2aa543bee63afe9651ba673818fb572c.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14

Regional Capacity Building Activities in the Caribbean UNFCCC Expert Workshop on Monitoring and Evaluating Capacity- building in Developing Countries Carlos Fuller Deputy Director

Caribbean Planning for Adaptation to Climate Change (CPACC) ● ● ● Objective: to support Caribbean countries in preparing to cope with the adverse effects of global climate change particularly sea-level rise, in coastal and marine areas, through vulnerability assessment, adaptation planning and related capacity-building initiatives. (a) Strengthen the regional capacity for monitoring and analyzing climate and sea-level dynamics and trends (d) Enhance regional and national capabilities to prepare for the advent of global climate change through institutional strengthening and human resource development

Component I: Design and Installation of Sea-level monitoring System ● ● ● Capacities of local technicians varied widely Capacity to develop applications in CZM and engineering Lack of local expertise in GPS surveying

Component II: Establishment of Databases and Information Systems ● IT technology changing rapidly ● Significant PEO required using the web ● ● Demand for more current information, news and non-technical information Support to maintain system

Component III: Inventory of Coastal Resources and Uses ● ● ● Successful, instructive and challenging Challenges: revised objectives & strategies; demands placed on national counterparts, limited imagery & budgetary cutbacks Flexibility necessary Regular reviews by key knowledgeable practitioners useful Use of national and regional expertise

Component IV: Formulation of Policy Framework for Integrated Adaptation Planning and Management ● ● ● Unique as it benefited from lessons learned in other components, ie. Component 6 (Impact & Vulnerability Assessments) Redesigned for a more customized approach Addressed climate variability rather than climate change to encourage buy-in by policymakers

Component V: Coral Reef Monitoring for Climate Change Impacts ● Government commitment required ● Not enough technical personnel ● PEO required ● ● Technical workshops and review exercises are invaluable Continuous coordination and technical support important for sustainability Acquisition of supporting data essential Critical importance of continuous dialogue among participating countries

Component VI: Coastal Vulnerability Assessment ● ● Great need identified in capacity to conduct vulnerability and risk assessments and develop climate change scenarios, Lack of data

Component VII: Economic Valuation of Coastal and Marine Resources ● Challenges: ● ● Limited resources and time Commitment of country teams Lack of opportunity to conduct more workshops and training sessions Lack of opportunity to share outputs with other countries Enhanced capacity in economic valuation and building of a regional team with experience and knowledge Needs: Development of methodology and capacity to implement More resources to support regional team building

Component VIII: Formulation of Economic and Regulatory Proposals ● Challenges: ● Time and resources too little Lessons: Consensus approach to market-based instruments is critical, politically feasible, requires a PEO strategy, based on economic analysis and health, should include regional compacts, and integrate environmental planning and management

● ● Component 9: GHG Inventory and Vulnerability Assessment of the Agriculture and Water Sectors in St. Vincent and the Grenadines Work conducted by domestic consultants, government officials and private entities More capacity building required

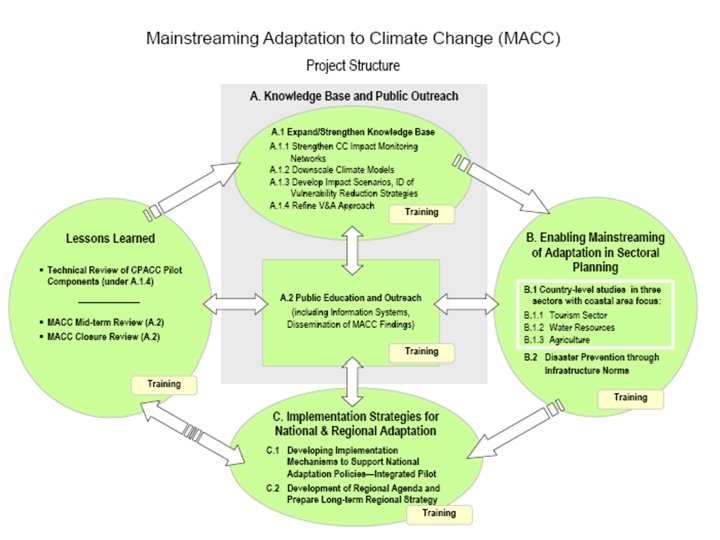
Adapting to Climate Change in the Caribbean (ACCC) ● Public Education and Outreach (PEO) ● Strengthen regional technical capacity
2aa543bee63afe9651ba673818fb572c.ppt