46e396d506003642a0b7978360f61a25.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 Reconstruction Of the South
Reconstruction Of the South
 Lincoln’s Plan w Pardon and grant amnesty w When 10% of the 1860 voters took an oath and agree to abide by the government which abolishes slavery, then the state government will be recognized w States had never left the union; some citizens were in rebellion; we are all country men again
Lincoln’s Plan w Pardon and grant amnesty w When 10% of the 1860 voters took an oath and agree to abide by the government which abolishes slavery, then the state government will be recognized w States had never left the union; some citizens were in rebellion; we are all country men again
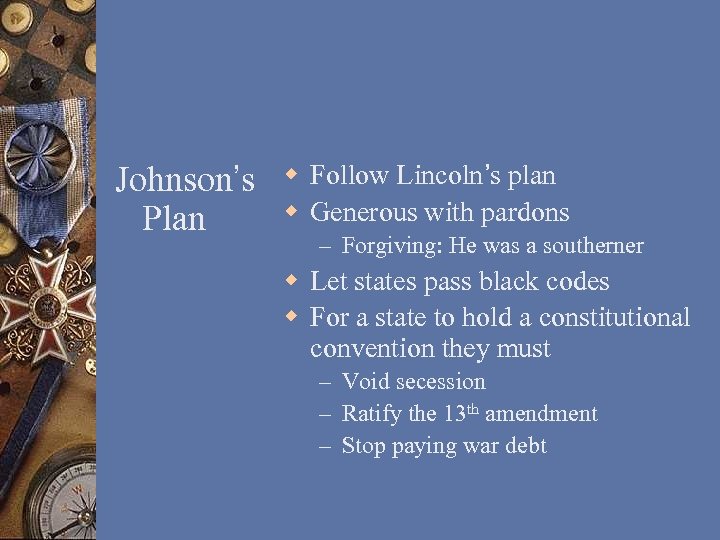 Johnson’s Plan w Follow Lincoln’s plan w Generous with pardons – Forgiving: He was a southerner w Let states pass black codes w For a state to hold a constitutional convention they must – Void secession – Ratify the 13 th amendment – Stop paying war debt
Johnson’s Plan w Follow Lincoln’s plan w Generous with pardons – Forgiving: He was a southerner w Let states pass black codes w For a state to hold a constitutional convention they must – Void secession – Ratify the 13 th amendment – Stop paying war debt
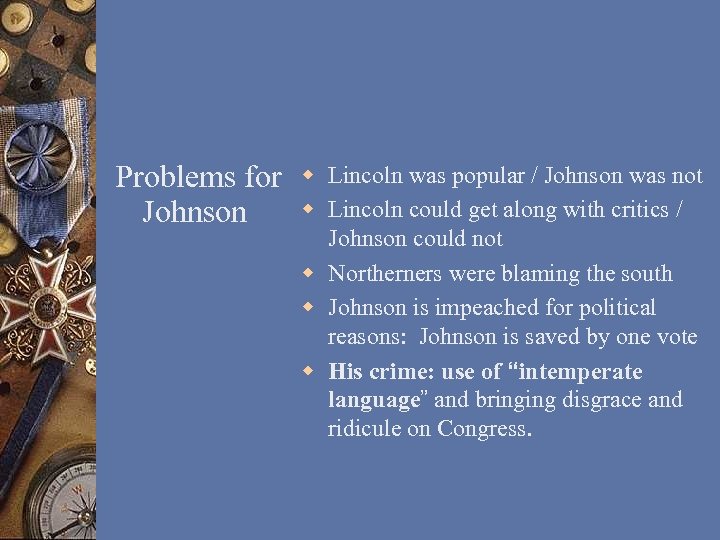 Problems for Johnson w Lincoln was popular / Johnson was not w Lincoln could get along with critics / Johnson could not w Northerners were blaming the south w Johnson is impeached for political reasons: Johnson is saved by one vote w His crime: use of “intemperate language” and bringing disgrace and ridicule on Congress.
Problems for Johnson w Lincoln was popular / Johnson was not w Lincoln could get along with critics / Johnson could not w Northerners were blaming the south w Johnson is impeached for political reasons: Johnson is saved by one vote w His crime: use of “intemperate language” and bringing disgrace and ridicule on Congress.
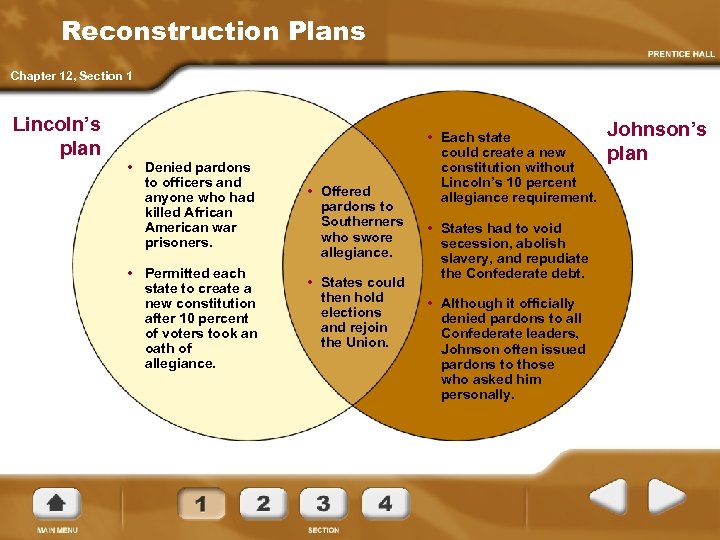 Reconstruction Plans Chapter 12, Section 1 Lincoln’s plan • Denied pardons to officers and anyone who had killed African American war prisoners. • Permitted each state to create a new constitution after 10 percent of voters took an oath of allegiance. • Offered pardons to Southerners who swore allegiance. • States could then hold elections and rejoin the Union. • Each state could create a new constitution without Lincoln’s 10 percent allegiance requirement. • States had to void secession, abolish slavery, and repudiate the Confederate debt. • Although it officially denied pardons to all Confederate leaders, Johnson often issued pardons to those who asked him personally. Johnson’s plan
Reconstruction Plans Chapter 12, Section 1 Lincoln’s plan • Denied pardons to officers and anyone who had killed African American war prisoners. • Permitted each state to create a new constitution after 10 percent of voters took an oath of allegiance. • Offered pardons to Southerners who swore allegiance. • States could then hold elections and rejoin the Union. • Each state could create a new constitution without Lincoln’s 10 percent allegiance requirement. • States had to void secession, abolish slavery, and repudiate the Confederate debt. • Although it officially denied pardons to all Confederate leaders, Johnson often issued pardons to those who asked him personally. Johnson’s plan
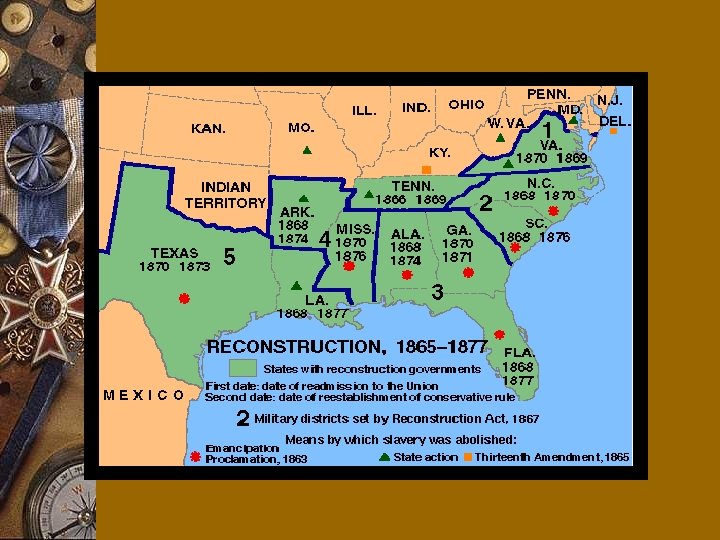
 w South must be Punished Radical Republicans’ w Military Reconstruction Act of 1867 Plan – Divides the South into 5 Military Districts • Each governed by a Union General – Confederacy can’t pay war debts or Southerners for the loss of their slaves. – Punish states which do not allow African-American males to vote
w South must be Punished Radical Republicans’ w Military Reconstruction Act of 1867 Plan – Divides the South into 5 Military Districts • Each governed by a Union General – Confederacy can’t pay war debts or Southerners for the loss of their slaves. – Punish states which do not allow African-American males to vote
 w RR Cont. All qualified voters not including those who supported the Confederacy could vote for delegates to a Constitutional Convention when – The 14 th amendment was ratified – Guaranteed the rights to all citizens – Permit African American males the right to vote
w RR Cont. All qualified voters not including those who supported the Confederacy could vote for delegates to a Constitutional Convention when – The 14 th amendment was ratified – Guaranteed the rights to all citizens – Permit African American males the right to vote
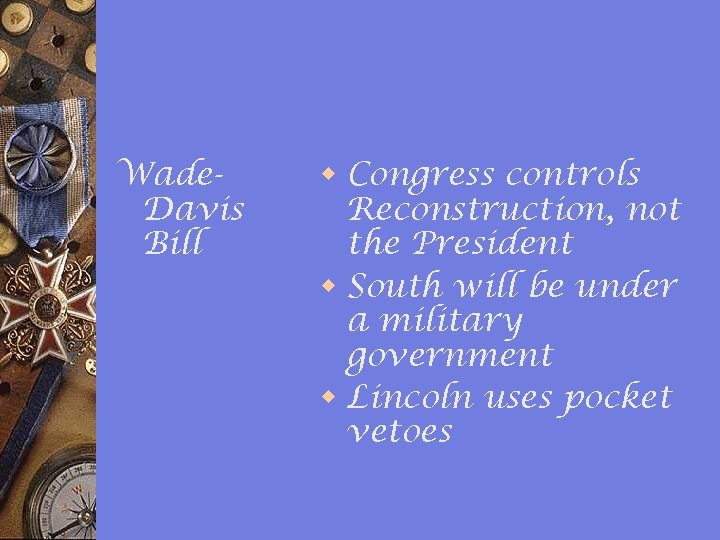 Wade. Davis Bill w Congress controls Reconstruction, not the President w South will be under a military government w Lincoln uses pocket vetoes
Wade. Davis Bill w Congress controls Reconstruction, not the President w South will be under a military government w Lincoln uses pocket vetoes
 North – Freedman’s Bureau: aid medical care to help newly freed blacks: built schools and hospitals – 13 th amendment: ends slavery – 14 th Amendment: everyone born in the U. S. A is a citizen; state can’t deny a citizen federal rights of life, liberty or property without due process – 15 th amendment: The right to vote for African American males
North – Freedman’s Bureau: aid medical care to help newly freed blacks: built schools and hospitals – 13 th amendment: ends slavery – 14 th Amendment: everyone born in the U. S. A is a citizen; state can’t deny a citizen federal rights of life, liberty or property without due process – 15 th amendment: The right to vote for African American males
 South – Black Codes: used to control the actions of ex-slaves examples are curfews, can’t serve on a jury, can’t marry whites, can’t carry a weapon – Sharecropping: ties workers to land; like slavery – Segregation: separate by race – Solid South: south votes strongly democratic
South – Black Codes: used to control the actions of ex-slaves examples are curfews, can’t serve on a jury, can’t marry whites, can’t carry a weapon – Sharecropping: ties workers to land; like slavery – Segregation: separate by race – Solid South: south votes strongly democratic
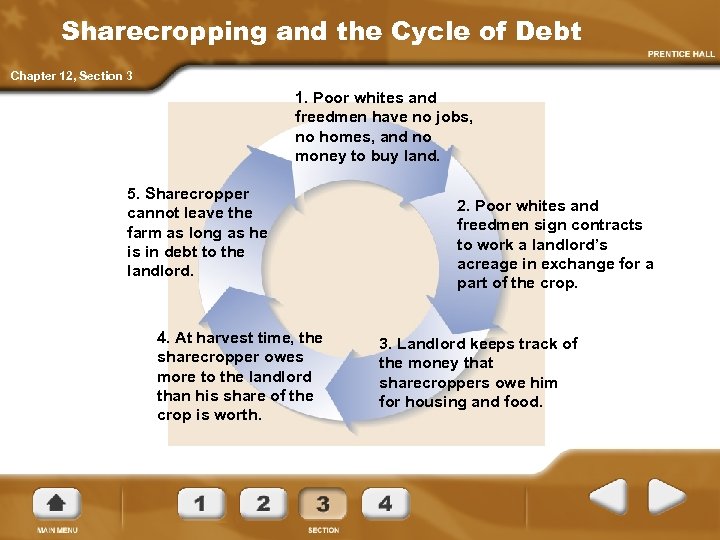 Sharecropping and the Cycle of Debt Chapter 12, Section 3 1. Poor whites and freedmen have no jobs, no homes, and no money to buy land. 5. Sharecropper cannot leave the farm as long as he is in debt to the landlord. 4. At harvest time, the sharecropper owes more to the landlord than his share of the crop is worth. 2. Poor whites and freedmen sign contracts to work a landlord’s acreage in exchange for a part of the crop. 3. Landlord keeps track of the money that sharecroppers owe him for housing and food.
Sharecropping and the Cycle of Debt Chapter 12, Section 3 1. Poor whites and freedmen have no jobs, no homes, and no money to buy land. 5. Sharecropper cannot leave the farm as long as he is in debt to the landlord. 4. At harvest time, the sharecropper owes more to the landlord than his share of the crop is worth. 2. Poor whites and freedmen sign contracts to work a landlord’s acreage in exchange for a part of the crop. 3. Landlord keeps track of the money that sharecroppers owe him for housing and food.
 Voting Restrictions w South passed laws to keep African-Americans from voting or holding office. w Poll Taxes: pay a fee in order to vote w Grandfather clause: you may vote only if your grandfather had voted in the past w Literacy test: you must show you can read in order to vote
Voting Restrictions w South passed laws to keep African-Americans from voting or holding office. w Poll Taxes: pay a fee in order to vote w Grandfather clause: you may vote only if your grandfather had voted in the past w Literacy test: you must show you can read in order to vote

 Attempts to profit from Reconstruction w Carpetbaggers: Northerner who moves to the south to exploit situations created by Reconstruction for their own advantage w. Scalawag: Southerner who cooperates with Reconstruction and joins the Republican party. These individuals are considered traitors by white Southerners.
Attempts to profit from Reconstruction w Carpetbaggers: Northerner who moves to the south to exploit situations created by Reconstruction for their own advantage w. Scalawag: Southerner who cooperates with Reconstruction and joins the Republican party. These individuals are considered traitors by white Southerners.
 Jim Crow Laws passed that separated blacks and whites in – – – – Trains Theaters Streetcars Playgrounds Hospitals Beaches Cemeteries
Jim Crow Laws passed that separated blacks and whites in – – – – Trains Theaters Streetcars Playgrounds Hospitals Beaches Cemeteries
 Post Civil War Agenda w Caring for the needs of newly freed slaves – Employment assistance – Housing assistance – Educational provision – Granting full rights as citizens w Mending the rift between North and south – Granting amnesty to confederates – Restoring states their full rights – Returning confiscated land to former confederate owners
Post Civil War Agenda w Caring for the needs of newly freed slaves – Employment assistance – Housing assistance – Educational provision – Granting full rights as citizens w Mending the rift between North and south – Granting amnesty to confederates – Restoring states their full rights – Returning confiscated land to former confederate owners
 Grant as President w Elected in 1868 w Radical Republicans want to divide the plantation land among slaves. Not supported by the Republican moderates w Sharecropping and tenant farming developed w 15 th amendment passed: voting rights
Grant as President w Elected in 1868 w Radical Republicans want to divide the plantation land among slaves. Not supported by the Republican moderates w Sharecropping and tenant farming developed w 15 th amendment passed: voting rights


