e69be34134abccd869e5b4ab090fb6ca.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 50

Real-time Data Quality for SAP Dietrich O. Banschbach Manager, R&D EMEA SAS International Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved.

Agenda § § § Overview df. Connector for SAP Scenarios Technology Additional Information Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 2

Overview: Companies § Companies involved: SAP AG - world’s largest Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) software company Data. Flux Corporation (a SAS company) a leading provider of data management solutions consisting of data quality, data profiling, data integration, data augmentation and data monitoring Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 3

Overview: SAP partnership § SAS is an SAP Software Partner with several SAP certified interfaces § Data. Flux, an SAP Software Partner in its own right, has attained SAP interface certification for its Data. Flux df. Connector for SAP product Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 4

df. Connector for SAP § Data. Flux df. Connector for SAP enhances data quality in SAP systems – in real-time § Facilitates communication between SAP applications and Data. Flux df. Intelli. Server § Offers transparent access from SAP applications to Data. Flux df. Intelli. Server services for data validation, standardization, deduplication, errortolerant search, etc. Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 5

df. Connector for SAP § Provides a remote function call (RFC) server that channels function calls from within SAP systems to df. Intelli. Server and returns results to SAP § Framework consisting of a set of Data. Flux supplied ABAP functions that map to df. Intelli. Server functions. These can be called by any SAP application. § Functions can be used to build new or extend existing data quality solutions in SAP using Data. Flux methods Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 6
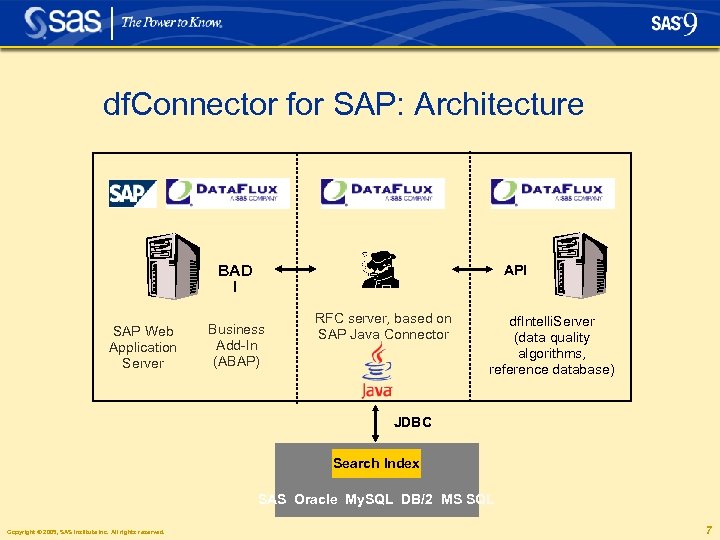
df. Connector for SAP: Architecture BAD I SAP Web Application Server API Business Add-In (ABAP) RFC server, based on SAP Java Connector df. Intelli. Server (data quality algorithms, reference database) JDBC Search Index SAS Oracle My. SQL DB/2 MS SQL Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 7
df. Connector for SAP: Framework § Function modules written in ABAP use a standard „call function destination“ to invoke a method that is not part of the current SAP system § The „call function destination“ invokes df. Connector listening at the specified destination § df. Connector gathers all parameters and initiates the appropriate call into df. Intelli. Server using its Java client API Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 8
df. Connector for SAP: Postal Address Validation § ABAP programmers can use the framework functions in any SAP application § As an example application that uses this framework, df. Connector for SAP supports postal address validation as defined in SAP’s BC-BASPV certification scenario. § Enhances SAP’s Business Address Services (formerly Central Address Management) § df. Connector is “Certified for SAP Net. Weaver”. Formally tested with R/3 Enterprise (4. 7) Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 9
df. Connector for SAP: Postal Address Validation § Customer, vendor and other addresses in SAP are checked in real-time for correct city names, street names, house numbers and zip codes § Missing information is auto completed from a reference database § Quarterly adjustment process keeps addresses up to date via a batch-run − Reports which addresses are correct and which ones could not be validated (stating the reason) − Process can be used to do initial validation of all addresses in SAP Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 10

df. Connector for SAP: Deduplication § In addition to postal address validation, a duplicate check is carried out before a new entry can be saved in SAP § Avoids multiple entries of the same customer or vendor name with slight differences in spelling § Offers error tolerant (fuzzy) search Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 11

Scenarios: Postal Address Validation § This scenario enhances data quality within SAP in real-time as address data is entered interactively § Addresses are checked for correct: − city names − street names − house numbers − zip codes § Input is standardized according to postal authority requirements (e. g. USPS rules) § Missing information can be auto completed Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 12

Scenario 1: Create new customer § Create new customer in SAPGUI using standard SAP transaction XD 01 § Fill in data: • • Company name City Country (No street) Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 13
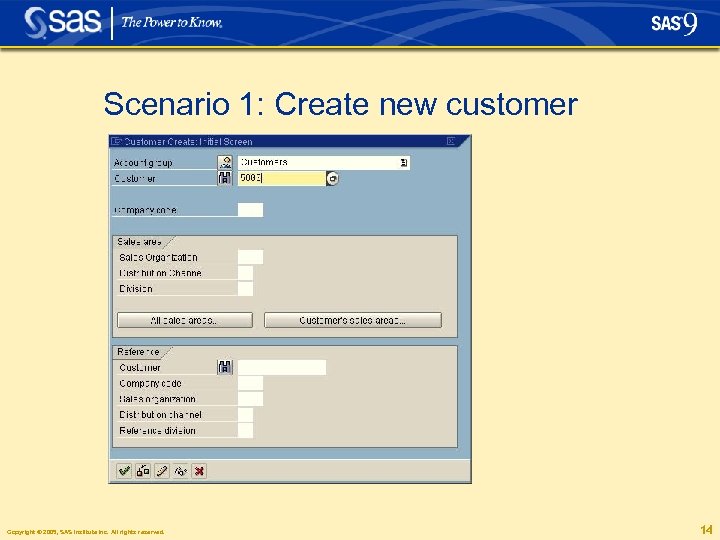
Scenario 1: Create new customer Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 14
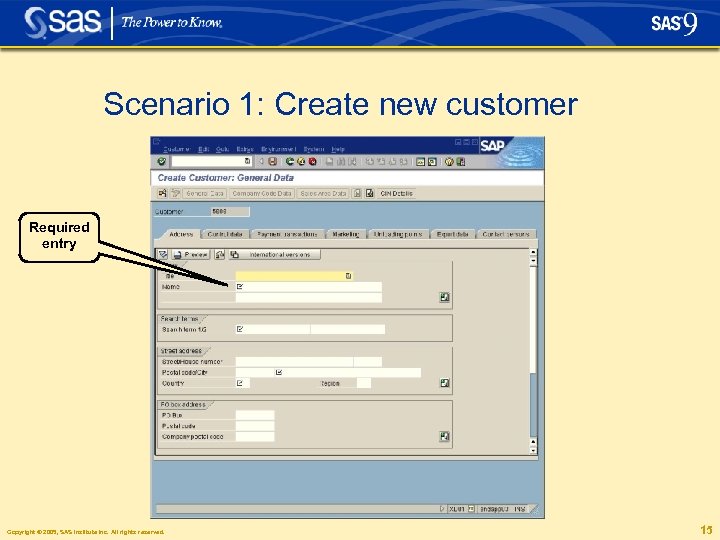
Scenario 1: Create new customer Required entry Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 15
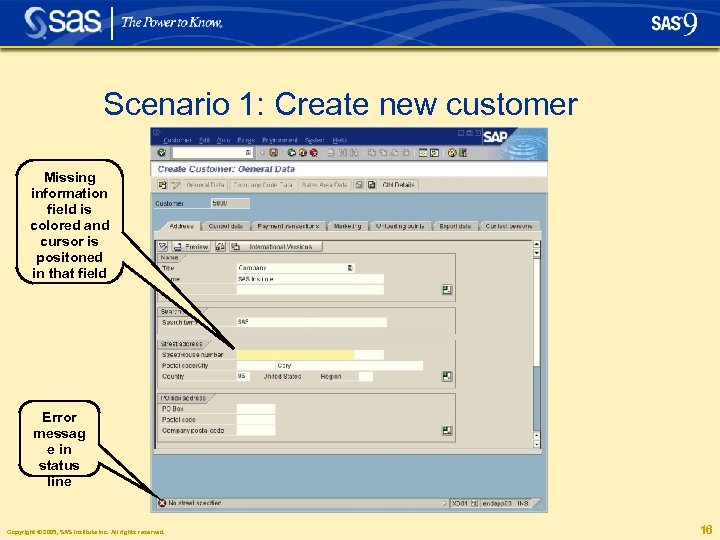
Scenario 1: Create new customer Missing information field is colored and cursor is positoned in that field Error messag e in status line Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 16
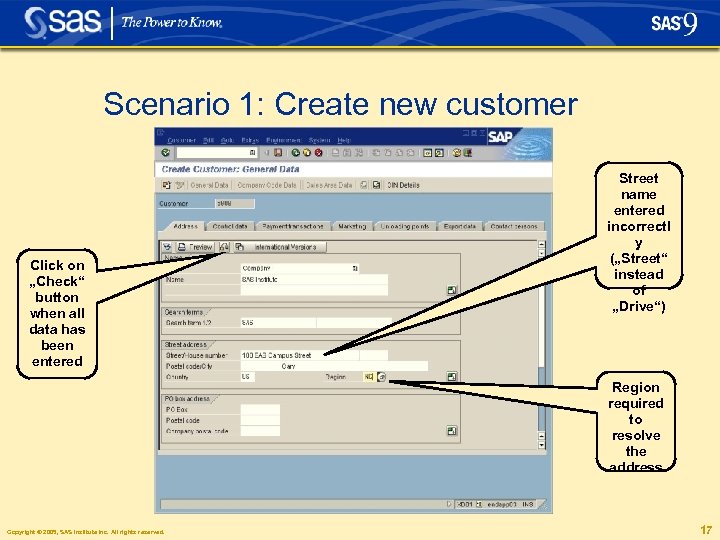
Scenario 1: Create new customer Click on „Check“ button when all data has been entered Street name entered incorrectl y („Street“ instead of „Drive“) Region required to resolve the address Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 17

Scenario 1: Create new customer § Address is validated by df. Intelli. Server • • City name converted to uppercase Postal code (Zi. P) added Street name uppercased and standardized (DR=Drive) District added automatically Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 18

Scenario 2: Creating a customer with minimal data entry § Data entered in SAP: • Part of a street name with a spelling mistake • Postal code • Country (required by SAP) Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 19
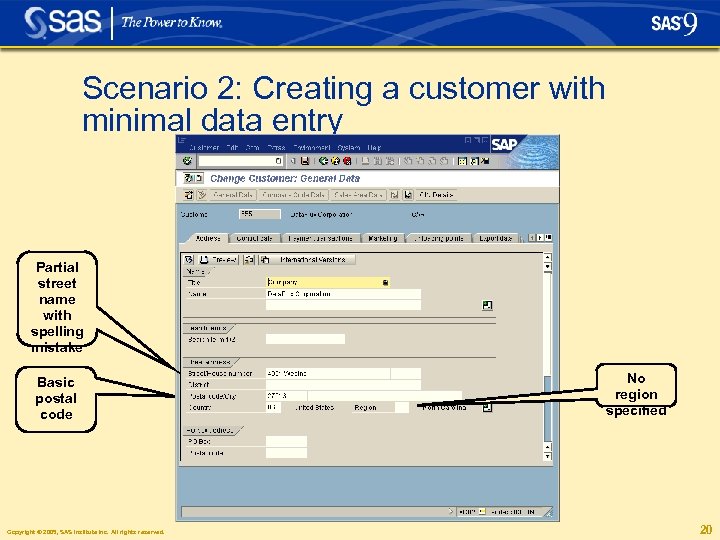
Scenario 2: Creating a customer with minimal data entry Partial street name with spelling mistake Basic postal code Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. No region specified 20
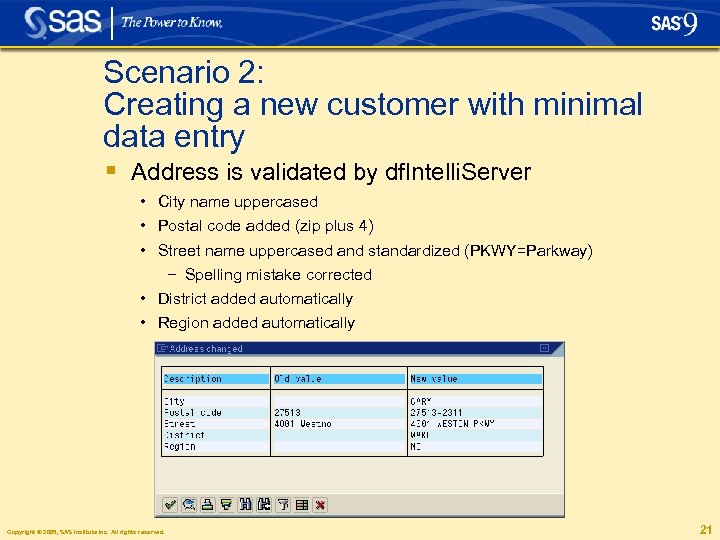
Scenario 2: Creating a new customer with minimal data entry § Address is validated by df. Intelli. Server • City name uppercased • Postal code added (zip plus 4) • Street name uppercased and standardized (PKWY=Parkway) − Spelling mistake corrected • District added automatically • Region added automatically Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 21

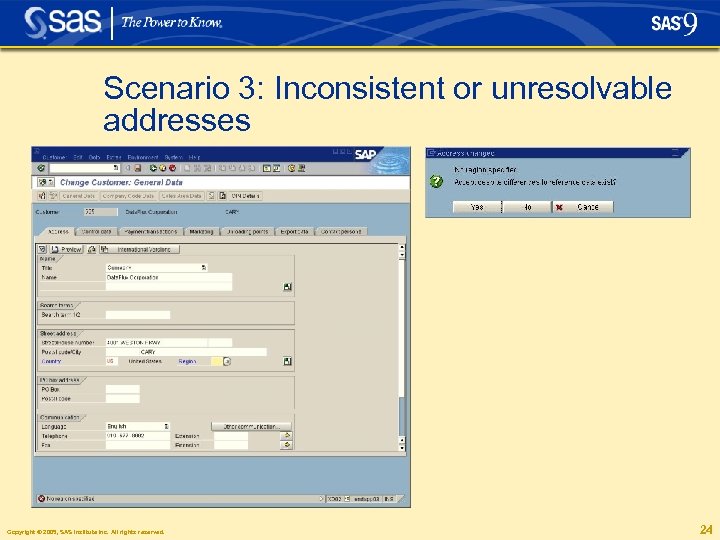
Scenario 3: Inconsistent or unresolvable addresses § Neither post code nor city are specified § User insists on saving a record even though the entry could not be validated § To ensure high availability of the SAP system, address data can still be entered and saved if df. Connector and/or df. Intelli. Server are temporarily unavailable. Entries are marked as not having been checked against official address reference data. Those addresses can be corrected in the df. Connector Quarterly Address Adjustment process which checks and updates in batch mode Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 22
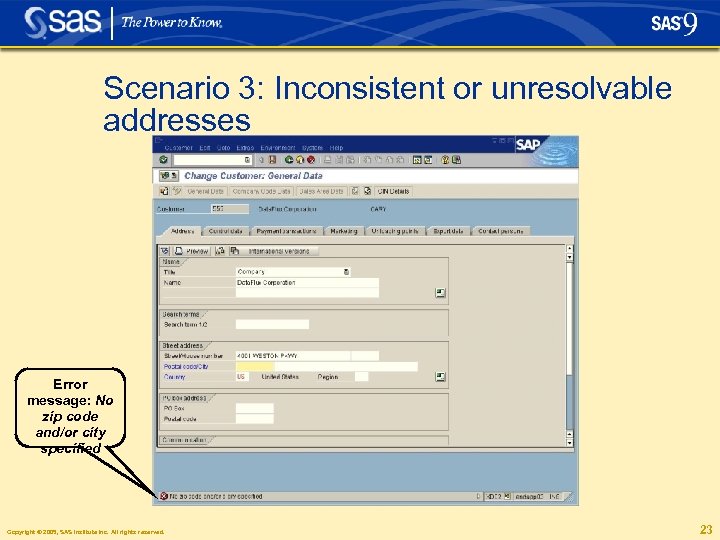
Scenario 3: Inconsistent or unresolvable addresses Error message: No zip code and/or city specified Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 23
Scenario 3: Inconsistent or unresolvable addresses Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 24

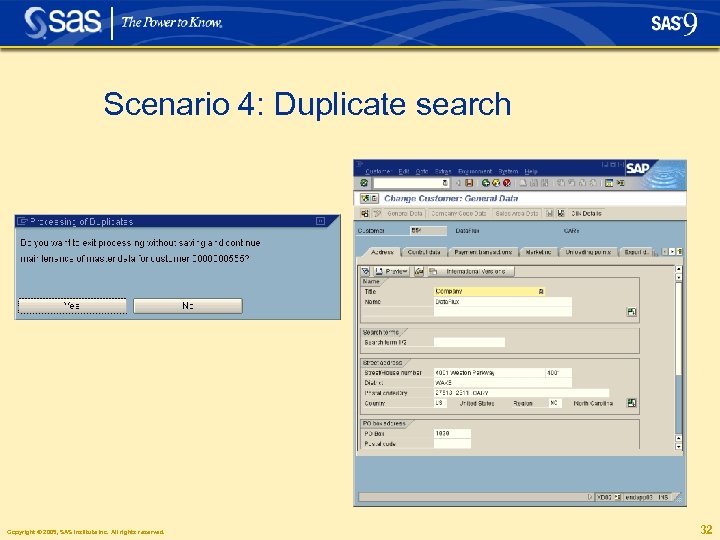
Scenario 4: Duplicate search § The following scenario shows the duplicate search and elimination capabilities of Data. Flux df. Connector for SAP § The scenario first shows how easy it is (caused by a small typo) to create a duplicate customer record in the SAP database without df. Connector § In comparison, the same process is performed using df. Connector for SAP to identify potential duplicates and resolve the situation Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 25
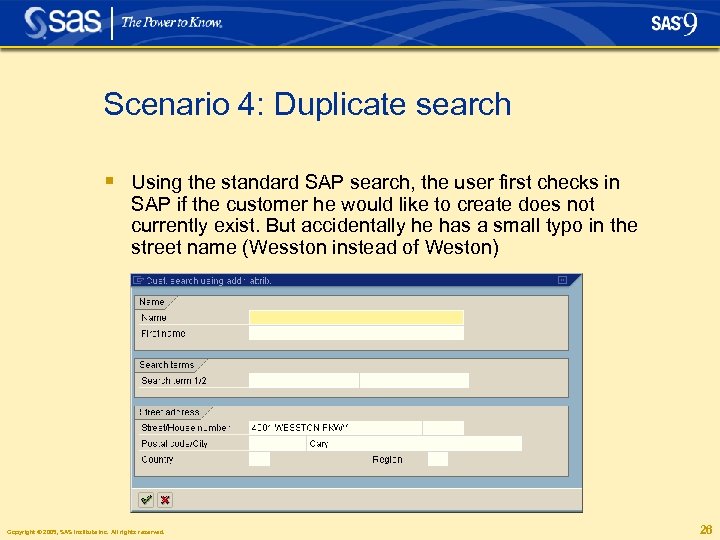
Scenario 4: Duplicate search § Using the standard SAP search, the user first checks in SAP if the customer he would like to create does not currently exist. But accidentally he has a small typo in the street name (Wesston instead of Weston) Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 26

Scenario 4: Duplicate search § The search returns no hits and the user proceeds under the assumption he can now create a unique customer § He creates and saves a new customer entry, thus creating a duplicate Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 27
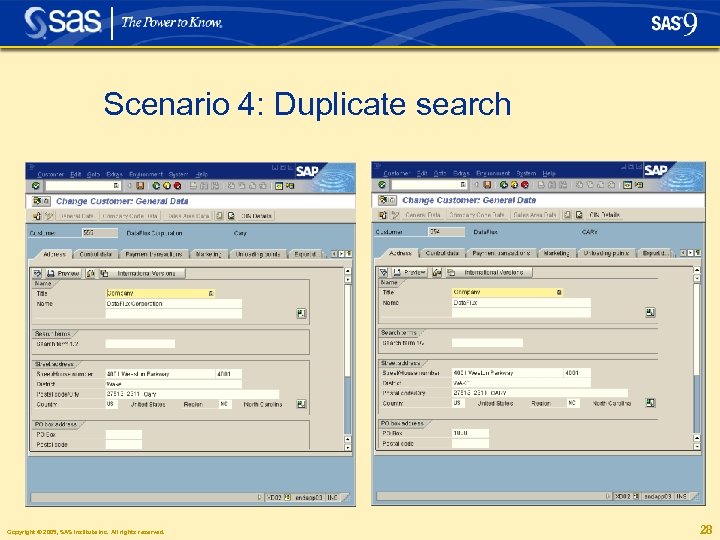
Scenario 4: Duplicate search Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 28
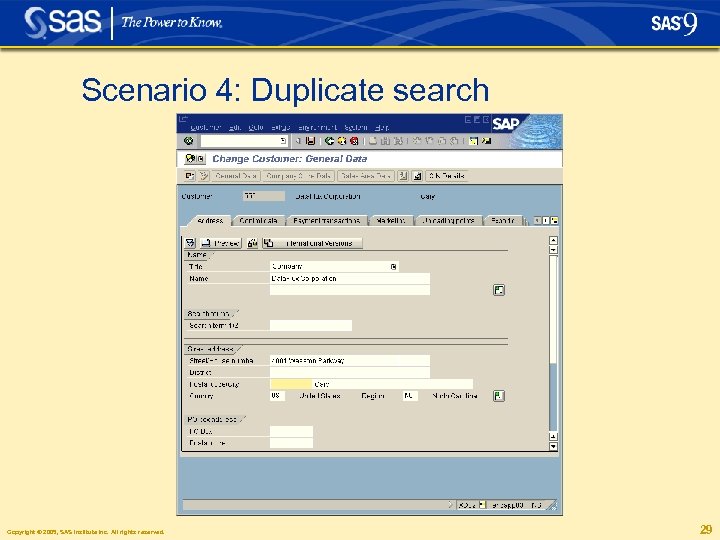
Scenario 4: Duplicate search Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 29
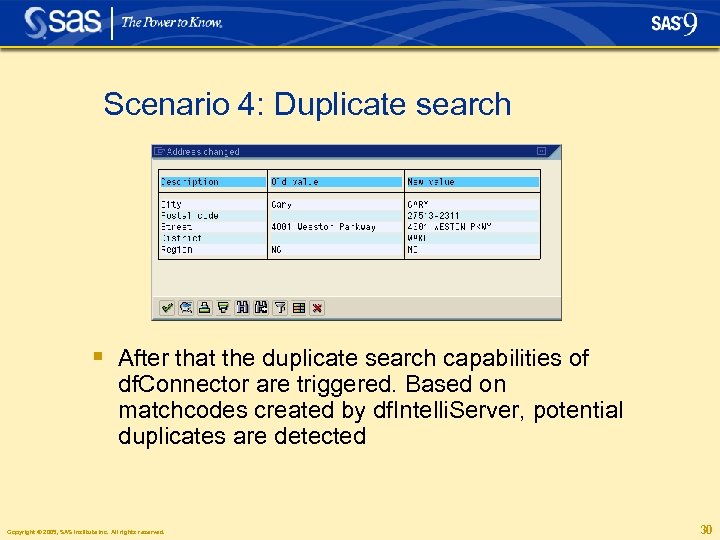
Scenario 4: Duplicate search § After that the duplicate search capabilities of df. Connector are triggered. Based on matchcodes created by df. Intelli. Server, potential duplicates are detected Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 30
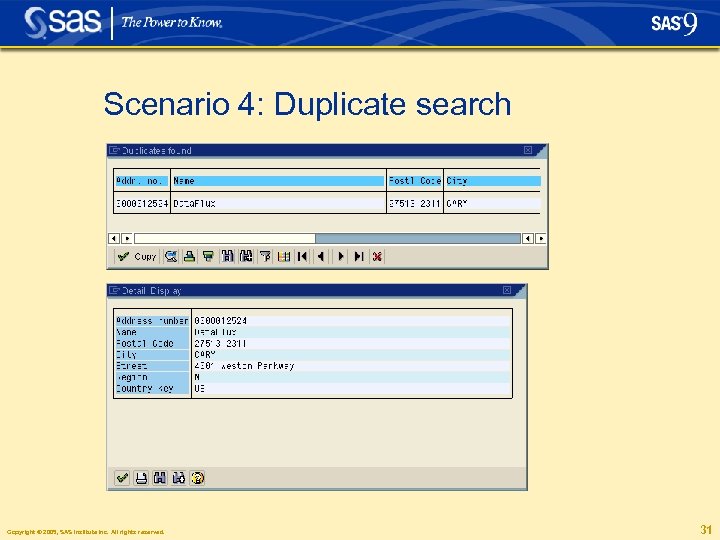
Scenario 4: Duplicate search Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 31
Scenario 4: Duplicate search Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 32
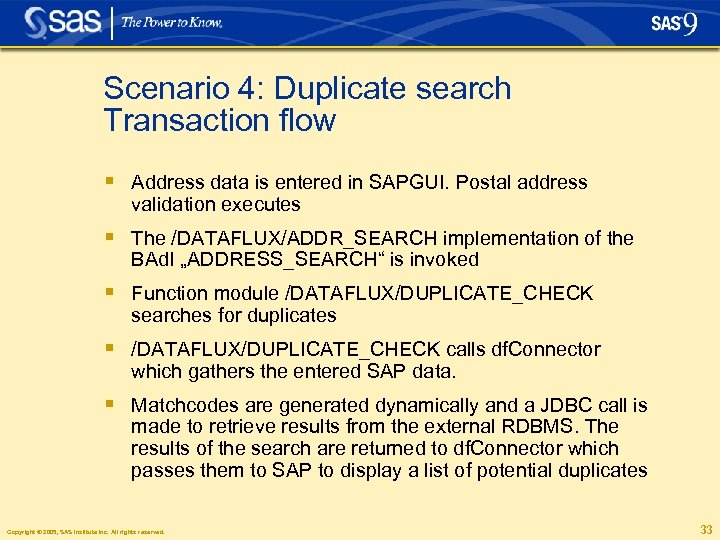
Scenario 4: Duplicate search Transaction flow § Address data is entered in SAPGUI. Postal address validation executes § The /DATAFLUX/ADDR_SEARCH implementation of the BAd. I „ADDRESS_SEARCH“ is invoked § Function module /DATAFLUX/DUPLICATE_CHECK searches for duplicates § /DATAFLUX/DUPLICATE_CHECK calls df. Connector which gathers the entered SAP data. § Matchcodes are generated dynamically and a JDBC call is made to retrieve results from the external RDBMS. The results of the search are returned to df. Connector which passes them to SAP to display a list of potential duplicates Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 33

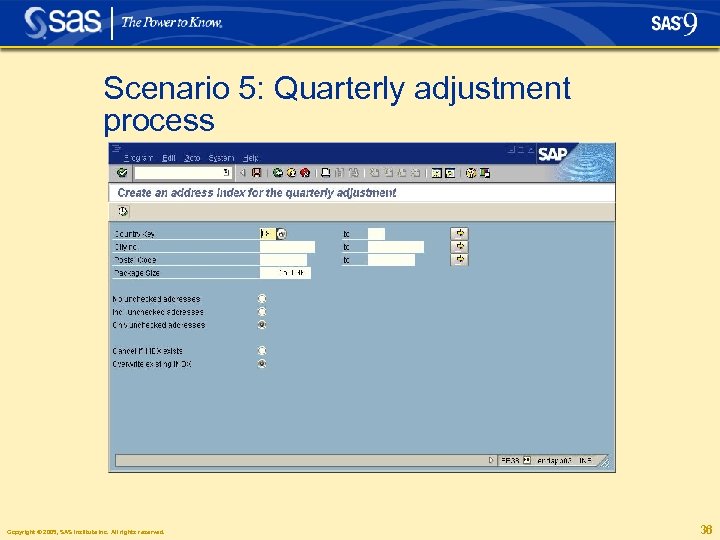
Scenario 5: Quarterly adjustment process § Quarterly Adjustment is a batch process that ensures address data stays up to date § If new address data are available e. g. from USPS, this can be activated in the system in three steps by running: • SAP report to get all addresses • Data. Flux provided report to check, standardize and auto complete addresses • SAP report to write the updated addresses back to the SAP database Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 34

Scenario 5: Quarterly adjustment process § RSADRQU 1 report scans all addresses for a certain country and inserts them into an index table § /DATAFLUX/RSADRQU 2 reads all SAP addresses from index table and validates each address. Addresses are checked, auto completed and standardized. If an address cannot be validated it is flagged for later reporting purposes. Indicates the level of address quality, i. e. how many addresses are correct and how many are incorrect § RSADRQU 3 writes back validated and corrected addresses to the operational SAP database. Alternatively reports reason for not being able to write them back Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 35
Scenario 5: Quarterly adjustment process Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 36
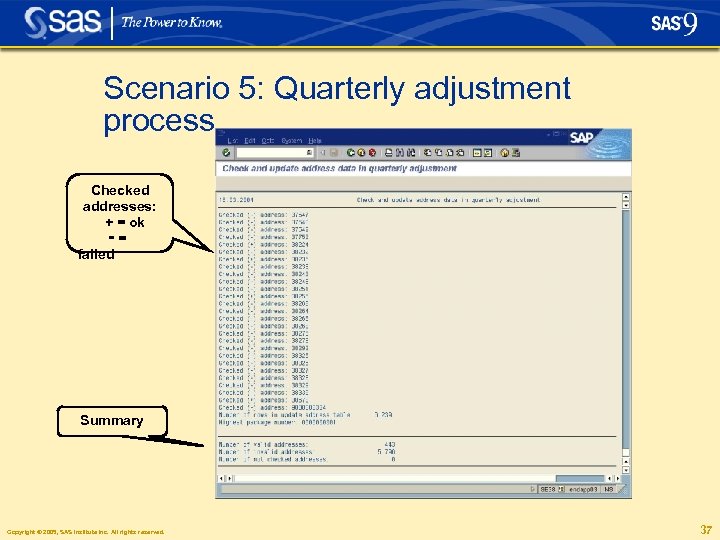
Scenario 5: Quarterly adjustment process Checked addresses: + = ok -= failed Summary Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 37
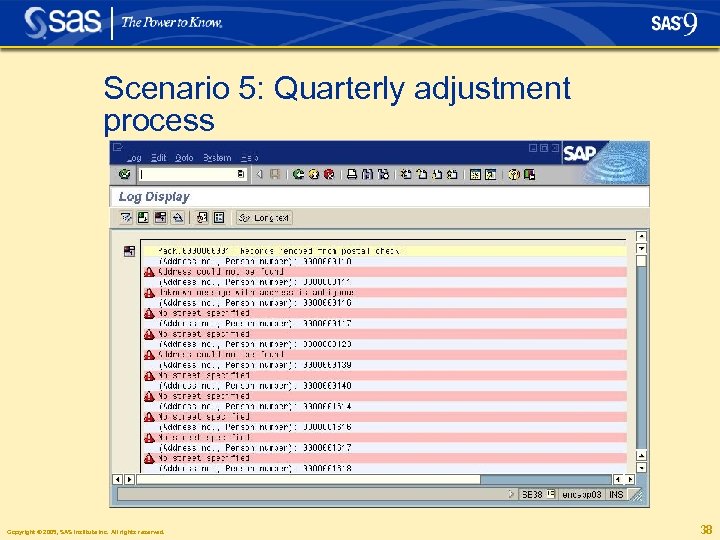
Scenario 5: Quarterly adjustment process Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 38

Technology § Java 1. 4. x/1. 5 to interface SAP with the Dataflux df. Intelli. Server 6 using SAP Java Connector 2. 1. 3 § ABAP programming to hook into the predefined interfaces (SAP Business Add-In) for address validation and deduplication § SAP Add-on Assembly Kit (AAK) to allow for SAP certification (e. g. Name spaces, installation, deployment, upgrade etc. ) § Search index creation in SAS data sets or in any external JDBC-compliant RDBMS Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 39

Technology: df. Connector Framework Functions § /DATAFLUX/AREA_CODE § § § § § /DATAFLUX/DETERMINE_GENDER /DATAFLUX/DETERMINE_LOCALE /DATAFLUX/DETERMINE_ENTITY /DATAFLUX/DIRECTORY_SEARCH /DATAFLUX/DUPLICATE_CHECK /DATAFLUX/GENERATE_MATCHCODE /DATAFLUX/GEN_MATCHCODE_PARSED /DATAFLUX/GEOCODE /DATAFLUX/LOOKUP_COUNTY /DATAFLUX/LOOKUP_PHONE /DATAFLUX/PARSE /DATAFLUX/QUERY_SERVER /DATAFLUX/STANDARDIZE_PARSED /DATAFLUX/STANDARDIZE_SCHEME /DATAFLUX/DELETE_INDEX_ENTRY /DATAFLUX/VERIFY_ADDRESS /DATAFLUX/MAINTAIN_INDEX_ENTRY Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 40
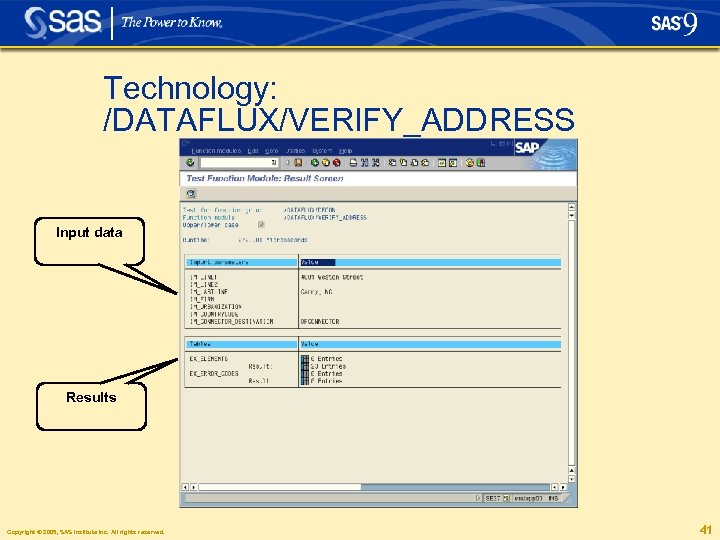
Technology: /DATAFLUX/VERIFY_ADDRESS Input data Results Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 41
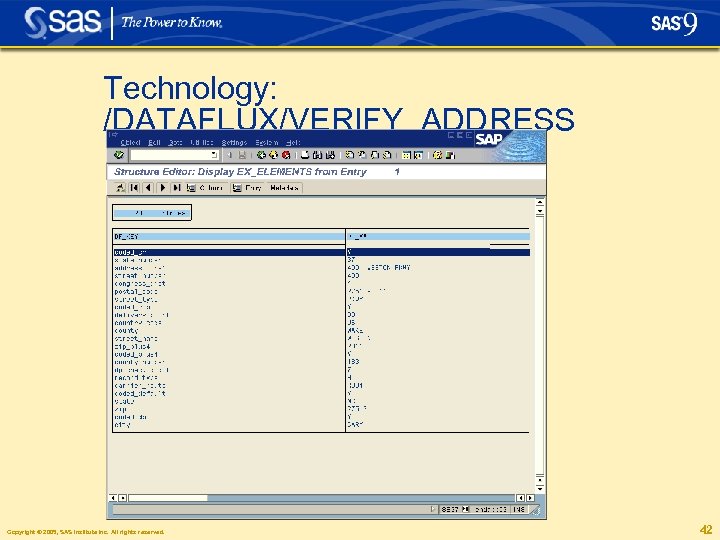
Technology: /DATAFLUX/VERIFY_ADDRESS Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 42

Technology: External Search Index § The external search index can be stored in an arbitrary RDBMS that supports the JDBC interface § Examples: • • • SAS data sets My. SQL Microsoft SQL Server Max. DB (formerly known as SAP DB) Oracle. . . Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 43
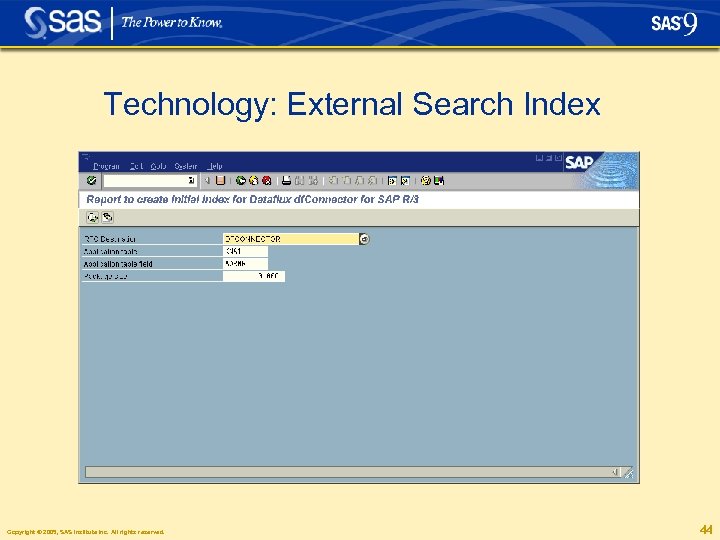
Technology: External Search Index Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 44
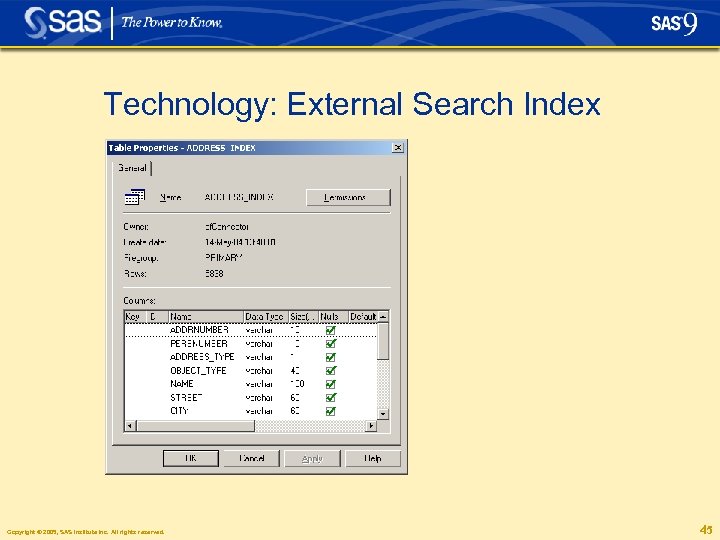
Technology: External Search Index Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 45
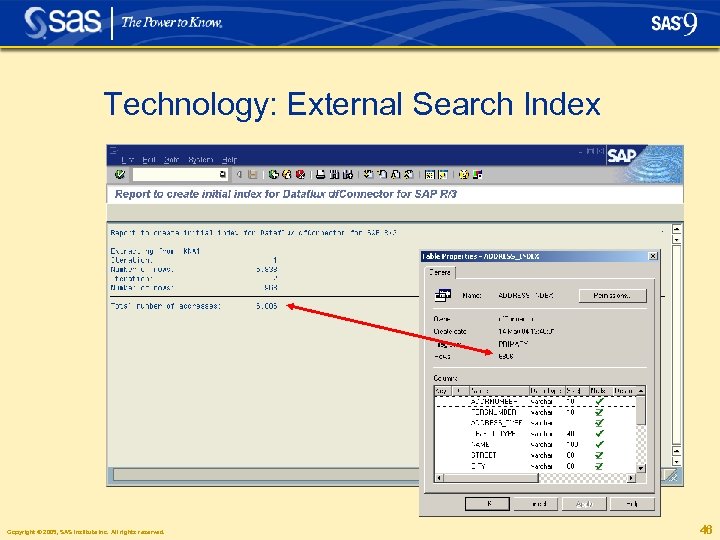
Technology: External Search Index Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 46
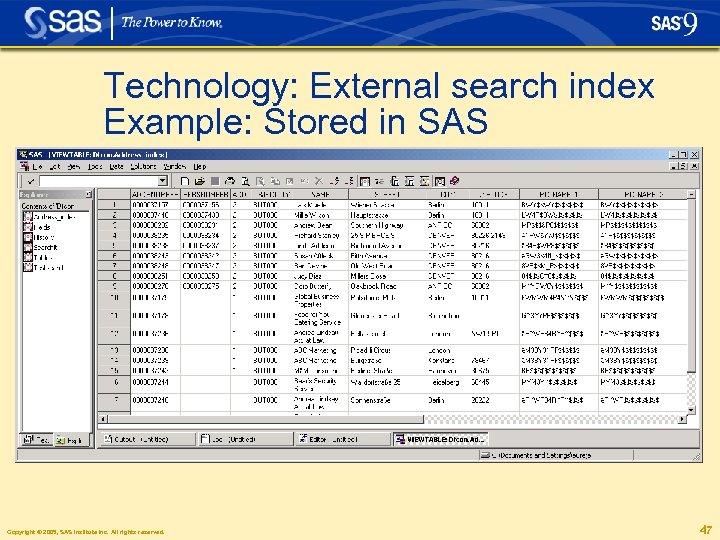
Technology: External search index Example: Stored in SAS Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 47
Technology: RFC server platforms § SAP supported Java Connector „JCo“ platforms (used by RFC server component of df. Connector): • • Windows NT SP 4 or later, Win 2000, XP, Win 2003 Server Sun Solaris/SPARC 8 or later IBM AIX 4. 3 or later HP-UX 11. 0 or later (PA_RISC processors, only) OS/400 V 5 R 1 or later (not for SAP JCo 2. 0. 5) COMPAQ Tru 64 5. 0 or later (not for SAP JCo 2. 1. x) Z/Linux on S/390 (Linux / Z-series GLIBC 2. 2. 4 or later) Linux Kernel 2. 2. 14 or later (Intel compatible processors) Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 48

Additional Information § SUGI Birds-of-a-Feather (Bo. F) session “Enhancing SAP with SAS”, room 107, Tuesday at 6 p. m. § www. dataflux. com Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 49

Copyright © 2005, SAS Institute Inc. All rights reserved. 50
e69be34134abccd869e5b4ab090fb6ca.ppt