812c3eac6ed1dd0bc1f25c9950afe79e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 93
 Regents Review!!
Regents Review!!
 Ecology
Ecology
 Ecology • The study of interactions between living things and their environment. • Energy is needed in order to keep the ecosystem going. • Energy comes from the sun. It is used by producers. (who are producers? )
Ecology • The study of interactions between living things and their environment. • Energy is needed in order to keep the ecosystem going. • Energy comes from the sun. It is used by producers. (who are producers? )
 Food Chain/Web • • • Draw a food web: 1. Include 5 organisms 2. Label producers and consumers 3. Label heterotrophs and autotrophs 4. Where is the most energy found? 5. How is energy given off?
Food Chain/Web • • • Draw a food web: 1. Include 5 organisms 2. Label producers and consumers 3. Label heterotrophs and autotrophs 4. Where is the most energy found? 5. How is energy given off?
 Energy in the Food Chain • Energy is lost as it is passed to the next step in the food chain. • We give energy off as heat. • As an organism consumes food, they consume a little bit of the food’s energy Among populations of any natural community, the basic food supply is always a critical factor because it is: A) produced by all organisms B) synthesized from oxygen C) a means of transferring energy D) present in surplus amounts
Energy in the Food Chain • Energy is lost as it is passed to the next step in the food chain. • We give energy off as heat. • As an organism consumes food, they consume a little bit of the food’s energy Among populations of any natural community, the basic food supply is always a critical factor because it is: A) produced by all organisms B) synthesized from oxygen C) a means of transferring energy D) present in surplus amounts
 Predator vs. Parasite • Predator – define and give an example of each Parasite -
Predator vs. Parasite • Predator – define and give an example of each Parasite -
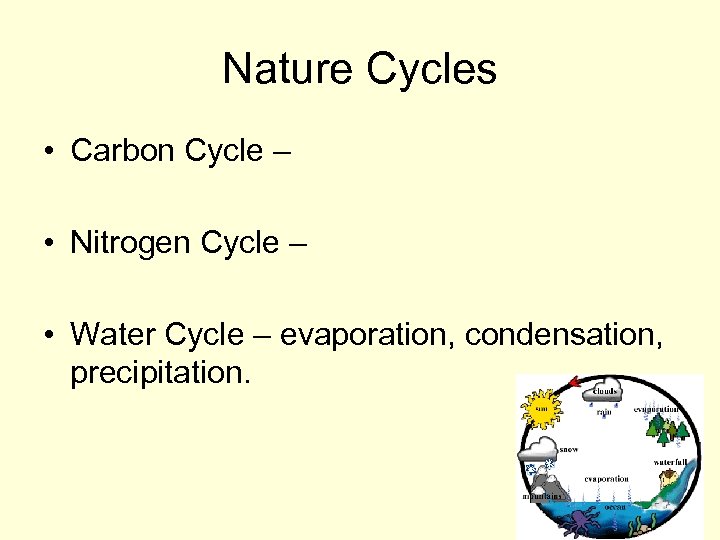 Nature Cycles • Carbon Cycle – • Nitrogen Cycle – • Water Cycle – evaporation, condensation, precipitation.
Nature Cycles • Carbon Cycle – • Nitrogen Cycle – • Water Cycle – evaporation, condensation, precipitation.
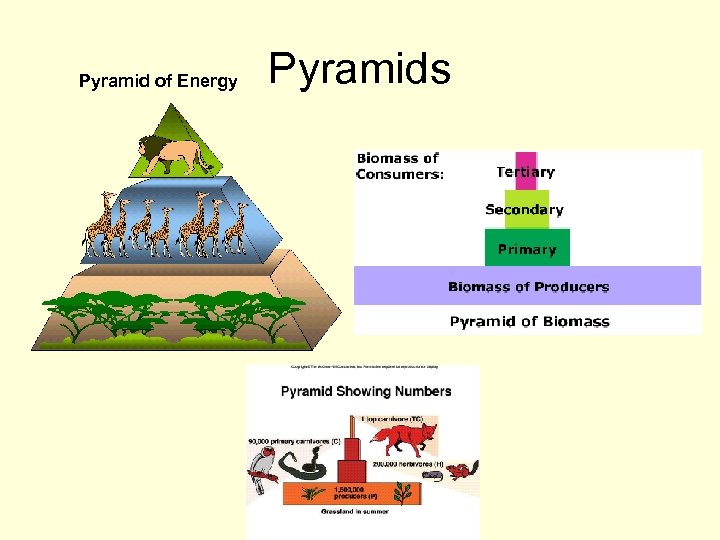 Pyramid of Energy Pyramids
Pyramid of Energy Pyramids
 Ecosystem • All of the living and non living things in an exact area that interact with one another. • These include biotic and abiotic factors. biotic abiotic List biotic and abiotic factors for a pond ecosystem
Ecosystem • All of the living and non living things in an exact area that interact with one another. • These include biotic and abiotic factors. biotic abiotic List biotic and abiotic factors for a pond ecosystem
 Important Abiotic Factors • • Air Water Light Temperature p. H Food Predators • **these determine which organisms can live in an ecosystem and controls their populations
Important Abiotic Factors • • Air Water Light Temperature p. H Food Predators • **these determine which organisms can live in an ecosystem and controls their populations
 Carrying Capacity • The maximum size that a population can have. • Name examples of factors controlling human population growth:
Carrying Capacity • The maximum size that a population can have. • Name examples of factors controlling human population growth:
 Niche • An animal’s role in the environment • For example – a bee must pollinate • Name another example of a niche.
Niche • An animal’s role in the environment • For example – a bee must pollinate • Name another example of a niche.
 Competition • This exists when more than one organism occupies one niche. • Animals do try to avoid this by keeping to their own territory. • Example – birds eat insects during the day, bats eat them at night. What is it called when two different species live in the same area and use the same limited resources?
Competition • This exists when more than one organism occupies one niche. • Animals do try to avoid this by keeping to their own territory. • Example – birds eat insects during the day, bats eat them at night. What is it called when two different species live in the same area and use the same limited resources?
 Ecological Succession • The gradual change in an ecosystem where one species is replaced by another and grown until stability is reached. • Climax – • Pioneer – Describe what happens during a forest fire and volcanic eruption
Ecological Succession • The gradual change in an ecosystem where one species is replaced by another and grown until stability is reached. • Climax – • Pioneer – Describe what happens during a forest fire and volcanic eruption
 Biodiversity • The variety of life on earth. • Extinction reduces biodiversity as well as habitat loss. This is a problem because: 1. We are losing valuable natural resources 2.
Biodiversity • The variety of life on earth. • Extinction reduces biodiversity as well as habitat loss. This is a problem because: 1. We are losing valuable natural resources 2.
 Human Impact • Development of land, industrialization, pollution, farming, over hunting, over grazing, introducing a foreign species are things humans do. • They all have negative affects on earth and ourselves. Pick one and explain why it is an issue to ecosystems on earth
Human Impact • Development of land, industrialization, pollution, farming, over hunting, over grazing, introducing a foreign species are things humans do. • They all have negative affects on earth and ourselves. Pick one and explain why it is an issue to ecosystems on earth
 What causes these problems? • An overpopulation of humans. • Actions being taken to reduce or repair the damage: • 1. recycling wastes • 2. conserving available resources • 3. cleaner resources (solar vs. fossil) • 4. protection of habitats and endangered species • 5. Farming native plants Pick one and give a specific example of • 6. Planting new trees how humans have developed a new way to use this.
What causes these problems? • An overpopulation of humans. • Actions being taken to reduce or repair the damage: • 1. recycling wastes • 2. conserving available resources • 3. cleaner resources (solar vs. fossil) • 4. protection of habitats and endangered species • 5. Farming native plants Pick one and give a specific example of • 6. Planting new trees how humans have developed a new way to use this.
 LONG ANSWER QUESTION! • For each of the following you should be able to identify the specific cause, their negative effects on the environment, and a way that people are trying to fix the problem. • 1. acid rain 2. deforestation • 3. loss of biodiversity 4. global warming • 5. loss of ozone layer 6. industrialization
LONG ANSWER QUESTION! • For each of the following you should be able to identify the specific cause, their negative effects on the environment, and a way that people are trying to fix the problem. • 1. acid rain 2. deforestation • 3. loss of biodiversity 4. global warming • 5. loss of ozone layer 6. industrialization
 GENETICS
GENETICS
 Humans • We have 46 chromosomes. • How many homologous pairs do we have? • Chromosome pairs carry alleles for the same trait. We all have two alleles for each gene. (why two? )
Humans • We have 46 chromosomes. • How many homologous pairs do we have? • Chromosome pairs carry alleles for the same trait. We all have two alleles for each gene. (why two? )
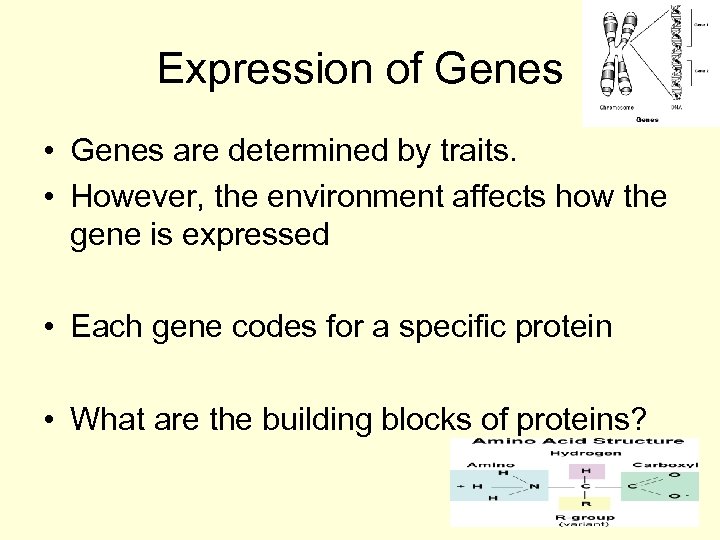 Expression of Genes • Genes are determined by traits. • However, the environment affects how the gene is expressed • Each gene codes for a specific protein • What are the building blocks of proteins?
Expression of Genes • Genes are determined by traits. • However, the environment affects how the gene is expressed • Each gene codes for a specific protein • What are the building blocks of proteins?
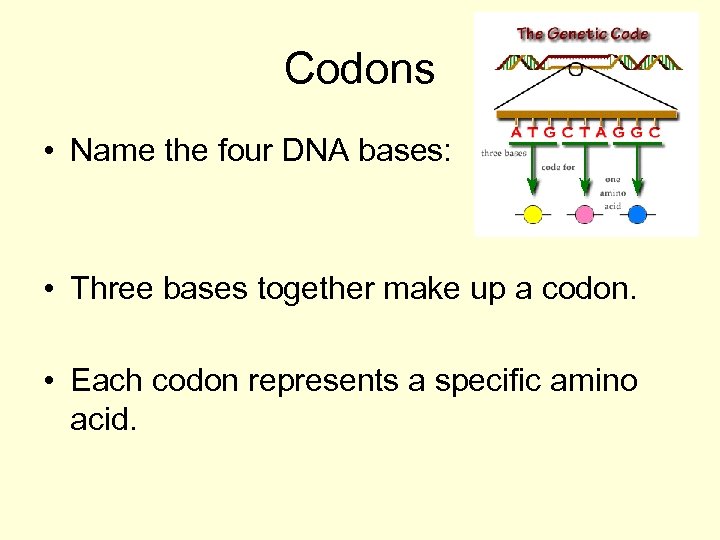 Codons • Name the four DNA bases: • Three bases together make up a codon. • Each codon represents a specific amino acid.
Codons • Name the four DNA bases: • Three bases together make up a codon. • Each codon represents a specific amino acid.
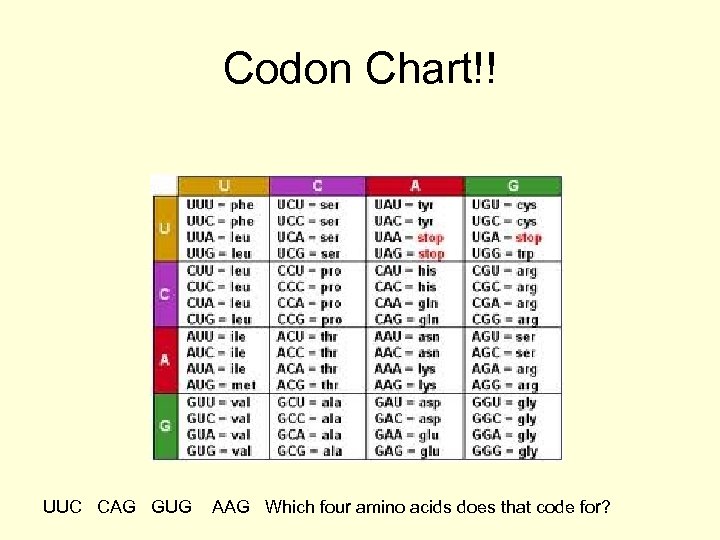 Codon Chart!! UUC CAG GUG AAG Which four amino acids does that code for?
Codon Chart!! UUC CAG GUG AAG Which four amino acids does that code for?
 RNA • Carries the genetic code to ribosomes. • What is the ribosome responsible for making? • If the ribosome codes wrong, what will it make?
RNA • Carries the genetic code to ribosomes. • What is the ribosome responsible for making? • If the ribosome codes wrong, what will it make?
 Mutation • Changes in DNA. • Can only be passed on if they occur in reproductive cells. • What are the two reproductive cells?
Mutation • Changes in DNA. • Can only be passed on if they occur in reproductive cells. • What are the two reproductive cells?
 Selective Breeding • Produces animals and plants with desired traits. • What is the biggest example of selective breeding? • Why is it so important?
Selective Breeding • Produces animals and plants with desired traits. • What is the biggest example of selective breeding? • Why is it so important?
 Genetic Engineering • Inserts genes of one organism into genes of another. • ____ are used to cut and copy DNA fragments. • What pathogen do we often use for this process?
Genetic Engineering • Inserts genes of one organism into genes of another. • ____ are used to cut and copy DNA fragments. • What pathogen do we often use for this process?
 Making Insulin • The gene to make human insulin was inserted into bacteria. • It can make insulin that we use for patients with diabetes. • How has this had a dramatic impact on the medical field?
Making Insulin • The gene to make human insulin was inserted into bacteria. • It can make insulin that we use for patients with diabetes. • How has this had a dramatic impact on the medical field?
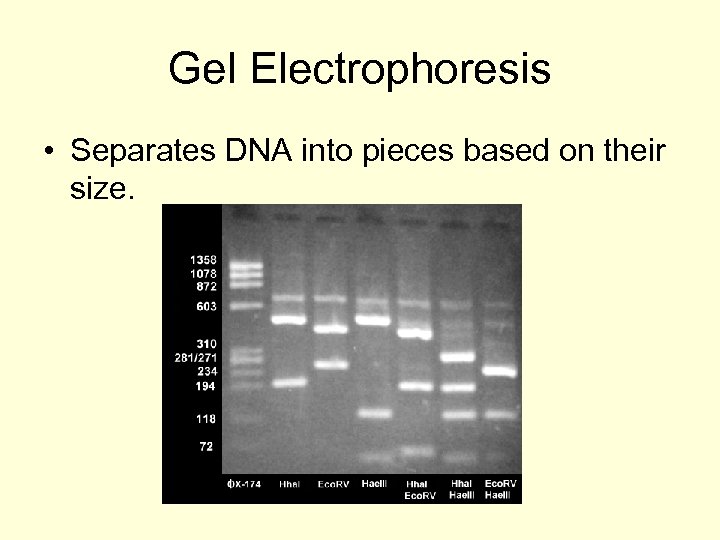 Gel Electrophoresis • Separates DNA into pieces based on their size.
Gel Electrophoresis • Separates DNA into pieces based on their size.
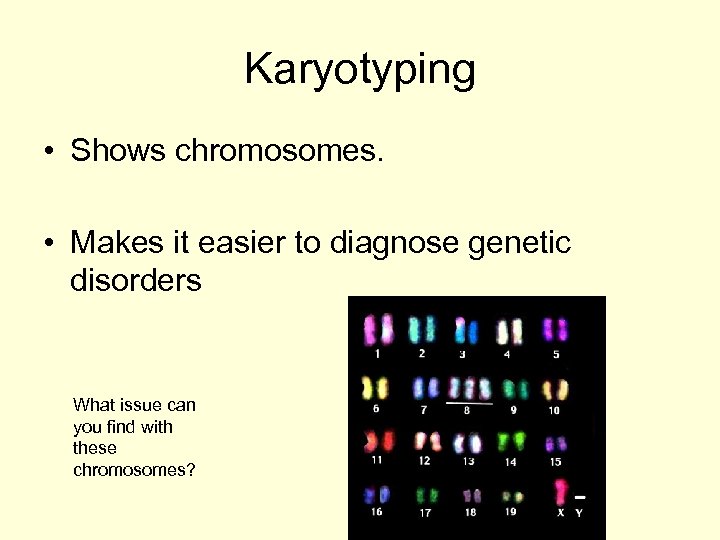 Karyotyping • Shows chromosomes. • Makes it easier to diagnose genetic disorders What issue can you find with these chromosomes?
Karyotyping • Shows chromosomes. • Makes it easier to diagnose genetic disorders What issue can you find with these chromosomes?
 Evolution
Evolution
 Theory of Modern Evolution • What does this theory propose? • Modern species have developed from earlier, different species and share a _______ • Give an example of a common human ancestor
Theory of Modern Evolution • What does this theory propose? • Modern species have developed from earlier, different species and share a _______ • Give an example of a common human ancestor
 Charles Darwin • Proposed natural selection. • • This includes: 1. overproduction of offspring 2. competition for limited resources 3. survival of the fittest The process of natural selection is based on the assumption that 1) environmental changes will cause changes in body structure in individuals 2) most changes from generation to generation are the result of mutations 3) part of the population of organisms always remains stable 4) different traits inherited by offspring have different survival value.
Charles Darwin • Proposed natural selection. • • This includes: 1. overproduction of offspring 2. competition for limited resources 3. survival of the fittest The process of natural selection is based on the assumption that 1) environmental changes will cause changes in body structure in individuals 2) most changes from generation to generation are the result of mutations 3) part of the population of organisms always remains stable 4) different traits inherited by offspring have different survival value.
 Fitness • What does fitness mean in terms of an animal’s ability to survive? • Organisms that are better adapted to their environment and able to reproduce successfully. • What happens to unfit organisms?
Fitness • What does fitness mean in terms of an animal’s ability to survive? • Organisms that are better adapted to their environment and able to reproduce successfully. • What happens to unfit organisms?
 Evolution • Define evolution – • It is driven by change in an environment. • In order to evolve, the change must be present in the species before the environment changes. These changes are caused by random _____
Evolution • Define evolution – • It is driven by change in an environment. • In order to evolve, the change must be present in the species before the environment changes. These changes are caused by random _____
 Variation • How do we get so much variation within a species? • 1. • 2. • The better the variation, the higher the rate of _____
Variation • How do we get so much variation within a species? • 1. • 2. • The better the variation, the higher the rate of _____
 Gradualism vs Punctuated Equilibrium • Gradualism – change occurs slowly • Punctuated equillibrium – evolution happens in quick spirts. • Which one is true in your opinion?
Gradualism vs Punctuated Equilibrium • Gradualism – change occurs slowly • Punctuated equillibrium – evolution happens in quick spirts. • Which one is true in your opinion?
 Isolation • Geographic isolation – • Reproductive isolation – caused by the inability to mate Name two reasons for geographic isolation
Isolation • Geographic isolation – • Reproductive isolation – caused by the inability to mate Name two reasons for geographic isolation
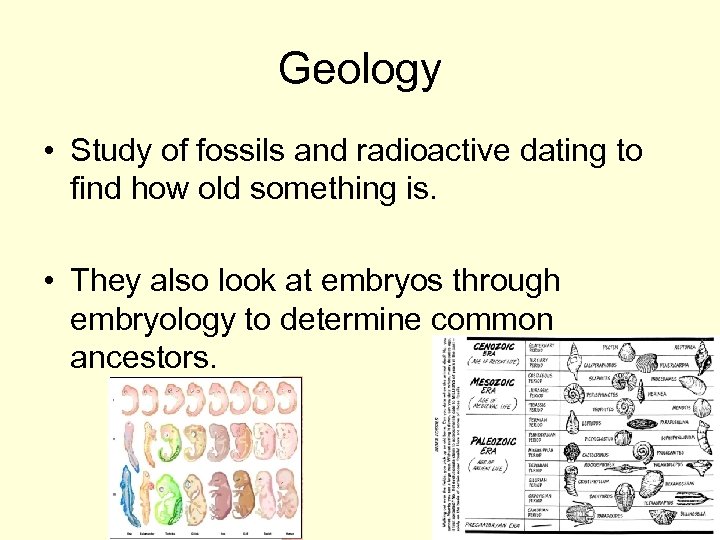 Geology • Study of fossils and radioactive dating to find how old something is. • They also look at embryos through embryology to determine common ancestors.
Geology • Study of fossils and radioactive dating to find how old something is. • They also look at embryos through embryology to determine common ancestors.
 Scientific Method
Scientific Method
 Observation vs. Inference • Observation – what is seen or measured • Inference – a conclusion based on observation or evidence What is this? The fold of the arm can appear to look like something else. Give an observation and an inference.
Observation vs. Inference • Observation – what is seen or measured • Inference – a conclusion based on observation or evidence What is this? The fold of the arm can appear to look like something else. Give an observation and an inference.
 Hypothesis • Define hypothesis An untested prediction • A good hypothesis states both cause and effect • (If…then… statements) I gave my car an oil change. I tried to start the car and it did not turn on. State a hypothesis for why my car did not work.
Hypothesis • Define hypothesis An untested prediction • A good hypothesis states both cause and effect • (If…then… statements) I gave my car an oil change. I tried to start the car and it did not turn on. State a hypothesis for why my car did not work.
 Experiment • Controlled experiment – compares the results of an experiment between two groups • Experimental group – group being tested or receiving treatment • Control group – normal group that should be identical to the experimental group in every way (except for treatment) If I wanted to measure the effects of coffee on morning alertness, what would be the control and experimen tal conditions ?
Experiment • Controlled experiment – compares the results of an experiment between two groups • Experimental group – group being tested or receiving treatment • Control group – normal group that should be identical to the experimental group in every way (except for treatment) If I wanted to measure the effects of coffee on morning alertness, what would be the control and experimen tal conditions ?
 Placebo • Fake treatment given to the control group so subjects do not know which group they are in. • What other benefit do placebos have?
Placebo • Fake treatment given to the control group so subjects do not know which group they are in. • What other benefit do placebos have?
 Variables • Independent variable – the variable that is being tested (X axis) • Dependent variable – variable that is measured at the end of the experiment (Y axis) If you wanted to measure the effects of exercise on the amount of times a clothespin would be squeezed, what would serve as your independent and dependent variables?
Variables • Independent variable – the variable that is being tested (X axis) • Dependent variable – variable that is measured at the end of the experiment (Y axis) If you wanted to measure the effects of exercise on the amount of times a clothespin would be squeezed, what would serve as your independent and dependent variables?
 Characteristics of Good Experiments • Name some: • 1. can be repeated by anyone and get the same result • 2. Have a large sample size and many text subjects • 3. are performed for longer periods of time • 4. tests only one variable • 5. are peer reviewed • 6. is objective
Characteristics of Good Experiments • Name some: • 1. can be repeated by anyone and get the same result • 2. Have a large sample size and many text subjects • 3. are performed for longer periods of time • 4. tests only one variable • 5. are peer reviewed • 6. is objective
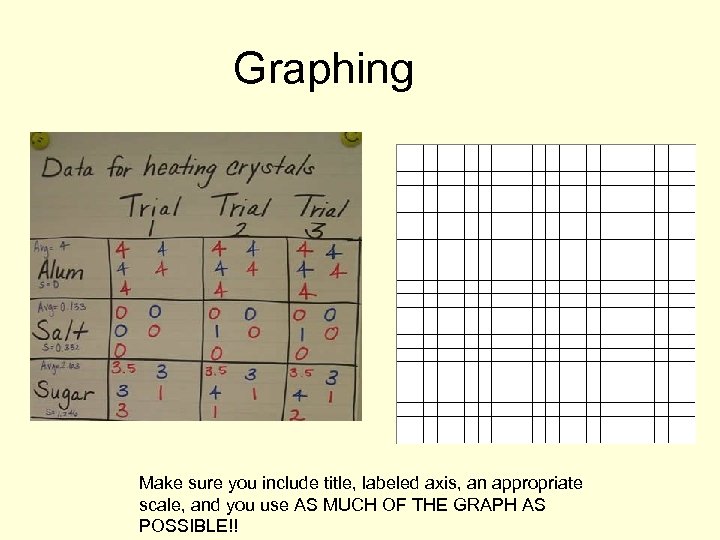 Graphing Make sure you include title, labeled axis, an appropriate scale, and you use AS MUCH OF THE GRAPH AS POSSIBLE!!
Graphing Make sure you include title, labeled axis, an appropriate scale, and you use AS MUCH OF THE GRAPH AS POSSIBLE!!
 Characteristics of Living Things
Characteristics of Living Things
 All Living Things • • In order to maintain homeostasis: 1. Nutrition 2. Transport 3. Respiration 4. Growth 5. Synthesis 6. Regulation 7. Reproduction All of these make up metabolism
All Living Things • • In order to maintain homeostasis: 1. Nutrition 2. Transport 3. Respiration 4. Growth 5. Synthesis 6. Regulation 7. Reproduction All of these make up metabolism
 Nutrition Write the equation for photosynthesis • Autotrophs – • Heterotrophs – • Photosynthesis – takes energy from the sun and puts it in the bonds of sugar molecules. (happens in the chloroplast)
Nutrition Write the equation for photosynthesis • Autotrophs – • Heterotrophs – • Photosynthesis – takes energy from the sun and puts it in the bonds of sugar molecules. (happens in the chloroplast)
 Plants • Stomata – small holes in the leaf where gas exchange occurs • Guard Cells – open and close stomates • Chloroplast – contain green pigment that captures light to make food Some plants respond to light with a sudden enlargement of their leaf pores. This response is important because it enables the plant to increase its intake of A) carbon dioxide B) water C) oxygen D) nitrogen
Plants • Stomata – small holes in the leaf where gas exchange occurs • Guard Cells – open and close stomates • Chloroplast – contain green pigment that captures light to make food Some plants respond to light with a sudden enlargement of their leaf pores. This response is important because it enables the plant to increase its intake of A) carbon dioxide B) water C) oxygen D) nitrogen
 Respiration • ALL organisms get energy by breaking the bonds of sugar molecules • Energy released makes ATP!! • This happens in the mitochondria Energy released from the cellular respiration of glucose is A) first stored within ATP B) stored in the liver as fat C) turned into fat D) used directly for body activity
Respiration • ALL organisms get energy by breaking the bonds of sugar molecules • Energy released makes ATP!! • This happens in the mitochondria Energy released from the cellular respiration of glucose is A) first stored within ATP B) stored in the liver as fat C) turned into fat D) used directly for body activity
 Aerobic vs. Anaerobic • Aerobic – requires oxygen and yields a ton of ATP. • Anaerobic – happens without oxygen. Makes little ATP • Lactic Acid – happens when muscles are forced to get energy from anaerobic respiration. What is a major type of anaerobic respiration?
Aerobic vs. Anaerobic • Aerobic – requires oxygen and yields a ton of ATP. • Anaerobic – happens without oxygen. Makes little ATP • Lactic Acid – happens when muscles are forced to get energy from anaerobic respiration. What is a major type of anaerobic respiration?
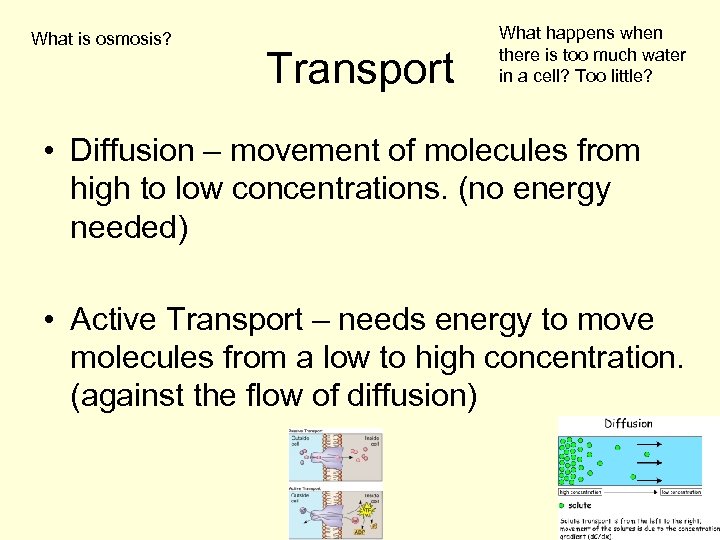 What is osmosis? Transport What happens when there is too much water in a cell? Too little? • Diffusion – movement of molecules from high to low concentrations. (no energy needed) • Active Transport – needs energy to move molecules from a low to high concentration. (against the flow of diffusion)
What is osmosis? Transport What happens when there is too much water in a cell? Too little? • Diffusion – movement of molecules from high to low concentrations. (no energy needed) • Active Transport – needs energy to move molecules from a low to high concentration. (against the flow of diffusion)
 Regulation • Coordination and control of other life functions • Stimulus – a change in the environment that you respond to. • This is done by neurons and hormones What is the function of the cell membrane in regards to regulation?
Regulation • Coordination and control of other life functions • Stimulus – a change in the environment that you respond to. • This is done by neurons and hormones What is the function of the cell membrane in regards to regulation?
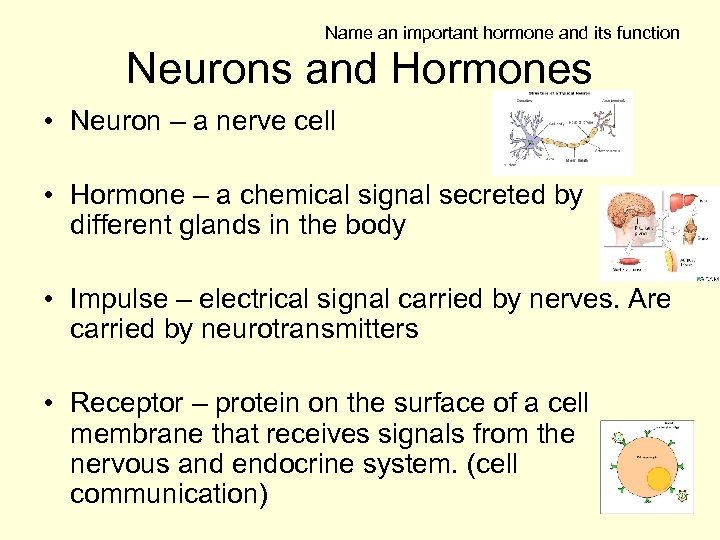 Name an important hormone and its function Neurons and Hormones • Neuron – a nerve cell • Hormone – a chemical signal secreted by different glands in the body • Impulse – electrical signal carried by nerves. Are carried by neurotransmitters • Receptor – protein on the surface of a cell membrane that receives signals from the nervous and endocrine system. (cell communication)
Name an important hormone and its function Neurons and Hormones • Neuron – a nerve cell • Hormone – a chemical signal secreted by different glands in the body • Impulse – electrical signal carried by nerves. Are carried by neurotransmitters • Receptor – protein on the surface of a cell membrane that receives signals from the nervous and endocrine system. (cell communication)
 Chemistry • Most common elements are – • Organic Compounds have Carbon and Hydrogen together. • The four main body molecules are: • 1. 3. • 2. 4.
Chemistry • Most common elements are – • Organic Compounds have Carbon and Hydrogen together. • The four main body molecules are: • 1. 3. • 2. 4.
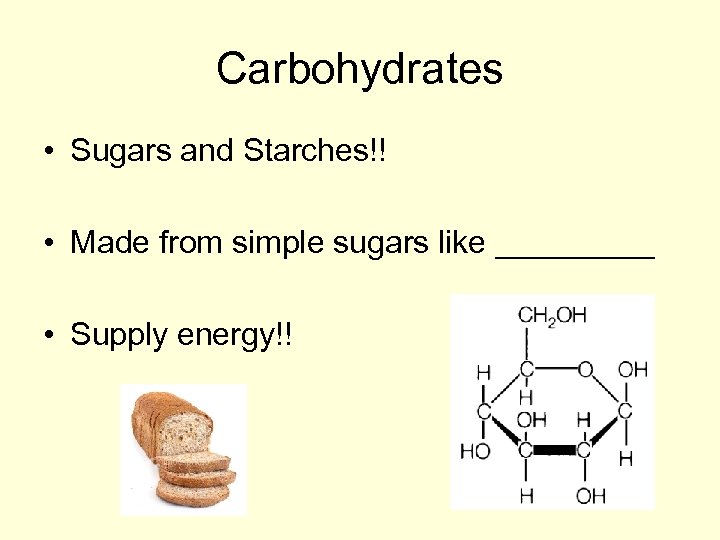 Carbohydrates • Sugars and Starches!! • Made from simple sugars like _____ • Supply energy!!
Carbohydrates • Sugars and Starches!! • Made from simple sugars like _____ • Supply energy!!
 Lipids • Fats, oils, and waxes! • Store energy! • Made from fatty acids and glycerol
Lipids • Fats, oils, and waxes! • Store energy! • Made from fatty acids and glycerol
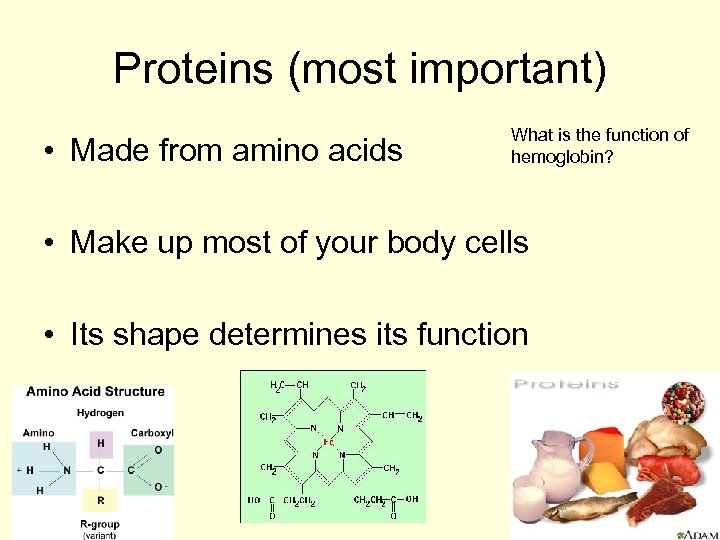 Proteins (most important) • Made from amino acids What is the function of hemoglobin? • Make up most of your body cells • Its shape determines its function
Proteins (most important) • Made from amino acids What is the function of hemoglobin? • Make up most of your body cells • Its shape determines its function
 Jobs of a Protein • 1. makes enzymes • 2. make receptor molecules on the membrane • 3. make antibodies • 4. make hormones
Jobs of a Protein • 1. makes enzymes • 2. make receptor molecules on the membrane • 3. make antibodies • 4. make hormones
 Enzymes • Act as a catalyst. They speed up reactions so things can happen quickly • Lock and Key model – one type of enzyme fits one type of molecules. If the shape changes, the enzyme won’t work. • TEMPERATURE AND p. H will cause proteins to not work. What do temperature and p. H do to the protein itself?
Enzymes • Act as a catalyst. They speed up reactions so things can happen quickly • Lock and Key model – one type of enzyme fits one type of molecules. If the shape changes, the enzyme won’t work. • TEMPERATURE AND p. H will cause proteins to not work. What do temperature and p. H do to the protein itself?
 p. H • Measures acids and bases • A low p. H is an acid –(0 - 6. 9) • A high p. H is a base – (7. 1 – 14) • Neutral is a p. H of 7 (water) Milk has a p. H of 6. Is that an acid or a base?
p. H • Measures acids and bases • A low p. H is an acid –(0 - 6. 9) • A high p. H is a base – (7. 1 – 14) • Neutral is a p. H of 7 (water) Milk has a p. H of 6. Is that an acid or a base?
 Name based on genus and species. What is the human genus and species? Classification • Classified based on evolutionary history • Kingdom – a large group of related organisms. • (fungi, bacteria, protists, animals, plants) • Species – able to successfully reproduce amongst its members.
Name based on genus and species. What is the human genus and species? Classification • Classified based on evolutionary history • Kingdom – a large group of related organisms. • (fungi, bacteria, protists, animals, plants) • Species – able to successfully reproduce amongst its members.
 Cells! • The basic unit of life. All living things except viruses are made of them. • They are specialized into tissues • Tissues – groups of cells specialized to do certain jobs
Cells! • The basic unit of life. All living things except viruses are made of them. • They are specialized into tissues • Tissues – groups of cells specialized to do certain jobs
 Cell Theory • 1. all living things are made of cells • 2. cells arise from pre-existing cells • 3. cells are the basic unit of structure and function in a living thing What pathogenic organism is not included in this theory?
Cell Theory • 1. all living things are made of cells • 2. cells arise from pre-existing cells • 3. cells are the basic unit of structure and function in a living thing What pathogenic organism is not included in this theory?
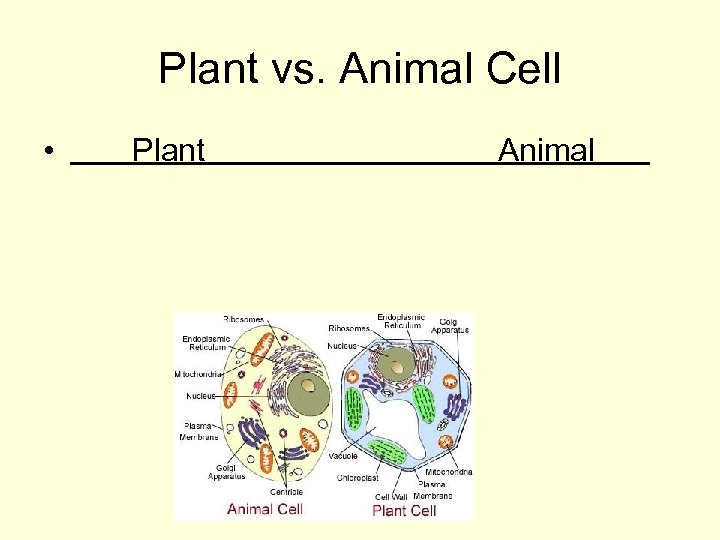 Plant vs. Animal Cell • Plant Animal
Plant vs. Animal Cell • Plant Animal
 Cell Organelles • Cell Wall – • Nucleus – • Cytoplasm – • Ribosome – • Vacuole -
Cell Organelles • Cell Wall – • Nucleus – • Cytoplasm – • Ribosome – • Vacuole -
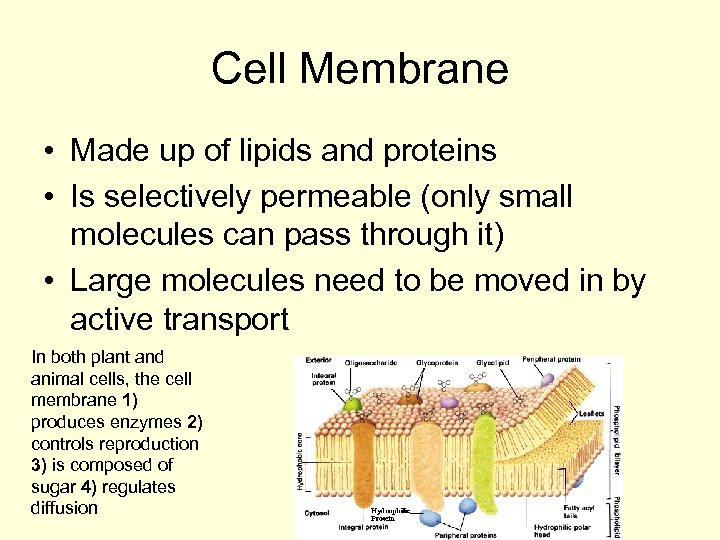 Cell Membrane • Made up of lipids and proteins • Is selectively permeable (only small molecules can pass through it) • Large molecules need to be moved in by active transport In both plant and animal cells, the cell membrane 1) produces enzymes 2) controls reproduction 3) is composed of sugar 4) regulates diffusion
Cell Membrane • Made up of lipids and proteins • Is selectively permeable (only small molecules can pass through it) • Large molecules need to be moved in by active transport In both plant and animal cells, the cell membrane 1) produces enzymes 2) controls reproduction 3) is composed of sugar 4) regulates diffusion
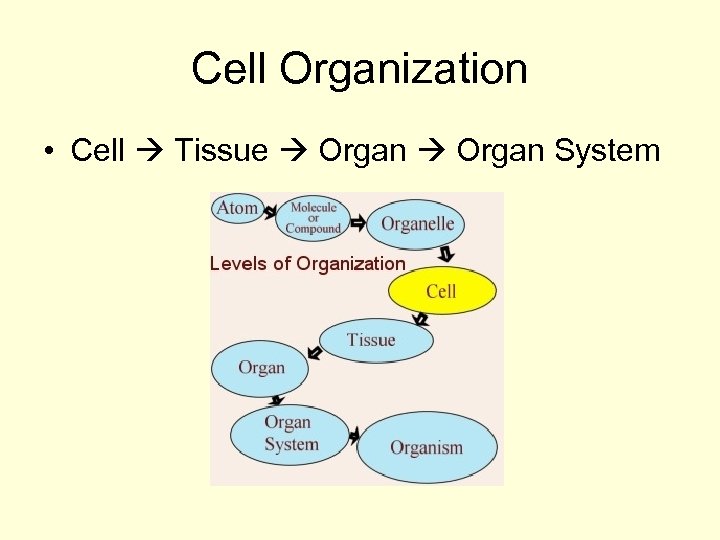 Cell Organization • Cell Tissue Organ System
Cell Organization • Cell Tissue Organ System
 Lab Skills
Lab Skills
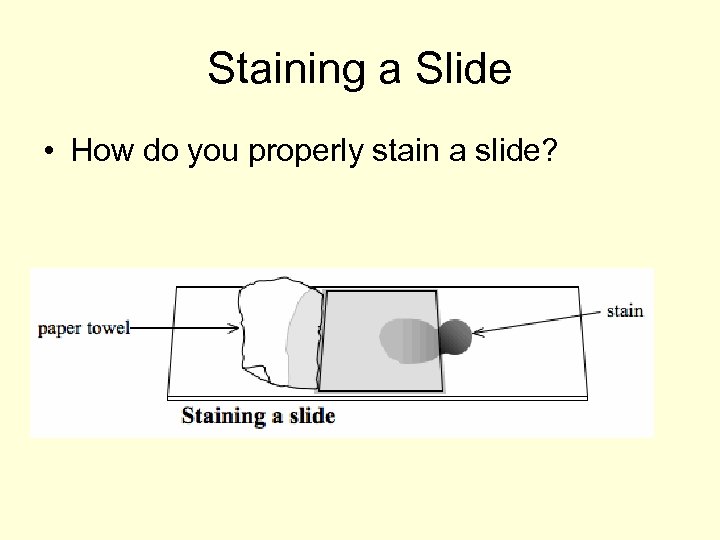 Staining a Slide • How do you properly stain a slide?
Staining a Slide • How do you properly stain a slide?
 Conversions • Under a microscope, things are measured in micrometers. (um) • 1 meter = 1, 000 micrometers • 1 millimeter = 1, 000 micrometers A bug is seen under a microscope at. 03 millimeters. How many micrometers is that?
Conversions • Under a microscope, things are measured in micrometers. (um) • 1 meter = 1, 000 micrometers • 1 millimeter = 1, 000 micrometers A bug is seen under a microscope at. 03 millimeters. How many micrometers is that?
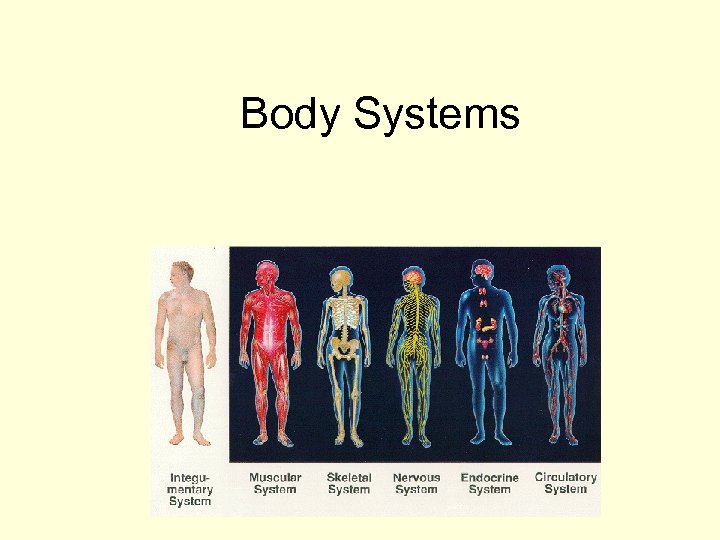 Body Systems
Body Systems
 Name three types of asexual reproduction. Reproduction • Asexual – makes identical offspring through mitosis (faster, easier) • Disadvantage – no variety • Sexual – offspring different from parent through meiosis (variety) • Disadvantage – more time, effort, risk
Name three types of asexual reproduction. Reproduction • Asexual – makes identical offspring through mitosis (faster, easier) • Disadvantage – no variety • Sexual – offspring different from parent through meiosis (variety) • Disadvantage – more time, effort, risk
 Mitosis How many chromosomes will the daughter cells have? • Asexual reproduction • One division – two identical, diploid cells • Chromosome number in the daughter cells is the same as in the parent cells • Large organisms use mitosis for growth and healing. Small organisms use it to reproduce.
Mitosis How many chromosomes will the daughter cells have? • Asexual reproduction • One division – two identical, diploid cells • Chromosome number in the daughter cells is the same as in the parent cells • Large organisms use mitosis for growth and healing. Small organisms use it to reproduce.
 Meiosis • Sexual Reproduction • One cell divides twice to make four different cells • All four cells are haploid and have half the number of chromosomes found in the parent cell • Makes gametes. Males make 4 sperm and females make 1 egg and three polar bodies
Meiosis • Sexual Reproduction • One cell divides twice to make four different cells • All four cells are haploid and have half the number of chromosomes found in the parent cell • Makes gametes. Males make 4 sperm and females make 1 egg and three polar bodies
 Fertilization • Occurs in the fallopian tube • A fertilized egg is called a zygote and has the normal number of chromosomes. • During this point, homologous chromosomes from each parent meet to form 46 chromosomes.
Fertilization • Occurs in the fallopian tube • A fertilized egg is called a zygote and has the normal number of chromosomes. • During this point, homologous chromosomes from each parent meet to form 46 chromosomes.
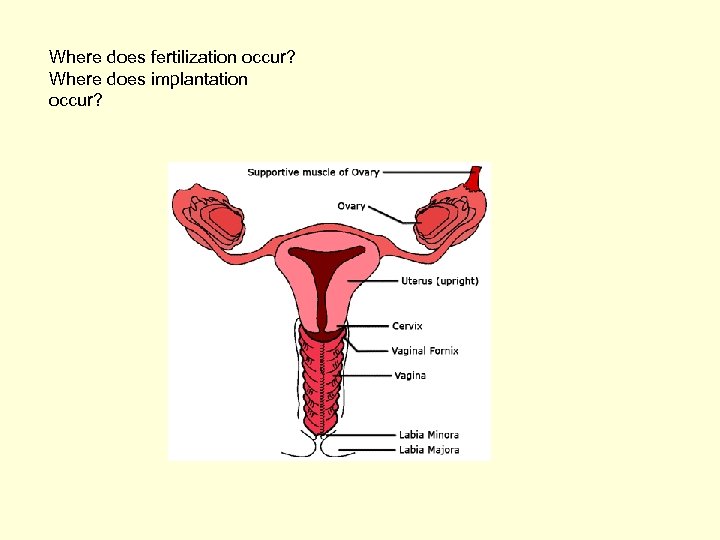 Where does fertilization occur? Where does implantation occur?
Where does fertilization occur? Where does implantation occur?
 Fetal Development • The fetus develops in the uterus. • Cells divide without becoming larger. After a few days they begin to differentiate and form nerve cells, skin, bones, etc. • At this stage the embryo is very vulnerable to alcohol and drugs.
Fetal Development • The fetus develops in the uterus. • Cells divide without becoming larger. After a few days they begin to differentiate and form nerve cells, skin, bones, etc. • At this stage the embryo is very vulnerable to alcohol and drugs.
 Digestive System • One way passage of food throughout the body that includes the mouth, stomach, and intestines. • Food is broken down small enough to enter the body tissues/cells • Peristalsis moves food through the digestive system. Before it can be used by individual cells, food must be broken down and distributed throughout the body. Name two systems that must interact to accomplish this.
Digestive System • One way passage of food throughout the body that includes the mouth, stomach, and intestines. • Food is broken down small enough to enter the body tissues/cells • Peristalsis moves food through the digestive system. Before it can be used by individual cells, food must be broken down and distributed throughout the body. Name two systems that must interact to accomplish this.
 Digestive System • Food is broken down chemically and mechanically. • Undigested food is eliminated as solid waste.
Digestive System • Food is broken down chemically and mechanically. • Undigested food is eliminated as solid waste.
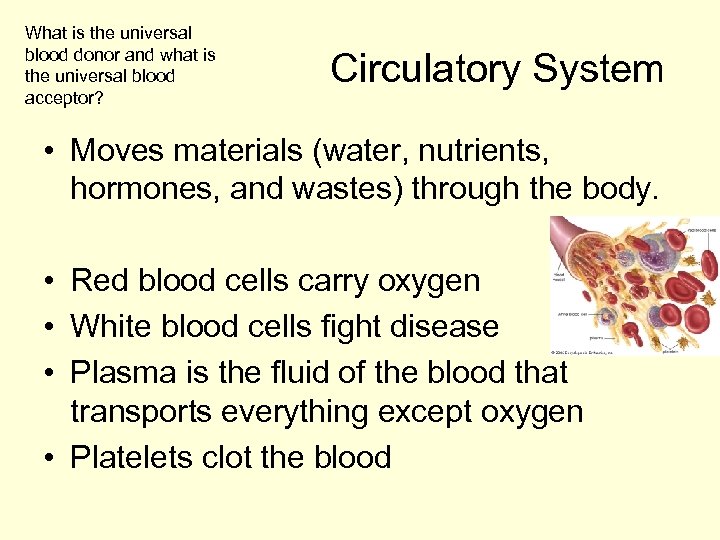 What is the universal blood donor and what is the universal blood acceptor? Circulatory System • Moves materials (water, nutrients, hormones, and wastes) through the body. • Red blood cells carry oxygen • White blood cells fight disease • Plasma is the fluid of the blood that transports everything except oxygen • Platelets clot the blood
What is the universal blood donor and what is the universal blood acceptor? Circulatory System • Moves materials (water, nutrients, hormones, and wastes) through the body. • Red blood cells carry oxygen • White blood cells fight disease • Plasma is the fluid of the blood that transports everything except oxygen • Platelets clot the blood
 Immune System How do the white blood cells prevent you from getting the same cold twice? • Protects the body against pathogens (viruses, bacteria, and parasites) • Contain white blood cells • The immune system protects the body against invaders. • An organ transplant requires a person to be placed on a immunosuppressant in order to prevent the body from rejecting the organ.
Immune System How do the white blood cells prevent you from getting the same cold twice? • Protects the body against pathogens (viruses, bacteria, and parasites) • Contain white blood cells • The immune system protects the body against invaders. • An organ transplant requires a person to be placed on a immunosuppressant in order to prevent the body from rejecting the organ.
 Immune Response • Antigens – cause an immune response What is the importance behind vaccinating young children? • Antibodies – a protein made by WBC to attack antigens • Vaccine – an injection of dead or weakened pathogen. Causes the body to make antigens against that pathogen • Antibiotics – drugs used to stop infections by bacteria. Does not work against a virus.
Immune Response • Antigens – cause an immune response What is the importance behind vaccinating young children? • Antibodies – a protein made by WBC to attack antigens • Vaccine – an injection of dead or weakened pathogen. Causes the body to make antigens against that pathogen • Antibiotics – drugs used to stop infections by bacteria. Does not work against a virus.
 Explain what occurs in the alveoli Respiratory System • Physical respiration (breathing) provides oxygen needed for chemical respiration (which releases energy from sugar) • Diaphragm – muscle that allows breathing to occur • You breathe faster when CO 2 builds up in the blood • The alveoli are very important. Gas exchange occurs here.
Explain what occurs in the alveoli Respiratory System • Physical respiration (breathing) provides oxygen needed for chemical respiration (which releases energy from sugar) • Diaphragm – muscle that allows breathing to occur • You breathe faster when CO 2 builds up in the blood • The alveoli are very important. Gas exchange occurs here.
 What do I mean by “the lungs excrete water? ” Excretory System • Removes metabolic waste from your body • Lungs excrete CO 2 and water • Skin excretes sweat • Kidneys filter waste from blood and reabsorb nutrients • Liver filters toxins and dead read blood cells
What do I mean by “the lungs excrete water? ” Excretory System • Removes metabolic waste from your body • Lungs excrete CO 2 and water • Skin excretes sweat • Kidneys filter waste from blood and reabsorb nutrients • Liver filters toxins and dead read blood cells
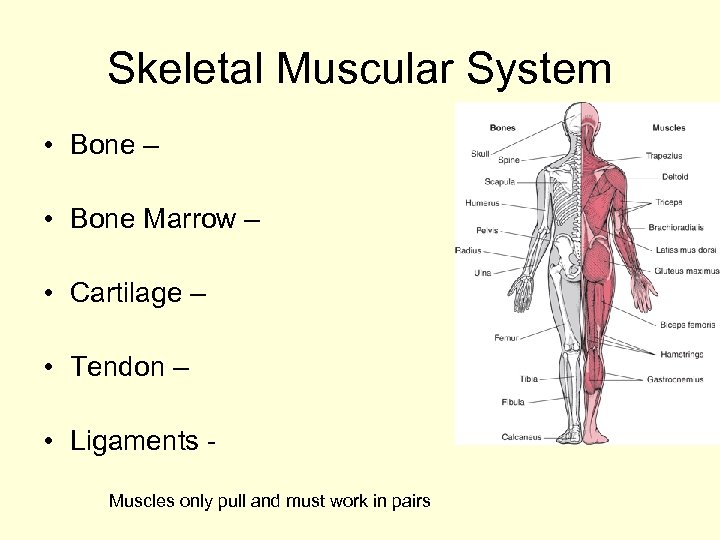 Skeletal Muscular System • Bone – • Bone Marrow – • Cartilage – • Tendon – • Ligaments Muscles only pull and must work in pairs
Skeletal Muscular System • Bone – • Bone Marrow – • Cartilage – • Tendon – • Ligaments Muscles only pull and must work in pairs
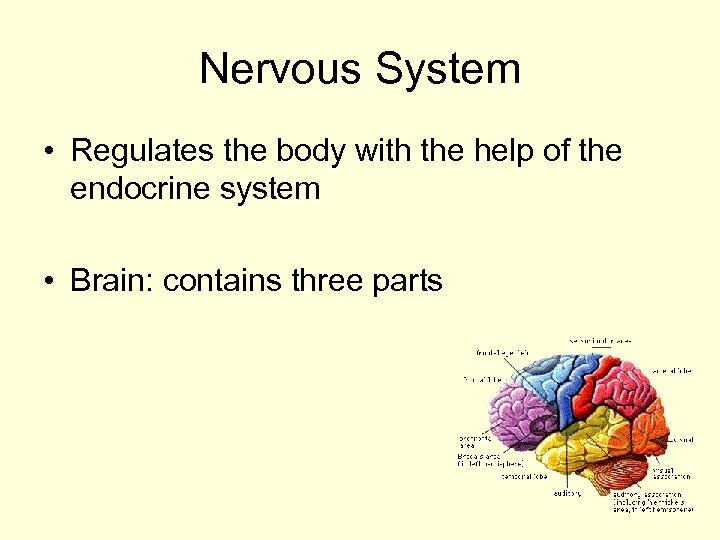 Nervous System • Regulates the body with the help of the endocrine system • Brain: contains three parts
Nervous System • Regulates the body with the help of the endocrine system • Brain: contains three parts
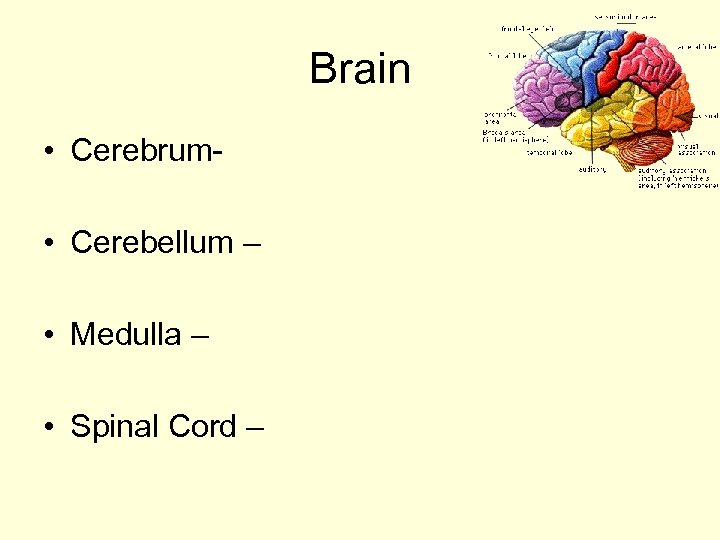 Brain • Cerebrum • Cerebellum – • Medulla – • Spinal Cord –
Brain • Cerebrum • Cerebellum – • Medulla – • Spinal Cord –
 Endocrine System • Regulates the body along with the nervous system • Pancreas makes insulin and glucagon to regulate blood sugar • Adrenal glands make adrenaline when the body is under stress • Testosterone, estrogen, and progesterone are made by sex organs • Hormone levels are controlled by negative feedback
Endocrine System • Regulates the body along with the nervous system • Pancreas makes insulin and glucagon to regulate blood sugar • Adrenal glands make adrenaline when the body is under stress • Testosterone, estrogen, and progesterone are made by sex organs • Hormone levels are controlled by negative feedback
 Interactions between systems • Explain how different systems of the body work together to maintain homeostasis
Interactions between systems • Explain how different systems of the body work together to maintain homeostasis
 Diseases • Name a disease and how it disrupts homeostasis • • • Caused by: 1. virus (AIDS, cold, flu) 2. bacteria (strep throat, syphilis) 3. fungus (athletes foot, ringworm) 4. parasites (tapeworm, leeches) 5. genetic disorders (Down’s Syndrome, sickle cell) 6. Environmental toxins (lead poisoning, radiation) 7. Poor Nutrition (scurvy, goiter) 8. Organ Malfunction (heart attack, diabetes) 9. High Risk Behavior (smoking, drug use)
Diseases • Name a disease and how it disrupts homeostasis • • • Caused by: 1. virus (AIDS, cold, flu) 2. bacteria (strep throat, syphilis) 3. fungus (athletes foot, ringworm) 4. parasites (tapeworm, leeches) 5. genetic disorders (Down’s Syndrome, sickle cell) 6. Environmental toxins (lead poisoning, radiation) 7. Poor Nutrition (scurvy, goiter) 8. Organ Malfunction (heart attack, diabetes) 9. High Risk Behavior (smoking, drug use)


