6e08c72df4c37efa2e0313b19bb5af72.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 47
 Reading Recovery: The Early Intervention Safety Net
Reading Recovery: The Early Intervention Safety Net
 What Do You Know About RR?
What Do You Know About RR?
 1. Georgia State University 2. Atkinson County 3. Atlanta Public Schools 4. Bacon County 5. Banks County 6. Charlton County 7. Clinch County 8. Cobb County 9. Coffee County 10. Dalton County 11. Dawson County 12. Decatur City 13. De. Kalb County 14. Effingham County 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Elbert County Gwinnett County Habersham County Hart County Evans County Houston County Lee County Pierce County Stephens County Tift County Towns County Valdosta City Ware County Wayne County White County
1. Georgia State University 2. Atkinson County 3. Atlanta Public Schools 4. Bacon County 5. Banks County 6. Charlton County 7. Clinch County 8. Cobb County 9. Coffee County 10. Dalton County 11. Dawson County 12. Decatur City 13. De. Kalb County 14. Effingham County 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. Elbert County Gwinnett County Habersham County Hart County Evans County Houston County Lee County Pierce County Stephens County Tift County Towns County Valdosta City Ware County Wayne County White County
 Total teachers trained at GSU Fall 1991 – Spring 2008 - 1, 127 Total teacher leaders trained at GSU Fall 1991 – Spring 2008 - 65
Total teachers trained at GSU Fall 1991 – Spring 2008 - 1, 127 Total teacher leaders trained at GSU Fall 1991 – Spring 2008 - 65
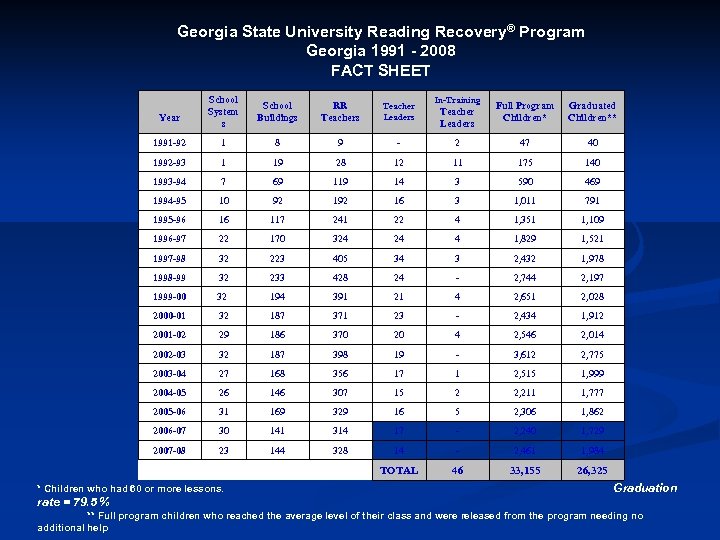 Georgia State University Reading Recovery® Program Georgia 1991 - 2008 FACT SHEET School System s School Buildings RR Teachers Teacher Leaders 1991 -92 1 8 9 - 1992 -93 1 19 28 1993 -94 7 69 1994 -95 10 1995 -96 In-Training Full Program Children* Graduated Children** 2 47 40 12 11 175 140 119 14 3 590 469 92 16 3 1, 011 791 16 117 241 22 4 1, 351 1, 109 1996 -97 22 170 324 24 4 1, 829 1, 521 1997 -98 32 223 405 34 3 2, 432 1, 978 1998 -99 32 233 428 24 - 2, 744 2, 197 1999 -00 32 194 391 21 4 2, 651 2, 028 2000 -01 32 187 371 23 - 2, 434 1, 912 2001 -02 29 186 370 20 4 2, 546 2, 014 2002 -03 32 187 398 19 - 3, 612 2, 775 2003 -04 27 168 356 17 1 2, 515 1, 999 2004 -05 26 146 307 15 2 2, 211 1, 777 2005 -06 31 169 329 16 5 2, 306 1, 862 2006 -07 30 141 314 17 - 2, 240 1, 729 2007 -08 23 144 328 14 - 2, 461 1, 984 TOTAL 46 33, 155 26, 325 Year * Children who had 60 or more lessons. Teacher Leaders Graduation rate = 79. 5 % ** Full program children who reached the average level of their class and were released from the program needing no additional help
Georgia State University Reading Recovery® Program Georgia 1991 - 2008 FACT SHEET School System s School Buildings RR Teachers Teacher Leaders 1991 -92 1 8 9 - 1992 -93 1 19 28 1993 -94 7 69 1994 -95 10 1995 -96 In-Training Full Program Children* Graduated Children** 2 47 40 12 11 175 140 119 14 3 590 469 92 16 3 1, 011 791 16 117 241 22 4 1, 351 1, 109 1996 -97 22 170 324 24 4 1, 829 1, 521 1997 -98 32 223 405 34 3 2, 432 1, 978 1998 -99 32 233 428 24 - 2, 744 2, 197 1999 -00 32 194 391 21 4 2, 651 2, 028 2000 -01 32 187 371 23 - 2, 434 1, 912 2001 -02 29 186 370 20 4 2, 546 2, 014 2002 -03 32 187 398 19 - 3, 612 2, 775 2003 -04 27 168 356 17 1 2, 515 1, 999 2004 -05 26 146 307 15 2 2, 211 1, 777 2005 -06 31 169 329 16 5 2, 306 1, 862 2006 -07 30 141 314 17 - 2, 240 1, 729 2007 -08 23 144 328 14 - 2, 461 1, 984 TOTAL 46 33, 155 26, 325 Year * Children who had 60 or more lessons. Teacher Leaders Graduation rate = 79. 5 % ** Full program children who reached the average level of their class and were released from the program needing no additional help
 Georgia State University affiliated sites outside of Georgia Tennessee Anderson County Athens City Campbell County Johnson City Knox County Oak Ridge Rhea County Scott County Bermuda
Georgia State University affiliated sites outside of Georgia Tennessee Anderson County Athens City Campbell County Johnson City Knox County Oak Ridge Rhea County Scott County Bermuda
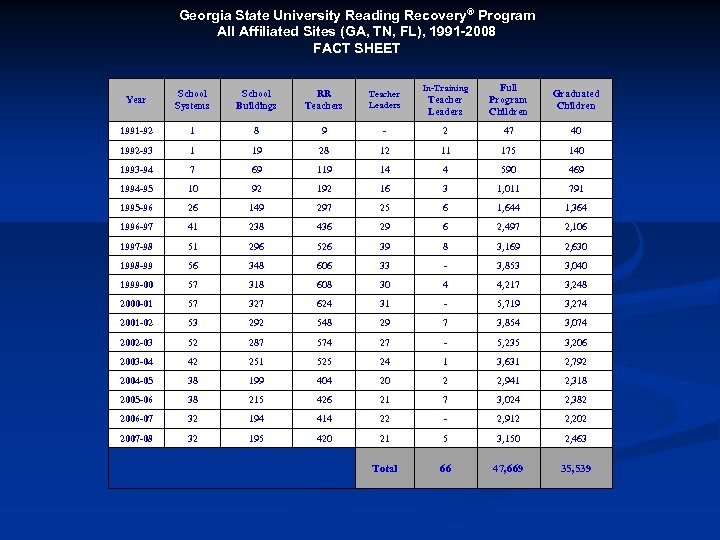 Georgia State University Reading Recovery® Program All Affiliated Sites (GA, TN, FL), 1991 -2008 FACT SHEET Teacher Leaders Full Program Children Graduated Children - 2 47 40 28 12 11 175 140 69 119 14 4 590 469 10 92 16 3 1, 011 791 1995 -96 26 149 297 25 6 1, 644 1, 364 1996 -97 41 238 436 29 6 2, 497 2, 106 1997 -98 51 296 526 39 8 3, 169 2, 630 1998 -99 56 348 606 33 - 3, 853 3, 040 1999 -00 57 318 608 30 4 4, 217 3, 248 2000 -01 57 327 624 31 - 5, 719 3, 274 2001 -02 53 292 548 29 7 3, 854 3, 074 2002 -03 52 287 574 27 - 5, 235 3, 206 2003 -04 42 251 525 24 1 3, 631 2, 792 2004 -05 38 199 404 20 2 2, 941 2, 318 2005 -06 38 215 426 21 7 3, 024 2, 382 2006 -07 32 194 414 22 - 2, 912 2, 202 2007 -08 32 195 420 21 5 3, 150 2, 463 Total 66 47, 669 35, 539 Year School Systems School Buildings RR Teachers Teacher Leaders 1991 -92 1 8 9 1992 -93 1 19 1993 -94 7 1994 -95 In-Training
Georgia State University Reading Recovery® Program All Affiliated Sites (GA, TN, FL), 1991 -2008 FACT SHEET Teacher Leaders Full Program Children Graduated Children - 2 47 40 28 12 11 175 140 69 119 14 4 590 469 10 92 16 3 1, 011 791 1995 -96 26 149 297 25 6 1, 644 1, 364 1996 -97 41 238 436 29 6 2, 497 2, 106 1997 -98 51 296 526 39 8 3, 169 2, 630 1998 -99 56 348 606 33 - 3, 853 3, 040 1999 -00 57 318 608 30 4 4, 217 3, 248 2000 -01 57 327 624 31 - 5, 719 3, 274 2001 -02 53 292 548 29 7 3, 854 3, 074 2002 -03 52 287 574 27 - 5, 235 3, 206 2003 -04 42 251 525 24 1 3, 631 2, 792 2004 -05 38 199 404 20 2 2, 941 2, 318 2005 -06 38 215 426 21 7 3, 024 2, 382 2006 -07 32 194 414 22 - 2, 912 2, 202 2007 -08 32 195 420 21 5 3, 150 2, 463 Total 66 47, 669 35, 539 Year School Systems School Buildings RR Teachers Teacher Leaders 1991 -92 1 8 9 1992 -93 1 19 1993 -94 7 1994 -95 In-Training
 What RR Is and Is Not Is Is not n n n n n One-one individual teaching Provided by specially trained, certified teachers On-going professional development for teachers Adopted as a school initiative by the school staff Supplementary to good classroom teaching For first-grade, lowest-achieving readers only Data-driven teaching to continuously monitor children’s progress A short-term early intervention that prevents further difficulties in literacy A long-term school commitment for lowest-achieving first graders n n n n n Group instruction Delivered by volunteers or paraprofessionals A program to buy & put in place for teachers One person's mandated program The only literacy instruction the child receives A program to improve literacy in all grades A program that labels children via extended testing for disabilities A long-term service for children A quick fix
What RR Is and Is Not Is Is not n n n n n One-one individual teaching Provided by specially trained, certified teachers On-going professional development for teachers Adopted as a school initiative by the school staff Supplementary to good classroom teaching For first-grade, lowest-achieving readers only Data-driven teaching to continuously monitor children’s progress A short-term early intervention that prevents further difficulties in literacy A long-term school commitment for lowest-achieving first graders n n n n n Group instruction Delivered by volunteers or paraprofessionals A program to buy & put in place for teachers One person's mandated program The only literacy instruction the child receives A program to improve literacy in all grades A program that labels children via extended testing for disabilities A long-term service for children A quick fix
 The Impact of Reading Recovery • Bridges the Achievement Gap. • Significant differences in low achievers. • Cost Effective. -
The Impact of Reading Recovery • Bridges the Achievement Gap. • Significant differences in low achievers. • Cost Effective. -
 Do Reading Recovery students close the literacy achievement gap? …. Yes!! White students continue to outperform African American students on literacy measures. • When compared to the progress of students in the random sample, Reading Recovery students are closing this gap.
Do Reading Recovery students close the literacy achievement gap? …. Yes!! White students continue to outperform African American students on literacy measures. • When compared to the progress of students in the random sample, Reading Recovery students are closing this gap.
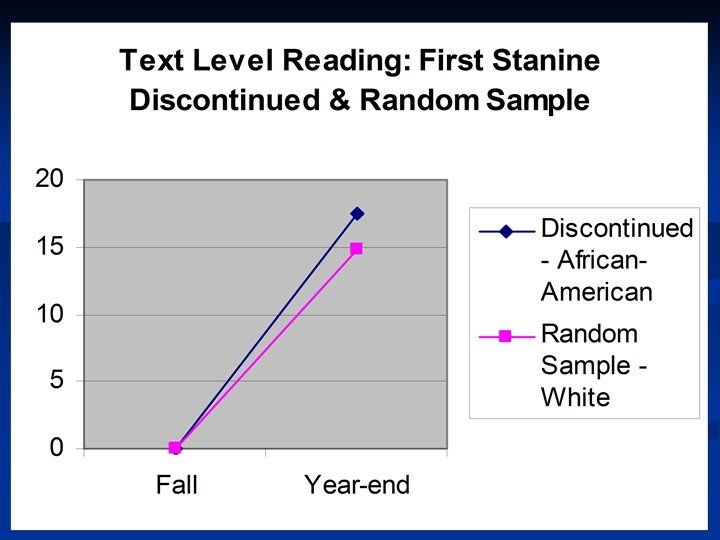
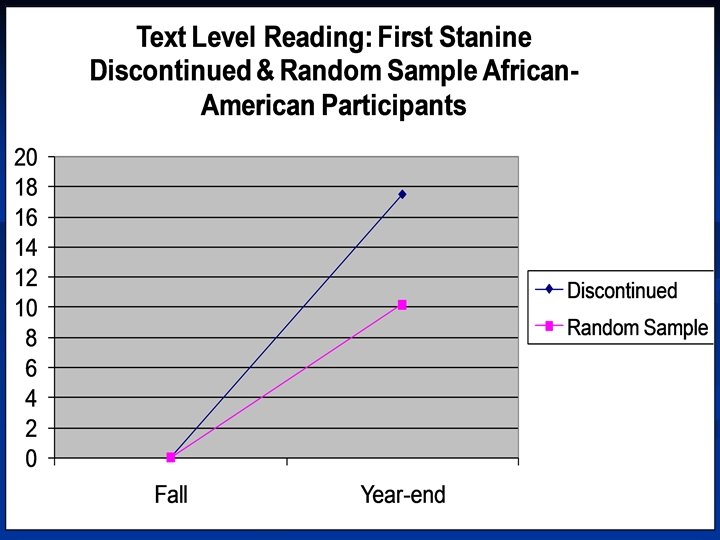
 RR reduces the gap … n n Across racial/ethnic groups Between low and average readers Across income groups Between English speakers and English language learners.
RR reduces the gap … n n Across racial/ethnic groups Between low and average readers Across income groups Between English speakers and English language learners.
 Cost Effectiveness of Reading Recovery What is the cost of other programs that target the same student population & seek to achieve the same results? n Both long-term & short term benefits must be considered when examining cost effectiveness. n One-to-one instruction is the only way for some children to become literate. n
Cost Effectiveness of Reading Recovery What is the cost of other programs that target the same student population & seek to achieve the same results? n Both long-term & short term benefits must be considered when examining cost effectiveness. n One-to-one instruction is the only way for some children to become literate. n
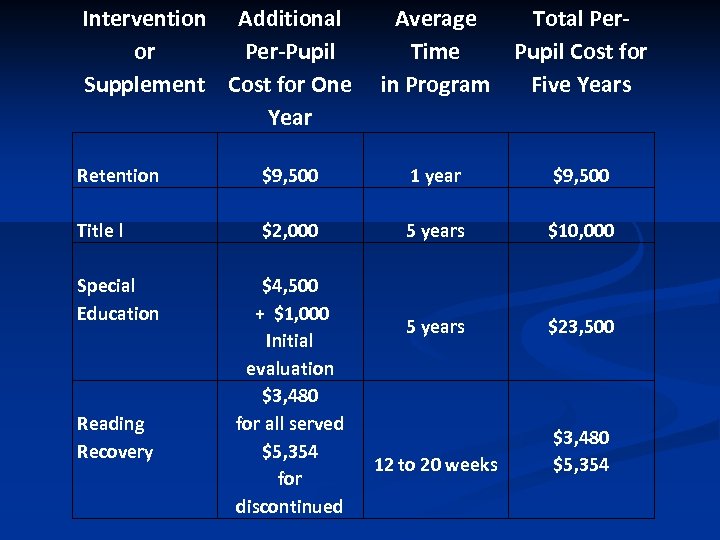 Intervention Additional or Per-Pupil Supplement Cost for One Year Average Total Per. Time Pupil Cost for in Program Five Years Retention $9, 500 1 year $9, 500 Title l $2, 000 5 years $10, 000 5 years $23, 500 12 to 20 weeks $3, 480 $5, 354 Special Education Reading Recovery $4, 500 + $1, 000 Initial evaluation $3, 480 for all served $5, 354 for discontinued
Intervention Additional or Per-Pupil Supplement Cost for One Year Average Total Per. Time Pupil Cost for in Program Five Years Retention $9, 500 1 year $9, 500 Title l $2, 000 5 years $10, 000 5 years $23, 500 12 to 20 weeks $3, 480 $5, 354 Special Education Reading Recovery $4, 500 + $1, 000 Initial evaluation $3, 480 for all served $5, 354 for discontinued
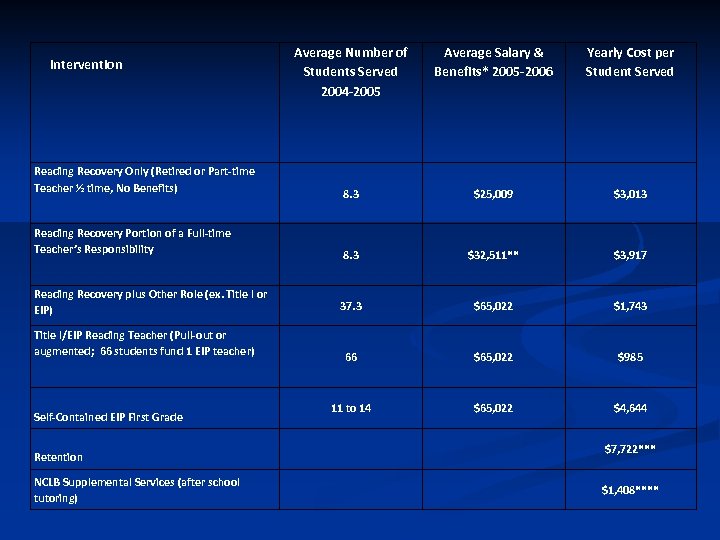 Average Number of Students Served 2004 -2005 Average Salary & Benefits* 2005 -2006 Yearly Cost per Student Served Reading Recovery Only (Retired or Part-time Teacher ½ time, No Benefits) 8. 3 $25, 009 $3, 013 Reading Recovery Portion of a Full-time Teacher’s Responsibility 8. 3 $32, 511** $3, 917 Reading Recovery plus Other Role (ex. Title l or EIP) 37. 3 $65, 022 $1, 743 66 $65, 022 $985 11 to 14 $65, 022 $4, 644 Intervention Title l/EIP Reading Teacher (Pull-out or augmented; 66 students fund 1 EIP teacher) Self-Contained EIP First Grade Retention NCLB Supplemental Services (after school tutoring) $7, 722*** $1, 408****
Average Number of Students Served 2004 -2005 Average Salary & Benefits* 2005 -2006 Yearly Cost per Student Served Reading Recovery Only (Retired or Part-time Teacher ½ time, No Benefits) 8. 3 $25, 009 $3, 013 Reading Recovery Portion of a Full-time Teacher’s Responsibility 8. 3 $32, 511** $3, 917 Reading Recovery plus Other Role (ex. Title l or EIP) 37. 3 $65, 022 $1, 743 66 $65, 022 $985 11 to 14 $65, 022 $4, 644 Intervention Title l/EIP Reading Teacher (Pull-out or augmented; 66 students fund 1 EIP teacher) Self-Contained EIP First Grade Retention NCLB Supplemental Services (after school tutoring) $7, 722*** $1, 408****
 Reading Recovery Cost Effective • 0. 5 FTE • Comparison by effect
Reading Recovery Cost Effective • 0. 5 FTE • Comparison by effect
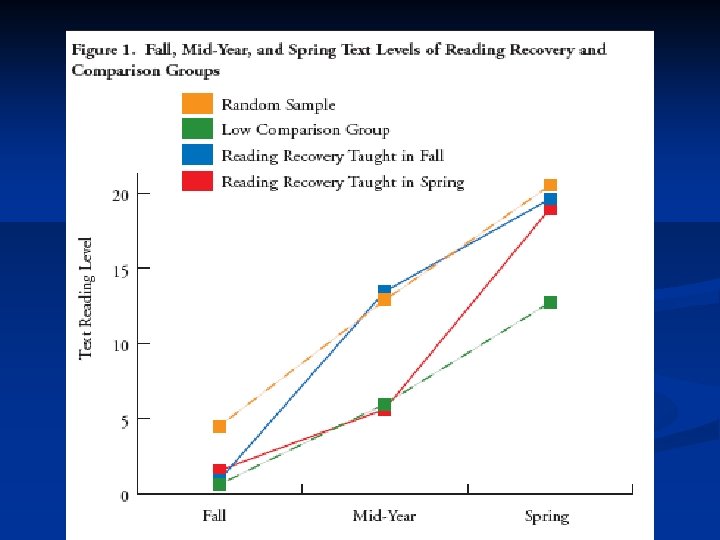
 RR is the only intervention program to receive the highest ranking for evidence of success by the What Works Clearing House (WWC). Clifford I. Johnson Georgia State University 21
RR is the only intervention program to receive the highest ranking for evidence of success by the What Works Clearing House (WWC). Clifford I. Johnson Georgia State University 21
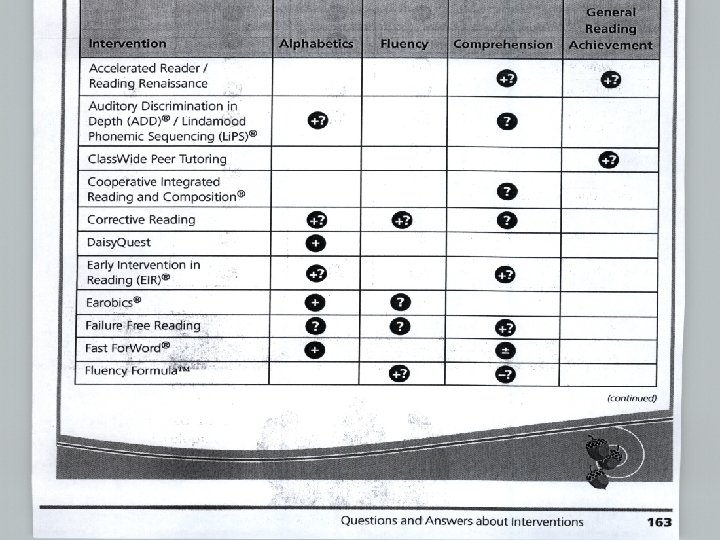 Clifford I. Johnson Georgia State University 22
Clifford I. Johnson Georgia State University 22
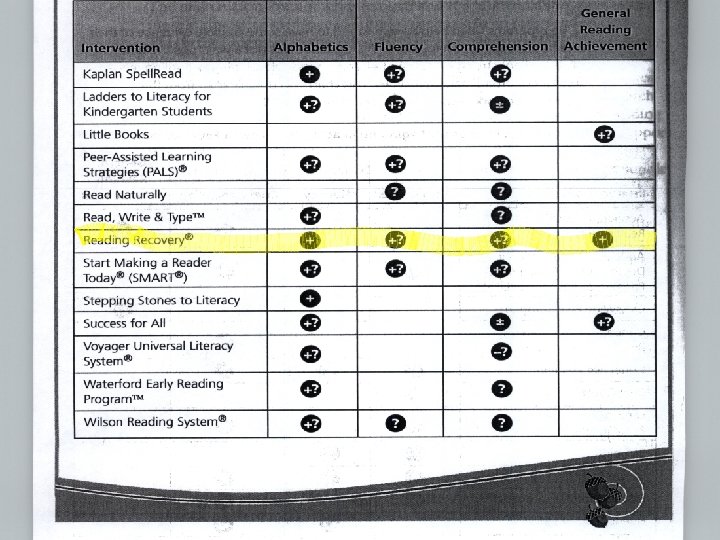
 Two Positive Outcomes of Reading Recovery for Children + + Children reach average levels of text reading for their class Clifford I. Johnson Georgia State University Children are referred appropriately for further long-term support 24
Two Positive Outcomes of Reading Recovery for Children + + Children reach average levels of text reading for their class Clifford I. Johnson Georgia State University Children are referred appropriately for further long-term support 24
 Reading Recovery can be a significant part of a comprehensive schoolwide literacy program Clifford I. Johnson Georgia State University 25
Reading Recovery can be a significant part of a comprehensive schoolwide literacy program Clifford I. Johnson Georgia State University 25
 Why? Some children require individual literacy lessons. n Struggling children deserve the “gold standard” which is individual literacy lessons. n RR provides short-term accelerated learning which enables struggling children to catch up with their peers. n RR provides the “safety net” against crippling literacy problems. n
Why? Some children require individual literacy lessons. n Struggling children deserve the “gold standard” which is individual literacy lessons. n RR provides short-term accelerated learning which enables struggling children to catch up with their peers. n RR provides the “safety net” against crippling literacy problems. n
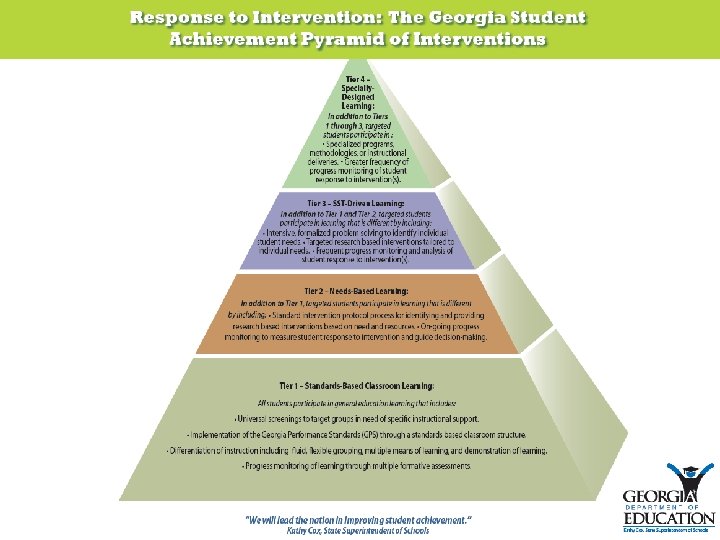
 RR teachers can play a major role in Tier 1, 2 & 3 if their expertise is employed as needed. Clifford I. Johnson Georgia State University 28
RR teachers can play a major role in Tier 1, 2 & 3 if their expertise is employed as needed. Clifford I. Johnson Georgia State University 28
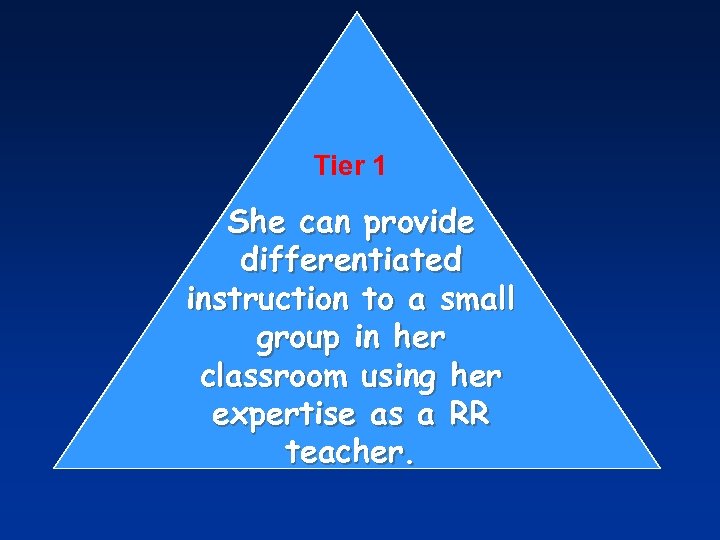 Tier 1 She can provide differentiated instruction to a small group in her classroom using her expertise as a RR teacher.
Tier 1 She can provide differentiated instruction to a small group in her classroom using her expertise as a RR teacher.
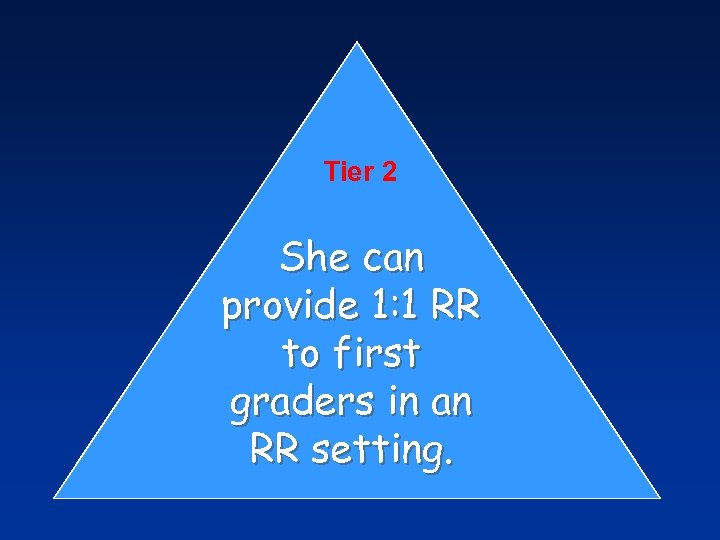 Tier 2 She can provide 1: 1 RR to first graders in an RR setting.
Tier 2 She can provide 1: 1 RR to first graders in an RR setting.
 Tier 3 She can serve on the SST team to assist with IEPs.
Tier 3 She can serve on the SST team to assist with IEPs.
 “No other program has ever come close to achieving the results demonstrated by Reading Recovery. ” Cunningham, P. M. and Allington, R. L. Classrooms That Work. 1994, New York: Harper Collins.
“No other program has ever come close to achieving the results demonstrated by Reading Recovery. ” Cunningham, P. M. and Allington, R. L. Classrooms That Work. 1994, New York: Harper Collins.
 Case Study Muscogee County Columbus, Georgia
Case Study Muscogee County Columbus, Georgia
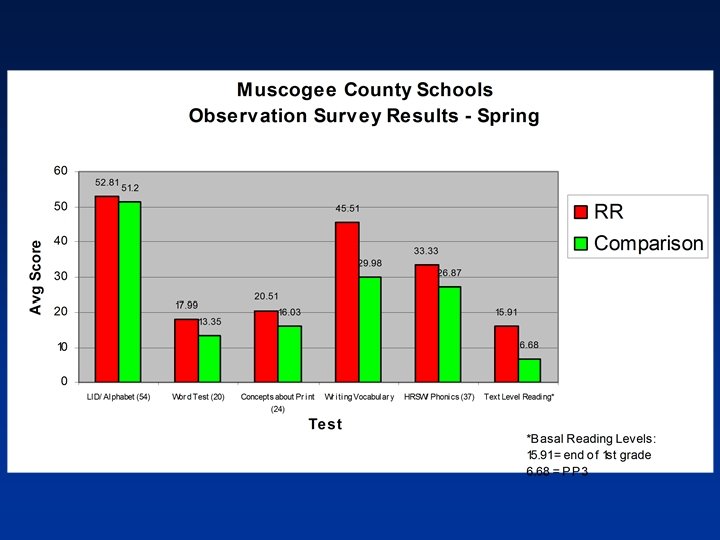
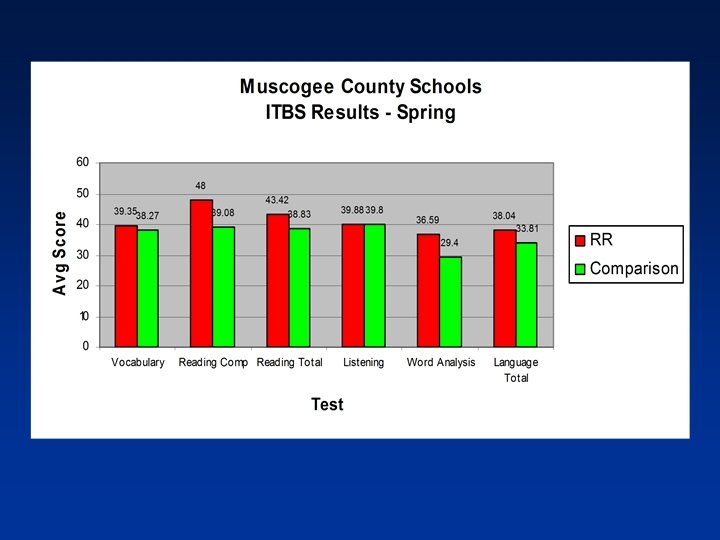
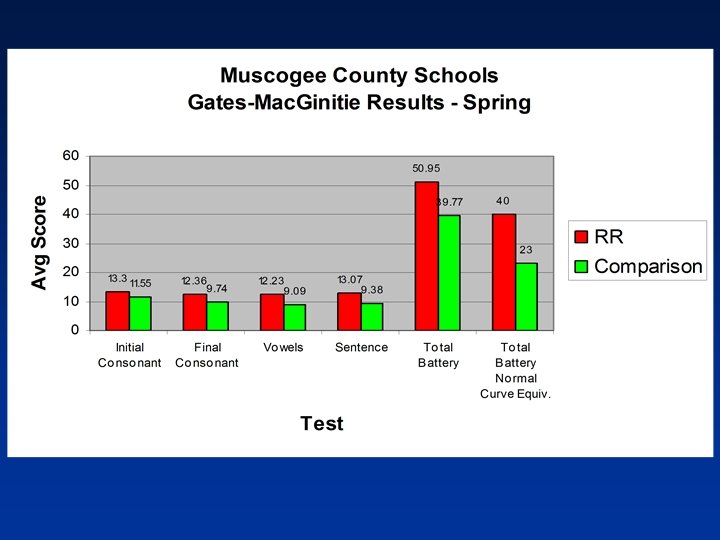
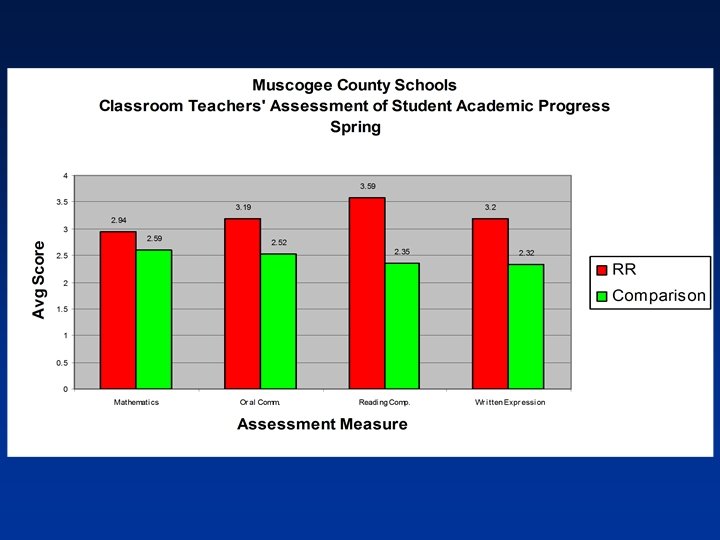

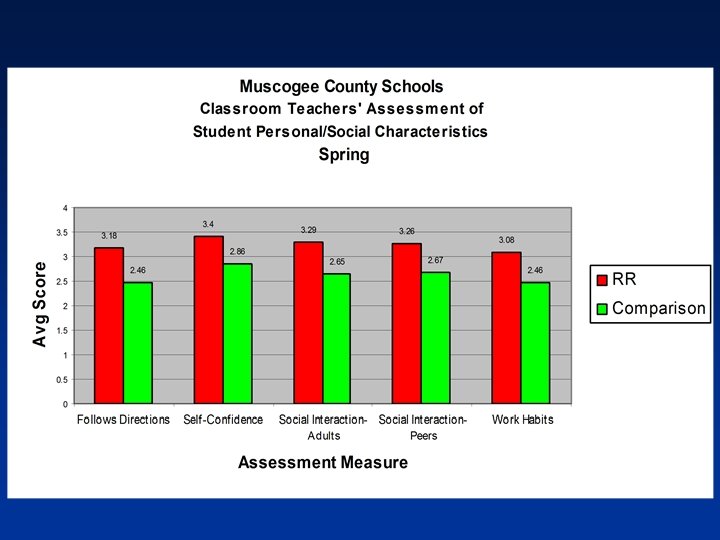
 CRCT Study
CRCT Study
 How Does Reading Recovery Bridge the Gap? Results of Study – Struggling Learners Grade 4 Percent Group Comparison RR - Recommended RR – Discontinued Percent Did not achieve Achieved or Expectation Exceeded Expectation 24 16 13 76 84 87 There was no statistically significant difference between the Comparison group and RR –Recommended. Greater percentages of the RR Discontinued achieved or exceeded expectation.
How Does Reading Recovery Bridge the Gap? Results of Study – Struggling Learners Grade 4 Percent Group Comparison RR - Recommended RR – Discontinued Percent Did not achieve Achieved or Expectation Exceeded Expectation 24 16 13 76 84 87 There was no statistically significant difference between the Comparison group and RR –Recommended. Greater percentages of the RR Discontinued achieved or exceeded expectation.
 How Does Reading Recovery Bridge the Gap? Results of Study – Struggling Learners Grade 3 Percent Group Comparison RR - Recommended RR – Discontinued Percent Did not achieve Achieved or Expectation Exceeded Expectation 14 28 13 86 72 87 There was no statistically significant difference between the Comparison group and RR – Discontinued.
How Does Reading Recovery Bridge the Gap? Results of Study – Struggling Learners Grade 3 Percent Group Comparison RR - Recommended RR – Discontinued Percent Did not achieve Achieved or Expectation Exceeded Expectation 14 28 13 86 72 87 There was no statistically significant difference between the Comparison group and RR – Discontinued.
 How Much Will It Cost? n Training Model for South-Georgia n n n Training Costs n n n Single site Consortia Tuition for academic credit Transporting children/teachers Materials Travel for training Affiliation Costs Apprentice model in which TLs & RRTs will be working within their own school systems during training.
How Much Will It Cost? n Training Model for South-Georgia n n n Training Costs n n n Single site Consortia Tuition for academic credit Transporting children/teachers Materials Travel for training Affiliation Costs Apprentice model in which TLs & RRTs will be working within their own school systems during training.
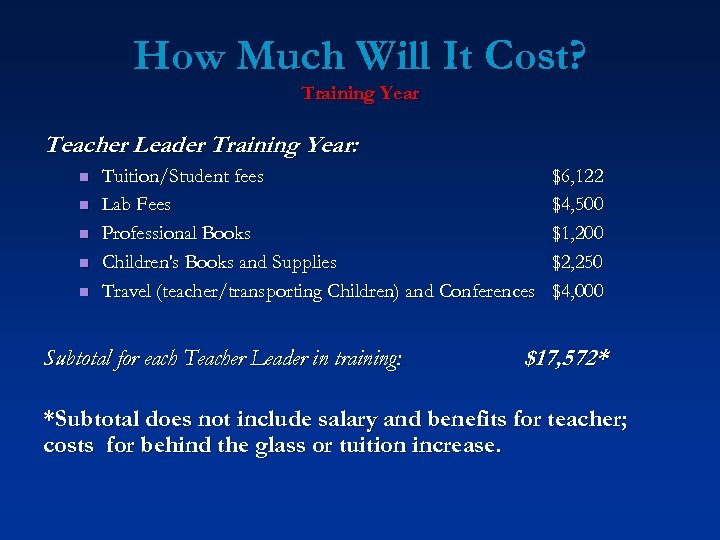 How Much Will It Cost? Training Year Teacher Leader Training Year: n n n Tuition/Student fees Lab Fees Professional Books Children's Books and Supplies Travel (teacher/transporting Children) and Conferences $6, 122 $4, 500 $1, 200 $2, 250 $4, 000 Subtotal for each Teacher Leader in training: $17, 572* *Subtotal does not include salary and benefits for teacher; costs for behind the glass or tuition increase.
How Much Will It Cost? Training Year Teacher Leader Training Year: n n n Tuition/Student fees Lab Fees Professional Books Children's Books and Supplies Travel (teacher/transporting Children) and Conferences $6, 122 $4, 500 $1, 200 $2, 250 $4, 000 Subtotal for each Teacher Leader in training: $17, 572* *Subtotal does not include salary and benefits for teacher; costs for behind the glass or tuition increase.
 How Much Will It Cost? Accreditation and Subsequent Years Accreditation Year following training year): (Field n n n Site affiliation fee Additional Site Visit Professional Development fee $ 2000 (includes one site visit) $ 800* $ 200 (per Teacher Leader) Subsequent Years n n Site affiliation fee Professional Development fee $ 2000 (includes one site visit) $ 200 (per Teacher Leader)
How Much Will It Cost? Accreditation and Subsequent Years Accreditation Year following training year): (Field n n n Site affiliation fee Additional Site Visit Professional Development fee $ 2000 (includes one site visit) $ 800* $ 200 (per Teacher Leader) Subsequent Years n n Site affiliation fee Professional Development fee $ 2000 (includes one site visit) $ 200 (per Teacher Leader)
 Support for Costs Foundation Support n Grant writing n Title I and other Title funds n EIP n Rt. I funds n
Support for Costs Foundation Support n Grant writing n Title I and other Title funds n EIP n Rt. I funds n
 Reading Recovery is a bargain! n n n Short-term intervention, prevention Effective Continuing progress Reduces retentions & SPE referrals Highly qualified teachers & teacher leaders Multi-tiered problem-solving literacy team
Reading Recovery is a bargain! n n n Short-term intervention, prevention Effective Continuing progress Reduces retentions & SPE referrals Highly qualified teachers & teacher leaders Multi-tiered problem-solving literacy team


