1146890dcdb7a5fe0bb7c3e58d6e4dc1.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20

Regression Basics Predicting a DV with a Single IV

Questions • What are predictors and • What does it mean to choose a regression line to satisfy criteria? the loss function of least • Write an equation for squares? the linear regression. • How do we find the slope and intercept for the Describe each term. regression line with a single • How do changes in the independent variable? slope and intercept (Either formula for the slope affect (move) the is acceptable. ) regression line? • Why does testing for the regression sum of squares • What does it mean to turn out to have the same test the significance of result as testing for Rthe regression sum of square? squares? R-square? • What is R-square?

Basic Ideas • Jargon – IV = X = Predictor (pl. predictors) – DV = Y = Criterion (pl. criteria) – Regression of Y on X e. g. , GPA on SAT • Linear Model = relations between IV and DV represented by straight line. (population values) • A score on Y has 2 parts – (1) linear function of X and (2) error.

Basic Ideas (2) • Sample value: • Intercept – place where X=0 • Slope – change in Y if X changes 1 unit. Rise over run. • If error is removed, we have a predicted value for each person at X (the line): Suppose on average houses are worth about $75. 00 a square foot. Then the equation relating price to size would be Y’=0+75 X. The predicted price for a 2000 square foot house would be $150, 000.

Linear Transformation • 1 to 1 mapping of variables via line • Permissible operations are addition and multiplication (interval data) Add a constant Multiply by a constant
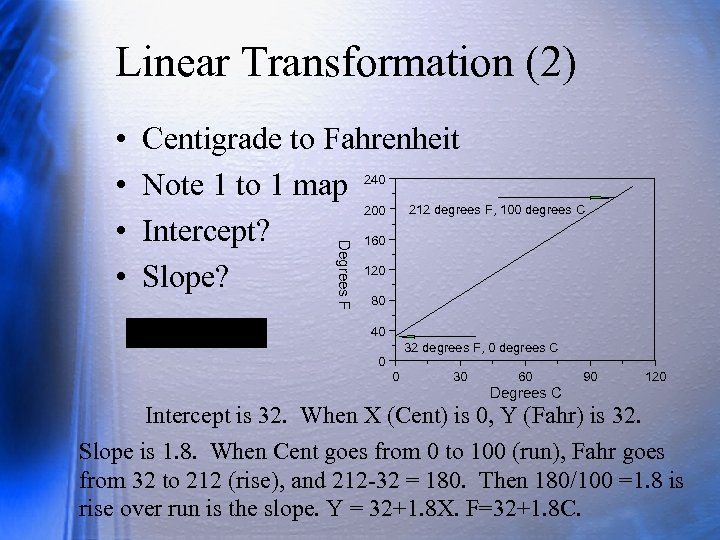
Linear Transformation (2) Centigrade to Fahrenheit Note 1 to 1 map 240 212 degrees F, 100 degrees C 200 Intercept? 160 120 Slope? Degrees F • • 80 40 32 degrees F, 0 degrees C 0 0 30 60 90 120 Degrees C Intercept is 32. When X (Cent) is 0, Y (Fahr) is 32. Slope is 1. 8. When Cent goes from 0 to 100 (run), Fahr goes from 32 to 212 (rise), and 212 -32 = 180. Then 180/100 =1. 8 is rise over run is the slope. Y = 32+1. 8 X. F=32+1. 8 C.

Review • What are predictors and criteria? • Write an equation for the linear regression with 1 IV. Describe each term. • How do changes in the slope and intercept affect (move) the regression line?
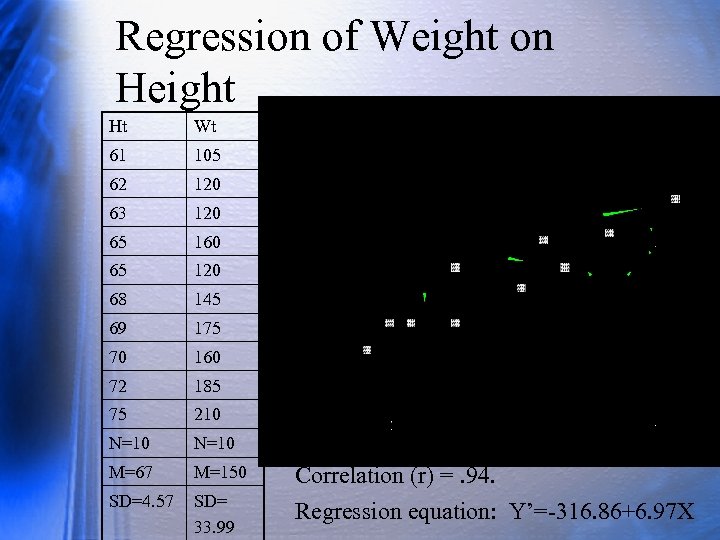
Regression of Weight on Height Ht Wt 61 105 62 120 63 120 65 160 65 120 68 145 69 175 70 160 72 185 75 210 N=10 M=67 M=150 SD=4. 57 SD= 33. 99 Correlation (r) =. 94. Regression equation: Y’=-316. 86+6. 97 X
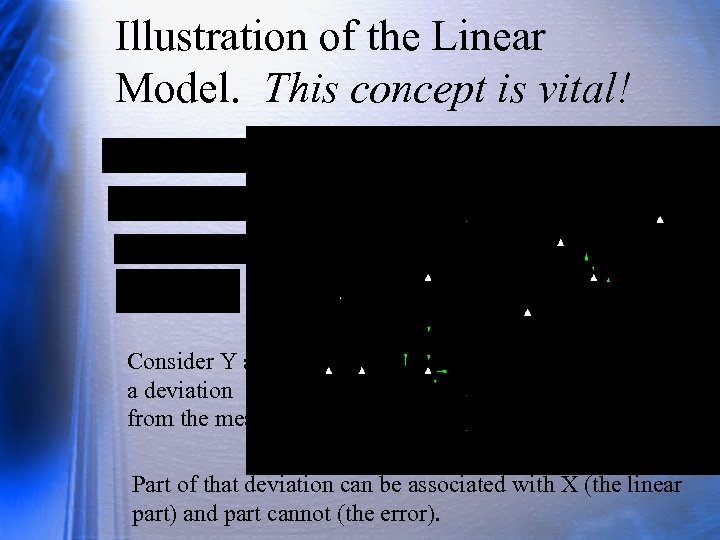
Illustration of the Linear Model. This concept is vital! Consider Y as a deviation from the mean. Part of that deviation can be associated with X (the linear part) and part cannot (the error).
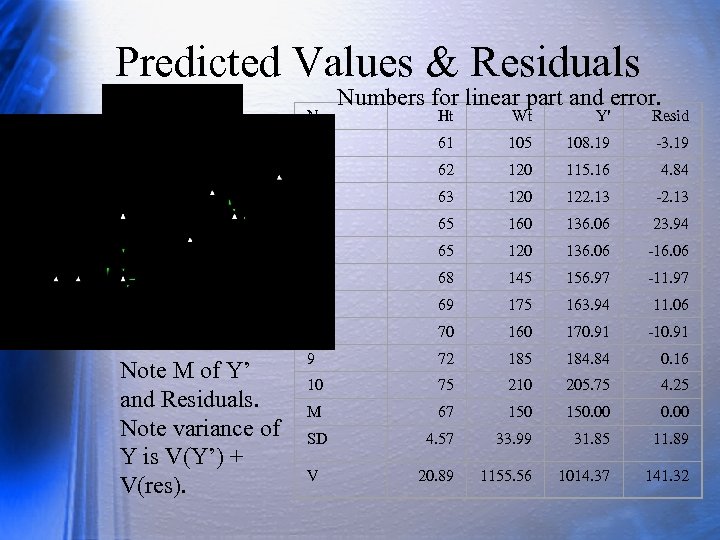
Predicted Values & Residuals N Numbers for linear part and error. Wt Y' Resid 1 61 105 108. 19 -3. 19 2 62 120 115. 16 4. 84 3 63 120 122. 13 -2. 13 4 65 160 136. 06 23. 94 5 65 120 136. 06 -16. 06 6 68 145 156. 97 -11. 97 7 69 175 163. 94 11. 06 8 Note M of Y’ and Residuals. Note variance of Y is V(Y’) + V(res). Ht 70 160 170. 91 -10. 91 9 72 185 184. 84 0. 16 10 75 210 205. 75 4. 25 M 67 150. 00 SD 4. 57 33. 99 31. 85 11. 89 V 20. 89 1155. 56 1014. 37 141. 32

Finding the Regression Line Need to know the correlation, SDs and means of X and Y. The correlation is the slope when both X and Y are expressed as z scores. To translate to raw scores, just bring back original SDs for both. (rise over run) To find the intercept, use: Suppose r =. 50, SDX =. 5, MX = 10, SDY = 2, MY = 5. Slope Intercept Equation

Line of Least Squares We have some points. Assume linear relations is reasonable, so the 2 vbls can be represented by a line. Where should the line go? Place the line so errors (residuals) are small. The line we calculate has a sum of errors = 0. It has a sum of squared errors that are as small as possible; the line provides the smallest sum of squared errors or least squares.
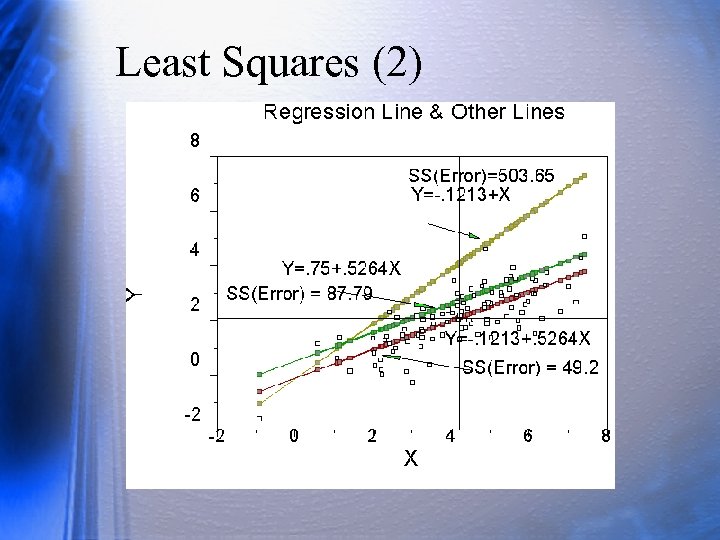
Least Squares (2)

Review • What does it mean to choose a regression line to satisfy the loss function of least squares? • What are predicted values and residuals? Suppose r =. 25, SDX = 1, MX = 10, SDY = 2, MY = 5. What is the regression equation (line)?
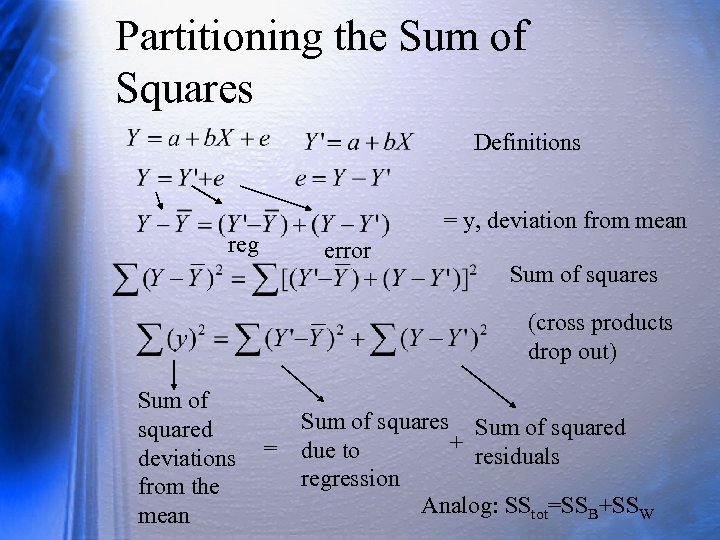
Partitioning the Sum of Squares Definitions reg = y, deviation from mean error Sum of squares (cross products drop out) Sum of squares Sum of squared + = due to residuals deviations regression from the Analog: SStot=SSB+SSW mean

Partitioning SS (2) SSY=SSReg + SSRes Total SS is regression SS plus residual SS. Can also get proportions of each. Can get variance by dividing SS by N if you want. Proportion of total SS due to regression = proportion of total variance due to regression = R 2 (R-square).
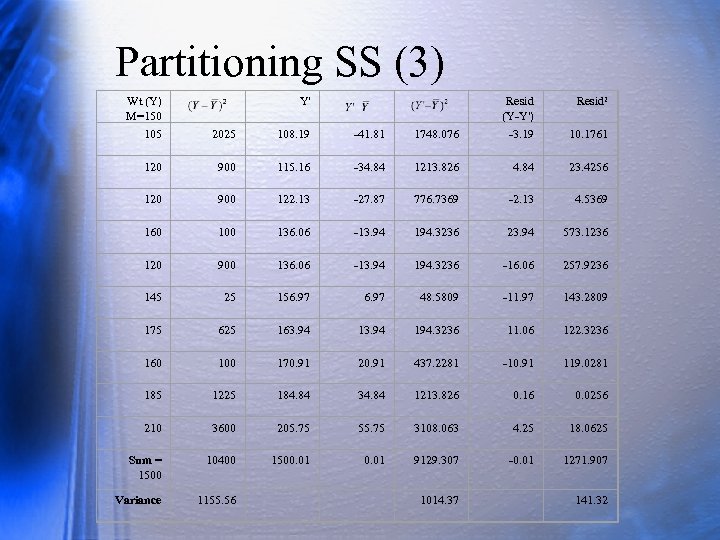
Partitioning SS (3) Wt (Y) M=150 Y' Resid (Y-Y') Resid 2 105 2025 108. 19 -41. 81 1748. 076 -3. 19 10. 1761 120 900 115. 16 -34. 84 1213. 826 4. 84 23. 4256 120 900 122. 13 -27. 87 776. 7369 -2. 13 4. 5369 160 100 136. 06 -13. 94 194. 3236 23. 94 573. 1236 120 900 136. 06 -13. 94 194. 3236 -16. 06 257. 9236 145 25 156. 97 48. 5809 -11. 97 143. 2809 175 625 163. 94 194. 3236 11. 06 122. 3236 160 100 170. 91 20. 91 437. 2281 -10. 91 119. 0281 185 1225 184. 84 34. 84 1213. 826 0. 16 0. 0256 210 3600 205. 75 55. 75 3108. 063 4. 25 18. 0625 Sum = 1500 10400 1500. 01 9129. 307 -0. 01 1271. 907 Variance 1155. 56 1014. 37 141. 32

Partitioning SS (4) Total Regress Residual SS 10400 9129. 31 1271. 91 Variance 1155. 56 1014. 37 141. 32 Proportion of SS Proportion of Variance R 2 =. 88 Note Y’ is linear function of X, so .

Significance Testing for the SS due to regression = testing for the variance due to regression = testing the significance of R 2. All are the same. k=number of IVs (here it’s 1) and N is the sample size (# people). F with k and (N-k-1) df. Equivalent test using R-square instead of SS. Results will be same within rounding error.

Review • What does it mean to test the significance of the regression sum of squares? R-square? • What is R-square? • Why does testing for the regression sum of squares turn out to have the same result as testing for R-square?
1146890dcdb7a5fe0bb7c3e58d6e4dc1.ppt