Lecture 3 Enzymes, vitamins.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 60

REGULATION OF ENZYME ACTIVITY
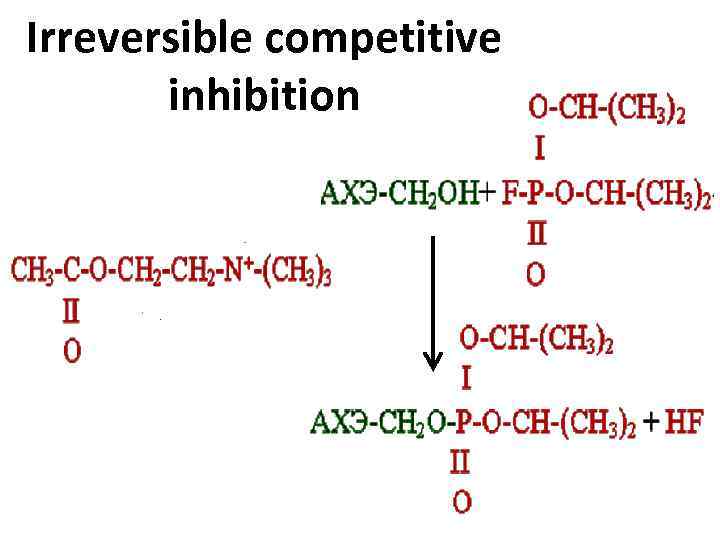
Irreversible competitive inhibition
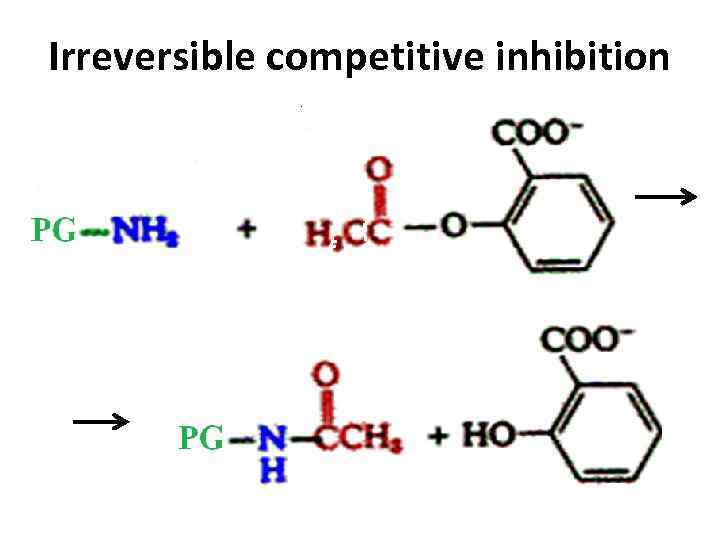
Irreversible competitive inhibition
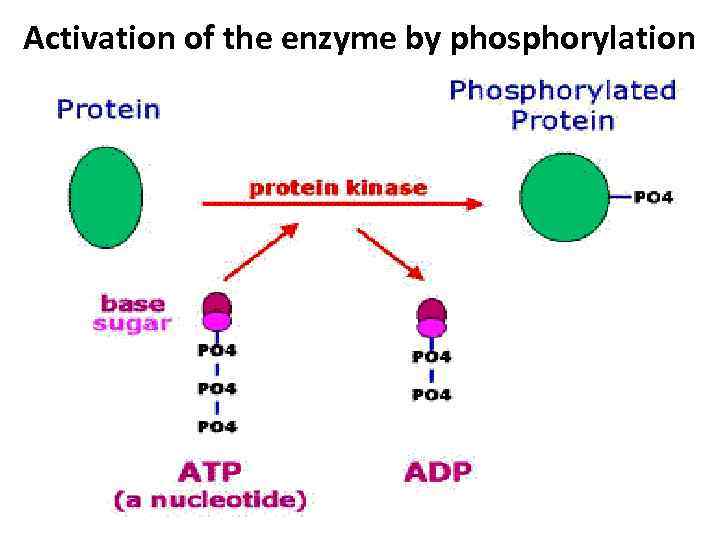
Activation of the enzyme by phosphorylation
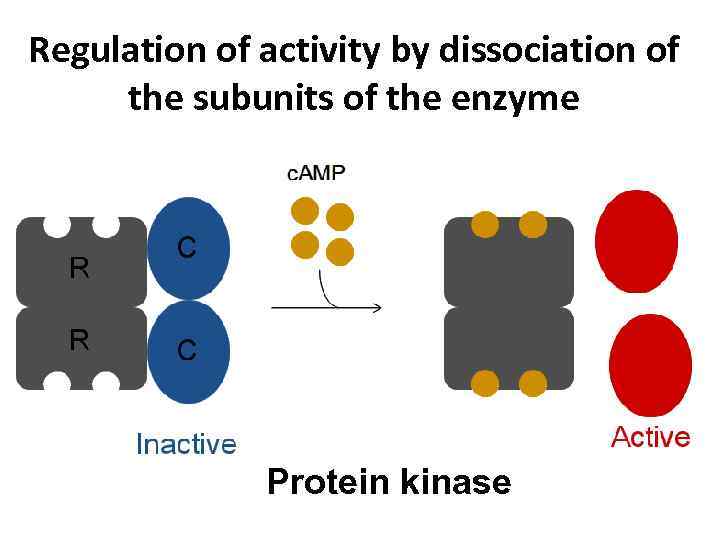
Regulation of activity by dissociation of the subunits of the enzyme Protein kinase

Partial proteolysis inactive enzyme
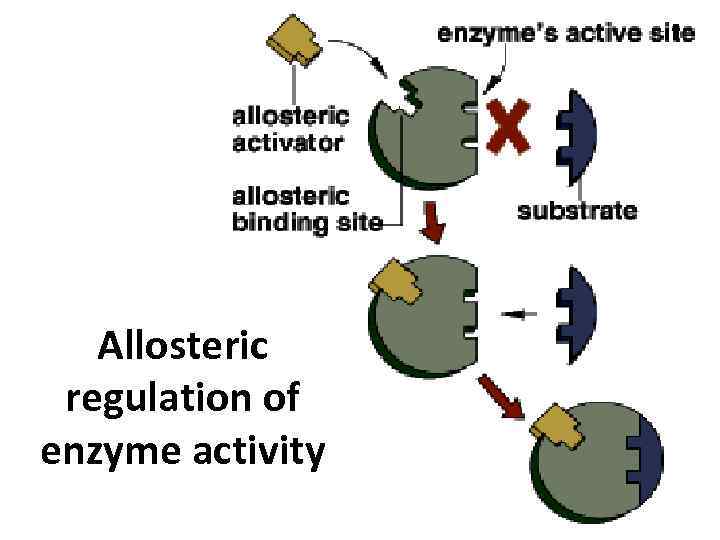
Allosteric regulation of enzyme activity
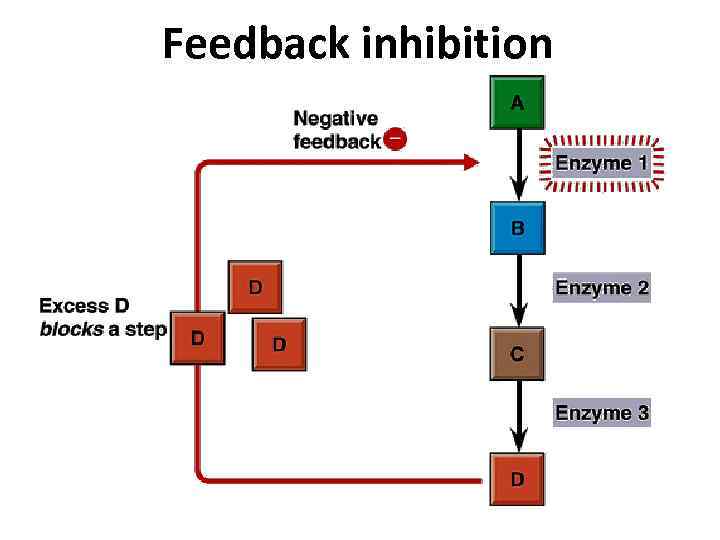
Feedback inhibition

ENZYMES IN MEDICINE

Enzymes as therapeutic agents Enzyme The use of enzymes Trypsin, lipase, Disturbances of the amylase digestion Urease Removal of urea from the body in the "artificial kidney" Ribonuclease, Antiviral drugs against deoxyribonucle herpetic keratitis, ase adenoviral conjunctivitis Streptokinase, Preventing blood clots urokinase during operations
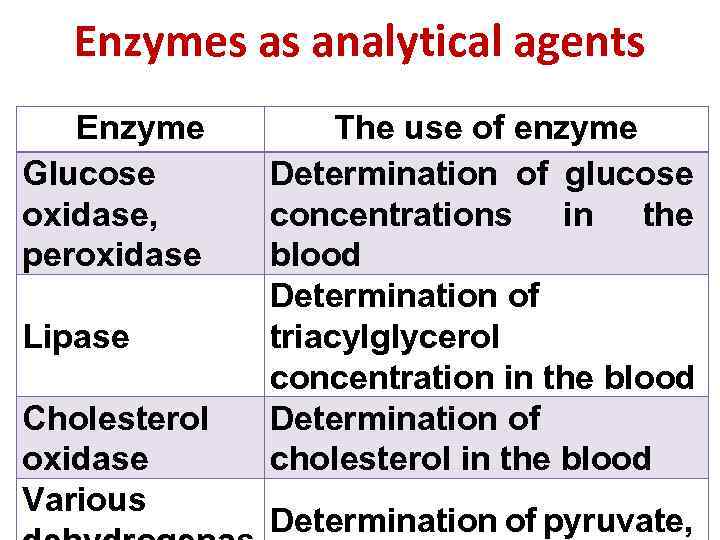
Enzymes as analytical agents Enzyme Glucose oxidase, peroxidase Lipase Cholesterol oxidase Various The use of enzyme Determination of glucose concentrations in the blood Determination of triacylglycerol concentration in the blood Determination of cholesterol in the blood Determination of pyruvate,
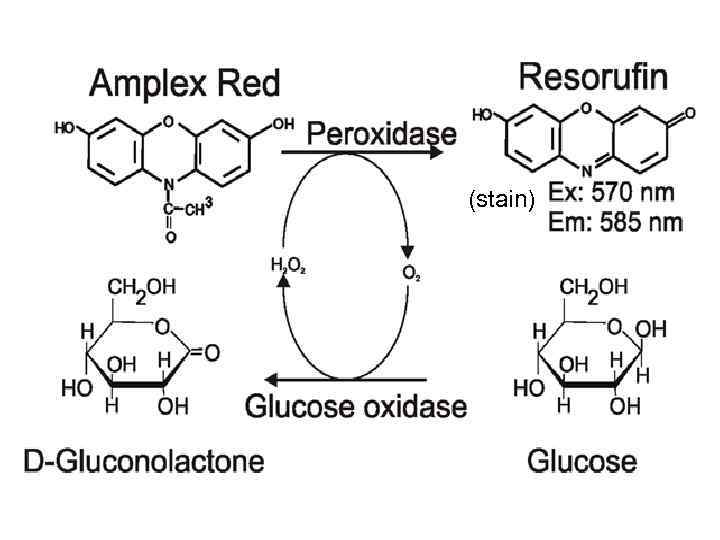
(stain)
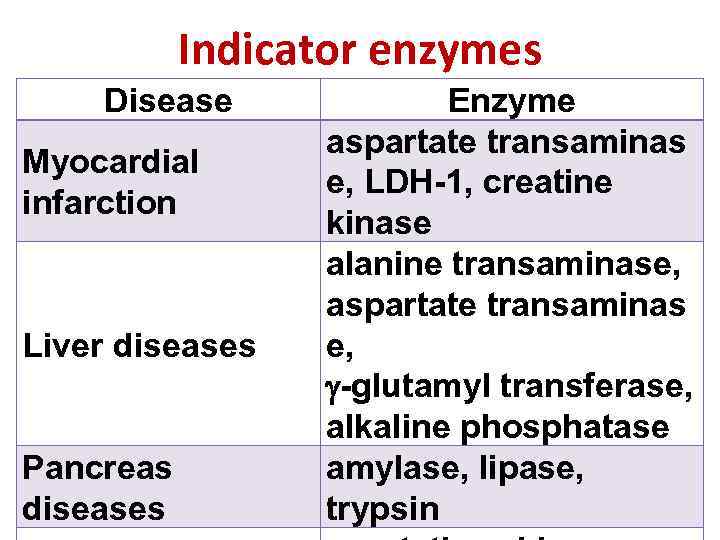
Indicator enzymes Disease Myocardial infarction Liver diseases Pancreas diseases Enzyme aspartate transaminas e, LDH-1, creatine kinase alanine transaminase, aspartate transaminas e, -glutamyl transferase, alkaline phosphatase amylase, lipase, trypsin


Vitamins

James Lind N. I. Lunin

K. Funk N. D. Zelinsky
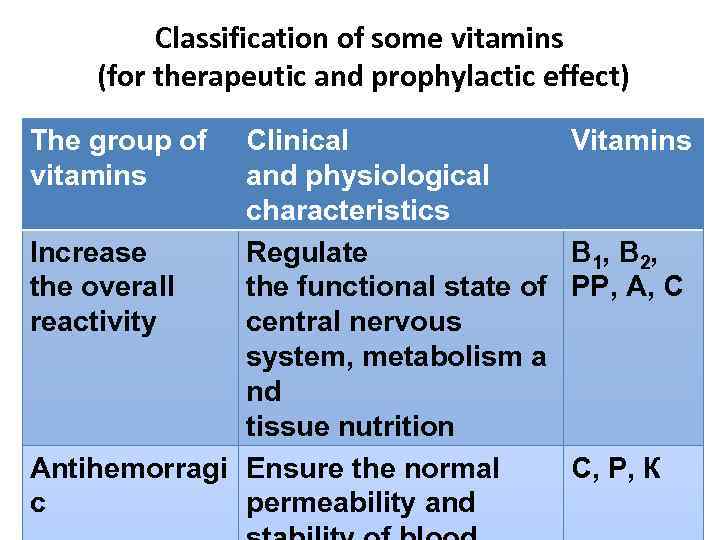
Classification of some vitamins (for therapeutic and prophylactic effect) The group of vitamins Clinical and physiological characteristics Increase Regulate the overall the functional state of reactivity central nervous system, metabolism a nd tissue nutrition Antihemorragi Ensure the normal c permeability and Vitamins В 1, В 2, РР, А, С С, Р, К
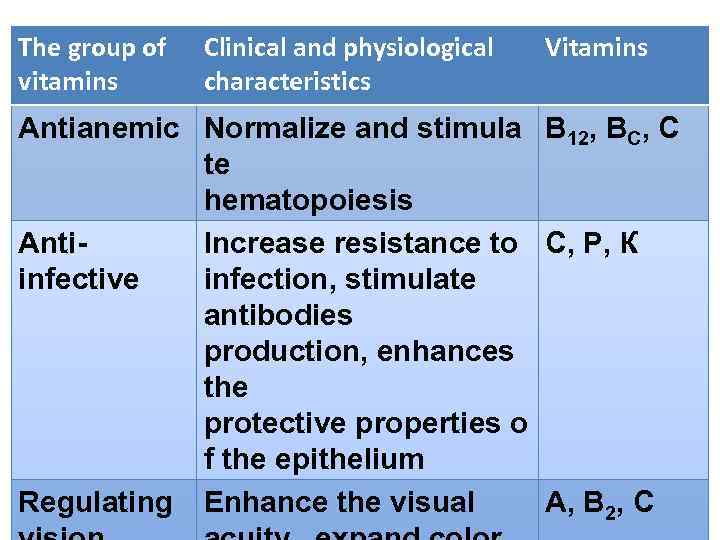
The group of vitamins Clinical and physiological characteristics Vitamins Antianemic Normalize and stimula В 12, ВС, С te hematopoiesis Anti. Increase resistance to С, Р, К infective infection, stimulate antibodies production, enhances the protective properties o f the epithelium Regulating Enhance the visual А, В 2, С
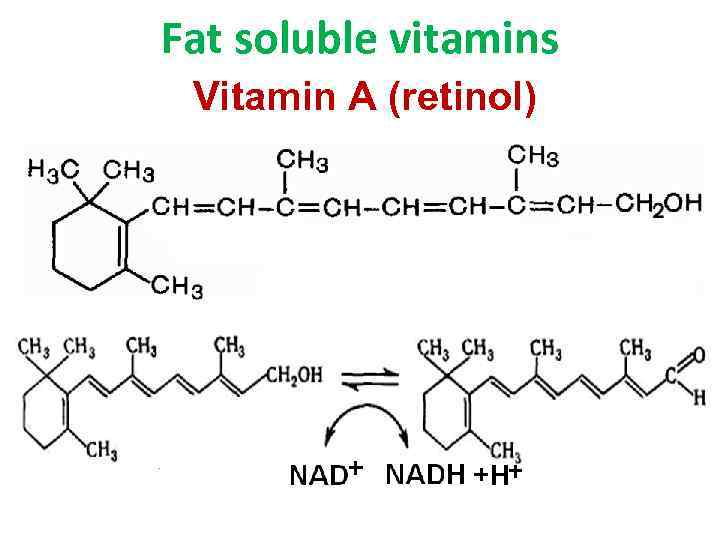
Fat soluble vitamins Vitamin A (retinol)
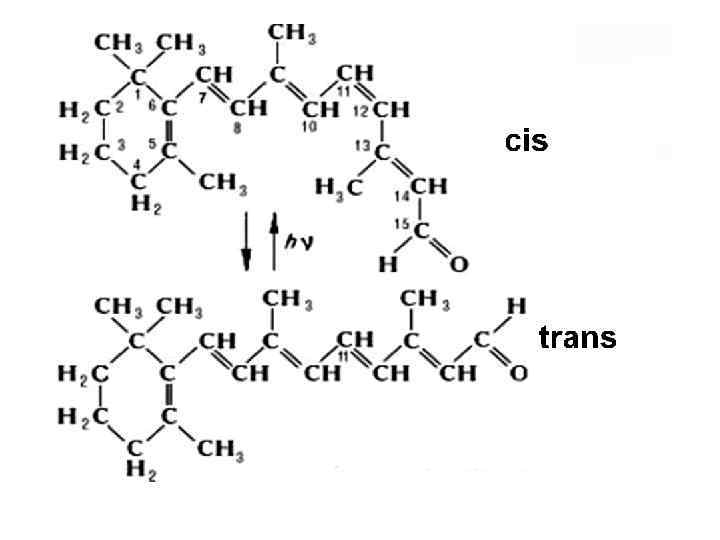

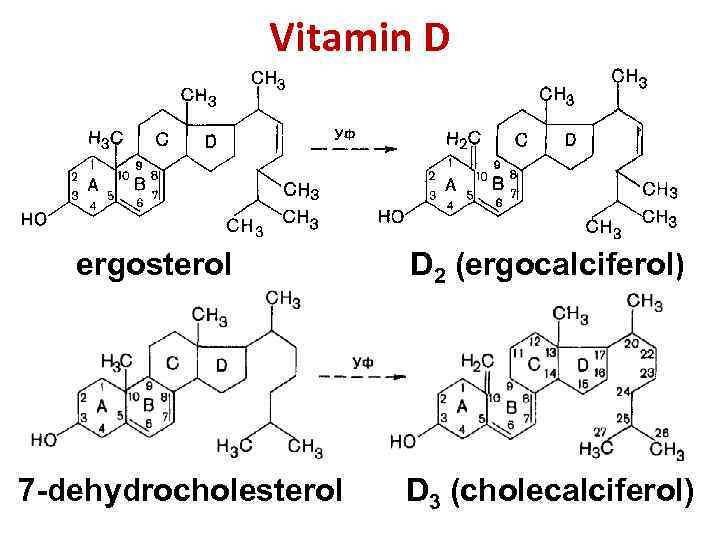
Vitamin D ergosterol D 2 (ergocalciferol) 7 -dehydrocholesterol D 3 (cholecalciferol)
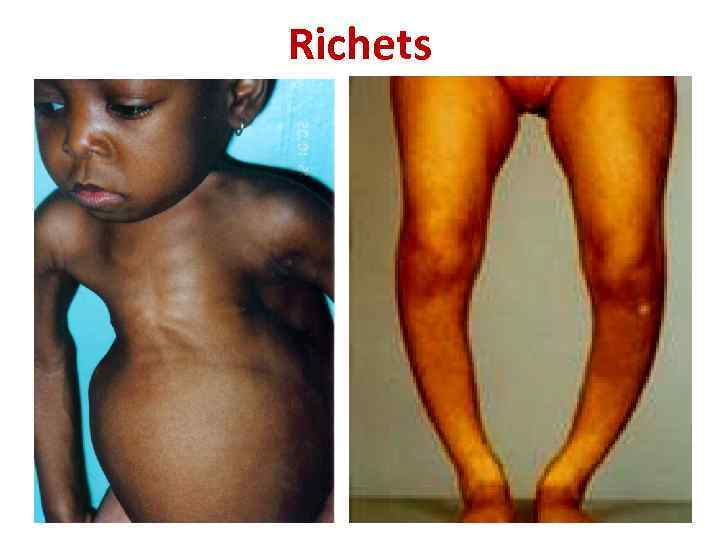
Richets
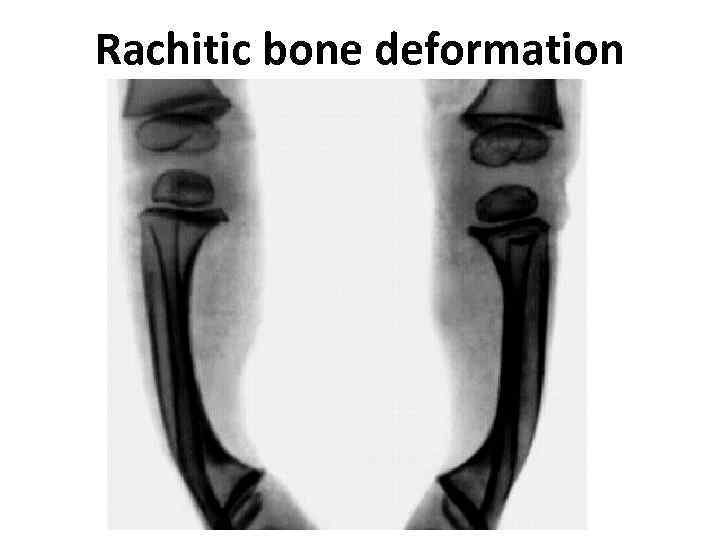
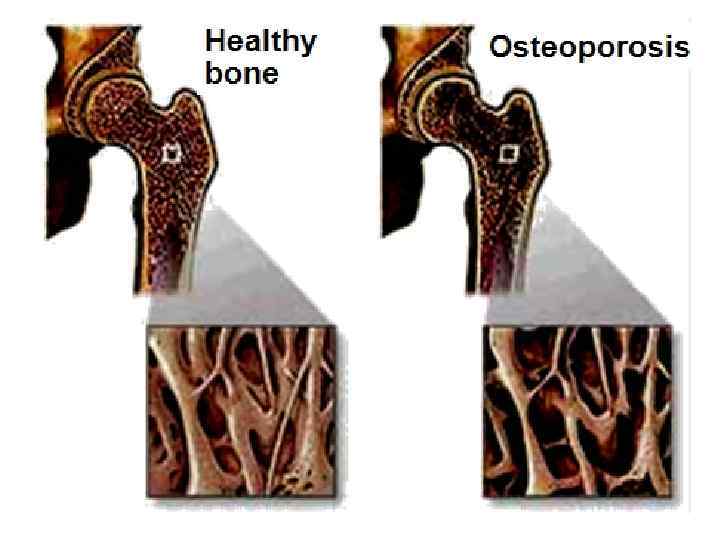
Rachitic bone deformation
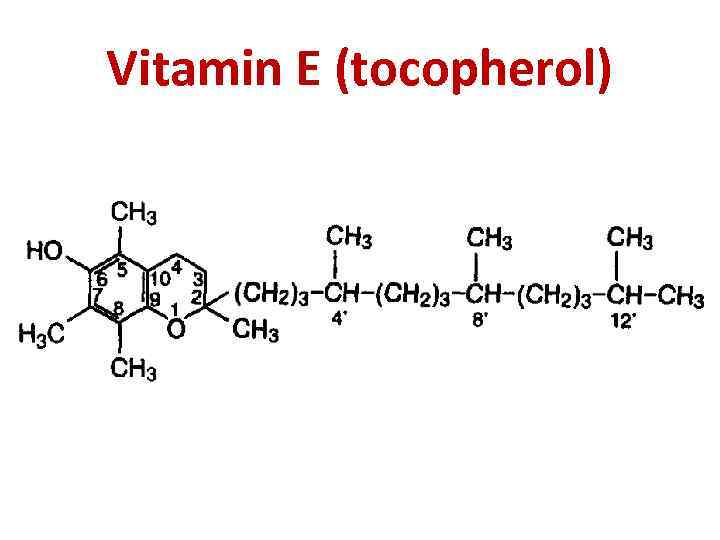
Vitamin E (tocopherol)
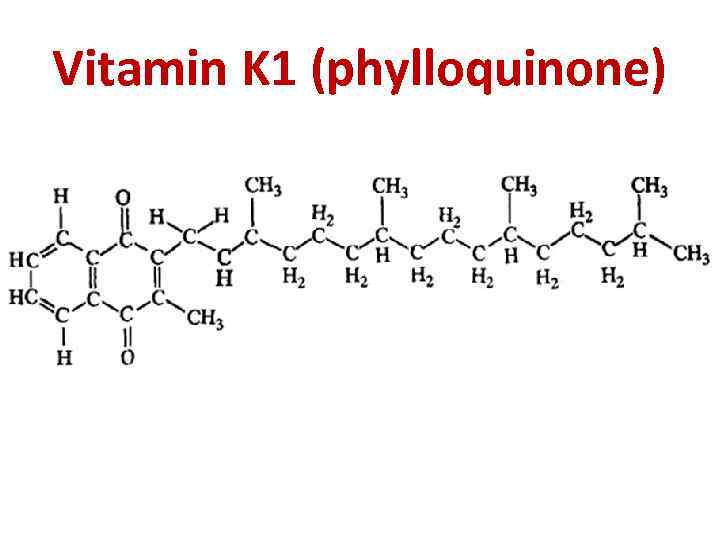
Vitamin K 1 (phylloquinone)
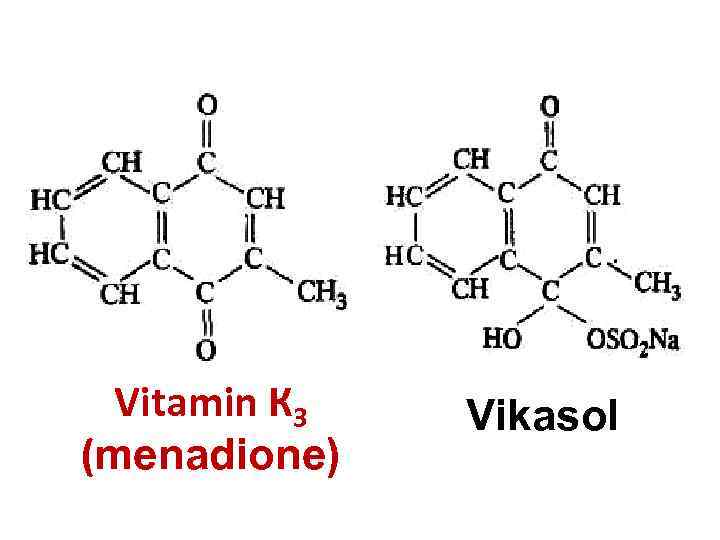
Vitamin К 3 (menadione) Vikasol
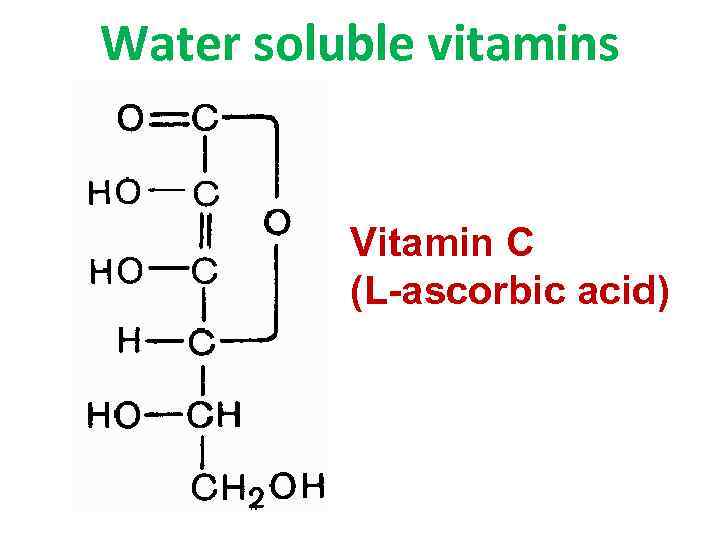
Water soluble vitamins Vitamin C (L-ascorbic acid)
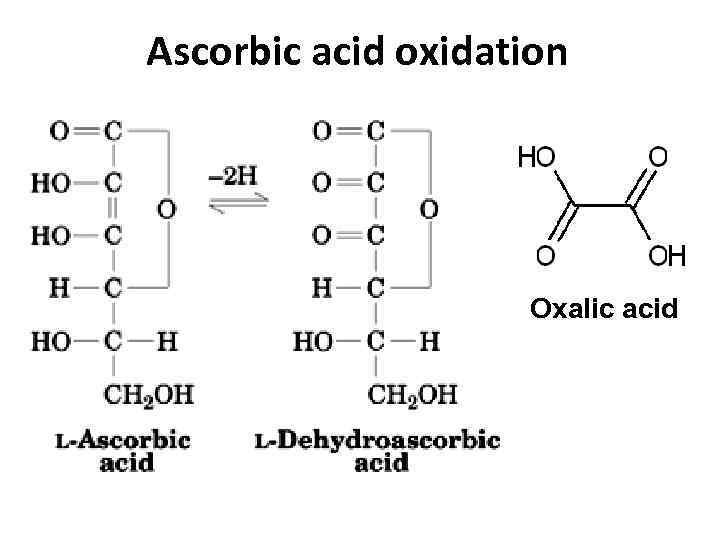
Ascorbic acid oxidation Oxalic acid
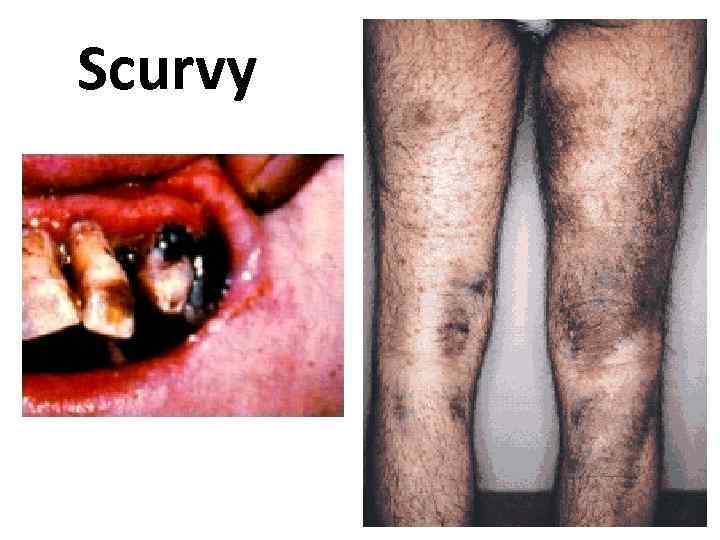
Scurvy
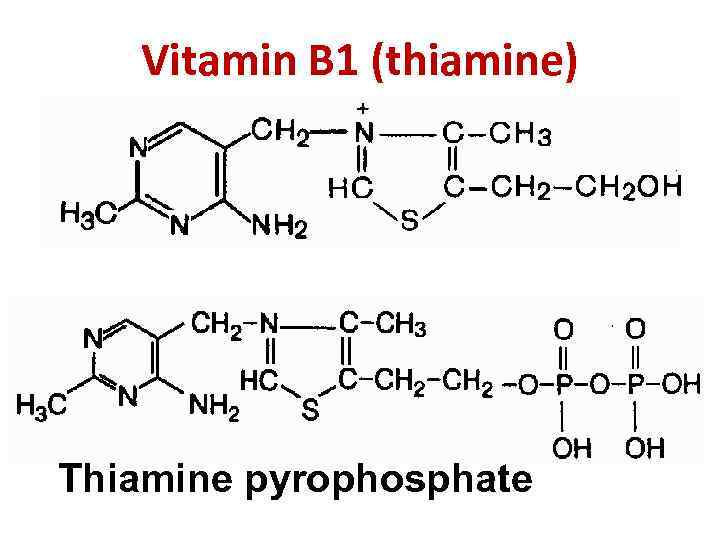
Vitamin B 1 (thiamine) Thiamine pyrophosphate
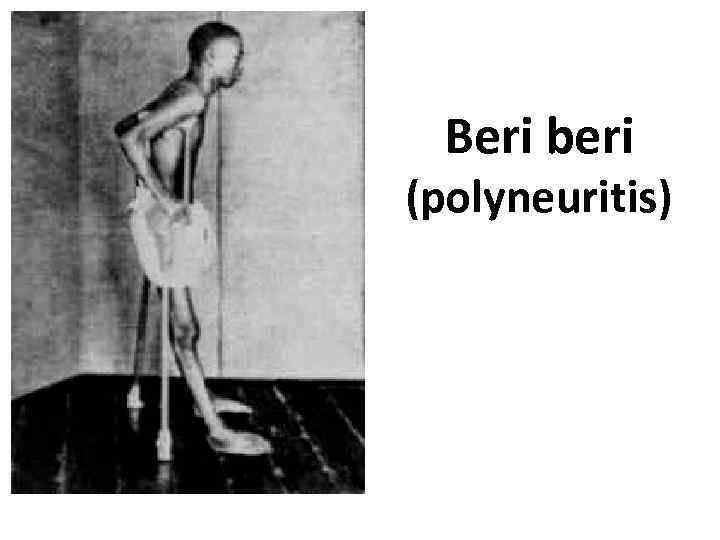
Beri beri (polyneuritis)
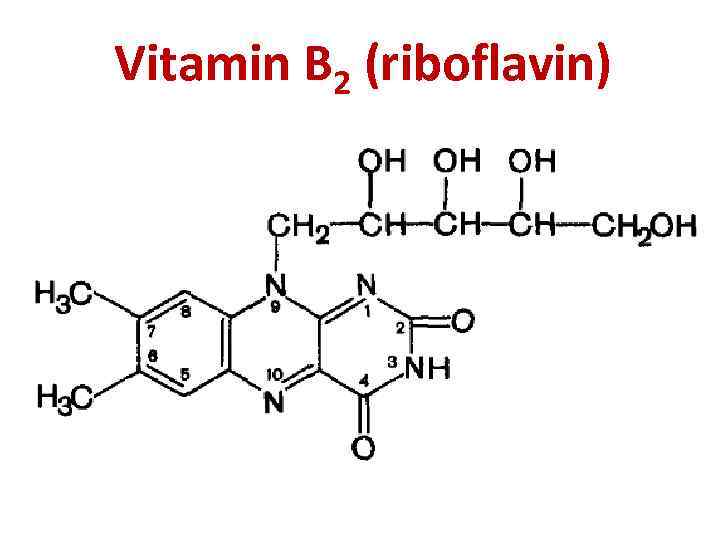
Vitamin B 2 (riboflavin)

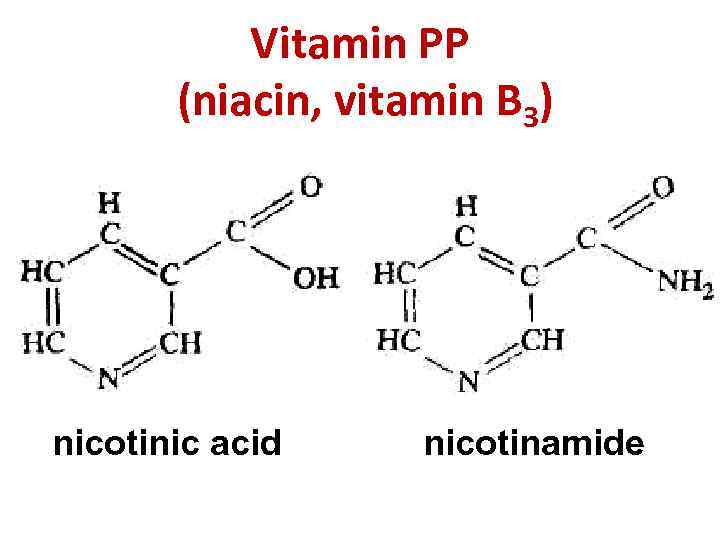
Vitamin PP (niacin, vitamin B 3) nicotinic acid nicotinamide
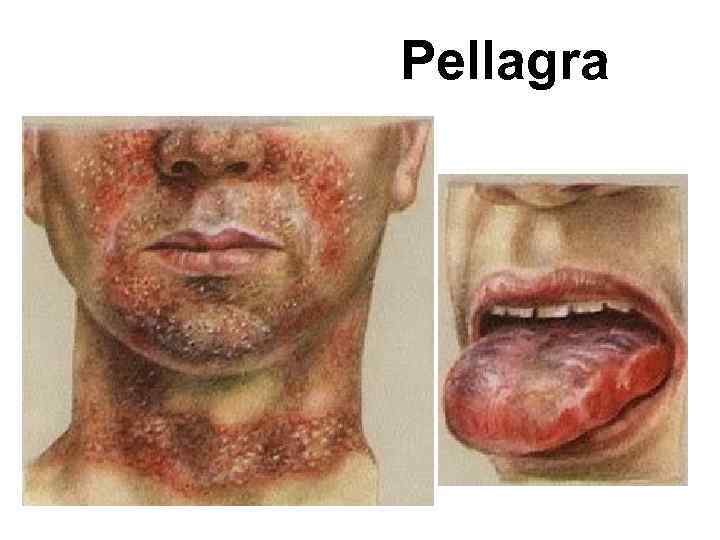
Pellagra
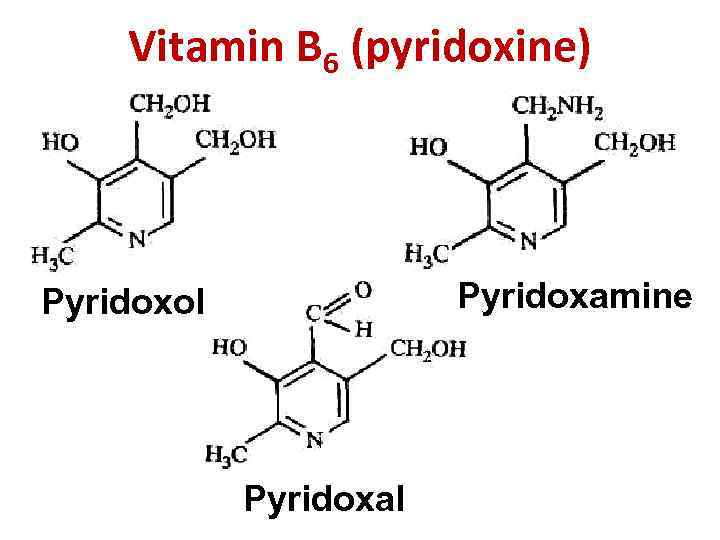
Vitamin B 6 (pyridoxine) Pyridoxamine Pyridoxol Pyridoxal
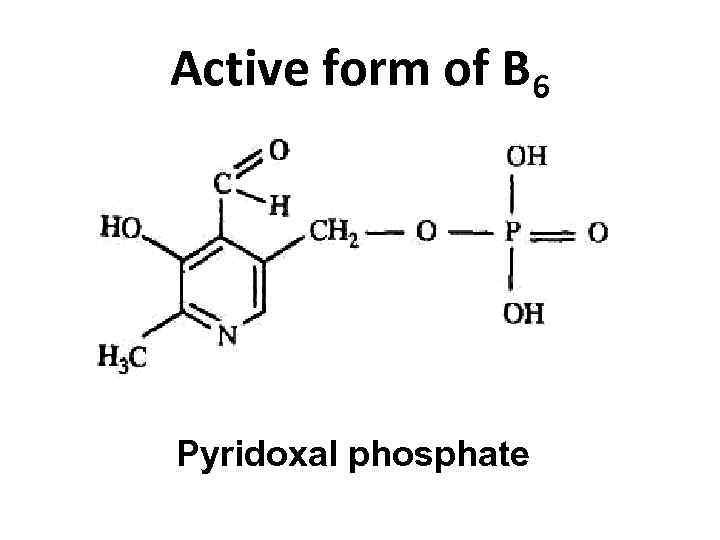
Active form of B 6 Pyridoxal phosphate

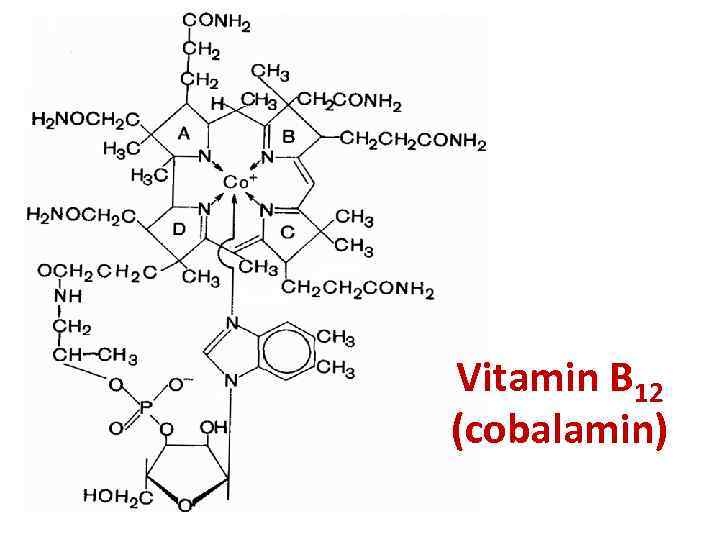
Vitamin B 12 (cobalamin)
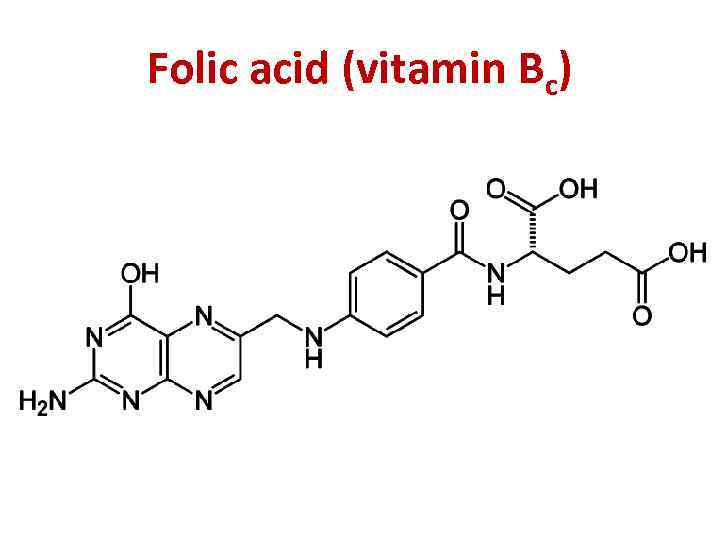
Folic acid (vitamin Bc)

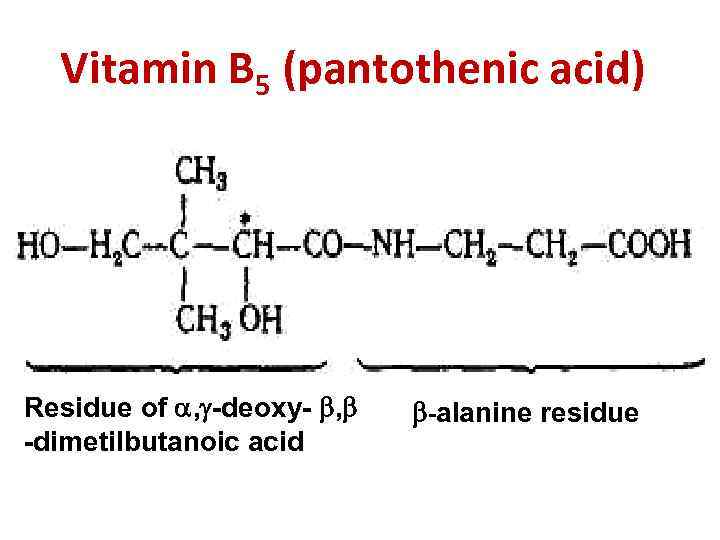
Vitamin B 5 (pantothenic acid) Residue of , -deoxy- , -dimetilbutanoic acid -alanine residue
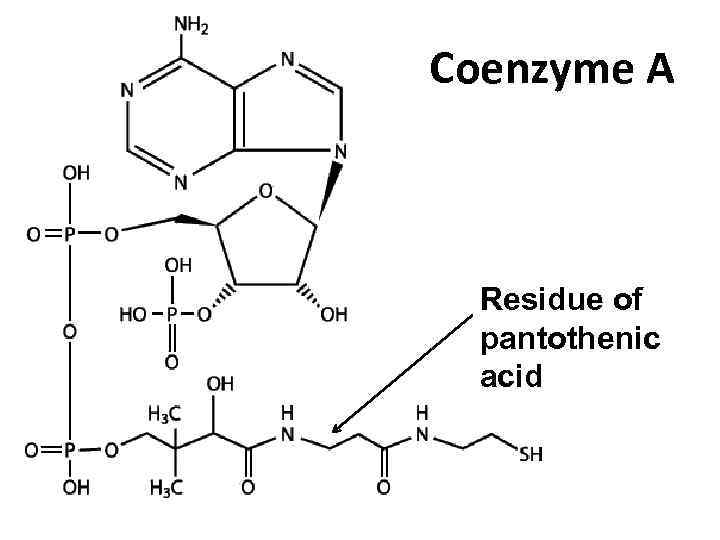
Coenzyme A Residue of pantothenic acid
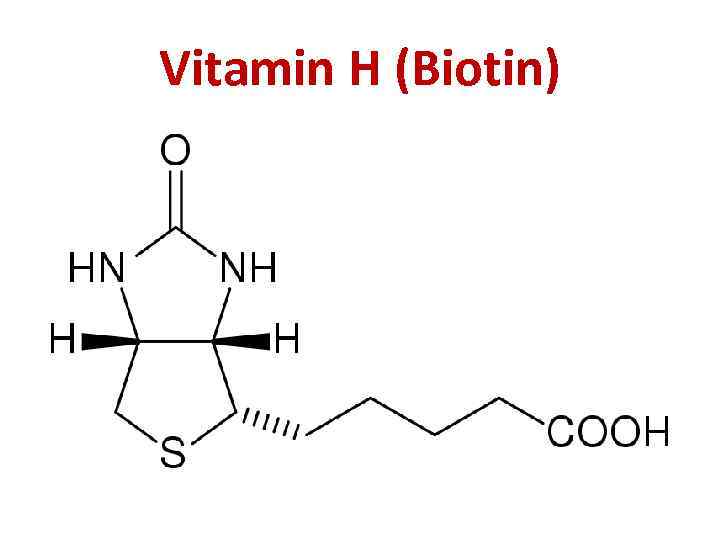
Vitamin H (Biotin)
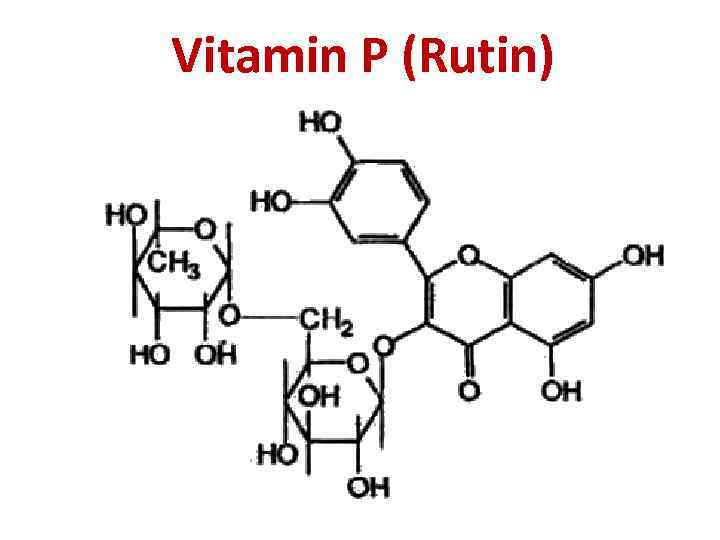
Vitamin P (Rutin)
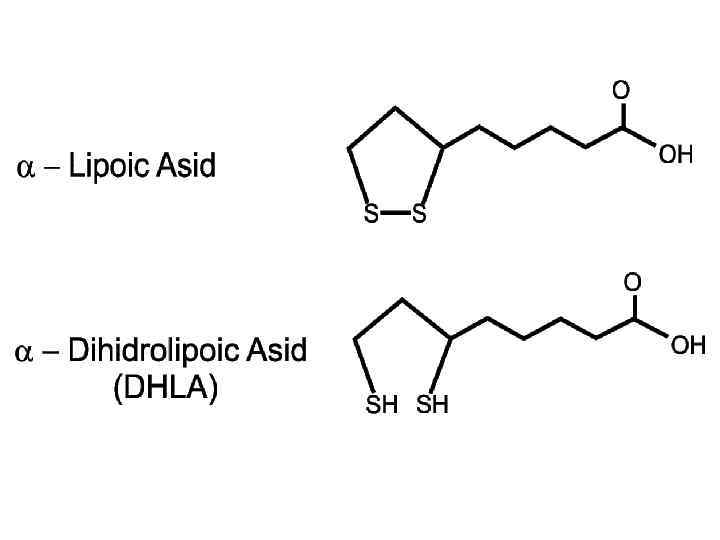
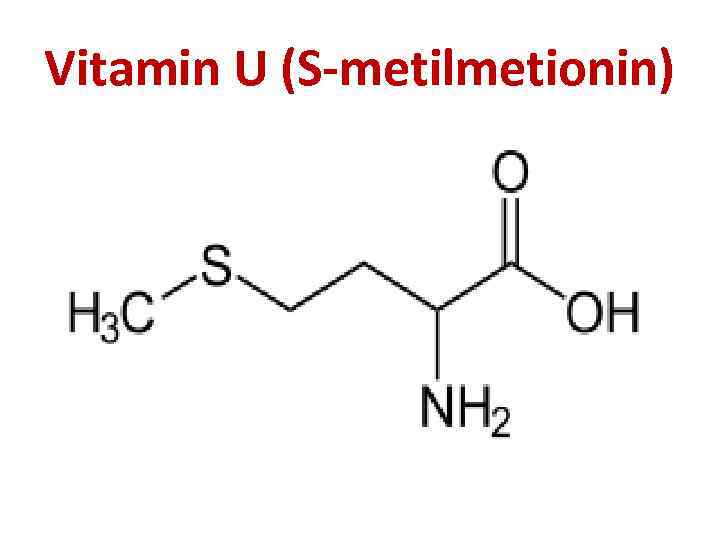
Vitamin U (S-metilmetionin)
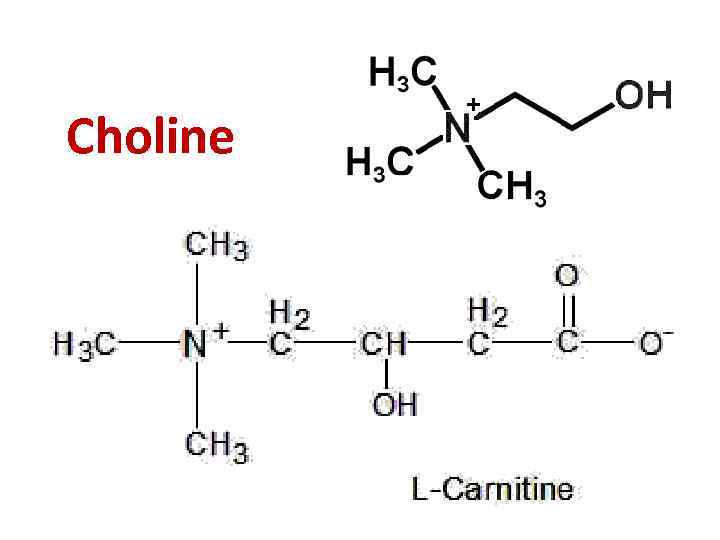
Choline
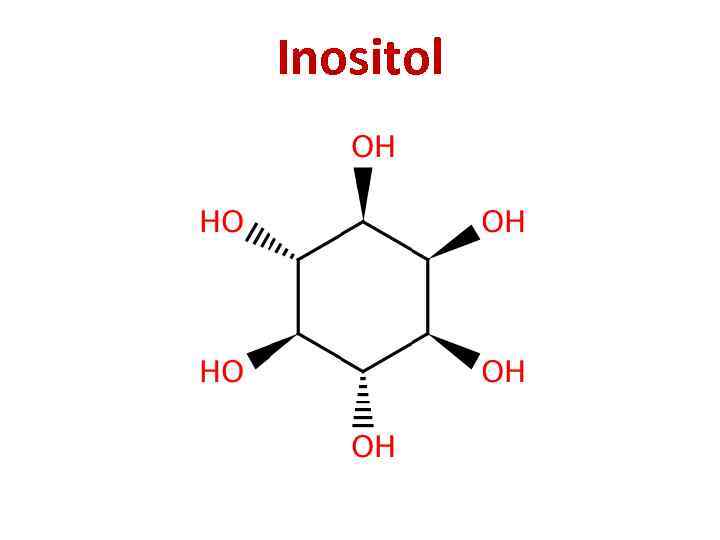
Inositol
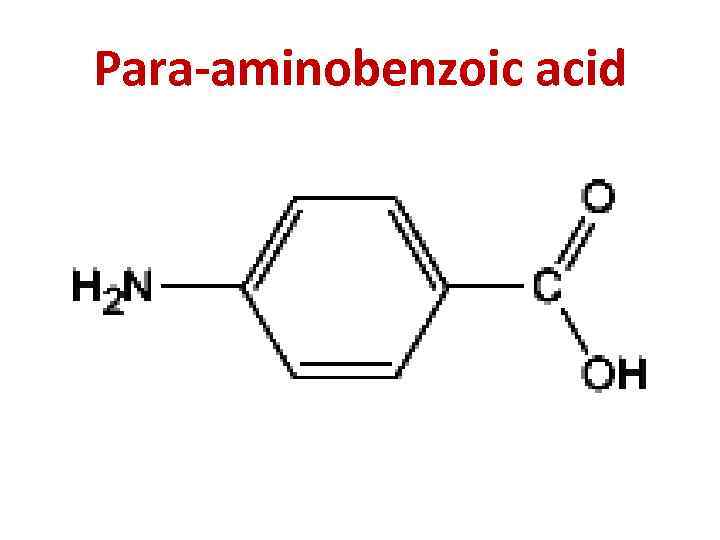
Para-aminobenzoic acid
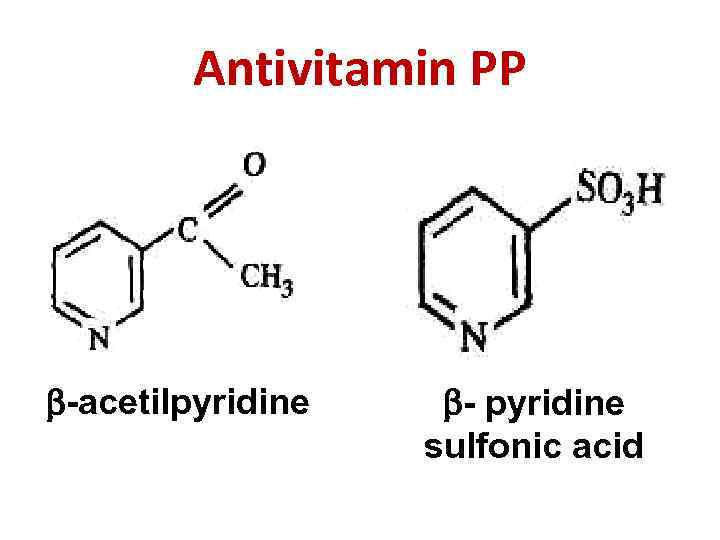
Antivitamin PP -acetilpyridine - pyridine sulfonic acid
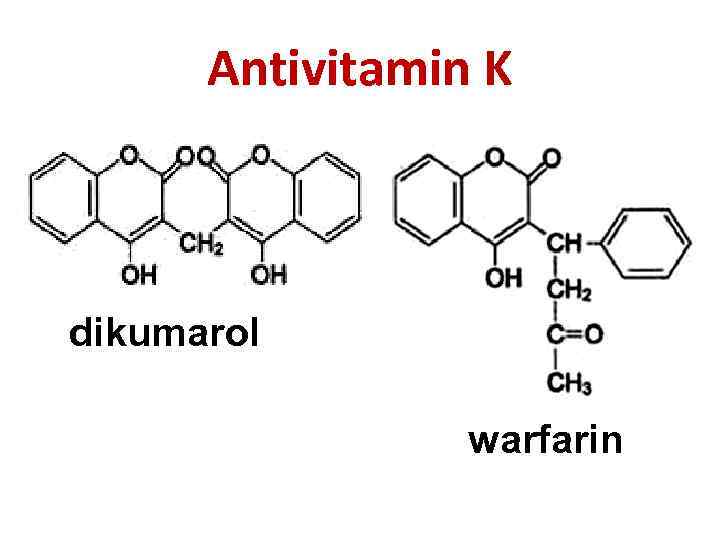
Antivitamin K dikumarol warfarin
Lecture 3 Enzymes, vitamins.ppt