840902f4e61c785f93793658138d7bac.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 31
 Real-Time PCR m. RNA quantification
Real-Time PCR m. RNA quantification
 What do m. RNA levels tell us? DNA m. RNA protein • Reflect level of gene expression • Information about cell response • Protein production (not always)
What do m. RNA levels tell us? DNA m. RNA protein • Reflect level of gene expression • Information about cell response • Protein production (not always)
 quantitative m. RNA/DNA analysis Direct -Northern blotting -In situ hybridization PCR amplification -Regular RT-PCR -Real time PCR (Microarrays)
quantitative m. RNA/DNA analysis Direct -Northern blotting -In situ hybridization PCR amplification -Regular RT-PCR -Real time PCR (Microarrays)
 Nomenclature RT-PCR = Reverse Transcriptase PCR q. Real time PCR = quantitative Real-Time PCR
Nomenclature RT-PCR = Reverse Transcriptase PCR q. Real time PCR = quantitative Real-Time PCR
 RT-PCR • Isolate RNA • c. DNA synthesis • PCR reaction
RT-PCR • Isolate RNA • c. DNA synthesis • PCR reaction
 Why isn´t this good enough?
Why isn´t this good enough?
 What’s Wrong With Agarose Gels? * * * • • Low sensitivity Low resolution Non-automated Size-based discrimination only Results are not expressed as numbers based on personal evaluation Ethidium bromide staining is not very quantitative End point analysis ABI: Real-Time PCR vs Traditional PCR (www)
What’s Wrong With Agarose Gels? * * * • • Low sensitivity Low resolution Non-automated Size-based discrimination only Results are not expressed as numbers based on personal evaluation Ethidium bromide staining is not very quantitative End point analysis ABI: Real-Time PCR vs Traditional PCR (www)
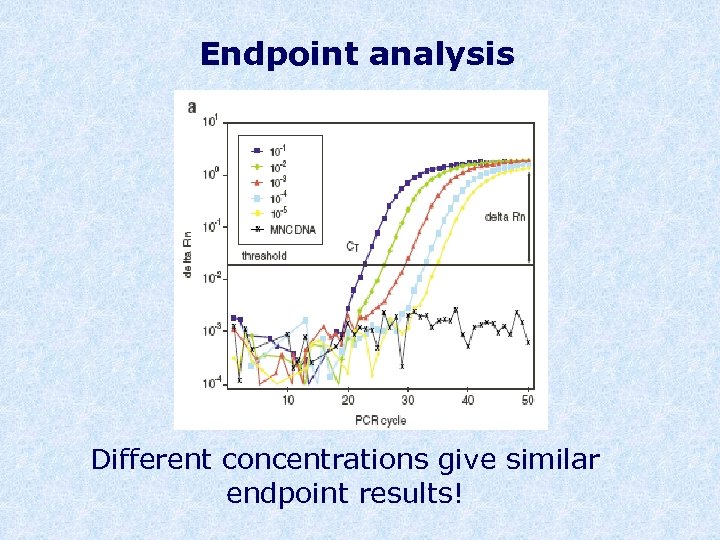 Endpoint analysis Different concentrations give similar endpoint results!
Endpoint analysis Different concentrations give similar endpoint results!
 Real-time Principles • based on the detection and quantitation of a fluorescent reporter • In stead of measuring the endpoint we focus on the first significant increase in the amount of PCR product. • The time of the increase correlates inversely to the initial amount of DNA template
Real-time Principles • based on the detection and quantitation of a fluorescent reporter • In stead of measuring the endpoint we focus on the first significant increase in the amount of PCR product. • The time of the increase correlates inversely to the initial amount of DNA template
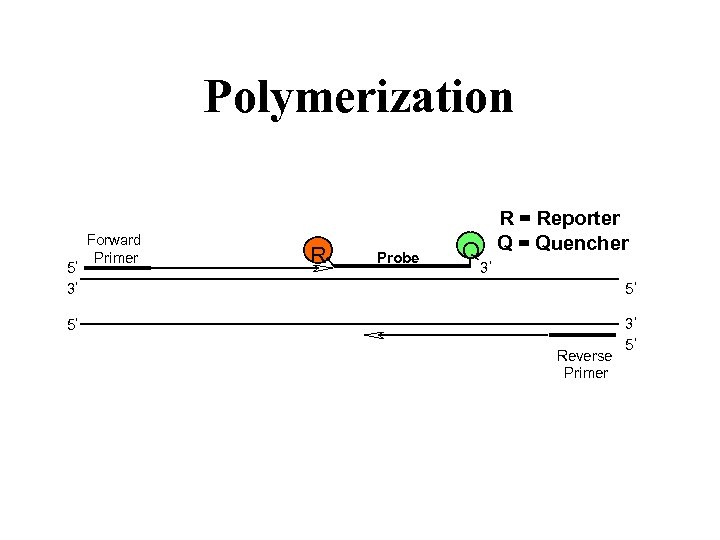 Polymerization 5 3 Forward Primer R Probe R = Reporter Q Q = Quencher 3 5 5 Reverse Primer 3 5
Polymerization 5 3 Forward Primer R Probe R = Reporter Q Q = Quencher 3 5 5 Reverse Primer 3 5
 For Real Time PCR we need a a specific probe with a fluorescent reporter. R Probe Q
For Real Time PCR we need a a specific probe with a fluorescent reporter. R Probe Q
 When in close contact with the reporter, the quencer absobes its emission.
When in close contact with the reporter, the quencer absobes its emission.
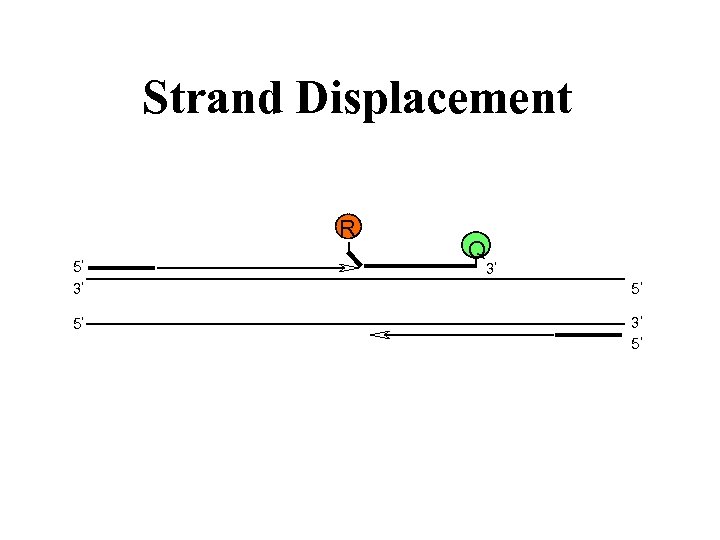 Strand Displacement R 5 3 5 Q 3 5
Strand Displacement R 5 3 5 Q 3 5
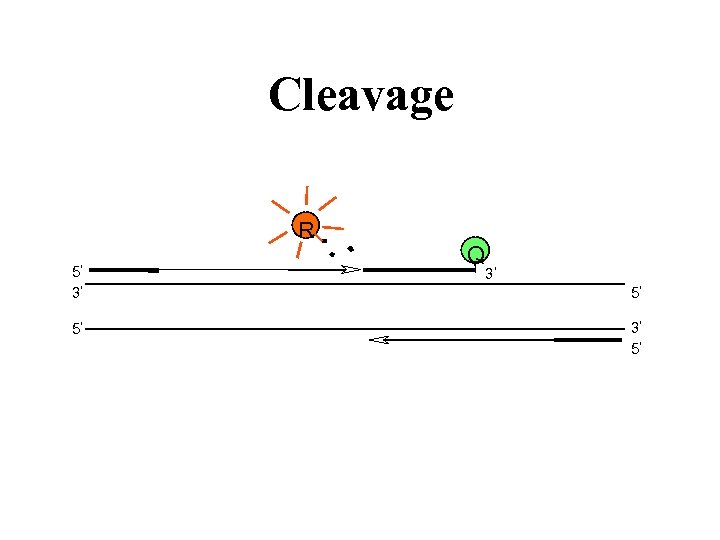 Cleavage R 5 Q 3 3 5 5 3 5
Cleavage R 5 Q 3 3 5 5 3 5
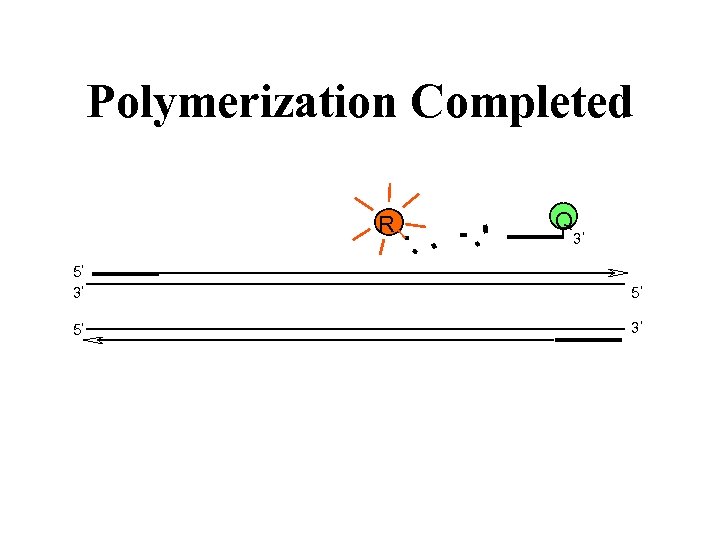 Polymerization Completed R Q 3 5 5 3
Polymerization Completed R Q 3 5 5 3
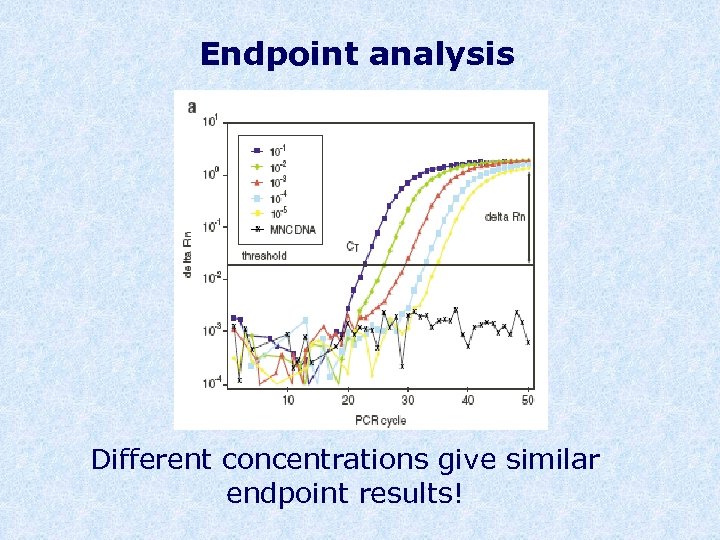 Endpoint analysis Different concentrations give similar endpoint results!
Endpoint analysis Different concentrations give similar endpoint results!
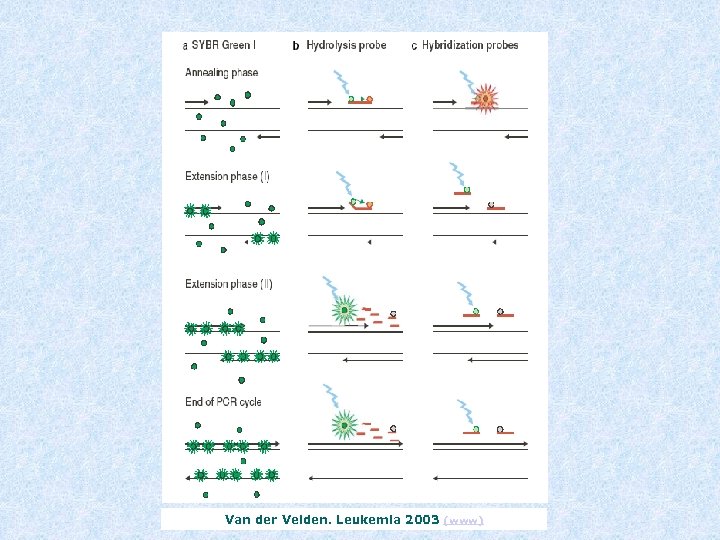 Van der Velden. Leukemia 2003 (www)
Van der Velden. Leukemia 2003 (www)
 SYBR Green (double-stranded DNA binding dye) * emits a strong fluorescent signal upon binding to double-stranded DNA * nonspecific binding is a disadvantage * requires extensive optimisation • longer amplicons create a stronger signal • It´s cheap
SYBR Green (double-stranded DNA binding dye) * emits a strong fluorescent signal upon binding to double-stranded DNA * nonspecific binding is a disadvantage * requires extensive optimisation • longer amplicons create a stronger signal • It´s cheap
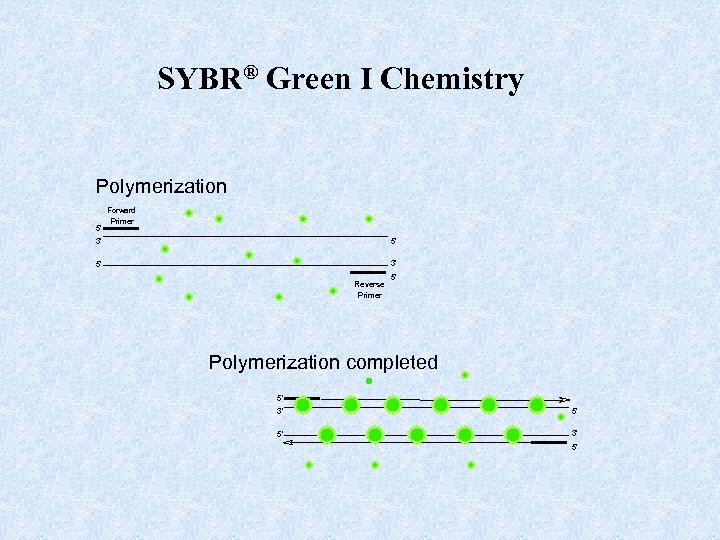 SYBR® Green I Chemistry Polymerization 5' Forward Primer 3' 5' 5' 3' Reverse Primer 5' Polymerization completed 5' 3' 5'
SYBR® Green I Chemistry Polymerization 5' Forward Primer 3' 5' 5' 3' Reverse Primer 5' Polymerization completed 5' 3' 5'
 Real-time PCR advantages * not influenced by non-specific amplification * amplification can be monitored real-time * no post-PCR processing of products (high throughput, low contamination risk) * requirement of 1000 -fold less RNA than conventional assays (3 picogram = one genome equivalent) * most specific, sensitive and reproducible
Real-time PCR advantages * not influenced by non-specific amplification * amplification can be monitored real-time * no post-PCR processing of products (high throughput, low contamination risk) * requirement of 1000 -fold less RNA than conventional assays (3 picogram = one genome equivalent) * most specific, sensitive and reproducible
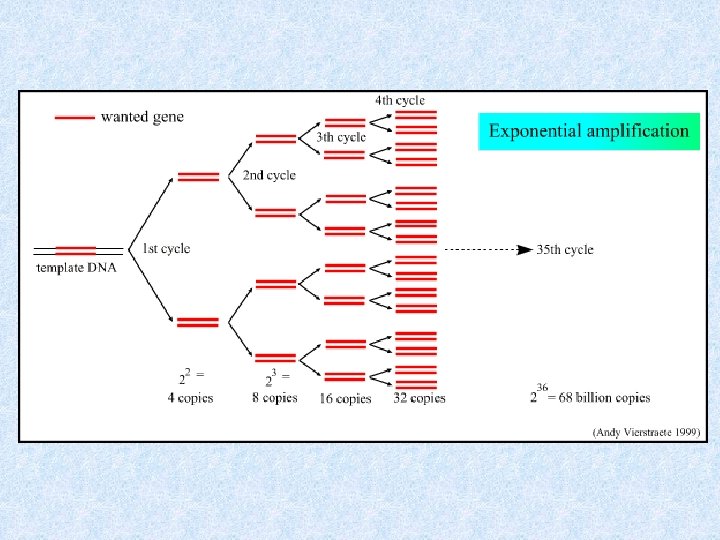
 Real-time PCR disadvantages * setting up requires high technical skill and support * high equipment cost * Runs are more expensive than conventional PCR * DNA contamination (in m. RNA analysis)
Real-time PCR disadvantages * setting up requires high technical skill and support * high equipment cost * Runs are more expensive than conventional PCR * DNA contamination (in m. RNA analysis)
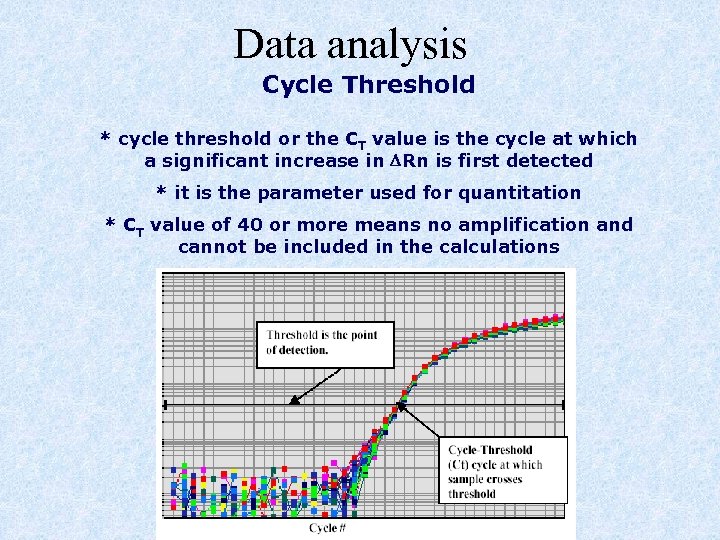 Data analysis Cycle Threshold * cycle threshold or the CT value is the cycle at which a significant increase in DRn is first detected * it is the parameter used for quantitation * CT value of 40 or more means no amplification and cannot be included in the calculations
Data analysis Cycle Threshold * cycle threshold or the CT value is the cycle at which a significant increase in DRn is first detected * it is the parameter used for quantitation * CT value of 40 or more means no amplification and cannot be included in the calculations
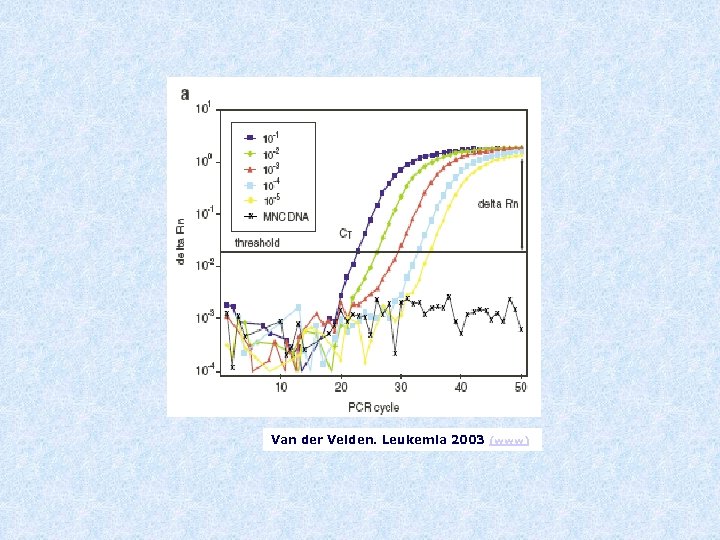 Van der Velden. Leukemia 2003 (www)
Van der Velden. Leukemia 2003 (www)
 (www)
(www)
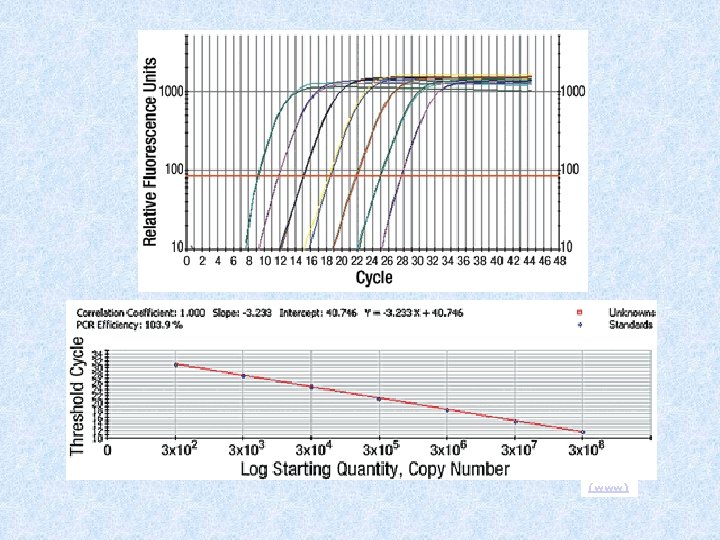 (www)
(www)
 Housekeeping gene • Knowing the amount of m. RNA in one sample from one specific gene does not tell us alot • You don´t know the total amount of m. RNA in your sample • You also dont know how much the m. RNA level has changed compared to other m. RNA levels Example: m. RNA levels increase 2 x after induction It is possable that all genexpression in the cell has increased We have to compare the expression of our gene to another gene which expression is normally constant, a housekeeping gene
Housekeeping gene • Knowing the amount of m. RNA in one sample from one specific gene does not tell us alot • You don´t know the total amount of m. RNA in your sample • You also dont know how much the m. RNA level has changed compared to other m. RNA levels Example: m. RNA levels increase 2 x after induction It is possable that all genexpression in the cell has increased We have to compare the expression of our gene to another gene which expression is normally constant, a housekeeping gene
 Multiplexing * Taq. Man: different dyes for each target (FAM, TET, VIC and JOE) * SYBR green: different melting points for each target * extensive optimisation is required * one-step PCR cannot be used
Multiplexing * Taq. Man: different dyes for each target (FAM, TET, VIC and JOE) * SYBR green: different melting points for each target * extensive optimisation is required * one-step PCR cannot be used
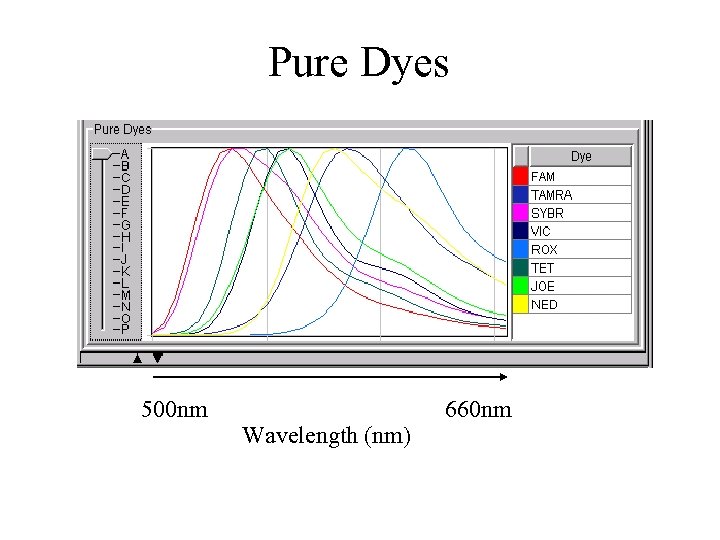 Pure Dyes 500 nm Wavelength (nm) 660 nm
Pure Dyes 500 nm Wavelength (nm) 660 nm
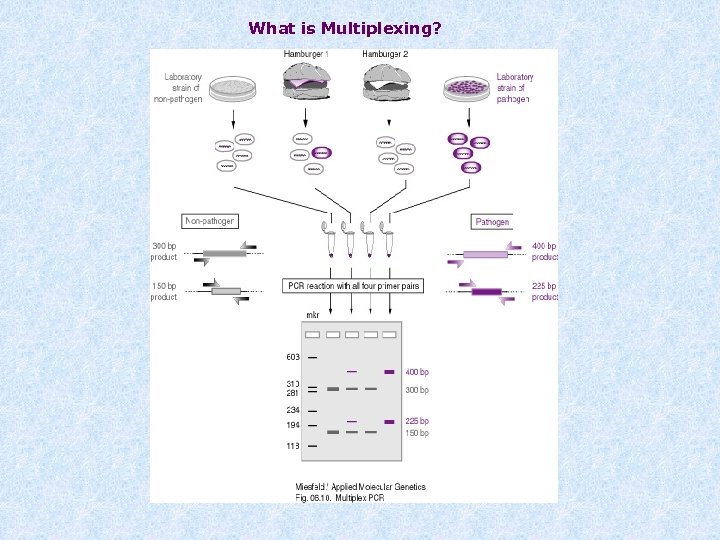 What is Multiplexing?
What is Multiplexing?
 Real-Time PCR Applications * quantitation of gene expression * drug therapy efficacy / drug monitoring * viral quantitation * pathogen detection
Real-Time PCR Applications * quantitation of gene expression * drug therapy efficacy / drug monitoring * viral quantitation * pathogen detection


