36eac80ba27080d8d82629a83089911e.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30

Real-time Monitoring with a Portable Miniaturized Surface Plasmon Resonance System Clement E. Furlong, Research Professor, Departments of Medicine (Div. Medical Genetics) & Genome Sciences University of Washington, Seattle, WA Presented by: Brian Marquardt CPAC/UW

Spreeta sensing components • Spreeta SPR components developed in collaboration with UW with TI • Miniaturized, robust, high performance devices. • Inexpensive in large quantity • Excellent manufacturing capabilities and quality control Each Spreeta chip contains all of the optical components needed for sensitive SPR measurement of biomolecular interactions

The SPIRIT system (Surface Plasmon Instrumentation for the Rapid Identification of Toxins) • Compact, lightweight (lunchbox size, 6 lb. ) • High performance • 24 simultaneous measurements • Low power (5 W) allows portable operation • Automated Current laboratory prototype
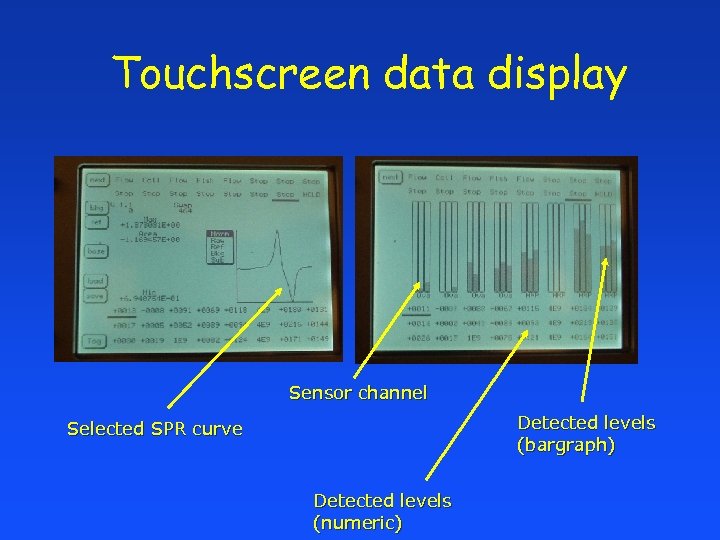
Touchscreen data display Sensor channel Detected levels (bargraph) Selected SPR curve Detected levels (numeric)

Sensor surface chemistry Each Spreeta chip has 3 useable channels Soluble protective coating Control receptors (dextran/trehalose) allows long-term dry storage at room temperature (usually antibodies) Designed NOT to respond to that agent Target receptors: (usually antibodies) Designed to capture a specific agent or analyte e. g. : • Toxins • Viruses • Spores • Bacteria YYYYY Gold layer (50 n. M) Glass substrate Spreeta sensor chip

Fundamentals of Surface Plasmon Resonance System software Sensorgram
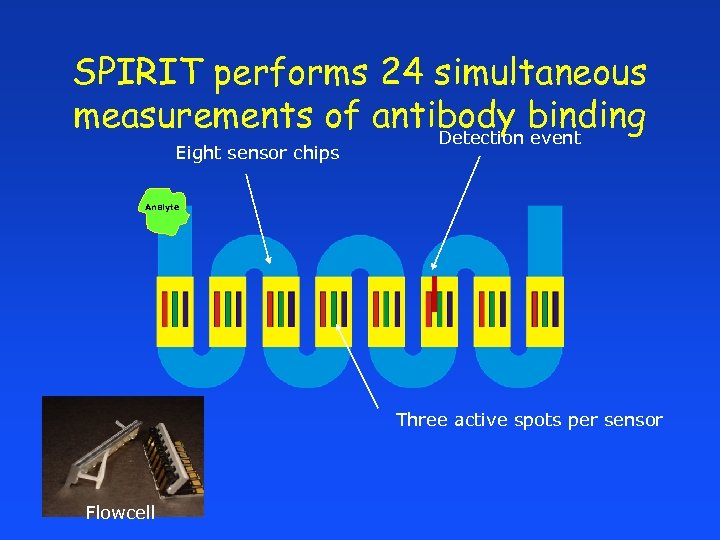
SPIRIT performs 24 simultaneous measurements of antibody binding Detection event Eight sensor chips Analyte Three active spots per sensor Flowcell

Examples of Assays Possible with SPR • Whole microbial cells -(F. tularensis, E. coli, Y. pestis) • Spores -(e. g. , anthrax) • Viruses with or without amplification -(e. g. Norwalk, flu) • Proteins by direct detection with or without amplification/verification -(protein toxins, industrial proteins, therapeutics) • Small molecular weight analytes using displacement or competition assays -(e. g. , domoic acid, cortisol, insecticides, toxic chemicals, TNT & other small organics)

Detection of Larger Analytes • Microbes • Spores • Viruses • Proteins/Toxic Proteins
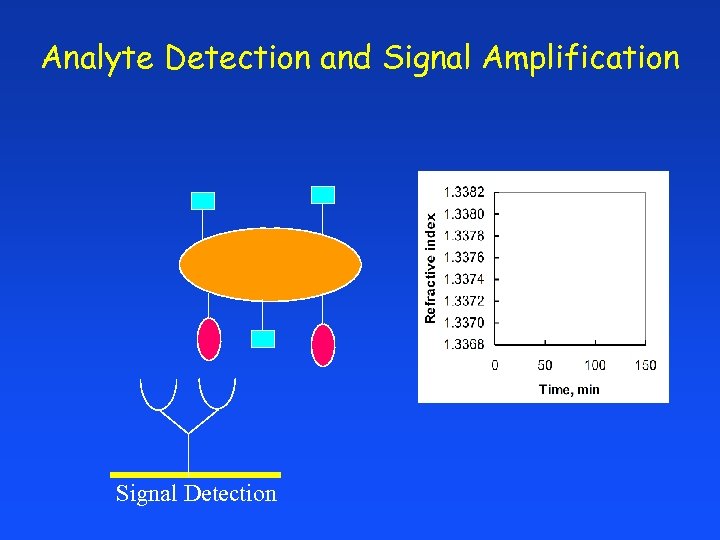
Analyte Detection and Signal Amplification Signal Detection
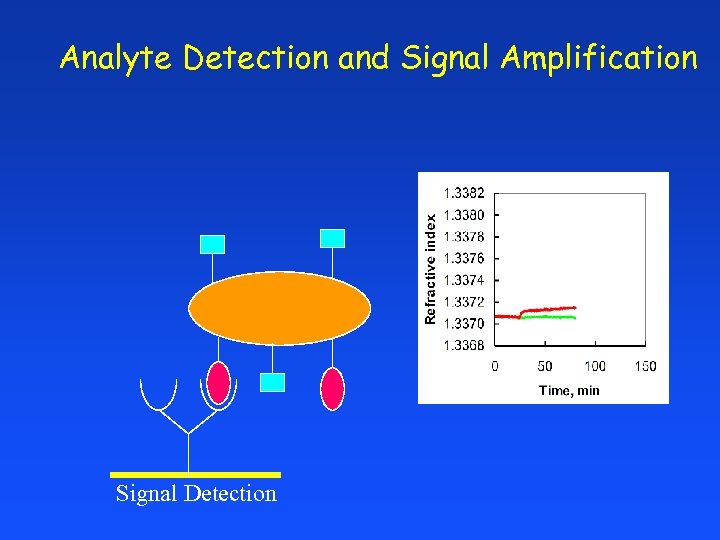
Analyte Detection and Signal Amplification Signal Detection
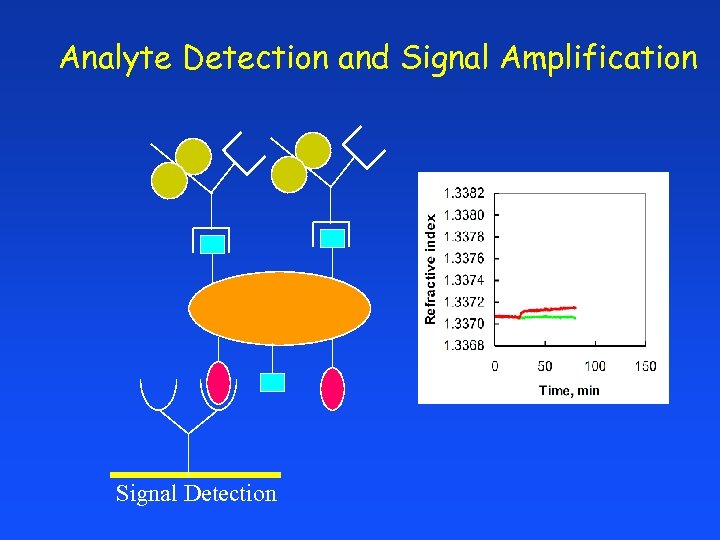
Analyte Detection and Signal Amplification Signal Detection
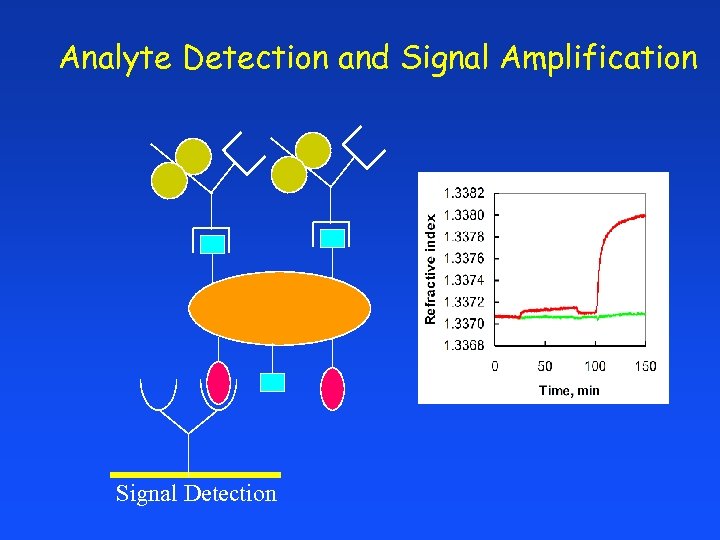
Analyte Detection and Signal Amplification Signal Detection
Detection of Microbes Amplification/verification Detection
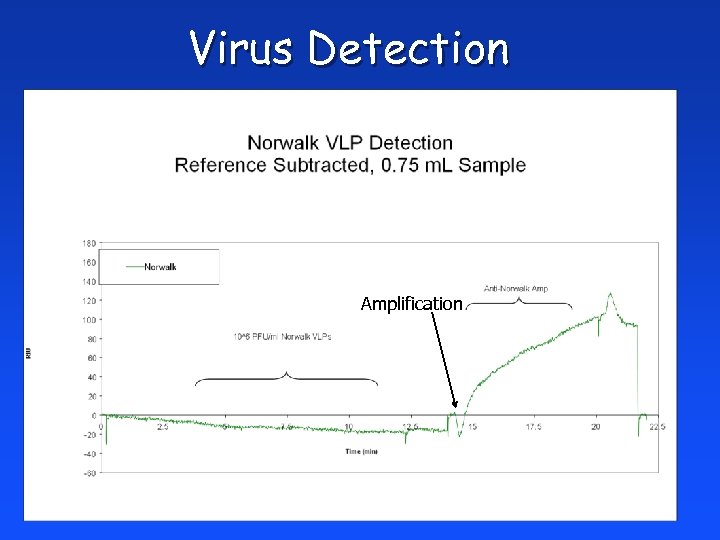
Virus Detection Amplification
Detection of Staphylococcal Enterotoxin B
Detection of 5 ng/m. L (5 ppb; 33 p. M) Bot. NT (denatured botulinum toxin)
Direct Detection of Ricin A Chain (64 ppb-320 ppb)
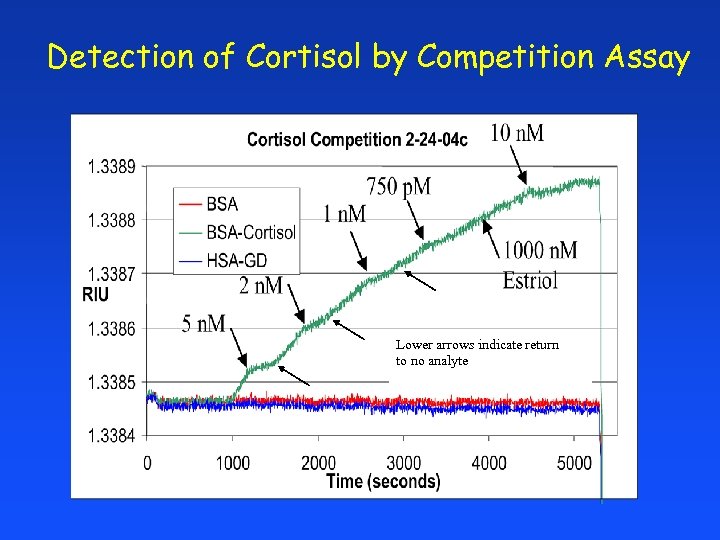
Detection of Cortisol by Competition Assay Lower arrows indicate return to no analyte
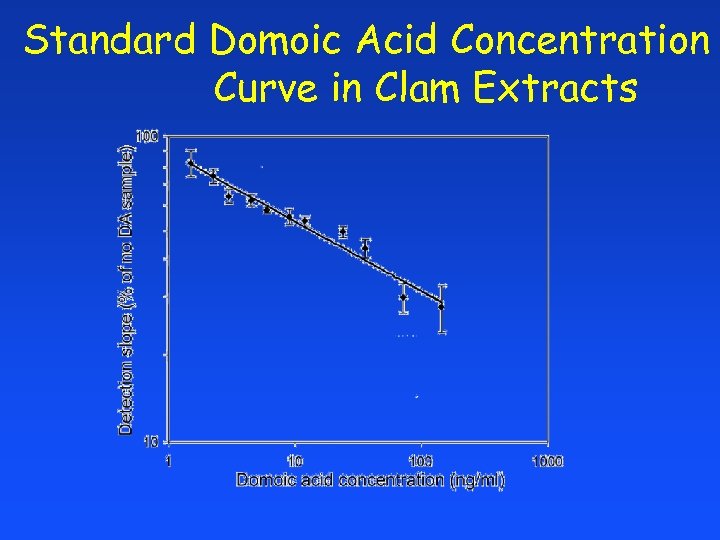
Standard Domoic Acid Concentration Curve in Clam Extracts
Other Useful Applications of SPR Sensing • Nucleic Acid Analyses • Many Other Molecular Interactions
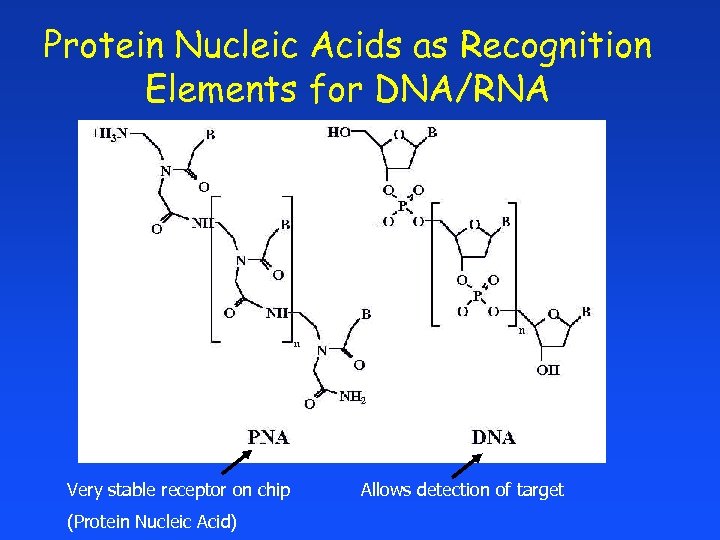
Protein Nucleic Acids as Recognition Elements for DNA/RNA Very stable receptor on chip (Protein Nucleic Acid) Allows detection of target
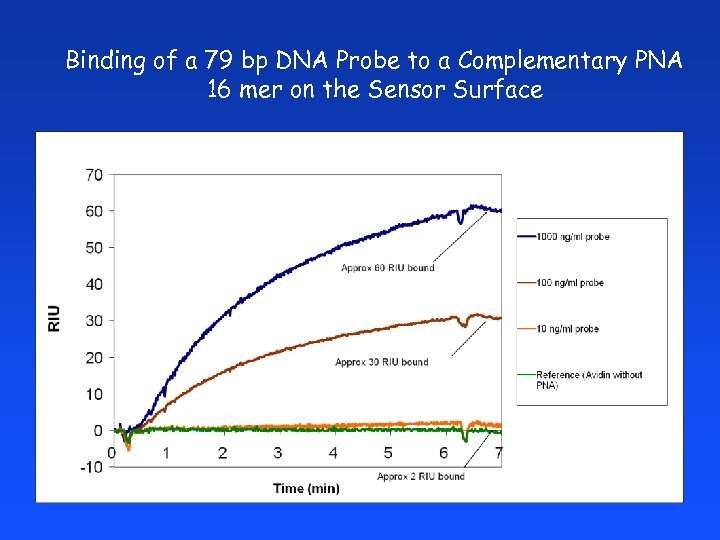
Binding of a 79 bp DNA Probe to a Complementary PNA 16 mer on the Sensor Surface

Detection of Analytes in Complex Matrices (e. g. , saliva, plasma, urine, stool extracts, sea water, fresh water, etc. )
Detection of 1 n. M (28 ppb) SEB in seawater Staphylococcal enterotoxin B
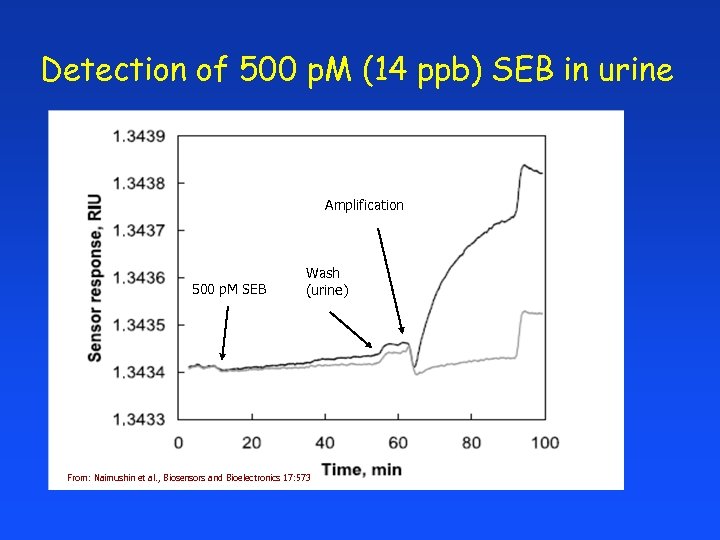
Detection of 500 p. M (14 ppb) SEB in urine Amplification 500 p. M SEB Wash (urine) From: Naimushin et al. , Biosensors and Bioelectronics 17: 573
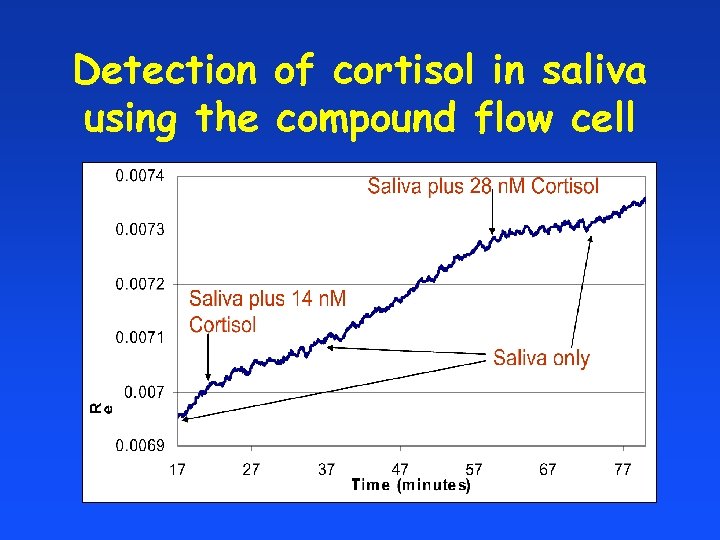
Detection of cortisol in saliva using the compound flow cell
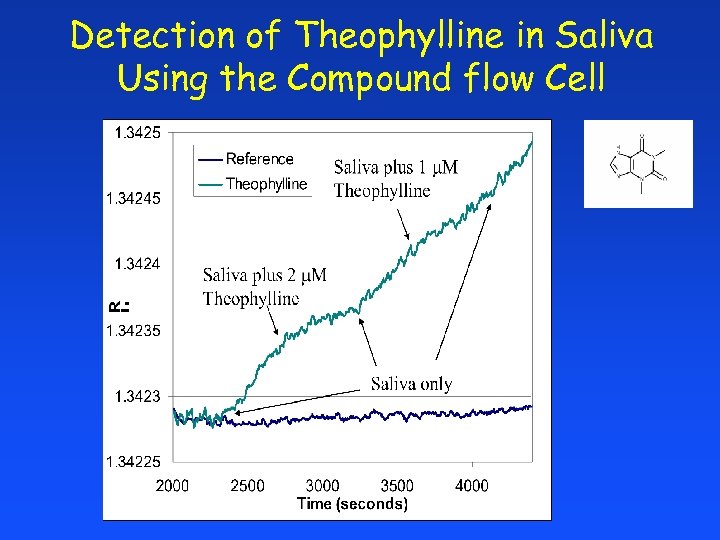
Detection of Theophylline in Saliva Using the Compound flow Cell
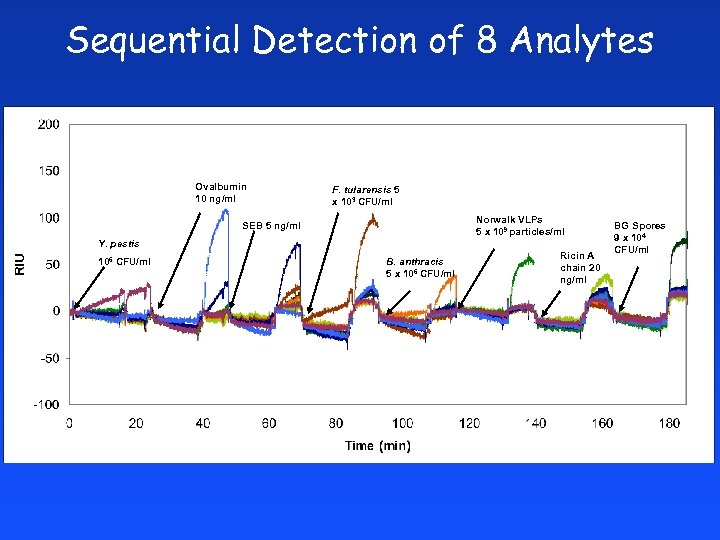
Sequential Detection of 8 Analytes Ovalbumin 10 ng/ml F. tularensis 5 x 103 CFU/ml Norwalk VLPs 5 x 109 particles/ml SEB 5 ng/ml Y. pestis 106 CFU/ml B. anthracis 5 x 106 CFU/ml Ricin A chain 20 ng/ml BG Spores 9 x 104 CFU/ml

SPIRIT Team & Sponsors • Medical Genetics Group: Dr. Clement Furlong Scott Soelberg Dr. Gary Geiss Dr. Rick Stevens Steve Near Matthew Probert Joshua Probert Nathaneal Swanson Dr. Paul Baker • • Electrical Engineering Group: Dr. Sinclair Yee Tim Chinowsky Peter Kauffman Jared Tritz Michael Grow Tony Mactutis • Texas Instruments: Jerry Elkind Dwight Bartholomew John Quinn Sponsors: DOD Texas Instruments Center for Process Analytical Chemistry (CPAC), UW, Seattle Washington State Sea Grant, NIH/NIEHS
36eac80ba27080d8d82629a83089911e.ppt