9eaa46a5e8a6ba9e5858e66f5f229e2e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 51
 Recurrent Pregnancy Loss-LPD Dr. USHA REDDY MRCOG
Recurrent Pregnancy Loss-LPD Dr. USHA REDDY MRCOG
 WHY LPD ?
WHY LPD ?
 Abortion & Infertility Profound personal tragedy a formidable challenge to physician.
Abortion & Infertility Profound personal tragedy a formidable challenge to physician.
 Human Reproduction Woefully inefficient 15 % of ova exposed to sperm fail to divide 15% fail to implant & 41% of implanted pregnancy are lost 41% implanted pregnancy are lost of which 2/3 after Hcg secretion and 1/3 even before Thus finally only 30% → Viable Preganancy
Human Reproduction Woefully inefficient 15 % of ova exposed to sperm fail to divide 15% fail to implant & 41% of implanted pregnancy are lost 41% implanted pregnancy are lost of which 2/3 after Hcg secretion and 1/3 even before Thus finally only 30% → Viable Preganancy
 l l Hormonal bio essays Imaging techniques Newer surgical endoscopic procedure Pharmaceutical treatment ▼ Successful management of this heterogeneous disorder and endowing the blessing of parenthood to many a despondent couple
l l Hormonal bio essays Imaging techniques Newer surgical endoscopic procedure Pharmaceutical treatment ▼ Successful management of this heterogeneous disorder and endowing the blessing of parenthood to many a despondent couple
 Spontaneous Abortion Incidence 16% of all clinically recognised pregnancies but 55% after 3 consecutive Spontaneous Abortions (in patients with Habitual/Recurrent Abortion) Vlaandeeren W 1987
Spontaneous Abortion Incidence 16% of all clinically recognised pregnancies but 55% after 3 consecutive Spontaneous Abortions (in patients with Habitual/Recurrent Abortion) Vlaandeeren W 1987
 Proposed causes of RSA l Endocrine etiologies - Luteal phase defect Thyroid dysfunction - Uncontrolled diabetes mellitus - * * * Immune-based Uterine anatomic anomalies Endometrial infections Antiphospholipid syndrome Inherited thrombophilias & Alloimmune causes Parental chromosomal abnormalities Lee RM, Silver RM 2000 Recurrent pregnancy loss: summary and clinical ecommendations. Semin Reprod Med 18: 433– 440
Proposed causes of RSA l Endocrine etiologies - Luteal phase defect Thyroid dysfunction - Uncontrolled diabetes mellitus - * * * Immune-based Uterine anatomic anomalies Endometrial infections Antiphospholipid syndrome Inherited thrombophilias & Alloimmune causes Parental chromosomal abnormalities Lee RM, Silver RM 2000 Recurrent pregnancy loss: summary and clinical ecommendations. Semin Reprod Med 18: 433– 440
 Pregnancy & Immunomodulation
Pregnancy & Immunomodulation
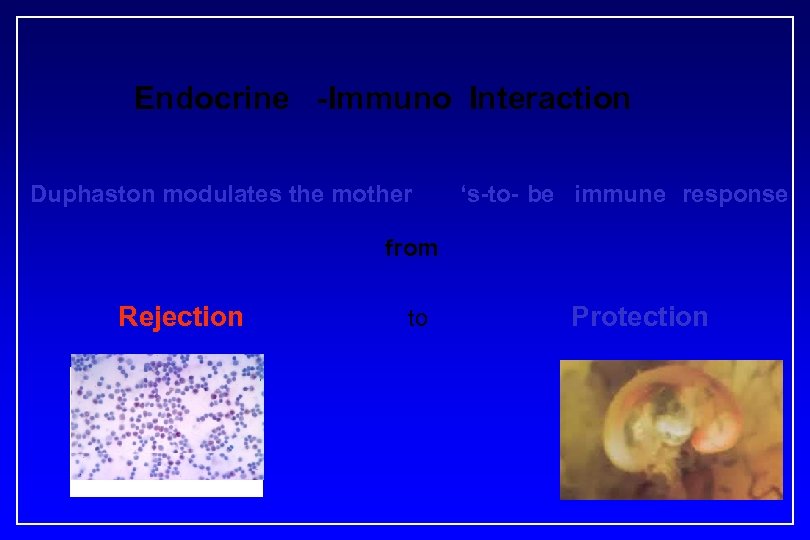 Endocrine -Immuno Interaction Duphaston modulates the mother ‘s-to- be immune response from Rejection to Protection
Endocrine -Immuno Interaction Duphaston modulates the mother ‘s-to- be immune response from Rejection to Protection
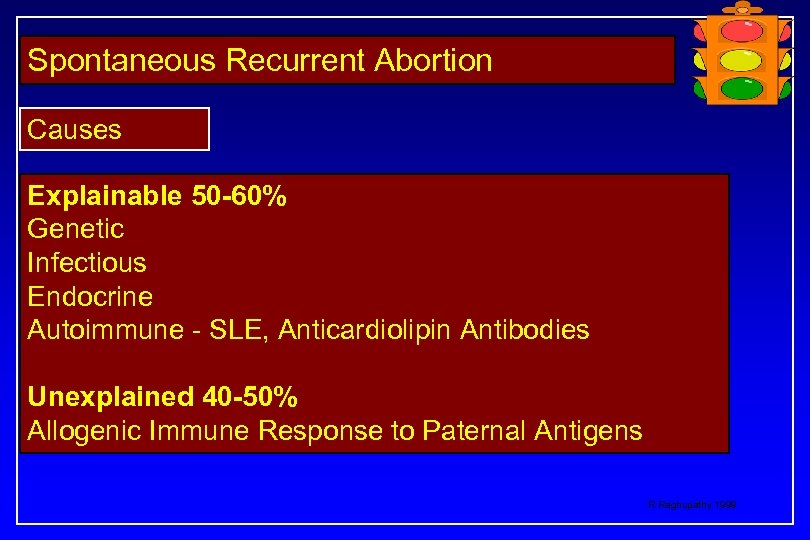 Spontaneous Recurrent Abortion Causes Explainable 50 -60% Genetic Infectious Endocrine Autoimmune - SLE, Anticardiolipin Antibodies Unexplained 40 -50% Allogenic Immune Response to Paternal Antigens R Raghupathy 1999
Spontaneous Recurrent Abortion Causes Explainable 50 -60% Genetic Infectious Endocrine Autoimmune - SLE, Anticardiolipin Antibodies Unexplained 40 -50% Allogenic Immune Response to Paternal Antigens R Raghupathy 1999
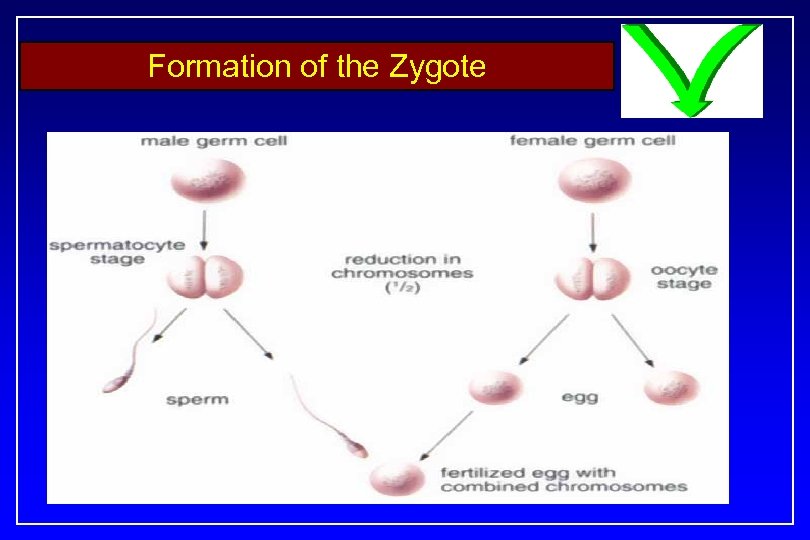 Formation of the Zygote
Formation of the Zygote
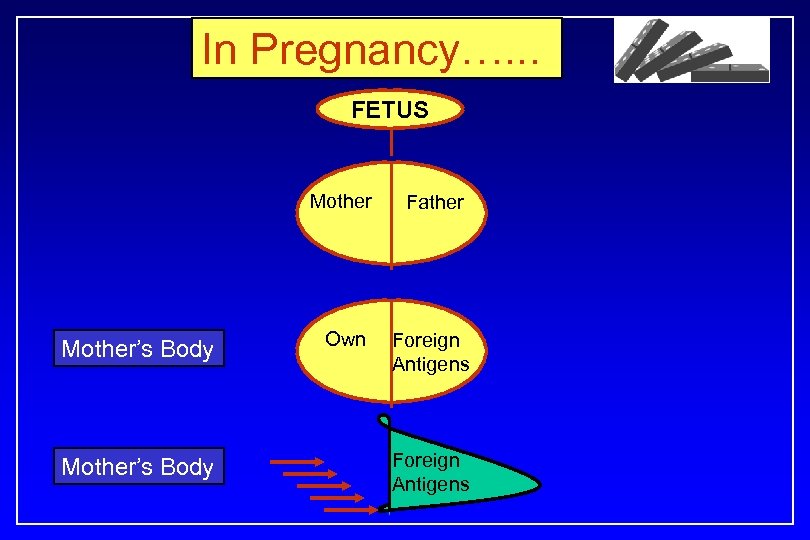 In Pregnancy…. . . FETUS Mother’s Body Father Own Foreign Antigens
In Pregnancy…. . . FETUS Mother’s Body Father Own Foreign Antigens
 We all agree that ……. Material from Father…………………. Is Foreign to Mother Therefore … Mother’s body will recognize it as An Antigen & set up an Immune reaction to Fetus
We all agree that ……. Material from Father…………………. Is Foreign to Mother Therefore … Mother’s body will recognize it as An Antigen & set up an Immune reaction to Fetus
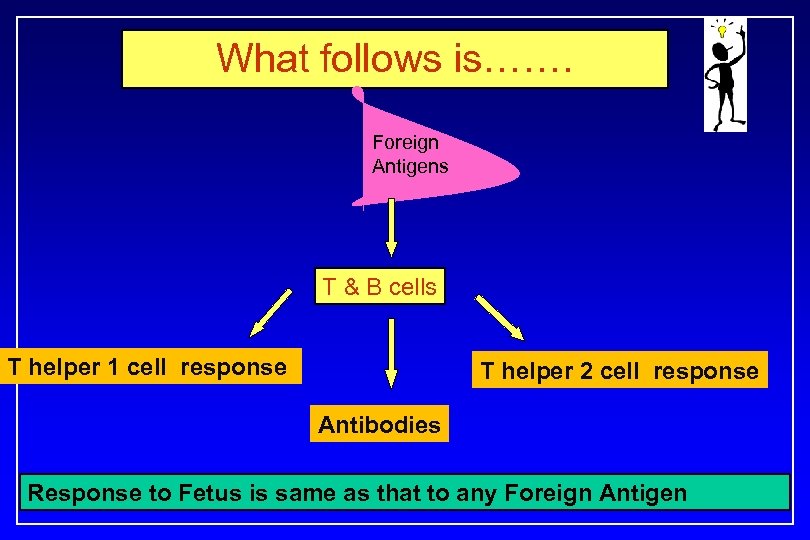 What follows is……. Foreign Antigens T & B cells T helper 1 cell response T helper 2 cell response Antibodies Response to Fetus is same as that to any Foreign Antigen
What follows is……. Foreign Antigens T & B cells T helper 1 cell response T helper 2 cell response Antibodies Response to Fetus is same as that to any Foreign Antigen
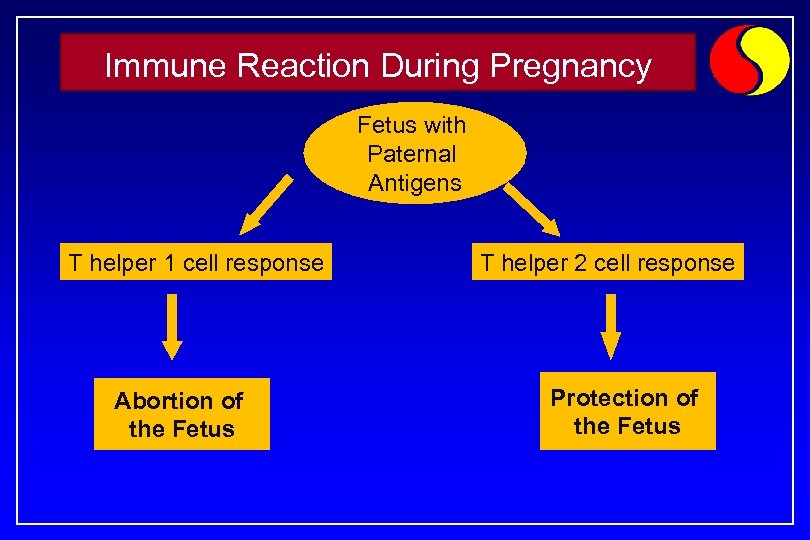 Immune Reaction During Pregnancy Fetus with Paternal Antigens T helper 1 cell response Abortion of the Fetus T helper 2 cell response Protection of the Fetus
Immune Reaction During Pregnancy Fetus with Paternal Antigens T helper 1 cell response Abortion of the Fetus T helper 2 cell response Protection of the Fetus
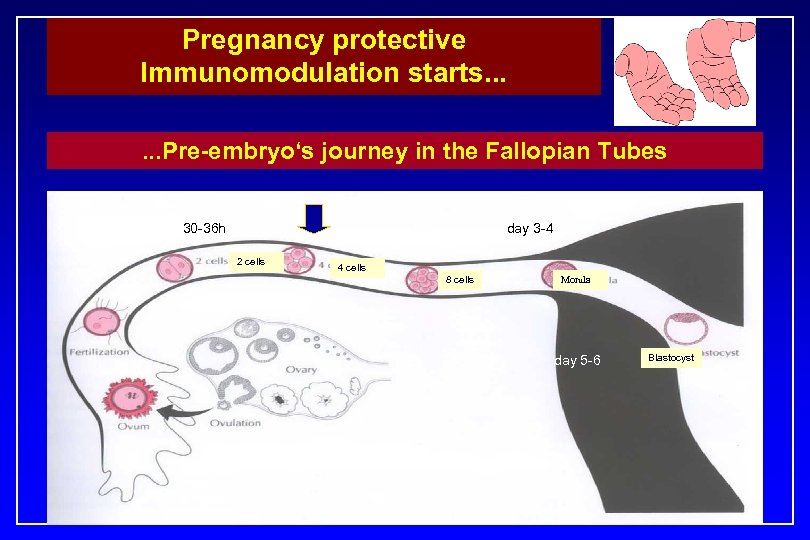 Pregnancy protective Immunomodulation starts. . . Pre-embryo‘s journey in the Fallopian Tubes 30 -36 h day 3 -4 2 cells 4 cells 8 cells Morula day 5 -6 Blastocyst
Pregnancy protective Immunomodulation starts. . . Pre-embryo‘s journey in the Fallopian Tubes 30 -36 h day 3 -4 2 cells 4 cells 8 cells Morula day 5 -6 Blastocyst
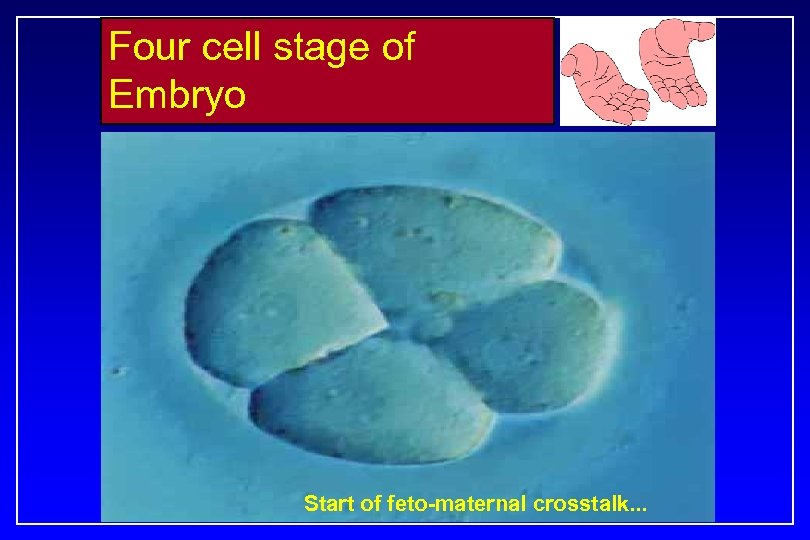 Four cell stage of Embryo Start of feto-maternal crosstalk. . .
Four cell stage of Embryo Start of feto-maternal crosstalk. . .
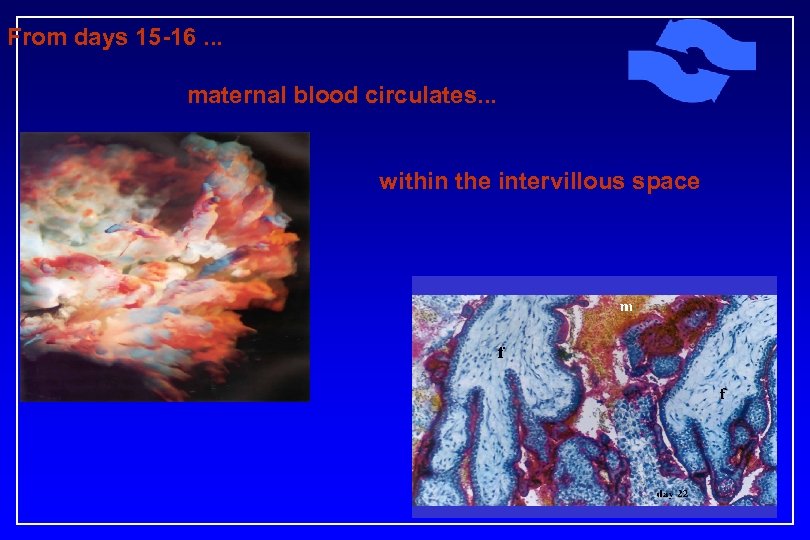 From days 15 -16. . . maternal blood circulates. . . within the intervillous space
From days 15 -16. . . maternal blood circulates. . . within the intervillous space

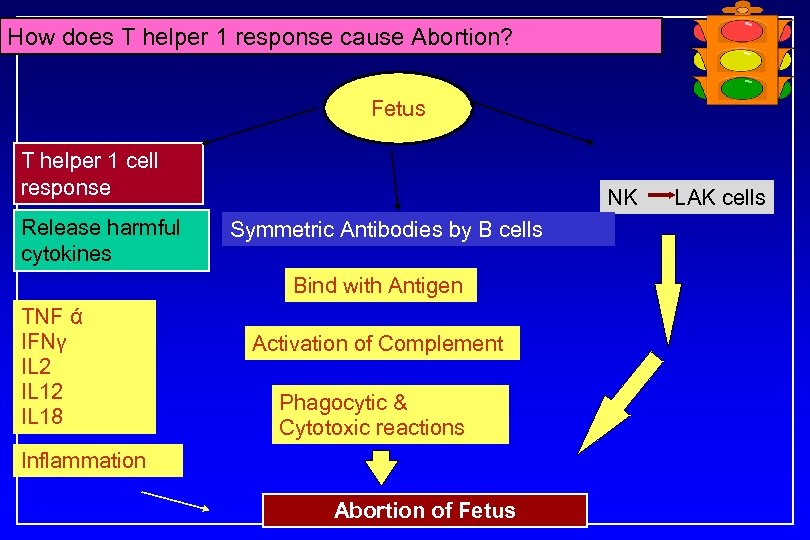 How does T helper 1 response cause Abortion? Fetus T helper 1 cell response Release harmful cytokines NK Symmetric Antibodies by B cells Bind with Antigen TNF ά IFNγ IL 2 IL 18 Activation of Complement Phagocytic & Cytotoxic reactions Inflammation Abortion of Fetus LAK cells
How does T helper 1 response cause Abortion? Fetus T helper 1 cell response Release harmful cytokines NK Symmetric Antibodies by B cells Bind with Antigen TNF ά IFNγ IL 2 IL 18 Activation of Complement Phagocytic & Cytotoxic reactions Inflammation Abortion of Fetus LAK cells
 Let us look at each of these reactions in detail now…………. .
Let us look at each of these reactions in detail now…………. .
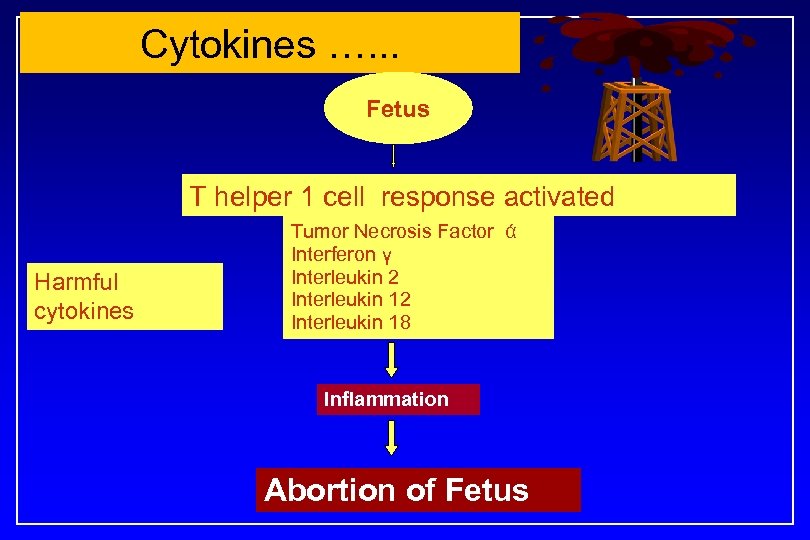 Cytokines …. . . Fetus T helper 1 cell response activated Harmful cytokines Tumor Necrosis Factor ά Interferon γ Interleukin 2 Interleukin 18 Inflammation Abortion of Fetus
Cytokines …. . . Fetus T helper 1 cell response activated Harmful cytokines Tumor Necrosis Factor ά Interferon γ Interleukin 2 Interleukin 18 Inflammation Abortion of Fetus
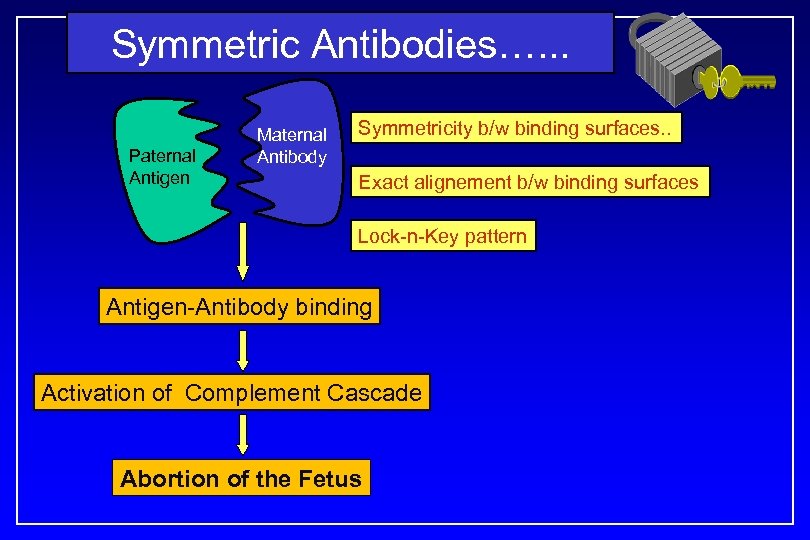 Symmetric Antibodies…. . . Paternal Antigen Maternal Antibody Symmetricity b/w binding surfaces. . Exact alignement b/w binding surfaces Lock-n-Key pattern Antigen-Antibody binding Activation of Complement Cascade Abortion of the Fetus
Symmetric Antibodies…. . . Paternal Antigen Maternal Antibody Symmetricity b/w binding surfaces. . Exact alignement b/w binding surfaces Lock-n-Key pattern Antigen-Antibody binding Activation of Complement Cascade Abortion of the Fetus
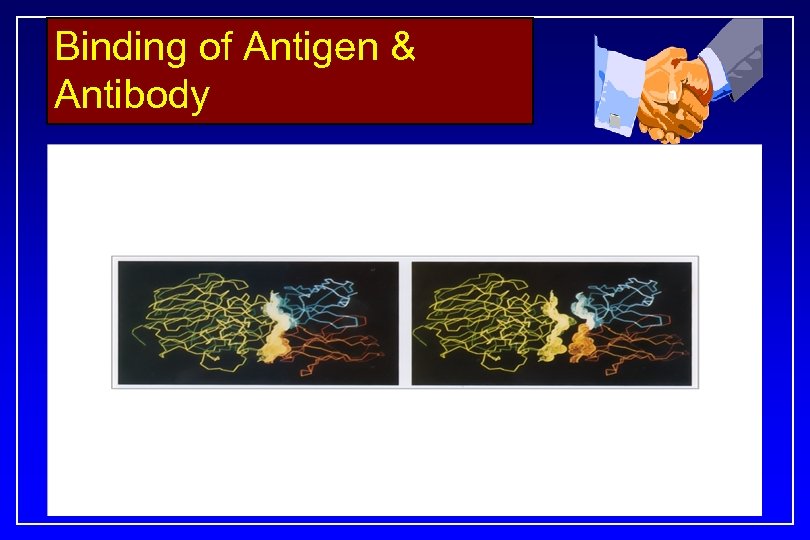 Binding of Antigen & Antibody
Binding of Antigen & Antibody
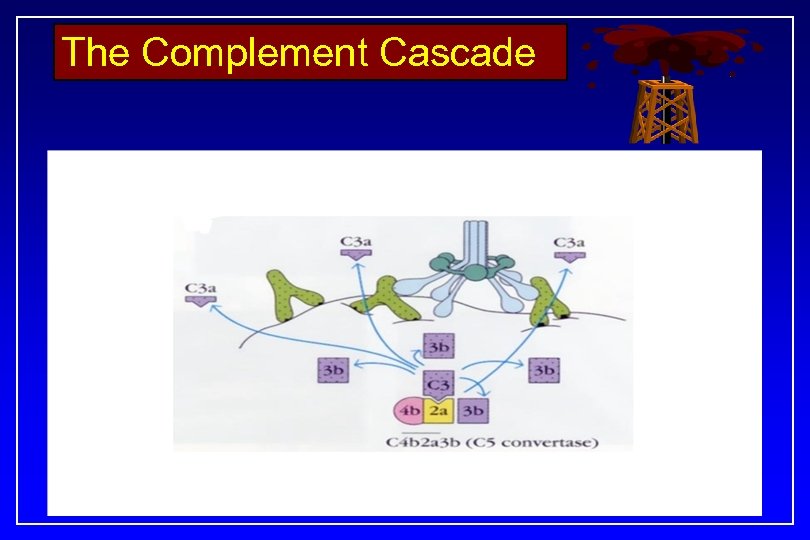 The Complement Cascade
The Complement Cascade
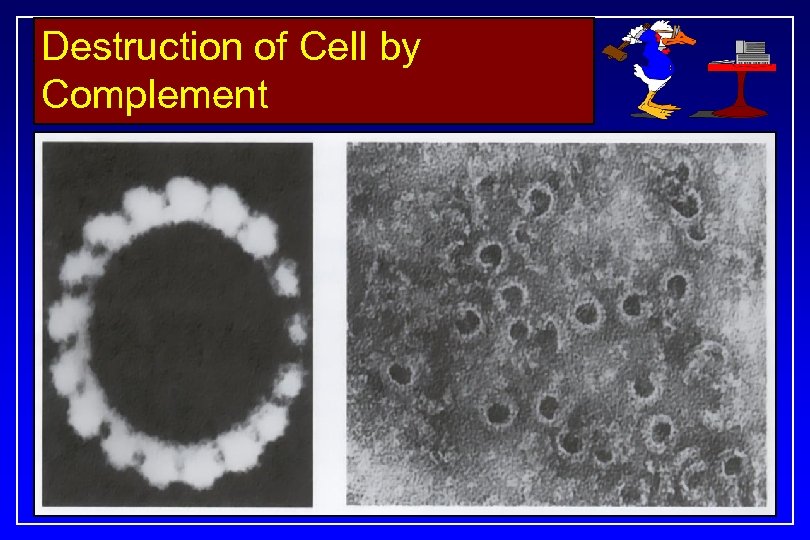 Destruction of Cell by Complement
Destruction of Cell by Complement
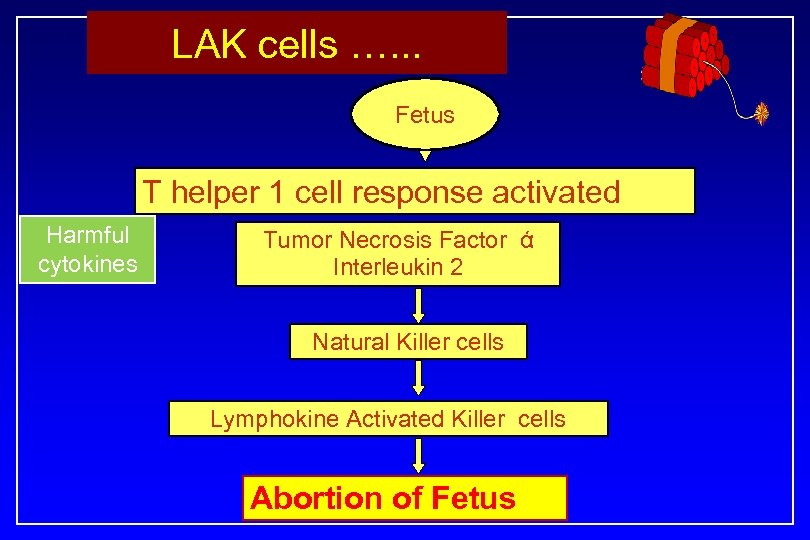 LAK cells …. . . Fetus T helper 1 cell response activated Harmful cytokines Tumor Necrosis Factor ά Interleukin 2 Natural Killer cells Lymphokine Activated Killer cells Abortion of Fetus
LAK cells …. . . Fetus T helper 1 cell response activated Harmful cytokines Tumor Necrosis Factor ά Interleukin 2 Natural Killer cells Lymphokine Activated Killer cells Abortion of Fetus
 Having shown the immune response in Abortion Let us see what happens in a successful Pregnancy
Having shown the immune response in Abortion Let us see what happens in a successful Pregnancy
 In successful Pregnancy Embryo protective Immunomodulation takes place
In successful Pregnancy Embryo protective Immunomodulation takes place
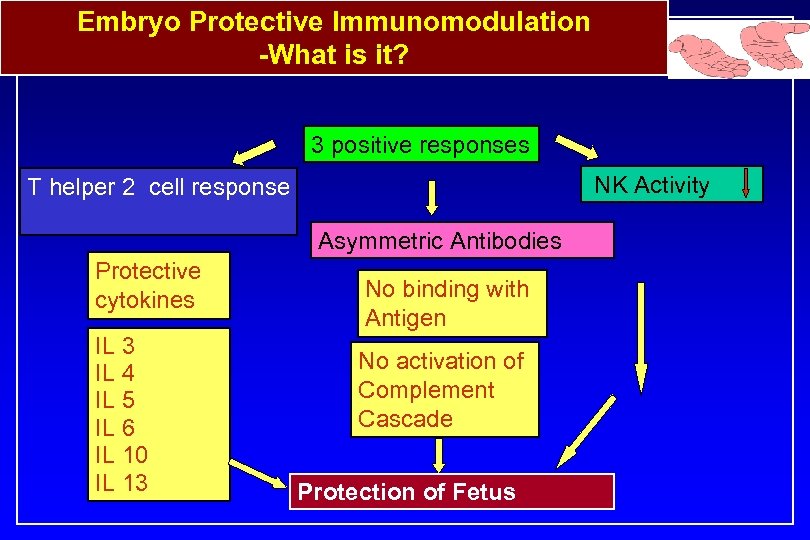 Embryo Protective Immunomodulation -What is it? 3 positive responses NK Activity T helper 2 cell response Asymmetric Antibodies Protective cytokines IL 3 IL 4 IL 5 IL 6 IL 10 IL 13 No binding with Antigen No activation of Complement Cascade Protection of Fetus
Embryo Protective Immunomodulation -What is it? 3 positive responses NK Activity T helper 2 cell response Asymmetric Antibodies Protective cytokines IL 3 IL 4 IL 5 IL 6 IL 10 IL 13 No binding with Antigen No activation of Complement Cascade Protection of Fetus
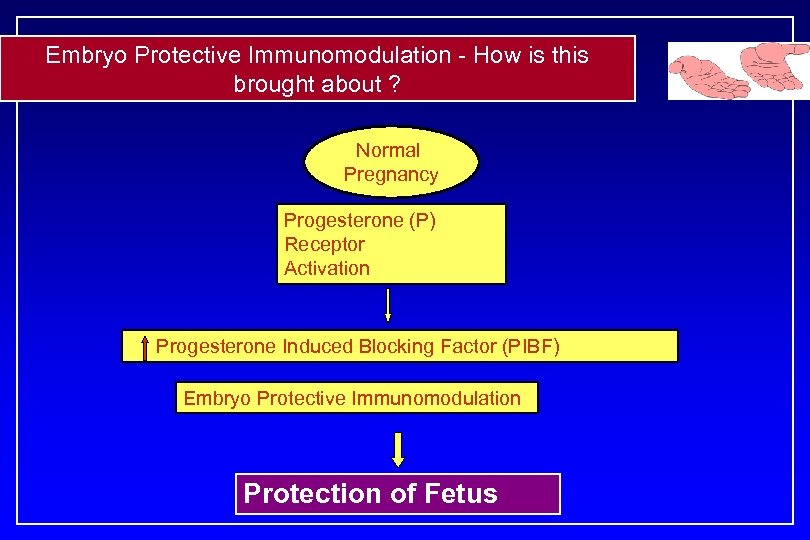 Embryo Protective Immunomodulation - How is this brought about ? Normal Pregnancy Progesterone (P) Receptor Activation Progesterone Induced Blocking Factor (PIBF) Embryo Protective Immunomodulation Protection of Fetus
Embryo Protective Immunomodulation - How is this brought about ? Normal Pregnancy Progesterone (P) Receptor Activation Progesterone Induced Blocking Factor (PIBF) Embryo Protective Immunomodulation Protection of Fetus
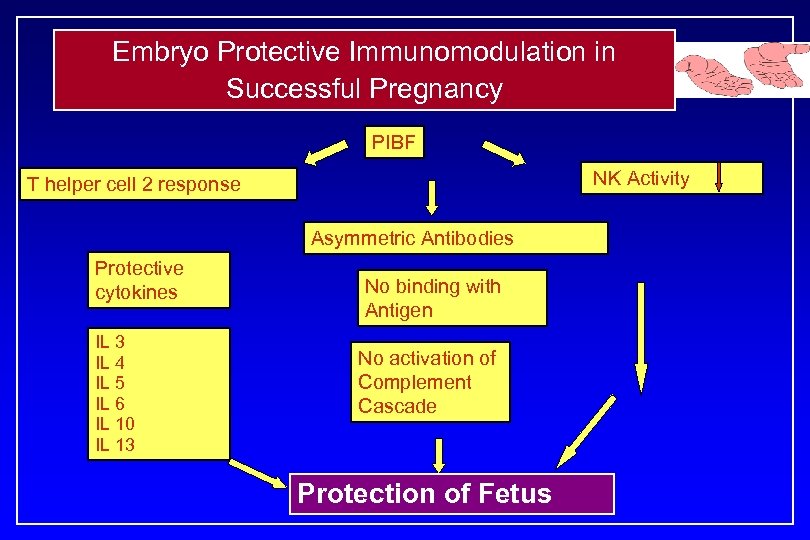 Embryo Protective Immunomodulation in Successful Pregnancy PIBF NK Activity T helper cell 2 response Asymmetric Antibodies Protective cytokines IL 3 IL 4 IL 5 IL 6 IL 10 IL 13 No binding with Antigen No activation of Complement Cascade Protection of Fetus
Embryo Protective Immunomodulation in Successful Pregnancy PIBF NK Activity T helper cell 2 response Asymmetric Antibodies Protective cytokines IL 3 IL 4 IL 5 IL 6 IL 10 IL 13 No binding with Antigen No activation of Complement Cascade Protection of Fetus
 Unfortunately …. . As we have seen …. In up to 50 % of women with Recurrent Abortion, Embryo-protective Immunomodulation does not take place
Unfortunately …. . As we have seen …. In up to 50 % of women with Recurrent Abortion, Embryo-protective Immunomodulation does not take place
 In these women with Recurrent Abortion duphaston is the key to Embryo survival
In these women with Recurrent Abortion duphaston is the key to Embryo survival
 Let us see…. . How duphaston ensures Embryo protective Immunomodulation
Let us see…. . How duphaston ensures Embryo protective Immunomodulation
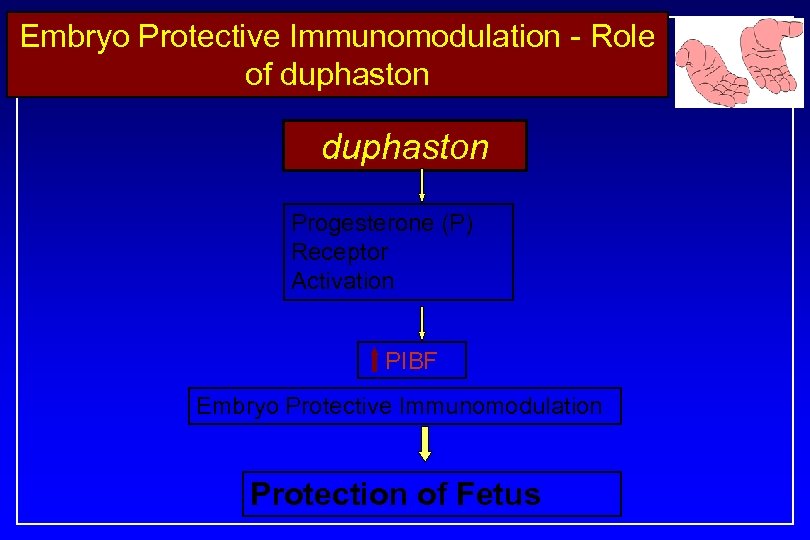 Embryo Protective Immunomodulation - Role of duphaston Progesterone (P) Receptor Activation PIBF Embryo Protective Immunomodulation Protection of Fetus
Embryo Protective Immunomodulation - Role of duphaston Progesterone (P) Receptor Activation PIBF Embryo Protective Immunomodulation Protection of Fetus
 Treatment of LPD can be by any of the following : l Progesterone l Non luteolytic progestogen l h. CG
Treatment of LPD can be by any of the following : l Progesterone l Non luteolytic progestogen l h. CG
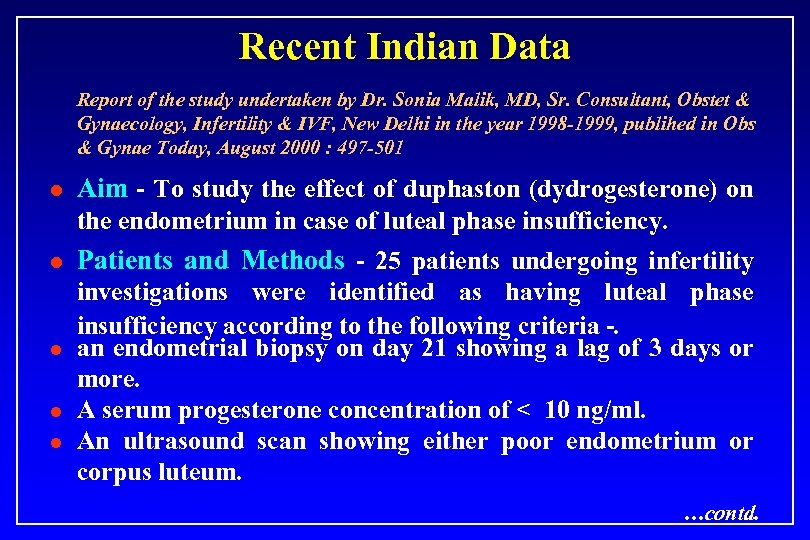 Recent Indian Data Report of the study undertaken by Dr. Sonia Malik, MD, Sr. Consultant, Obstet & Gynaecology, Infertility & IVF, New Delhi in the year 1998 -1999, publihed in Obs & Gynae Today, August 2000 : 497 -501 l Aim - To study the effect of duphaston (dydrogesterone) on the endometrium in case of luteal phase insufficiency. l l Patients and Methods - 25 patients undergoing infertility investigations were identified as having luteal phase insufficiency according to the following criteria -. an endometrial biopsy on day 21 showing a lag of 3 days or more. A serum progesterone concentration of < 10 ng/ml. An ultrasound scan showing either poor endometrium or corpus luteum. …contd.
Recent Indian Data Report of the study undertaken by Dr. Sonia Malik, MD, Sr. Consultant, Obstet & Gynaecology, Infertility & IVF, New Delhi in the year 1998 -1999, publihed in Obs & Gynae Today, August 2000 : 497 -501 l Aim - To study the effect of duphaston (dydrogesterone) on the endometrium in case of luteal phase insufficiency. l l Patients and Methods - 25 patients undergoing infertility investigations were identified as having luteal phase insufficiency according to the following criteria -. an endometrial biopsy on day 21 showing a lag of 3 days or more. A serum progesterone concentration of < 10 ng/ml. An ultrasound scan showing either poor endometrium or corpus luteum. …contd.
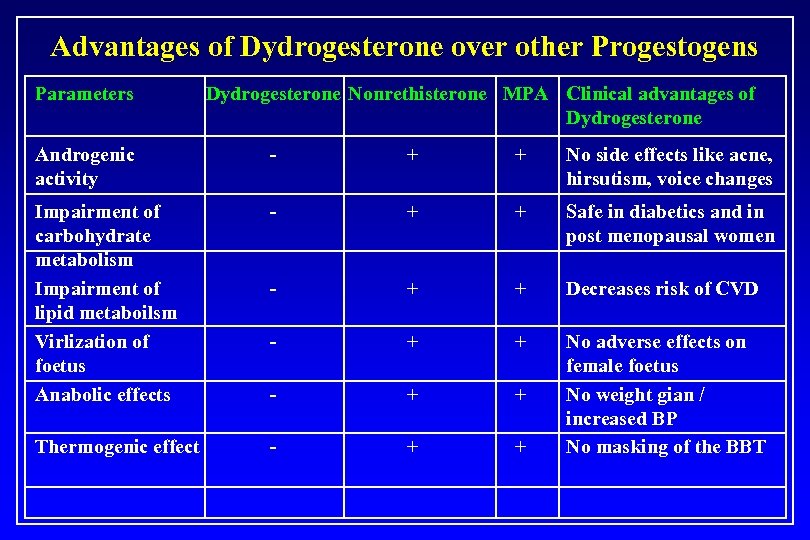 Advantages of Dydrogesterone over other Progestogens Parameters Dydrogesterone Nonrethisterone MPA Clinical advantages of Dydrogesterone Androgenic activity - + + No side effects like acne, hirsutism, voice changes Impairment of carbohydrate metabolism Impairment of lipid metaboilsm Virlization of foetus Anabolic effects - + + Safe in diabetics and in post menopausal women - + + Decreases risk of CVD - + + Thermogenic effect - + + No adverse effects on female foetus No weight gian / increased BP No masking of the BBT
Advantages of Dydrogesterone over other Progestogens Parameters Dydrogesterone Nonrethisterone MPA Clinical advantages of Dydrogesterone Androgenic activity - + + No side effects like acne, hirsutism, voice changes Impairment of carbohydrate metabolism Impairment of lipid metaboilsm Virlization of foetus Anabolic effects - + + Safe in diabetics and in post menopausal women - + + Decreases risk of CVD - + + Thermogenic effect - + + No adverse effects on female foetus No weight gian / increased BP No masking of the BBT
 Human Chorionic Gonadotrophin l l HCG stimulates cells of the corpus luteum to produce progesterone. In the normal corpus luteum, the luteal cells are adequate in number and have adequate capacity to produce progesterone. However, malfunctioning corpus luteum has less number of luteal cells. Also, the capacity of each luteal cell to produce progesterone in response to HCG is compromised ( decreased ) in luteal phase defect. Therefore progesterone production via stimulation of malfunctioning corpus luteum by HCG will be less. ( ref. Momoeda et al, Human Reproduction, 1998, July; 13 (7), 1907 -11 ) …contd.
Human Chorionic Gonadotrophin l l HCG stimulates cells of the corpus luteum to produce progesterone. In the normal corpus luteum, the luteal cells are adequate in number and have adequate capacity to produce progesterone. However, malfunctioning corpus luteum has less number of luteal cells. Also, the capacity of each luteal cell to produce progesterone in response to HCG is compromised ( decreased ) in luteal phase defect. Therefore progesterone production via stimulation of malfunctioning corpus luteum by HCG will be less. ( ref. Momoeda et al, Human Reproduction, 1998, July; 13 (7), 1907 -11 ) …contd.
 l Stimulatory effect of exogenous HCG on progesterone production is minimal on malfunctioning corpus luteum. This suggests that LPD does not benefit from HCG administration. ( ref. Momoeda et al, Human Reproduction, 1998, July; 13 (7), 1907 -11 ) …contd.
l Stimulatory effect of exogenous HCG on progesterone production is minimal on malfunctioning corpus luteum. This suggests that LPD does not benefit from HCG administration. ( ref. Momoeda et al, Human Reproduction, 1998, July; 13 (7), 1907 -11 ) …contd.
 l Among the characteristics of LPD in women is the inability of the corpus luteum to respond appropriately to LH/HCG. This defect may be caused by inappropriate formation of new LH/HCG receptors. ( Felig P, Endocrinology & Metabolism, 1995, third edition, 994 ) l HCG will not correct the luteal phase defect in patients with inadequate ovarian LH/HCG receptors. ( Mishell’s Text Book of Infertility, Contraception and Reproductive Endocrinology, 1997, Fourth edition, 739 -40 ) l There is a risk of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome ( OHSS )associated with h. CG use. …contd.
l Among the characteristics of LPD in women is the inability of the corpus luteum to respond appropriately to LH/HCG. This defect may be caused by inappropriate formation of new LH/HCG receptors. ( Felig P, Endocrinology & Metabolism, 1995, third edition, 994 ) l HCG will not correct the luteal phase defect in patients with inadequate ovarian LH/HCG receptors. ( Mishell’s Text Book of Infertility, Contraception and Reproductive Endocrinology, 1997, Fourth edition, 739 -40 ) l There is a risk of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome ( OHSS )associated with h. CG use. …contd.
 Micronised progesterone…NATURAL? l The term natural progesterone ( as used to describe micronised progesterone ) is misleading. Diosgenin ( plant source - Dioscorea villosa ) Synthetic Steps Micronised Progesterone Dydrogesterone Either both are natural or both are synthetic. ( Ref: : Peterson C M, Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology, 1995, 38 ( 4 ) : 819; http: //www. skinbiology. com/menopause&aging. html; data on file )
Micronised progesterone…NATURAL? l The term natural progesterone ( as used to describe micronised progesterone ) is misleading. Diosgenin ( plant source - Dioscorea villosa ) Synthetic Steps Micronised Progesterone Dydrogesterone Either both are natural or both are synthetic. ( Ref: : Peterson C M, Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology, 1995, 38 ( 4 ) : 819; http: //www. skinbiology. com/menopause&aging. html; data on file )
 DIOSGENIN the same natural source of dydrogesterone and micronised progesterone What is the difference between dydrogesterone and micronised progesterone?
DIOSGENIN the same natural source of dydrogesterone and micronised progesterone What is the difference between dydrogesterone and micronised progesterone?
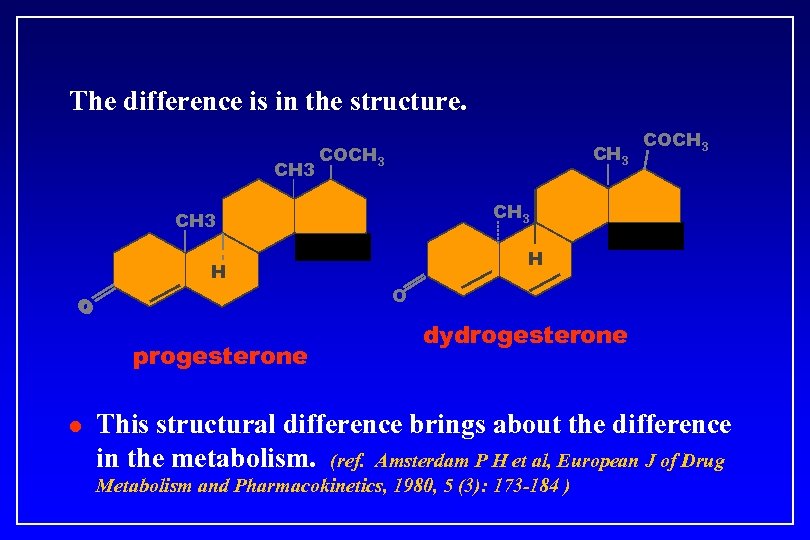 The difference is in the structure. CH 3 COCH 3 H O O progesterone l COCH 3 H O dydrogesterone This structural difference brings about the difference in the metabolism. (ref. Amsterdam P H et al, European J of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics, 1980, 5 (3): 173 -184 )
The difference is in the structure. CH 3 COCH 3 H O O progesterone l COCH 3 H O dydrogesterone This structural difference brings about the difference in the metabolism. (ref. Amsterdam P H et al, European J of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics, 1980, 5 (3): 173 -184 )
 Dydrogesterone’s different metabolism. . . l l l The metabolites of dydrogesterone retain 4, 6 - diene-3 one structure. The major metabolite of dydrogesterone retains progestational activity. Hence, it is orally effective. Dydrogesterone has very good oral bioavailability. It brings about 100% conversion to secretory endometrium ( Identical endometrial histological appearance as seen in natural cycles ). (ref. Amsterdam P H et al, European J of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics, 1980, 5 (3): 173 -184; Malik S, Nagpal S, Obs & Gynae Today, August 2000, V ( 8 ) : 497 -501 )
Dydrogesterone’s different metabolism. . . l l l The metabolites of dydrogesterone retain 4, 6 - diene-3 one structure. The major metabolite of dydrogesterone retains progestational activity. Hence, it is orally effective. Dydrogesterone has very good oral bioavailability. It brings about 100% conversion to secretory endometrium ( Identical endometrial histological appearance as seen in natural cycles ). (ref. Amsterdam P H et al, European J of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics, 1980, 5 (3): 173 -184; Malik S, Nagpal S, Obs & Gynae Today, August 2000, V ( 8 ) : 497 -501 )
 Oral micronised progesterone’s different metabolism l The metabolites of progesterone do not retain 4 - ene - 3 one structure. Hence, it is not orally effective. l 95% of micronised progesterone administered orally was converted to inactive metabolites due to first pass effect. l Incomplete secretory conversion of endometrium has been reported with oral micronised progesterone. (ref. Amsterdam P H et al, European J of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics, 1980, 5 (3): 173 -184 ; Levine H L, Watson N A, Abstract presented at the 8 th International Congress on the menopause, Sydney, Australia, November 3 -7, 1996; )
Oral micronised progesterone’s different metabolism l The metabolites of progesterone do not retain 4 - ene - 3 one structure. Hence, it is not orally effective. l 95% of micronised progesterone administered orally was converted to inactive metabolites due to first pass effect. l Incomplete secretory conversion of endometrium has been reported with oral micronised progesterone. (ref. Amsterdam P H et al, European J of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics, 1980, 5 (3): 173 -184 ; Levine H L, Watson N A, Abstract presented at the 8 th International Congress on the menopause, Sydney, Australia, November 3 -7, 1996; )
 Safety. . . Dydrogesterone vs micronised progesterone l Unlike oral micronised progesterone, dydrogesterone does not cause hepatotoxicity, natriuresis. l Unlike progesterone, dydrogesterone does not cause impairment of carbohydrate metabolism. ( Ref. - AICOG News, December 2000, ; Martin A J, Supplement to Modern Medicine, December , 1986, 31(12) ).
Safety. . . Dydrogesterone vs micronised progesterone l Unlike oral micronised progesterone, dydrogesterone does not cause hepatotoxicity, natriuresis. l Unlike progesterone, dydrogesterone does not cause impairment of carbohydrate metabolism. ( Ref. - AICOG News, December 2000, ; Martin A J, Supplement to Modern Medicine, December , 1986, 31(12) ).
 Dydrogesterone vs vaginal micronised progesterone l Vaginal administration of progesterone is complicated by a marked variability within and among patients. l Side effects include vaginal irritation, discharge, monilial vaginitis. l Dydrogesterone being administered by oral route, the above limitations, side effects are not observed. l Vaginal micronised progesterone is found to deter embryo implantation and decrease pregnancy rates. Dydrogesterone maintains implantation site and achieves good pregnancy rates. ( Maxson W S , Clin Exp Obst & Gyn, June 1987, 30(2): 470, Wang H S, Soong Y K, Gynecol Endocrinol, 1996, 10(5): 349 -355 )
Dydrogesterone vs vaginal micronised progesterone l Vaginal administration of progesterone is complicated by a marked variability within and among patients. l Side effects include vaginal irritation, discharge, monilial vaginitis. l Dydrogesterone being administered by oral route, the above limitations, side effects are not observed. l Vaginal micronised progesterone is found to deter embryo implantation and decrease pregnancy rates. Dydrogesterone maintains implantation site and achieves good pregnancy rates. ( Maxson W S , Clin Exp Obst & Gyn, June 1987, 30(2): 470, Wang H S, Soong Y K, Gynecol Endocrinol, 1996, 10(5): 349 -355 )
 Efficacy of Dydrogesterone comparable with parenteral progesterone l The implantation rate and pregnancy rate with dydrogesterone was similar to intramuscular progesterone injection in IVF programme. l Pregnancy rate in oocyte donation programme using dydrogesterone is comparable to that reported with natural products. l The activity of dydrogesterone is comparable to that of parenterally administered progesterone. { ref. : Jan Domitrz et al Ginekol Pol 1999 Jan 70 (1) : 8 -12; Abu Musa, Clin Exp Obst & Gyn, 1998, XXV (3 ) : 84; Gelfand M M et al, Menopause: The J of North American Menopause Society, 1997, 4(1): 11 ;
Efficacy of Dydrogesterone comparable with parenteral progesterone l The implantation rate and pregnancy rate with dydrogesterone was similar to intramuscular progesterone injection in IVF programme. l Pregnancy rate in oocyte donation programme using dydrogesterone is comparable to that reported with natural products. l The activity of dydrogesterone is comparable to that of parenterally administered progesterone. { ref. : Jan Domitrz et al Ginekol Pol 1999 Jan 70 (1) : 8 -12; Abu Musa, Clin Exp Obst & Gyn, 1998, XXV (3 ) : 84; Gelfand M M et al, Menopause: The J of North American Menopause Society, 1997, 4(1): 11 ;
 Conclusion l Based on the results of various studies and looking at the various pharmacological advantages duphaston offers as compared to other drug therapies, it is concluded that therapy with duphaston is very effective in treatment of LPD without any side effects.
Conclusion l Based on the results of various studies and looking at the various pharmacological advantages duphaston offers as compared to other drug therapies, it is concluded that therapy with duphaston is very effective in treatment of LPD without any side effects.


