a1b58ac17810309c482f411cc59c61d2.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26

Refinement parameters What are the parameters to be determined? atom positional parameters atom thermal motion parameters atom site occupancy parameters background function parameters sample displacement, sample transparency, zero-shift errors peak shape parameters unit cell dimensions preferred orientation, absorption, porosity, extinction parameters scale factor(s) 1

Refinement parameters What are the parameters to be determined? atom positional parameters atom thermal motion parameters atom site occupancy parameters background function parameters sample displacement, sample transparency, zero-shift errors peak shape parameters unit cell dimensions preferred orientation, absorption, porosity, extinction parameters scale factor(s) 2

Atom positional parameters Ihkl ~ |Fhkl|2 Fhkl = S ƒj e 2πi (hxj + kyj + lzj) need xj, yj, zj for all atoms in unit cell – except for symmetry-related atom positions certain "special position" coordinates 3
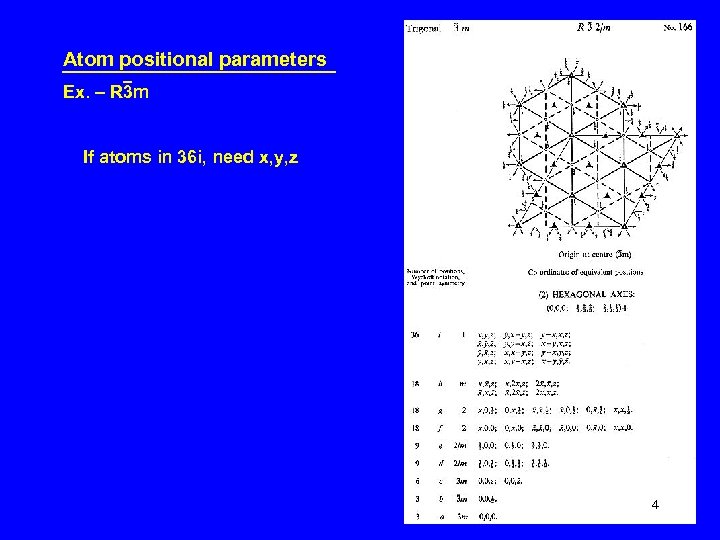
Atom positional parameters Ex. – R 3 m If atoms in 36 i, need x, y, z 4
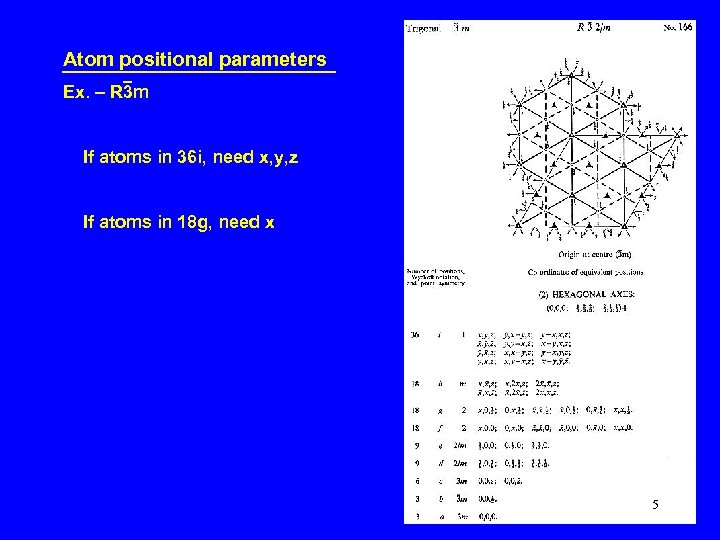
Atom positional parameters Ex. – R 3 m If atoms in 36 i, need x, y, z If atoms in 18 g, need x 5
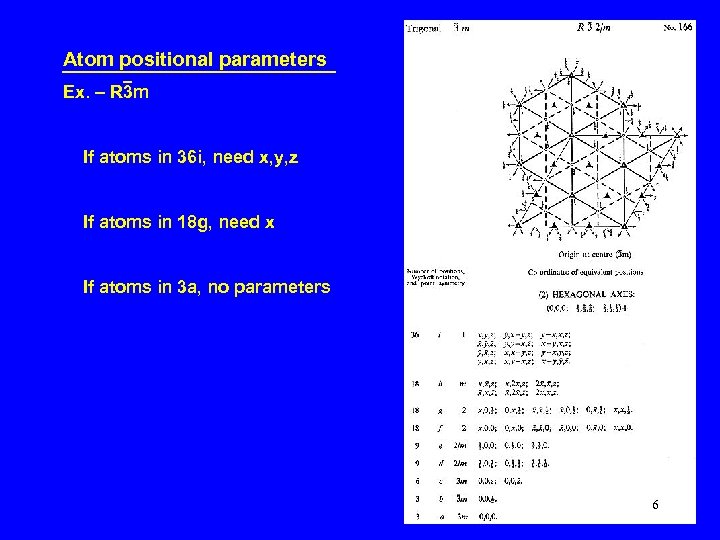
Atom positional parameters Ex. – R 3 m If atoms in 36 i, need x, y, z If atoms in 18 g, need x If atoms in 3 a, no parameters 6

Atomic displacement parameters Debye-Waller factor (see R. W. James, Optical Principles of the Diffraction of X-rays) I(T)/Io(T) = exp(– 16π2 m 2 (sin 2 q)/l 2) 7

Atomic displacement parameters Debye-Waller factor (see R. W. James, Optical Principles of the Diffraction of X-rays) I(T)/Io(T) = exp(– 16π2 m 2 (sin 2 q)/l 2) mean square amplitude of atomic vibration for isotropic motion 8

Atomic displacement parameters Debye-Waller factor (see R. W. James, Optical Principles of the Diffraction of X-rays) I(T)/Io(T) = exp(– 16π2 m 2 (sin 2 q)/l 2) Usually considered part of atomic scattering factor ƒj = ƒoj exp(-8π2 mj 2 (sin 2 q)/l 2) = ƒoj exp(-Bj (sin 2 q)/l 2) B is "temperature factor" 9

Atomic displacement parameters Debye-Waller factor (see R. W. James, Optical Principles of the Diffraction of X-rays) I(T)/Io(T) = exp(– 16π2 m 2 (sin 2 q)/l 2) Usually considered part of atomic scattering factor ƒj = ƒoj exp(-8π2 mj 2 (sin 2 q)/l 2) = ƒoj exp(-Bj (sin 2 q)/l 2) B is "temperature factor" Generally, B approx. 0. 5 - 1. 0 Å2, larger for many organic materials, & never negative 10

Atomic displacement parameters When motion is anisotropic: 11

Atomic displacement parameters When motion is anisotropic: (sin 2 q)/l 2 = 1/4 d*2 d* = ha* + kb* + lc* 12

Atomic displacement parameters When motion is anisotropic: Bij = 8π2 Uij 13
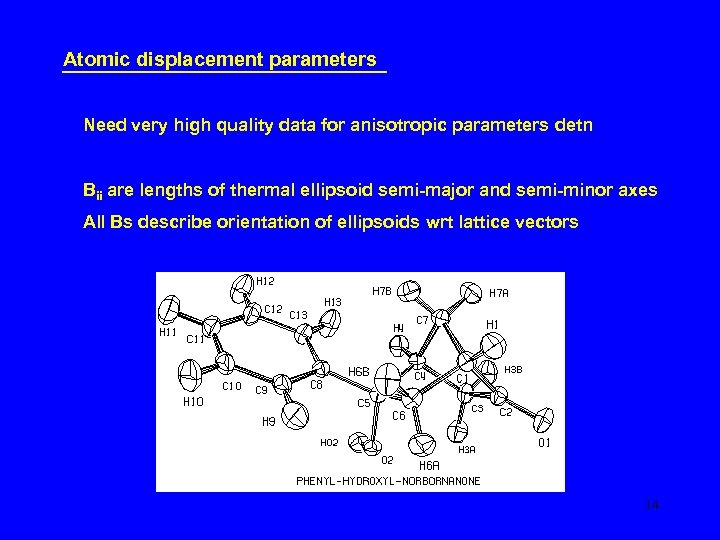
Atomic displacement parameters Need very high quality data for anisotropic parameters detn Bii are lengths of thermal ellipsoid semi-major and semi-minor axes All Bs describe orientation of ellipsoids wrt lattice vectors 14

Atomic displacement parameters Depending on site symmetry, some bs may be equivalent & some = 0 Ex. - Na. NO 3 R 3 c but can use hexagonal cell (2 nd setting) 15

Atomic displacement parameters for b relationships use tables in Pryor and Willis - Thermal Vibrations in Crystallography, pp 104 -110 Na, N O 16
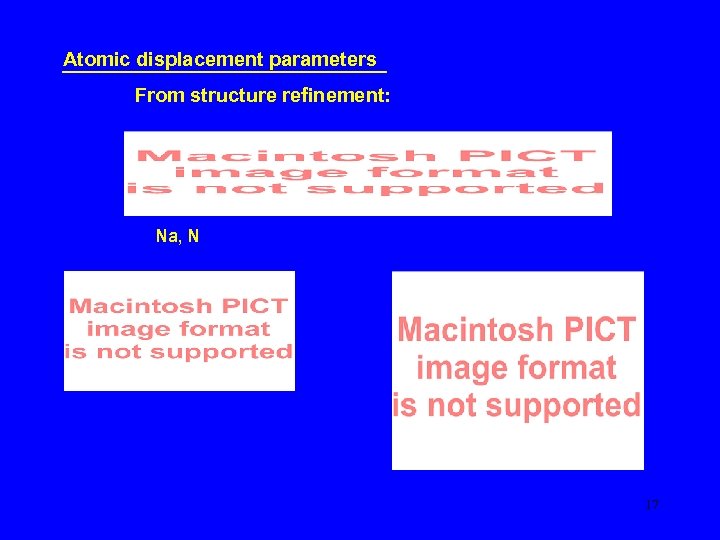
Atomic displacement parameters From structure refinement: Na, N 17
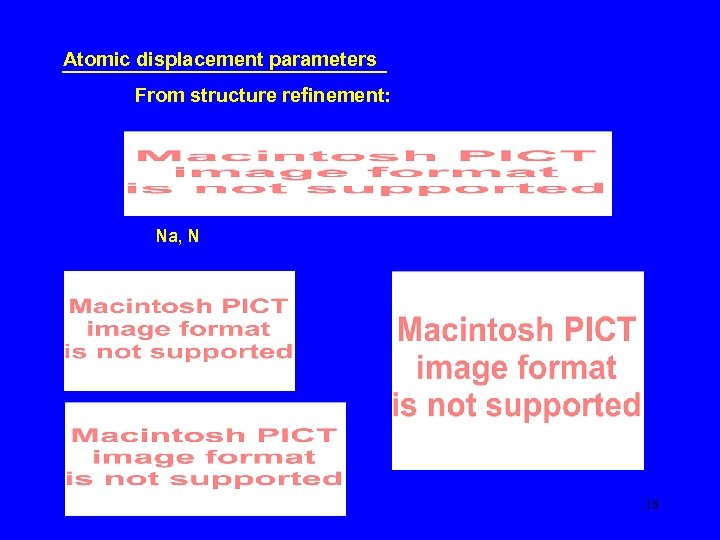
Atomic displacement parameters From structure refinement: Na, N 18

Atomic displacement parameters From structure refinement: O (tilted 49° wrt c axis) 19

Atomic displacement parameters Need very high quality data for anisotropic parameters detn Bii are lengths of thermal ellipsoid semi-major and semi-minor axes All Bs describe orientation of ellipsoids wrt lattice vectors Need: Bii > 0 Bii Bjj > Bij 2 B 11 B 22 B 33 + B 122 B 132 B 232 > B 11 B 232 + B 22 B 132 + B 33 B 122 20

Site occupancy ƒj = gj ƒoj g = 1 - fully occupied g = 0 - unoccupied 21
Site occupancy ƒj = gj ƒoj g = 1 - fully occupied g = 0 - unoccupied Two cases: vacancies – must correspond to stoichiometry substitutions – S gi = 1 (including vacancies) & must correspond to stoichiometry 22

Refinement parameters What are the parameters to be determined? atom positional parameters atom thermal motion parameters atom site occupancy parameters background function parameters sample displacement, sample transparency, zero-shift errors peak shape parameters unit cell dimensions preferred orientation, absorption, porosity, extinction parameters scale factor(s) 23

Refinement parameters What contributes to background? general instrumental scattering air scattering fluorescence incoherent scattering TDS – thermal diffuse scattering amorphous material – internal or external 24

Refinement parameters Common background function - polynomial N bi = S Bm (2 qi)m m=0 determine Bs to get backgrd intensity bi at ith point 25
Refinement parameters Common background function - polynomial N bi = S Bm (2 qi)m m=0 determine Bs to get backgrd intensity bi at ith point Many other functions N bi = B 1 + S Bm cos(2 qm-1) m=2 Amorphous contribution N-2 bi = B 1 + B 2 Qi + S (B 2 m+1 sin(Qi. B 2 m+2))/ Qi. B 2 m+2 m=1 Qi = 2π/di 26
a1b58ac17810309c482f411cc59c61d2.ppt