5cfa007fc84e52714982eac1edd2e562.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 58

Recent developments in IT for libraries Margaret Flett IT Services Group UCL Library Services

Overview • • • Introduction Online document delivery Resource gateways Personalisation Integration Implications & Discussion

Context: UCL Library Services • Exists to support teaching, learning, research and clinical practice • Serves UCL members (students, staff), partners, others • 10, 000 electronic journals, 150 subscription databases, growing e-books collection • Aleph library management system

Context: UCL Library Services • • • Meta. Lib library gateway SFX resource linking Online reading lists Digitised exam papers Digitised images from special collections E-Prints institutional repository

Trends in Library IT Driven by: • • IT industry developments Library software supplier developments Library requirements User requirements How do these factors interact?

Examples of trends - Google-style interfaces - Electronic resource management systems - Management information tools

Where are we now? • Web-based services • Third- and fourth-generation Library Management Systems (LMS) • Add-on / stand-alone products from LMS suppliers – no longer “Integrated LMS” • Standards – Z 39. 50, XML, Open. URL, etc.

Some recent trends: • • Online document delivery Resource gateways Personalisation Integration

1. Online document delivery

Online document delivery From library holdings and paper ILL to: • Electronic journals (subscription/free) • Pay-per-view • E-prints • Electronic books • Locally-digitised documents • Electronic ILL • Informal/Ephemeral internet information

Online document delivery The “appropriate copy” problem 1. Proprietary links – May or may not lead to licensed document – Depend on publisher/supplier agreements – Maintained by service provider 2. Digital Object Identifier (DOI) links – May or may not lead to licensed document – Maintained by publisher

Online document delivery 3. Open. URL • Provides inter-operability between a multitude of resources • International standard • Bundles object metadata plus information about the origin of the request • Local “link server” required, to interpret Open. URL and provide appropriate links
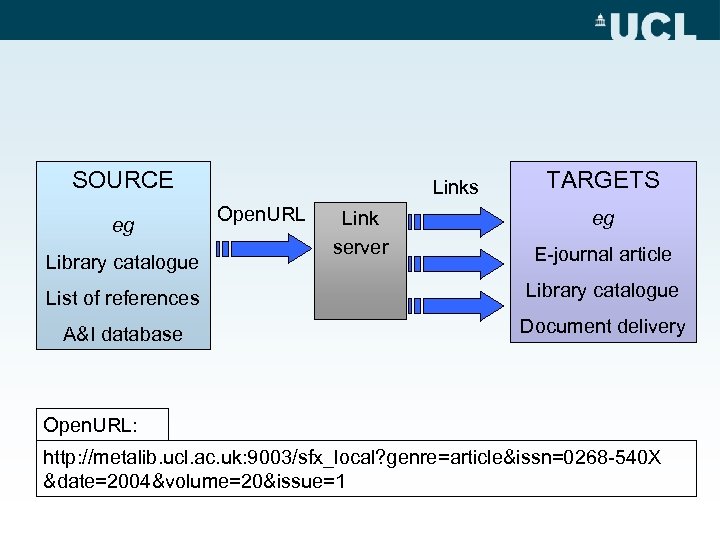
SOURCE eg Library catalogue Links Open. URL Link server TARGETS eg E-journal article List of references Library catalogue A&I database Document delivery Open. URL: http: //metalib. ucl. ac. uk: 9003/sfx_local? genre=article&issn=0268 -540 X &date=2004&volume=20&issue=1

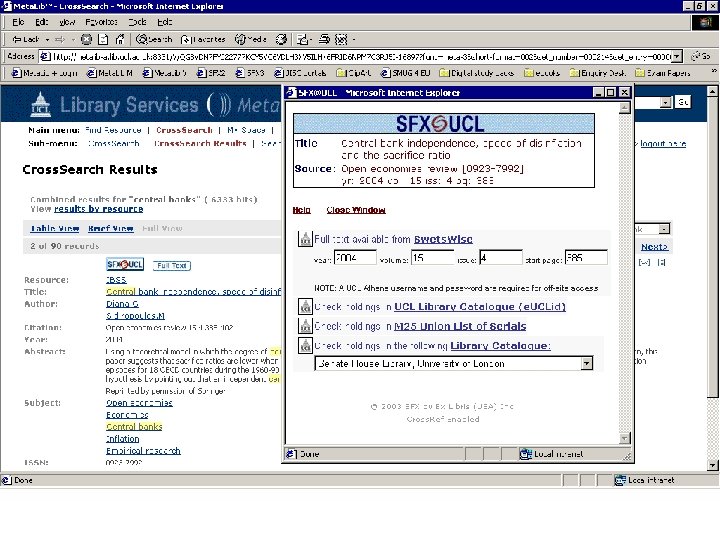
Online document delivery Open. URL menu services: • Full Text • Library holdings (catalogue search[es]) • Related searches (author, citation, …) • Web searches • Export citation • ILL request All can be context-sensitive
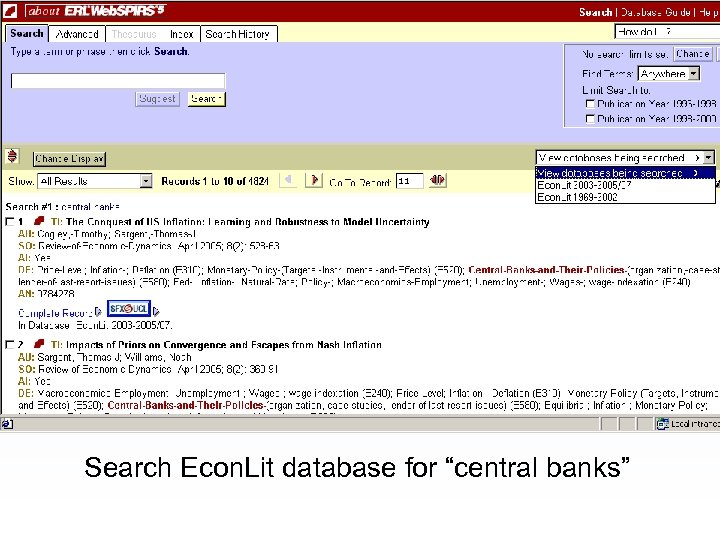
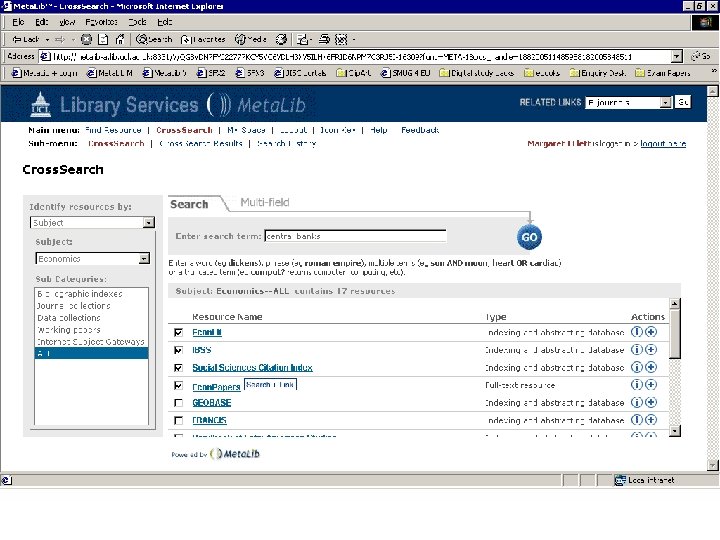
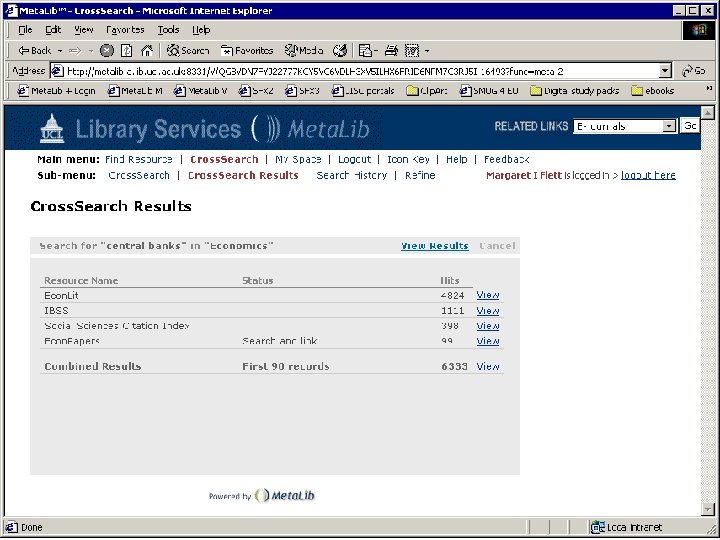
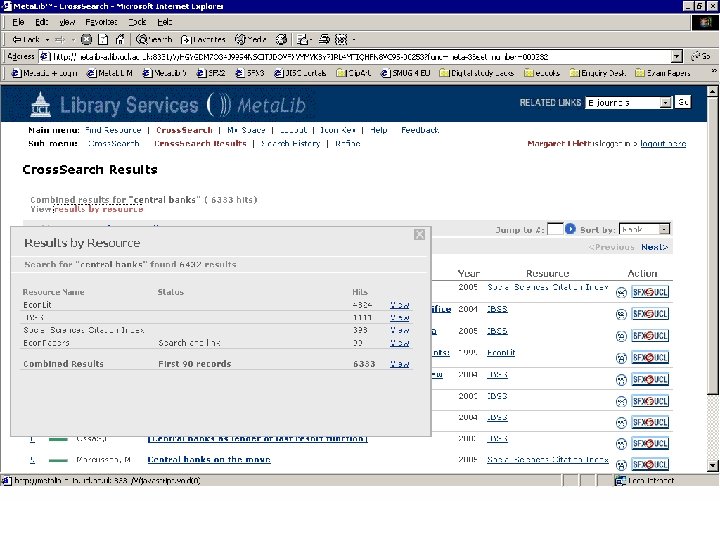
Search Econ. Lit database for “central banks”
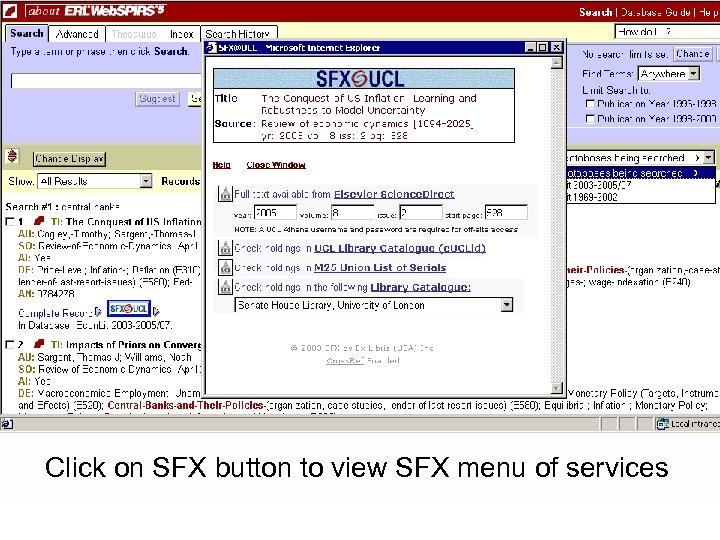
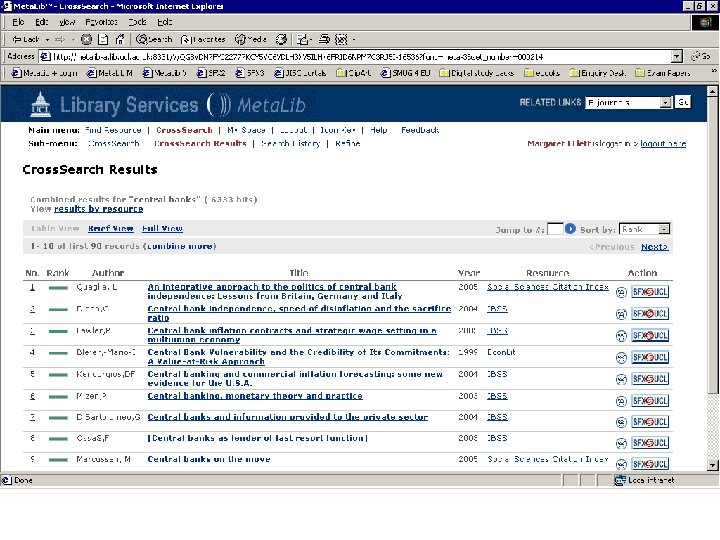
Click on SFX button to view SFX menu of services
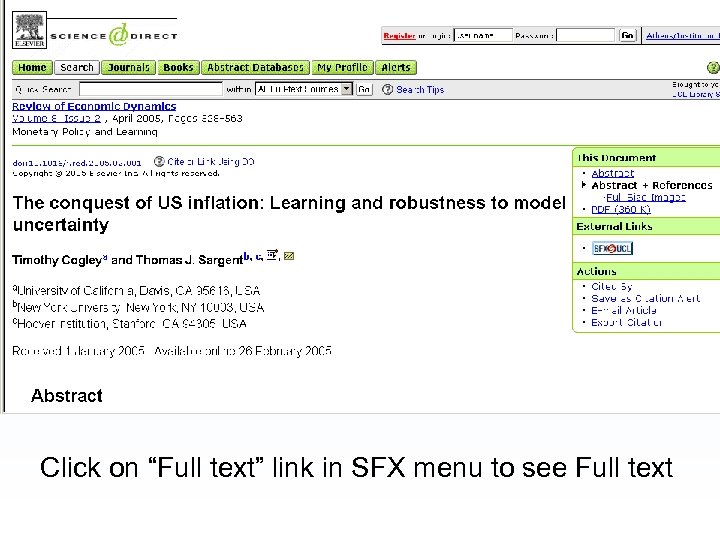
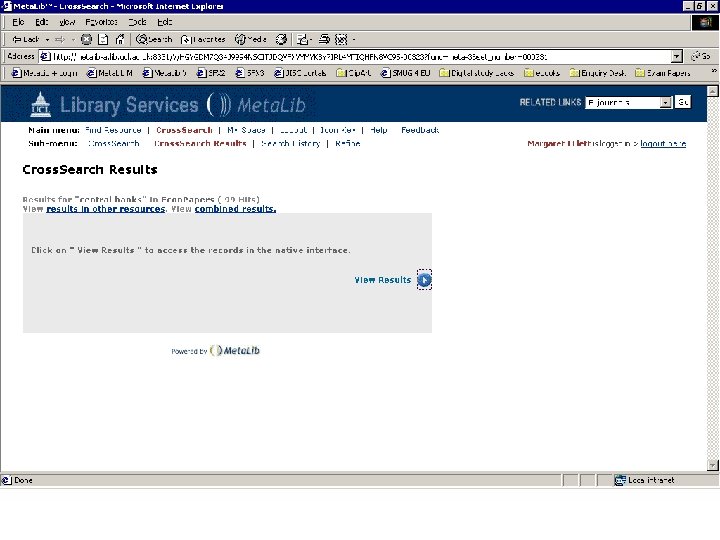
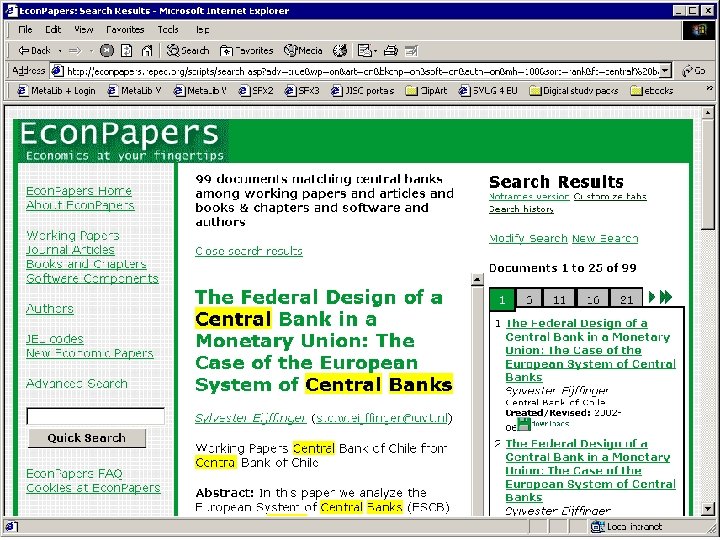
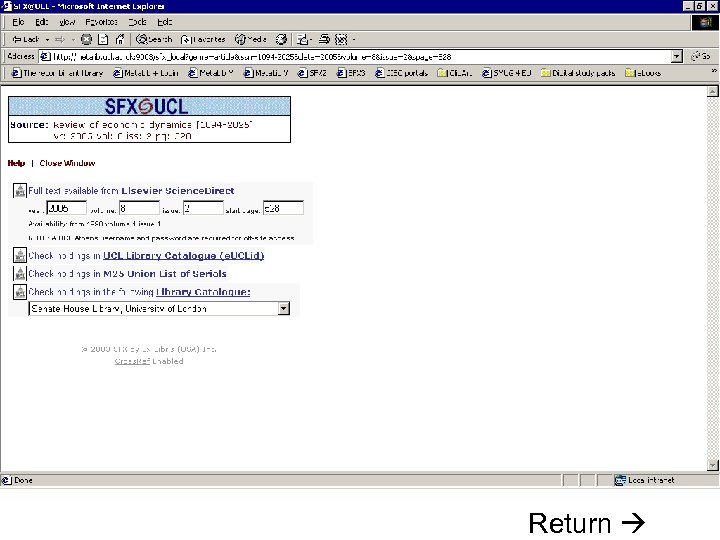
Click on “Full text” link in SFX menu to see Full text

Online document delivery Electronic Resource Management: • Library admin side of user experience • Manage e-resource life-cycle (acquisitions, maintenance, collection development) • Complement (traditional) LMS, link resolver database, financial systems

2. Resource gateways
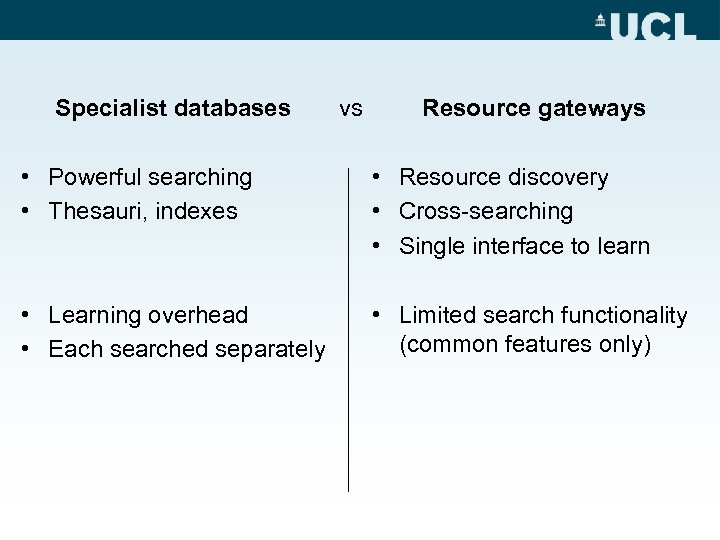
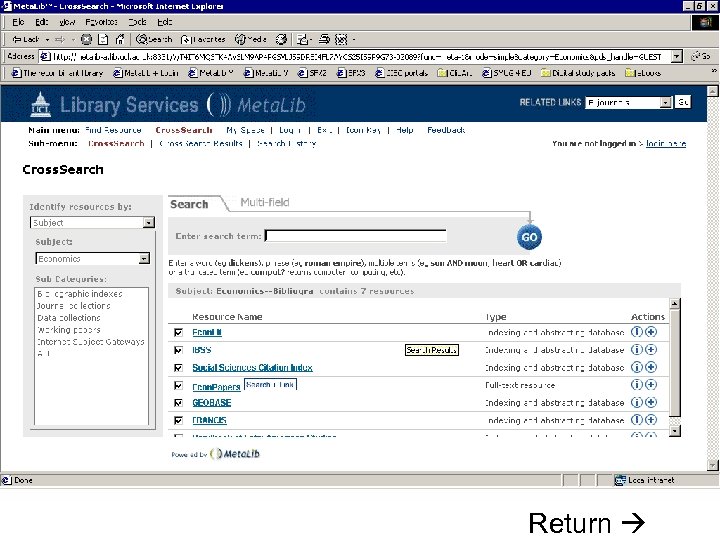
Specialist databases vs Resource gateways • Powerful searching • Thesauri, indexes • Resource discovery • Cross-searching • Single interface to learn • Learning overhead • Each searched separately • Limited search functionality (common features only)
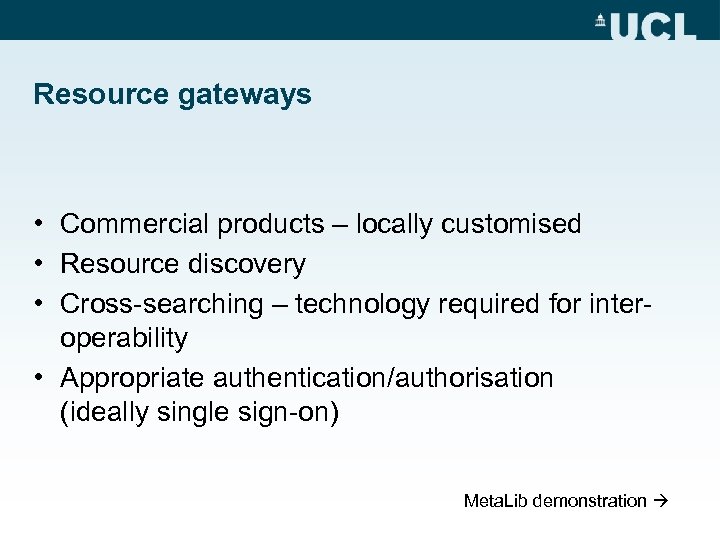
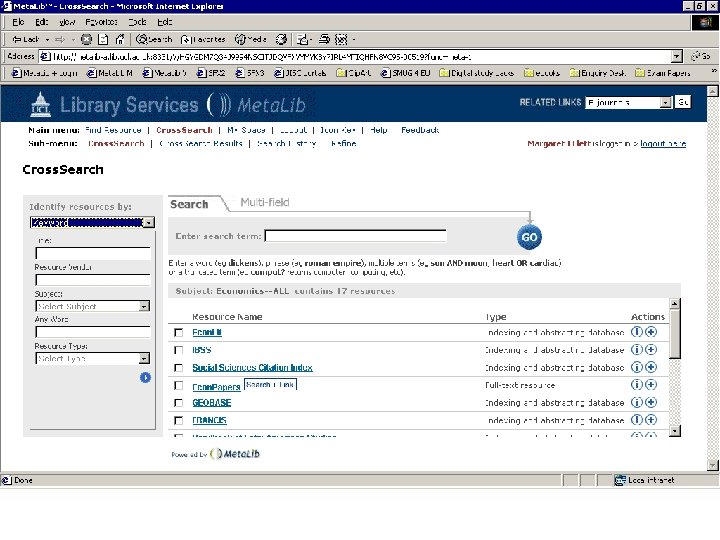
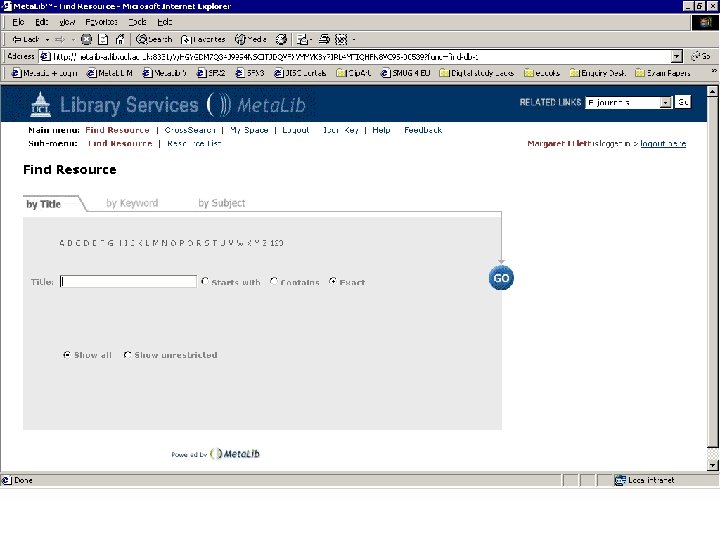
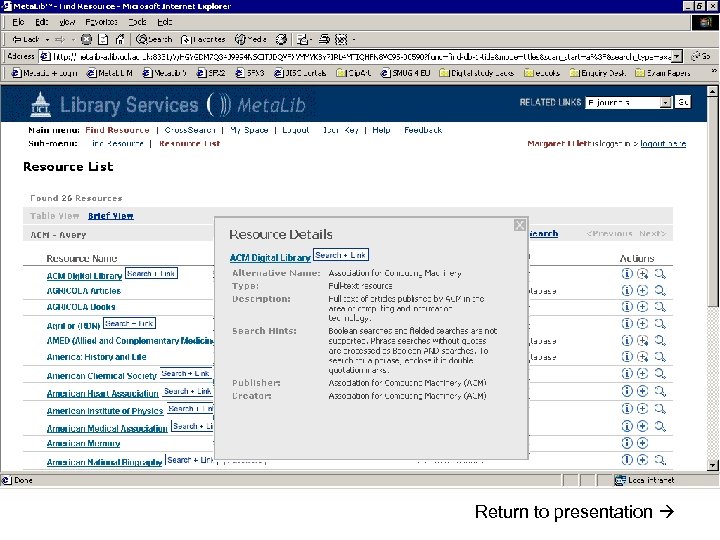
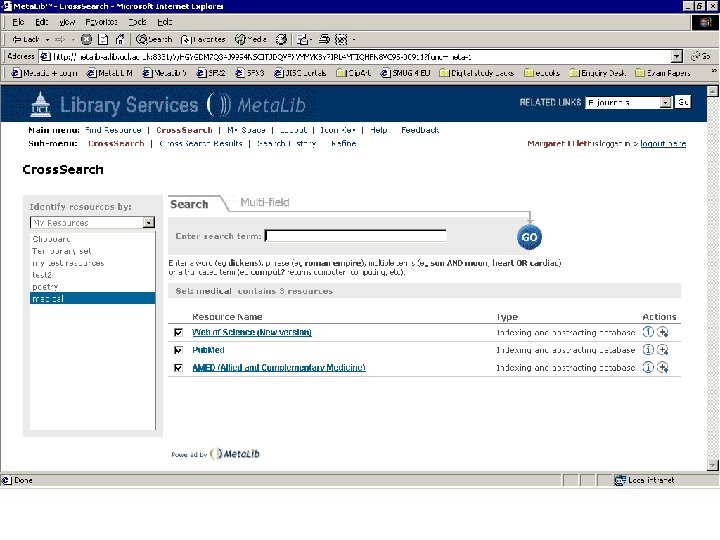
Resource gateways • Commercial products – locally customised • Resource discovery • Cross-searching – technology required for interoperability • Appropriate authentication/authorisation (ideally single sign-on) Meta. Lib demonstration

3. Personalisation

Personalisation • Personal view on information resources • Helps to combat information overload • Influenced by Web search engines/portals, plus organisational portals • “My. Library”, etc. • SDI, alerts, RSS
“Search engine” portal
University Portal
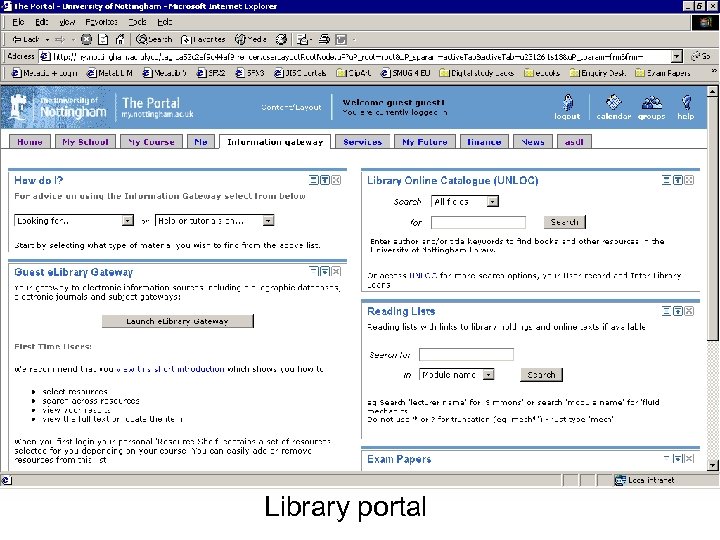
Library portal
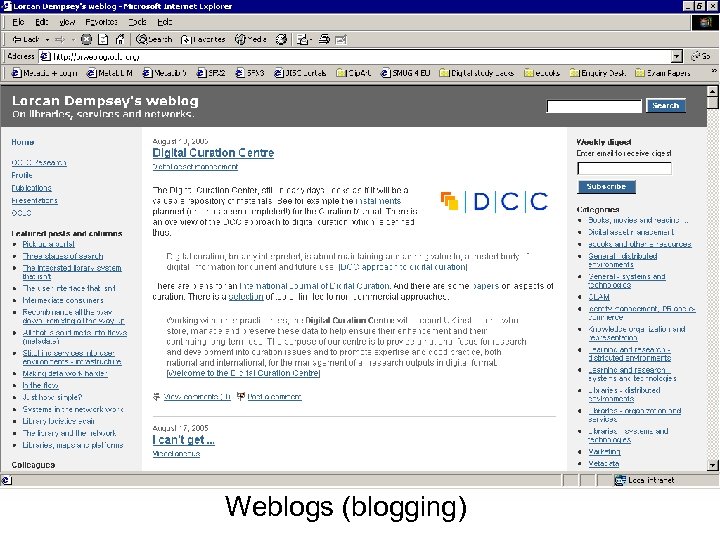
Weblogs (blogging)

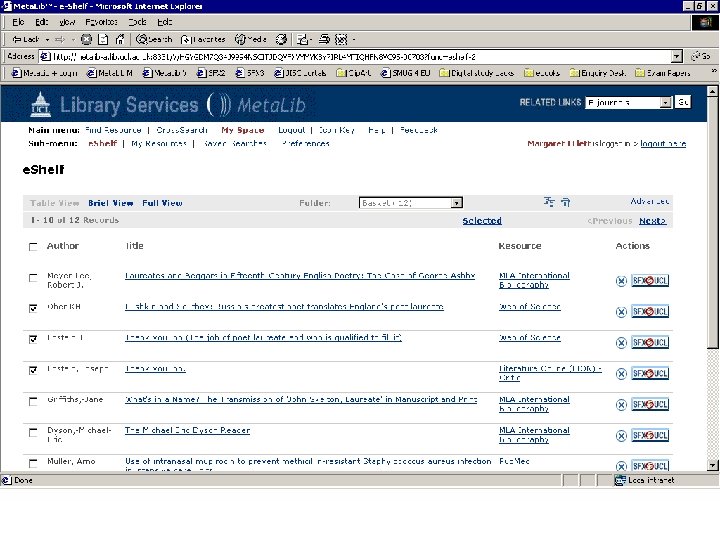
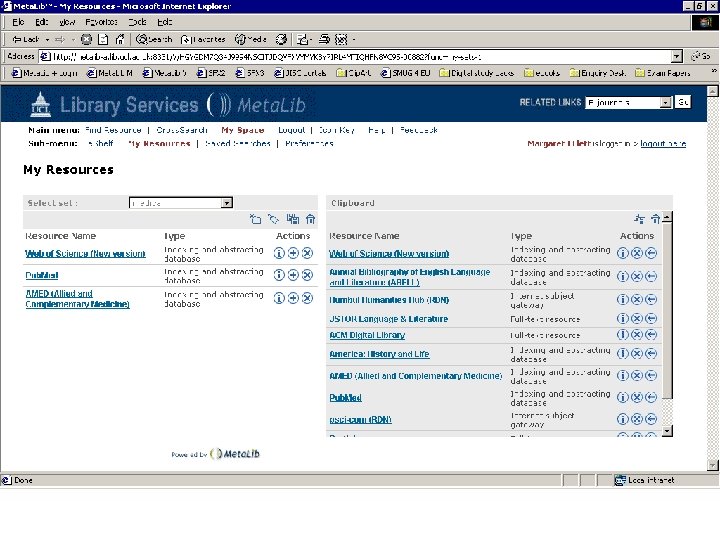
Personalisation • Library-driven: authorised resources, tailored resource sets, SDI • User-driven: look and feel, tailored resource sets, SDI Meta. Lib demonstration

4. Integration
Integration • Portals • Integration of library resources within wider contexts • Re-purposing of information • Technical issues
Integration - Examples 1. Deep linking 2. Embedding 3. Integration

1. Deep linking From any webpage, eg: • Find this journal article • Cross-search Economics resources
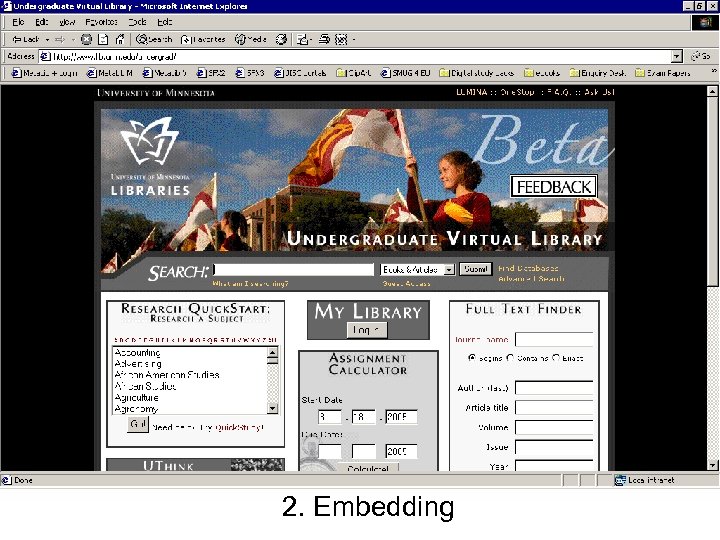
2. Embedding

3. Integration • • Flexible embedding of library services At user’s point of need Combining of library data with related data Personalisation
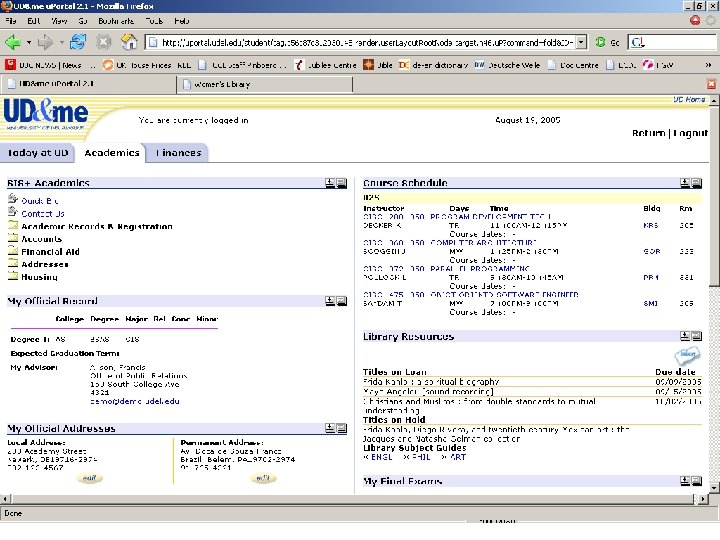
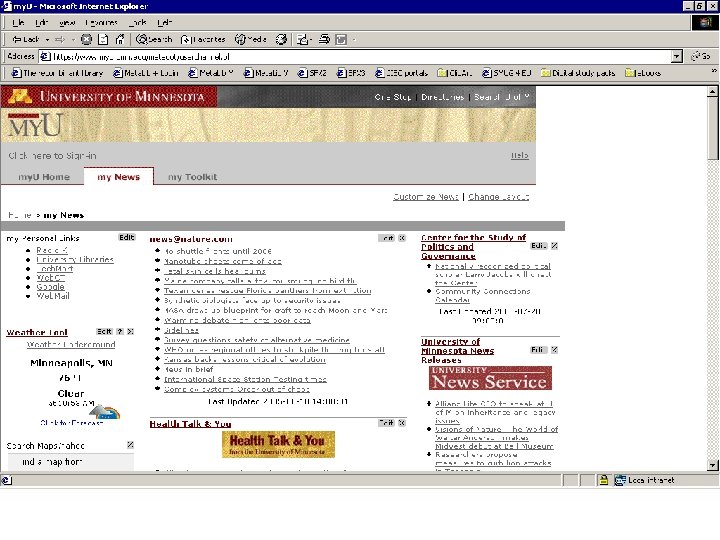

Integration Issues for library staff: • Marketing • Collaboration • Technology / data

In conclusion…

Implications for library/information services • • Priorities User and/or administrative developments? Cost Technological expertise

Discussion 1) Online document delivery What are your service’s priorities for development in this area? What barriers are there? 2) Resource gateways Is there a need for a single point of access to the electronic resources your service provides? What are the benefits? What are the barriers?

Discussion 3) Personalisation Would your users benefit from a personalised information environment? What steps can you take in this direction? 4) Integration What scope is there within your organisation or beyond to integrate your online services into a wider environment?
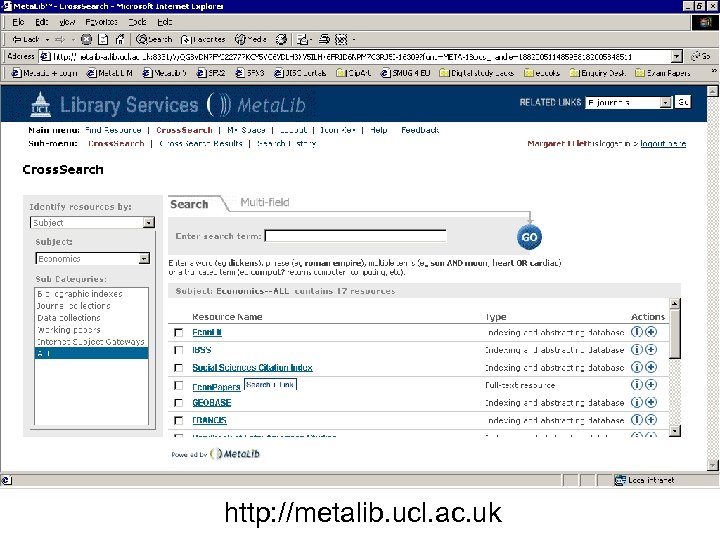
http: //metalib. ucl. ac. uk
Return to presentation
Return to presentation
Return
Return
5cfa007fc84e52714982eac1edd2e562.ppt