36b9e686eab6e9faaf446024da05e49d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 9

Reconstruction and Its Effects The U. S. begins to rebuild the South, but former slaves face new challenges as support fades for the policies of Reconstruction. NEXT

12. 1 The Politics of Reconstruction Congress opposes Lincoln’s and Johnson’s plans for Reconstruction and instead implements its own plan to rebuild the South. NEXT

http: //www. schooltube. com/video/f 2733 e 6 d 83 a 04 fc 98908/Radical%20 Reconstruction SECTION 1 I. Lincoln’s Plan for Reconstruction A. Lincoln’s Ten-Percent Plan • Reconstruction —period of rebuilding after Civil War, 1865– 1877 • Proclamation of Amnesty & Reconstruction calls for 10% allegiance • Radical Republicans led by Thaddeus Stevens - want to destroy power of former slaveholders - give full citizenship, suffrage to Af-Ams B. Radical Reaction • 1864 Wade-Davis Bill makes Congress responsible for Reconstruction • Lincoln uses pocket veto to kill Wade-Davis; Radicals outraged NEXT

https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=pt. XRF Hulc. ZQ SECTION 1 II. Johnson’s Plan A. Johnson Continues Lincoln’s Policies • • President Andrew Johnson proposes own Presidential Reconstruction: - states must swear allegiance, annul war debts, ratify 13 th Amendment - does not address voting rights, land, laws former slaves States that had not applied under Lincoln agree to Johnson’s terms - some states do not fully comply Continued. . . NEXT

https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=W 5 x. TRhw-Zw SECTION 1 B. Presidential Reconstruction Comes to a Standstill • Rad-Reps in Congress refuse new Southern legislators • Congress enlarges Freedmen’s Bureau —helps former slaves, poor whites - gives social services, medical care, education African Americans line up at the Freedmen’s Bureau office. Continued. . . NEXT

SECTION 1 C. Civil Rights Act of 1866 • Congress passes: - grants citizenship to Af-Ams - forbids black codes or discriminatory laws • Black codes restore many restrictions of slavery • Whites use violence to prevent blacks from improving their lives • Johnson vetoes Freedmen’s Bureau & Civil Rights Act • Alienates moderate Republicans; angers Radicals NEXT

SECTION 1 III. Congressional Reconstruction A. Moderates and Radicals Join Forces • • • In mid-1866, moderate Republicans join Radicals to override veto Draft 14 th Amendment —makes Af-Ams full citizens Most Southern states reject amendment; not ratified until 1868 "All persons born or naturalized in the United States, and subject to the jurisdiction thereof, are citizens of the United States and the State wherein they reside. " B. 1866 Congressional Elections • Moderates, Radicals win 2/3 majority in Congress, can override veto Continued. . . NEXT

https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=r. CSQb iyb. Lj. Y SECTION 1 C. Reconstruction Act of 1867 • doesn’t recognize most new state govts - divides South into military districts (5) - sets new conditions for reentry in Union • Johnson believes act unconstitutional, vetoes; Congress overrides D. Johnson Impeached • Radicals seek to impeach —formally charge with misconduct in office • Johnson fires Stanton—test constitutionality of Tenure of Office Act • House Radicals impeach Johnson; Senate does not convict (found not guilty by 1 vote) Continued. . . NEXT
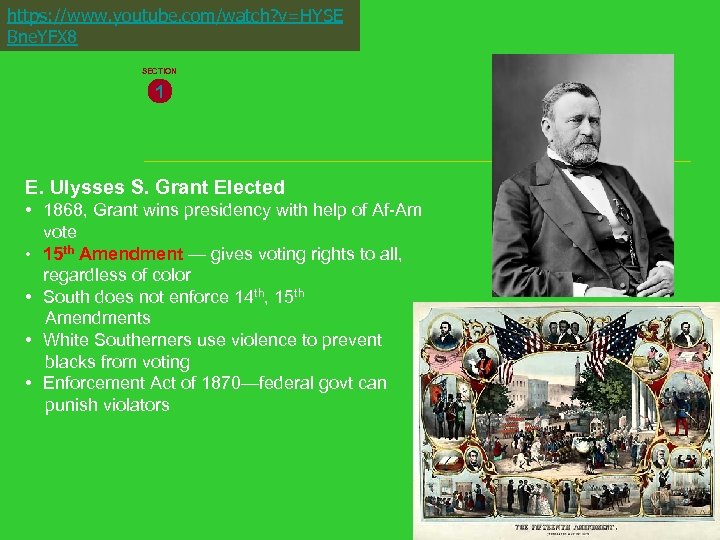
https: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=HYSE Bne. YFX 8 SECTION 1 E. Ulysses S. Grant Elected • 1868, Grant wins presidency with help of Af-Am vote • 15 th Amendment — gives voting rights to all, regardless of color • South does not enforce 14 th, 15 th Amendments • White Southerners use violence to prevent blacks from voting • Enforcement Act of 1870—federal govt can punish violators NEXT
36b9e686eab6e9faaf446024da05e49d.ppt