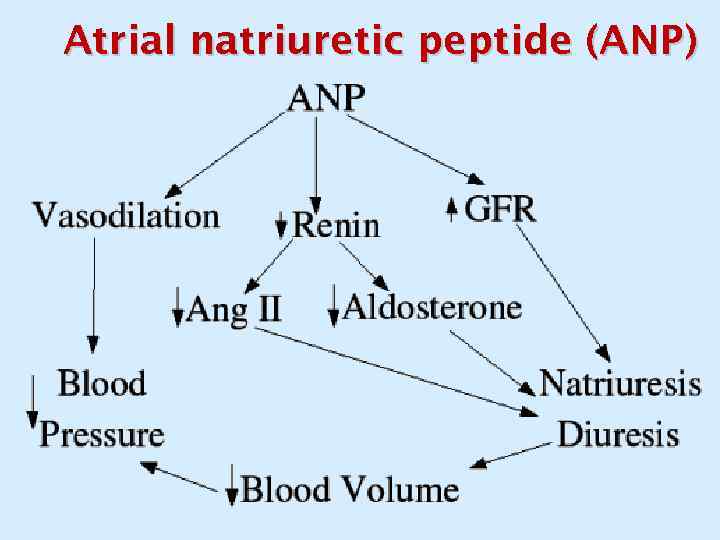
Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
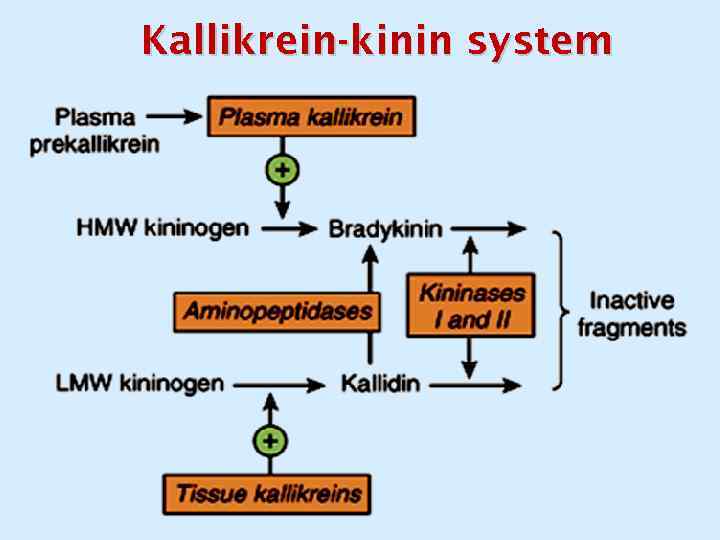
Kallikrein-kinin system
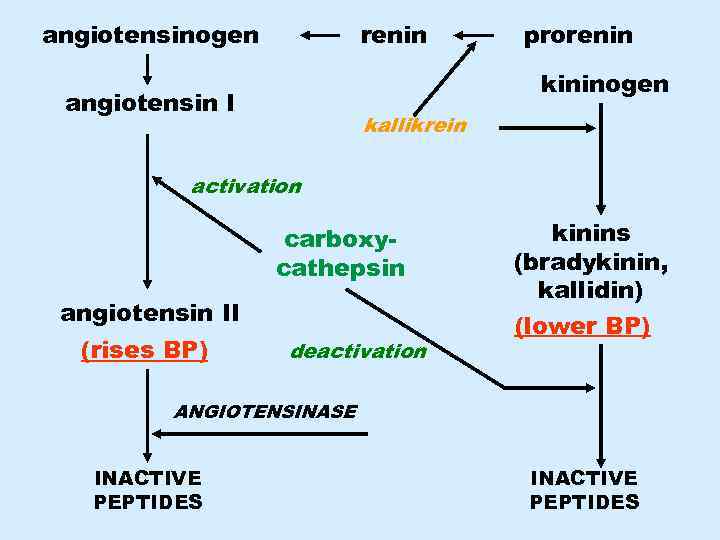
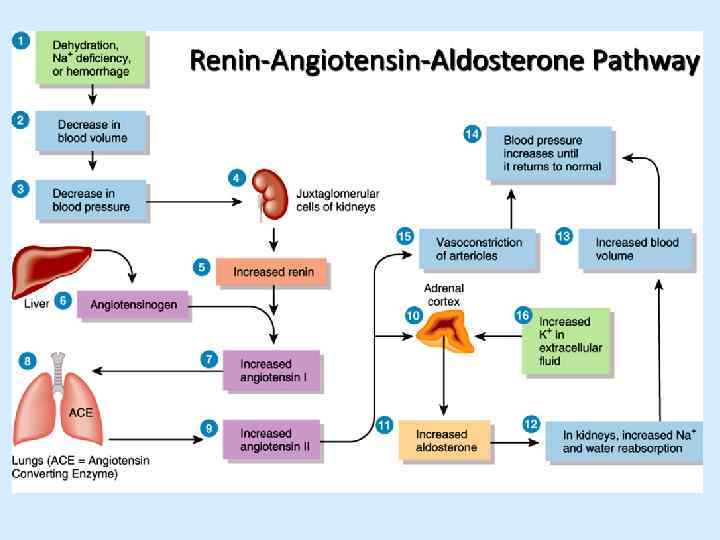
angiotensinogen renin prorenin kininogen angiotensin I kallikrein activation carboxycathepsin angiotensin II (rises BP) deactivation kinins (bradykinin, kallidin) (lower BP) ANGIOTENSINASE INACTIVE PEPTIDES
Metabolism regulation 2016.pptx