8582688bd1b1705211803cd195fe02ee.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24
 RECTAS www. rectas. org RECTAS: Profile Isi A. Ikhuoria Executive Director, RECTAS, Ile-Ife, Nigeria e-mail: edrectas@rectas. org +234 803 371 2799
RECTAS www. rectas. org RECTAS: Profile Isi A. Ikhuoria Executive Director, RECTAS, Ile-Ife, Nigeria e-mail: edrectas@rectas. org +234 803 371 2799
 The Centre • RECTAS was established on 21 st October 1972 under the auspices of the United Nations Economic Commission for Africa (UNECA). • A joint Institution of African countries. The current participating countries are Benin, Burkina, Cameroon, Ghana, Mali, Nigeria (host country) and Senegal. - Interested countries may apply for admission
The Centre • RECTAS was established on 21 st October 1972 under the auspices of the United Nations Economic Commission for Africa (UNECA). • A joint Institution of African countries. The current participating countries are Benin, Burkina, Cameroon, Ghana, Mali, Nigeria (host country) and Senegal. - Interested countries may apply for admission
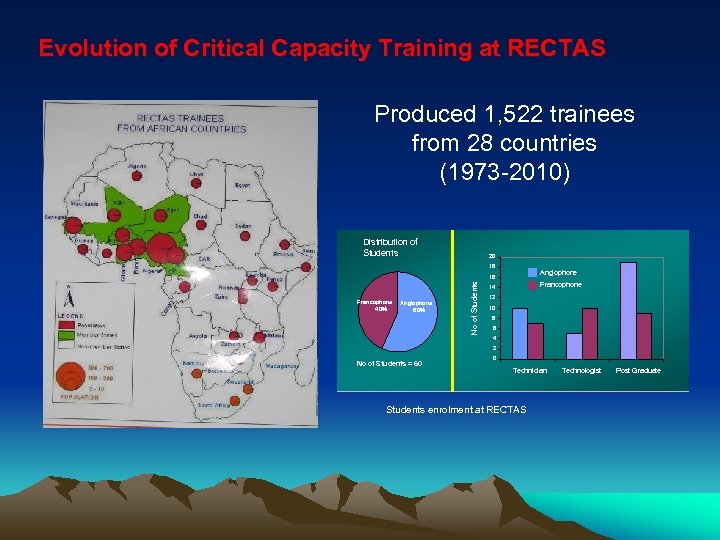 Evolution of Critical Capacity Training at RECTAS Produced 1, 522 trainees from 28 countries (1973 -2010) Distribution of Students 20 18 Anglophone Francophone 40% Anglophone 60% No of Students 16 Francophone 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 No of Students = 60 0 Technician Students enrolment at RECTAS Technologist Post Graduate
Evolution of Critical Capacity Training at RECTAS Produced 1, 522 trainees from 28 countries (1973 -2010) Distribution of Students 20 18 Anglophone Francophone 40% Anglophone 60% No of Students 16 Francophone 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 No of Students = 60 0 Technician Students enrolment at RECTAS Technologist Post Graduate
 Auditorium RECTAS Management Staff International Trainees Academic Block International Workshop
Auditorium RECTAS Management Staff International Trainees Academic Block International Workshop
 Vision a leading Centre of Excellence provid. To be ing one-stop solution for quality geospatial science training, education and research and critical capacity for sustainable development in Africa.
Vision a leading Centre of Excellence provid. To be ing one-stop solution for quality geospatial science training, education and research and critical capacity for sustainable development in Africa.
 Mission To contribute to rapid development of member states in particular and Africa in general, through capacity building for timely delivery and responsible use of appropriate geospatial information.
Mission To contribute to rapid development of member states in particular and Africa in general, through capacity building for timely delivery and responsible use of appropriate geospatial information.
 Objectives: • provide theoretical and practical training in Geoinformatics and applications • conduct seminars and courses • carry out studies and research • provide advisory and consultancy services
Objectives: • provide theoretical and practical training in Geoinformatics and applications • conduct seminars and courses • carry out studies and research • provide advisory and consultancy services
 Conceptual Framework • There is inadequacy of manpower needs in the mapping sciences in Africa (Ihemadu, 1987 and 1992; Ikhuoria, 1995 and Ayeni, 1996). • The capacity development and adoption of Geoinformatics is examined under the concepts of professionalism & innovation diffusion in Africa.
Conceptual Framework • There is inadequacy of manpower needs in the mapping sciences in Africa (Ihemadu, 1987 and 1992; Ikhuoria, 1995 and Ayeni, 1996). • The capacity development and adoption of Geoinformatics is examined under the concepts of professionalism & innovation diffusion in Africa.
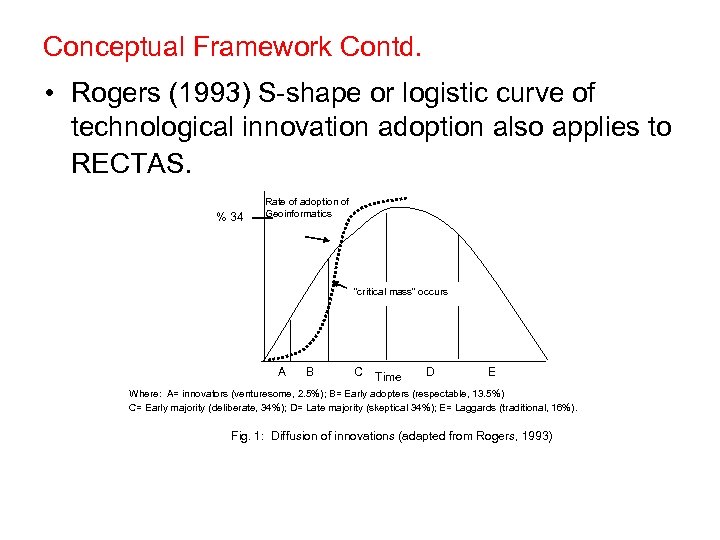 Conceptual Framework Contd. • Rogers (1993) S-shape or logistic curve of technological innovation adoption also applies to RECTAS. % 34 Rate of adoption of Geoinformatics “critical mass” occurs A B C Time D E Where: A= innovators (venturesome, 2. 5%); B= Early adopters (respectable, 13. 5%) C= Early majority (deliberate, 34%); D= Late majority (skeptical 34%); E= Laggards (traditional, 16%). Fig. 1: Diffusion of innovations (adapted from Rogers, 1993)
Conceptual Framework Contd. • Rogers (1993) S-shape or logistic curve of technological innovation adoption also applies to RECTAS. % 34 Rate of adoption of Geoinformatics “critical mass” occurs A B C Time D E Where: A= innovators (venturesome, 2. 5%); B= Early adopters (respectable, 13. 5%) C= Early majority (deliberate, 34%); D= Late majority (skeptical 34%); E= Laggards (traditional, 16%). Fig. 1: Diffusion of innovations (adapted from Rogers, 1993)
 In fulfillment of the vision and objectives of the Centre, the following academic programmes and qualifications are offered: Department of Photogrammetry & Remote Sensing • Professional Master (PM) degree in Geoinformation Production & Management (English & French) • MSc degree in Photogrammetry & Remote Sensing (English & French) • Ph. D degree in Photogrammetry & Remote Sensing (English & French)
In fulfillment of the vision and objectives of the Centre, the following academic programmes and qualifications are offered: Department of Photogrammetry & Remote Sensing • Professional Master (PM) degree in Geoinformation Production & Management (English & French) • MSc degree in Photogrammetry & Remote Sensing (English & French) • Ph. D degree in Photogrammetry & Remote Sensing (English & French)
 Dept of Geographic Information Science • Technologist Diploma (TD) in Geoinformation Production & Management (English & French) • Executive Master (EM) degree in Geoinformation & Environmental Mgt (English only) Note: weekend programme. Venue is Abuja, Nigeria. • MSc degree in Geographic Information Science (French) • Master of Technology (M. Tech) degree in Geoinformation Technology (English) • Ph. D degree in Geographic Information Science (English & French)
Dept of Geographic Information Science • Technologist Diploma (TD) in Geoinformation Production & Management (English & French) • Executive Master (EM) degree in Geoinformation & Environmental Mgt (English only) Note: weekend programme. Venue is Abuja, Nigeria. • MSc degree in Geographic Information Science (French) • Master of Technology (M. Tech) degree in Geoinformation Technology (English) • Ph. D degree in Geographic Information Science (English & French)
 Department of Cartography • Professional Master (PM) degree in Cartography & Geospatial Techniques (English & French) • M. Sc degree in Cartography & Geospatial Sciences (English & French) • Ph. D degree in Cartography & Geospatial Sciences (English & French)
Department of Cartography • Professional Master (PM) degree in Cartography & Geospatial Techniques (English & French) • M. Sc degree in Cartography & Geospatial Sciences (English & French) • Ph. D degree in Cartography & Geospatial Sciences (English & French)
 Levels of Professionalism in Africa • Technical: technicians with <2 years practical training. • Technological: technologist 2 -3 years theoretical & practical training. • Professional: university graduates (involved in management and policy decisions).
Levels of Professionalism in Africa • Technical: technicians with <2 years practical training. • Technological: technologist 2 -3 years theoretical & practical training. • Professional: university graduates (involved in management and policy decisions).
 Strategies of Education and Training (3) Equip graduates of various disciplines with adequate technical capability in GIS, remote sensing and usage of geospatial data and infrastructure for environmental management.
Strategies of Education and Training (3) Equip graduates of various disciplines with adequate technical capability in GIS, remote sensing and usage of geospatial data and infrastructure for environmental management.
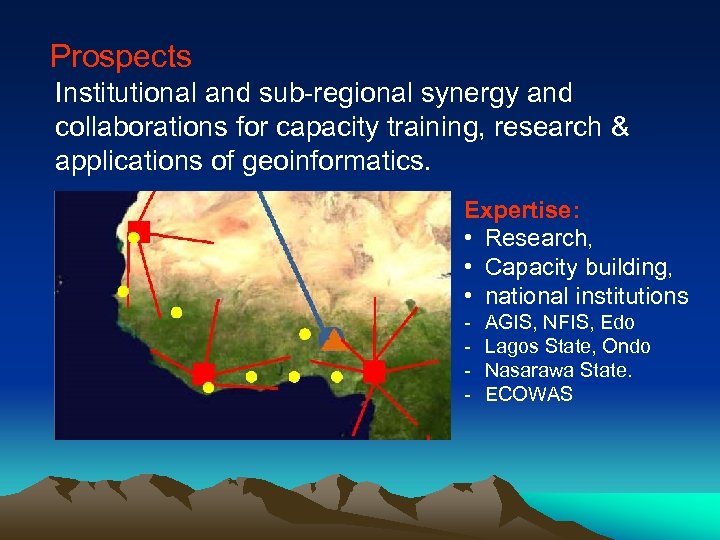 Prospects Institutional and sub-regional synergy and collaborations for capacity training, research & applications of geoinformatics. Expertise: • Research, • Capacity building, • national institutions - AGIS, NFIS, Edo Lagos State, Ondo Nasarawa State. ECOWAS
Prospects Institutional and sub-regional synergy and collaborations for capacity training, research & applications of geoinformatics. Expertise: • Research, • Capacity building, • national institutions - AGIS, NFIS, Edo Lagos State, Ondo Nasarawa State. ECOWAS
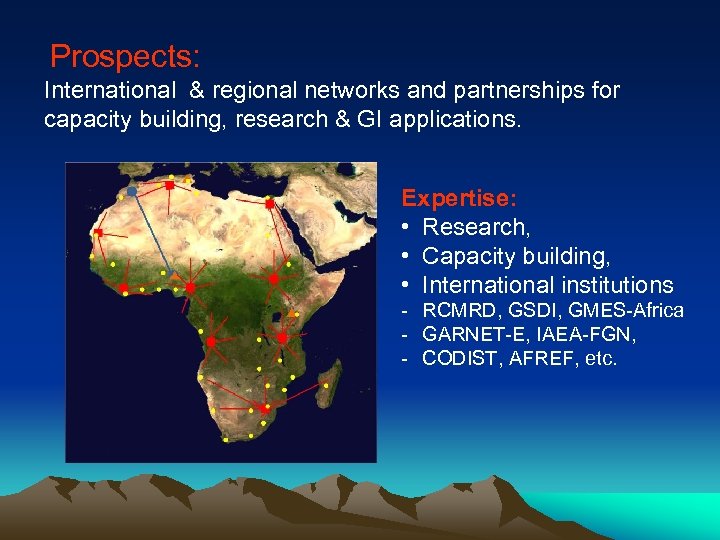 Prospects: International & regional networks and partnerships for capacity building, research & GI applications. Expertise: • Research, • Capacity building, • International institutions - RCMRD, GSDI, GMES-Africa - GARNET-E, IAEA-FGN, - CODIST, AFREF, etc.
Prospects: International & regional networks and partnerships for capacity building, research & GI applications. Expertise: • Research, • Capacity building, • International institutions - RCMRD, GSDI, GMES-Africa - GARNET-E, IAEA-FGN, - CODIST, AFREF, etc.
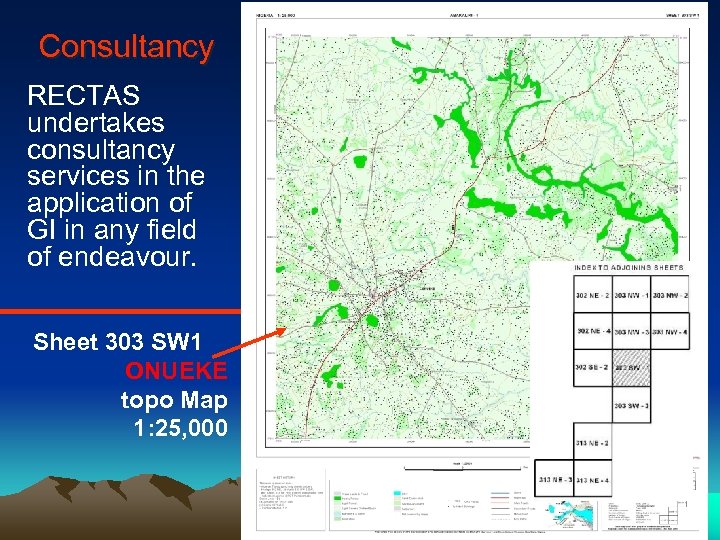 Consultancy RECTAS undertakes consultancy services in the application of GI in any field of endeavour. Sheet 303 SW 1 ONUEKE topo Map 1: 25, 000
Consultancy RECTAS undertakes consultancy services in the application of GI in any field of endeavour. Sheet 303 SW 1 ONUEKE topo Map 1: 25, 000
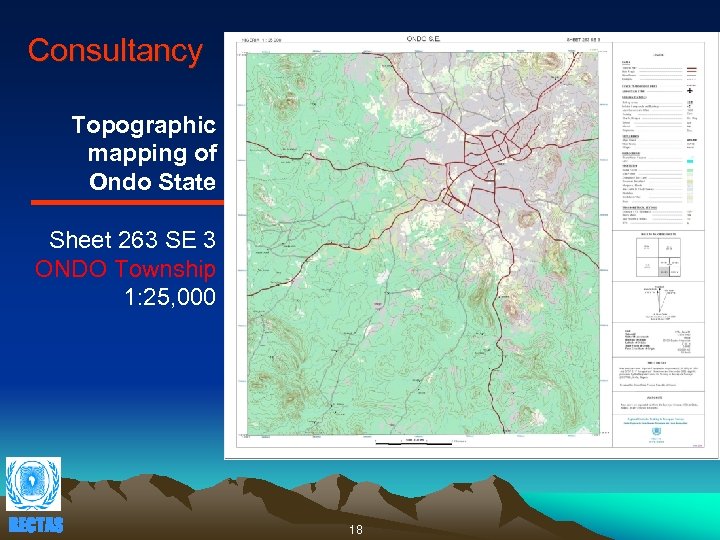 Consultancy Topographic mapping of Ondo State Sheet 263 SE 3 ONDO Township 1: 25, 000 RECTAS 18
Consultancy Topographic mapping of Ondo State Sheet 263 SE 3 ONDO Township 1: 25, 000 RECTAS 18
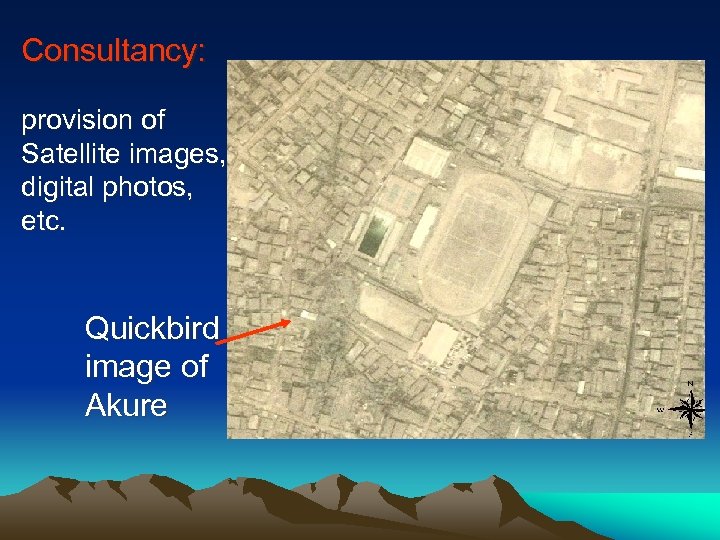 Consultancy: provision of Satellite images, digital photos, etc. Quickbird image of Akure
Consultancy: provision of Satellite images, digital photos, etc. Quickbird image of Akure
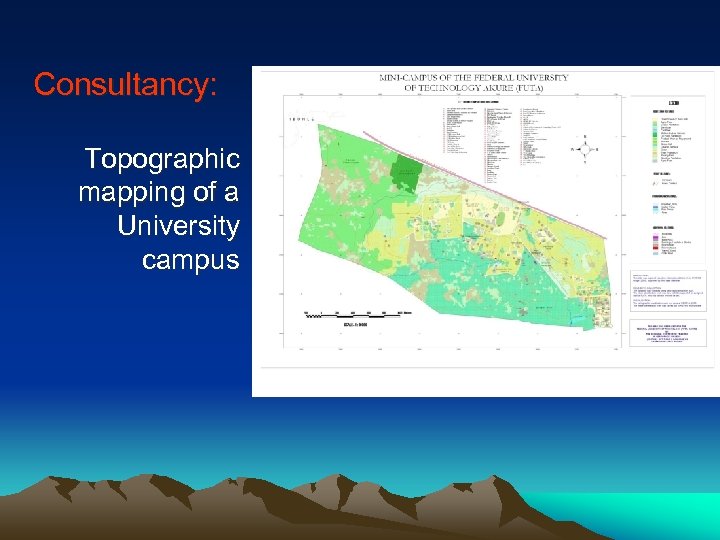 Consultancy: Topographic mapping of a University campus
Consultancy: Topographic mapping of a University campus
 Short courses: – modular formats of 3 weeks duration – customised formats of 1 -3 weeks duration Examples are: • RS/GIS applications military operations • RS/GIS applications in geology/mineral resources exploration (Mines & Steel Dev. ) • Space-based technologies in Disaster Management (NEMA) • GIS-Day seminar (11 Dec. 2008) • AFREF workshop (2 -5 Aug. 2009) • AFREF workshop (9 -11 Feb. 2010)
Short courses: – modular formats of 3 weeks duration – customised formats of 1 -3 weeks duration Examples are: • RS/GIS applications military operations • RS/GIS applications in geology/mineral resources exploration (Mines & Steel Dev. ) • Space-based technologies in Disaster Management (NEMA) • GIS-Day seminar (11 Dec. 2008) • AFREF workshop (2 -5 Aug. 2009) • AFREF workshop (9 -11 Feb. 2010)
 Advisory • • GI applications missions RS/GIS lab installations software licence & satellite Image acquisition instruments maintenance, etc. Examples are: ü Installation of GIS laboratory in Universities ü UN-SPIDER missions (Lome - June, 2009; Dakar Cameroon, 2010 ) Dec, 2009
Advisory • • GI applications missions RS/GIS lab installations software licence & satellite Image acquisition instruments maintenance, etc. Examples are: ü Installation of GIS laboratory in Universities ü UN-SPIDER missions (Lome - June, 2009; Dakar Cameroon, 2010 ) Dec, 2009
 Sustenance • Biennial Budget – shared by member countries - Nigeria 29. % - Ghana Cameroon Senegal Niger Mali Benin Burkina RECTAS 14% 10% 06% 04% 03% 03% 28. 0% • Capital budget for Infrastructures by Nigeria (2008 – 2013 = $5. 3 m) • Internally Generation Revenue & Donors
Sustenance • Biennial Budget – shared by member countries - Nigeria 29. % - Ghana Cameroon Senegal Niger Mali Benin Burkina RECTAS 14% 10% 06% 04% 03% 03% 28. 0% • Capital budget for Infrastructures by Nigeria (2008 – 2013 = $5. 3 m) • Internally Generation Revenue & Donors



