1d830e00f3feb101ad6f4c0f1a34cfa7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 18
 Readmission as a mechanism of general return management process history, statistics and practices, forms of agreements, main components 1
Readmission as a mechanism of general return management process history, statistics and practices, forms of agreements, main components 1
 Readmission • What is readmission? • History of development of readmission agreements • Readmission as a tool for responding to irregular migration • Readmission and international migration law • Readmission agreements: content, features, main provisions • Different readmission approaches and future prospects 2
Readmission • What is readmission? • History of development of readmission agreements • Readmission as a tool for responding to irregular migration • Readmission and international migration law • Readmission agreements: content, features, main provisions • Different readmission approaches and future prospects 2
 What is Readmission? Readmission — act by a State accepting the re-entry of an individual (own national or third-country national), who has been found illegally entering or being present in another State. Readmission agreement – agreement which addresses procedures for one State to return aliens in an irregular situation to their home State or a State through which they passed en route to the State which seeks to return them. IOM Glossary 3
What is Readmission? Readmission — act by a State accepting the re-entry of an individual (own national or third-country national), who has been found illegally entering or being present in another State. Readmission agreement – agreement which addresses procedures for one State to return aliens in an irregular situation to their home State or a State through which they passed en route to the State which seeks to return them. IOM Glossary 3
 Readmission - purpose • *“To establish… rapid and effective procedures for the identification and return of persons who do not, or no longer, fulfill the conditions for entry to, presence in, or residence on a territory” – EC and Russian Federation, 2006 • “To facilitate readmission of persons in an irregular situation in the spirit of cooperation on the basis of reciprocity” – Spain and Romania, 1996¨ • “To establish the basis which permits ordinary and safe return of the migrants apprehended in the territory of the contracting party” – El Salvador and Mexico, 2005 4
Readmission - purpose • *“To establish… rapid and effective procedures for the identification and return of persons who do not, or no longer, fulfill the conditions for entry to, presence in, or residence on a territory” – EC and Russian Federation, 2006 • “To facilitate readmission of persons in an irregular situation in the spirit of cooperation on the basis of reciprocity” – Spain and Romania, 1996¨ • “To establish the basis which permits ordinary and safe return of the migrants apprehended in the territory of the contracting party” – El Salvador and Mexico, 2005 4
 History of Development of Readmission Agreements • First readmission agreements – 1950 s – Neighbouring countries regulating borders post WW 2 – different context – different aims of agreements • 1990 s – 2000 s – second wave of readmission agreements – move towards cooperation (eg migration and development) 5
History of Development of Readmission Agreements • First readmission agreements – 1950 s – Neighbouring countries regulating borders post WW 2 – different context – different aims of agreements • 1990 s – 2000 s – second wave of readmission agreements – move towards cooperation (eg migration and development) 5
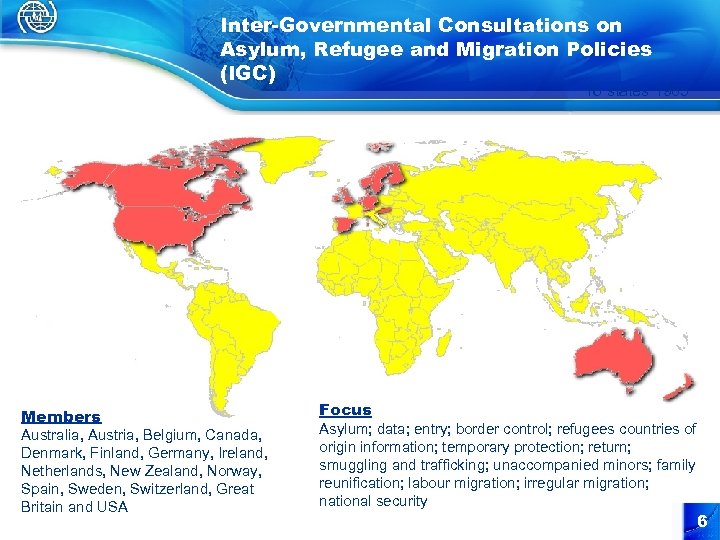 Inter-Governmental Consultations on Asylum, Refugee and Migration Policies (IGC) 16 states 1985 Members Australia, Austria, Belgium, Canada, Denmark, Finland, Germany, Ireland, Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Great Britain and USA Focus Asylum; data; entry; border control; refugees countries of origin information; temporary protection; return; smuggling and trafficking; unaccompanied minors; family reunification; labour migration; irregular migration; national security 6
Inter-Governmental Consultations on Asylum, Refugee and Migration Policies (IGC) 16 states 1985 Members Australia, Austria, Belgium, Canada, Denmark, Finland, Germany, Ireland, Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, Great Britain and USA Focus Asylum; data; entry; border control; refugees countries of origin information; temporary protection; return; smuggling and trafficking; unaccompanied minors; family reunification; labour migration; irregular migration; national security 6
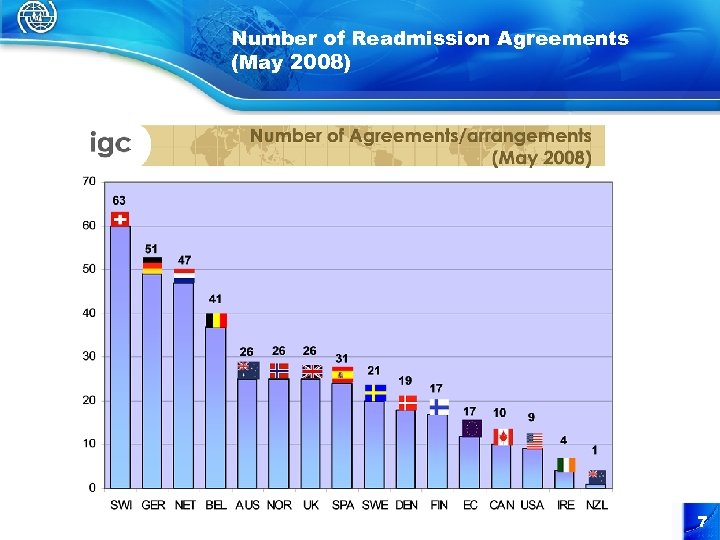 Number of Readmission Agreements (May 2008) 7
Number of Readmission Agreements (May 2008) 7
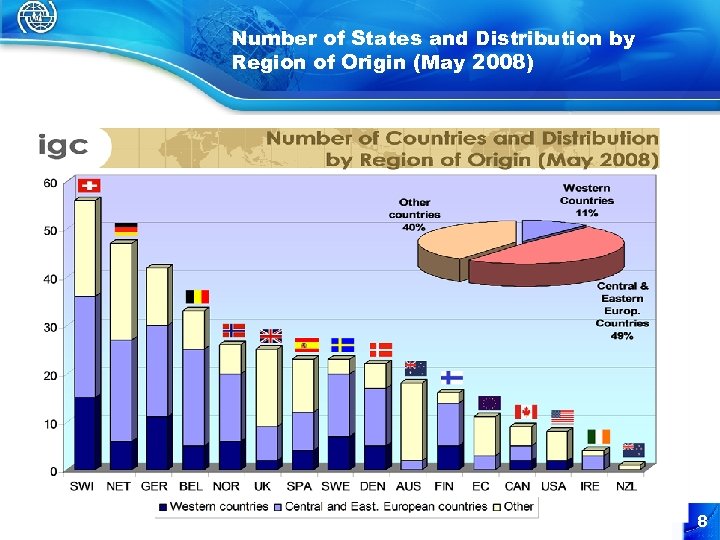 Number of States and Distribution by Region of Origin (May 2008) 8
Number of States and Distribution by Region of Origin (May 2008) 8
 Readmission and International Migration Law • Different approaches to the issue of obligation of states to accept their citizens. • No one can be arbitrary deprived of the right to enter his own country, art. 12 of ICCPR • In relation to non-citizens, there is no international obligation of states to allow entry to their territory 9
Readmission and International Migration Law • Different approaches to the issue of obligation of states to accept their citizens. • No one can be arbitrary deprived of the right to enter his own country, art. 12 of ICCPR • In relation to non-citizens, there is no international obligation of states to allow entry to their territory 9
 Readmission Agreements • Forms of readmission agreements: - Official - Readmission provisions included in other agreements • Types: – Bilateral – Multilateral • Categories of persons agreements applies to: – Own citizens – Third country nationals – Stateless persons 10
Readmission Agreements • Forms of readmission agreements: - Official - Readmission provisions included in other agreements • Types: – Bilateral – Multilateral • Categories of persons agreements applies to: – Own citizens – Third country nationals – Stateless persons 10
 Readmission Agreements: Content, Features, Main Provisions • Definition and incidence of readmission agreement: for example, readmission of only own citizens or including third country nationals who have transited through the territory • Procedures of identification / confirmation of citizenship of returnee: presumption of citizenship, establishing of the list of documents for identification of citizenship (driving license, extracts from documents, evidences, witness statements) • Issuing of travel documents: travel documents are issued either by the accepting state, or other state in accordance with the agreement 11
Readmission Agreements: Content, Features, Main Provisions • Definition and incidence of readmission agreement: for example, readmission of only own citizens or including third country nationals who have transited through the territory • Procedures of identification / confirmation of citizenship of returnee: presumption of citizenship, establishing of the list of documents for identification of citizenship (driving license, extracts from documents, evidences, witness statements) • Issuing of travel documents: travel documents are issued either by the accepting state, or other state in accordance with the agreement 11
 Readmission Agreements: Content, Features, Main Provisions • Defining the standard readmission procedures: submission of requests, replies, forms of requests • Time frames for submission / proceeding of readmission requests • Costs of parties on readmission • Rules for protection of private data • Conditions for determining need for escort • Institutions responsible for implementation • Obligation to admit those outlined in the agreement 12
Readmission Agreements: Content, Features, Main Provisions • Defining the standard readmission procedures: submission of requests, replies, forms of requests • Time frames for submission / proceeding of readmission requests • Costs of parties on readmission • Rules for protection of private data • Conditions for determining need for escort • Institutions responsible for implementation • Obligation to admit those outlined in the agreement 12
 Evidence of nationality • Passport • ID card (actual/provisional) • Any kind of document issued by the competent national authorities which have requirements for identification of the person • Documents of consular registration • Birth certificate • Statements by officials 13
Evidence of nationality • Passport • ID card (actual/provisional) • Any kind of document issued by the competent national authorities which have requirements for identification of the person • Documents of consular registration • Birth certificate • Statements by officials 13
 Presumed nationality • Expired documents listed as proof of nationality • Copies of documents listed as proof of nationality • Driving licenses/copies thereof • Testimonies of witnesses • Language tests • An extract from register officials NB: some agms do not provide an exhaustive list; other “proof” may also be used. 14
Presumed nationality • Expired documents listed as proof of nationality • Copies of documents listed as proof of nationality • Driving licenses/copies thereof • Testimonies of witnesses • Language tests • An extract from register officials NB: some agms do not provide an exhaustive list; other “proof” may also be used. 14
 Entry/presumed entry: 3 CNs • Valid visa issued by requested state • Entry stamp of requested state • States of border guards who can prove crossing of border • Air/other tickets with name of passenger & route • List of travelers • Documents/bills 15
Entry/presumed entry: 3 CNs • Valid visa issued by requested state • Entry stamp of requested state • States of border guards who can prove crossing of border • Air/other tickets with name of passenger & route • List of travelers • Documents/bills 15
 Obligations on requesting state • Prove grounds for readmission • Liaise with the competent authorities re travel documents • Submit request/supporting documentation to receiving authorities • Notify time of arrival • Cover expenses until transfer to border of requested state (also for escort) • Readmit person back where grounds for readmission found to be non-existent 16
Obligations on requesting state • Prove grounds for readmission • Liaise with the competent authorities re travel documents • Submit request/supporting documentation to receiving authorities • Notify time of arrival • Cover expenses until transfer to border of requested state (also for escort) • Readmit person back where grounds for readmission found to be non-existent 16
 Obligations on state to whom request is made • Accept back nationals/3 CNs • Issue travel documents • Identify 3 CN in order to return them to country of origin (NB requesting country does not need to identify the person before return, simply to show is a national of that state/arrived from territory of that state • Respond within specified time limits 17
Obligations on state to whom request is made • Accept back nationals/3 CNs • Issue travel documents • Identify 3 CN in order to return them to country of origin (NB requesting country does not need to identify the person before return, simply to show is a national of that state/arrived from territory of that state • Respond within specified time limits 17
 Readmission Approaches and Future Prospects • In general, the number of readmission agreements is increasing • Readmission is only one approach to return • Readmission agreements are concluded together with other agreements – Visa facilitation – recruitment 18
Readmission Approaches and Future Prospects • In general, the number of readmission agreements is increasing • Readmission is only one approach to return • Readmission agreements are concluded together with other agreements – Visa facilitation – recruitment 18


