6110c5dc814cef1dc2338dcf1113463a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 26
 Recycling polypropylene carpets In association with Carpet Recycling UK Funded by Envirolink Northwest Jane Gardner
Recycling polypropylene carpets In association with Carpet Recycling UK Funded by Envirolink Northwest Jane Gardner
 Presentation Summary • • • Project aims Types of carpet Current recycling routes Demonstration trial results Economic assessment Project conclusions
Presentation Summary • • • Project aims Types of carpet Current recycling routes Demonstration trial results Economic assessment Project conclusions
 Project aims • To develop a process for recycling polypropylene carpets • To assess commercial viability of the process
Project aims • To develop a process for recycling polypropylene carpets • To assess commercial viability of the process
 UK Carpet sustainability • Over half a million tonnes/year of carpet enters the UK waste stream • Recycling rate currently less than 2% • Carpets have high carbon footprint due to use of virgin materials – big sustainability gain if recycled
UK Carpet sustainability • Over half a million tonnes/year of carpet enters the UK waste stream • Recycling rate currently less than 2% • Carpets have high carbon footprint due to use of virgin materials – big sustainability gain if recycled
 Carpet materials • Polymers: – – Polypropylene (PP); Polyester/Polyethylene terephthalate (PET); Nylon; Chalk-filled elastomers; • Natural fibres: – Wool; and – Hessian/Jute.
Carpet materials • Polymers: – – Polypropylene (PP); Polyester/Polyethylene terephthalate (PET); Nylon; Chalk-filled elastomers; • Natural fibres: – Wool; and – Hessian/Jute.
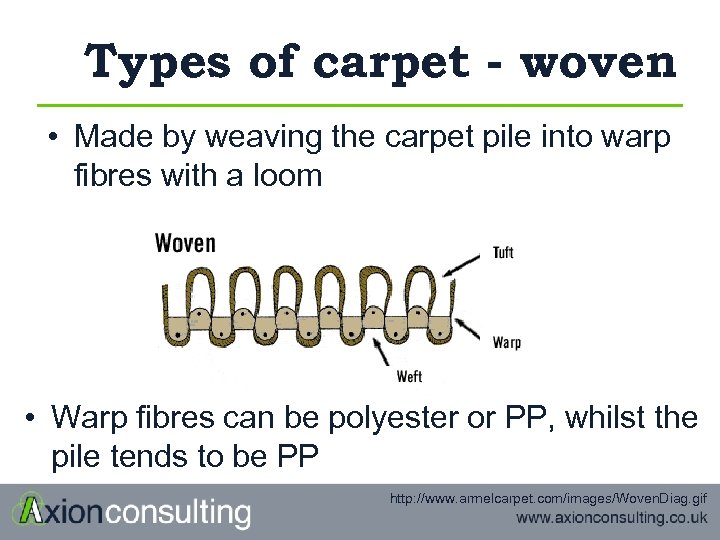 Types of carpet - woven • Made by weaving the carpet pile into warp fibres with a loom • Warp fibres can be polyester or PP, whilst the pile tends to be PP http: //www. armelcarpet. com/images/Woven. Diag. gif
Types of carpet - woven • Made by weaving the carpet pile into warp fibres with a loom • Warp fibres can be polyester or PP, whilst the pile tends to be PP http: //www. armelcarpet. com/images/Woven. Diag. gif
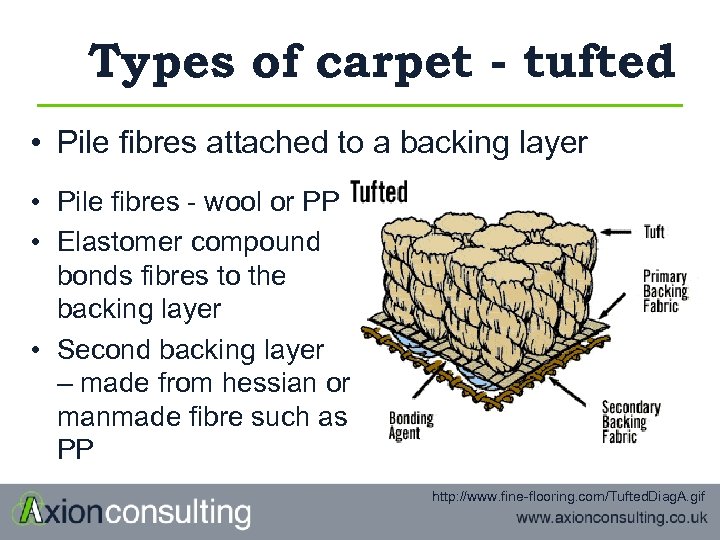 Types of carpet - tufted • Pile fibres attached to a backing layer • Pile fibres - wool or PP • Elastomer compound bonds fibres to the backing layer • Second backing layer – made from hessian or manmade fibre such as PP http: //www. fine-flooring. com/Tufted. Diag. A. gif
Types of carpet - tufted • Pile fibres attached to a backing layer • Pile fibres - wool or PP • Elastomer compound bonds fibres to the backing layer • Second backing layer – made from hessian or manmade fibre such as PP http: //www. fine-flooring. com/Tufted. Diag. A. gif
 Carpet recycling initiatives America: • CARE – Carpet America Recovery Effort – founded 2002 Europe – late 1990’s: • RECAM - Recovery of Carpet Materials • CRE - Carpet Recycling Europe • Polyamid 2000 in Germany UK – late 2000’s: • Greenback Recycling • Reeds Carpets – exhibition/temporary floors
Carpet recycling initiatives America: • CARE – Carpet America Recovery Effort – founded 2002 Europe – late 1990’s: • RECAM - Recovery of Carpet Materials • CRE - Carpet Recycling Europe • Polyamid 2000 in Germany UK – late 2000’s: • Greenback Recycling • Reeds Carpets – exhibition/temporary floors
 Existing end markets • Typically low value • Equestrian surfaces – additive to sand based all weather surfaces • Plastic cannot be recovered once used as equestrian surface • Other applications: • Horticultural market http: //www. equestriansurfaces. co. uk/aboutus. html
Existing end markets • Typically low value • Equestrian surfaces – additive to sand based all weather surfaces • Plastic cannot be recovered once used as equestrian surface • Other applications: • Horticultural market http: //www. equestriansurfaces. co. uk/aboutus. html
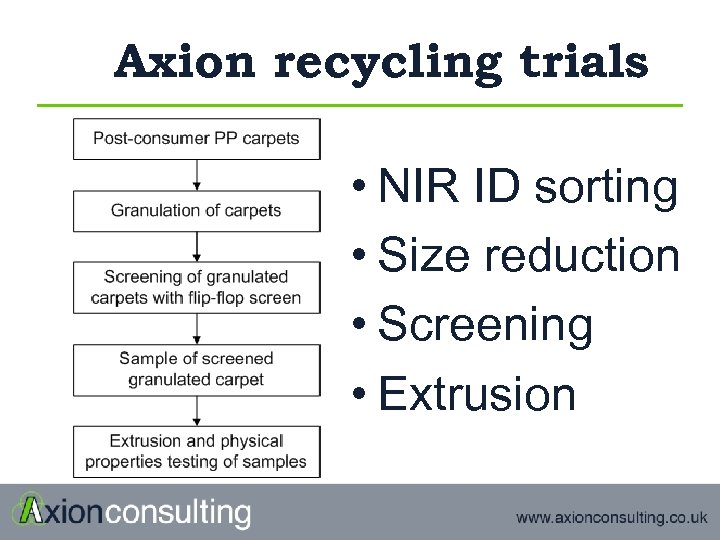 Axion recycling trials • NIR ID sorting • Size reduction • Screening • Extrusion
Axion recycling trials • NIR ID sorting • Size reduction • Screening • Extrusion
 Size reduction • Granulation – 15 mm screen • Alternative options: – Shearing – Shredding
Size reduction • Granulation – 15 mm screen • Alternative options: – Shearing – Shredding
 Granulated PP carpet
Granulated PP carpet
 Screen to remove dust, fines • High energy flip-flop screen • 12 x 12 mm deck • Alternative technique – dry cleaning
Screen to remove dust, fines • High energy flip-flop screen • 12 x 12 mm deck • Alternative technique – dry cleaning
 Screening results Target fraction Non-target fraction Losses Oversized Undersized - 38% 59% 3% • Oversized fraction cleaner and less dusty than feed • High yield loss - due to screen size of granulator (15 mm) relative to flip-flop (12 mm) • For 12 mm flip-flop - granulator needs to be 20 -25 mm • For 15 mm granulator screen - flip-flop needs to be 68 mm
Screening results Target fraction Non-target fraction Losses Oversized Undersized - 38% 59% 3% • Oversized fraction cleaner and less dusty than feed • High yield loss - due to screen size of granulator (15 mm) relative to flip-flop (12 mm) • For 12 mm flip-flop - granulator needs to be 20 -25 mm • For 15 mm granulator screen - flip-flop needs to be 68 mm
 Lab scale extrusion • Sorted PP carpet samples: – Post industrial – Post consumer • Material prepared for extrusion by partial melting then granulation
Lab scale extrusion • Sorted PP carpet samples: – Post industrial – Post consumer • Material prepared for extrusion by partial melting then granulation
 Extrusion problems • Initial batch of carpets could not be extruded • Presence of un-melted fibres made from different polymers – nylon and PET • Problem due to different types of carpet – woven and tufted • Second batch of tufted carpet processed successfully
Extrusion problems • Initial batch of carpets could not be extruded • Presence of un-melted fibres made from different polymers – nylon and PET • Problem due to different types of carpet – woven and tufted • Second batch of tufted carpet processed successfully
 Moulded polymer • Post industrial – injection moulding applications • Post consumer – lower grade injection moulding, for example plant pots and buckets
Moulded polymer • Post industrial – injection moulding applications • Post consumer – lower grade injection moulding, for example plant pots and buckets
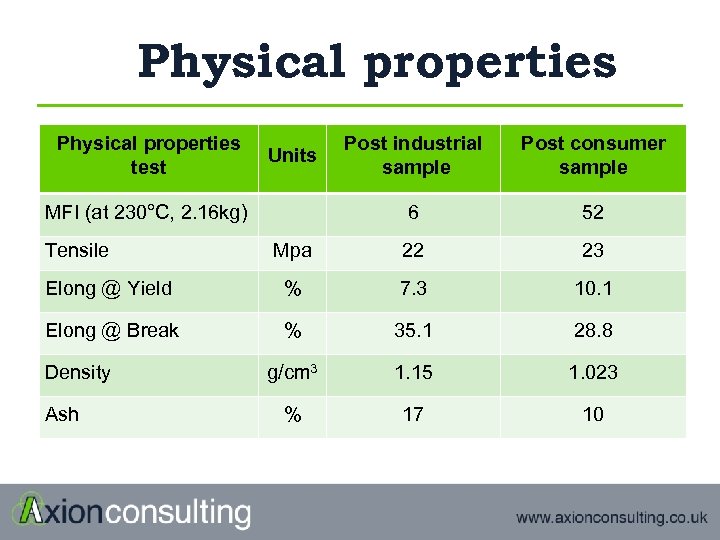 Physical properties test Post industrial sample Post consumer sample 6 52 Mpa 22 23 Elong @ Yield % 7. 3 10. 1 Elong @ Break % 35. 1 28. 8 g/cm 3 1. 15 1. 023 % 17 10 Units MFI (at 230°C, 2. 16 kg) Tensile Density Ash
Physical properties test Post industrial sample Post consumer sample 6 52 Mpa 22 23 Elong @ Yield % 7. 3 10. 1 Elong @ Break % 35. 1 28. 8 g/cm 3 1. 15 1. 023 % 17 10 Units MFI (at 230°C, 2. 16 kg) Tensile Density Ash
 Commercial assessment • Feed stock in Northwest - estimated at over 6, 000 tonnes per annum meeting specification of: – Tufted construction; – Positively identified PP pile and backing fibres; – Dry and with no heavy contamination; – Suitable for manual handling.
Commercial assessment • Feed stock in Northwest - estimated at over 6, 000 tonnes per annum meeting specification of: – Tufted construction; – Positively identified PP pile and backing fibres; – Dry and with no heavy contamination; – Suitable for manual handling.
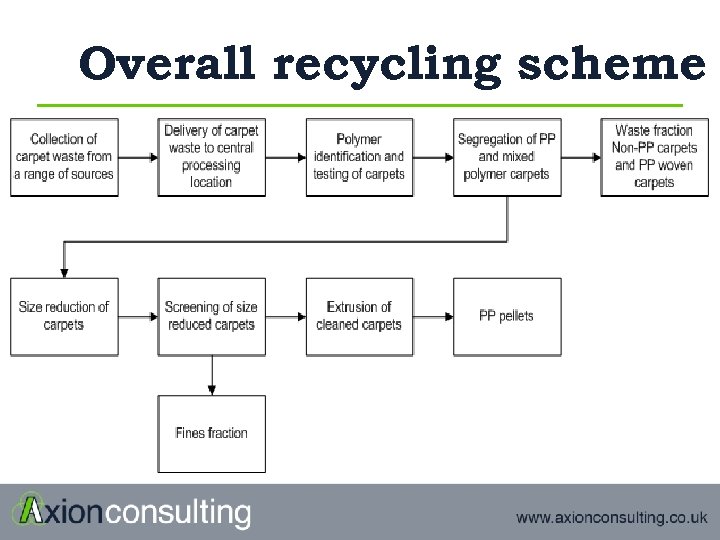 Overall recycling scheme
Overall recycling scheme
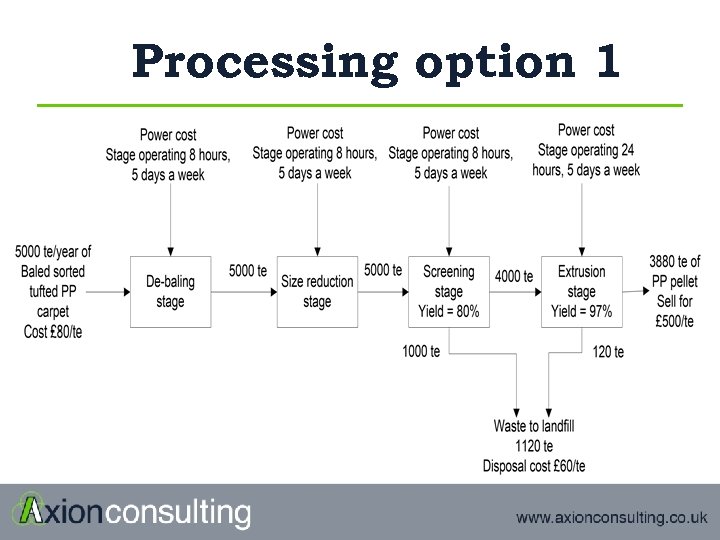 Processing option 1
Processing option 1
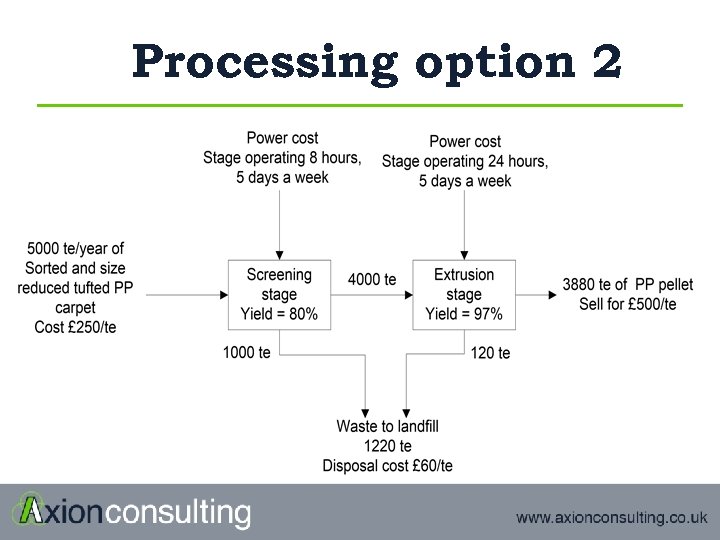 Processing option 2
Processing option 2
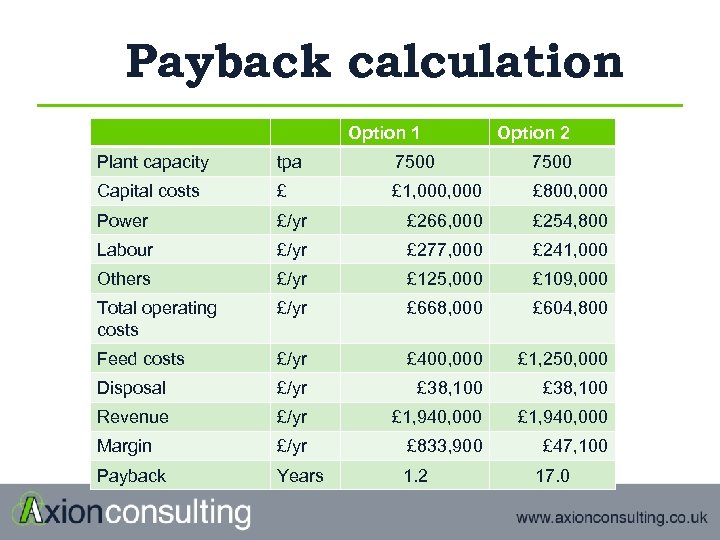 Payback calculation Option 1 Option 2 Plant capacity tpa 7500 Capital costs £ £ 1, 000 £ 800, 000 Power £/yr £ 266, 000 £ 254, 800 Labour £/yr £ 277, 000 £ 241, 000 Others £/yr £ 125, 000 £ 109, 000 Total operating costs £/yr £ 668, 000 £ 604, 800 Feed costs £/yr £ 400, 000 £ 1, 250, 000 Disposal £/yr £ 38, 100 Revenue £/yr £ 1, 940, 000 Margin £/yr £ 833, 900 £ 47, 100 Payback Years 1. 2 17. 0
Payback calculation Option 1 Option 2 Plant capacity tpa 7500 Capital costs £ £ 1, 000 £ 800, 000 Power £/yr £ 266, 000 £ 254, 800 Labour £/yr £ 277, 000 £ 241, 000 Others £/yr £ 125, 000 £ 109, 000 Total operating costs £/yr £ 668, 000 £ 604, 800 Feed costs £/yr £ 400, 000 £ 1, 250, 000 Disposal £/yr £ 38, 100 Revenue £/yr £ 1, 940, 000 Margin £/yr £ 833, 900 £ 47, 100 Payback Years 1. 2 17. 0
 Technical conclusions • Straight forward processing route: – Rigorous PP identification and sorting – Size reduction – Screening – Extrusion • Finished PP: – Good physical properties, – Suitable for use in medium to low grade applications, Eg injection moulded plant pots
Technical conclusions • Straight forward processing route: – Rigorous PP identification and sorting – Size reduction – Screening – Extrusion • Finished PP: – Good physical properties, – Suitable for use in medium to low grade applications, Eg injection moulded plant pots
 Commercial conclusions • Critical success factor - correct identification of all polymer fibres within the carpet • Economics of the recycling process are promising • Next step: Commercial scale testing
Commercial conclusions • Critical success factor - correct identification of all polymer fibres within the carpet • Economics of the recycling process are promising • Next step: Commercial scale testing
 Axion Consulting Tudor House Meadway Bramhall SK 2 2 DG 0161 426 7731 info@axionconsulting. co. uk
Axion Consulting Tudor House Meadway Bramhall SK 2 2 DG 0161 426 7731 info@axionconsulting. co. uk


