b55fe71696eb10cd845fa9829b1da639.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 Regional Optical Networking - The Next Steps I 2 Member Meeting May 2, 2005 1
Regional Optical Networking - The Next Steps I 2 Member Meeting May 2, 2005 1
 Quilt RON Workshops • Goal: Educate the regional community about fiber and optical network opportunities and technologies. – 1 st Workshop June ‘ 04 in Denver • “So you think you want some dark fiber? ” – 2 nd Workshop Nov. ‘ 04 in Raleigh • “So you’ve got some dark fiber-now what? ” – 3 rd Workshop June ‘ 05 Newport. RI • “So you’ve lit your fiber-now what? ” 2
Quilt RON Workshops • Goal: Educate the regional community about fiber and optical network opportunities and technologies. – 1 st Workshop June ‘ 04 in Denver • “So you think you want some dark fiber? ” – 2 nd Workshop Nov. ‘ 04 in Raleigh • “So you’ve got some dark fiber-now what? ” – 3 rd Workshop June ‘ 05 Newport. RI • “So you’ve lit your fiber-now what? ” 2
 Inaugural Workshop • June 2004 at Level 3’s Facility in Broomfield, CO • Focus on learning about the acquisition and operational issues associated optical networks. – A “Who’s Who of RON Experts from the R&E Community” – Not Bad for Beginners! – Archive available at: http: //www. thequilt. net/ • Specific topics – Where is the fiber? – IRU’s and other legal issues – Technical Design 3
Inaugural Workshop • June 2004 at Level 3’s Facility in Broomfield, CO • Focus on learning about the acquisition and operational issues associated optical networks. – A “Who’s Who of RON Experts from the R&E Community” – Not Bad for Beginners! – Archive available at: http: //www. thequilt. net/ • Specific topics – Where is the fiber? – IRU’s and other legal issues – Technical Design 3
 Where’s the fiber? • Presenter - Victor Braud • Basic Issues – – – What kind of fiber is it? Where does it go? Who owns it? Do they have any extra? Do they have the right to sell it; if so will they sell it? • Can you afford it, including the cost of the: – IRU @ $500 to $2500/fiber/mile – Collocation @ $500 to $1, 200/rack/month + power – O&M @ $100 to $300/route mile/year – Optronics to light and staff to maintain it? • Will the owner allow you reasonable access to it? • 20 year partnership with Owner? 4
Where’s the fiber? • Presenter - Victor Braud • Basic Issues – – – What kind of fiber is it? Where does it go? Who owns it? Do they have any extra? Do they have the right to sell it; if so will they sell it? • Can you afford it, including the cost of the: – IRU @ $500 to $2500/fiber/mile – Collocation @ $500 to $1, 200/rack/month + power – O&M @ $100 to $300/route mile/year – Optronics to light and staff to maintain it? • Will the owner allow you reasonable access to it? • 20 year partnership with Owner? 4
 Indefeasible Right to Use • Presenter - Alex Preiser - Associate Legal Counsel, UCAR • Key Legal issues associated with IRU Agreements • • 5 IRU Defined Key Terms Considerations Strategies
Indefeasible Right to Use • Presenter - Alex Preiser - Associate Legal Counsel, UCAR • Key Legal issues associated with IRU Agreements • • 5 IRU Defined Key Terms Considerations Strategies
 IRU - Key Terms • • • 6 Connection Acceptance Testing Maintenance Construction Fees Performance Property Rights Term/Usage Rights Payments/Taxes Force Majeure
IRU - Key Terms • • • 6 Connection Acceptance Testing Maintenance Construction Fees Performance Property Rights Term/Usage Rights Payments/Taxes Force Majeure
 Funding the Network(s) • Several models presented – Almost as many funding models as there are organizational models • Basic Costs – – – 7 General Operations Network Operations Center Allocation of Optical Network Equipment Maintenance Equipment Replacement Allocation
Funding the Network(s) • Several models presented – Almost as many funding models as there are organizational models • Basic Costs – – – 7 General Operations Network Operations Center Allocation of Optical Network Equipment Maintenance Equipment Replacement Allocation
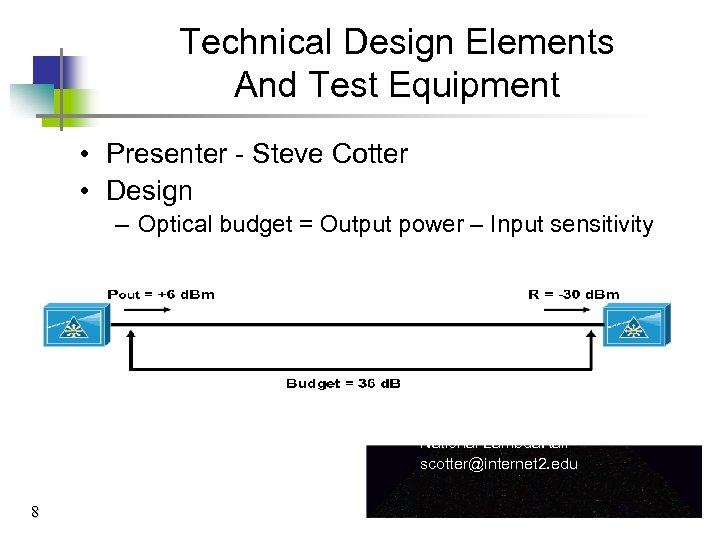 Technical Design Elements And Test Equipment • Presenter - Steve Cotter • Design – Optical budget = Output power – Input sensitivity Steve Cotter – Internet 2 / National Lambda. Rail scotter@internet 2. edu 8
Technical Design Elements And Test Equipment • Presenter - Steve Cotter • Design – Optical budget = Output power – Input sensitivity Steve Cotter – Internet 2 / National Lambda. Rail scotter@internet 2. edu 8
 Technical Design • Optical budget is affected by: – – – 9 Fiber attenuation Splices Patch panels / connectors Optical components (filters, amplifiers, etc. ) Bends in the fiber Contamination (dirt, oil, etc. )
Technical Design • Optical budget is affected by: – – – 9 Fiber attenuation Splices Patch panels / connectors Optical components (filters, amplifiers, etc. ) Bends in the fiber Contamination (dirt, oil, etc. )
 Fiber Types • SMF (standard, 1310 nm optimized, G. 652) – Most widely deployed so far, introduced in 1986, cheapest – Corning SMF-28 e • ‘extended band fiber – optimized for CWDM • DSF (Dispersion Shifted, G. 653) – Intended for single channel operation at 1550 nm – Corning DSF 10
Fiber Types • SMF (standard, 1310 nm optimized, G. 652) – Most widely deployed so far, introduced in 1986, cheapest – Corning SMF-28 e • ‘extended band fiber – optimized for CWDM • DSF (Dispersion Shifted, G. 653) – Intended for single channel operation at 1550 nm – Corning DSF 10
 Fiber Types, Con’t • NZDSF (Non-Zero Dispersion Shifted, G. 655) – SMF/LS (limited slope) fiber from Corning – Later fiber types are engineered for WDM operation in the 1550 nm region only • True. Wave, Free. Light, LEAF, E-LEAF, Tera. Light… – These are the latest generation fibers developed in mid 90’s – For better performance with high capacity DWDM systems – Optimized for DWDM in the C-band & L-band • Metro. Cor, Wide. Light are other types • Low PMD ULH fibers are also out there 11
Fiber Types, Con’t • NZDSF (Non-Zero Dispersion Shifted, G. 655) – SMF/LS (limited slope) fiber from Corning – Later fiber types are engineered for WDM operation in the 1550 nm region only • True. Wave, Free. Light, LEAF, E-LEAF, Tera. Light… – These are the latest generation fibers developed in mid 90’s – For better performance with high capacity DWDM systems – Optimized for DWDM in the C-band & L-band • Metro. Cor, Wide. Light are other types • Low PMD ULH fibers are also out there 11
 Ins and Outs of Co-location • Presenter - Steve Cotter • Co-location Site Survey – – – Know How to Get to the site Access Equipment Delivery Inspect the facility Know your costs • Power, • Cross-connects • Labor 12 Steve Cotter – Internet 2 / National Lambda. Rail scotter@internet 2. edu
Ins and Outs of Co-location • Presenter - Steve Cotter • Co-location Site Survey – – – Know How to Get to the site Access Equipment Delivery Inspect the facility Know your costs • Power, • Cross-connects • Labor 12 Steve Cotter – Internet 2 / National Lambda. Rail scotter@internet 2. edu
 Acceptance Testing • Presenter - Paul Schopis • Main Issues – Background – – – – – 13 Adapted lab approach Examples on Web at ITEC sites http: //www. nc-itec. org/archive/CAR/plan. html http: //www. adec. edu/nsf/index. html Layered approach Specific targets Physical Layer Optical Layer Full System
Acceptance Testing • Presenter - Paul Schopis • Main Issues – Background – – – – – 13 Adapted lab approach Examples on Web at ITEC sites http: //www. nc-itec. org/archive/CAR/plan. html http: //www. adec. edu/nsf/index. html Layered approach Specific targets Physical Layer Optical Layer Full System
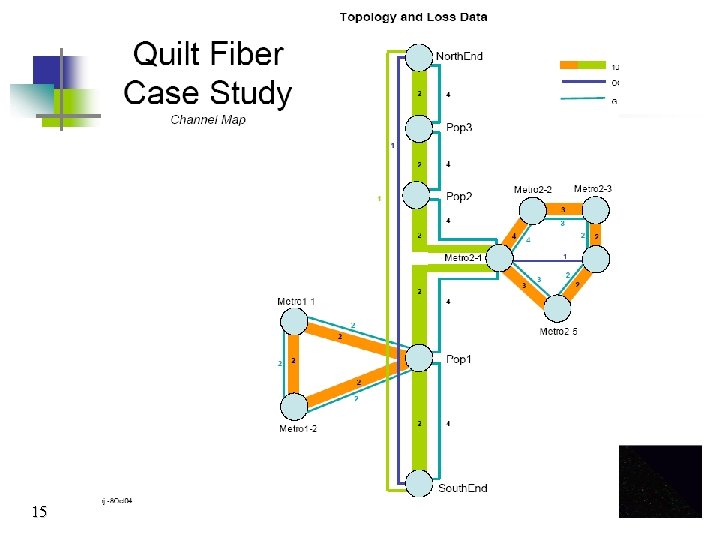
 Quilt 2 nd RON Workshop • November/December 2004 – Raleigh, NC hosted by MCNC. • Focus on Equipment available to light up the network. • New Approach – RFI with a Case Study served as discussion tool. • Selected Equipment Vendors Presented 14
Quilt 2 nd RON Workshop • November/December 2004 – Raleigh, NC hosted by MCNC. • Focus on Equipment available to light up the network. • New Approach – RFI with a Case Study served as discussion tool. • Selected Equipment Vendors Presented 14
 15
15
 Example Equipment RFP • Presenter - Scott Gerstenberger – • • RFP Purpose – Gives the vendors the big picture of why you’re doing this. – Reduces the number of questions – Gives your project more credibility Components – – 16 Mi. LR Optronics Acquisition Background and Overview • Include: general R&E RON activities, about the fiber you have, and an overview of the optronics you want to buy Network Topology and Fiber Specifications • Specifics of your fiber (maps, distances, fiber types, fiber providers, loss specifications, colo sites, etc. ) 16
Example Equipment RFP • Presenter - Scott Gerstenberger – • • RFP Purpose – Gives the vendors the big picture of why you’re doing this. – Reduces the number of questions – Gives your project more credibility Components – – 16 Mi. LR Optronics Acquisition Background and Overview • Include: general R&E RON activities, about the fiber you have, and an overview of the optronics you want to buy Network Topology and Fiber Specifications • Specifics of your fiber (maps, distances, fiber types, fiber providers, loss specifications, colo sites, etc. ) 16
 Example RFP Components (cont’d) • DWDM System and Bid Requirements - Major section – Lay out your optronics design (list of OADM sites, wavelength capacity needed), – Trib interfaces you need, the initial specific configuration you plan to buy through the RFP – Expected network growth over time and how the vendor’s initial design needs to accommodate this growth, – Requirements for alien wavelengths, – Timetable, management and maintenance plan. 17
Example RFP Components (cont’d) • DWDM System and Bid Requirements - Major section – Lay out your optronics design (list of OADM sites, wavelength capacity needed), – Trib interfaces you need, the initial specific configuration you plan to buy through the RFP – Expected network growth over time and how the vendor’s initial design needs to accommodate this growth, – Requirements for alien wavelengths, – Timetable, management and maintenance plan. 17
 Example RFP Components (cont’d) • Evaluation Criteria – Don’t make this too limiting or overly specific – Specifics: • • Vendor’s ability to comply with the RFP specifications Vendor’s ability to demonstrate the product in their lab Customer references Overall cost (put this last) • How to Respond – Boiler plate and procedural material your purchasing department requires 18
Example RFP Components (cont’d) • Evaluation Criteria – Don’t make this too limiting or overly specific – Specifics: • • Vendor’s ability to comply with the RFP specifications Vendor’s ability to demonstrate the product in their lab Customer references Overall cost (put this last) • How to Respond – Boiler plate and procedural material your purchasing department requires 18
 Connecting to the Backbone • Presenter - Dave Reese • Option 1: Co-location – RON co-locates in same facility (not in same cage/space) as backbone. – Consider bulk fiber bundle between RON and backbone • Watch cross-connect fees! • Option 2: High fiber count – RON builds/buys/leases bulk fiber from nearby location into backbone facility – Distance is the limiting factor - some backbone interfaces are short reach ONLY 19
Connecting to the Backbone • Presenter - Dave Reese • Option 1: Co-location – RON co-locates in same facility (not in same cage/space) as backbone. – Consider bulk fiber bundle between RON and backbone • Watch cross-connect fees! • Option 2: High fiber count – RON builds/buys/leases bulk fiber from nearby location into backbone facility – Distance is the limiting factor - some backbone interfaces are short reach ONLY 19
 Common RON Issues • Diversity – Do you need diverse entrance into backbone facility? • Common facility – Can you incorporate the backbone facility as integral part of your RON? • Will the ILEC make “waves? ” – Some are now offering reasonable Gig-E, and indicating 10 GE availability – Depending on your visibility, ILEC may apply pressure to use their services! 20
Common RON Issues • Diversity – Do you need diverse entrance into backbone facility? • Common facility – Can you incorporate the backbone facility as integral part of your RON? • Will the ILEC make “waves? ” – Some are now offering reasonable Gig-E, and indicating 10 GE availability – Depending on your visibility, ILEC may apply pressure to use their services! 20
 Quilt 3 rd RON Workshop • June 1 -3, 2005 – Newport, RI, co-hosted by OSHEAN – Focus will be on learning more about the issues of operating an optical network – Vendor Presentation May 31 – June 1 • Agenda Topics – – – 21 Optical Network Testing Transition from Layer 3 to Layer 1 Optical Network Management Tools Issues Connecting URL: http: //www. thequilt. net/meetings
Quilt 3 rd RON Workshop • June 1 -3, 2005 – Newport, RI, co-hosted by OSHEAN – Focus will be on learning more about the issues of operating an optical network – Vendor Presentation May 31 – June 1 • Agenda Topics – – – 21 Optical Network Testing Transition from Layer 3 to Layer 1 Optical Network Management Tools Issues Connecting URL: http: //www. thequilt. net/meetings
 Optical Network Testing and Test Kits 22
Optical Network Testing and Test Kits 22
 Fiber Testing Goals • Operations and Maintenance – Is this fiber contiguous – Are optical components functioning as they should – Are there dirty connectors or bad splices • Initial Fiber Characterization – Measure span loss – Measure optical return loss (reflections) – Measure Dispersion • Chromatic Dispersion testing required at 10 G • Chromatic and Polarization mode required at 40 G 23
Fiber Testing Goals • Operations and Maintenance – Is this fiber contiguous – Are optical components functioning as they should – Are there dirty connectors or bad splices • Initial Fiber Characterization – Measure span loss – Measure optical return loss (reflections) – Measure Dispersion • Chromatic Dispersion testing required at 10 G • Chromatic and Polarization mode required at 40 G 23
 Test Equipment - Overview • Optical Time Domain Reflectometer – Measure attenuation along span – Can be used to troubleshoot fiber cuts • Optical Spectrum Analyzer – – Display and measure the power levels of all the lambdas on the fiber Helps ensure waves are balanced Consider purchasing two Want one with at least 2 nm sensitivity • Bit Test Set – Perform packet loss test to determine your BER – We require a 24 hour test before accepting circuits • • 24 1310 nm / 1550 nm Light Source Optical Power Meter Chromatic Dispersion test set SONET / GE / 10 GE test sets
Test Equipment - Overview • Optical Time Domain Reflectometer – Measure attenuation along span – Can be used to troubleshoot fiber cuts • Optical Spectrum Analyzer – – Display and measure the power levels of all the lambdas on the fiber Helps ensure waves are balanced Consider purchasing two Want one with at least 2 nm sensitivity • Bit Test Set – Perform packet loss test to determine your BER – We require a 24 hour test before accepting circuits • • 24 1310 nm / 1550 nm Light Source Optical Power Meter Chromatic Dispersion test set SONET / GE / 10 GE test sets
 Fiber Test Equipment Kit • Fiber Inspection Scope – Optical Inspection Scope (<$500) – Video Inspection Scope (USB or standalone) ($2 -3 K) • Cleaning Kit ($100) – Cleaning sticks, alcohol, and wipes. • Laser glasses/goggles ($300) • Visual Fault Locator ($300) • Loss test set ($1 K) – Stabilized light source – Power meter – Look for multi-wavelength units (1310/1550/1625 is common) – Loss testing often included with OTDR. Recommend you get both standalone and OTDR option. 25
Fiber Test Equipment Kit • Fiber Inspection Scope – Optical Inspection Scope (<$500) – Video Inspection Scope (USB or standalone) ($2 -3 K) • Cleaning Kit ($100) – Cleaning sticks, alcohol, and wipes. • Laser glasses/goggles ($300) • Visual Fault Locator ($300) • Loss test set ($1 K) – Stabilized light source – Power meter – Look for multi-wavelength units (1310/1550/1625 is common) – Loss testing often included with OTDR. Recommend you get both standalone and OTDR option. 25
 OTDR Configuration • Optical Time Domain Reflectometer – Buy modular unit that can add features – For operations and maintenance (>$50 K) • OTDR with order of 40 d. B of dynamic range ($30 K) • Optical Spectrum Analyzer (OSA) ($30 K) – For initial fiber characterization, add (total >$100 K) • Chromatic Dispersion analyzer. Often, vendors will have a CM module with an integrated OTDR, so you can save some money getting this rather than discrete CM and OTDR modules ($20 -30 K) • Polarization Mode Dispersion testing ($60 K) 26
OTDR Configuration • Optical Time Domain Reflectometer – Buy modular unit that can add features – For operations and maintenance (>$50 K) • OTDR with order of 40 d. B of dynamic range ($30 K) • Optical Spectrum Analyzer (OSA) ($30 K) – For initial fiber characterization, add (total >$100 K) • Chromatic Dispersion analyzer. Often, vendors will have a CM module with an integrated OTDR, so you can save some money getting this rather than discrete CM and OTDR modules ($20 -30 K) • Polarization Mode Dispersion testing ($60 K) 26
 Best of Breed Modular OTDR • Agilent N 3900 • EXFO FTB 400 • Nettest CMA 5000 – This unit is OEMed by Corning and sold as the Corning 500 Plus Multitester • Informal survey of RON operators indicate most folks have Nettest/Corning or EXFO • Some vendors have a trade-in program, so if you have an old crusty OTDR…. . 27
Best of Breed Modular OTDR • Agilent N 3900 • EXFO FTB 400 • Nettest CMA 5000 – This unit is OEMed by Corning and sold as the Corning 500 Plus Multitester • Informal survey of RON operators indicate most folks have Nettest/Corning or EXFO • Some vendors have a trade-in program, so if you have an old crusty OTDR…. . 27


