ad6ccfb5fd78a50592e989167b0abfee.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 33
 Reference: AM and T. Hirano, ar. Xiv: 1003: 3087 Causal Viscous Hydrodynamics for Relativistic Systems with Multi-Components and Multi-Conserved Currents Akihiko Monnai Department of Physics, The University of Tokyo Collaborator: Tetsufumi Hirano Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010 June 29 th 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada
Reference: AM and T. Hirano, ar. Xiv: 1003: 3087 Causal Viscous Hydrodynamics for Relativistic Systems with Multi-Components and Multi-Conserved Currents Akihiko Monnai Department of Physics, The University of Tokyo Collaborator: Tetsufumi Hirano Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010 June 29 th 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada
 Outline 1. Introduction Relativistic hydrodynamics and Heavy ion collisions 2. Formulation of Viscous Hydro Israel-Stewart theory for multi-component/conserved current systems 3. Results and Discussion Constitutive equations and their implications 4. Summary and Outlook A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
Outline 1. Introduction Relativistic hydrodynamics and Heavy ion collisions 2. Formulation of Viscous Hydro Israel-Stewart theory for multi-component/conserved current systems 3. Results and Discussion Constitutive equations and their implications 4. Summary and Outlook A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
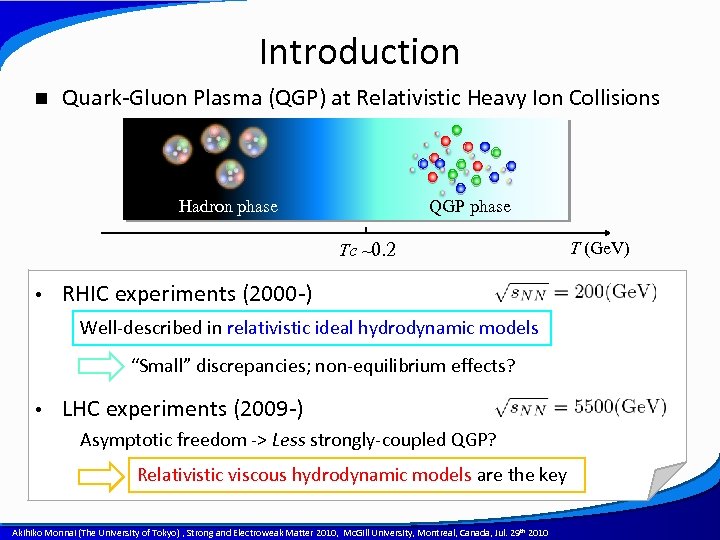 Introduction n Quark-Gluon Plasma (QGP) at Relativistic Heavy Ion Collisions Hadron phase QGP phase Tc ~0. 2 • T (Ge. V) RHIC experiments (2000 -) Well-described in relativistic ideal hydrodynamic models “Small” discrepancies; non-equilibrium effects? • LHC experiments (2009 -) Asymptotic freedom -> Less strongly-coupled QGP? Relativistic viscous hydrodynamic models are the key A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
Introduction n Quark-Gluon Plasma (QGP) at Relativistic Heavy Ion Collisions Hadron phase QGP phase Tc ~0. 2 • T (Ge. V) RHIC experiments (2000 -) Well-described in relativistic ideal hydrodynamic models “Small” discrepancies; non-equilibrium effects? • LHC experiments (2009 -) Asymptotic freedom -> Less strongly-coupled QGP? Relativistic viscous hydrodynamic models are the key A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
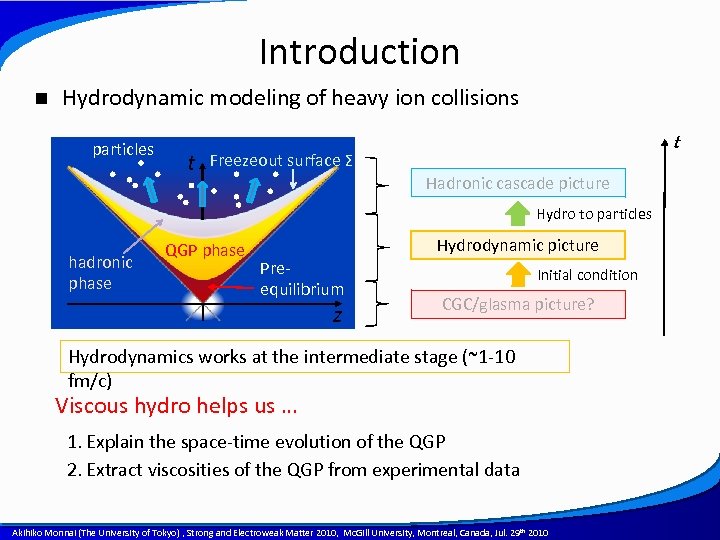 Introduction n Hydrodynamic modeling of heavy ion collisions particles t t Freezeout surface Σ Hadronic cascade picture Hydro to particles hadronic phase QGP phase Hydrodynamic picture Preequilibrium z Initial condition CGC/glasma picture? Hydrodynamics works at the intermediate stage (~1 -10 fm/c) Viscous hydro helps us … 1. Explain the space-time evolution of the QGP 2. Extract viscosities of the QGP from experimental data A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
Introduction n Hydrodynamic modeling of heavy ion collisions particles t t Freezeout surface Σ Hadronic cascade picture Hydro to particles hadronic phase QGP phase Hydrodynamic picture Preequilibrium z Initial condition CGC/glasma picture? Hydrodynamics works at the intermediate stage (~1 -10 fm/c) Viscous hydro helps us … 1. Explain the space-time evolution of the QGP 2. Extract viscosities of the QGP from experimental data A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
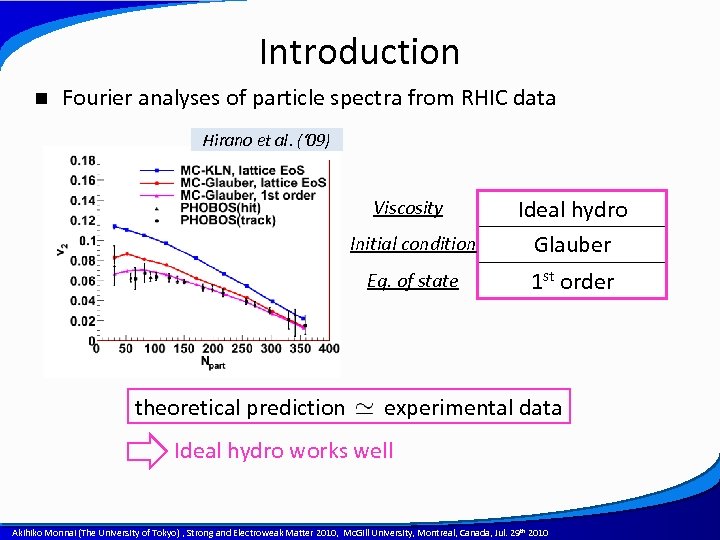 Introduction n Fourier analyses of particle spectra from RHIC data Hirano et al. (‘ 09) Initial condition Ideal hydro Glauber Eq. of state 1 st order Viscosity theoretical prediction experimental data Ideal hydro works well A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
Introduction n Fourier analyses of particle spectra from RHIC data Hirano et al. (‘ 09) Initial condition Ideal hydro Glauber Eq. of state 1 st order Viscosity theoretical prediction experimental data Ideal hydro works well A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
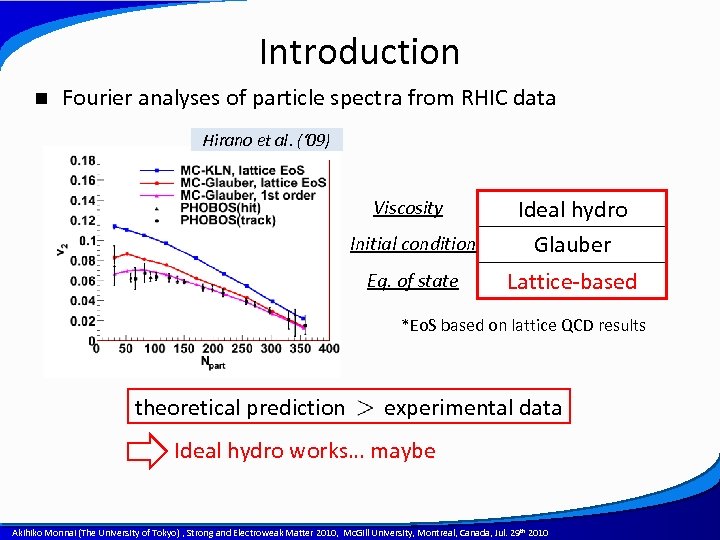 Introduction n Fourier analyses of particle spectra from RHIC data Hirano et al. (‘ 09) Initial condition Ideal hydro Glauber Eq. of state Lattice-based 1 st order Viscosity *Eo. S based on lattice QCD results theoretical prediction experimental data Ideal hydro works… maybe A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
Introduction n Fourier analyses of particle spectra from RHIC data Hirano et al. (‘ 09) Initial condition Ideal hydro Glauber Eq. of state Lattice-based 1 st order Viscosity *Eo. S based on lattice QCD results theoretical prediction experimental data Ideal hydro works… maybe A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
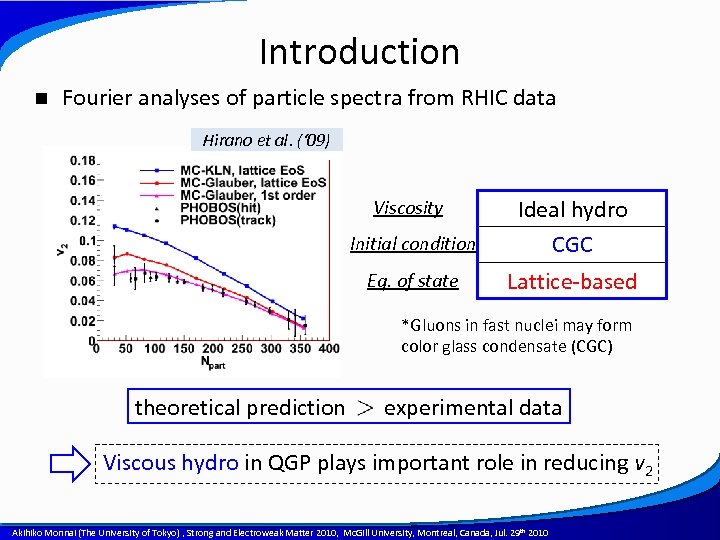 Introduction n Fourier analyses of particle spectra from RHIC data Hirano et al. (‘ 09) Initial condition Ideal hydro CGC Glauber Eq. of state Lattice-based Viscosity *Gluons in fast nuclei may form color glass condensate (CGC) theoretical prediction experimental data Viscous hydro in QGP plays important role in reducing v 2 A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
Introduction n Fourier analyses of particle spectra from RHIC data Hirano et al. (‘ 09) Initial condition Ideal hydro CGC Glauber Eq. of state Lattice-based Viscosity *Gluons in fast nuclei may form color glass condensate (CGC) theoretical prediction experimental data Viscous hydro in QGP plays important role in reducing v 2 A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
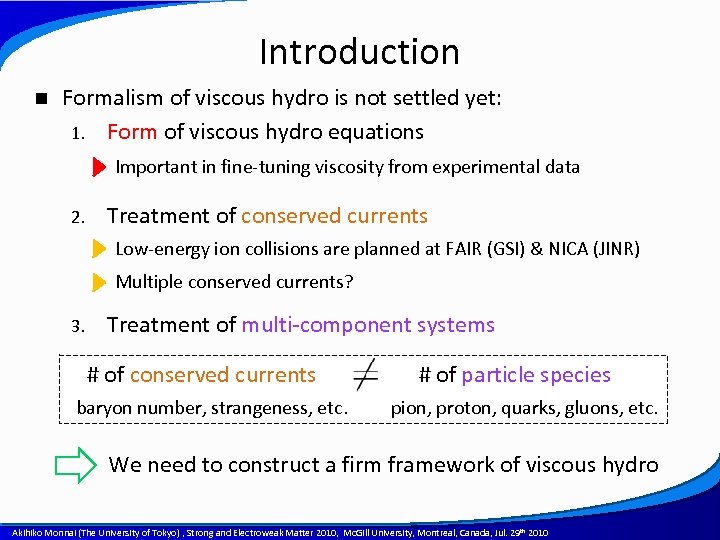 Introduction n Formalism of viscous hydro is not settled yet: 1. Form of viscous hydro equations Important in fine-tuning viscosity from experimental data 2. Treatment of conserved currents Low-energy ion collisions are planned at FAIR (GSI) & NICA (JINR) Multiple conserved currents? 3. Treatment of multi-component systems # of conserved currents baryon number, strangeness, etc. # of particle species pion, proton, quarks, gluons, etc. We need to construct a firm framework of viscous hydro A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
Introduction n Formalism of viscous hydro is not settled yet: 1. Form of viscous hydro equations Important in fine-tuning viscosity from experimental data 2. Treatment of conserved currents Low-energy ion collisions are planned at FAIR (GSI) & NICA (JINR) Multiple conserved currents? 3. Treatment of multi-component systems # of conserved currents baryon number, strangeness, etc. # of particle species pion, proton, quarks, gluons, etc. We need to construct a firm framework of viscous hydro A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
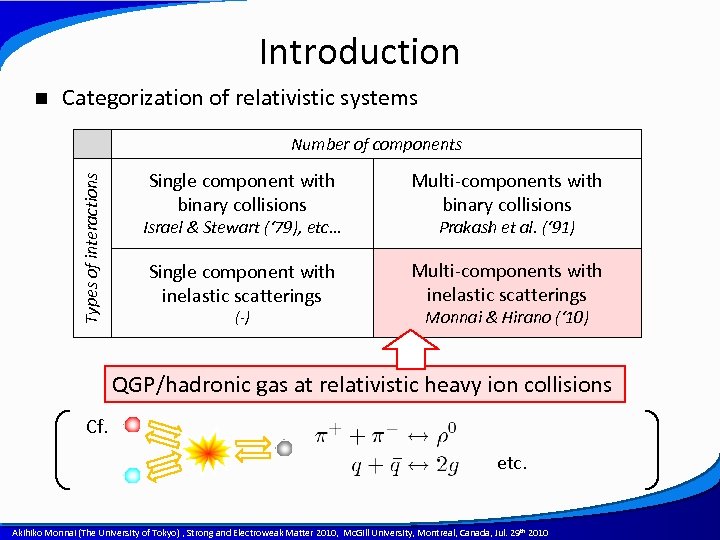 Introduction n Categorization of relativistic systems Types of interactions Number of components Single component with binary collisions Multi-components with binary collisions Single component with inelastic scatterings Multi-components with inelastic scatterings Israel & Stewart (‘ 79), etc… (-) Prakash et al. (‘ 91) Monnai & Hirano (‘ 10) QGP/hadronic gas at relativistic heavy ion collisions Cf. etc. A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
Introduction n Categorization of relativistic systems Types of interactions Number of components Single component with binary collisions Multi-components with binary collisions Single component with inelastic scatterings Multi-components with inelastic scatterings Israel & Stewart (‘ 79), etc… (-) Prakash et al. (‘ 91) Monnai & Hirano (‘ 10) QGP/hadronic gas at relativistic heavy ion collisions Cf. etc. A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
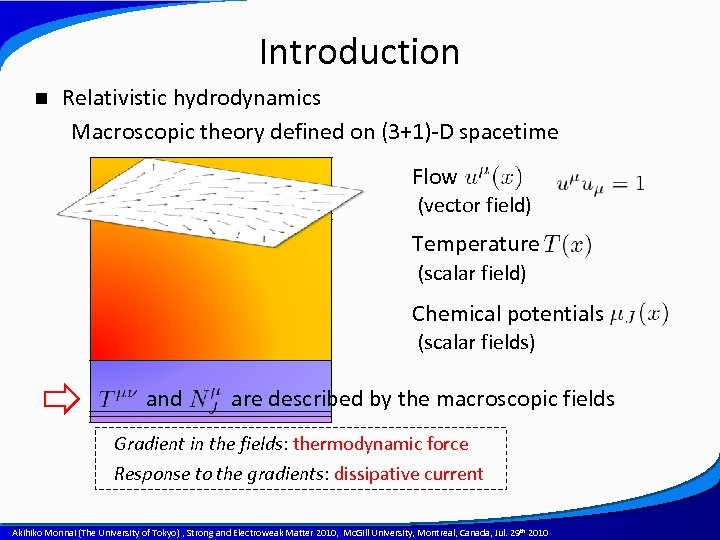 Introduction n Relativistic hydrodynamics Macroscopic theory defined on (3+1)-D spacetime Flow (vector field) Temperature (scalar field) Chemical potentials (scalar fields) and are described by the macroscopic fields Gradient in the fields: thermodynamic force Response to the gradients: dissipative current A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
Introduction n Relativistic hydrodynamics Macroscopic theory defined on (3+1)-D spacetime Flow (vector field) Temperature (scalar field) Chemical potentials (scalar fields) and are described by the macroscopic fields Gradient in the fields: thermodynamic force Response to the gradients: dissipative current A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
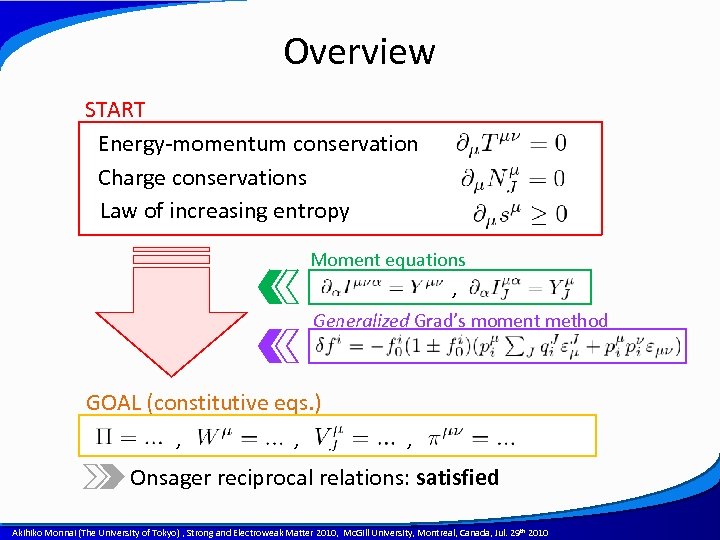 Overview START Energy-momentum conservation Charge conservations Law of increasing entropy Moment equations , Generalized Grad’s moment method GOAL (constitutive eqs. ) , , , Onsager reciprocal relations: satisfied A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
Overview START Energy-momentum conservation Charge conservations Law of increasing entropy Moment equations , Generalized Grad’s moment method GOAL (constitutive eqs. ) , , , Onsager reciprocal relations: satisfied A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
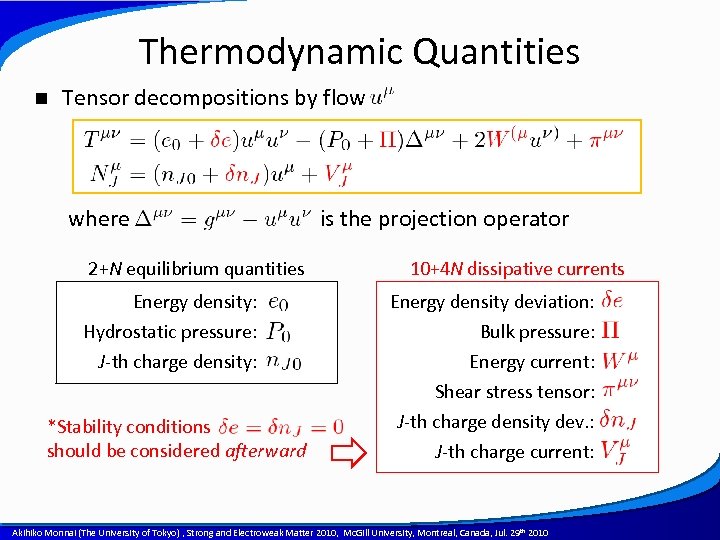 Thermodynamic Quantities n Tensor decompositions by flow where is the projection operator 2+N equilibrium quantities 10+4 N dissipative currents Energy density: Energy density deviation: Hydrostatic pressure: J-th charge density: Bulk pressure: Energy current: Shear stress tensor: J-th charge density dev. : J-th charge current: *Stability conditions should be considered afterward A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
Thermodynamic Quantities n Tensor decompositions by flow where is the projection operator 2+N equilibrium quantities 10+4 N dissipative currents Energy density: Energy density deviation: Hydrostatic pressure: J-th charge density: Bulk pressure: Energy current: Shear stress tensor: J-th charge density dev. : J-th charge current: *Stability conditions should be considered afterward A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
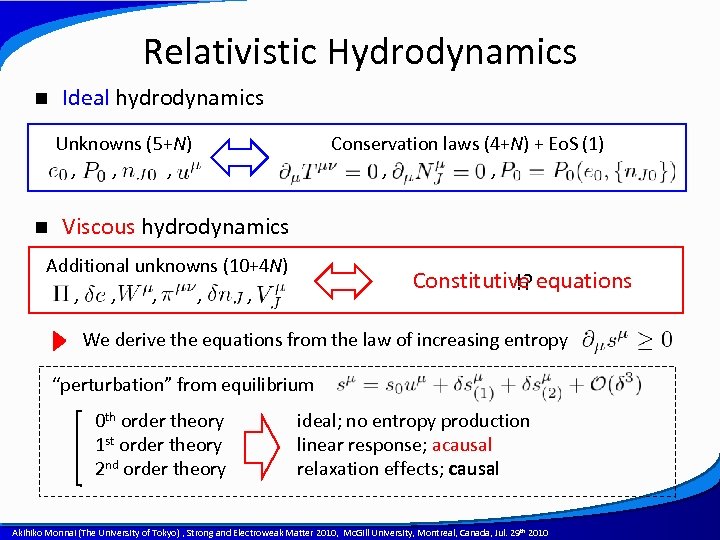 Relativistic Hydrodynamics n Ideal hydrodynamics Unknowns (5+N) , , , n Conservation laws (4+N) + Eo. S (1) , , Viscous hydrodynamics Additional unknowns (10+4 N) , , , Constitutive equations !? We derive the equations from the law of increasing entropy “perturbation” from equilibrium 0 th order theory 1 st order theory 2 nd order theory ideal; no entropy production linear response; acausal relaxation effects; causal A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
Relativistic Hydrodynamics n Ideal hydrodynamics Unknowns (5+N) , , , n Conservation laws (4+N) + Eo. S (1) , , Viscous hydrodynamics Additional unknowns (10+4 N) , , , Constitutive equations !? We derive the equations from the law of increasing entropy “perturbation” from equilibrium 0 th order theory 1 st order theory 2 nd order theory ideal; no entropy production linear response; acausal relaxation effects; causal A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
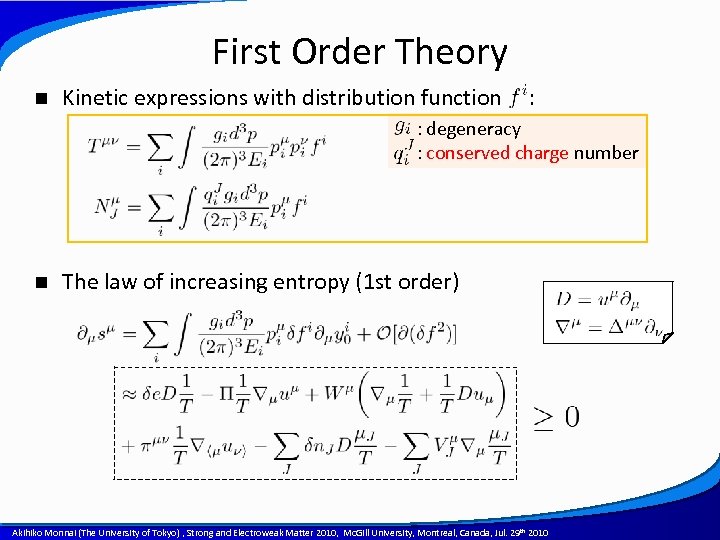 First Order Theory n Kinetic expressions with distribution function : : degeneracy : conserved charge number n The law of increasing entropy (1 st order) A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
First Order Theory n Kinetic expressions with distribution function : : degeneracy : conserved charge number n The law of increasing entropy (1 st order) A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
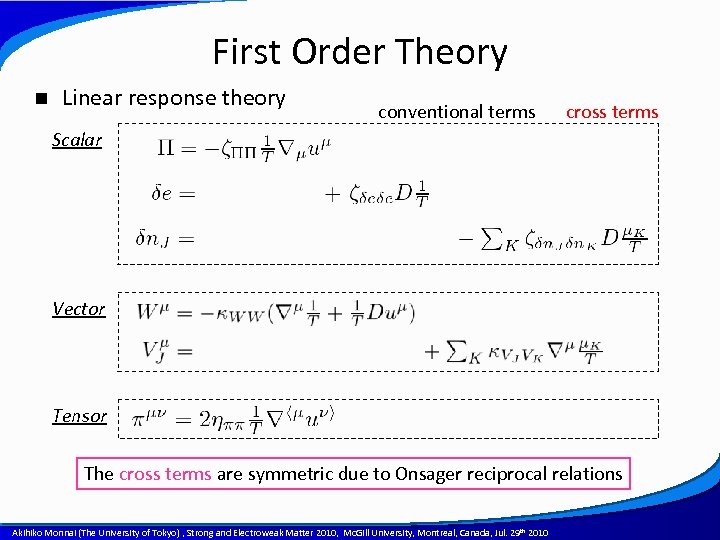 First Order Theory n Linear response theory conventional terms cross terms Scalar Vector Tensor The cross terms are symmetric due to Onsager reciprocal relations A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
First Order Theory n Linear response theory conventional terms cross terms Scalar Vector Tensor The cross terms are symmetric due to Onsager reciprocal relations A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
 First Order Theory n Linear response theory Dufour effect Soret effect n Cool down once – for cooking tasty oden (Japanese pot-au-feu) Vector Permeation of ingredients potato soup Thermal gradient Chemical diffusion caused by thermal gradient (Soret effect) A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
First Order Theory n Linear response theory Dufour effect Soret effect n Cool down once – for cooking tasty oden (Japanese pot-au-feu) Vector Permeation of ingredients potato soup Thermal gradient Chemical diffusion caused by thermal gradient (Soret effect) A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
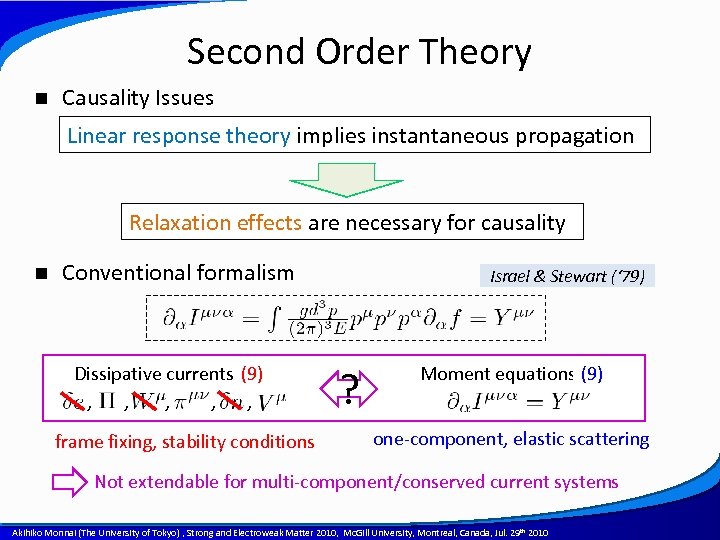 Second Order Theory n Causality Issues Linear response theory implies instantaneous propagation Relaxation effects are necessary for causality n Conventional formalism Dissipative currents (14) (9) , , , frame fixing, stability conditions Israel & Stewart (‘ 79) ? Moment equations (10) (9) one-component, elastic scattering Not extendable for multi-component/conserved current systems A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
Second Order Theory n Causality Issues Linear response theory implies instantaneous propagation Relaxation effects are necessary for causality n Conventional formalism Dissipative currents (14) (9) , , , frame fixing, stability conditions Israel & Stewart (‘ 79) ? Moment equations (10) (9) one-component, elastic scattering Not extendable for multi-component/conserved current systems A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
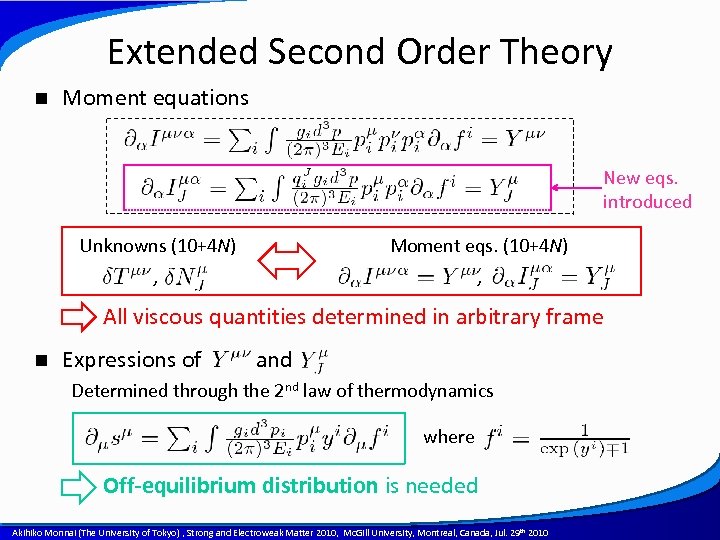 Extended Second Order Theory n Moment equations New eqs. introduced Unknowns (10+4 N) Moment eqs. (10+4 N) , , All viscous quantities determined in arbitrary frame n Expressions of and Determined through the 2 nd law of thermodynamics where Off-equilibrium distribution is needed A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
Extended Second Order Theory n Moment equations New eqs. introduced Unknowns (10+4 N) Moment eqs. (10+4 N) , , All viscous quantities determined in arbitrary frame n Expressions of and Determined through the 2 nd law of thermodynamics where Off-equilibrium distribution is needed A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
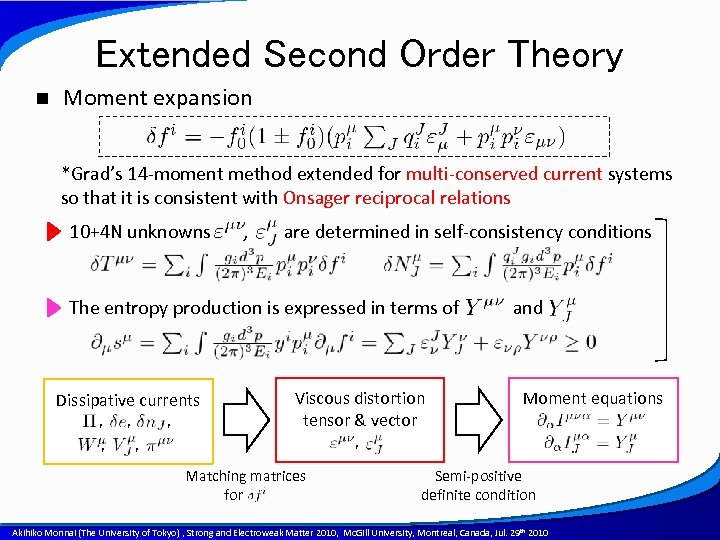 Extended Second Order Theory n Moment expansion *Grad’s 14 -moment method extended for multi-conserved current systems so that it is consistent with Onsager reciprocal relations 10+4 N unknowns , are determined in self-consistency conditions The entropy production is expressed in terms of Dissipative currents , , , , Viscous distortion tensor & vector and Moment equations , , Matching matrices for dfi Semi-positive definite condition A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
Extended Second Order Theory n Moment expansion *Grad’s 14 -moment method extended for multi-conserved current systems so that it is consistent with Onsager reciprocal relations 10+4 N unknowns , are determined in self-consistency conditions The entropy production is expressed in terms of Dissipative currents , , , , Viscous distortion tensor & vector and Moment equations , , Matching matrices for dfi Semi-positive definite condition A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
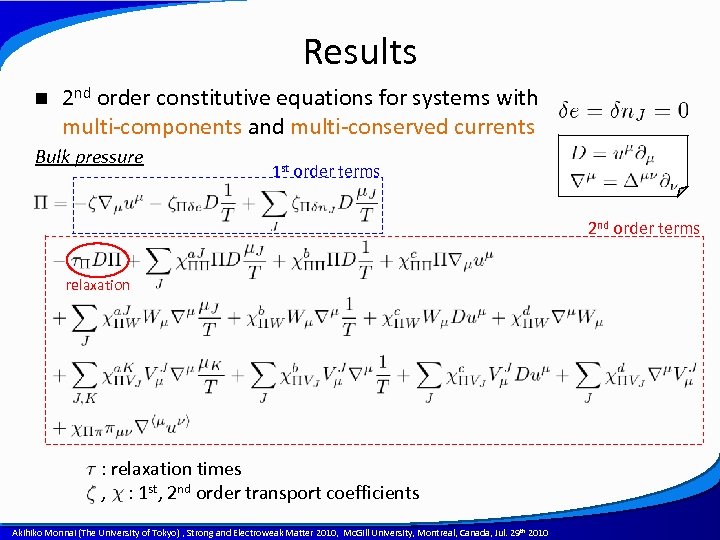 Results n 2 nd order constitutive equations for systems with multi-components and multi-conserved currents Bulk pressure 1 st order terms 2 nd order terms relaxation : relaxation times , : 1 st, 2 nd order transport coefficients A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
Results n 2 nd order constitutive equations for systems with multi-components and multi-conserved currents Bulk pressure 1 st order terms 2 nd order terms relaxation : relaxation times , : 1 st, 2 nd order transport coefficients A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
 Results n (Cont’d) Energy current Dufour effect 1 st order terms 2 nd order terms relaxation A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
Results n (Cont’d) Energy current Dufour effect 1 st order terms 2 nd order terms relaxation A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
 Results n (Cont’d) J-th charge current Soret effect 1 st order terms 2 nd order terms relaxation A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
Results n (Cont’d) J-th charge current Soret effect 1 st order terms 2 nd order terms relaxation A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
 Results n (Cont’d) Shear stress tensor 1 st order terms 2 nd order terms relaxation n Our results in the limit of single component/conserved current Consistent with other results based on Baier et al. (‘ 08) Ad. S/CFT approach Renormalization group method Tsumura and Kunihiro (‘ 09) Betz et al. (‘ 09) Grad’s 14 -moment method A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
Results n (Cont’d) Shear stress tensor 1 st order terms 2 nd order terms relaxation n Our results in the limit of single component/conserved current Consistent with other results based on Baier et al. (‘ 08) Ad. S/CFT approach Renormalization group method Tsumura and Kunihiro (‘ 09) Betz et al. (‘ 09) Grad’s 14 -moment method A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
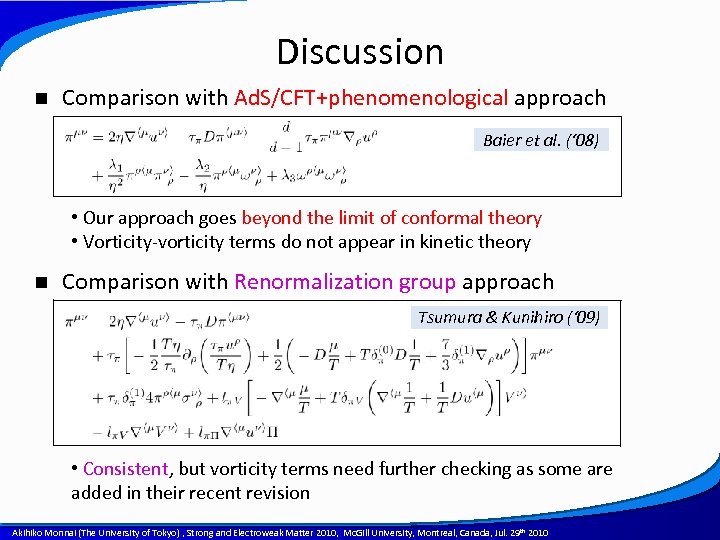 Discussion n Comparison with Ad. S/CFT+phenomenological approach Baier et al. (‘ 08) • Our approach goes beyond the limit of conformal theory • Vorticity-vorticity terms do not appear in kinetic theory n Comparison with Renormalization group approach Tsumura & Kunihiro (‘ 09) • Consistent, but vorticity terms need further checking as some are added in their recent revision A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
Discussion n Comparison with Ad. S/CFT+phenomenological approach Baier et al. (‘ 08) • Our approach goes beyond the limit of conformal theory • Vorticity-vorticity terms do not appear in kinetic theory n Comparison with Renormalization group approach Tsumura & Kunihiro (‘ 09) • Consistent, but vorticity terms need further checking as some are added in their recent revision A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
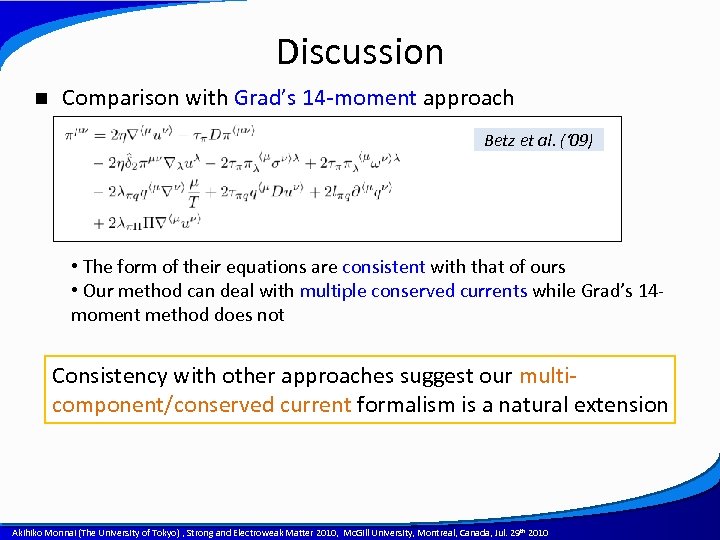 Discussion n Comparison with Grad’s 14 -moment approach Betz et al. (‘ 09) • The form of their equations are consistent with that of ours • Our method can deal with multiple conserved currents while Grad’s 14 moment method does not Consistency with other approaches suggest our multicomponent/conserved current formalism is a natural extension A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
Discussion n Comparison with Grad’s 14 -moment approach Betz et al. (‘ 09) • The form of their equations are consistent with that of ours • Our method can deal with multiple conserved currents while Grad’s 14 moment method does not Consistency with other approaches suggest our multicomponent/conserved current formalism is a natural extension A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
 Summary and Outlook n We formulated generalized 2 nd order theory from the entropy production w/o violating causality 1. Multi-component systems with multiple conserved currents Inelastic scattering (e. g. pair creation/annihilation) implied 2. Frame independent Independent equations for energy and charge currents 3. Onsager reciprocal relations ( 1 st order theory) Justifies the moment expansion n Future prospects include applications to… • Hydrodynamic modeling of the Quark-gluon plasma at heavy ion collisions • Cosmological fluid etc… A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
Summary and Outlook n We formulated generalized 2 nd order theory from the entropy production w/o violating causality 1. Multi-component systems with multiple conserved currents Inelastic scattering (e. g. pair creation/annihilation) implied 2. Frame independent Independent equations for energy and charge currents 3. Onsager reciprocal relations ( 1 st order theory) Justifies the moment expansion n Future prospects include applications to… • Hydrodynamic modeling of the Quark-gluon plasma at heavy ion collisions • Cosmological fluid etc… A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
 The End n Thank you for listening! A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
The End n Thank you for listening! A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
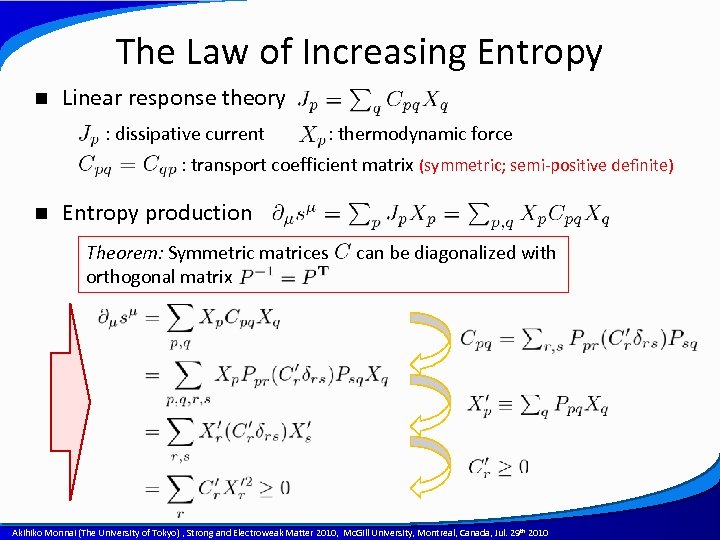 The Law of Increasing Entropy n Linear response theory : dissipative current : thermodynamic force : transport coefficient matrix (symmetric; semi-positive definite) n Entropy production Theorem: Symmetric matrices orthogonal matrix can be diagonalized with A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
The Law of Increasing Entropy n Linear response theory : dissipative current : thermodynamic force : transport coefficient matrix (symmetric; semi-positive definite) n Entropy production Theorem: Symmetric matrices orthogonal matrix can be diagonalized with A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
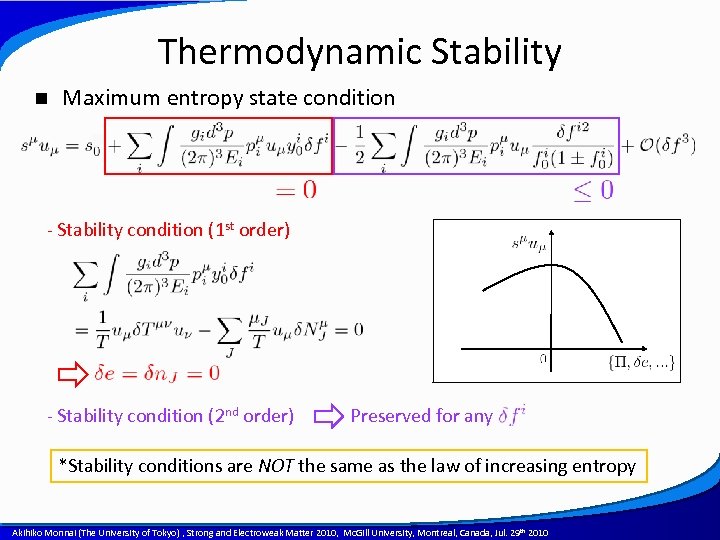 Thermodynamic Stability n Maximum entropy state condition - Stability condition (1 st order) - Stability condition (2 nd order) Preserved for any *Stability conditions are NOT the same as the law of increasing entropy A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
Thermodynamic Stability n Maximum entropy state condition - Stability condition (1 st order) - Stability condition (2 nd order) Preserved for any *Stability conditions are NOT the same as the law of increasing entropy A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
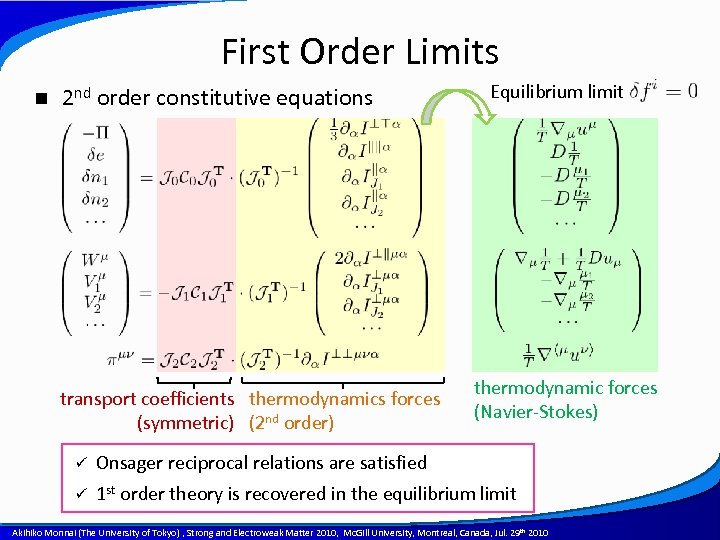 First Order Limits n 2 nd order constitutive equations transport coefficients thermodynamics forces (symmetric) (2 nd order) Equilibrium limit thermodynamic forces (Navier-Stokes) ü Onsager reciprocal relations are satisfied ü 1 st order theory is recovered in the equilibrium limit A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
First Order Limits n 2 nd order constitutive equations transport coefficients thermodynamics forces (symmetric) (2 nd order) Equilibrium limit thermodynamic forces (Navier-Stokes) ü Onsager reciprocal relations are satisfied ü 1 st order theory is recovered in the equilibrium limit A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
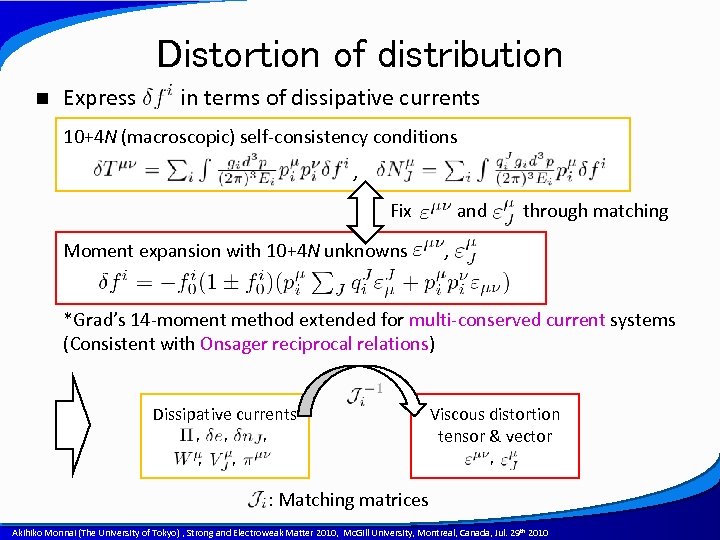 Distortion of distribution n Express in terms of dissipative currents 10+4 N (macroscopic) self-consistency conditions , Fix and Moment expansion with 10+4 N unknowns through matching , *Grad’s 14 -moment method extended for multi-conserved current systems (Consistent with Onsager reciprocal relations) Dissipative currents , , , , Viscous distortion tensor & vector , , : Matching matrices A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
Distortion of distribution n Express in terms of dissipative currents 10+4 N (macroscopic) self-consistency conditions , Fix and Moment expansion with 10+4 N unknowns through matching , *Grad’s 14 -moment method extended for multi-conserved current systems (Consistent with Onsager reciprocal relations) Dissipative currents , , , , Viscous distortion tensor & vector , , : Matching matrices A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
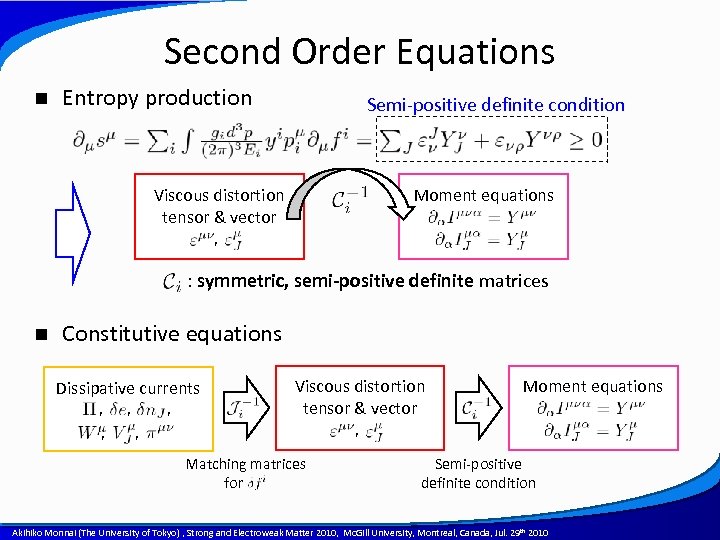 Second Order Equations n Entropy production Semi-positive definite condition Viscous distortion tensor & vector Moment equations , : symmetric, semi-positive definite matrices n Constitutive equations Dissipative currents , , , , Viscous distortion tensor & vector Moment equations , , Matching matrices for dfi Semi-positive definite condition A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
Second Order Equations n Entropy production Semi-positive definite condition Viscous distortion tensor & vector Moment equations , : symmetric, semi-positive definite matrices n Constitutive equations Dissipative currents , , , , Viscous distortion tensor & vector Moment equations , , Matching matrices for dfi Semi-positive definite condition A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
 Discussion n Expanding universe Einstein equation with Robertson-Walker metric in flat space Only “ideal hydrodynamic” energy-momentum tensor is allowed: because the R-W metric assumes isotropic and homogeneous expansion. Viscous correction to the pressure (= bulk pressure ) is allowed “Bulk viscous cosmological model” A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010
Discussion n Expanding universe Einstein equation with Robertson-Walker metric in flat space Only “ideal hydrodynamic” energy-momentum tensor is allowed: because the R-W metric assumes isotropic and homogeneous expansion. Viscous correction to the pressure (= bulk pressure ) is allowed “Bulk viscous cosmological model” A power point template created by Akihiko Monnai (The University of Tokyo) , Strong and Electroweak Matter 2010, Mc. Gill University, Montreal, Canada, Jul. 29 th 2010


