11b6962d63b1803ad676472fffb8b272.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 123
 Reducing Risks in the Field Safety Awareness for Environmental Health Professionals CIT September 2012 Nancy Deal Non-point Source Pollution Program Coordinator (EPA 319) Onsite Water Protection Branch 919 -710 -4188 nancy. deal@dhhs. nc. gov 1
Reducing Risks in the Field Safety Awareness for Environmental Health Professionals CIT September 2012 Nancy Deal Non-point Source Pollution Program Coordinator (EPA 319) Onsite Water Protection Branch 919 -710 -4188 nancy. deal@dhhs. nc. gov 1
 Mission Statement To safeguard life, promote human health and protect the environment through the practice of modern environmental health science, the use of technology, rules, public education and above all, dedication to the public trust. 2
Mission Statement To safeguard life, promote human health and protect the environment through the practice of modern environmental health science, the use of technology, rules, public education and above all, dedication to the public trust. 2
 Overview General safety for all disciplines Authorization-specific safety Pathogens 3
Overview General safety for all disciplines Authorization-specific safety Pathogens 3
 Questions and comments… …are welcome 4
Questions and comments… …are welcome 4
 Safety is a culture: It starts at the top and filters down. – The boss must buy into the concept – Each worker must also take responsibility
Safety is a culture: It starts at the top and filters down. – The boss must buy into the concept – Each worker must also take responsibility
 Safety When safety is the most important goal on the job, everyone gets to come back to work the next day.
Safety When safety is the most important goal on the job, everyone gets to come back to work the next day.
 Safety An accident is an unforeseen incident that occurs while following established protocol instead of an incident resulting from an unsafe condition. You must plan to be safe!
Safety An accident is an unforeseen incident that occurs while following established protocol instead of an incident resulting from an unsafe condition. You must plan to be safe!
 Why do accidents happen? Eyes not on Path – Slips, trips and falls Eyes not on Task – Impact injuries Line of Fire – Exposure to liquids by “splash back” Rushing – Slow and steady is better
Why do accidents happen? Eyes not on Path – Slips, trips and falls Eyes not on Task – Impact injuries Line of Fire – Exposure to liquids by “splash back” Rushing – Slow and steady is better
 So… Don’t get in a hurry Pay attention 9
So… Don’t get in a hurry Pay attention 9
 First aid and emergency response Emergency phone numbers Cell phones are great, but – Got a signal? Where is the nearest help? – Know how to get there?
First aid and emergency response Emergency phone numbers Cell phones are great, but – Got a signal? Where is the nearest help? – Know how to get there?
 First aid and emergency response Keep a well-stocked first aid kit handy Know your co-workers or employees’ health issues – Diabetes – Anaphylaxis – Heart conditions
First aid and emergency response Keep a well-stocked first aid kit handy Know your co-workers or employees’ health issues – Diabetes – Anaphylaxis – Heart conditions
 First aid and emergency response The first 15 minutes is critical – Precious time is lost if you cannot make a decision to act Get safety training, including CPR! – Your health department – Red Cross – Extension – Department of Labor – OSHA
First aid and emergency response The first 15 minutes is critical – Precious time is lost if you cannot make a decision to act Get safety training, including CPR! – Your health department – Red Cross – Extension – Department of Labor – OSHA
 On-site safety equipment First aid kits – In the truck – On the wall 13
On-site safety equipment First aid kits – In the truck – On the wall 13
 On-site safety equipment AEDs 14
On-site safety equipment AEDs 14
 On-site safety equipment Fire extinguishers are specific to the source of combustion A B C D K – Class A: ordinary combustibles, many plastics – Class B: flammable liquids, grease and oil – Class C: wiring, other electrical sources – Class D: Chemical fires – Class K: Cooking oils (commercial settings)
On-site safety equipment Fire extinguishers are specific to the source of combustion A B C D K – Class A: ordinary combustibles, many plastics – Class B: flammable liquids, grease and oil – Class C: wiring, other electrical sources – Class D: Chemical fires – Class K: Cooking oils (commercial settings)
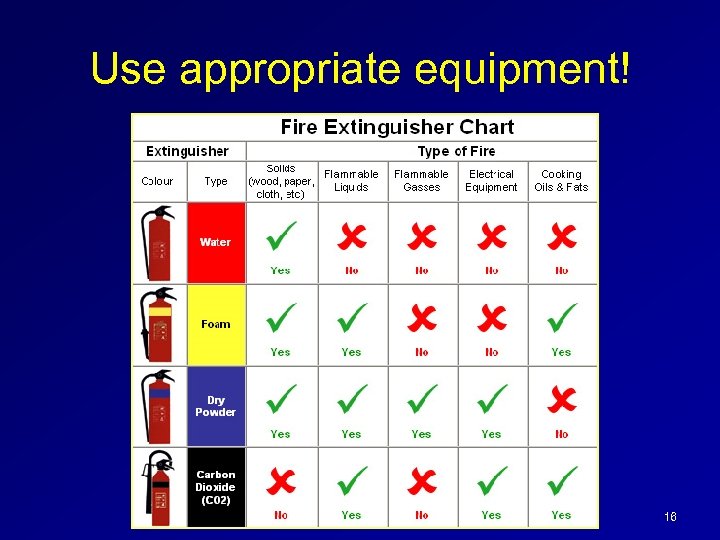 Use appropriate equipment! 16
Use appropriate equipment! 16
 Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) What to wear and when to wear it – Steel-toed shoes 17
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) What to wear and when to wear it – Steel-toed shoes 17
 Personal protective equipment: Gloves Latex for potential contact with – Effluent – Bodily fluids – Other unpleasantries Gauntleted overgloves – Sewage applications
Personal protective equipment: Gloves Latex for potential contact with – Effluent – Bodily fluids – Other unpleasantries Gauntleted overgloves – Sewage applications
 Personal protective equipment: Eye Protection Safety glasses Face shields as appropriate
Personal protective equipment: Eye Protection Safety glasses Face shields as appropriate
 Personal protective equipment: Hearing protection Around heavy equipment Industrial settings
Personal protective equipment: Hearing protection Around heavy equipment Industrial settings
 Hearing protection: “ 4 C’s” Clean hands – Before inserting to avoid infection Consistent use – When noise levels exceed 85 db (A) Correct insertion – NIOSH recommendation The Roll, Pull, Hold method Comfortable fit – Or they will not be worn 21
Hearing protection: “ 4 C’s” Clean hands – Before inserting to avoid infection Consistent use – When noise levels exceed 85 db (A) Correct insertion – NIOSH recommendation The Roll, Pull, Hold method Comfortable fit – Or they will not be worn 21
 Personal protective equipment: Hard hats and high-vis vests Required by OSHA if loads will be lifted overhead
Personal protective equipment: Hard hats and high-vis vests Required by OSHA if loads will be lifted overhead
 Personal protective equipment: Inhalation protection For hazardous atmospheres Should be precisely fit 23
Personal protective equipment: Inhalation protection For hazardous atmospheres Should be precisely fit 23
 Personal protective equipment Wooded sites – Long sleeved jackets – Snake boots – Chaps Messy sites – Coveralls – Tyvek® suits
Personal protective equipment Wooded sites – Long sleeved jackets – Snake boots – Chaps Messy sites – Coveralls – Tyvek® suits
 Personal protective equipment What must the employer provide for you? – Generally, anything that is not specific to the user Boots, prescription safety glasses would be your responsibility Check your employer’s policies
Personal protective equipment What must the employer provide for you? – Generally, anything that is not specific to the user Boots, prescription safety glasses would be your responsibility Check your employer’s policies
 Personal protection: hygiene Hand-washing - soap or waterless hand sanitizers – After toilet use – Before breaks and lunch Keep hands and fingers away from eyes, ears, nose, and mouth. Wear rubber gloves that are “fit for use. ”
Personal protection: hygiene Hand-washing - soap or waterless hand sanitizers – After toilet use – Before breaks and lunch Keep hands and fingers away from eyes, ears, nose, and mouth. Wear rubber gloves that are “fit for use. ”
 Personal protection: hygiene Clothing may be contaminated – Do not store personal clothes with work clothes. – Wash work clothes separately.
Personal protection: hygiene Clothing may be contaminated – Do not store personal clothes with work clothes. – Wash work clothes separately.
 Conclusion – and point of beginning… To STAY SAFE: Each person is responsible for his or her own safety and thus the safety of those around them Know how to be safe Know how to respond to an emergency
Conclusion – and point of beginning… To STAY SAFE: Each person is responsible for his or her own safety and thus the safety of those around them Know how to be safe Know how to respond to an emergency
 Authorization-specific safety Water wells Wastewater Food/Lodging/Institutional Pools Tattoo parlors Child Health Protection 29
Authorization-specific safety Water wells Wastewater Food/Lodging/Institutional Pools Tattoo parlors Child Health Protection 29
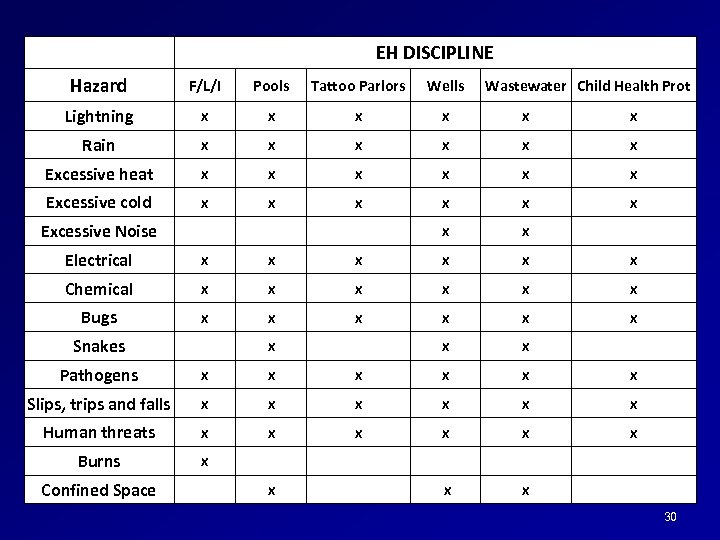 EH DISCIPLINE Hazard F/L/I Pools Tattoo Parlors Wells Lightning x x x Rain x x x Excessive heat x x x Excessive cold x x x Excessive Noise x x Electrical x x x Chemical x x x Bugs x x x Snakes x x x Pathogens x x x Slips, trips and falls x x x Human threats x x x Burns x Confined Space x x x Wastewater Child Health Prot 30
EH DISCIPLINE Hazard F/L/I Pools Tattoo Parlors Wells Lightning x x x Rain x x x Excessive heat x x x Excessive cold x x x Excessive Noise x x Electrical x x x Chemical x x x Bugs x x x Snakes x x x Pathogens x x x Slips, trips and falls x x x Human threats x x x Burns x Confined Space x x x Wastewater Child Health Prot 30
 Water wells and Onsite 31
Water wells and Onsite 31
 Safety concerns: Water Wells and Onsite Wastewater Programs Weather – Lightning – Excessive heat and cold – Excessively wet or dry soils Site hazards – Uneven topography – Equipment Excessive noise 32
Safety concerns: Water Wells and Onsite Wastewater Programs Weather – Lightning – Excessive heat and cold – Excessively wet or dry soils Site hazards – Uneven topography – Equipment Excessive noise 32
 Noise • Noise levels on a typical water well worksite. • Noise levels above 90 d. B(A) within 6 meters of the rig, particularly near the compressor. • Wear hearing protection • Avoid standing in these areas if not required to conduct a work task. 33
Noise • Noise levels on a typical water well worksite. • Noise levels above 90 d. B(A) within 6 meters of the rig, particularly near the compressor. • Wear hearing protection • Avoid standing in these areas if not required to conduct a work task. 33
 General site issues Electronic devices are a distraction – Cell phones Concentrate on the job – Personal music devices Are NOT designed for hearing protection
General site issues Electronic devices are a distraction – Cell phones Concentrate on the job – Personal music devices Are NOT designed for hearing protection
 “Biological” hazards 35
“Biological” hazards 35
 Snakes: whether venomous or not… Surprise! 36
Snakes: whether venomous or not… Surprise! 36
 Creepy crawlers – and fliers Ticks – Wear white – Tuck pants in shoes – Use DEET – Keep duct tape handy Bees, wasps and hornets – Look for their nests – Carry your EPI pen if you are allergic – Benadryl is a decent alternative 37
Creepy crawlers – and fliers Ticks – Wear white – Tuck pants in shoes – Use DEET – Keep duct tape handy Bees, wasps and hornets – Look for their nests – Carry your EPI pen if you are allergic – Benadryl is a decent alternative 37
 Black Widows ALWAYS present in valve boxes, tank risers, well houses, etc.
Black Widows ALWAYS present in valve boxes, tank risers, well houses, etc.
 Vegetation “Widow makers” Briars, etc. Walking too closely behind the person in front of you - branches!
Vegetation “Widow makers” Briars, etc. Walking too closely behind the person in front of you - branches!
 Vegetation 40
Vegetation 40
 Newly-cleared land What are the hazards? – Fire ant nests – Yellow jackets – Stump holes – Carrying equipment 41
Newly-cleared land What are the hazards? – Fire ant nests – Yellow jackets – Stump holes – Carrying equipment 41
 Aggressive domestic animals
Aggressive domestic animals
 Aggressive livestock Watch out if you are in a pasture – Goats and bulls can make life interesting 43
Aggressive livestock Watch out if you are in a pasture – Goats and bulls can make life interesting 43
 Angry owners and tenants 44
Angry owners and tenants 44
 Electric fences Do you believe the person when they tell you it is OFF? How do you check it? 45
Electric fences Do you believe the person when they tell you it is OFF? How do you check it? 45
 Safety concerns (cont. ): Water Wells and Onsite Wastewater Programs Waterborne pathogens – We’ll get your attention on this later… 46
Safety concerns (cont. ): Water Wells and Onsite Wastewater Programs Waterborne pathogens – We’ll get your attention on this later… 46
 Safety concerns (cont. ): Water Wells and Onsite Wastewater Programs Ergonomics – Road warriors – Extensive deskwork – Lifting 47
Safety concerns (cont. ): Water Wells and Onsite Wastewater Programs Ergonomics – Road warriors – Extensive deskwork – Lifting 47
 Personal protection: ergonomics Lifting – Use tools – Get help “Buddy system” – Legs, not back Good footing Close to load Back straight
Personal protection: ergonomics Lifting – Use tools – Get help “Buddy system” – Legs, not back Good footing Close to load Back straight
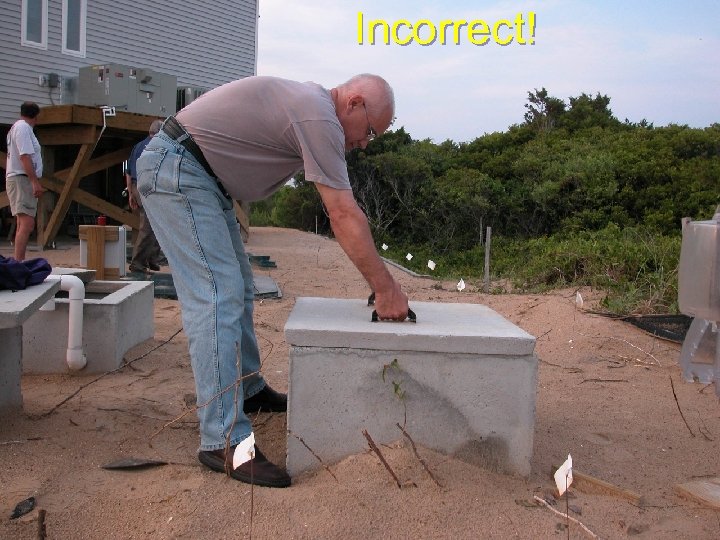 Incorrect!
Incorrect!
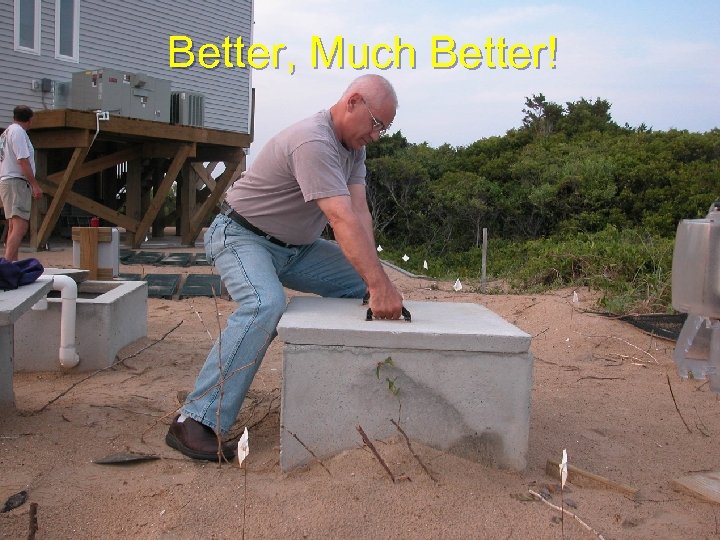 Better, Much Better!
Better, Much Better!
 Dum. . Dee. . Dum Two working together is always better than one! HEY, BUDDY! A LITTLE HELP WOULD BE NICE!!!
Dum. . Dee. . Dum Two working together is always better than one! HEY, BUDDY! A LITTLE HELP WOULD BE NICE!!!
 Equipment or component hazards Disinfection components – Chlorine and UV Electrical systems for components 52
Equipment or component hazards Disinfection components – Chlorine and UV Electrical systems for components 52
 Before you probe or dig… Margin of error Homeowner installed utilities Is it a straight line? Where are shut-off valves for gas and water lines?
Before you probe or dig… Margin of error Homeowner installed utilities Is it a straight line? Where are shut-off valves for gas and water lines?
 Electrical hazards Proper training and/or licensure to perform repairs to electrical systems Lock-out/tag-out procedures – All workers should be familiar with these – Get training!
Electrical hazards Proper training and/or licensure to perform repairs to electrical systems Lock-out/tag-out procedures – All workers should be familiar with these – Get training!
 Electrical hazards: basics Be aware of the potential hazard at all times. Do not use metal ladders. Never override any electrical safety device. Check extension cords for abrasion and breaks as well as for missing grounding prongs
Electrical hazards: basics Be aware of the potential hazard at all times. Do not use metal ladders. Never override any electrical safety device. Check extension cords for abrasion and breaks as well as for missing grounding prongs
 Electrical hazards: basics Use only grounded or insulated (UL approved) electrical equipment. Energize AC-powered equipment through a connection with a ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI).
Electrical hazards: basics Use only grounded or insulated (UL approved) electrical equipment. Energize AC-powered equipment through a connection with a ground fault circuit interrupter (GFCI).
 Excavation and trench safety measures For excavations > 4 feet deep that workers will enter While excavation is open and while workers might be in it, proper safety precautions must be observed There must be a ‘competent person’ on the site
Excavation and trench safety measures For excavations > 4 feet deep that workers will enter While excavation is open and while workers might be in it, proper safety precautions must be observed There must be a ‘competent person’ on the site
 Competent person By way of training and/or experience, is… – Knowledgeable of applicable standards, – Capable of identifying commonly foreseeable workplace hazards, – Designated by the employer, and – Has authority to take appropriate actions. Can even shut down the job if conditions are unsafe. Requires special training.
Competent person By way of training and/or experience, is… – Knowledgeable of applicable standards, – Capable of identifying commonly foreseeable workplace hazards, – Designated by the employer, and – Has authority to take appropriate actions. Can even shut down the job if conditions are unsafe. Requires special training.
 Competent person
Competent person
 Excavation and trench safety Competent person Soil classification Protective measures and equipment Access and egress Stability of nearby structures Water accumulation Clear line of sight Spoil pile Re-inspection
Excavation and trench safety Competent person Soil classification Protective measures and equipment Access and egress Stability of nearby structures Water accumulation Clear line of sight Spoil pile Re-inspection
 Consider: Most trench fatalities occur in trenches 5 to 15 feet deep One cubic yd of soil = about 3, 000 pounds
Consider: Most trench fatalities occur in trenches 5 to 15 feet deep One cubic yd of soil = about 3, 000 pounds
 Confined space What is it? – Limited ingress and egress – Not designed for continuous human occupancy http: //www. osha. gov/SLTC/confinedspaces/index. html 62
Confined space What is it? – Limited ingress and egress – Not designed for continuous human occupancy http: //www. osha. gov/SLTC/confinedspaces/index. html 62
 Confined Space New Installations – Any tank is a confined space Repairs, systems in use. – Lack of oxygen – Hydrogen sulfide gas, methane – Respiratory stress or arrest. – First aid
Confined Space New Installations – Any tank is a confined space Repairs, systems in use. – Lack of oxygen – Hydrogen sulfide gas, methane – Respiratory stress or arrest. – First aid
 To safely and legally enter a tank, one must have proper training and equipment
To safely and legally enter a tank, one must have proper training and equipment
 This is an unsafe practice. Your head, body, etc. should never be in a confined space.
This is an unsafe practice. Your head, body, etc. should never be in a confined space.
 Hazardous atmospheres Where a hazardous atmosphere exists or could reasonably be expected to exist: Atmospheres shall be tested before employees enter excavations greater than 4 feet in depth If atmospheres contain less than 19. 5% oxygen – Provide ventilation/respiratory protection
Hazardous atmospheres Where a hazardous atmosphere exists or could reasonably be expected to exist: Atmospheres shall be tested before employees enter excavations greater than 4 feet in depth If atmospheres contain less than 19. 5% oxygen – Provide ventilation/respiratory protection
 Hazardous atmospheres Where might there be one? Landfill or dumping area. Chemical or hazardous waste recycling or collection, storage center Water/wastewater treatment sites Inside any tank – new or used
Hazardous atmospheres Where might there be one? Landfill or dumping area. Chemical or hazardous waste recycling or collection, storage center Water/wastewater treatment sites Inside any tank – new or used
 Hazardous conditions can develop quickly Heavier-than-air gases can render a safe site unsafe quickly – Equipment exhaust – Carbon dioxide – Propane – Etc.
Hazardous conditions can develop quickly Heavier-than-air gases can render a safe site unsafe quickly – Equipment exhaust – Carbon dioxide – Propane – Etc.
 Hazardous atmospheres Emergency rescue equipment on site if hazardous atmospheres could exist: – – – Breathing apparatus A safety harness and line A basket stretcher
Hazardous atmospheres Emergency rescue equipment on site if hazardous atmospheres could exist: – – – Breathing apparatus A safety harness and line A basket stretcher
 Food, Lodging and Institutional Inspections 70
Food, Lodging and Institutional Inspections 70
 Safety concerns: Food, Lodging and Institutional Program All of the above, plus… Slips, trips and falls Burns 71
Safety concerns: Food, Lodging and Institutional Program All of the above, plus… Slips, trips and falls Burns 71
 Safety concerns (cont. ): Food, Lodging and Institutional Program Equipment – Do not break it down Recalled food – Safe handling instructions 72
Safety concerns (cont. ): Food, Lodging and Institutional Program Equipment – Do not break it down Recalled food – Safe handling instructions 72
 Inside the facility Where is the First Aid Kit? How about the fire extinguisher? Do you know how to get out? 73
Inside the facility Where is the First Aid Kit? How about the fire extinguisher? Do you know how to get out? 73
 Safety concerns (cont. ): Food, Lodging and Institutional Program Wash/sanitize hands! – Regularly – Risk of dermatitis 74
Safety concerns (cont. ): Food, Lodging and Institutional Program Wash/sanitize hands! – Regularly – Risk of dermatitis 74
 Institutional issues Isolation areas – Watch for signage Soiled linens and furniture – Where are your gloves? ? ? 75
Institutional issues Isolation areas – Watch for signage Soiled linens and furniture – Where are your gloves? ? ? 75
 Safety concerns: Child Environmental Health Branch Contaminated surfaces – inside and out! – Don’t take it home to your family! 76
Safety concerns: Child Environmental Health Branch Contaminated surfaces – inside and out! – Don’t take it home to your family! 76
 Safety concerns: Pools Weather Slips, trips and falls in wet areas Spiders and snakes – Storage areas – Skimmer covers 77
Safety concerns: Pools Weather Slips, trips and falls in wet areas Spiders and snakes – Storage areas – Skimmer covers 77
 Safety concerns: Pools Chemicals – Mixing two types of chlorine tablets can be explosive! Trichloroisocyanuric acid for pools Calcium hypochlorite for water and wastewater – Storage areas Leaking containers – Equipment Electrical – Proper pump ground – a REAL hazard in these wet areas 78
Safety concerns: Pools Chemicals – Mixing two types of chlorine tablets can be explosive! Trichloroisocyanuric acid for pools Calcium hypochlorite for water and wastewater – Storage areas Leaking containers – Equipment Electrical – Proper pump ground – a REAL hazard in these wet areas 78
 Safety concerns: Pools Can you swim? ? ? 79
Safety concerns: Pools Can you swim? ? ? 79
 Safety concerns: Tattoo Parlors Equipment – Needles, etc. Contaminated inks Chemicals – Disinfection chemicals – Equipment Clientele? ? ? 80
Safety concerns: Tattoo Parlors Equipment – Needles, etc. Contaminated inks Chemicals – Disinfection chemicals – Equipment Clientele? ? ? 80
 Safety concerns: All disciplines Methamphetamine labs – Often discovered through Septic tank investigations Lead investigations Complaint investigations – Trash accumulation – Odors – Excessive traffic – Typically rental properties but not always! Hotel-based enterprises 81
Safety concerns: All disciplines Methamphetamine labs – Often discovered through Septic tank investigations Lead investigations Complaint investigations – Trash accumulation – Odors – Excessive traffic – Typically rental properties but not always! Hotel-based enterprises 81
 Methamphetamine labs Associated dangers – Firearms – Booby traps – Vicious dogs – Volatiles used in ‘cooking’ process are flammable – Improperly stored or used chemicals can explode 82
Methamphetamine labs Associated dangers – Firearms – Booby traps – Vicious dogs – Volatiles used in ‘cooking’ process are flammable – Improperly stored or used chemicals can explode 82
 Methamphetamine labs If you suspect you have found one GET OUT and call the law 83
Methamphetamine labs If you suspect you have found one GET OUT and call the law 83
 Pathogen Hazards 84
Pathogen Hazards 84
 Pathogens Infectious agents that can cause disease Contact with such agents is to be expected in our line of work – A fundamental part of protecting public and environmental health 85
Pathogens Infectious agents that can cause disease Contact with such agents is to be expected in our line of work – A fundamental part of protecting public and environmental health 85
 “Knowledge is the only thing you can give away and still keep” Scott Hutchinson “Whoever said that never heard of infectious disease” J. Hoch 86
“Knowledge is the only thing you can give away and still keep” Scott Hutchinson “Whoever said that never heard of infectious disease” J. Hoch 86
 Good Bugs : Water Microbiology Many are part of the natural soil/water ecology and crucial to biogeochemical cycles 87
Good Bugs : Water Microbiology Many are part of the natural soil/water ecology and crucial to biogeochemical cycles 87
 Waterborne diseases Results from contact with pathogencontaminated water Annual occurrence of diarrheal disease – 4. 1% of daily global disease – 1. 8 to 5 million people per year Most concentrated in children 88
Waterborne diseases Results from contact with pathogencontaminated water Annual occurrence of diarrheal disease – 4. 1% of daily global disease – 1. 8 to 5 million people per year Most concentrated in children 88
 Categories of Pathogens Bacteria Viruses Fungi Parasites Protozoa
Categories of Pathogens Bacteria Viruses Fungi Parasites Protozoa
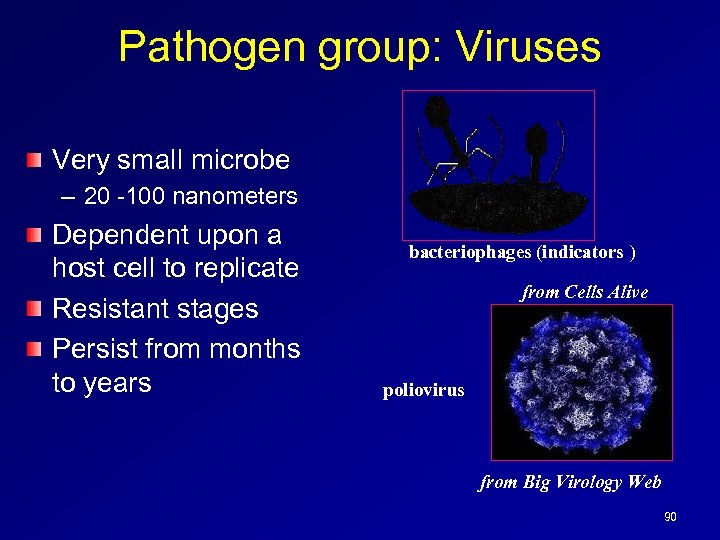 Pathogen group: Viruses Very small microbe – 20 -100 nanometers Dependent upon a host cell to replicate Resistant stages Persist from months to years bacteriophages (indicators ) from Cells Alive poliovirus from Big Virology Web 90
Pathogen group: Viruses Very small microbe – 20 -100 nanometers Dependent upon a host cell to replicate Resistant stages Persist from months to years bacteriophages (indicators ) from Cells Alive poliovirus from Big Virology Web 90
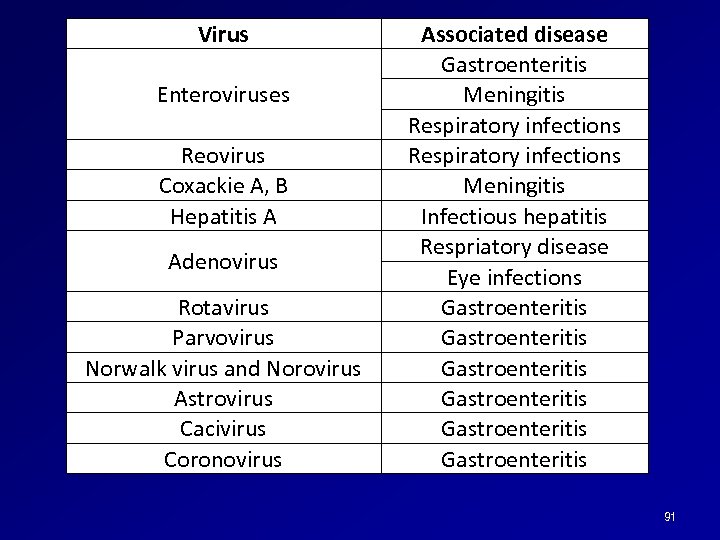 Virus Enteroviruses Reovirus Coxackie A, B Hepatitis A Adenovirus Rotavirus Parvovirus Norwalk virus and Norovirus Astrovirus Cacivirus Coronovirus Associated disease Gastroenteritis Meningitis Respiratory infections Meningitis Infectious hepatitis Respriatory disease Eye infections Gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis 91
Virus Enteroviruses Reovirus Coxackie A, B Hepatitis A Adenovirus Rotavirus Parvovirus Norwalk virus and Norovirus Astrovirus Cacivirus Coronovirus Associated disease Gastroenteritis Meningitis Respiratory infections Meningitis Infectious hepatitis Respriatory disease Eye infections Gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis 91
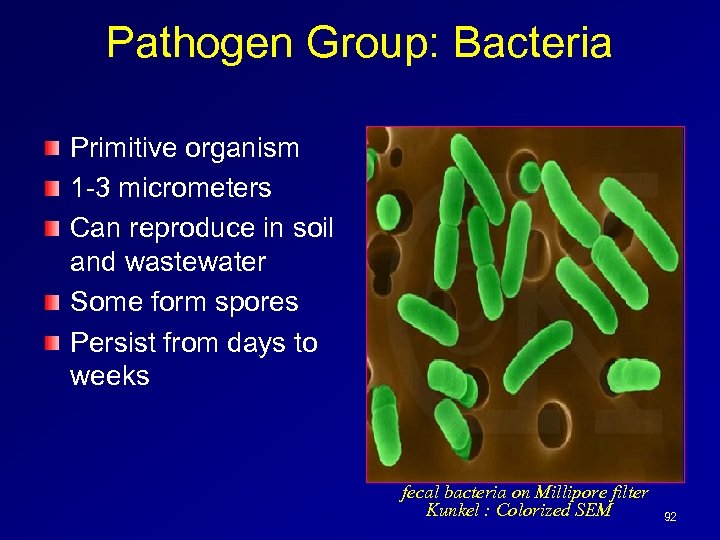 Pathogen Group: Bacteria Primitive organism 1 -3 micrometers Can reproduce in soil and wastewater Some form spores Persist from days to weeks fecal bacteria on Millipore filter Kunkel : Colorized SEM 92
Pathogen Group: Bacteria Primitive organism 1 -3 micrometers Can reproduce in soil and wastewater Some form spores Persist from days to weeks fecal bacteria on Millipore filter Kunkel : Colorized SEM 92
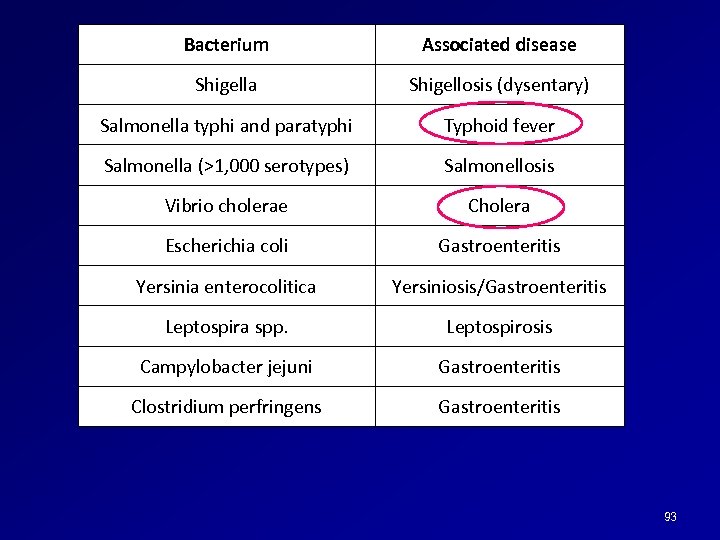 Bacterium Associated disease Shigella Shigellosis (dysentary) Salmonella typhi and paratyphi Typhoid fever Salmonella (>1, 000 serotypes) Salmonellosis Vibrio cholerae Cholera Escherichia coli Gastroenteritis Yersinia enterocolitica Yersiniosis/Gastroenteritis Leptospira spp. Leptospirosis Campylobacter jejuni Gastroenteritis Clostridium perfringens Gastroenteritis 93
Bacterium Associated disease Shigella Shigellosis (dysentary) Salmonella typhi and paratyphi Typhoid fever Salmonella (>1, 000 serotypes) Salmonellosis Vibrio cholerae Cholera Escherichia coli Gastroenteritis Yersinia enterocolitica Yersiniosis/Gastroenteritis Leptospira spp. Leptospirosis Campylobacter jejuni Gastroenteritis Clostridium perfringens Gastroenteritis 93
 Pathogen Group: Fungi Micrometers to millimeters in size Live on decaying matter Can form spores Airborne (aerosols) or waterborne Aspergillus cosmic light web Candida 10 micrometers av Www. meddean. luc. edu 94
Pathogen Group: Fungi Micrometers to millimeters in size Live on decaying matter Can form spores Airborne (aerosols) or waterborne Aspergillus cosmic light web Candida 10 micrometers av Www. meddean. luc. edu 94
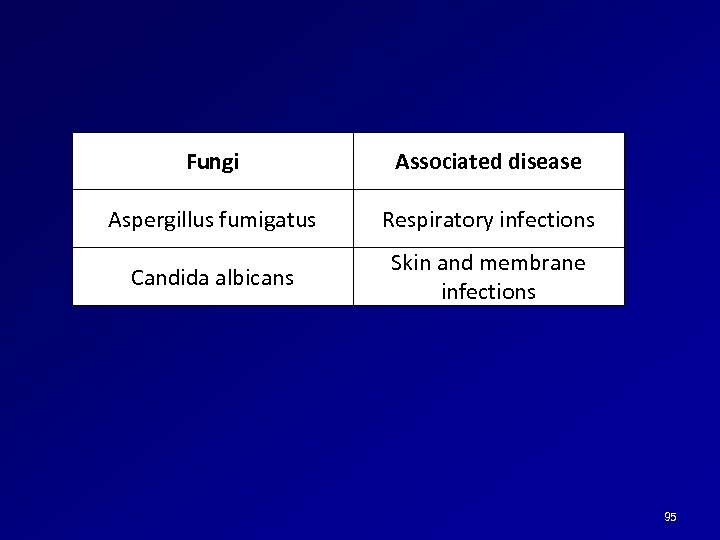 Fungi Associated disease Aspergillus fumigatus Respiratory infections Candida albicans Skin and membrane infections 95
Fungi Associated disease Aspergillus fumigatus Respiratory infections Candida albicans Skin and membrane infections 95
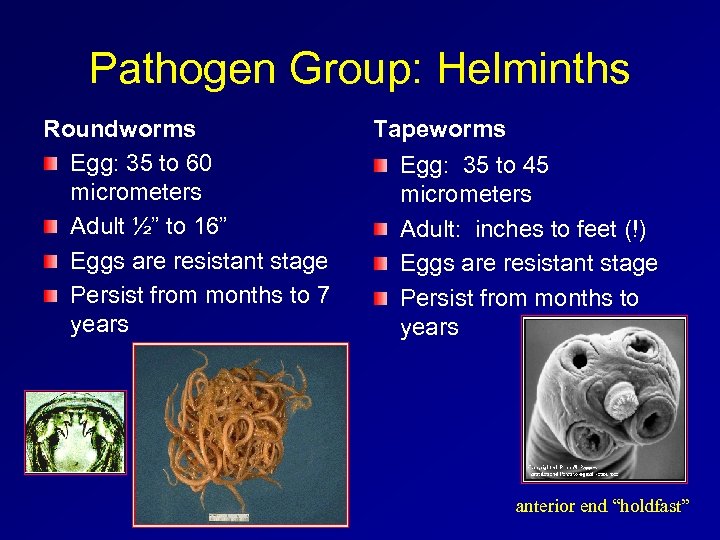 Pathogen Group: Helminths Roundworms Egg: 35 to 60 micrometers Adult ½” to 16” Eggs are resistant stage Persist from months to 7 years Tapeworms Egg: 35 to 45 micrometers Adult: inches to feet (!) Eggs are resistant stage Persist from months to years anterior end “holdfast”
Pathogen Group: Helminths Roundworms Egg: 35 to 60 micrometers Adult ½” to 16” Eggs are resistant stage Persist from months to 7 years Tapeworms Egg: 35 to 45 micrometers Adult: inches to feet (!) Eggs are resistant stage Persist from months to years anterior end “holdfast”
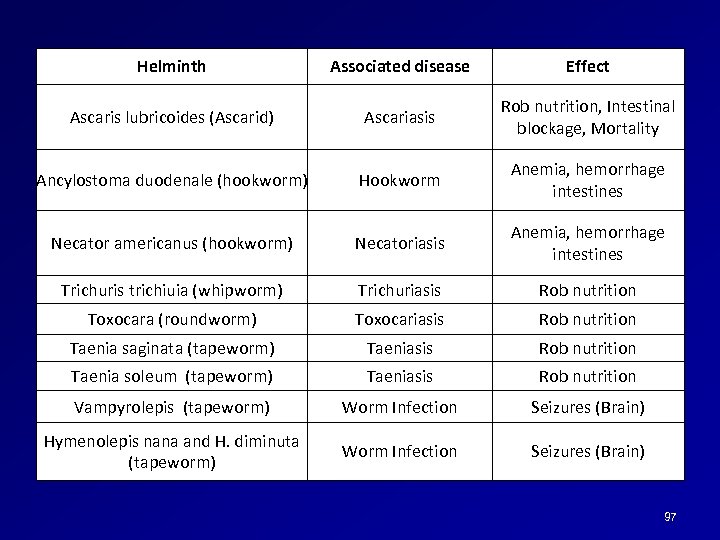 Helminth Associated disease Effect Ascaris lubricoides (Ascarid) Ascariasis Rob nutrition, Intestinal blockage, Mortality Ancylostoma duodenale (hookworm) Hookworm Anemia, hemorrhage intestines Necator americanus (hookworm) Necatoriasis Anemia, hemorrhage intestines Trichuris trichiuia (whipworm) Trichuriasis Rob nutrition Toxocara (roundworm) Toxocariasis Rob nutrition Taenia saginata (tapeworm) Taeniasis Rob nutrition Taenia soleum (tapeworm) Taeniasis Rob nutrition Vampyrolepis (tapeworm) Worm Infection Seizures (Brain) Hymenolepis nana and H. diminuta (tapeworm) Worm Infection Seizures (Brain) 97
Helminth Associated disease Effect Ascaris lubricoides (Ascarid) Ascariasis Rob nutrition, Intestinal blockage, Mortality Ancylostoma duodenale (hookworm) Hookworm Anemia, hemorrhage intestines Necator americanus (hookworm) Necatoriasis Anemia, hemorrhage intestines Trichuris trichiuia (whipworm) Trichuriasis Rob nutrition Toxocara (roundworm) Toxocariasis Rob nutrition Taenia saginata (tapeworm) Taeniasis Rob nutrition Taenia soleum (tapeworm) Taeniasis Rob nutrition Vampyrolepis (tapeworm) Worm Infection Seizures (Brain) Hymenolepis nana and H. diminuta (tapeworm) Worm Infection Seizures (Brain) 97
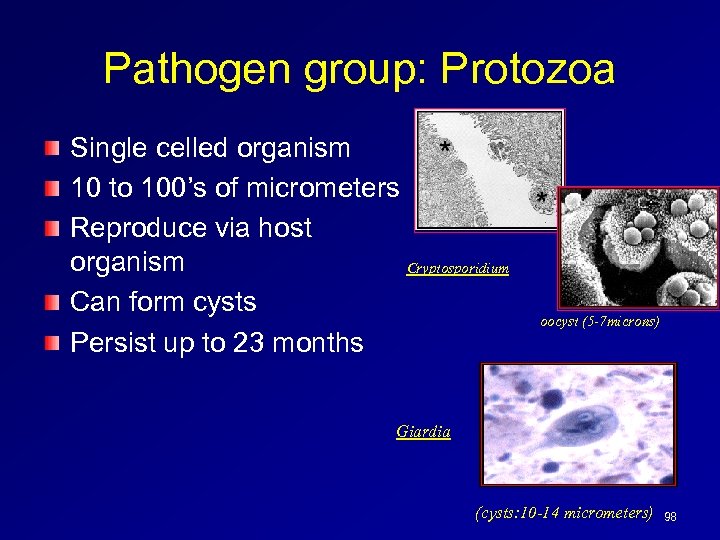 Pathogen group: Protozoa Single celled organism 10 to 100’s of micrometers Reproduce via host organism Cryptosporidium Can form cysts Persist up to 23 months oocyst (5 -7 microns) Giardia (cysts: 10 -14 micrometers) 98
Pathogen group: Protozoa Single celled organism 10 to 100’s of micrometers Reproduce via host organism Cryptosporidium Can form cysts Persist up to 23 months oocyst (5 -7 microns) Giardia (cysts: 10 -14 micrometers) 98
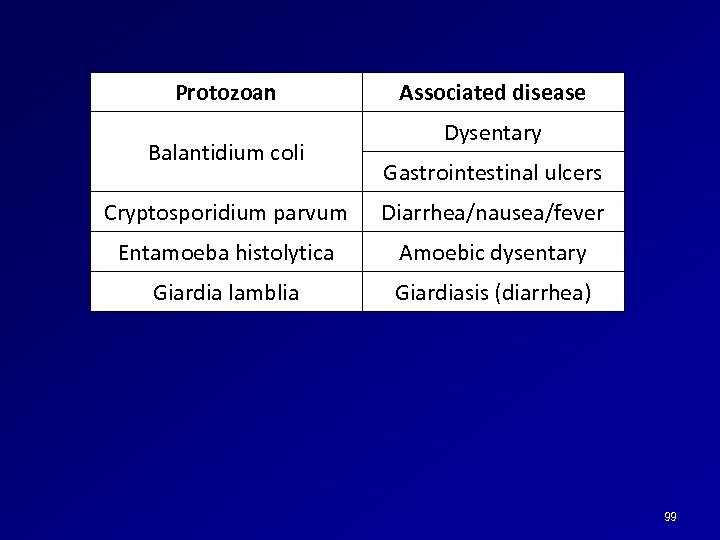 Protozoan Balantidium coli Associated disease Dysentary Gastrointestinal ulcers Cryptosporidium parvum Diarrhea/nausea/fever Entamoeba histolytica Amoebic dysentary Giardia lamblia Giardiasis (diarrhea) 99
Protozoan Balantidium coli Associated disease Dysentary Gastrointestinal ulcers Cryptosporidium parvum Diarrhea/nausea/fever Entamoeba histolytica Amoebic dysentary Giardia lamblia Giardiasis (diarrhea) 99
 Special focus on Crypto Extremely persistent – nearly 2 years Resistant to disinfection Short Life Cycle: <1 day life cycle within one host Many (fecal – oral) routes of infection – – – – Day care (diaper changing rules) Family Drinking water Contact with infected animals Contaminated food (e. g. Cider, lettuce, chicken salad) Contaminated soils (risk assessment USGS) Recreational water (Pools, fountains, water slides…) 100
Special focus on Crypto Extremely persistent – nearly 2 years Resistant to disinfection Short Life Cycle: <1 day life cycle within one host Many (fecal – oral) routes of infection – – – – Day care (diaper changing rules) Family Drinking water Contact with infected animals Contaminated food (e. g. Cider, lettuce, chicken salad) Contaminated soils (risk assessment USGS) Recreational water (Pools, fountains, water slides…) 100
 Crypto Largest waterborne illness outbreak – Wisconsin in 1993 – Flood-contaminated drinking water Toll – 400, 000 infected – 4, 000 people (1%) hospitalized – 104 died 101
Crypto Largest waterborne illness outbreak – Wisconsin in 1993 – Flood-contaminated drinking water Toll – 400, 000 infected – 4, 000 people (1%) hospitalized – 104 died 101
 Crypto Host list is growing – Humans, cattle, swine, geese, oysters High mortality especially if immunocompromised No effective cure 102
Crypto Host list is growing – Humans, cattle, swine, geese, oysters High mortality especially if immunocompromised No effective cure 102
 Pathogens in Wastewater Any pathogen in fecal material can be present in wastewater! Estimated viruses concentrations in septic tanks – Range from 107 to 1010 virus particles per liter of wastewater if residents are ill Canter and Knox (1985) and Charles et al. (2003)
Pathogens in Wastewater Any pathogen in fecal material can be present in wastewater! Estimated viruses concentrations in septic tanks – Range from 107 to 1010 virus particles per liter of wastewater if residents are ill Canter and Knox (1985) and Charles et al. (2003)
 Wastewater pathogens Septic tank provides limited pathogen inactivation Effluent – – – Fecal Coliform counts 5 X 10 6/liter Bacteria can reproduce here Some viruses not significantly inactivated Sludge – Protozoan/ worm eggs attached to floc 104
Wastewater pathogens Septic tank provides limited pathogen inactivation Effluent – – – Fecal Coliform counts 5 X 10 6/liter Bacteria can reproduce here Some viruses not significantly inactivated Sludge – Protozoan/ worm eggs attached to floc 104
 Limited documentation of health effects from onsite systems TYPICALLY, there is something wrong if exposure occurs – Surfacing effluent – Inadequate separation – Improper installation and leaking components 105
Limited documentation of health effects from onsite systems TYPICALLY, there is something wrong if exposure occurs – Surfacing effluent – Inadequate separation – Improper installation and leaking components 105
 Improperly managed wastewater treatment systems May contaminate – Drinking Water – Recreational Water – Irrigation Water – Food – Land – Environmental Surfaces – Air (as aerosols)
Improperly managed wastewater treatment systems May contaminate – Drinking Water – Recreational Water – Irrigation Water – Food – Land – Environmental Surfaces – Air (as aerosols)
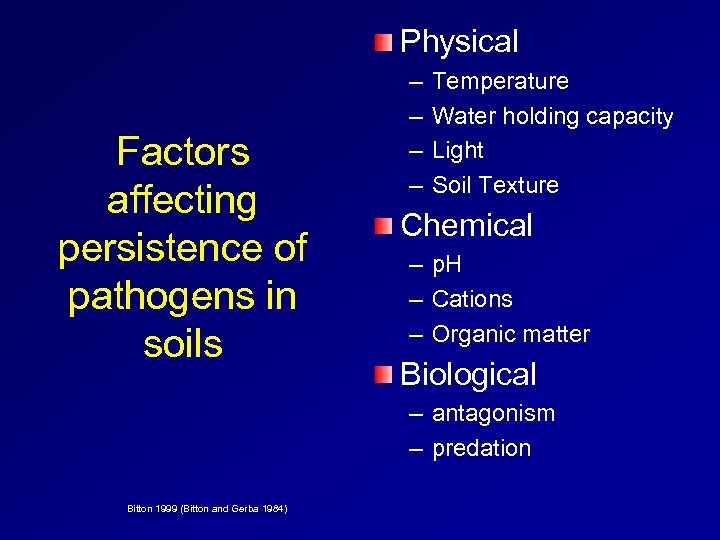 Physical Factors affecting persistence of pathogens in soils – – Temperature Water holding capacity Light Soil Texture Chemical – – – p. H Cations Organic matter Biological – antagonism – predation Bitton 1999 (Bitton and Gerba 1984)
Physical Factors affecting persistence of pathogens in soils – – Temperature Water holding capacity Light Soil Texture Chemical – – – p. H Cations Organic matter Biological – antagonism – predation Bitton 1999 (Bitton and Gerba 1984)
 Pathogen persistence in biological aerosols Travel – Initial shock and desiccation – Slow decline thereafter Specific characteristics • Viruses – enteroviruses hardier than bacteria or coliphages • Bacteria - encapsulated survive better than nonencapsulated • Fungal - can travel great distances (Aspergillus) (Bitton, 1999) 108
Pathogen persistence in biological aerosols Travel – Initial shock and desiccation – Slow decline thereafter Specific characteristics • Viruses – enteroviruses hardier than bacteria or coliphages • Bacteria - encapsulated survive better than nonencapsulated • Fungal - can travel great distances (Aspergillus) (Bitton, 1999) 108
 Environmental survival factors on surfaces Attachment of viruses and bacteria Moisture Temperature Presence of organic matter food source
Environmental survival factors on surfaces Attachment of viruses and bacteria Moisture Temperature Presence of organic matter food source
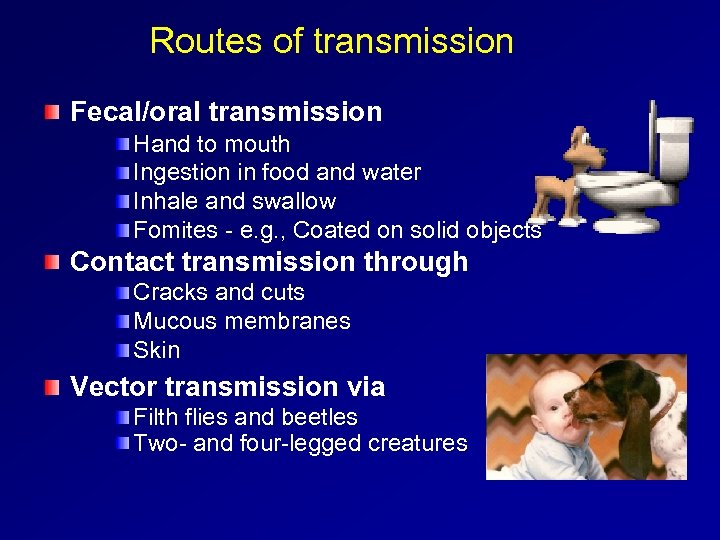 Routes of transmission Fecal/oral transmission Hand to mouth Ingestion in food and water Inhale and swallow Fomites - e. g. , Coated on solid objects Contact transmission through Cracks and cuts Mucous membranes Skin Vector transmission via Filth flies and beetles Two- and four-legged creatures
Routes of transmission Fecal/oral transmission Hand to mouth Ingestion in food and water Inhale and swallow Fomites - e. g. , Coated on solid objects Contact transmission through Cracks and cuts Mucous membranes Skin Vector transmission via Filth flies and beetles Two- and four-legged creatures
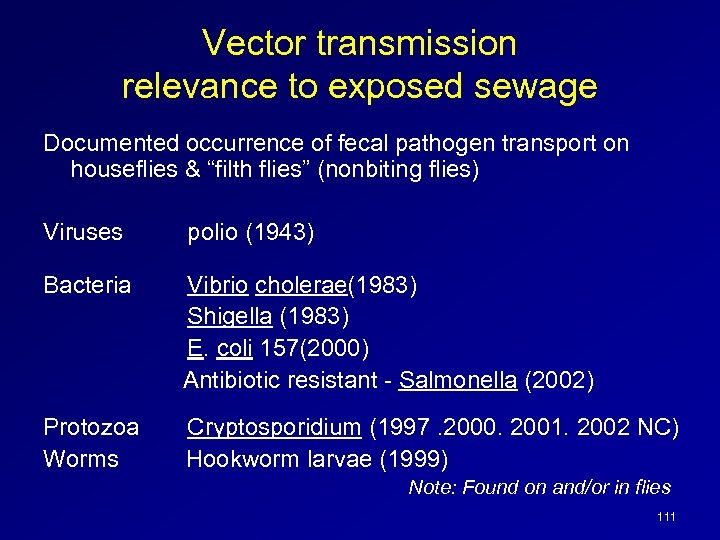 Vector transmission relevance to exposed sewage Documented occurrence of fecal pathogen transport on houseflies & “filth flies” (nonbiting flies) Viruses polio (1943) Bacteria Vibrio cholerae(1983) Shigella (1983) E. coli 157(2000) Antibiotic resistant - Salmonella (2002) Protozoa Worms Cryptosporidium (1997. 2000. 2001. 2002 NC) Hookworm larvae (1999) Note: Found on and/or in flies 111
Vector transmission relevance to exposed sewage Documented occurrence of fecal pathogen transport on houseflies & “filth flies” (nonbiting flies) Viruses polio (1943) Bacteria Vibrio cholerae(1983) Shigella (1983) E. coli 157(2000) Antibiotic resistant - Salmonella (2002) Protozoa Worms Cryptosporidium (1997. 2000. 2001. 2002 NC) Hookworm larvae (1999) Note: Found on and/or in flies 111
 Occurrence of wastewaterrelated illness Pathogen must be present in the population to be present in the wastewater It must survive the treatment process and persist in the environment In a susceptible host population Exposure at the infectious dose range
Occurrence of wastewaterrelated illness Pathogen must be present in the population to be present in the wastewater It must survive the treatment process and persist in the environment In a susceptible host population Exposure at the infectious dose range
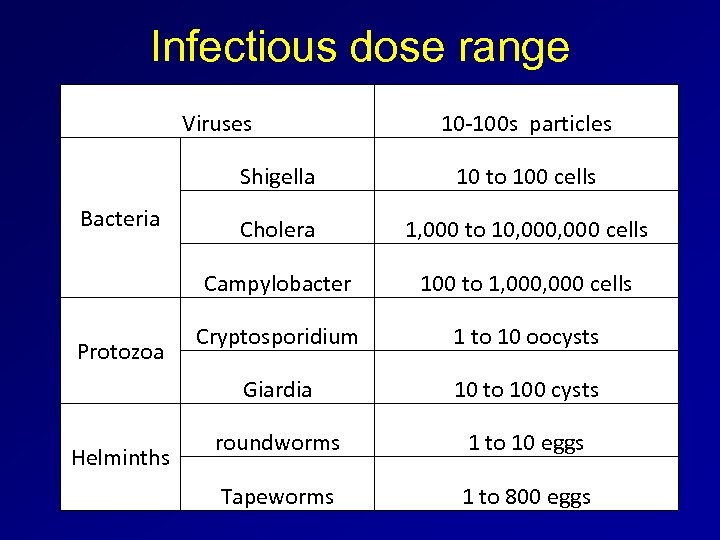 Infectious dose range Viruses 10 -100 s particles Shigella Helminths 1, 000 to 10, 000 cells 100 to 1, 000 cells Cryptosporidium 1 to 10 oocysts Giardia Protozoa Cholera Campylobacter Bacteria 10 to 100 cells 10 to 100 cysts roundworms 1 to 10 eggs Tapeworms 1 to 800 eggs
Infectious dose range Viruses 10 -100 s particles Shigella Helminths 1, 000 to 10, 000 cells 100 to 1, 000 cells Cryptosporidium 1 to 10 oocysts Giardia Protozoa Cholera Campylobacter Bacteria 10 to 100 cells 10 to 100 cysts roundworms 1 to 10 eggs Tapeworms 1 to 800 eggs
 Occupational health issues Inexperienced people working in sewagerelated jobs 2 -4 times higher rate of gastrointestinal illnesses Higher viral antibody titers
Occupational health issues Inexperienced people working in sewagerelated jobs 2 -4 times higher rate of gastrointestinal illnesses Higher viral antibody titers
 Occupational health issues In general, WWTP workers Viral, bacterial, and chronic helminth infestations Well-documented risk for Hepatitis A & Leptospirosis Inconsistent results for parasites Increase in nonspecific illnesses – nausea, fatigue, headaches…. More dermatological complaints Respiratory – allergens – biosolids – insects Urine mutagens higher in ST workers
Occupational health issues In general, WWTP workers Viral, bacterial, and chronic helminth infestations Well-documented risk for Hepatitis A & Leptospirosis Inconsistent results for parasites Increase in nonspecific illnesses – nausea, fatigue, headaches…. More dermatological complaints Respiratory – allergens – biosolids – insects Urine mutagens higher in ST workers
 Protect yourself, your co-workers and your family – Vaccinations – No regulations but probably LHD requirements – At a minimum, Tetanus – Probably Hepatitis – Do Not Wear contaminated clothing home if possible – If you do, wash it separately
Protect yourself, your co-workers and your family – Vaccinations – No regulations but probably LHD requirements – At a minimum, Tetanus – Probably Hepatitis – Do Not Wear contaminated clothing home if possible – If you do, wash it separately
 Now that we have your attention… Let’s wrap it up!
Now that we have your attention… Let’s wrap it up!
 Safety as a State of Mind There is no substitute for common sense. Ø Be aware of potential hazards ü Stay alert ü Be prepared ü Have and use proper equipment ü Practice good safety habits ü Get good information and training 119
Safety as a State of Mind There is no substitute for common sense. Ø Be aware of potential hazards ü Stay alert ü Be prepared ü Have and use proper equipment ü Practice good safety habits ü Get good information and training 119
 Safety resources NC Safety Handbook OSHA CDC 120
Safety resources NC Safety Handbook OSHA CDC 120
 Staying safe: SIPDE Scan Identify Predict Decide Execute
Staying safe: SIPDE Scan Identify Predict Decide Execute
 Safety FIRST, never last. Have a future, not a past.
Safety FIRST, never last. Have a future, not a past.
 Questions?
Questions?


