dae88736a3b5cf7961c6e79415573cff.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 Realising the Value in Information Technology Ken Doughty CISA CBCP Senior Manager, Risk Management ING Australia
Realising the Value in Information Technology Ken Doughty CISA CBCP Senior Manager, Risk Management ING Australia
 Presentation Outline Introduction 1. IT Asset Management and ITIL 2. Organizational IT Asset Management Framework 3. IT Asset Maturity Model 4. The Asset Management Lifecycle Conclusion
Presentation Outline Introduction 1. IT Asset Management and ITIL 2. Organizational IT Asset Management Framework 3. IT Asset Maturity Model 4. The Asset Management Lifecycle Conclusion
 Introduction • Organisations have failed to realised the value in their investment in IT and manage the operational risks associated with their IT assets. • IT Asset Management (ITAM) is all about being able to cohesively merge the physical, financial and contractual attributes of software and hardware to enable the delivery of cost-efficient, timely business solutions and minimize the operational risks to the organization. • It has a logical connection to Configuration Management
Introduction • Organisations have failed to realised the value in their investment in IT and manage the operational risks associated with their IT assets. • IT Asset Management (ITAM) is all about being able to cohesively merge the physical, financial and contractual attributes of software and hardware to enable the delivery of cost-efficient, timely business solutions and minimize the operational risks to the organization. • It has a logical connection to Configuration Management
 Don’t just take our word for it “Tangible cost savings from IT asset management will result from better management decisions that bring value to the business. ” Jack Heine, Gartner Research Note, December 2004 “Internal IT groups are being forced by their businesses to compete for preferred provider status with external suppliers. ” META - IT Product Models: Services, Catalogs, Chargeback Operations Strategies / Service Management Strategies “It is not uncommon for IT Groups to over-purchase desktop software by as much as 40%. Typical organisations over-purchase by 10 – 15%. ” META Trend: META Delta, 2/18/2003, William Snyder “An accurate inventory of installed hardware and software forms the foundation of a solid IT asset management program. This baseline identifies which assets need to be redeployed, reused or retired. ” P. Adams, Gartner. Research Note, 30 November 2004
Don’t just take our word for it “Tangible cost savings from IT asset management will result from better management decisions that bring value to the business. ” Jack Heine, Gartner Research Note, December 2004 “Internal IT groups are being forced by their businesses to compete for preferred provider status with external suppliers. ” META - IT Product Models: Services, Catalogs, Chargeback Operations Strategies / Service Management Strategies “It is not uncommon for IT Groups to over-purchase desktop software by as much as 40%. Typical organisations over-purchase by 10 – 15%. ” META Trend: META Delta, 2/18/2003, William Snyder “An accurate inventory of installed hardware and software forms the foundation of a solid IT asset management program. This baseline identifies which assets need to be redeployed, reused or retired. ” P. Adams, Gartner. Research Note, 30 November 2004
 1. IT Asset Management and ITIL® • The ITIL framework provides two service models: – Service Support – Service Delivery • IT Asset Management within the ITIL context is addressed within Configuration Management, but not very well. • Configuration Management largely ignores Asset Management and concentrates on Services and the relationships between IT assets (CI’s).
1. IT Asset Management and ITIL® • The ITIL framework provides two service models: – Service Support – Service Delivery • IT Asset Management within the ITIL context is addressed within Configuration Management, but not very well. • Configuration Management largely ignores Asset Management and concentrates on Services and the relationships between IT assets (CI’s).
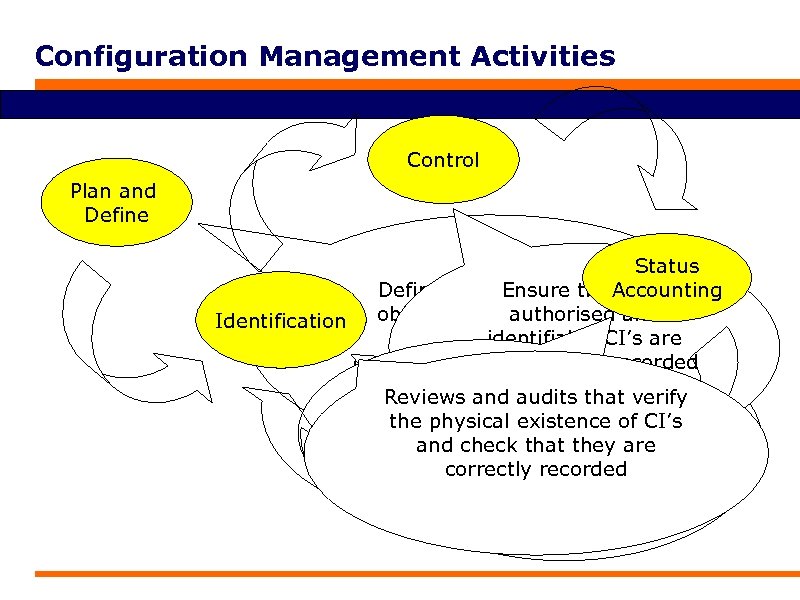 Configuration Management Activities Control Plan and Define Status Define purpose, scope, Accounting Ensure that only authorised Identification objectives, policies and procedures, and the CI’s are identifiable organisational and technical accepted and recorded Selecting Reporting of all currentthe context Reviews and audits structures configuration that verify and historical data the physicalthe CI’s, of CI’s for all existence concerned with each CIincluding Verify and check that they are throughouttheir ‘owner’, their its life cycle. Audit recorded and correctly interrelationships configuration documentation
Configuration Management Activities Control Plan and Define Status Define purpose, scope, Accounting Ensure that only authorised Identification objectives, policies and procedures, and the CI’s are identifiable organisational and technical accepted and recorded Selecting Reporting of all currentthe context Reviews and audits structures configuration that verify and historical data the physicalthe CI’s, of CI’s for all existence concerned with each CIincluding Verify and check that they are throughouttheir ‘owner’, their its life cycle. Audit recorded and correctly interrelationships configuration documentation
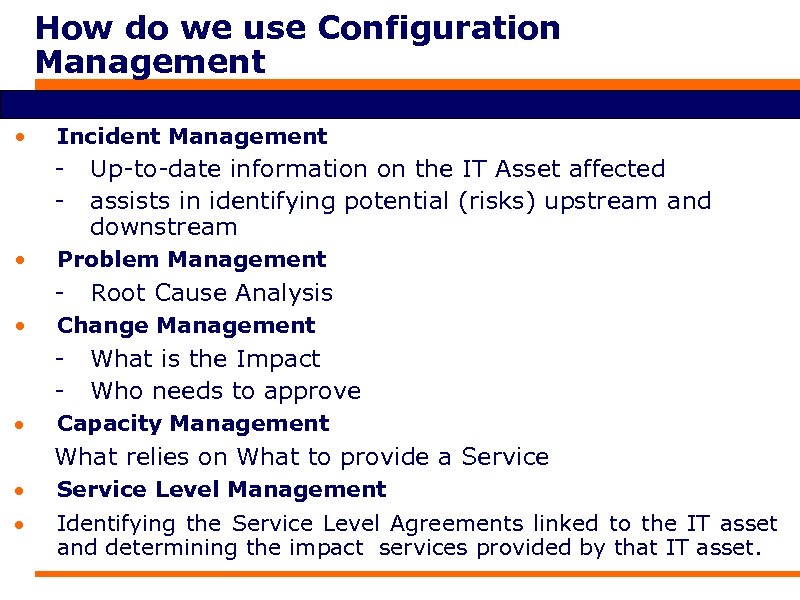 How do we use Configuration Management • Incident Management • Problem Management • Root Cause Analysis Change Management Up-to-date information on the IT Asset affected assists in identifying potential (risks) upstream and downstream What is the Impact Who needs to approve Capacity Management What relies on What to provide a Service Level Management Identifying the Service Level Agreements linked to the IT asset and determining the impact services provided by that IT asset.
How do we use Configuration Management • Incident Management • Problem Management • Root Cause Analysis Change Management Up-to-date information on the IT Asset affected assists in identifying potential (risks) upstream and downstream What is the Impact Who needs to approve Capacity Management What relies on What to provide a Service Level Management Identifying the Service Level Agreements linked to the IT asset and determining the impact services provided by that IT asset.
 2. Organizational IT Asset Management Framework ITAM Policy • Acquisition of the asset – – – – Who can do what Allowable hardware and software How information is recorded Rental and leases Reuse of assets Change Management Unique identification • Deployment • Tracking • Managing • Disposal
2. Organizational IT Asset Management Framework ITAM Policy • Acquisition of the asset – – – – Who can do what Allowable hardware and software How information is recorded Rental and leases Reuse of assets Change Management Unique identification • Deployment • Tracking • Managing • Disposal
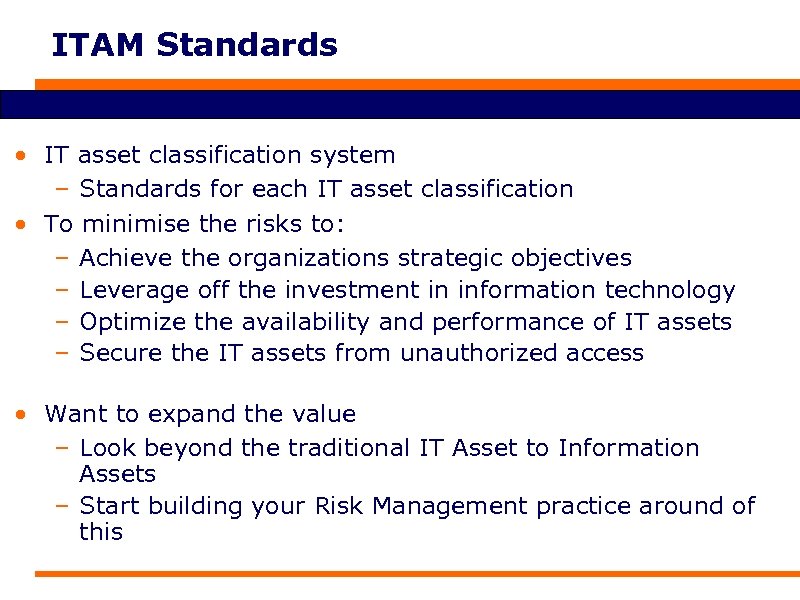 ITAM Standards • IT asset classification system – Standards for each IT asset classification • To minimise the risks to: – Achieve the organizations strategic objectives – Leverage off the investment in information technology – Optimize the availability and performance of IT assets – Secure the IT assets from unauthorized access • Want to expand the value – Look beyond the traditional IT Asset to Information Assets – Start building your Risk Management practice around of this
ITAM Standards • IT asset classification system – Standards for each IT asset classification • To minimise the risks to: – Achieve the organizations strategic objectives – Leverage off the investment in information technology – Optimize the availability and performance of IT assets – Secure the IT assets from unauthorized access • Want to expand the value – Look beyond the traditional IT Asset to Information Assets – Start building your Risk Management practice around of this
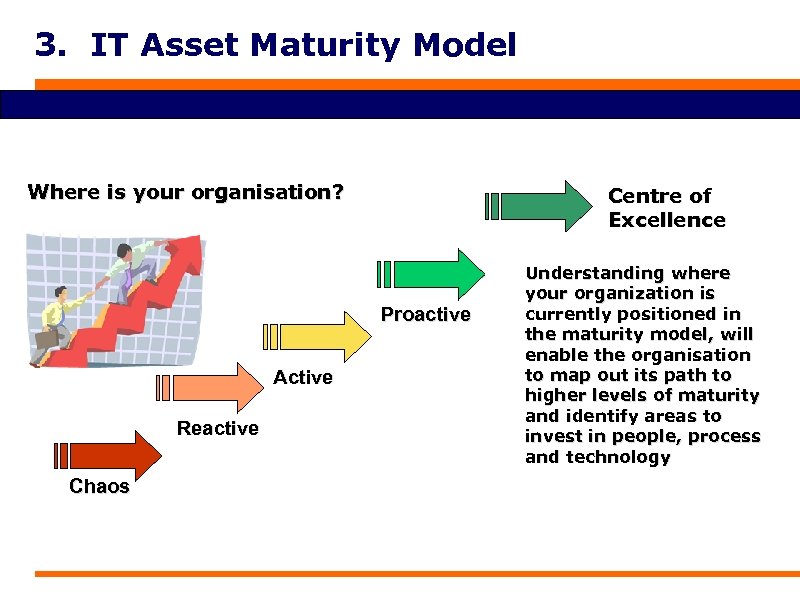 3. IT Asset Maturity Model Where is your organisation? Centre of Excellence Proactive Active Reactive Chaos Understanding where your organization is currently positioned in the maturity model, will enable the organisation to map out its path to higher levels of maturity and identify areas to invest in people, process and technology
3. IT Asset Maturity Model Where is your organisation? Centre of Excellence Proactive Active Reactive Chaos Understanding where your organization is currently positioned in the maturity model, will enable the organisation to map out its path to higher levels of maturity and identify areas to invest in people, process and technology
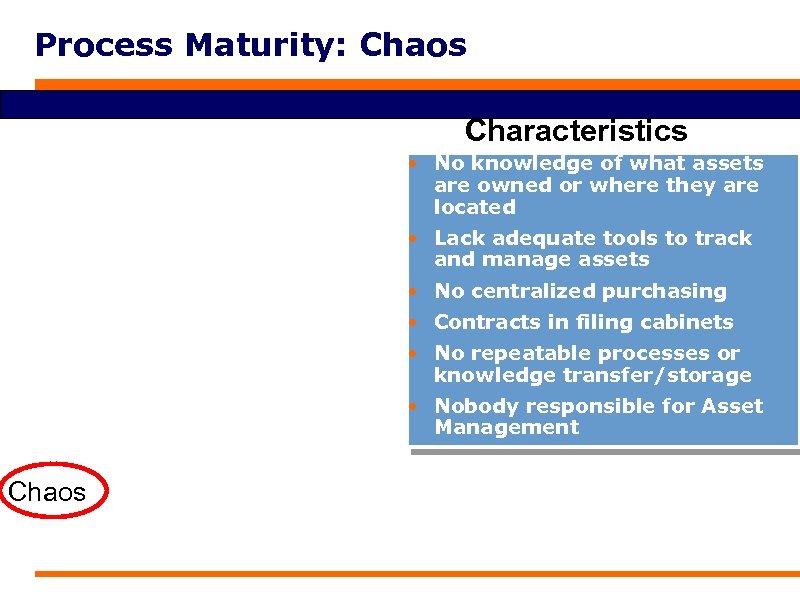 Process Maturity: Chaos Characteristics • No knowledge of what assets are owned or where they are located • Lack adequate tools to track and manage assets • No centralized purchasing • Contracts in filing cabinets • No repeatable processes or knowledge transfer/storage • Nobody responsible for Asset Management Chaos
Process Maturity: Chaos Characteristics • No knowledge of what assets are owned or where they are located • Lack adequate tools to track and manage assets • No centralized purchasing • Contracts in filing cabinets • No repeatable processes or knowledge transfer/storage • Nobody responsible for Asset Management Chaos
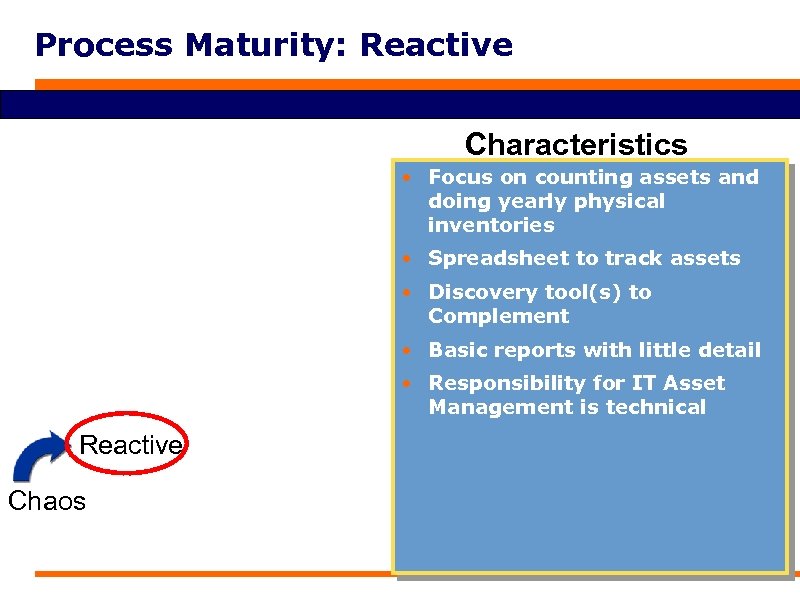 Process Maturity: Reactive Characteristics • Focus on counting assets and doing yearly physical inventories • Spreadsheet to track assets • Discovery tool(s) to Complement • Basic reports with little detail • Responsibility for IT Asset Management is technical Reactive Chaos
Process Maturity: Reactive Characteristics • Focus on counting assets and doing yearly physical inventories • Spreadsheet to track assets • Discovery tool(s) to Complement • Basic reports with little detail • Responsibility for IT Asset Management is technical Reactive Chaos
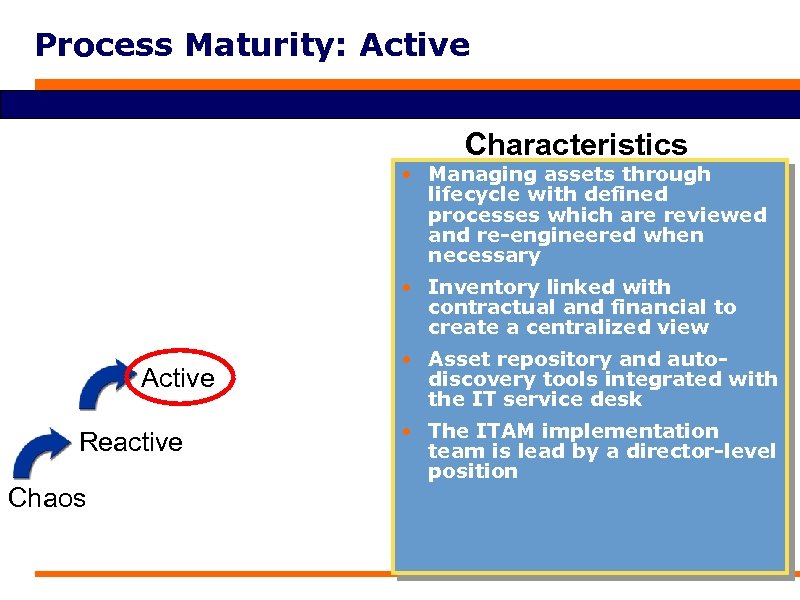 Process Maturity: Active Characteristics • Managing assets through lifecycle with defined processes which are reviewed and re-engineered when necessary • Inventory linked with contractual and financial to create a centralized view Active Reactive Chaos • Asset repository and autodiscovery tools integrated with the IT service desk • The ITAM implementation team is lead by a director-level position
Process Maturity: Active Characteristics • Managing assets through lifecycle with defined processes which are reviewed and re-engineered when necessary • Inventory linked with contractual and financial to create a centralized view Active Reactive Chaos • Asset repository and autodiscovery tools integrated with the IT service desk • The ITAM implementation team is lead by a director-level position
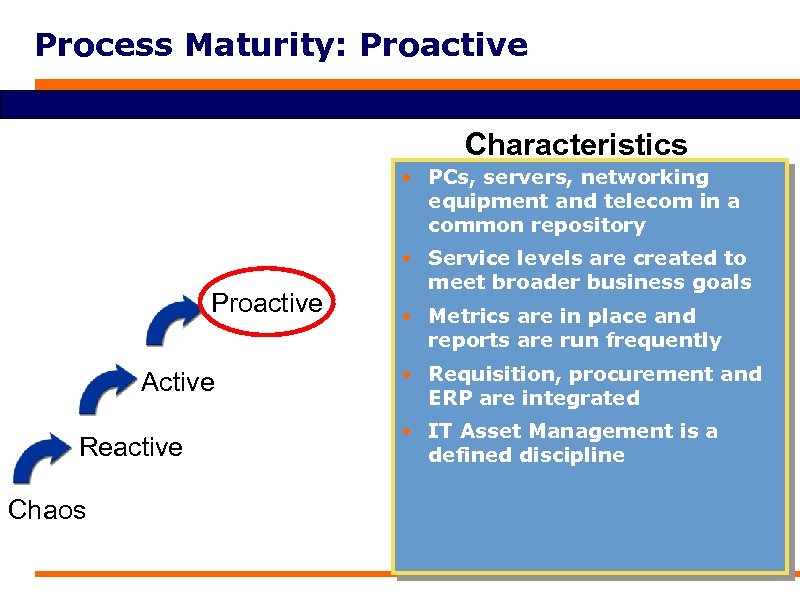 Process Maturity: Proactive Characteristics • PCs, servers, networking equipment and telecom in a common repository Proactive Active Reactive Chaos • Service levels are created to meet broader business goals • Metrics are in place and reports are run frequently • Requisition, procurement and ERP are integrated • IT Asset Management is a defined discipline
Process Maturity: Proactive Characteristics • PCs, servers, networking equipment and telecom in a common repository Proactive Active Reactive Chaos • Service levels are created to meet broader business goals • Metrics are in place and reports are run frequently • Requisition, procurement and ERP are integrated • IT Asset Management is a defined discipline
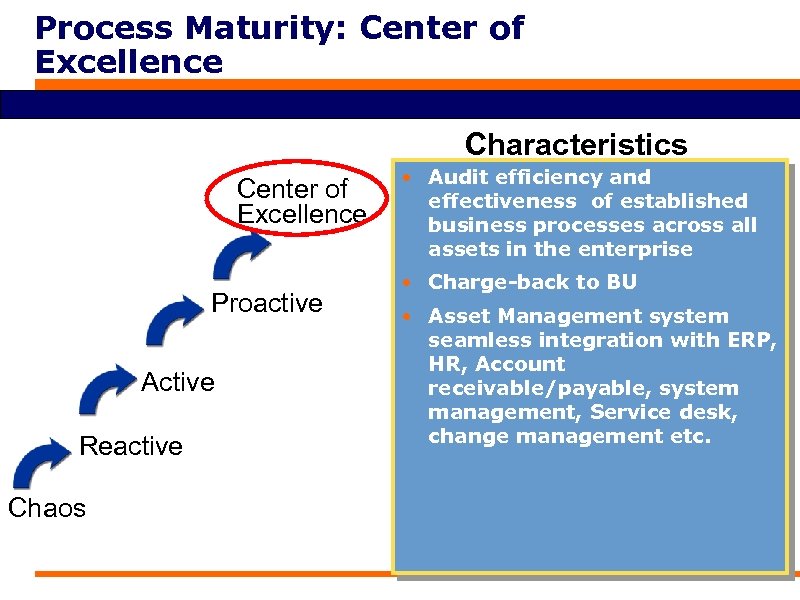 Process Maturity: Center of Excellence Characteristics Center of Excellence Proactive Active Reactive Chaos • Audit efficiency and effectiveness of established business processes across all assets in the enterprise • Charge-back to BU • Asset Management system seamless integration with ERP, HR, Account receivable/payable, system management, Service desk, change management etc.
Process Maturity: Center of Excellence Characteristics Center of Excellence Proactive Active Reactive Chaos • Audit efficiency and effectiveness of established business processes across all assets in the enterprise • Charge-back to BU • Asset Management system seamless integration with ERP, HR, Account receivable/payable, system management, Service desk, change management etc.
 4. Asset Management Life Cycle • Planning – Aligning the need for the IT assets with the key business processes, which are being serviced from either an existing IT asset or proposed to be delivered from a new IT asset – How do you actually get the money for that Desktop refresh? • Acquisition of the asset – Looking at the most cost effective way to acquire the IT assets. • Deployment – How to deploy – pilot, staged, big bang!! – Automate the process where possible
4. Asset Management Life Cycle • Planning – Aligning the need for the IT assets with the key business processes, which are being serviced from either an existing IT asset or proposed to be delivered from a new IT asset – How do you actually get the money for that Desktop refresh? • Acquisition of the asset – Looking at the most cost effective way to acquire the IT assets. • Deployment – How to deploy – pilot, staged, big bang!! – Automate the process where possible
 Asset Management Life Cycle • Operation / Maintenance – Ensuring that not only all the financial obligations associated with maintaining the asset are met, but also the operational risks associated with the IT asset namely, Change Management, CMDB, etc. • Disposal – IT Asset Value - maintaining a history of the IT asset throughout its lifecycle will assist in the replacement decision. – Ecologically Asset Disposal – today there is legislation in many countries that governs the ecologically responsibility of the disposal of IT assets. - Contractual Obligations - that need to be met if the organization does not want the IT asset, for example leasing, renting etc. - Maintaining - the accuracy and completeness of IT asset Maintainin records including the financial records.
Asset Management Life Cycle • Operation / Maintenance – Ensuring that not only all the financial obligations associated with maintaining the asset are met, but also the operational risks associated with the IT asset namely, Change Management, CMDB, etc. • Disposal – IT Asset Value - maintaining a history of the IT asset throughout its lifecycle will assist in the replacement decision. – Ecologically Asset Disposal – today there is legislation in many countries that governs the ecologically responsibility of the disposal of IT assets. - Contractual Obligations - that need to be met if the organization does not want the IT asset, for example leasing, renting etc. - Maintaining - the accuracy and completeness of IT asset Maintainin records including the financial records.
 The Starting Point • Physical Audit – A physical audit can actually be a combination of reconciling records that already exists with the results of a physical audit. – Most organizations, no matter what their level of maturity will have some IT asset information stored either in spreadsheets, databases or even paper based. – Many organizations undertook massive physical audits as part of their preparation for Y 2 K and promptly on the 1 st January 2000 forgot about maintaining them.
The Starting Point • Physical Audit – A physical audit can actually be a combination of reconciling records that already exists with the results of a physical audit. – Most organizations, no matter what their level of maturity will have some IT asset information stored either in spreadsheets, databases or even paper based. – Many organizations undertook massive physical audits as part of their preparation for Y 2 K and promptly on the 1 st January 2000 forgot about maintaining them.
 Automated Discovery tools • The advantage of software discovery tools is that they can automatically discover the hardware and software that is being run across the network. • Regardless, of the automated discovery tool at times an inspection of the asset will have be undertaken to physically locate the IT asset • The drawbacks are: – If the IT asset is not connected to the network, it cannot be discovered. – That discovery tools do not have the ability to connect the asset with its owner or the process (service) it is delivering/supporting.
Automated Discovery tools • The advantage of software discovery tools is that they can automatically discover the hardware and software that is being run across the network. • Regardless, of the automated discovery tool at times an inspection of the asset will have be undertaken to physically locate the IT asset • The drawbacks are: – If the IT asset is not connected to the network, it cannot be discovered. – That discovery tools do not have the ability to connect the asset with its owner or the process (service) it is delivering/supporting.
 Information Collection • After the initial discovery, lock down the production environment and only allow moves, additions or changes that have been through proper Change Management. This will assist in preventing the security risk occurring through poorly applied security standards across the production environment. • At this stage the organization has two key elements to ITAM i. e. physical IT asset inventory linked to associated financial and contractual details.
Information Collection • After the initial discovery, lock down the production environment and only allow moves, additions or changes that have been through proper Change Management. This will assist in preventing the security risk occurring through poorly applied security standards across the production environment. • At this stage the organization has two key elements to ITAM i. e. physical IT asset inventory linked to associated financial and contractual details.
 Software Discovery • The next level of automated discovery is that of discovering the software that is running across the IT infrastructure. This should cover not only packaged, commercially purchased software but also in-house developed applications. • Contract Scrape - Objectives are to identify the currency of maintenance contracts for IT assets and to determine if the organization is paying the correct amount for maintenance. • Process Integration - Integrate the processes that discover, audit, procure, and manage, etc. , the IT Assets.
Software Discovery • The next level of automated discovery is that of discovering the software that is running across the IT infrastructure. This should cover not only packaged, commercially purchased software but also in-house developed applications. • Contract Scrape - Objectives are to identify the currency of maintenance contracts for IT assets and to determine if the organization is paying the correct amount for maintenance. • Process Integration - Integrate the processes that discover, audit, procure, and manage, etc. , the IT Assets.
 IT Asset Security • Any IT asset with a piece of wire or wireless capability is a potential point of entry into the organizations network. • This lack of security framework is often indicted by a number or all of the following: – No dedicated resource/s for information security – Little or no information security policies – Little or no hardware and software security configuration standards – No security awareness program – No deployment of security software and hardware to facilitate security violation logging, monitoring and reporting
IT Asset Security • Any IT asset with a piece of wire or wireless capability is a potential point of entry into the organizations network. • This lack of security framework is often indicted by a number or all of the following: – No dedicated resource/s for information security – Little or no information security policies – Little or no hardware and software security configuration standards – No security awareness program – No deployment of security software and hardware to facilitate security violation logging, monitoring and reporting
 Data Management • IT Asset Optimization - IT asset optimization is concerned with making sure you are getting the optimal use of the organization’s IT assets. Asset optimization will allow the organization to harvest under utilized assets and leverage from them to minimize current operational expense and minimize future capital expenditure. • Software Licensing – Integrating IT assets information with the financial information through the discovery processes of what is installed. • Service Support – Being able to define Business Services and map the relationship of the underlying infrastructure you are supporting one of the key requirements to achieving a high level of maturity across the ITIL Service Support processes.
Data Management • IT Asset Optimization - IT asset optimization is concerned with making sure you are getting the optimal use of the organization’s IT assets. Asset optimization will allow the organization to harvest under utilized assets and leverage from them to minimize current operational expense and minimize future capital expenditure. • Software Licensing – Integrating IT assets information with the financial information through the discovery processes of what is installed. • Service Support – Being able to define Business Services and map the relationship of the underlying infrastructure you are supporting one of the key requirements to achieving a high level of maturity across the ITIL Service Support processes.
 Conclusion • Organizations have failed to not only effectively manage their IT assets, but also to leverage of this investment to build and sustain their competitive edge. • Organizations need to continue to renew their investment in IT assets. However, in absence of an ITAM framework and its supporting processes, for some organizations Chaos will continue and the pain that goes with it.
Conclusion • Organizations have failed to not only effectively manage their IT assets, but also to leverage of this investment to build and sustain their competitive edge. • Organizations need to continue to renew their investment in IT assets. However, in absence of an ITAM framework and its supporting processes, for some organizations Chaos will continue and the pain that goes with it.
 Questions & Answers Thank you for attending session!
Questions & Answers Thank you for attending session!


