afb5c564baa01de7d80c27fa335960f0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Reference model for Networks An e. Learning network in New Zealand
Reference model for Networks An e. Learning network in New Zealand
 New Zealand Context • Small economy – 4 million people • Remote from world markets • Geographical remoteness within NZ – Small population size spread across same geographical size (approx. ) as Italy
New Zealand Context • Small economy – 4 million people • Remote from world markets • Geographical remoteness within NZ – Small population size spread across same geographical size (approx. ) as Italy
 Objectives of Moodle Networks • Design and implement a technical solution -MNet • Design and pilot network model(s) – Identify issues and design solutions – NZ Diploma of Business • Run pilot focused on shared delivery – Reduce duplication in investment – Build capacity across the system – Share good practice to develop excellence in eteaching
Objectives of Moodle Networks • Design and implement a technical solution -MNet • Design and pilot network model(s) – Identify issues and design solutions – NZ Diploma of Business • Run pilot focused on shared delivery – Reduce duplication in investment – Build capacity across the system – Share good practice to develop excellence in eteaching
 Acknowledgements • Tertiary Education Commission of New Zealand – – Strategic contestable funding Reduce duplication in investment Build capacity across the system Share good practice to develop excellence in eteaching – Has supported Moodle focused projects since 2004 • Open Polytechnic of New Zealand • Tertiary Accord of New Zealand (six institutions)
Acknowledgements • Tertiary Education Commission of New Zealand – – Strategic contestable funding Reduce duplication in investment Build capacity across the system Share good practice to develop excellence in eteaching – Has supported Moodle focused projects since 2004 • Open Polytechnic of New Zealand • Tertiary Accord of New Zealand (six institutions)
 Potential Key Benefits • Complement each institution’s offerings • Strengthens sustainability for regional provision • Broadens access (scope) for learners through networking lower demand but valuable courses • Economies of scale for course providers • Sharing of expertise and leveraging expert knowledge across network • Collaboration in development and delivery • Centralised support and administration
Potential Key Benefits • Complement each institution’s offerings • Strengthens sustainability for regional provision • Broadens access (scope) for learners through networking lower demand but valuable courses • Economies of scale for course providers • Sharing of expertise and leveraging expert knowledge across network • Collaboration in development and delivery • Centralised support and administration
 e. Learning Network configuration possibilities • Network hub (and spoke) for centrally hosted & administered courses • Institution-to-Institution pairing • Fully distributed (i. e. multi-hubs)
e. Learning Network configuration possibilities • Network hub (and spoke) for centrally hosted & administered courses • Institution-to-Institution pairing • Fully distributed (i. e. multi-hubs)
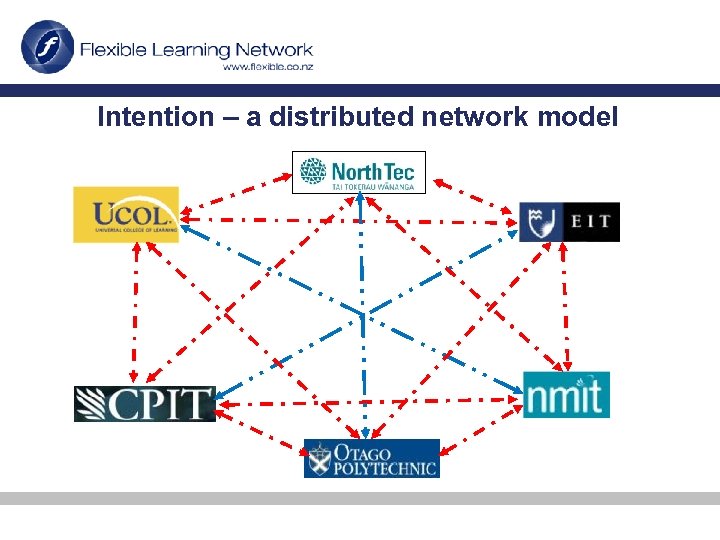 Intention – a distributed network model
Intention – a distributed network model
 Distributed Network - advantages • Pluralistic framework with each organisation focusing on distinct competencies • Autonomous e. Learning capability • Allows for additional bilateral or ancillary arrangements • Optimises provision at a systemic level
Distributed Network - advantages • Pluralistic framework with each organisation focusing on distinct competencies • Autonomous e. Learning capability • Allows for additional bilateral or ancillary arrangements • Optimises provision at a systemic level
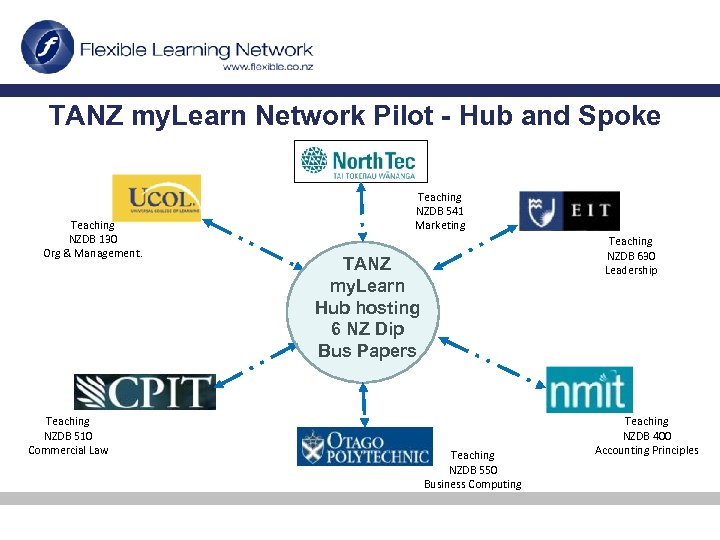 TANZ my. Learn Network Pilot - Hub and Spoke Teaching NZDB 130 Org & Management. Teaching NZDB 510 Commercial Law Teaching NZDB 541 Marketing Teaching NZDB 630 Leadership TANZ my. Learn Hub hosting 6 NZ Dip Bus Papers Teaching NZDB 550 Business Computing Teaching NZDB 400 Accounting Principles
TANZ my. Learn Network Pilot - Hub and Spoke Teaching NZDB 130 Org & Management. Teaching NZDB 510 Commercial Law Teaching NZDB 541 Marketing Teaching NZDB 630 Leadership TANZ my. Learn Hub hosting 6 NZ Dip Bus Papers Teaching NZDB 550 Business Computing Teaching NZDB 400 Accounting Principles
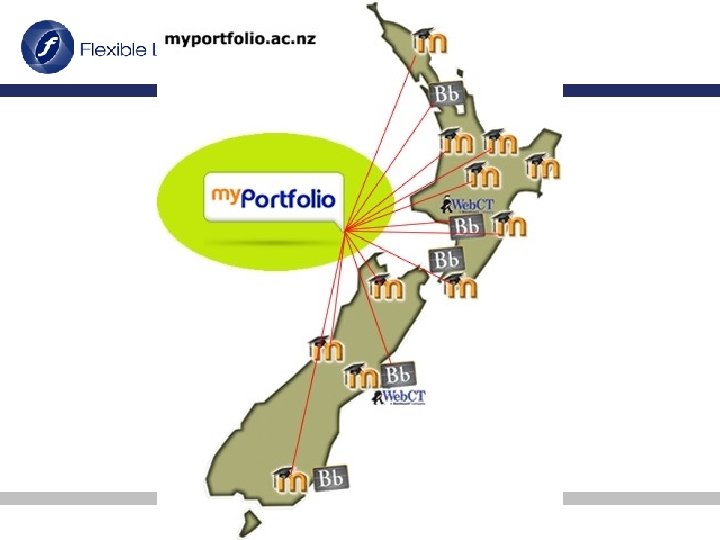
 My Learn Network Characteristics • Learner’s home institution brand follows learner regardless of who delivers what, to which learner (i. e. Theme defined by User profile) • Authentication is with enrolling institution • Logs on at home Moodle, SSO seamless access to networked courses • Learner centred • One size does not fit all, multiple configurations accommodated.
My Learn Network Characteristics • Learner’s home institution brand follows learner regardless of who delivers what, to which learner (i. e. Theme defined by User profile) • Authentication is with enrolling institution • Logs on at home Moodle, SSO seamless access to networked courses • Learner centred • One size does not fit all, multiple configurations accommodated.
 Challenges / Issues • • Lots of bug testing Knowledge transfer for creating multiple MNet links Insufficient documentation – are they bugs, undeveloped features or false expectations for the way we want MNET to work? Enrolling students uses Moodle’s manual enrolment process - need further development to scale up Managing the patches – versions across multiple Moodles New processes needed Quality control / consistent design on courses Highlighted professional development requirements
Challenges / Issues • • Lots of bug testing Knowledge transfer for creating multiple MNet links Insufficient documentation – are they bugs, undeveloped features or false expectations for the way we want MNET to work? Enrolling students uses Moodle’s manual enrolment process - need further development to scale up Managing the patches – versions across multiple Moodles New processes needed Quality control / consistent design on courses Highlighted professional development requirements
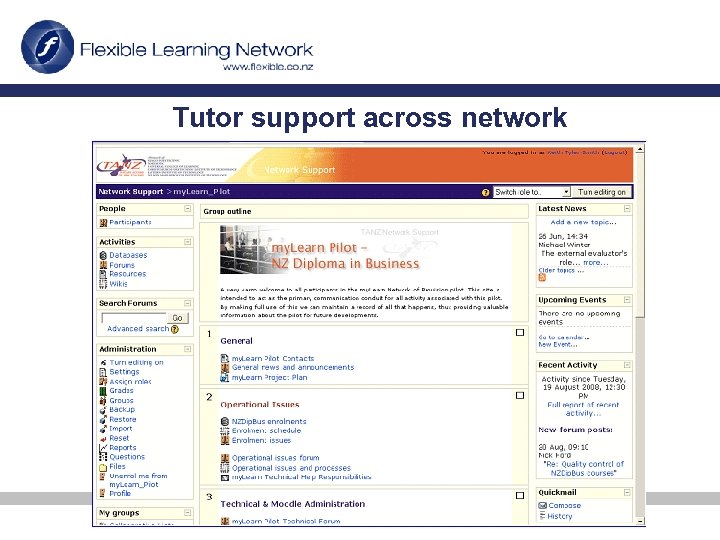 Tutor support across network
Tutor support across network
 Future direction 1. Academic harmonisation 2. Network management – develop more process 3. Automated/bulk enrolments 4. Administration systems adapted 5. Quality control processes – common standards 6. Building support communities by subject area 7. Shared professional development 8. Shared support 9. Shared ancillary services – e. g. library databases 10. Move from hub & spoke to explore potential of distributed network model
Future direction 1. Academic harmonisation 2. Network management – develop more process 3. Automated/bulk enrolments 4. Administration systems adapted 5. Quality control processes – common standards 6. Building support communities by subject area 7. Shared professional development 8. Shared support 9. Shared ancillary services – e. g. library databases 10. Move from hub & spoke to explore potential of distributed network model

 Thank-you Questions?
Thank-you Questions?


