1b5252076a252f5a14caae28df5fbc22.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Records Management Chapter 8 Numeric Records Management 7 th Edition Read-Smith, Ginn © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
Records Management Chapter 8 Numeric Records Management 7 th Edition Read-Smith, Ginn © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
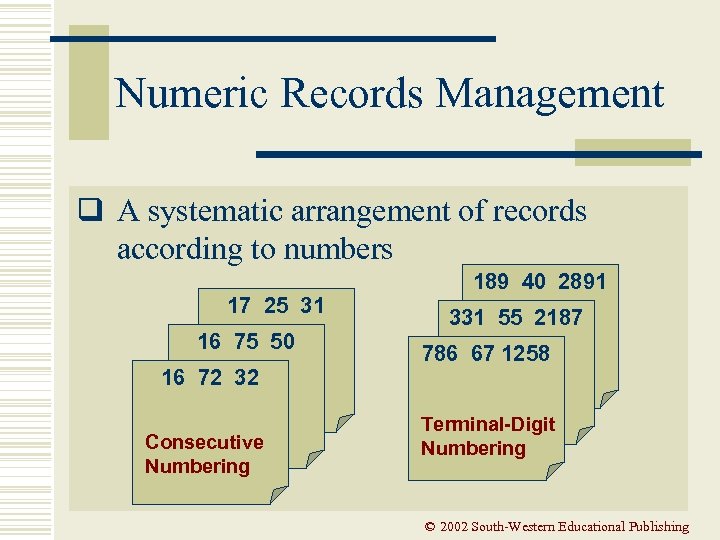 Numeric Records Management q A systematic arrangement of records according to numbers 17 25 31 16 75 50 16 72 32 Consecutive Numbering 189 40 2891 331 55 2187 786 67 1258 Terminal-Digit Numbering © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
Numeric Records Management q A systematic arrangement of records according to numbers 17 25 31 16 75 50 16 72 32 Consecutive Numbering 189 40 2891 331 55 2187 786 67 1258 Terminal-Digit Numbering © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
 Examples q Numeric filing systems are used by § Physicians and medical-related organizations § Banks and financial institutions § Lawyers § Architects § Insurance companies § Social welfare agencies © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
Examples q Numeric filing systems are used by § Physicians and medical-related organizations § Banks and financial institutions § Lawyers § Architects § Insurance companies § Social welfare agencies © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
 Advantages q Advantages of numeric filing systems § Easy to expand numeric files § Impersonal numbers ensure confidentiality of records § Working with numbers is faster and easier than with letters § Existing numbers can be used for coding (purchase order or invoice numbers) © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
Advantages q Advantages of numeric filing systems § Easy to expand numeric files § Impersonal numbers ensure confidentiality of records § Working with numbers is faster and easier than with letters § Existing numbers can be used for coding (purchase order or invoice numbers) © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
 Disadvantages q Disadvantages of numeric filing systems § § Indirect access system, index required More guides are needed than for other systems More time needed to index and code Some methods cause congestion at the end of the files © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
Disadvantages q Disadvantages of numeric filing systems § § Indirect access system, index required More guides are needed than for other systems More time needed to index and code Some methods cause congestion at the end of the files © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
 Consecutive Arrangement q Assigns numbers to records in ascending order sequence q Also called serial or sequential numbering q Numbers are considered in normal reading order from left to right Consecutive Numbering 17 25 31 16 75 50 16 72 32 © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
Consecutive Arrangement q Assigns numbers to records in ascending order sequence q Also called serial or sequential numbering q Numbers are considered in normal reading order from left to right Consecutive Numbering 17 25 31 16 75 50 16 72 32 © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
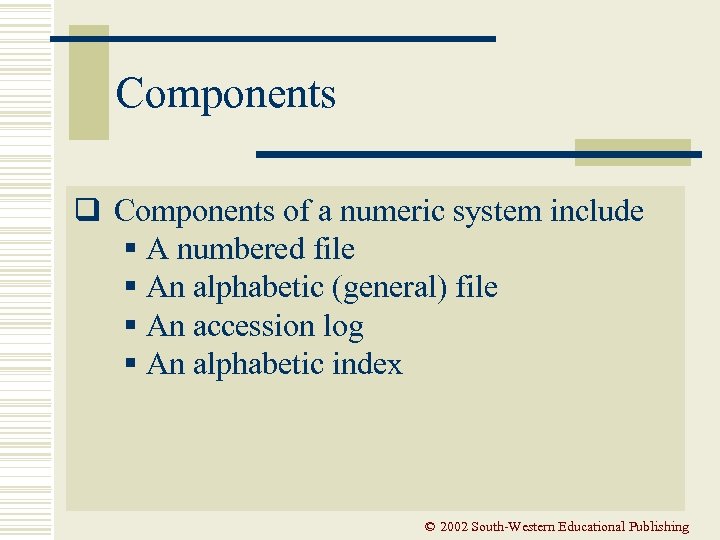 Components q Components of a numeric system include § A numbered file § An alphabetic (general) file § An accession log § An alphabetic index © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
Components q Components of a numeric system include § A numbered file § An alphabetic (general) file § An accession log § An alphabetic index © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
 Numbered Files q Numbered guides and folders for the numbered file Main guide 100 102 FREY GEORGE C 101 HIGH SEAS FUEL 100 BROWN SUSAN D Folder © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
Numbered Files q Numbered guides and folders for the numbered file Main guide 100 102 FREY GEORGE C 101 HIGH SEAS FUEL 100 BROWN SUSAN D Folder © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
 Alphabetic File q Alphabetic guides and folders for the general alphabetic file Main guide A AP-AZ AG-AO AA-AF Folder © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
Alphabetic File q Alphabetic guides and folders for the general alphabetic file Main guide A AP-AZ AG-AO AA-AF Folder © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
 Accession Log q A serial list of numbers assigned to records ACCESSION LOG Code No. Correspondent Date 100 BROWN SUSAN D 9/03/00 101 102 103 HIGH SEAS FUEL FREY GEORGE C LOSARCOS EQUIPMENT 9/03/00 9/04/00 9/05/00 © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
Accession Log q A serial list of numbers assigned to records ACCESSION LOG Code No. Correspondent Date 100 BROWN SUSAN D 9/03/00 101 102 103 HIGH SEAS FUEL FREY GEORGE C LOSARCOS EQUIPMENT 9/03/00 9/04/00 9/05/00 © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
 Alphabetic Index q A list of correspondent names or subjects for a numeric file ALPHABETIC INDEX APACHE ADVERTISING 122 APPLICATIONS BROWN SUSAN D COOK MARIETTA FREY GEORGE C LASTRADA PRODUCTS 106 100 G 102 122 X SEE APACHE ADVERTISING © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
Alphabetic Index q A list of correspondent names or subjects for a numeric file ALPHABETIC INDEX APACHE ADVERTISING 122 APPLICATIONS BROWN SUSAN D COOK MARIETTA FREY GEORGE C LASTRADA PRODUCTS 106 100 G 102 122 X SEE APACHE ADVERTISING © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
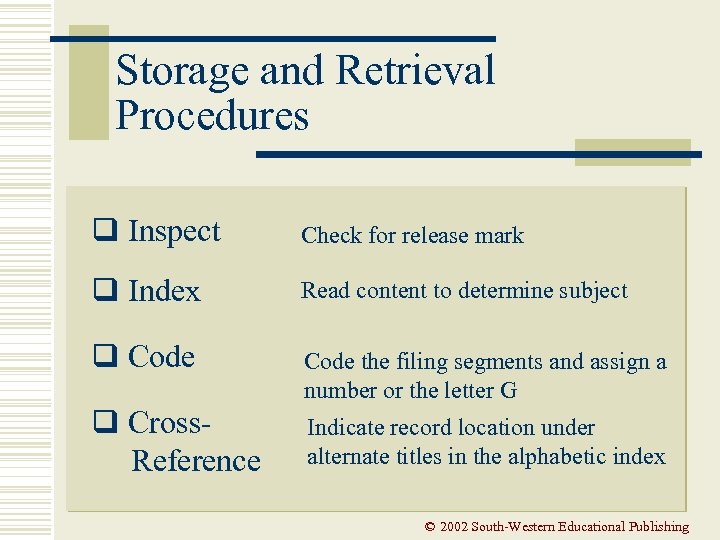 Storage and Retrieval Procedures q Inspect Check for release mark q Index Read content to determine subject q Code the filing segments and assign a number or the letter G q Cross. Reference Indicate record location under alternate titles in the alphabetic index © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
Storage and Retrieval Procedures q Inspect Check for release mark q Index Read content to determine subject q Code the filing segments and assign a number or the letter G q Cross. Reference Indicate record location under alternate titles in the alphabetic index © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
 Storage and Retrieval Procedures q Sort Arrange records numerically q Store Place record in appropriate folder q Retrieve Locate record under code identified on the alphabetic index © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
Storage and Retrieval Procedures q Sort Arrange records numerically q Store Place record in appropriate folder q Retrieve Locate record under code identified on the alphabetic index © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
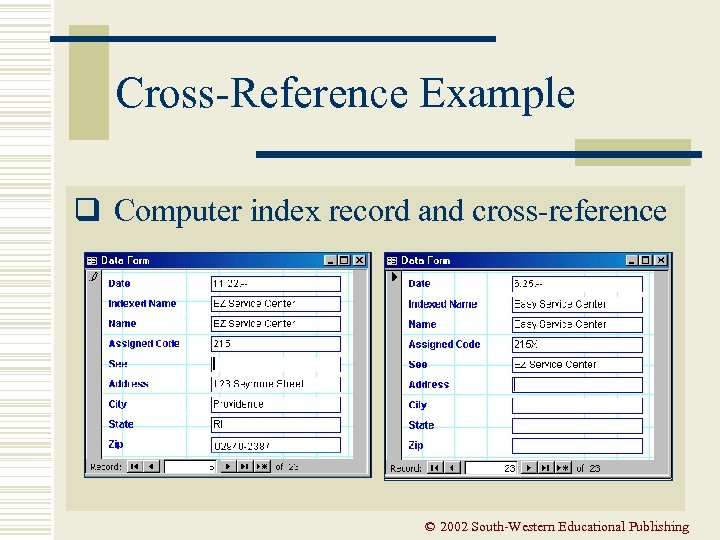 Cross-Reference Example q Computer index record and cross-reference © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
Cross-Reference Example q Computer index record and cross-reference © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
 Terminal-Digit Arrangement q A nonconsecutive numeric storage method § Breaks numbers into groups § The last group of digits used as the primary file division § Number groups read left to right 058 32 Tertiary Group Secondary Primary Group 6401 © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
Terminal-Digit Arrangement q A nonconsecutive numeric storage method § Breaks numbers into groups § The last group of digits used as the primary file division § Number groups read left to right 058 32 Tertiary Group Secondary Primary Group 6401 © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
 Middle-Digit Arrangement q A nonconsecutive numeric storage method § Breaks numbers into groups § The secondary group of digits used as the primary file division § Number groups read middle to left to right 058 32 Secondary Group Primary Tertiary Group 6401 © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
Middle-Digit Arrangement q A nonconsecutive numeric storage method § Breaks numbers into groups § The secondary group of digits used as the primary file division § Number groups read middle to left to right 058 32 Secondary Group Primary Tertiary Group 6401 © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
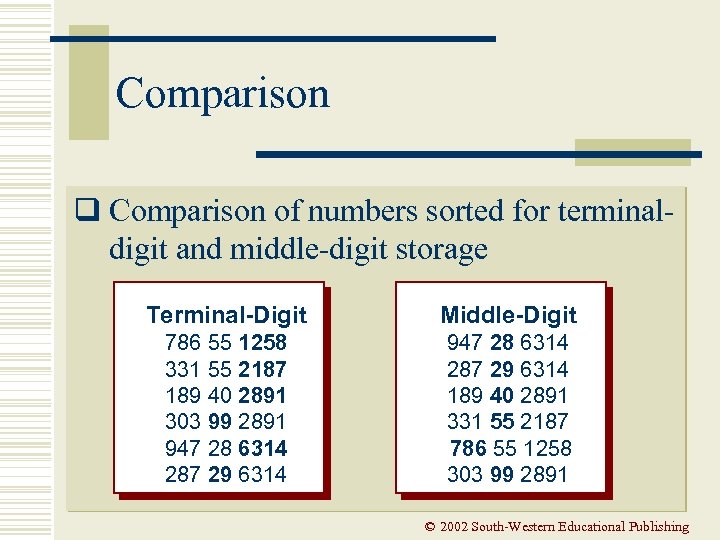 Comparison q Comparison of numbers sorted for terminaldigit and middle-digit storage Terminal-Digit Middle-Digit 786 55 1258 331 55 2187 189 40 2891 303 99 2891 947 28 6314 287 29 6314 189 40 2891 331 55 2187 786 55 1258 303 99 2891 © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
Comparison q Comparison of numbers sorted for terminaldigit and middle-digit storage Terminal-Digit Middle-Digit 786 55 1258 331 55 2187 189 40 2891 303 99 2891 947 28 6314 287 29 6314 189 40 2891 331 55 2187 786 55 1258 303 99 2891 © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
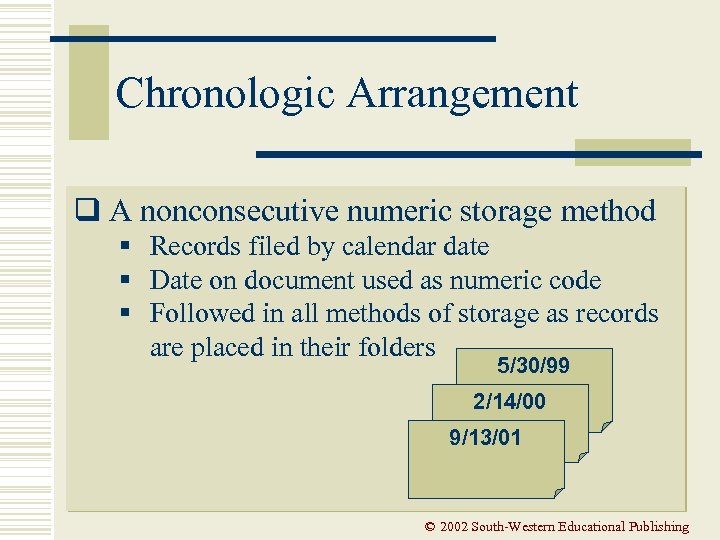 Chronologic Arrangement q A nonconsecutive numeric storage method § Records filed by calendar date § Date on document used as numeric code § Followed in all methods of storage as records are placed in their folders 5/30/99 2/14/00 9/13/01 © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
Chronologic Arrangement q A nonconsecutive numeric storage method § Records filed by calendar date § Date on document used as numeric code § Followed in all methods of storage as records are placed in their folders 5/30/99 2/14/00 9/13/01 © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
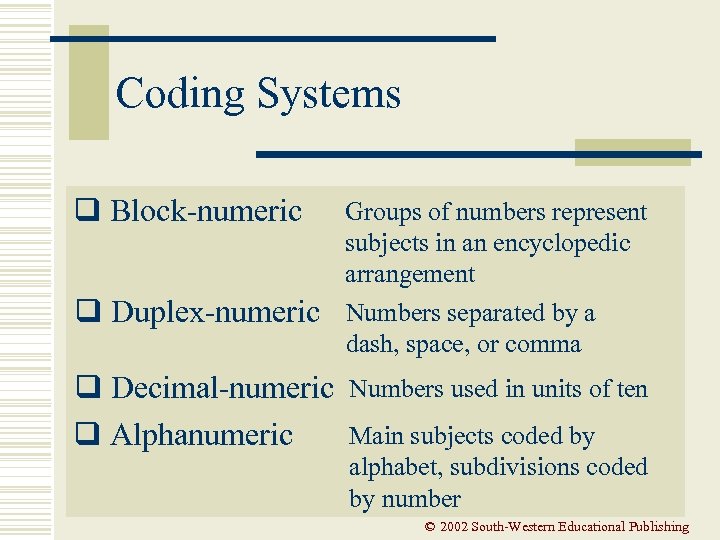 Coding Systems q Block-numeric q Duplex-numeric q Decimal-numeric q Alphanumeric Groups of numbers represent subjects in an encyclopedic arrangement Numbers separated by a dash, space, or comma Numbers used in units of ten Main subjects coded by alphabet, subdivisions coded by number © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
Coding Systems q Block-numeric q Duplex-numeric q Decimal-numeric q Alphanumeric Groups of numbers represent subjects in an encyclopedic arrangement Numbers separated by a dash, space, or comma Numbers used in units of ten Main subjects coded by alphabet, subdivisions coded by number © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
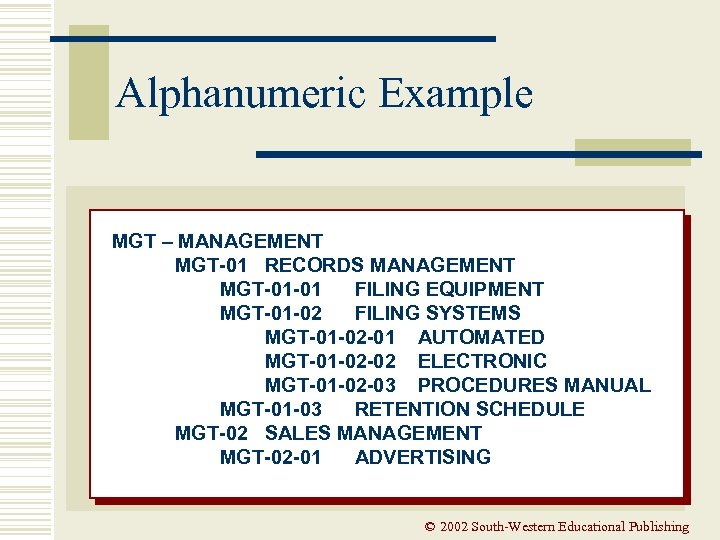 Alphanumeric Example MGT – MANAGEMENT MGT-01 RECORDS MANAGEMENT MGT-01 -01 FILING EQUIPMENT MGT-01 -02 FILING SYSTEMS MGT-01 -02 -01 AUTOMATED MGT-01 -02 -02 ELECTRONIC MGT-01 -02 -03 PROCEDURES MANUAL MGT-01 -03 RETENTION SCHEDULE MGT-02 SALES MANAGEMENT MGT-02 -01 ADVERTISING © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
Alphanumeric Example MGT – MANAGEMENT MGT-01 RECORDS MANAGEMENT MGT-01 -01 FILING EQUIPMENT MGT-01 -02 FILING SYSTEMS MGT-01 -02 -01 AUTOMATED MGT-01 -02 -02 ELECTRONIC MGT-01 -02 -03 PROCEDURES MANUAL MGT-01 -03 RETENTION SCHEDULE MGT-02 SALES MANAGEMENT MGT-02 -01 ADVERTISING © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
 Computer Indexes q Eliminate re-entering data q Are easy to access and update q Can be sorted for consecutive, terminaldigit, or middle-digit arrangements © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing
Computer Indexes q Eliminate re-entering data q Are easy to access and update q Can be sorted for consecutive, terminaldigit, or middle-digit arrangements © 2002 South-Western Educational Publishing


