dd6f43df18dd7373b11e7ac83351e91d.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 41
 Reconstruction 1863 -1877
Reconstruction 1863 -1877
 Phase 1: Presidential Reconstruction Plans 1863 -Spring 1866
Phase 1: Presidential Reconstruction Plans 1863 -Spring 1866
 Presidential Reconstruction Plans Lincoln’s Plan n n Wanted the process to be simple, meeting a minimum test of loyalty Proclamation of Amnesty and Reconstruction (1863) Full presidential pardons to southerners who (1) took an oath of allegiance to the Union and the Constitution and (2) accepted the emancipation of slaves State governments could be reestablished as soon as 10% of the population took the oath
Presidential Reconstruction Plans Lincoln’s Plan n n Wanted the process to be simple, meeting a minimum test of loyalty Proclamation of Amnesty and Reconstruction (1863) Full presidential pardons to southerners who (1) took an oath of allegiance to the Union and the Constitution and (2) accepted the emancipation of slaves State governments could be reestablished as soon as 10% of the population took the oath
 Presidential Reconstruction Plans Congressional Republican Plan n Wade-Davis Bill (1864) n n Response by many Republicans who thought that Lincoln’s plan would allow disloyal secessionists to run state governments Required 50% of voters to take the loyalty oath Only non-confederates could vote on a new state constitution Lincoln pocket-vetoes the bill n Leaves it alone until after congress adjourns
Presidential Reconstruction Plans Congressional Republican Plan n Wade-Davis Bill (1864) n n Response by many Republicans who thought that Lincoln’s plan would allow disloyal secessionists to run state governments Required 50% of voters to take the loyalty oath Only non-confederates could vote on a new state constitution Lincoln pocket-vetoes the bill n Leaves it alone until after congress adjourns
 Presidential Reconstruction Plans n Congress was ready to reassert its power after the war in 1865 n n Retake power of the president Freedmen’s Bureau (Bureau of Refugees, Freedmen, and Abandoned Lands) n n n Provided food, shelter, medical aid for the destitute Benefited both blacks (mostly freed slaves) and homeless whites Had the authority to resettle freed blacks on confiscated farmland
Presidential Reconstruction Plans n Congress was ready to reassert its power after the war in 1865 n n Retake power of the president Freedmen’s Bureau (Bureau of Refugees, Freedmen, and Abandoned Lands) n n n Provided food, shelter, medical aid for the destitute Benefited both blacks (mostly freed slaves) and homeless whites Had the authority to resettle freed blacks on confiscated farmland
 Presidential Reconstruction Plans n n n Led by General Oliver O. Howard Greatest success in education Established almost 3, 000 schools for freed blacks as well as several colleges Helped approximately 200, 000 African. Americans how to read Funding ended in 1870
Presidential Reconstruction Plans n n n Led by General Oliver O. Howard Greatest success in education Established almost 3, 000 schools for freed blacks as well as several colleges Helped approximately 200, 000 African. Americans how to read Funding ended in 1870
 n n Last public address on April 11, 1865 Says he wants to grant the right to vote to “very intelligent” freedmen and those who were soldiers Suggests that he would have adopted the congressional Republican agenda Loss of intelligent & flexible leader makes lasting reform impossible
n n Last public address on April 11, 1865 Says he wants to grant the right to vote to “very intelligent” freedmen and those who were soldiers Suggests that he would have adopted the congressional Republican agenda Loss of intelligent & flexible leader makes lasting reform impossible
 Presidential Reconstruction Plans Andrew Johnson’s Plan n Chosen as running mate in 1864 to encourage pro-Union democrats to vote for the Union (Republican) party n Was the only senator from a Confederate state who stayed loyal to the Union n Tennessee’s war governor n Problem with him leading reconstruction: He’s a white supremacist
Presidential Reconstruction Plans Andrew Johnson’s Plan n Chosen as running mate in 1864 to encourage pro-Union democrats to vote for the Union (Republican) party n Was the only senator from a Confederate state who stayed loyal to the Union n Tennessee’s war governor n Problem with him leading reconstruction: He’s a white supremacist
 Presidential Reconstruction Plans n n Plan is similar to Lincoln’s 10% Plan Provided for disfranchisement of certain groups (1) All former leaders and officeholders of the Confederacy (2) Confederates with more than $20, 000 in taxable property n n Retains power to pardon “disloyal” southerners Frequently pardoned wealthy planters n Many former Confederates in power by fall, 1865
Presidential Reconstruction Plans n n Plan is similar to Lincoln’s 10% Plan Provided for disfranchisement of certain groups (1) All former leaders and officeholders of the Confederacy (2) Confederates with more than $20, 000 in taxable property n n Retains power to pardon “disloyal” southerners Frequently pardoned wealthy planters n Many former Confederates in power by fall, 1865
 Presidential Reconstruction Plans Southern Governments of 1865 n 8 months after Johnson takes office, all 11 of the ex-Confederate states qualified to rejoin the Union n They repudiated secession, negated debts of the Confederacy, ratified the 13 th Amendment. n But they didn’t give blacks voting rights and ex. Confederates elected to congress n Alexander Stephens, VP of the CSA elected senator from Georgia
Presidential Reconstruction Plans Southern Governments of 1865 n 8 months after Johnson takes office, all 11 of the ex-Confederate states qualified to rejoin the Union n They repudiated secession, negated debts of the Confederacy, ratified the 13 th Amendment. n But they didn’t give blacks voting rights and ex. Confederates elected to congress n Alexander Stephens, VP of the CSA elected senator from Georgia
 Presidential Reconstruction Plans Black Codes n n n Prohibited blacks from renting land or borrowing money to buy land Placed freedmen into a form of servitude by forcing them as “vagrants” and “apprentices” to sign work contracts n n Restricted the rights of newly freed blacks Worked in cotton fields under white supervision for deferred wages Prohibited blacks from testifying against whites in court
Presidential Reconstruction Plans Black Codes n n n Prohibited blacks from renting land or borrowing money to buy land Placed freedmen into a form of servitude by forcing them as “vagrants” and “apprentices” to sign work contracts n n Restricted the rights of newly freed blacks Worked in cotton fields under white supervision for deferred wages Prohibited blacks from testifying against whites in court
 Presidential Reconstruction Plans Republicans begin to ask “Who won the war? ” Begin to demonstrate unhappiness w/Johnson n In 1866, Congress refuses to seat elected representatives and senators from former Confederate states
Presidential Reconstruction Plans Republicans begin to ask “Who won the war? ” Begin to demonstrate unhappiness w/Johnson n In 1866, Congress refuses to seat elected representatives and senators from former Confederate states
 Johnson angers them again by vetoing 2 bills: (1) a bill increasing services and protection of Freedmen’s bureau (2) a civil rights bill nullifying black codes and guaranteeing full citizenship and equal rights to blacks
Johnson angers them again by vetoing 2 bills: (1) a bill increasing services and protection of Freedmen’s bureau (2) a civil rights bill nullifying black codes and guaranteeing full citizenship and equal rights to blacks
 Election of 1866 n n n Johnson launches campaign against Republicans Appeals to racial prejudices Says Equal Rights = “Africanization” of society n Republicans “wave the bloody shirt” n n n Inflame northern voters by reminding them of wartime hardships Propaganda campaign against Democrats Since southerners are Democrats, all Democrats belong to the party of Rebellion and Treason
Election of 1866 n n n Johnson launches campaign against Republicans Appeals to racial prejudices Says Equal Rights = “Africanization” of society n Republicans “wave the bloody shirt” n n n Inflame northern voters by reminding them of wartime hardships Propaganda campaign against Democrats Since southerners are Democrats, all Democrats belong to the party of Rebellion and Treason
 Phase 2: Congressional Reconstruction 1866 -1872
Phase 2: Congressional Reconstruction 1866 -1872
 Congressional Reconstruction n n After election of 1866, Republicans have a 2/3 majority in the House and Senate Most Republicans join the Radicals n n Feared strength of unified Democrats, especially since the South gained seats in Congress Led by Senator Charles Sumner of Massachusetts and Rep. Thaddeus Stevens of Pennsylvania
Congressional Reconstruction n n After election of 1866, Republicans have a 2/3 majority in the House and Senate Most Republicans join the Radicals n n Feared strength of unified Democrats, especially since the South gained seats in Congress Led by Senator Charles Sumner of Massachusetts and Rep. Thaddeus Stevens of Pennsylvania
 Congressional Reconstruction The Radical Program Civil Rights Act of 1866 n Pronounces all African-Americans to be U. S. citizens, repudiating the Dred Scott decision, shield against black codes Fourteenth Amendment n All people born/naturalized in U. S. are citizens n “equal protection” of laws & “due process” need to be protected by the states
Congressional Reconstruction The Radical Program Civil Rights Act of 1866 n Pronounces all African-Americans to be U. S. citizens, repudiating the Dred Scott decision, shield against black codes Fourteenth Amendment n All people born/naturalized in U. S. are citizens n “equal protection” of laws & “due process” need to be protected by the states
 Congressional Reconstruction Joint Committee of June 1866 n Decide that the Confederates are not entitled to representation in Congress n Determines that Congress, not the president has the power to set the conditions of readmitting a state n All but renders Johnson’s powers useless
Congressional Reconstruction Joint Committee of June 1866 n Decide that the Confederates are not entitled to representation in Congress n Determines that Congress, not the president has the power to set the conditions of readmitting a state n All but renders Johnson’s powers useless
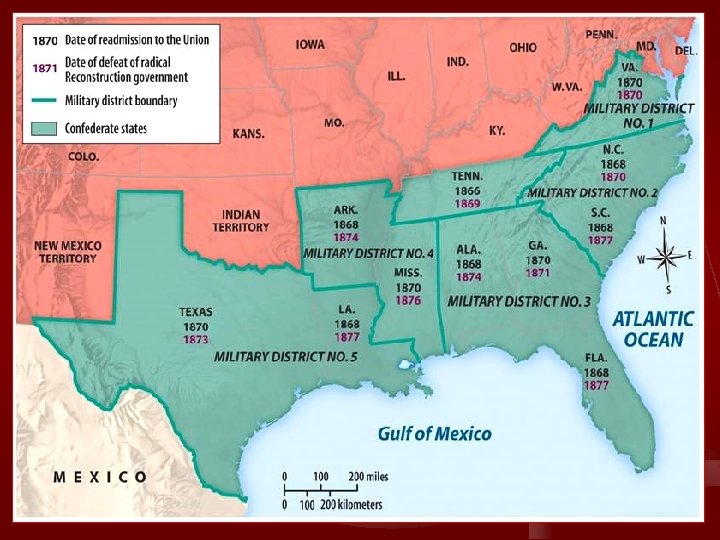
 Congressional Reconstruction Acts of 1867 n Passed over Johnson’s vetoes n Placed the South under military occupation n Divides the former Confederacy into five military districts under the control of the Union army n Added the condition of ratifying the 14 th Amendment as a readmission requirement
Congressional Reconstruction Acts of 1867 n Passed over Johnson’s vetoes n Placed the South under military occupation n Divides the former Confederacy into five military districts under the control of the Union army n Added the condition of ratifying the 14 th Amendment as a readmission requirement
 Congressional Reconstruction Andrew Johnson’s Impeachment n 1867—Congress passes Tenure of Office Act n Prohibits the president form removing federal officials or military commanders without the Senate’s approval n Probably unconstitutional n Designed to protect cabinet Radical Republicans n Congress wanted to maintain the military governments installed in the South
Congressional Reconstruction Andrew Johnson’s Impeachment n 1867—Congress passes Tenure of Office Act n Prohibits the president form removing federal officials or military commanders without the Senate’s approval n Probably unconstitutional n Designed to protect cabinet Radical Republicans n Congress wanted to maintain the military governments installed in the South
 Congressional Reconstruction n n Johnson dismisses Edwin Stanton, Secretary of War House charges Johnson with 11 “high crimes and misdemeanors” Impeaches, or indicts him Senate falls one vote short of removing him from office n n Needed 2/3 of Senate Democrats and more moderate Republicans don’t want to set precedent of removal for political reasons
Congressional Reconstruction n n Johnson dismisses Edwin Stanton, Secretary of War House charges Johnson with 11 “high crimes and misdemeanors” Impeaches, or indicts him Senate falls one vote short of removing him from office n n Needed 2/3 of Senate Democrats and more moderate Republicans don’t want to set precedent of removal for political reasons
 Congressional Reconstruction n n Fall 1868—Presidential election Democrats had nominated Horatio Seymour n n Republicans nominate Ulysses S. Grant n n Johnson’s out no matter what War hero, but no political experience Very close election—would have lost without black votes
Congressional Reconstruction n n Fall 1868—Presidential election Democrats had nominated Horatio Seymour n n Republicans nominate Ulysses S. Grant n n Johnson’s out no matter what War hero, but no political experience Very close election—would have lost without black votes
 Congressional Reconstruction Fifteenth Amendment (1869) n Prohibits states from denying a citizen’s right to vote on condition of race, color, or previous condition of servitude n Civil Rights Act of 1875 n Guaranteed equal accommodations in public places, including hotels, railroads, and theaters n Poorly enforced, and largely ignored
Congressional Reconstruction Fifteenth Amendment (1869) n Prohibits states from denying a citizen’s right to vote on condition of race, color, or previous condition of servitude n Civil Rights Act of 1875 n Guaranteed equal accommodations in public places, including hotels, railroads, and theaters n Poorly enforced, and largely ignored
 Reconstruction in the South n n n Military rule by the Union army until ready for readmission Whites are the majority in all state legislatures except for lower house of South Carolina in 1873 Most Republicans were native-born whites, freemen, and northern transplants
Reconstruction in the South n n n Military rule by the Union army until ready for readmission Whites are the majority in all state legislatures except for lower house of South Carolina in 1873 Most Republicans were native-born whites, freemen, and northern transplants
 Reconstruction in the South n Scalawags n n Carpetbaggers n n n Conservative Democrat name for Southern Republicans Northern newcomers who supported Republican policies Most southern white Republican interested in economic development for their state Northerners interested in new business, missionary work, teachers, and some were just plain greedy
Reconstruction in the South n Scalawags n n Carpetbaggers n n n Conservative Democrat name for Southern Republicans Northern newcomers who supported Republican policies Most southern white Republican interested in economic development for their state Northerners interested in new business, missionary work, teachers, and some were just plain greedy
 Reconstruction in the South n n n African-American legislators Most were educated property-holders Moderates Two black Senators and over a dozen Representatives sent to Congress Hiram Revels takes Jefferson Davis’s Senate seat from Mississippi Causes bitter resentment among disfranchised ex-Confederates
Reconstruction in the South n n n African-American legislators Most were educated property-holders Moderates Two black Senators and over a dozen Representatives sent to Congress Hiram Revels takes Jefferson Davis’s Senate seat from Mississippi Causes bitter resentment among disfranchised ex-Confederates
 Reconstruction in the South The Republican Record n n n n Universal male suffrage Property Rights for Women Debt relief Modernized penal codes Built roads, bridges, railroads Hospitals, asylums, public schools for all Overhauled tax systems, issued bonds n n Graft and wasteful spending Kickbacks and bribes from gov’t contractors Decline in gov’t ethics Sharecropping n n Economic picture didn’t improve for blacks By 1880, less than 5% of southern blacks are independent landowners
Reconstruction in the South The Republican Record n n n n Universal male suffrage Property Rights for Women Debt relief Modernized penal codes Built roads, bridges, railroads Hospitals, asylums, public schools for all Overhauled tax systems, issued bonds n n Graft and wasteful spending Kickbacks and bribes from gov’t contractors Decline in gov’t ethics Sharecropping n n Economic picture didn’t improve for blacks By 1880, less than 5% of southern blacks are independent landowners
 Reconstruction in the North n n Idealism pushed aside, marked by greed and corruption in politics and business Rise of spoilsmen n Give gov’t jobs and favors to supporters Crédit Mobilier Affair n Influential Congressmen given stock by insiders n Hiding profits of up to 348% from gov’t subsidies for building the transcontinental railroad
Reconstruction in the North n n Idealism pushed aside, marked by greed and corruption in politics and business Rise of spoilsmen n Give gov’t jobs and favors to supporters Crédit Mobilier Affair n Influential Congressmen given stock by insiders n Hiding profits of up to 348% from gov’t subsidies for building the transcontinental railroad

 Reconstruction in the North Election of 1872 n Republicans break apart due to scandals and corruption of Grant Administration n Select Horace Greeley to run as Liberal Republican n Also nominated by Democrats n “Bloody Shirt” waved again n Grant wins in a landslide
Reconstruction in the North Election of 1872 n Republicans break apart due to scandals and corruption of Grant Administration n Select Horace Greeley to run as Liberal Republican n Also nominated by Democrats n “Bloody Shirt” waved again n Grant wins in a landslide
 Reconstruction in the North Panic of 1873 n Overspeculation by financiers and overbuilding by industry and railroads n Debtors wanted more paper money issued that wasn’t supported by gold n In 1874, Grant sides with hard-money bankers
Reconstruction in the North Panic of 1873 n Overspeculation by financiers and overbuilding by industry and railroads n Debtors wanted more paper money issued that wasn’t supported by gold n In 1874, Grant sides with hard-money bankers
 Phase 3 End of Reconstruction 1872 -1877
Phase 3 End of Reconstruction 1872 -1877
 The End of Reconstruction n During Grant’s second term, Radical Republicanism declining Corruption, economic problems in the north, waning interest in idealistic policies Rise of the redeemers n n Southern conservatives Different social backgrounds, but all wanted States’ rights, lower taxes n Reduced spending on social programs n White supremacy n
The End of Reconstruction n During Grant’s second term, Radical Republicanism declining Corruption, economic problems in the north, waning interest in idealistic policies Rise of the redeemers n n Southern conservatives Different social backgrounds, but all wanted States’ rights, lower taxes n Reduced spending on social programs n White supremacy n
 The End of Reconstruction n n During Republican rule, southern whites organized secret societies to intimidate white reformers and blacks Ku Klux Klan Founded by an ex-Confederate General—Nathaniel Bedford Forrest “Invisible Empire” n n n Burned black-owned buildings Flogged, murdered freedmen to prevent voting Congress passes Force Acts in 1870 n n to stop the worst of the violence Enforce 14 th and 15 th Amendments
The End of Reconstruction n n During Republican rule, southern whites organized secret societies to intimidate white reformers and blacks Ku Klux Klan Founded by an ex-Confederate General—Nathaniel Bedford Forrest “Invisible Empire” n n n Burned black-owned buildings Flogged, murdered freedmen to prevent voting Congress passes Force Acts in 1870 n n to stop the worst of the violence Enforce 14 th and 15 th Amendments
 The End of Reconstruction Amnesty Act of 1872 n Removes restrictions on ex-Confederates, except the highest leaders n n By 1876 Federal troops withdrawn from everywhere except Louisiana, Florida, South Carolina Democrats regain control of House of Representatives
The End of Reconstruction Amnesty Act of 1872 n Removes restrictions on ex-Confederates, except the highest leaders n n By 1876 Federal troops withdrawn from everywhere except Louisiana, Florida, South Carolina Democrats regain control of House of Representatives
 The End of Reconstruction Election of 1876 n Republicans nominate Rutherford B. Hayes n n n Democrats nominate Samuel J. Tilden n n Governor of Ohio Not involved with corruption of Grant Administration Governor of New York Fought corruption of the Tweed Ring Votes contested in LA, FL, SC Tilden wins popular vote, needs only one electoral vote from one of the three states to win
The End of Reconstruction Election of 1876 n Republicans nominate Rutherford B. Hayes n n n Democrats nominate Samuel J. Tilden n n Governor of Ohio Not involved with corruption of Grant Administration Governor of New York Fought corruption of the Tweed Ring Votes contested in LA, FL, SC Tilden wins popular vote, needs only one electoral vote from one of the three states to win
 The End of Reconstruction n n Special electoral commission created to decide who gets disputed votes Commission: 8 Republicans, 7 Democrats Votes 8 -7 to give all electoral votes to Hayes Democrats threaten to filibuster the results, send election to the House
The End of Reconstruction n n Special electoral commission created to decide who gets disputed votes Commission: 8 Republicans, 7 Democrats Votes 8 -7 to give all electoral votes to Hayes Democrats threaten to filibuster the results, send election to the House

 The End of Reconstruction n (1) (2) n Compromise of 1877 Deal worked out between the parties Hayes becomes President on two conditions: Federal support for Republicans on the south ended immediately Support the building of a Southern transcontinental railroad Hayes complies with conditions, agrees to only serve one term
The End of Reconstruction n (1) (2) n Compromise of 1877 Deal worked out between the parties Hayes becomes President on two conditions: Federal support for Republicans on the south ended immediately Support the building of a Southern transcontinental railroad Hayes complies with conditions, agrees to only serve one term
 The End of Reconstruction Reasons for the final failure n End of federal military presence n Throughout 1880 s and 1890 s, Supreme Court strikes down anti-discrimination laws n New South supporters promised industrial development that never was realized n n Most blacks and whites remain poor farmers South increasingly fell behind the rest of the nation
The End of Reconstruction Reasons for the final failure n End of federal military presence n Throughout 1880 s and 1890 s, Supreme Court strikes down anti-discrimination laws n New South supporters promised industrial development that never was realized n n Most blacks and whites remain poor farmers South increasingly fell behind the rest of the nation


