146db358b90afd862697fac2ec3beeee.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 64
 Real Time Systems Design The RTS design is investigated using common component based model 1
Real Time Systems Design The RTS design is investigated using common component based model 1
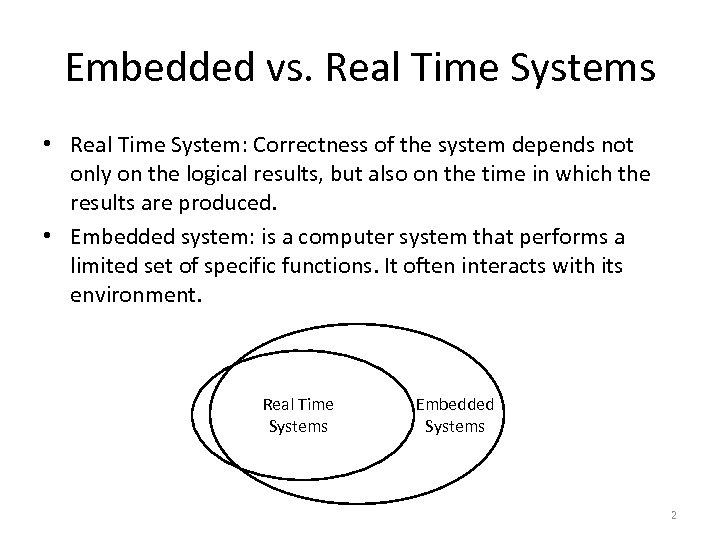 Embedded vs. Real Time Systems • Real Time System: Correctness of the system depends not only on the logical results, but also on the time in which the results are produced. • Embedded system: is a computer system that performs a limited set of specific functions. It often interacts with its environment. Real Time Systems Embedded Systems 2
Embedded vs. Real Time Systems • Real Time System: Correctness of the system depends not only on the logical results, but also on the time in which the results are produced. • Embedded system: is a computer system that performs a limited set of specific functions. It often interacts with its environment. Real Time Systems Embedded Systems 2
 Examples • Real Time Embedded: – – – Nuclear reactor control Flight control Basically any safety critical system GPS MP 3 player Mobile phone • Real Time, but not Embedded: – Stock trading system – Skype – Pandora • Embedded, but not Real Time: – – Home temperature control Sprinkler system Washing machine, refrigerator, etc. Blood pressure meter 3
Examples • Real Time Embedded: – – – Nuclear reactor control Flight control Basically any safety critical system GPS MP 3 player Mobile phone • Real Time, but not Embedded: – Stock trading system – Skype – Pandora • Embedded, but not Real Time: – – Home temperature control Sprinkler system Washing machine, refrigerator, etc. Blood pressure meter 3
 Characteristics of RTS • • • Event-driven, reactive. High cost of failure. Concurrency/multiprogramming. Stand-alone/continuous operation. Reliability/fault-tolerance requirements. Predictable behavior. 4
Characteristics of RTS • • • Event-driven, reactive. High cost of failure. Concurrency/multiprogramming. Stand-alone/continuous operation. Reliability/fault-tolerance requirements. Predictable behavior. 4
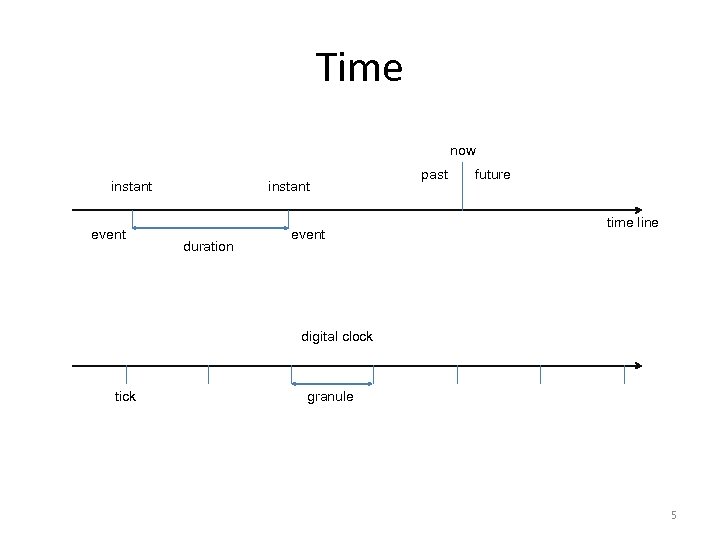 Time now instant event instant duration event past future time line digital clock tick granule 5
Time now instant event instant duration event past future time line digital clock tick granule 5
 Definitions • Hard real-time — systems where it is absolutely imperative that responses occur within the required deadline. E. g. Flight control systems. • Soft real-time — systems where deadlines are important but which will still function correctly if deadlines are occasionally missed. E. g. Data acquisition system. • Real real-time — systems which are hard real-time and which the response times are very short. E. g. Missile guidance system. A single system may have all hard, soft and real-time subsystems. In reality many systems will have a cost function associated with missing each deadline 6
Definitions • Hard real-time — systems where it is absolutely imperative that responses occur within the required deadline. E. g. Flight control systems. • Soft real-time — systems where deadlines are important but which will still function correctly if deadlines are occasionally missed. E. g. Data acquisition system. • Real real-time — systems which are hard real-time and which the response times are very short. E. g. Missile guidance system. A single system may have all hard, soft and real-time subsystems. In reality many systems will have a cost function associated with missing each deadline 6
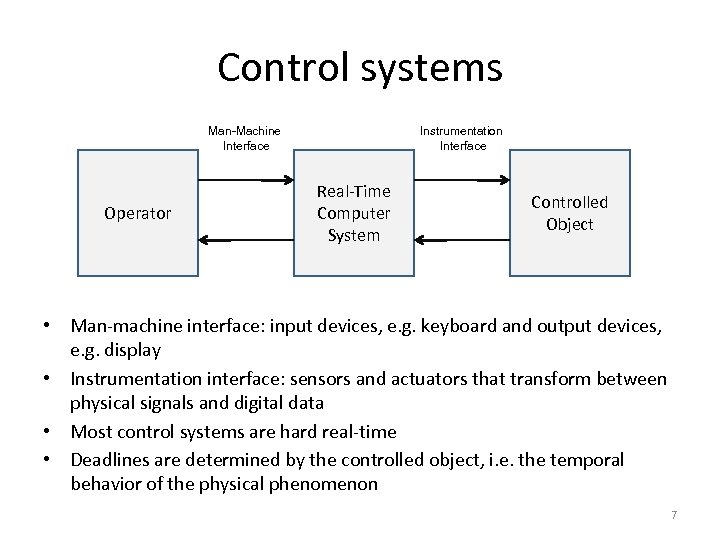 Control systems Man-Machine Interface Operator Instrumentation Interface Real-Time Computer System Controlled Object • Man-machine interface: input devices, e. g. keyboard and output devices, e. g. display • Instrumentation interface: sensors and actuators that transform between physical signals and digital data • Most control systems are hard real-time • Deadlines are determined by the controlled object, i. e. the temporal behavior of the physical phenomenon 7
Control systems Man-Machine Interface Operator Instrumentation Interface Real-Time Computer System Controlled Object • Man-machine interface: input devices, e. g. keyboard and output devices, e. g. display • Instrumentation interface: sensors and actuators that transform between physical signals and digital data • Most control systems are hard real-time • Deadlines are determined by the controlled object, i. e. the temporal behavior of the physical phenomenon 7
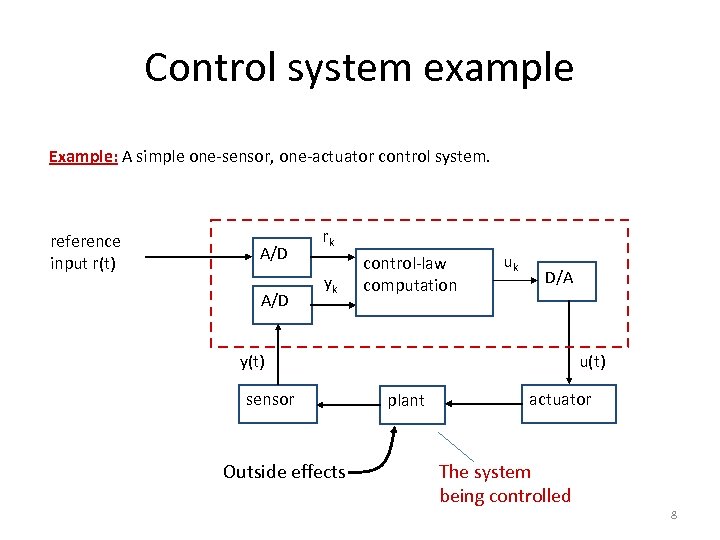 Control system example Example: A simple one-sensor, one-actuator control system. reference input r(t) A/D rk yk control-law computation uk D/A y(t) sensor Outside effects u(t) plant actuator The system being controlled 8
Control system example Example: A simple one-sensor, one-actuator control system. reference input r(t) A/D rk yk control-law computation uk D/A y(t) sensor Outside effects u(t) plant actuator The system being controlled 8
 Control systems cont’d. Pseudo-code for this system: set timer to interrupt periodically with period T; at each timer interrupt do do analog-to-digital conversion to get y; compute control output u; output u and do digital-to-analog conversion; end do T is called the sampling period. T is a key design choice. Typical range for T: seconds to milliseconds. 9
Control systems cont’d. Pseudo-code for this system: set timer to interrupt periodically with period T; at each timer interrupt do do analog-to-digital conversion to get y; compute control output u; output u and do digital-to-analog conversion; end do T is called the sampling period. T is a key design choice. Typical range for T: seconds to milliseconds. 9
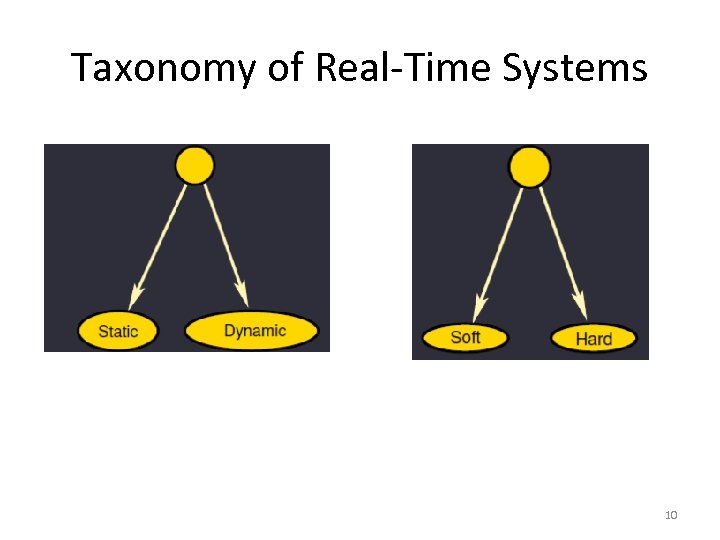 Taxonomy of Real-Time Systems 10
Taxonomy of Real-Time Systems 10
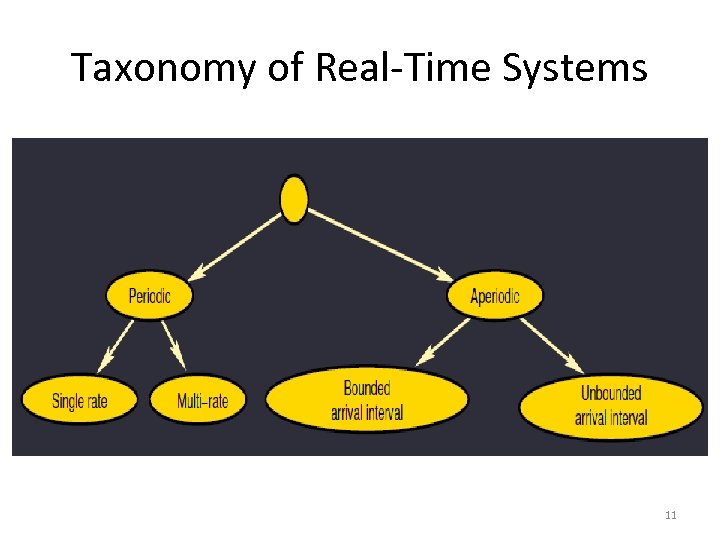 Taxonomy of Real-Time Systems 11
Taxonomy of Real-Time Systems 11
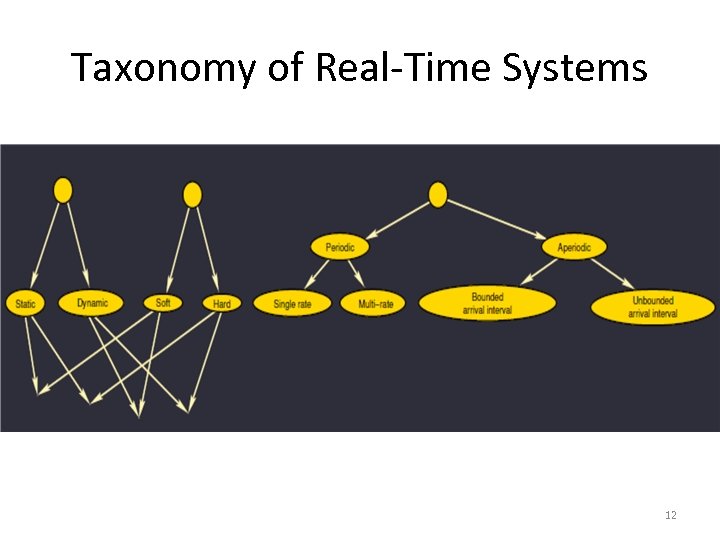 Taxonomy of Real-Time Systems 12
Taxonomy of Real-Time Systems 12
 Taxonomy: Static • Task arrival times can be predicted • Static (compile-time) analysis possible • Allows good resource usage (low idle time for processors). 13
Taxonomy: Static • Task arrival times can be predicted • Static (compile-time) analysis possible • Allows good resource usage (low idle time for processors). 13
 Taxonomy: Dynamic • Arrival times unpredictable • Static (compile-time) analysis possible only for simple cases. • Processor utilization decreases dramatically. • In many real systems, this is very difficult to handle. • Must avoid over-simplifying assumptions – e. g. , assuming that all tasks are independent, when this is unlikely. 14
Taxonomy: Dynamic • Arrival times unpredictable • Static (compile-time) analysis possible only for simple cases. • Processor utilization decreases dramatically. • In many real systems, this is very difficult to handle. • Must avoid over-simplifying assumptions – e. g. , assuming that all tasks are independent, when this is unlikely. 14
 Taxonomy: Soft Real-Time • Allows more slack in the implementation • Timings may be suboptimal without being incorrect. • Problem formulation can be much more complicated than hard real-time • Two common and an uncommon way of handling non-trivial soft real-time system requirements – Set somewhat loose hard timing constraints – Informal design and testing – Formulate as an optimization problem 15
Taxonomy: Soft Real-Time • Allows more slack in the implementation • Timings may be suboptimal without being incorrect. • Problem formulation can be much more complicated than hard real-time • Two common and an uncommon way of handling non-trivial soft real-time system requirements – Set somewhat loose hard timing constraints – Informal design and testing – Formulate as an optimization problem 15
 Taxonomy: Hard Real-Time • Creates difficult problems. – Some timing constraints are inflexible • Simplifies problem formulation. 16
Taxonomy: Hard Real-Time • Creates difficult problems. – Some timing constraints are inflexible • Simplifies problem formulation. 16
 Taxonomy: Periodic • Each task (or group of tasks) executes repeatedly with a particular period. • Allows some static analysis techniques to be used. • Matches characteristics of many real problems • It is possible to have tasks with deadlines smaller, equal to, or greater than their period. – The later are difficult to handle (i. e. , multiple concurrent task instances occur). 17
Taxonomy: Periodic • Each task (or group of tasks) executes repeatedly with a particular period. • Allows some static analysis techniques to be used. • Matches characteristics of many real problems • It is possible to have tasks with deadlines smaller, equal to, or greater than their period. – The later are difficult to handle (i. e. , multiple concurrent task instances occur). 17
 Periodic • Single rate: – One period in the system – Simple but inflexible – Used in implementing a lot of wireless sensor networks. • Multi rate: – Multiple periods – Should be harmonics to simplify system design 18
Periodic • Single rate: – One period in the system – Simple but inflexible – Used in implementing a lot of wireless sensor networks. • Multi rate: – Multiple periods – Should be harmonics to simplify system design 18
 Taxonomy: Aperiodic • Are also called sporadic, asynchronous, or reactive. • Creates a dynamic situation • Bounded arrival time interval are easier to handle • Unbounded arrival time intervals are impossible to handle with resourceconstrained systems. 19
Taxonomy: Aperiodic • Are also called sporadic, asynchronous, or reactive. • Creates a dynamic situation • Bounded arrival time interval are easier to handle • Unbounded arrival time intervals are impossible to handle with resourceconstrained systems. 19
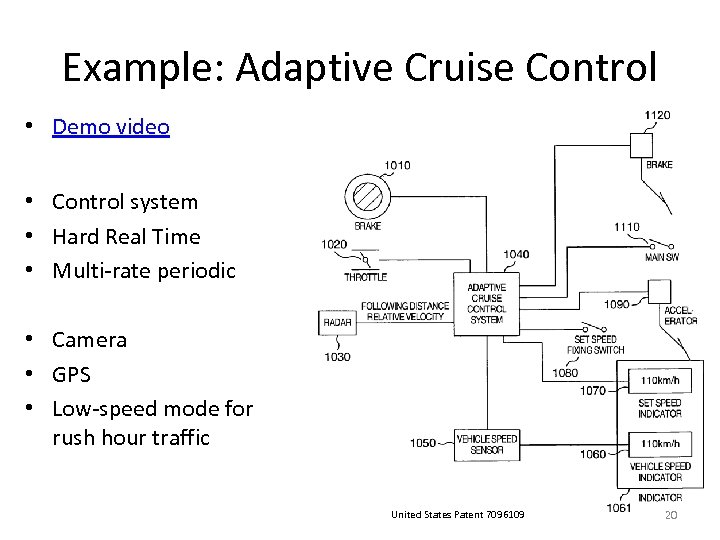 Example: Adaptive Cruise Control • Demo video • Control system • Hard Real Time • Multi-rate periodic • Camera • GPS • Low-speed mode for rush hour traffic United States Patent 7096109 20
Example: Adaptive Cruise Control • Demo video • Control system • Hard Real Time • Multi-rate periodic • Camera • GPS • Low-speed mode for rush hour traffic United States Patent 7096109 20
 Data Acquisition and Signal-Processing Systems • Examples: – – Video capture. Digital filtering. Video and voice compression/decompression. Radar signal processing. • Response times range from a few milliseconds to a few seconds. • Typically simpler than control systems 21
Data Acquisition and Signal-Processing Systems • Examples: – – Video capture. Digital filtering. Video and voice compression/decompression. Radar signal processing. • Response times range from a few milliseconds to a few seconds. • Typically simpler than control systems 21
 Other Real-Time Applications • Real-time databases. • Examples: stock market, airline reservations, etc. • Transactions must complete by deadlines. • Main dilemma: Transaction scheduling algorithms and real-time scheduling algorithms often have conflicting goals. • Data is subject temporal consistency requirements. • Multimedia. • Want to process audio and video frames at steady rates. – TV video rate is 30 frames/sec. HDTV is 60 frames/sec. – Telephone audio is 16 Kbits/sec. CD audio is 128 Kbits/sec. • Other requirements: Lip synchronization, low jitter, low end-to-end response times (if interactive). 22
Other Real-Time Applications • Real-time databases. • Examples: stock market, airline reservations, etc. • Transactions must complete by deadlines. • Main dilemma: Transaction scheduling algorithms and real-time scheduling algorithms often have conflicting goals. • Data is subject temporal consistency requirements. • Multimedia. • Want to process audio and video frames at steady rates. – TV video rate is 30 frames/sec. HDTV is 60 frames/sec. – Telephone audio is 16 Kbits/sec. CD audio is 128 Kbits/sec. • Other requirements: Lip synchronization, low jitter, low end-to-end response times (if interactive). 22
 Are All Systems Real-Time Systems? • Question: Is a payroll processing system a real-time system? – It has a time constraint: Print the pay checks every two weeks. • Perhaps it is a real-time system in a definitional sense, but it doesn’t pay us to view it as such. • We are interested in systems for which it is not a priori obvious how to meet timing constraints. 23
Are All Systems Real-Time Systems? • Question: Is a payroll processing system a real-time system? – It has a time constraint: Print the pay checks every two weeks. • Perhaps it is a real-time system in a definitional sense, but it doesn’t pay us to view it as such. • We are interested in systems for which it is not a priori obvious how to meet timing constraints. 23
 The “Window of Scarcity” • Resources may be categorized as: – Abundant: Virtually any system design methodology can be used to realize the timing requirements of the application. – Insufficient: The application is ahead of the technology curve; no design methodology can be used to realize the timing requirements of the application. – Sufficient but scarce: It is possible to realize the timing requirements of the application, but careful resource allocation is required. 24
The “Window of Scarcity” • Resources may be categorized as: – Abundant: Virtually any system design methodology can be used to realize the timing requirements of the application. – Insufficient: The application is ahead of the technology curve; no design methodology can be used to realize the timing requirements of the application. – Sufficient but scarce: It is possible to realize the timing requirements of the application, but careful resource allocation is required. 24
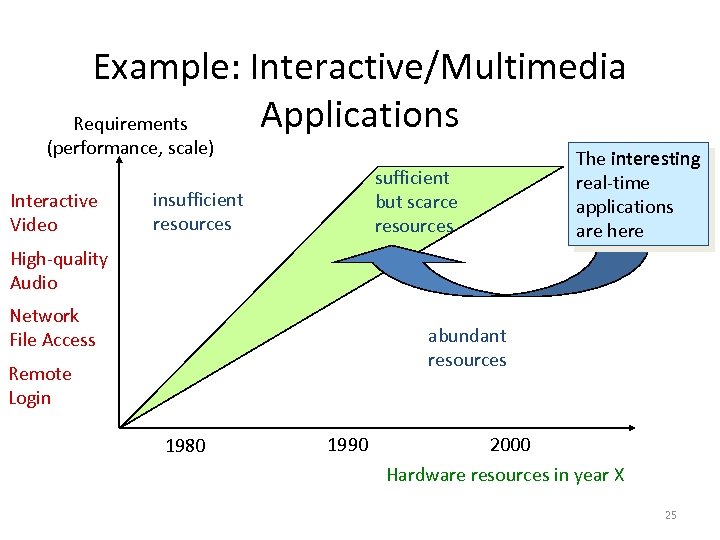 Example: Interactive/Multimedia Applications Requirements (performance, scale) Interactive Video The interesting real-time applications are here sufficient but scarce resources insufficient resources High-quality Audio Network File Access abundant resources Remote Login 1980 1990 2000 Hardware resources in year X 25
Example: Interactive/Multimedia Applications Requirements (performance, scale) Interactive Video The interesting real-time applications are here sufficient but scarce resources insufficient resources High-quality Audio Network File Access abundant resources Remote Login 1980 1990 2000 Hardware resources in year X 25
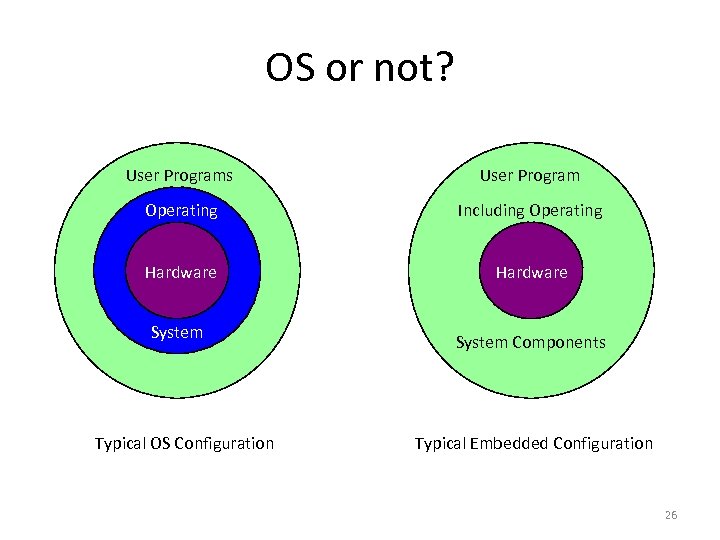 OS or not? User Programs User Program Operating Including Operating Hardware System Typical OS Configuration System Components Typical Embedded Configuration 26
OS or not? User Programs User Program Operating Including Operating Hardware System Typical OS Configuration System Components Typical Embedded Configuration 26
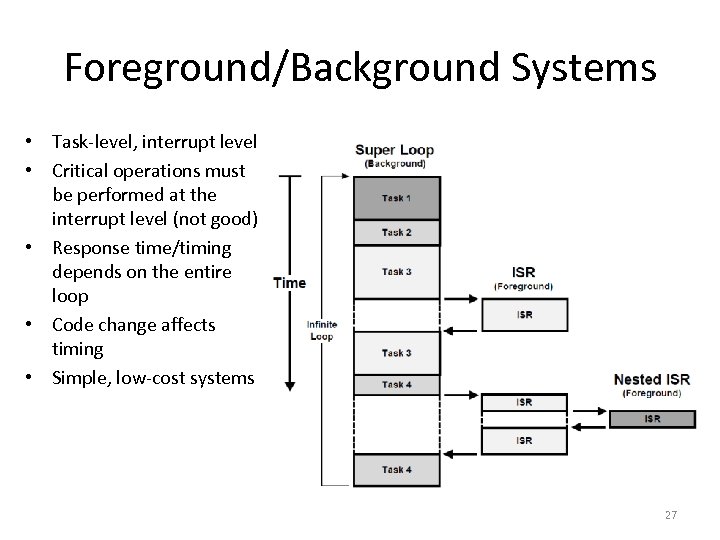 Foreground/Background Systems • Task-level, interrupt level • Critical operations must be performed at the interrupt level (not good) • Response time/timing depends on the entire loop • Code change affects timing • Simple, low-cost systems 27
Foreground/Background Systems • Task-level, interrupt level • Critical operations must be performed at the interrupt level (not good) • Response time/timing depends on the entire loop • Code change affects timing • Simple, low-cost systems 27
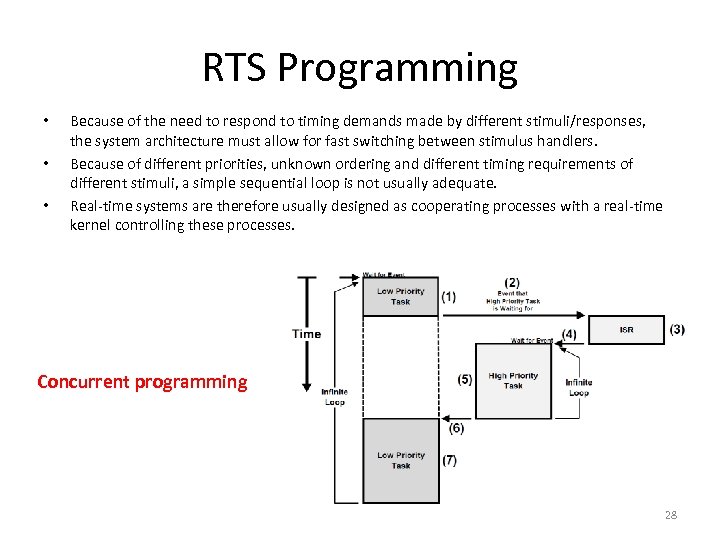 RTS Programming • • • Because of the need to respond to timing demands made by different stimuli/responses, the system architecture must allow for fast switching between stimulus handlers. Because of different priorities, unknown ordering and different timing requirements of different stimuli, a simple sequential loop is not usually adequate. Real-time systems are therefore usually designed as cooperating processes with a real-time kernel controlling these processes. Concurrent programming 28
RTS Programming • • • Because of the need to respond to timing demands made by different stimuli/responses, the system architecture must allow for fast switching between stimulus handlers. Because of different priorities, unknown ordering and different timing requirements of different stimuli, a simple sequential loop is not usually adequate. Real-time systems are therefore usually designed as cooperating processes with a real-time kernel controlling these processes. Concurrent programming 28
 Real Time Java? • Java supports lightweight concurrency (threads and synchronized methods) and can be used for some soft real -time systems. • Java is not suitable for hard RT programming but real-time versions of Java are now available that address problems such as – Not possible to specify thread execution time; – Uncontrollable garbage collection; – Not possible to access system hardware; – Etc. – Real-Time Specification for Java – Sun Java Real-Time System Requires a Real Time OS underneath (e. g. , no Windows support) 29
Real Time Java? • Java supports lightweight concurrency (threads and synchronized methods) and can be used for some soft real -time systems. • Java is not suitable for hard RT programming but real-time versions of Java are now available that address problems such as – Not possible to specify thread execution time; – Uncontrollable garbage collection; – Not possible to access system hardware; – Etc. – Real-Time Specification for Java – Sun Java Real-Time System Requires a Real Time OS underneath (e. g. , no Windows support) 29
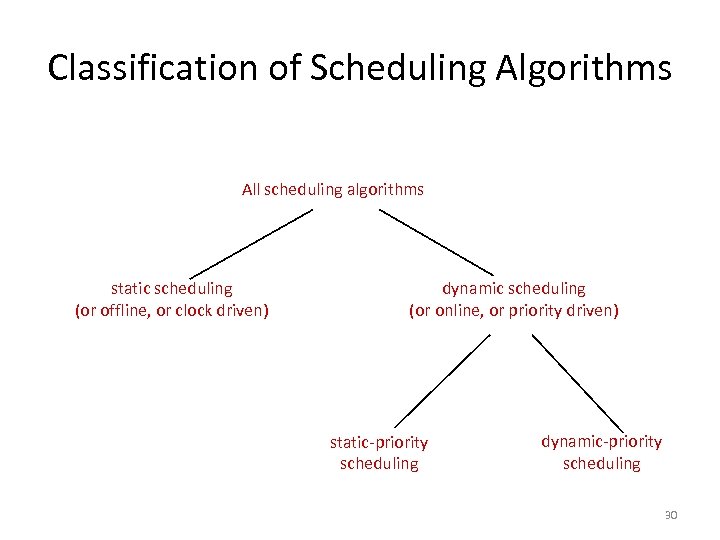 Classification of Scheduling Algorithms All scheduling algorithms static scheduling (or offline, or clock driven) dynamic scheduling (or online, or priority driven) static-priority scheduling dynamic-priority scheduling 30
Classification of Scheduling Algorithms All scheduling algorithms static scheduling (or offline, or clock driven) dynamic scheduling (or online, or priority driven) static-priority scheduling dynamic-priority scheduling 30
 Scheduling strategies • Non pre-emptive scheduling – Once a process has been scheduled for execution, it runs to completion or until it is blocked for some reason (e. g. waiting for I/O). • Pre-emptive scheduling – The execution of an executing processes may be stopped if a higher priority process requires service. • Scheduling algorithms – – Round-robin; Rate monotonic; Shortest deadline first; Etc. 31
Scheduling strategies • Non pre-emptive scheduling – Once a process has been scheduled for execution, it runs to completion or until it is blocked for some reason (e. g. waiting for I/O). • Pre-emptive scheduling – The execution of an executing processes may be stopped if a higher priority process requires service. • Scheduling algorithms – – Round-robin; Rate monotonic; Shortest deadline first; Etc. 31
 Real-time operating systems • Real-time operating systems are specialised operating systems which manage the processes in the RTS. • Responsible for process management and resource (processor and memory) allocation. • Do not normally include facilities such as file management. 14 32
Real-time operating systems • Real-time operating systems are specialised operating systems which manage the processes in the RTS. • Responsible for process management and resource (processor and memory) allocation. • Do not normally include facilities such as file management. 14 32
 Operating system components • Real-time clock – Provides information for process scheduling. • Interrupt handler – Manages aperiodic requests for service. • Scheduler – Chooses the next process to be run. • Resource manager – Allocates memory and processor resources. • Dispatcher – Starts process execution. 33
Operating system components • Real-time clock – Provides information for process scheduling. • Interrupt handler – Manages aperiodic requests for service. • Scheduler – Chooses the next process to be run. • Resource manager – Allocates memory and processor resources. • Dispatcher – Starts process execution. 33
 Interrupt servicing • Control is transferred automatically to a pre-determined memory location. • This location contains an instruction to jump to an interrupt service routine. • Further interrupts are disabled, the interrupt serviced and control returned to the interrupted process. • Interrupt service routines MUST be short, simple and fast. 34
Interrupt servicing • Control is transferred automatically to a pre-determined memory location. • This location contains an instruction to jump to an interrupt service routine. • Further interrupts are disabled, the interrupt serviced and control returned to the interrupted process. • Interrupt service routines MUST be short, simple and fast. 34
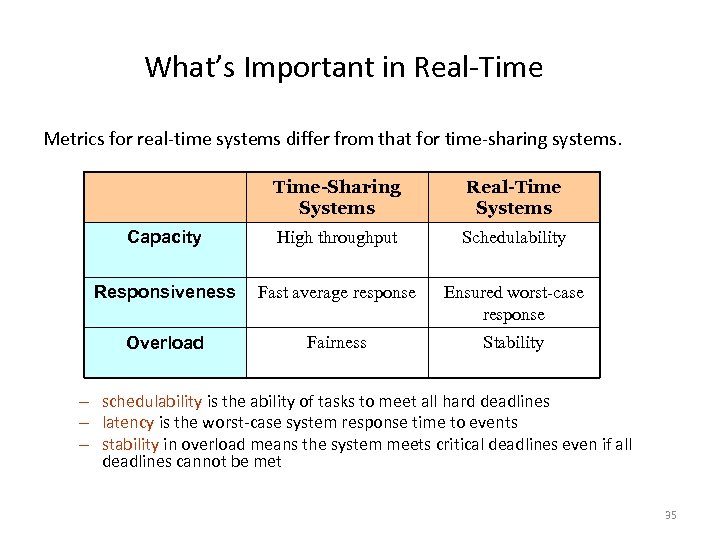 What’s Important in Real-Time Metrics for real-time systems differ from that for time-sharing systems. Time-Sharing Systems Real-Time Systems Capacity High throughput Schedulability Responsiveness Fast average response Ensured worst-case response Overload Fairness Stability – schedulability is the ability of tasks to meet all hard deadlines – latency is the worst-case system response time to events – stability in overload means the system meets critical deadlines even if all deadlines cannot be met 35
What’s Important in Real-Time Metrics for real-time systems differ from that for time-sharing systems. Time-Sharing Systems Real-Time Systems Capacity High throughput Schedulability Responsiveness Fast average response Ensured worst-case response Overload Fairness Stability – schedulability is the ability of tasks to meet all hard deadlines – latency is the worst-case system response time to events – stability in overload means the system meets critical deadlines even if all deadlines cannot be met 35
 Limited Resources q Common Component based software engineering (CBSE) technologies (Java. Beans, CORBA and COM) are seldom used as they: l Require excessive processing requirements l Require excessive memory requirements l Provide unpredictable timing characteristics Page 36
Limited Resources q Common Component based software engineering (CBSE) technologies (Java. Beans, CORBA and COM) are seldom used as they: l Require excessive processing requirements l Require excessive memory requirements l Provide unpredictable timing characteristics Page 36
 System Level Analysis q At system level we analyze to determine if the system composed fulfils the timing requirements. l Several different mature analysis methods exist, for example, analysis for priority-based systems and pre-run -time scheduling techniques Page 37
System Level Analysis q At system level we analyze to determine if the system composed fulfils the timing requirements. l Several different mature analysis methods exist, for example, analysis for priority-based systems and pre-run -time scheduling techniques Page 37
 Real-time Component Models q Using a standard operating system in a real-time application, such as windows NT must be done carefully, as it was designed to be used so. Page 38
Real-time Component Models q Using a standard operating system in a real-time application, such as windows NT must be done carefully, as it was designed to be used so. Page 38
 Application-specific Component Models q Maintain a component library which the application engineer can use when developing an application. q In addition to infrastructure components, domain specific component models, which in fact have been used for many years for certain domains must be considered. Page 39
Application-specific Component Models q Maintain a component library which the application engineer can use when developing an application. q In addition to infrastructure components, domain specific component models, which in fact have been used for many years for certain domains must be considered. Page 39
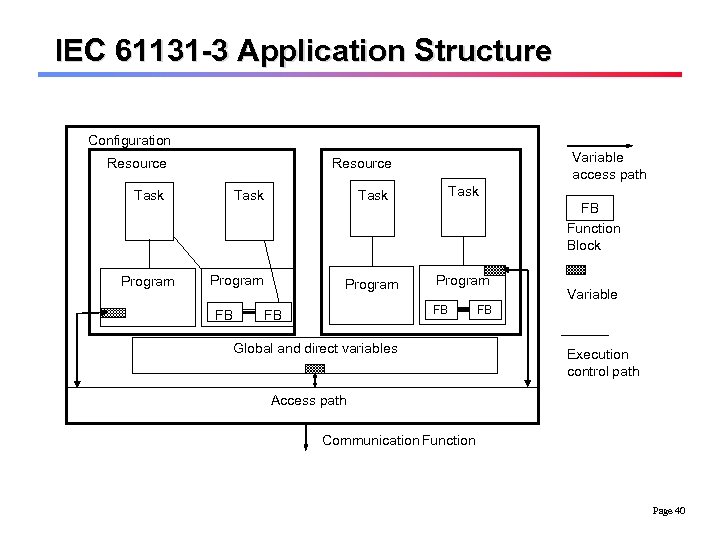 IEC 61131 -3 Application Structure Configuration Resource Task Program Variable access path Resource Task Program FB FB Function Block FB FB Global and direct variables Variable FB Execution control path Access path Communication Function Page 40
IEC 61131 -3 Application Structure Configuration Resource Task Program Variable access path Resource Task Program FB FB Function Block FB FB Global and direct variables Variable FB Execution control path Access path Communication Function Page 40
 A Configuration in IEC 61131 -3 q Encapsulates all software for an application and consists of one or several resources which provide the computational mechanisms. Page 41
A Configuration in IEC 61131 -3 q Encapsulates all software for an application and consists of one or several resources which provide the computational mechanisms. Page 41
 A Program in IEC 61131 -3 q A program is written in any of the languages proposed in the standard, for example: l Instruction lists l Assembly languages l Structured text l A high level language similar to Pascal l Ladder diagrams l Function block diagrams (FBD) Page 42
A Program in IEC 61131 -3 q A program is written in any of the languages proposed in the standard, for example: l Instruction lists l Assembly languages l Structured text l A high level language similar to Pascal l Ladder diagrams l Function block diagrams (FBD) Page 42
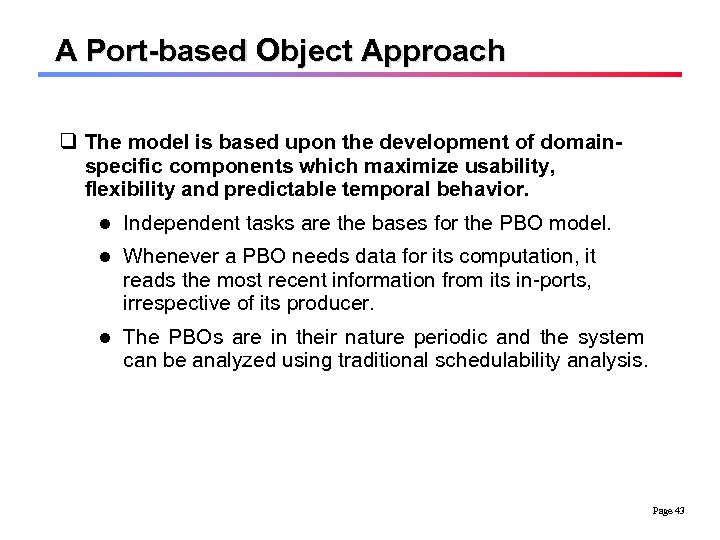 A Port-based Object Approach q The model is based upon the development of domainspecific components which maximize usability, flexibility and predictable temporal behavior. l Independent tasks are the bases for the PBO model. l Whenever a PBO needs data for its computation, it reads the most recent information from its in-ports, irrespective of its producer. l The PBOs are in their nature periodic and the system can be analyzed using traditional schedulability analysis. Page 43
A Port-based Object Approach q The model is based upon the development of domainspecific components which maximize usability, flexibility and predictable temporal behavior. l Independent tasks are the bases for the PBO model. l Whenever a PBO needs data for its computation, it reads the most recent information from its in-ports, irrespective of its producer. l The PBOs are in their nature periodic and the system can be analyzed using traditional schedulability analysis. Page 43
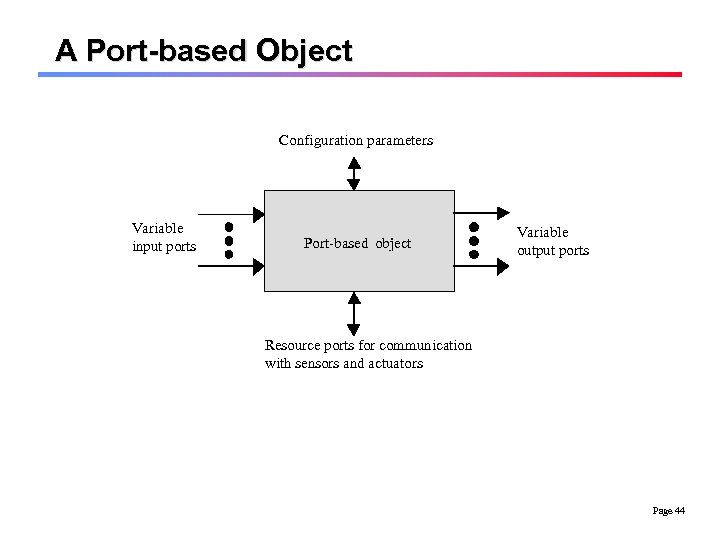 A Port-based Object Configuration parameters Variable input ports Port-based object Variable output ports Resource ports for communication with sensors and actuators Page 44
A Port-based Object Configuration parameters Variable input ports Port-based object Variable output ports Resource ports for communication with sensors and actuators Page 44
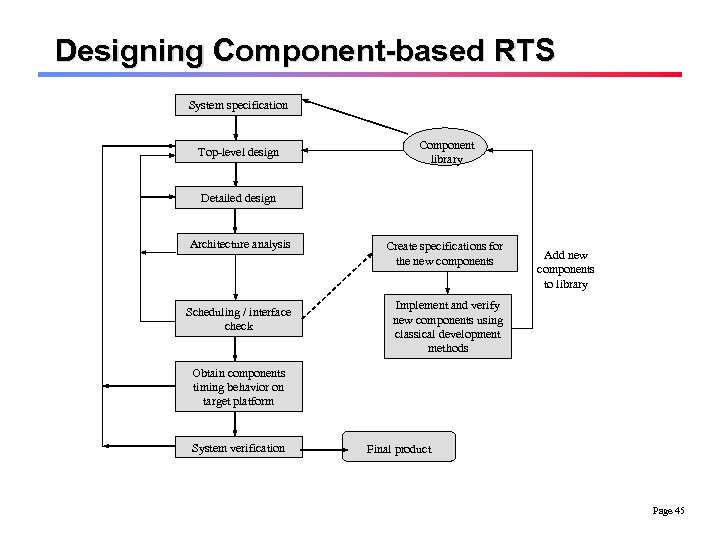 Designing Component-based RTS System specification Top-level design Component library Detailed design Architecture analysis Scheduling / interface check Create specifications for the new components Add new components to library Implement and verify new components using classical development methods Obtain components timing behavior on target platform System verification Final product Page 45
Designing Component-based RTS System specification Top-level design Component library Detailed design Architecture analysis Scheduling / interface check Create specifications for the new components Add new components to library Implement and verify new components using classical development methods Obtain components timing behavior on target platform System verification Final product Page 45
 Top-level Design q The first stage of the development process involves decomposition of the system into manageable components Page 46
Top-level Design q The first stage of the development process involves decomposition of the system into manageable components Page 46
 Detailed Design q At this stage a detailed component design is performed, by selecting components to be used from the candidate set. Page 47
Detailed Design q At this stage a detailed component design is performed, by selecting components to be used from the candidate set. Page 47
 Architecture Analysis q At this stage it is time to check that the system under development satisfies extra-functional requirements such as: l Maintainability l Reusability l Modifiability l Testability Page 48
Architecture Analysis q At this stage it is time to check that the system under development satisfies extra-functional requirements such as: l Maintainability l Reusability l Modifiability l Testability Page 48
 Scheduling q At this point we must check that the temporal requirements of the system can be satisfied, assuming time budgets assigned in the detailed design stage. q In other words, we need to make a schedulability analysis of the system based on the temporal requirements of each component Page 49
Scheduling q At this point we must check that the temporal requirements of the system can be satisfied, assuming time budgets assigned in the detailed design stage. q In other words, we need to make a schedulability analysis of the system based on the temporal requirements of each component Page 49
 WCET Verification q Performing a worst-case analysis can either be based on measurements or on a static analysis of the source code. q What is more interesting in the test cases is the execution time behavior shown as a function of input parameters as shown in the following slide. Page 50
WCET Verification q Performing a worst-case analysis can either be based on measurements or on a static analysis of the source code. q What is more interesting in the test cases is the execution time behavior shown as a function of input parameters as shown in the following slide. Page 50
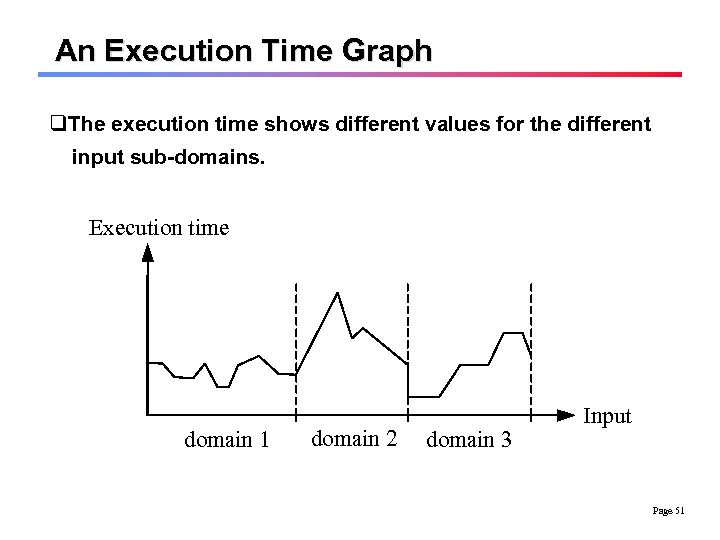 An Execution Time Graph q. The execution time shows different values for the different input sub-domains. Execution time domain 1 domain 2 domain 3 Input Page 51
An Execution Time Graph q. The execution time shows different values for the different input sub-domains. Execution time domain 1 domain 2 domain 3 Input Page 51
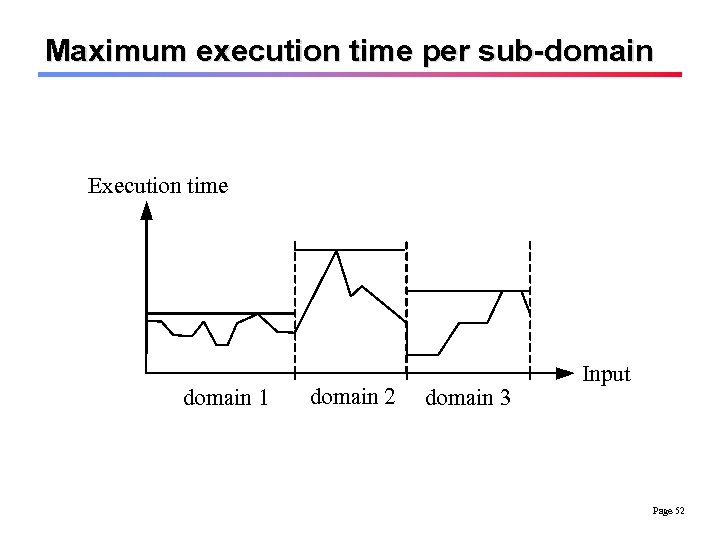 Maximum execution time per sub-domain Execution time domain 1 domain 2 domain 3 Input Page 52
Maximum execution time per sub-domain Execution time domain 1 domain 2 domain 3 Input Page 52
 Implementation of New Components q New components; Those not already in the library must be implemented. The designer of the component has two requirements: l The functional requirements l The assigned time budget Page 53
Implementation of New Components q New components; Those not already in the library must be implemented. The designer of the component has two requirements: l The functional requirements l The assigned time budget Page 53
 System Build and Test q Finally, we build the system using old and new components. q We must now verify the functional and temporal properties of the system obtained. q If the verification test fails, we must return to the relevant stage of the development process and correct the error. Page 54
System Build and Test q Finally, we build the system using old and new components. q We must now verify the functional and temporal properties of the system obtained. q If the verification test fails, we must return to the relevant stage of the development process and correct the error. Page 54
 Component Library q Is the most central part of any CBSE system as it contains binaries of components and their descriptions. q A component library containing real-time components should provide the following: l Memory requirements l Worst cast execution time (WCET) test cases l Dependencies l Environment assumptions Page 55
Component Library q Is the most central part of any CBSE system as it contains binaries of components and their descriptions. q A component library containing real-time components should provide the following: l Memory requirements l Worst cast execution time (WCET) test cases l Dependencies l Environment assumptions Page 55
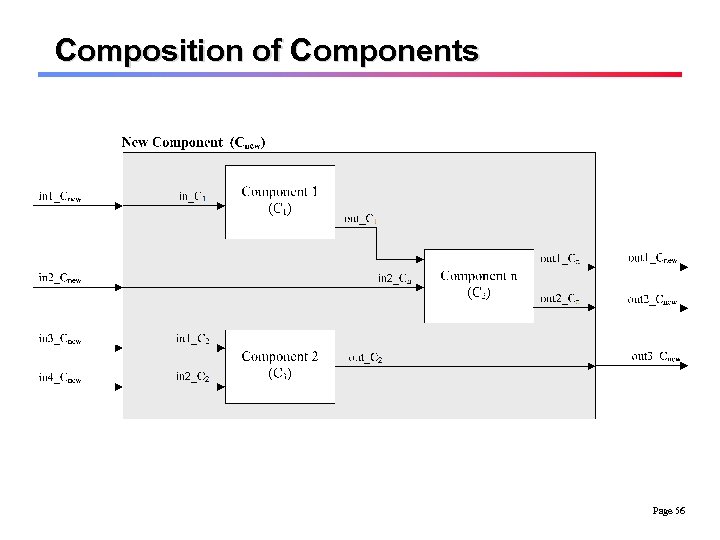 Composition of Components Page 56
Composition of Components Page 56
 End-To-End Deadlines q End-to-end deadlines l Are set such that the system requirements are fulfilled in the same way as the time budgets are set l Should be specified for the input to and output from the component since the WCET cannot be computed since its parts may be executing with different periods. Page 57
End-To-End Deadlines q End-to-end deadlines l Are set such that the system requirements are fulfilled in the same way as the time budgets are set l Should be specified for the input to and output from the component since the WCET cannot be computed since its parts may be executing with different periods. Page 57
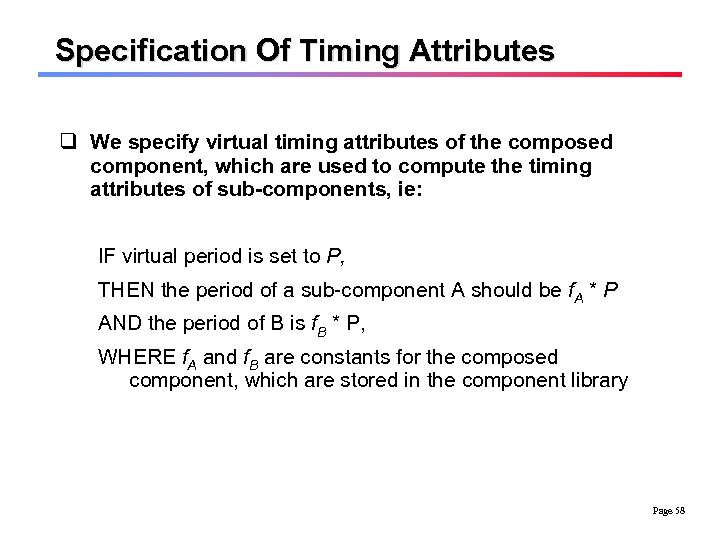 Specification Of Timing Attributes q We specify virtual timing attributes of the composed component, which are used to compute the timing attributes of sub-components, ie: IF virtual period is set to P, THEN the period of a sub-component A should be f. A * P AND the period of B is f. B * P, WHERE f. A and f. B are constants for the composed component, which are stored in the component library Page 58
Specification Of Timing Attributes q We specify virtual timing attributes of the composed component, which are used to compute the timing attributes of sub-components, ie: IF virtual period is set to P, THEN the period of a sub-component A should be f. A * P AND the period of B is f. B * P, WHERE f. A and f. B are constants for the composed component, which are stored in the component library Page 58
 RT Components in Rubus OS q Rubus: l Is one of a few real-time operating systems currently available which have some concept of components. l Is a hybrid operating system, in the sense that it supports both pre-emptive static scheduling and fixed priority scheduling. Page 59
RT Components in Rubus OS q Rubus: l Is one of a few real-time operating systems currently available which have some concept of components. l Is a hybrid operating system, in the sense that it supports both pre-emptive static scheduling and fixed priority scheduling. Page 59
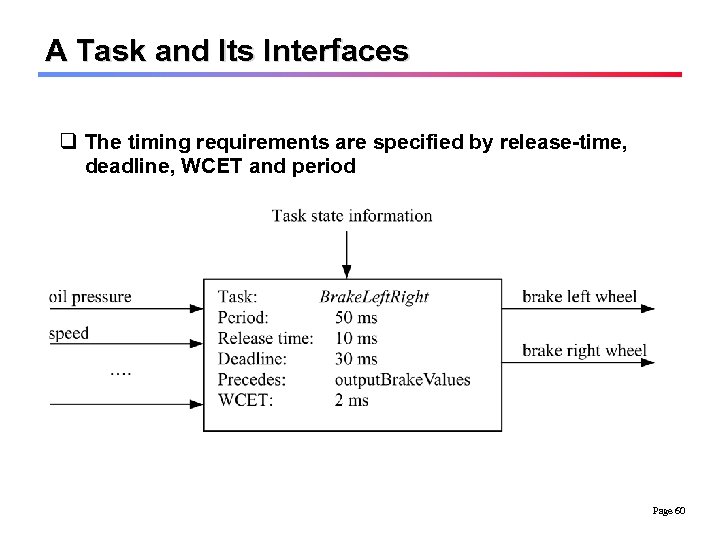 A Task and Its Interfaces q The timing requirements are specified by release-time, deadline, WCET and period Page 60
A Task and Its Interfaces q The timing requirements are specified by release-time, deadline, WCET and period Page 60
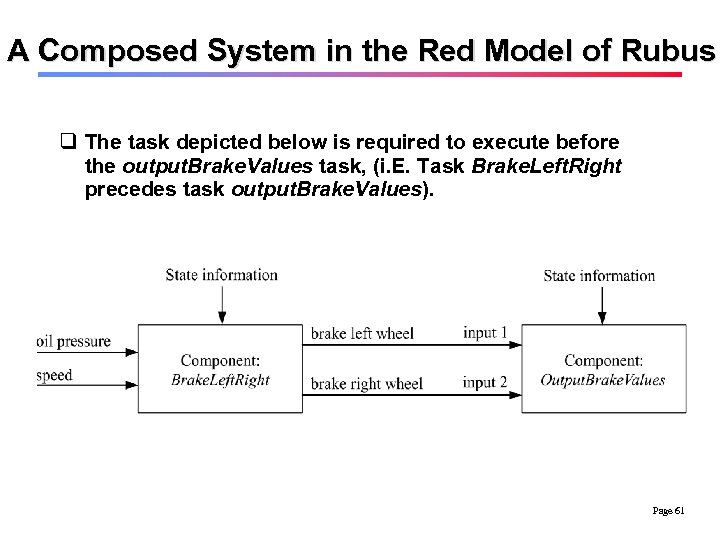 A Composed System in the Red Model of Rubus q The task depicted below is required to execute before the output. Brake. Values task, (i. E. Task Brake. Left. Right precedes task output. Brake. Values). Page 61
A Composed System in the Red Model of Rubus q The task depicted below is required to execute before the output. Brake. Values task, (i. E. Task Brake. Left. Right precedes task output. Brake. Values). Page 61
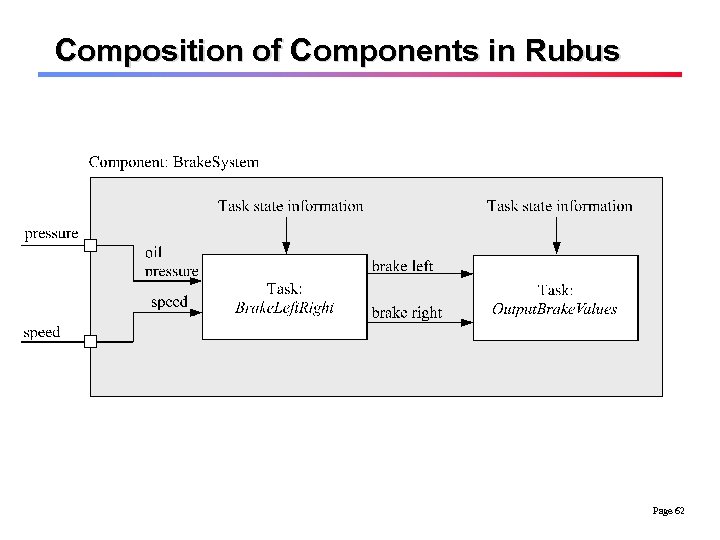 Composition of Components in Rubus Page 62
Composition of Components in Rubus Page 62
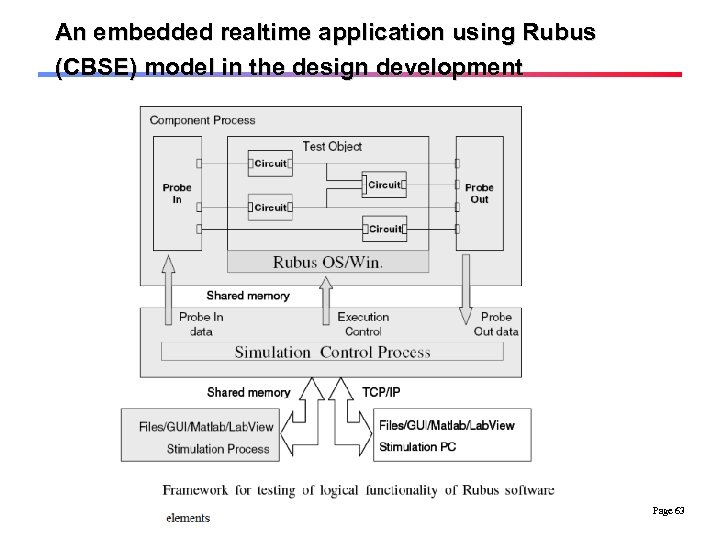 An embedded realtime application using Rubus (CBSE) model in the design development Page 63
An embedded realtime application using Rubus (CBSE) model in the design development Page 63
 Conclusion • The Rubus component model (CBSE) provides: – Methods to express the infrastructure of software functions, i. e. , the interaction between software functions in terms of data-flow and control-flow – The resulting architecture is formal enough for analysis of timing and memory properties – The components and the infrastructure allow for a resource efficient mapping onto a run-time structure 64
Conclusion • The Rubus component model (CBSE) provides: – Methods to express the infrastructure of software functions, i. e. , the interaction between software functions in terms of data-flow and control-flow – The resulting architecture is formal enough for analysis of timing and memory properties – The components and the infrastructure allow for a resource efficient mapping onto a run-time structure 64


