d3340f980086f338ec8d26c5d7424753.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 53
 Records Management Overview
Records Management Overview
 Why? n n n It’s the Law It’s University Policy Fiscal and Legal Compliance Reduced Costs and Increased Efficiency Preserve the Institutional Memory
Why? n n n It’s the Law It’s University Policy Fiscal and Legal Compliance Reduced Costs and Increased Efficiency Preserve the Institutional Memory
 What’s in it for me? n n n More organized and efficient Easily find and retrieve records Less work for supervisors
What’s in it for me? n n n More organized and efficient Easily find and retrieve records Less work for supervisors
 What is Records Management? n Systematic control of recorded information, regardless of format, from the time a record is created until its ultimate disposition.
What is Records Management? n Systematic control of recorded information, regardless of format, from the time a record is created until its ultimate disposition.
 Terms and Forms n n Retention Schedule Record Series Transmittal Form Records Destruction Certificate
Terms and Forms n n Retention Schedule Record Series Transmittal Form Records Destruction Certificate
 Retention Schedule n n n Different types of public records. How long records must be kept. When or if records may be destroyed.
Retention Schedule n n n Different types of public records. How long records must be kept. When or if records may be destroyed.
 Record Series n …Basic unit for organizing and controlling files. It is a group of files or documents kept together (either physically or intellectually) because they relate to a particular subject or function, result from the same activity, document a specific type of transaction, take a particular physical form, or have some other relationship arising out of their creation, receipt, maintenance, or use (36 CFR 1220. 14). National Archives http: //www. archives. gov/records-mgmt/faqs/federal. html#series
Record Series n …Basic unit for organizing and controlling files. It is a group of files or documents kept together (either physically or intellectually) because they relate to a particular subject or function, result from the same activity, document a specific type of transaction, take a particular physical form, or have some other relationship arising out of their creation, receipt, maintenance, or use (36 CFR 1220. 14). National Archives http: //www. archives. gov/records-mgmt/faqs/federal. html#series
 Schedules used by NKU n State University Model Records Retention Schedule n General Schedule for Electronic and Related Records
Schedules used by NKU n State University Model Records Retention Schedule n General Schedule for Electronic and Related Records
 State University Model n Identifies records by series, title, function and content. n Gives retention time and disposition instructions. n Provides legal authority to destroy records.
State University Model n Identifies records by series, title, function and content. n Gives retention time and disposition instructions. n Provides legal authority to destroy records.
 Process n Determine the type of record – Content matters not the format n Locate the series on the records schedule n Apply the retention period to your records
Process n Determine the type of record – Content matters not the format n Locate the series on the records schedule n Apply the retention period to your records
 A–Z Index
A–Z Index
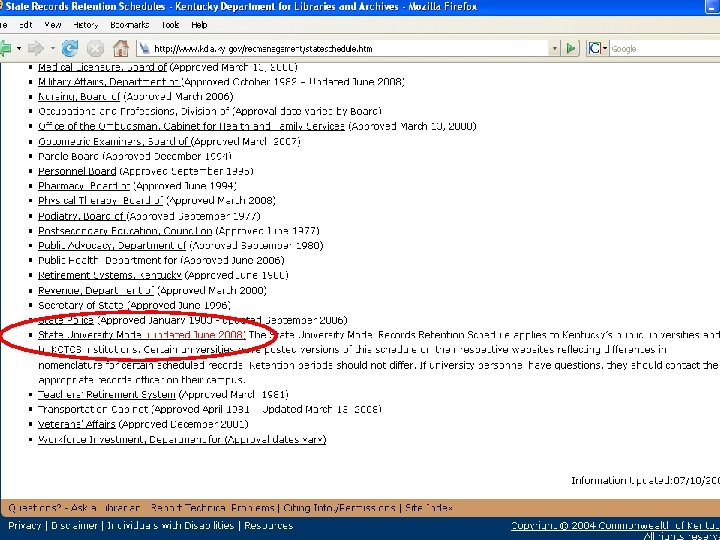
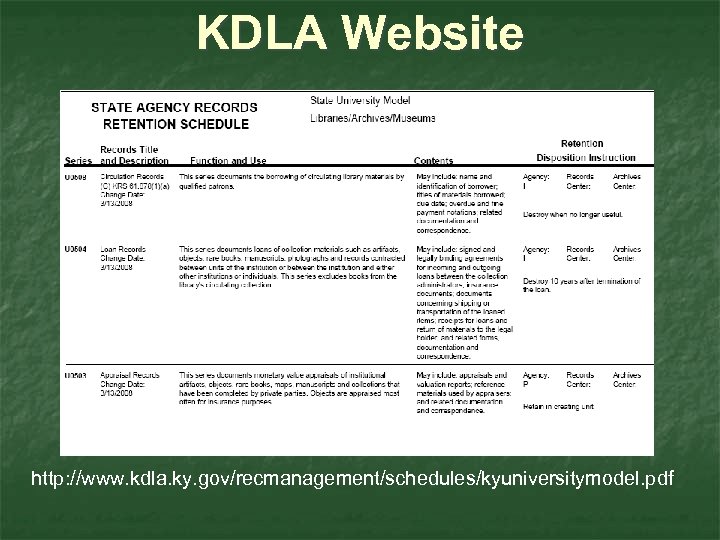 KDLA Website http: //www. kdla. ky. gov/recmanagement/schedules/kyuniversitymodel. pdf
KDLA Website http: //www. kdla. ky. gov/recmanagement/schedules/kyuniversitymodel. pdf
 University Records Formats Paper Files Electronic Records Video Tapes Audio Tapes Printed Publications Web Pages Photographs CD, DVD, Flash drive
University Records Formats Paper Files Electronic Records Video Tapes Audio Tapes Printed Publications Web Pages Photographs CD, DVD, Flash drive
 Records Recommendations GOOD vs. BAD
Records Recommendations GOOD vs. BAD
 Bad Records n Documents with: No title No author No date, draft or version status n Multiple copies of a report, but missing the signed, authorized copy. n Emails with subject lines that bear no relation to the current content (fw: fw)
Bad Records n Documents with: No title No author No date, draft or version status n Multiple copies of a report, but missing the signed, authorized copy. n Emails with subject lines that bear no relation to the current content (fw: fw)
 Good Records n n n Titled Dated Labeled
Good Records n n n Titled Dated Labeled
 Good Bad SACs committee report, 2009 Important, need to keep History Dept, Official Correspondence, 200809 (U 0100, permanent) Dept mail
Good Bad SACs committee report, 2009 Important, need to keep History Dept, Official Correspondence, 200809 (U 0100, permanent) Dept mail
 Electronic Records n Directory and Folder Structure Ø n Naming Ø n Establish and follow standard naming convention Security Ø n Office wide adoption best Control access… shared drives Back up Ø When, what format and where stored
Electronic Records n Directory and Folder Structure Ø n Naming Ø n Establish and follow standard naming convention Security Ø n Office wide adoption best Control access… shared drives Back up Ø When, what format and where stored
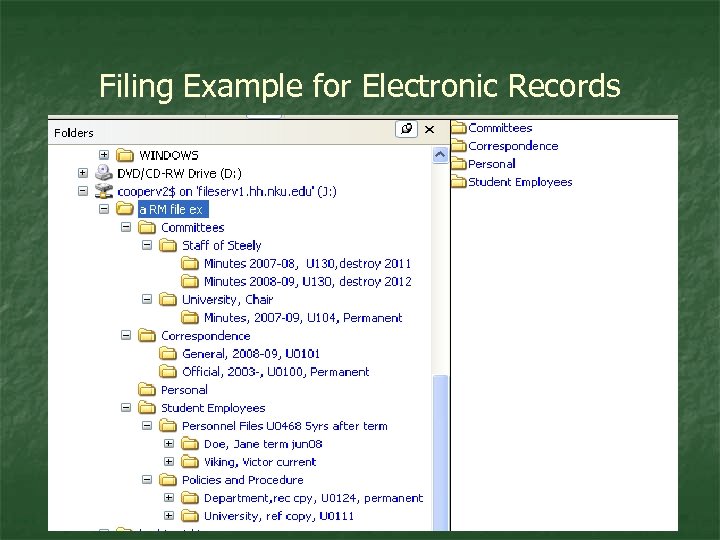 Filing Example for Electronic Records
Filing Example for Electronic Records
 Best Advice n n Start immediately, even if only small steps. Don’t create unnecessary records. Reduce duplicate copies. Create and use a file structure for all records, no matter what format. The Result:
Best Advice n n Start immediately, even if only small steps. Don’t create unnecessary records. Reduce duplicate copies. Create and use a file structure for all records, no matter what format. The Result:
 Records that are EASY to: Organize n Retrieve n Preserve n Delete or Transfer n
Records that are EASY to: Organize n Retrieve n Preserve n Delete or Transfer n
 When your office no longer uses or needs a set of records… 4 Possibilities n n Inactive Temporary Storage Permanently Stored by Original Office Transferred to University Archives Records Destruction
When your office no longer uses or needs a set of records… 4 Possibilities n n Inactive Temporary Storage Permanently Stored by Original Office Transferred to University Archives Records Destruction
 Office Maintains n n Records not actively used … but not at end of retention time. Permanent Records
Office Maintains n n Records not actively used … but not at end of retention time. Permanent Records
 Record Transfers n Permanent Retention – those permanent records with historical significance are transferred to Special Collections and Archives
Record Transfers n Permanent Retention – those permanent records with historical significance are transferred to Special Collections and Archives
 Archives Collecting Guidelines Colleges, Schools, Research Centers, Institutes & Departments n n n n n Meeting minutes and agendas Official correspondence – especially from department heads Policies, guidelines, reports Organizational charts, staff lists Publications Photographs-names, dates, place/event Information on events, meetings, participants Recordings of events, lectures, presentations, publicity Any other records which document/describe your department, its history and function
Archives Collecting Guidelines Colleges, Schools, Research Centers, Institutes & Departments n n n n n Meeting minutes and agendas Official correspondence – especially from department heads Policies, guidelines, reports Organizational charts, staff lists Publications Photographs-names, dates, place/event Information on events, meetings, participants Recordings of events, lectures, presentations, publicity Any other records which document/describe your department, its history and function
 Records Destruction Procedures
Records Destruction Procedures
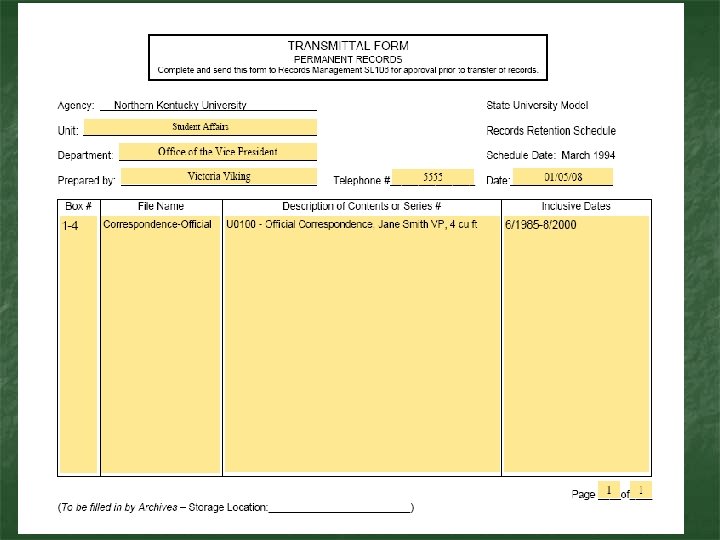
 Records Destruction n Records past their retention period can be destroyed n Destruction must be documented – complete the Records Destruction Certificate Exception è Records with litigation holds
Records Destruction n Records past their retention period can be destroyed n Destruction must be documented – complete the Records Destruction Certificate Exception è Records with litigation holds
 Records Destruction Certificate n Legal proof of authorized destruction. n Form is on the Records Management website
Records Destruction Certificate n Legal proof of authorized destruction. n Form is on the Records Management website
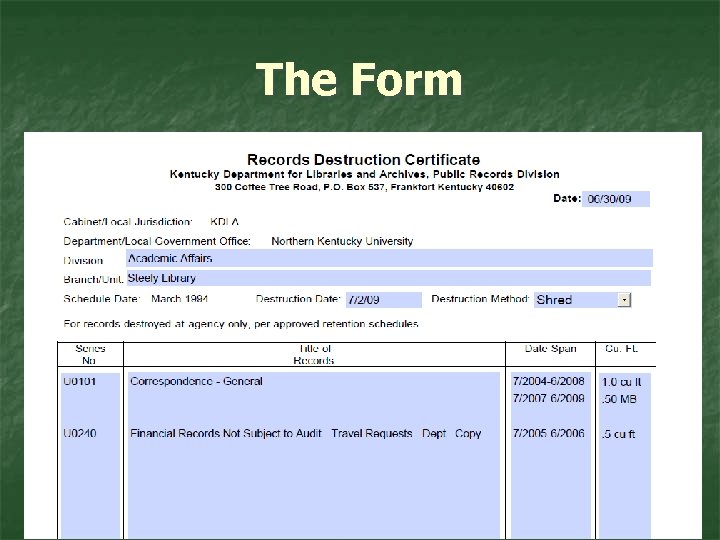 The Form
The Form
 The Form. . . continued University Archivist’s Signature Here Your Signature Here
The Form. . . continued University Archivist’s Signature Here Your Signature Here
 Email
Email
 Email: What’s the Retention? n n n Email is a format Records retention is based on content Evaluate the content of each email to determine retention period
Email: What’s the Retention? n n n Email is a format Records retention is based on content Evaluate the content of each email to determine retention period
 Email Most common types of email records n n n Official Correspondence General Correspondence Informational and Reference Material
Email Most common types of email records n n n Official Correspondence General Correspondence Informational and Reference Material
 Non-business Related Email n n n Spam Personal Messages Unsolicited email
Non-business Related Email n n n Spam Personal Messages Unsolicited email
 Email Delete messages that are not needed n n Spam and other non-business messages General Announcements-NKU All, Midweek Transitory messages Informational and Reference material
Email Delete messages that are not needed n n Spam and other non-business messages General Announcements-NKU All, Midweek Transitory messages Informational and Reference material
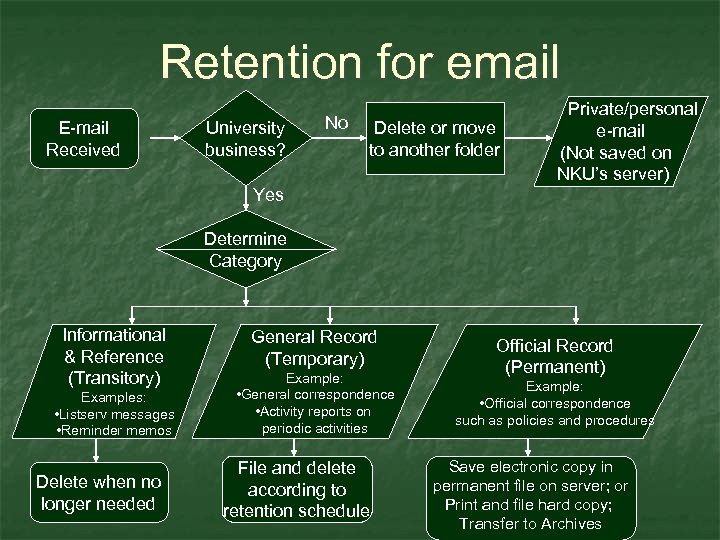 Retention for email E-mail Received University business? No Delete or move to another folder Private/personal e-mail (Not saved on NKU’s server) Yes Determine Category Informational & Reference (Transitory) Examples: • Listserv messages • Reminder memos Delete when no longer needed General Record (Temporary) Example: • General correspondence • Activity reports on periodic activities File and delete according to retention schedule Official Record (Permanent) Example: • Official correspondence such as policies and procedures Save electronic copy in permanent file on server; or Print and file hard copy; Transfer to Archives
Retention for email E-mail Received University business? No Delete or move to another folder Private/personal e-mail (Not saved on NKU’s server) Yes Determine Category Informational & Reference (Transitory) Examples: • Listserv messages • Reminder memos Delete when no longer needed General Record (Temporary) Example: • General correspondence • Activity reports on periodic activities File and delete according to retention schedule Official Record (Permanent) Example: • Official correspondence such as policies and procedures Save electronic copy in permanent file on server; or Print and file hard copy; Transfer to Archives
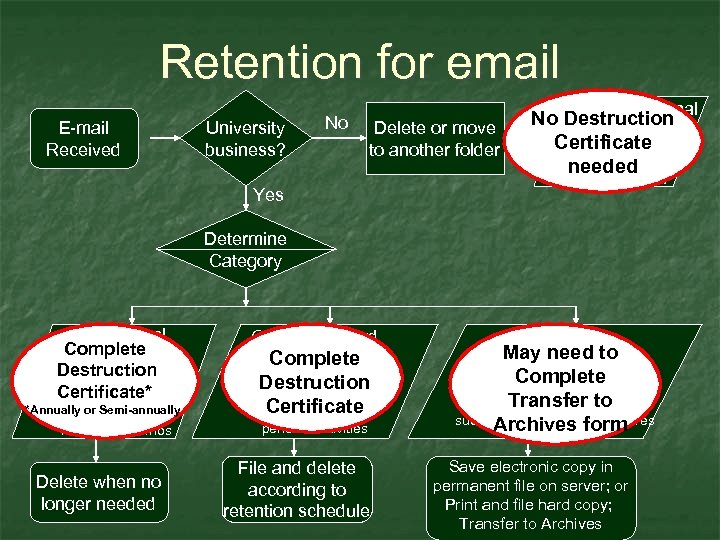 Retention for email E-mail Received University business? No Delete or move to another folder Private/personal No Destruction e-mail Certificateon (Not saved needed NKU’s server) Yes Determine Category Informational Complete & Reference Destruction (Transitory) Certificate* Examples: *Annually or Semi-annually • Listserv messages • Reminder memos Delete when no longer needed General Record (Temporary) Complete Example: Destruction • General correspondence Certificate • Activity reports on periodic activities File and delete according to retention schedule Official Record May need to (Permanent) Complete Example: Transfer to • Official correspondence such as policies and form Archives procedures Save electronic copy in permanent file on server; or Print and file hard copy; Transfer to Archives
Retention for email E-mail Received University business? No Delete or move to another folder Private/personal No Destruction e-mail Certificateon (Not saved needed NKU’s server) Yes Determine Category Informational Complete & Reference Destruction (Transitory) Certificate* Examples: *Annually or Semi-annually • Listserv messages • Reminder memos Delete when no longer needed General Record (Temporary) Complete Example: Destruction • General correspondence Certificate • Activity reports on periodic activities File and delete according to retention schedule Official Record May need to (Permanent) Complete Example: Transfer to • Official correspondence such as policies and form Archives procedures Save electronic copy in permanent file on server; or Print and file hard copy; Transfer to Archives
 Email Folders Filing formats examples
Email Folders Filing formats examples
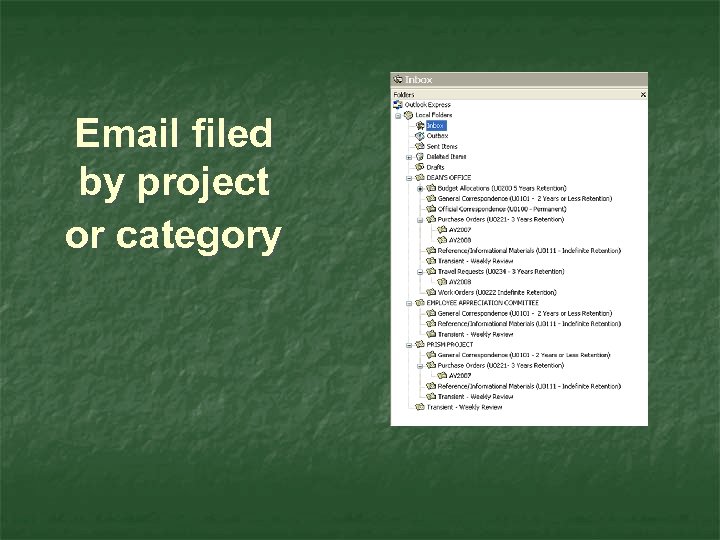 Email filed by project or category
Email filed by project or category
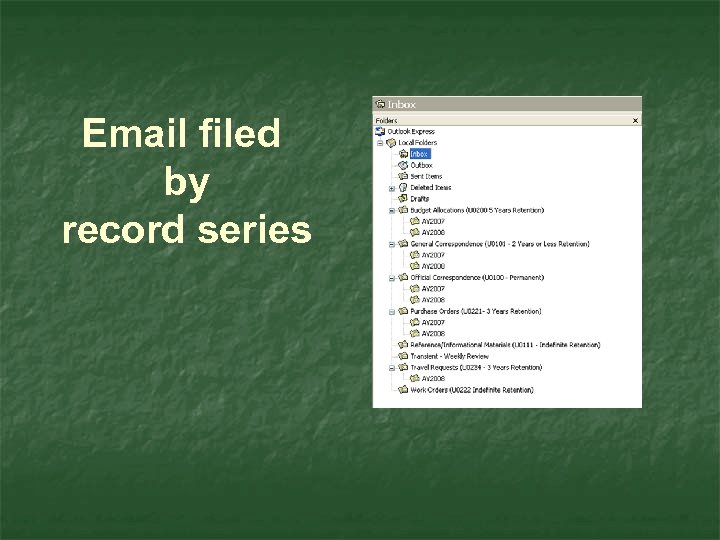 Email filed by record series
Email filed by record series
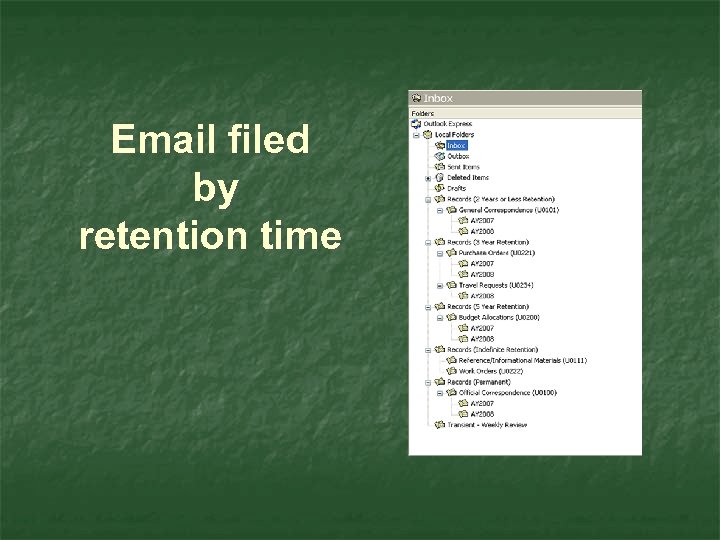 Email filed by retention time
Email filed by retention time
 Most Importantly n n Find a method that works for you Use it consistently
Most Importantly n n Find a method that works for you Use it consistently
 Email: CAUTION n n Auto Archiving Replies to listserv/___ All’s
Email: CAUTION n n Auto Archiving Replies to listserv/___ All’s
 Email Management Tips Be Proactive – Email does not manage itself! n Effective email management = effective time management. n Is email the right tool? n Set up and use rules and filters. n Slow the Flow. n Use specific and descriptive subject lines n Restrict messages to one topic or subject.
Email Management Tips Be Proactive – Email does not manage itself! n Effective email management = effective time management. n Is email the right tool? n Set up and use rules and filters. n Slow the Flow. n Use specific and descriptive subject lines n Restrict messages to one topic or subject.
 Remember to… n Manage email on content, not space quotas. n Use folders and sub-folders; sort & categorize by record type or series and retention. n Keep only the last message in a chain; clear out sent messages once a reply is received. n Schedule time to review, move and delete files and stick to it! Do not use your inbox for long- term storage. n Empty your deleted files and junk mail folders.
Remember to… n Manage email on content, not space quotas. n Use folders and sub-folders; sort & categorize by record type or series and retention. n Keep only the last message in a chain; clear out sent messages once a reply is received. n Schedule time to review, move and delete files and stick to it! Do not use your inbox for long- term storage. n Empty your deleted files and junk mail folders.
 And n Email is a searchable record. n Scary thought, ……. . E-Discovery. n Keep email professional, limit personal. Would you want to see it on the evening news?
And n Email is a searchable record. n Scary thought, ……. . E-Discovery. n Keep email professional, limit personal. Would you want to see it on the evening news?
 And finally….
And finally….
 #1 Records Management Hint AVOID BECOMING A FELON! Ignorance is not a valid excuse!! Tampering with public records without the authority to do so is a Class D felony KRS 519. 060 (1) (b)
#1 Records Management Hint AVOID BECOMING A FELON! Ignorance is not a valid excuse!! Tampering with public records without the authority to do so is a Class D felony KRS 519. 060 (1) (b)


