d62f9a22a3737a74c796ae8864ca319d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 22
 Register entries/exits and demographic flows: some comparisons for statistical aggregates Caterina Viviano 18 th Roundtable Beijing, China October 2004
Register entries/exits and demographic flows: some comparisons for statistical aggregates Caterina Viviano 18 th Roundtable Beijing, China October 2004
 Issue: Verify differences in the production of demographic statistics using registration and deregistration instead of identifying the real births and deaths by the harmonised methodology Contents: • BD methodology • Indicators comparison: • birth rate • gross turnover • net turnover • Main outcomes
Issue: Verify differences in the production of demographic statistics using registration and deregistration instead of identifying the real births and deaths by the harmonised methodology Contents: • BD methodology • Indicators comparison: • birth rate • gross turnover • net turnover • Main outcomes
 Eurostat BD project aims to harmonise methodology to obtain comparable statistics BD methodology is already operative in participating EU countries Developed internal procedures are costly and complex
Eurostat BD project aims to harmonise methodology to obtain comparable statistics BD methodology is already operative in participating EU countries Developed internal procedures are costly and complex
 BD methodology -summary Purpose: identify the real new enterprise births and deaths Id process for births: step 0 - Population of active enterprises in year t: P(t) • source of data: BR • units: legal units • active units: employment/turnover or other national method
BD methodology -summary Purpose: identify the real new enterprise births and deaths Id process for births: step 0 - Population of active enterprises in year t: P(t) • source of data: BR • units: legal units • active units: employment/turnover or other national method
 step 1 - The new enterprises (entries) in year t • subset of Pop(t) • need of Pop(t-1) • need of Pop(t-2) for elimination of reactivations E 1 = new enterprises = units not active in t-2 not active in t-1 active in t E 1 entries without reactivated units
step 1 - The new enterprises (entries) in year t • subset of Pop(t) • need of Pop(t-1) • need of Pop(t-2) for elimination of reactivations E 1 = new enterprises = units not active in t-2 not active in t-1 active in t E 1 entries without reactivated units
 step 2 - Other creations: events of structural changes (merger, demerger, take-off, split-off) • need of updating information through administrative data and manual profiling activities E 2 = E 1 - Eev E 2 entries without reactivated units and without events
step 2 - Other creations: events of structural changes (merger, demerger, take-off, split-off) • need of updating information through administrative data and manual profiling activities E 2 = E 1 - Eev E 2 entries without reactivated units and without events
 step 3 - Other creations: Links for continuity (change of legal status, inheritance successions, partnerships) • Continuity rules: 3 id variables (name, location, sector) • name & location • name & sector • sector & location Tool: Record linkage process E 3 = E 2 - Econt
step 3 - Other creations: Links for continuity (change of legal status, inheritance successions, partnerships) • Continuity rules: 3 id variables (name, location, sector) • name & location • name & sector • sector & location Tool: Record linkage process E 3 = E 2 - Econt
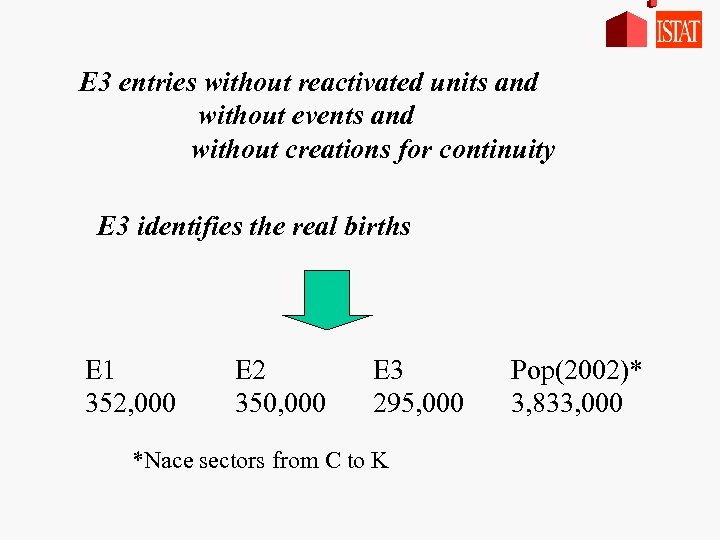 E 3 entries without reactivated units and without events and without creations for continuity E 3 identifies the real births E 1 352, 000 E 2 350, 000 E 3 295, 000 *Nace sectors from C to K Pop(2002)* 3, 833, 000
E 3 entries without reactivated units and without events and without creations for continuity E 3 identifies the real births E 1 352, 000 E 2 350, 000 E 3 295, 000 *Nace sectors from C to K Pop(2002)* 3, 833, 000
 Problematic areas 1. Identification of active population - impact on E 1 • methodology to determine the status of activity 2. Identification of events -impact on E 2 • monitor of large enterprise • skilled staff • updated administrative information. 3. Continuity rules: identification and assignment • weakness of RL automatic procedures • links with high risk of errors • continuity concepts limitations
Problematic areas 1. Identification of active population - impact on E 1 • methodology to determine the status of activity 2. Identification of events -impact on E 2 • monitor of large enterprise • skilled staff • updated administrative information. 3. Continuity rules: identification and assignment • weakness of RL automatic procedures • links with high risk of errors • continuity concepts limitations
 Analysis of some demographic indicators Indicators calculated on the basis of the three subset of data E 1, E 2 and E 3
Analysis of some demographic indicators Indicators calculated on the basis of the three subset of data E 1, E 2 and E 3
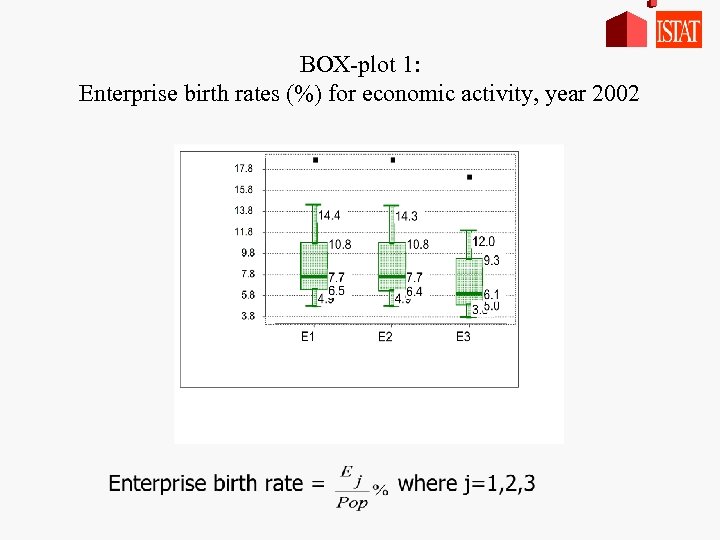 BOX-plot 1: Enterprise birth rates (%) for economic activity, year 2002
BOX-plot 1: Enterprise birth rates (%) for economic activity, year 2002
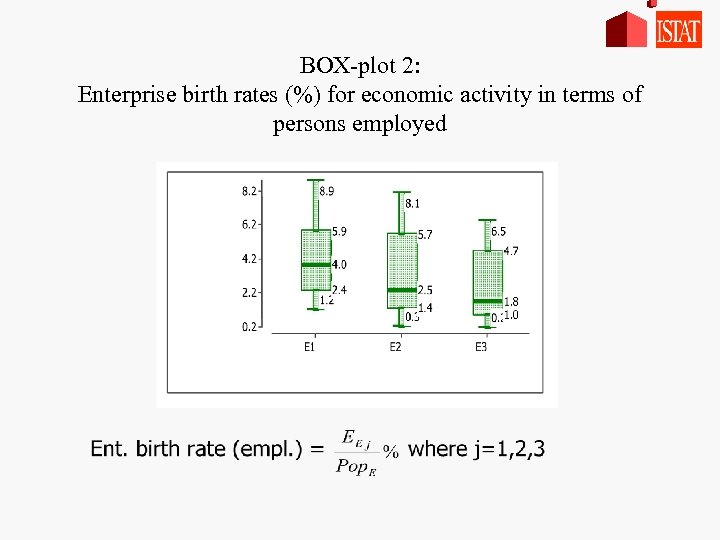 BOX-plot 2: Enterprise birth rates (%) for economic activity in terms of persons employed
BOX-plot 2: Enterprise birth rates (%) for economic activity in terms of persons employed
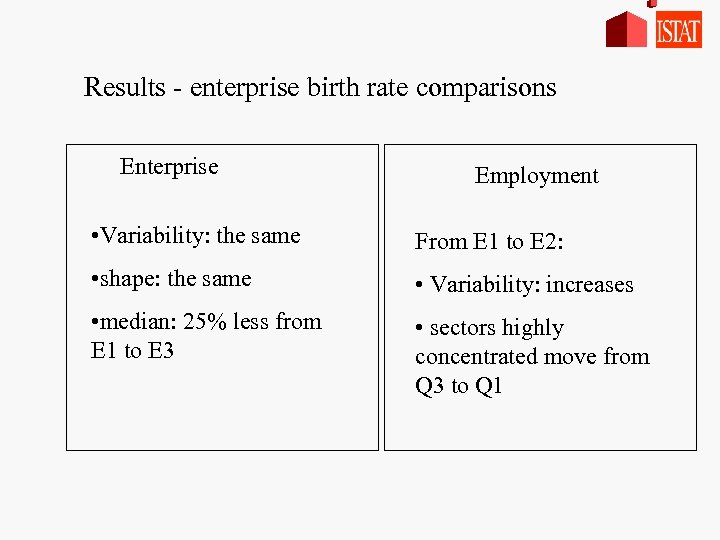 Results - enterprise birth rate comparisons Enterprise Employment • Variability: the same From E 1 to E 2: • shape: the same • Variability: increases • median: 25% less from E 1 to E 3 • sectors highly concentrated move from Q 3 to Q 1
Results - enterprise birth rate comparisons Enterprise Employment • Variability: the same From E 1 to E 2: • shape: the same • Variability: increases • median: 25% less from E 1 to E 3 • sectors highly concentrated move from Q 3 to Q 1
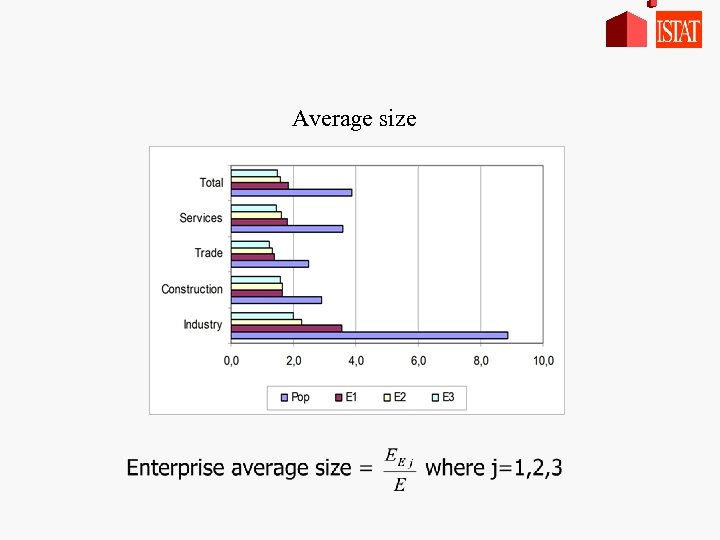 Average size
Average size
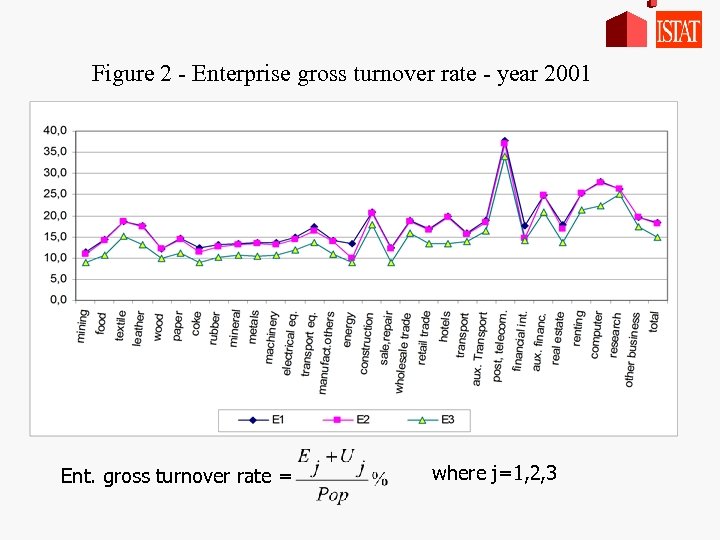 Figure 2 - Enterprise gross turnover rate - year 2001 Ent. gross turnover rate = where j=1, 2, 3
Figure 2 - Enterprise gross turnover rate - year 2001 Ent. gross turnover rate = where j=1, 2, 3
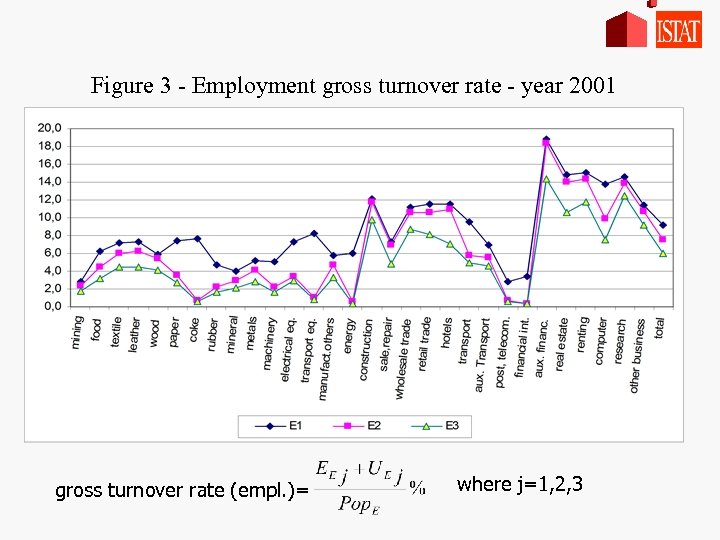 Figure 3 - Employment gross turnover rate - year 2001 gross turnover rate (empl. )= where j=1, 2, 3
Figure 3 - Employment gross turnover rate - year 2001 gross turnover rate (empl. )= where j=1, 2, 3
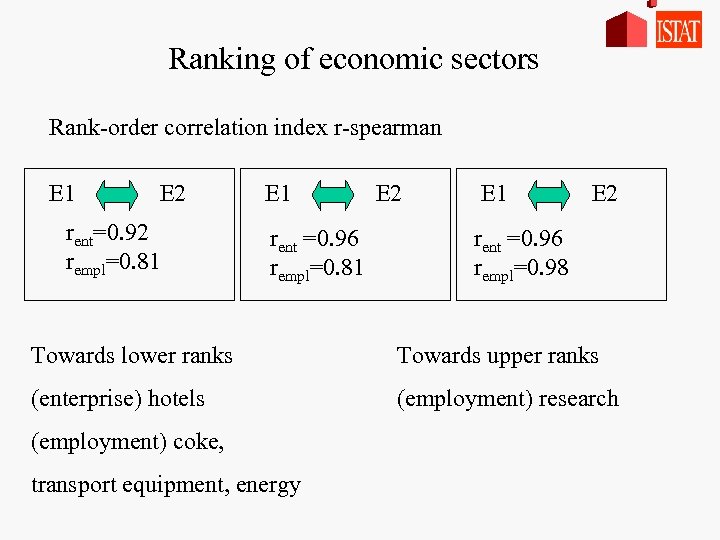 Ranking of economic sectors Rank-order correlation index r-spearman E 1 E 2 rent=0. 92 rempl=0. 81 E 1 rent =0. 96 rempl=0. 81 E 2 E 1 E 2 rent =0. 96 rempl=0. 98 Towards lower ranks Towards upper ranks (enterprise) hotels (employment) research (employment) coke, transport equipment, energy
Ranking of economic sectors Rank-order correlation index r-spearman E 1 E 2 rent=0. 92 rempl=0. 81 E 1 rent =0. 96 rempl=0. 81 E 2 E 1 E 2 rent =0. 96 rempl=0. 98 Towards lower ranks Towards upper ranks (enterprise) hotels (employment) research (employment) coke, transport equipment, energy
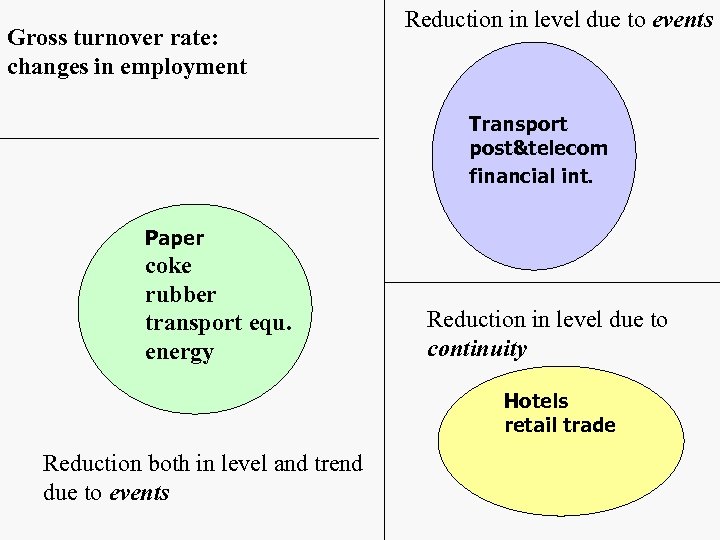 Gross turnover rate: changes in employment Reduction in level due to events Transport post&telecom financial int. Paper coke rubber transport equ. energy Reduction in level due to continuity Hotels retail trade Reduction both in level and trend due to events
Gross turnover rate: changes in employment Reduction in level due to events Transport post&telecom financial int. Paper coke rubber transport equ. energy Reduction in level due to continuity Hotels retail trade Reduction both in level and trend due to events
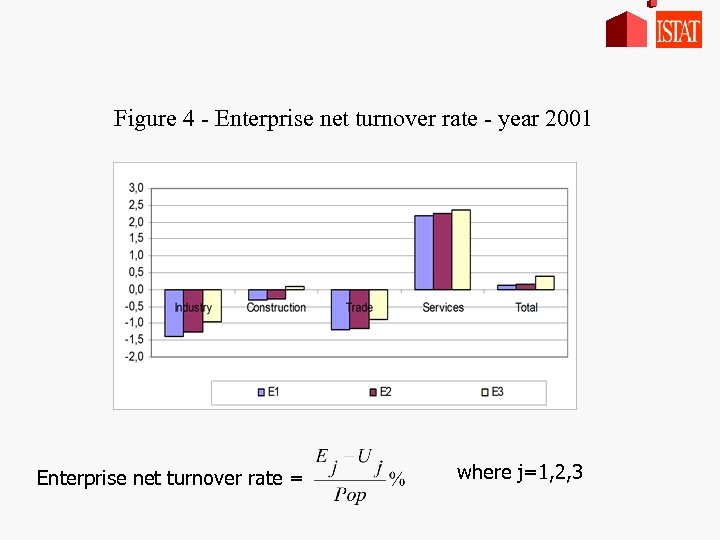 Figure 4 - Enterprise net turnover rate - year 2001 Enterprise net turnover rate = where j=1, 2, 3
Figure 4 - Enterprise net turnover rate - year 2001 Enterprise net turnover rate = where j=1, 2, 3
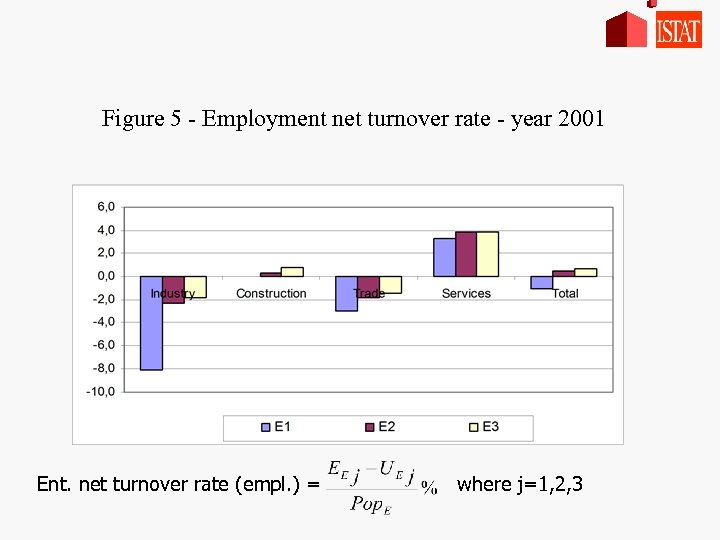 Figure 5 - Employment net turnover rate - year 2001 Ent. net turnover rate (empl. ) = where j=1, 2, 3
Figure 5 - Employment net turnover rate - year 2001 Ent. net turnover rate (empl. ) = where j=1, 2, 3
 Summary BD methodology (continuity rules): with reference to enterprises: • impacts on levels of indicators • does not produce significant changes in the economic activity distribution • produces significant changes in the net turnover rate with reference to employment: • impacts on levels of indicators, on the sectors’ distribution and produces very significant changes in the net turnover rate due to events
Summary BD methodology (continuity rules): with reference to enterprises: • impacts on levels of indicators • does not produce significant changes in the economic activity distribution • produces significant changes in the net turnover rate with reference to employment: • impacts on levels of indicators, on the sectors’ distribution and produces very significant changes in the net turnover rate due to events
 Conclusion Results demonstrate the importance to concentrate efforts in the identification of mergers and demergers the necessity of • more updated information on events • to increase the manual controls activities above all in presence of a large birth or death.
Conclusion Results demonstrate the importance to concentrate efforts in the identification of mergers and demergers the necessity of • more updated information on events • to increase the manual controls activities above all in presence of a large birth or death.


