faaa5c32301210455ffaa96fc307d294.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 21
 Reading Strategies for High School Students: A Review of the Literature Bill Muth Virginia Commonwealth University Metropolitan Educational Research Consortium Policy & Planning Council Meeting Wednesday, March 4 th, 2009
Reading Strategies for High School Students: A Review of the Literature Bill Muth Virginia Commonwealth University Metropolitan Educational Research Consortium Policy & Planning Council Meeting Wednesday, March 4 th, 2009
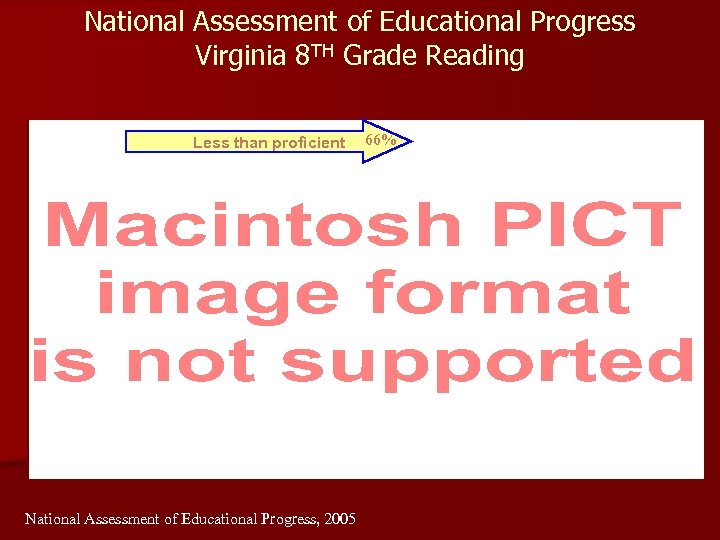 National Assessment of Educational Progress Virginia 8 TH Grade Reading Less than proficient National Assessment of Educational Progress, 2005 66%
National Assessment of Educational Progress Virginia 8 TH Grade Reading Less than proficient National Assessment of Educational Progress, 2005 66%
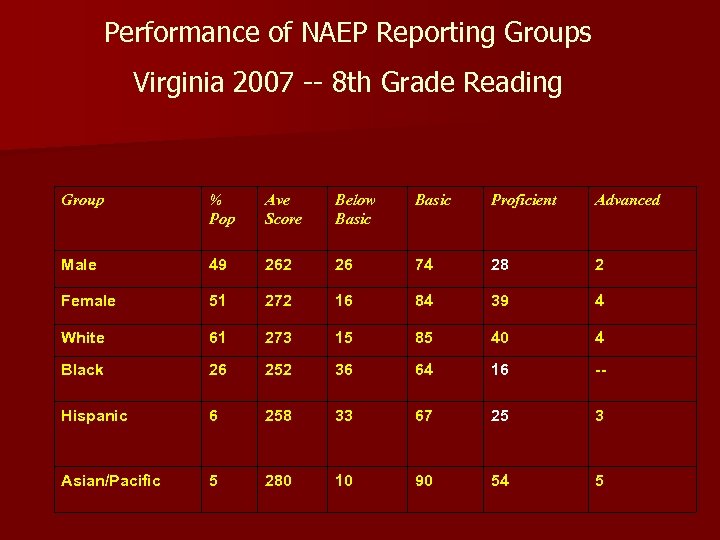 Performance of NAEP Reporting Groups Virginia 2007 -- 8 th Grade Reading Group % Pop Ave Score Below Basic Proficient Advanced Male 49 262 26 74 28 2 Female 51 272 16 84 39 4 White 61 273 15 85 40 4 Black 26 252 36 64 16 -- Hispanic 6 258 33 67 25 3 Asian/Pacific 5 280 10 90 54 5
Performance of NAEP Reporting Groups Virginia 2007 -- 8 th Grade Reading Group % Pop Ave Score Below Basic Proficient Advanced Male 49 262 26 74 28 2 Female 51 272 16 84 39 4 White 61 273 15 85 40 4 Black 26 252 36 64 16 -- Hispanic 6 258 33 67 25 3 Asian/Pacific 5 280 10 90 54 5
 proficient readers n fluent n deep and broad vocabularies n read strategically n self-directed and engaged
proficient readers n fluent n deep and broad vocabularies n read strategically n self-directed and engaged
 what works Kamil et al. (2008) n explicit instruction: vocabulary n explicit instruction: comprehension strategies n extended discussions of text n student engagement n intensive interventions for struggling readers
what works Kamil et al. (2008) n explicit instruction: vocabulary n explicit instruction: comprehension strategies n extended discussions of text n student engagement n intensive interventions for struggling readers
 explicit vocabulary instruction n 3, 000 new words per year, grades 3 -12 n extensive reading, but… n direct instruction – new words § Tier 1, 2, 3 – How to learn words independently n ↑ word consciousness
explicit vocabulary instruction n 3, 000 new words per year, grades 3 -12 n extensive reading, but… n direct instruction – new words § Tier 1, 2, 3 – How to learn words independently n ↑ word consciousness
 explicit vocabulary instruction n multiple exposures in multiple contexts n strategies – – – n semantic feature analysis, semantic mapping games running records word-rich classrooms – dictionaries, thesauruses, word walls, crossword puzzles, Scrabble and other word games, literature, poetry books, and word-play and joke books
explicit vocabulary instruction n multiple exposures in multiple contexts n strategies – – – n semantic feature analysis, semantic mapping games running records word-rich classrooms – dictionaries, thesauruses, word walls, crossword puzzles, Scrabble and other word games, literature, poetry books, and word-play and joke books
 direct instruction of comprehension strategies n active comprehension monitoring & fix-up strategies n graphic and semantic organizers & story maps n question generation n summarization and paraphrasing n selective rereading
direct instruction of comprehension strategies n active comprehension monitoring & fix-up strategies n graphic and semantic organizers & story maps n question generation n summarization and paraphrasing n selective rereading
 direct instruction of comprehension strategies n content reading strategies – win-win solutions – boost discipline learning and general reading n explicit instruction – demonstrations (e. g. , teacher think-alouds) – Discussion n professional development support.
direct instruction of comprehension strategies n content reading strategies – win-win solutions – boost discipline learning and general reading n explicit instruction – demonstrations (e. g. , teacher think-alouds) – Discussion n professional development support.
 extended discussion of text n n engage students in… – – – predicting questioning clarifying summarizing interpreting connecting to prior learning examples: – anticipation Guides – directed reading and thinking activities – reciprocal teaching
extended discussion of text n n engage students in… – – – predicting questioning clarifying summarizing interpreting connecting to prior learning examples: – anticipation Guides – directed reading and thinking activities – reciprocal teaching
 extended discussion of text n students scaffold each other n model literate thinking n ↑ Comprehension of difficult text n adjustments to curriculum: – tension between depth and breadth
extended discussion of text n students scaffold each other n model literate thinking n ↑ Comprehension of difficult text n adjustments to curriculum: – tension between depth and breadth
 motivation and engagement n interesting and relevant content n goals tied to “big picture” n being challenged (“academic press”) n examples: – – range of choice and autonomy hands-on learning experiences interesting and accessible tests collaboration through discussions and assignments.
motivation and engagement n interesting and relevant content n goals tied to “big picture” n being challenged (“academic press”) n examples: – – range of choice and autonomy hands-on learning experiences interesting and accessible tests collaboration through discussions and assignments.
 motivation and engagement understanding the potential of non-canonical literacies n n n canon of methods ELLs funds of knowledge girls portrayed in traditional & pop culture African American boys and masculinity digital literacies
motivation and engagement understanding the potential of non-canonical literacies n n n canon of methods ELLs funds of knowledge girls portrayed in traditional & pop culture African American boys and masculinity digital literacies
 intensive interventions struggling readers triaged: n those with word-level proficiency n those lacking word-level proficiency n if significantly behind, (e. g. , 2+ years) – content area reading support for vocabulary, fluency and comprehension. – specialized intensive help – system approach such as Response to Intervention
intensive interventions struggling readers triaged: n those with word-level proficiency n those lacking word-level proficiency n if significantly behind, (e. g. , 2+ years) – content area reading support for vocabulary, fluency and comprehension. – specialized intensive help – system approach such as Response to Intervention
 intensive interventions all learners, including ELLs and struggling readers, benefit from: n formative assessment n differentiated instruction
intensive interventions all learners, including ELLs and struggling readers, benefit from: n formative assessment n differentiated instruction
 formative assessment & differentiated instruction n rich questioning & discussion to uncover student thinking n comment-only marking n sharing (co-constructing) scoring and grading criteria n ↑ opportunities for peer- and self-assessment. n group review of outcomes from tests.
formative assessment & differentiated instruction n rich questioning & discussion to uncover student thinking n comment-only marking n sharing (co-constructing) scoring and grading criteria n ↑ opportunities for peer- and self-assessment. n group review of outcomes from tests.
 formative assessment & differentiated instruction differentiation starts with accurate assessment FA starts with clear knowledge of standards & tasks. classroom-based FA: – “unpack” State standards – but—some literacy standards point to competencies that have less well-developed “theory of task” – e. g. , “describe the relationship between theme, setting, and character…”
formative assessment & differentiated instruction differentiation starts with accurate assessment FA starts with clear knowledge of standards & tasks. classroom-based FA: – “unpack” State standards – but—some literacy standards point to competencies that have less well-developed “theory of task” – e. g. , “describe the relationship between theme, setting, and character…”
 formative assessment & differentiated instruction differentiation starts with accurate assessment FA starts with clear knowledge of standards & tasks. intervention classrooms: – – targeting word-level skills (e. g. , phonics) maintain meaningful purposes for reading – – NAEP is insensitive to instructional needs of struggling readers NAEP treats literacy as general skill, not content specific
formative assessment & differentiated instruction differentiation starts with accurate assessment FA starts with clear knowledge of standards & tasks. intervention classrooms: – – targeting word-level skills (e. g. , phonics) maintain meaningful purposes for reading – – NAEP is insensitive to instructional needs of struggling readers NAEP treats literacy as general skill, not content specific
 formative assessment & differentiated instruction challenges: changing attitudes and instructional practices n tensions between teachers and administrators n educators’ attitudes & beliefs about indicators of student success n teachers need concrete FA examples: – – – assessment exemplars discussion questions think alouds text sets student-constructed rubrics
formative assessment & differentiated instruction challenges: changing attitudes and instructional practices n tensions between teachers and administrators n educators’ attitudes & beliefs about indicators of student success n teachers need concrete FA examples: – – – assessment exemplars discussion questions think alouds text sets student-constructed rubrics
 other findings n integrate SOLs “essential knowledge” with instruction n buy-in at all levels n teachers focus on no more than 2 -4 strategies n content teachers need incentives & PD n content teachers need to know what is and is not expected of them n each discipline needs to define its own essential literacy skills.
other findings n integrate SOLs “essential knowledge” with instruction n buy-in at all levels n teachers focus on no more than 2 -4 strategies n content teachers need incentives & PD n content teachers need to know what is and is not expected of them n each discipline needs to define its own essential literacy skills.
 conclusions fostering: deep knowledge of the tasks deep understanding of our students making connections between the two
conclusions fostering: deep knowledge of the tasks deep understanding of our students making connections between the two


