012c0e1a0f8126456b82caee63a10cfc.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Regional specific aspects WS 2 : Central Asia Technische Universiteit Eindhoven
Regional specific aspects WS 2 : Central Asia Technische Universiteit Eindhoven
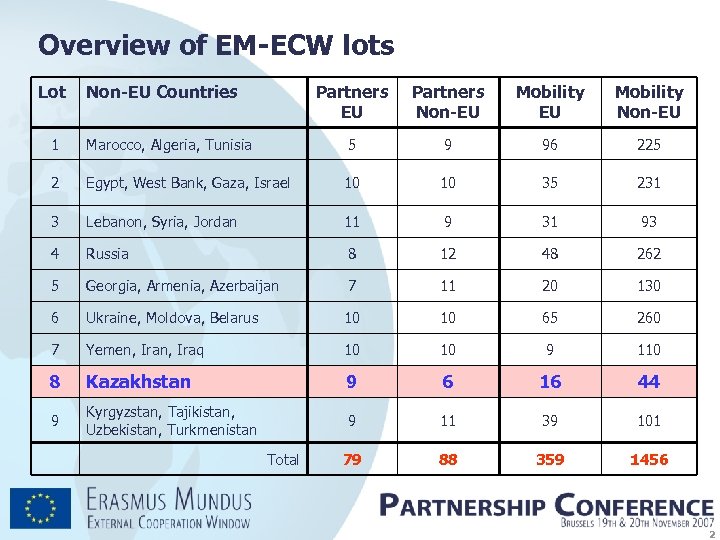 Overview of EM-ECW lots Lot Non-EU Countries Partners EU Partners Non-EU Mobility Non-EU 1 Marocco, Algeria, Tunisia 5 9 96 225 2 Egypt, West Bank, Gaza, Israel 10 10 35 231 3 Lebanon, Syria, Jordan 11 9 31 93 4 Russia 8 12 48 262 5 Georgia, Armenia, Azerbaijan 7 11 20 130 6 Ukraine, Moldova, Belarus 10 10 65 260 7 Yemen, Iraq 10 10 9 110 8 Kazakhstan 9 6 16 44 9 Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan 9 11 39 101 79 88 359 1456 Total 2
Overview of EM-ECW lots Lot Non-EU Countries Partners EU Partners Non-EU Mobility Non-EU 1 Marocco, Algeria, Tunisia 5 9 96 225 2 Egypt, West Bank, Gaza, Israel 10 10 35 231 3 Lebanon, Syria, Jordan 11 9 31 93 4 Russia 8 12 48 262 5 Georgia, Armenia, Azerbaijan 7 11 20 130 6 Ukraine, Moldova, Belarus 10 10 65 260 7 Yemen, Iraq 10 10 9 110 8 Kazakhstan 9 6 16 44 9 Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan 9 11 39 101 79 88 359 1456 Total 2
 6 Partners from Kazakhstan Institute of Management, Economics & Strategic Research (KIMEP) Almaty Kazakh Economic University Almaty Kazakh National Technical University Almaty Eurasian National University Astana International Kazakh-Turkish University Turkestan Karaganda State University Karaganda 3
6 Partners from Kazakhstan Institute of Management, Economics & Strategic Research (KIMEP) Almaty Kazakh Economic University Almaty Kazakh National Technical University Almaty Eurasian National University Astana International Kazakh-Turkish University Turkestan Karaganda State University Karaganda 3
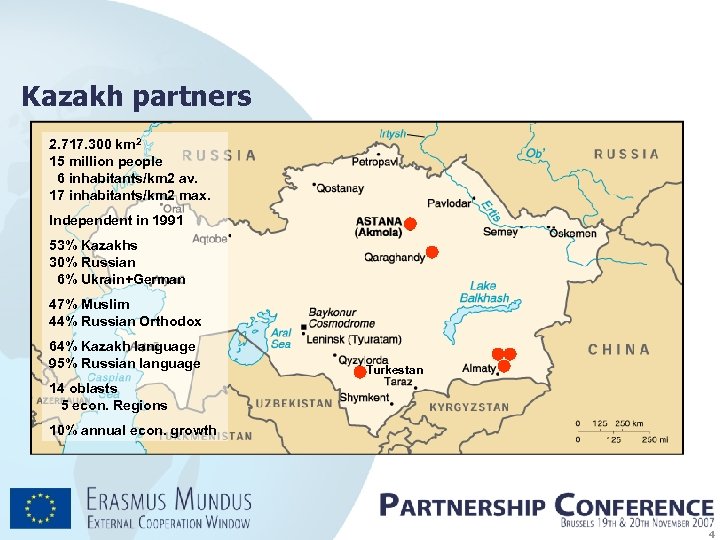 Kazakh partners 2. 717. 300 km 2 15 million people 6 inhabitants/km 2 av. 17 inhabitants/km 2 max. Independent in 1991 53% Kazakhs 30% Russian 6% Ukrain+German 47% Muslim 44% Russian Orthodox 64% Kazakh language 95% Russian language Turkestan 14 oblasts 5 econ. Regions 10% annual econ. growth 4
Kazakh partners 2. 717. 300 km 2 15 million people 6 inhabitants/km 2 av. 17 inhabitants/km 2 max. Independent in 1991 53% Kazakhs 30% Russian 6% Ukrain+German 47% Muslim 44% Russian Orthodox 64% Kazakh language 95% Russian language Turkestan 14 oblasts 5 econ. Regions 10% annual econ. growth 4
 9 Partners from European Union in Lot 8 Eindhoven University of Technology (coordinator) Free University Berlin (lot 7) Humboldt University Berlin (lot 6) Lund University (lot 3*, 7) Deusto University (lot 6*, 7) Algarve University (lot 6, 7) University of Ljubljana University of Bucharest METU Ankara (lot 6, 7) Netherlands Germany Sweden Spain Portugal Slovenia Romenia Turkey 5
9 Partners from European Union in Lot 8 Eindhoven University of Technology (coordinator) Free University Berlin (lot 7) Humboldt University Berlin (lot 6) Lund University (lot 3*, 7) Deusto University (lot 6*, 7) Algarve University (lot 6, 7) University of Ljubljana University of Bucharest METU Ankara (lot 6, 7) Netherlands Germany Sweden Spain Portugal Slovenia Romenia Turkey 5
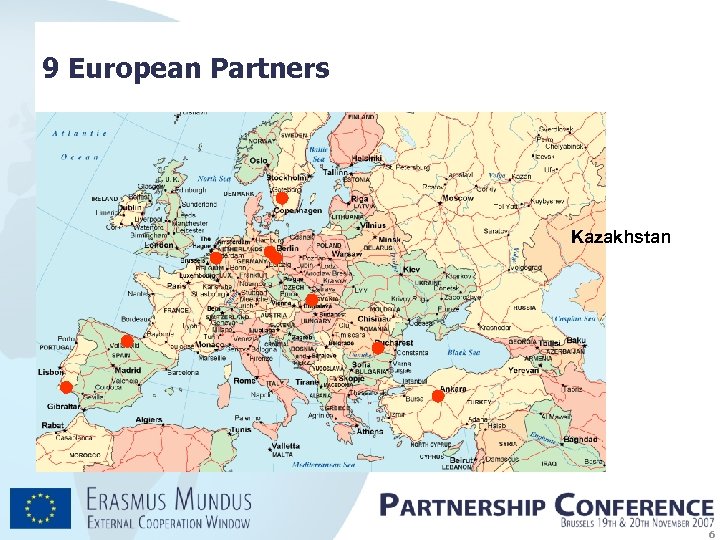 9 European Partners Kazakhstan 6
9 European Partners Kazakhstan 6
 Topics for discussion § Implication of EU Delegations in the monitoring and promotion of the programme § Country needs § Integration of University in society § Expected output and impact of the mobility and its multipliers effect § Sustainability 7
Topics for discussion § Implication of EU Delegations in the monitoring and promotion of the programme § Country needs § Integration of University in society § Expected output and impact of the mobility and its multipliers effect § Sustainability 7
 Implication of EU Delegations in the monitoring and promotion of the programme • Very limited time frame § to establish good contacts § to promote widely the program § to reach all target groups (e. g. vulnerable groups) • Promotion via website, announcements by partners in KZ and EU. • Handling applicants and coordination § § § About 400 registrations About 110 application files received Common website to exchange files (privacy protected) Meeting Selection Committee 21 nov 2007 in Brussels Safeguarding procedures and planning as agreed in Consortium Board. Processing and monitoring is labour intensive task. 8
Implication of EU Delegations in the monitoring and promotion of the programme • Very limited time frame § to establish good contacts § to promote widely the program § to reach all target groups (e. g. vulnerable groups) • Promotion via website, announcements by partners in KZ and EU. • Handling applicants and coordination § § § About 400 registrations About 110 application files received Common website to exchange files (privacy protected) Meeting Selection Committee 21 nov 2007 in Brussels Safeguarding procedures and planning as agreed in Consortium Board. Processing and monitoring is labour intensive task. 8
 Country Needs: President Nazarbayev says at Eurasia Economic Summit 2000 held in Almaty: "First and foremost, we must transform our population which is already educated and motivated into a work force for the future: 21 st century training for the 21 st century jobs The battle for the future will be determined not by armies but by education, not by tanks but by technology, not by cannons but by computers. It is vital that we insure that Central Asia is on the right side of history in all respects politically, economically and technologically". 9
Country Needs: President Nazarbayev says at Eurasia Economic Summit 2000 held in Almaty: "First and foremost, we must transform our population which is already educated and motivated into a work force for the future: 21 st century training for the 21 st century jobs The battle for the future will be determined not by armies but by education, not by tanks but by technology, not by cannons but by computers. It is vital that we insure that Central Asia is on the right side of history in all respects politically, economically and technologically". 9
 Needs in Kazakhstan Many reports available • World Bank § Several reports • Organisation for Economic Co-operation and development § Higher education in Kazakhstan • UN Development Program § Human development report • National Research Council (USA) § Sci & Techn. In Kazakhstan: status & future prospects • …. . • … Reports from KZ authorities (in English? ) 10
Needs in Kazakhstan Many reports available • World Bank § Several reports • Organisation for Economic Co-operation and development § Higher education in Kazakhstan • UN Development Program § Human development report • National Research Council (USA) § Sci & Techn. In Kazakhstan: status & future prospects • …. . • … Reports from KZ authorities (in English? ) 10
 Country needs – historical context • After independence (1991) § no focus on and funding for education § focus on nation building and economic development • Academics § Big outflow of talented academics to businesses (higher salaries!) § Small inflow of new talent into educational sector • End of nineties start with policies to link higher education to western practices and step by step more funds for education • Bologna system implemented since 2004/2005 • Big amount of Universities, many still based on “old” Sovjet principles, many of minor quality • Focus international collaboration on CIS Universities • Considerable amount of Kazakhs study abroad (Boloshak program) 11
Country needs – historical context • After independence (1991) § no focus on and funding for education § focus on nation building and economic development • Academics § Big outflow of talented academics to businesses (higher salaries!) § Small inflow of new talent into educational sector • End of nineties start with policies to link higher education to western practices and step by step more funds for education • Bologna system implemented since 2004/2005 • Big amount of Universities, many still based on “old” Sovjet principles, many of minor quality • Focus international collaboration on CIS Universities • Considerable amount of Kazakhs study abroad (Boloshak program) 11
 Country needs – general characteristics • Money not necessarily a problem in Kazakhstan § high economic growth for many years at a row • Big need for expertise § more than experts – both in content and how to actually implement and maintain it • Education sector not segmented in levels: § one level secondary schools § predominantly followed by university education • massive in- and outflow § almost no vocational education = big need! • one of the priority fields of EC-DCI programme in KZ 12
Country needs – general characteristics • Money not necessarily a problem in Kazakhstan § high economic growth for many years at a row • Big need for expertise § more than experts – both in content and how to actually implement and maintain it • Education sector not segmented in levels: § one level secondary schools § predominantly followed by university education • massive in- and outflow § almost no vocational education = big need! • one of the priority fields of EC-DCI programme in KZ 12
 Country needs – focus areas • President’s economic diversification programme on basis of cluster analysis Porter to diversify from Oil & Gas • Most promising clusters for Kazakhstan: § Food processing § Metallurgy § Oil and Gas equipment § Textiles § Tourism ($ billions FDI coming 10/15 years!) § ……. • Also promising: Investment banking, Furniture, Construction materials, Transport/logistics 13
Country needs – focus areas • President’s economic diversification programme on basis of cluster analysis Porter to diversify from Oil & Gas • Most promising clusters for Kazakhstan: § Food processing § Metallurgy § Oil and Gas equipment § Textiles § Tourism ($ billions FDI coming 10/15 years!) § ……. • Also promising: Investment banking, Furniture, Construction materials, Transport/logistics 13
 Integration of University in society-1 Adaptation of universities to demands of democratic society with market economy: § More intertwining of research and education at universities § More different sources for funding § More involvelement of industries and public bodies in university research § Curricula stimulating independent and creative attitude of students § International cooperation 14
Integration of University in society-1 Adaptation of universities to demands of democratic society with market economy: § More intertwining of research and education at universities § More different sources for funding § More involvelement of industries and public bodies in university research § Curricula stimulating independent and creative attitude of students § International cooperation 14
 15
15
 Integration of Universities in society • Universities dominant in higher education • Education often quite theoretical – less applied • Research not well developed, often theoretical or not up-todate and not publishable in the West (not only language problem!) • Some relations between Universities and companies, mainly related to internships and hiring graduates • Community service projects diminishing • Leading Universities often politically connected 16
Integration of Universities in society • Universities dominant in higher education • Education often quite theoretical – less applied • Research not well developed, often theoretical or not up-todate and not publishable in the West (not only language problem!) • Some relations between Universities and companies, mainly related to internships and hiring graduates • Community service projects diminishing • Leading Universities often politically connected 16
 Expected output and impact of the mobility and its multipliers effect • Capacity building at levels of: § individual § university/institute/organisaton § country • • Creating international awareness Academics well-qualified to international standards Intensification of ties between KZ and EU Seeds for future cooperation 17
Expected output and impact of the mobility and its multipliers effect • Capacity building at levels of: § individual § university/institute/organisaton § country • • Creating international awareness Academics well-qualified to international standards Intensification of ties between KZ and EU Seeds for future cooperation 17
 Multiplier effects - opportunities • Initial mobility can lead to: § Student exchange programmes § Intensive Summer course programmes § Joint research programmes (Kazakhstan interesting studyfield!), publications and conferences/workshops § Faculty exchange § Joint/dual degree programmes § Internship programmes § Joint executive training programmes 18
Multiplier effects - opportunities • Initial mobility can lead to: § Student exchange programmes § Intensive Summer course programmes § Joint research programmes (Kazakhstan interesting studyfield!), publications and conferences/workshops § Faculty exchange § Joint/dual degree programmes § Internship programmes § Joint executive training programmes 18
 Multiplier effects - restraints • Not many Kazakh Universities offer programmes in English (predominantly in Russian) • Number of English language programmes at EU partner Universities also limited • Level and structure of education is different • For mobility of faculty: work permit restraints (both ways? ) • In Kazakhstan limited management capacity to effectively manage collaborations (especially joint research and dual/joint educational programmes) • But: great willingness and openness to collaborate and adopt western practices 19
Multiplier effects - restraints • Not many Kazakh Universities offer programmes in English (predominantly in Russian) • Number of English language programmes at EU partner Universities also limited • Level and structure of education is different • For mobility of faculty: work permit restraints (both ways? ) • In Kazakhstan limited management capacity to effectively manage collaborations (especially joint research and dual/joint educational programmes) • But: great willingness and openness to collaborate and adopt western practices 19
 Sustainability • Opportunities for establishing contacts at all levels • May depend on personal inititative • Yearly continuation of program with new batch of applicants needed • Funds from EU and/or other parties will be needed • Possible formal agreement between EU university and KZuniversity (cooperation in research and/or education) • Sustainability requires long term strategies. 20
Sustainability • Opportunities for establishing contacts at all levels • May depend on personal inititative • Yearly continuation of program with new batch of applicants needed • Funds from EU and/or other parties will be needed • Possible formal agreement between EU university and KZuniversity (cooperation in research and/or education) • Sustainability requires long term strategies. 20
 Thanks for your attention 21
Thanks for your attention 21


