868ca32c88230f6a47e5e098e4f9726a.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 Recoger el papel de la mesa y completa
Recoger el papel de la mesa y completa
 Presente Progressivo ¡ Someone IS -ing ¡ Estar + Present Participle Conjugate estar for Who Is… ¡ Change next verb into pres. Participle for the -ing ¡
Presente Progressivo ¡ Someone IS -ing ¡ Estar + Present Participle Conjugate estar for Who Is… ¡ Change next verb into pres. Participle for the -ing ¡
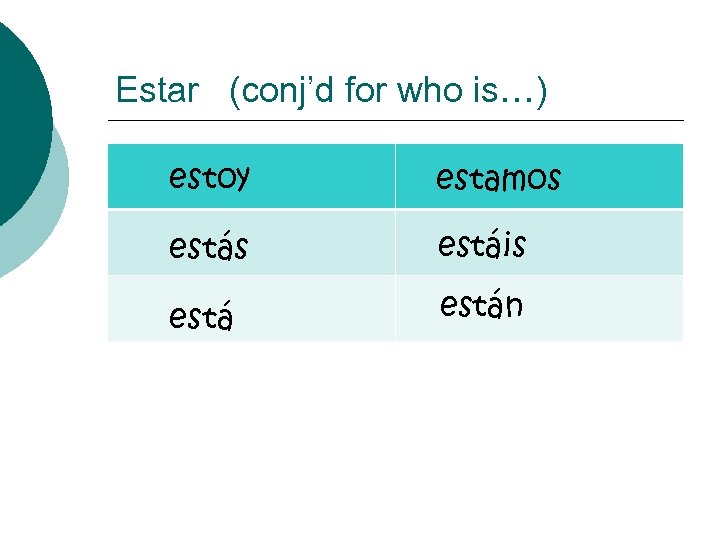 Estar (conj’d for who is…) estoy estamos estáis están
Estar (conj’d for who is…) estoy estamos estáis están
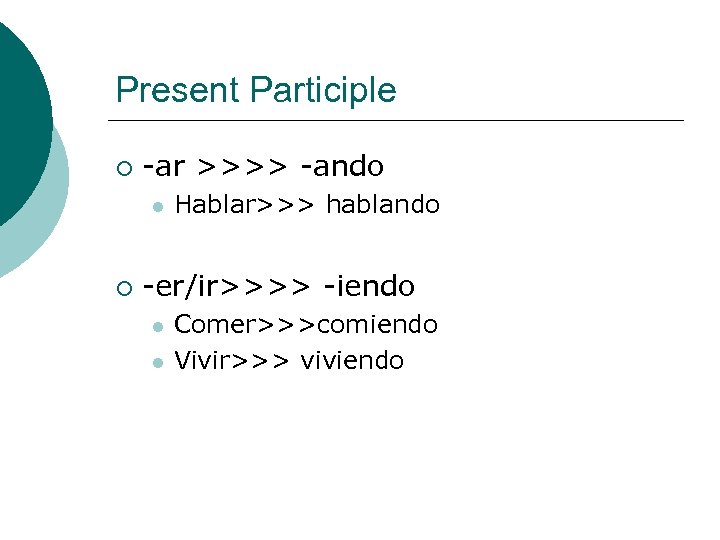 Present Participle ¡ -ar >>>> -ando l ¡ Hablar>>> hablando -er/ir>>>> -iendo l l Comer>>>comiendo Vivir>>> viviendo
Present Participle ¡ -ar >>>> -ando l ¡ Hablar>>> hablando -er/ir>>>> -iendo l l Comer>>>comiendo Vivir>>> viviendo
 Practicamos ¡ We are riding the horse. ¡ Juan is working at the mall. ¡ You are swimming at the beach.
Practicamos ¡ We are riding the horse. ¡ Juan is working at the mall. ¡ You are swimming at the beach.
 Direct Object Pronouns
Direct Object Pronouns
 ¿Por qué es importante? ¡ Porque no queremos hablar así: l The poet writes verses. He wrote the verses on the little piece of paper. He gave the verses to Lucy. He asked Lucy to sing the verses.
¿Por qué es importante? ¡ Porque no queremos hablar así: l The poet writes verses. He wrote the verses on the little piece of paper. He gave the verses to Lucy. He asked Lucy to sing the verses.
 Direct Objects ¡ The object (noun) that directly receives the action of the verb is called the direct object Ex. I want the book. Yo quiero el libro. ¡ What is receiving the action of the verb?
Direct Objects ¡ The object (noun) that directly receives the action of the verb is called the direct object Ex. I want the book. Yo quiero el libro. ¡ What is receiving the action of the verb?
 Direct Objects ¡ The direct object can also be a person Ex. I love Sammy. Yo amo a Samuelito. ¡ Who is receiving the action of the verb?
Direct Objects ¡ The direct object can also be a person Ex. I love Sammy. Yo amo a Samuelito. ¡ Who is receiving the action of the verb?
 What are the direct objects? ¡ Therefore, the direct object answers the question WHO or WHAT about the verb ¡ Yo lavo la ropa. ¡ Mamá lava los platos. ¡ Pablo lava el carro. ¡ Yo amo a mi esposo.
What are the direct objects? ¡ Therefore, the direct object answers the question WHO or WHAT about the verb ¡ Yo lavo la ropa. ¡ Mamá lava los platos. ¡ Pablo lava el carro. ¡ Yo amo a mi esposo.
 Direct Object Pronouns A direct object pronoun replaces the direct object (noun). Copy this in your notebooks: ¡ ____ – me ___ – you le- you(formal) lo – ____, it ___ – her, it ____ – us os – y’all ___ – them, you all (m) las – ____, ____(__)
Direct Object Pronouns A direct object pronoun replaces the direct object (noun). Copy this in your notebooks: ¡ ____ – me ___ – you le- you(formal) lo – ____, it ___ – her, it ____ – us os – y’all ___ – them, you all (m) las – ____, ____(__)
 Examples: ¡ ¡ ¡ The DO pronoun comes BEFORE the conjugated verb (if there is only one verb in the sentence) lo El hombre ^ lava el carro la Dylan ^ ama a Marta. las ¡ Scott ^ toca las guitarras.
Examples: ¡ ¡ ¡ The DO pronoun comes BEFORE the conjugated verb (if there is only one verb in the sentence) lo El hombre ^ lava el carro la Dylan ^ ama a Marta. las ¡ Scott ^ toca las guitarras.
 Práctica ¡ (yo) la como = ¡ (yo) los escribo = ¡ (yo) la quiero = ¡ (yo) las tengo = ¡ (yo) lo compro =
Práctica ¡ (yo) la como = ¡ (yo) los escribo = ¡ (yo) la quiero = ¡ (yo) las tengo = ¡ (yo) lo compro =
 Práctica ¡ I have them. ¡ She loves him. ¡ He loves me. ¡ Juan sees her. ¡ They call us. ¡ We call them.
Práctica ¡ I have them. ¡ She loves him. ¡ He loves me. ¡ Juan sees her. ¡ They call us. ¡ We call them.
 Frases negativas ¡ If you have a negative sentence the D. O. pronoun goes between the negative word and the conjugated verb. Ex: I don't buy the books. No compro los libros. No los compro. (I don't buy them. )
Frases negativas ¡ If you have a negative sentence the D. O. pronoun goes between the negative word and the conjugated verb. Ex: I don't buy the books. No compro los libros. No los compro. (I don't buy them. )
 Práctica ¡ I don’t want it. (the book) ¡ Jorge never studies it. (Spanish) ¡ They don’t want it. (the money)
Práctica ¡ I don’t want it. (the book) ¡ Jorge never studies it. (Spanish) ¡ They don’t want it. (the money)
 Matamoscas con DOPs, participios y ser/estar
Matamoscas con DOPs, participios y ser/estar

 Placement ¡ ¡ You can have two verbs in a sentence, the first is conjugated and the second remains in the infinitive form. Ex. Quiero comprar.
Placement ¡ ¡ You can have two verbs in a sentence, the first is conjugated and the second remains in the infinitive form. Ex. Quiero comprar.
 Placement ¡ In sentences with two verbs there are two options: l Place it immediately before the conjugated verb l Attach it directly to the infinitive l Ex. Quiero verlo Lo quiero ver
Placement ¡ In sentences with two verbs there are two options: l Place it immediately before the conjugated verb l Attach it directly to the infinitive l Ex. Quiero verlo Lo quiero ver
 Placement ¡ When you are expressing “-ing” or present or past progressive the same two options apply: l Place it immediately before the conjugated verb l Attach it directly to the end of the gerund form of the verb (i. e. “-ing”) l Ex: Estoy explicándolo Lo estoy explicando
Placement ¡ When you are expressing “-ing” or present or past progressive the same two options apply: l Place it immediately before the conjugated verb l Attach it directly to the end of the gerund form of the verb (i. e. “-ing”) l Ex: Estoy explicándolo Lo estoy explicando
 Práctica ¡ Escribe las dos opciones: ¡ I want to understand him. ¡ I’m drawing it. (the drawing) ¡ I have to see you. (informal) ¡ I’m going to buy it. (the book)
Práctica ¡ Escribe las dos opciones: ¡ I want to understand him. ¡ I’m drawing it. (the drawing) ¡ I have to see you. (informal) ¡ I’m going to buy it. (the book)
 Placement When you are expressing an affirmative command, the D. O. pronoun MUST go on the back of the command verb. ¡ Ex: Dígame Tómela Escúchenme ¡
Placement When you are expressing an affirmative command, the D. O. pronoun MUST go on the back of the command verb. ¡ Ex: Dígame Tómela Escúchenme ¡
 Práctica ¡ Write the formal command in Spanish with the correct D. O. pronoun l Answer me l Tell us l Find them (the keys)
Práctica ¡ Write the formal command in Spanish with the correct D. O. pronoun l Answer me l Tell us l Find them (the keys)
 Repaso ¡ ¡ ¡ The direct object answers the question WHO or WHAT about the verb The DO pronoun comes BEFORE the conjugated verb (if there is only one verb in the sentence) If you have a negative sentence the D. O. pronoun goes between the word “no” and the conjugated verb. In a sentence with two verbs you have two options: Place it immediately before the conjugated verb OR attach it directly to the infinitive or “ing” (gerund) In affirmative commands the D. O. pronoun MUST go on the back of the command verb.
Repaso ¡ ¡ ¡ The direct object answers the question WHO or WHAT about the verb The DO pronoun comes BEFORE the conjugated verb (if there is only one verb in the sentence) If you have a negative sentence the D. O. pronoun goes between the word “no” and the conjugated verb. In a sentence with two verbs you have two options: Place it immediately before the conjugated verb OR attach it directly to the infinitive or “ing” (gerund) In affirmative commands the D. O. pronoun MUST go on the back of the command verb.


