aefb55f60515462b25de2529e0111b3f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24

RE-EXPORT (Subsequent Transfers) Control for Conventional weapons 1

WA Key Objective To contribute to regional and international security and stability by promoting transparency and greater responsibility in transfers of conventional arms and dual-use goods and technologies, thus preventing destabilizing accumulations 2

WA Key Documents • INITIAL ELEMENTS (1996) • Elements for Objective Analysis and Advice Concerning Potentially Destabilizing Accumulations of Conventional Weapons (1998) • Best Practice Guidelines for Exports of Small Arms and Light Weapons (2002) • Statement of Understanding on Arms Brokerage (2002) • Elements for Export Controls of MANPADs (2003) • Elements for Effective Legislation on Arms Brokering (2003) • … 3

WA Key Documents • INITIAL ELEMENTS (1996) • Elements for Objective Analysis and Advice Concerning Potentially Destabilizing Accumulations of Conventional Weapons (1998) • Best Practice Guidelines for Exports of Small Arms and Light Weapons (2002) • Statement of Understanding on Arms Brokerage (2002) • Elements for Export Controls of MANPADs (2003) • Elements for Effective Legislation on Arms Brokering (2003) • … • Best Practice Guidelines on Subsequent Transfer (Re-export) Controls for Conventional Weapons Systems contained in Appendix 3 of the Initial Elements (2011) 4

Why control re-export COUNTRY A (WA PS) Transfer of weapons COUNTRY B Stringent export control measures; Reliable transfer 5
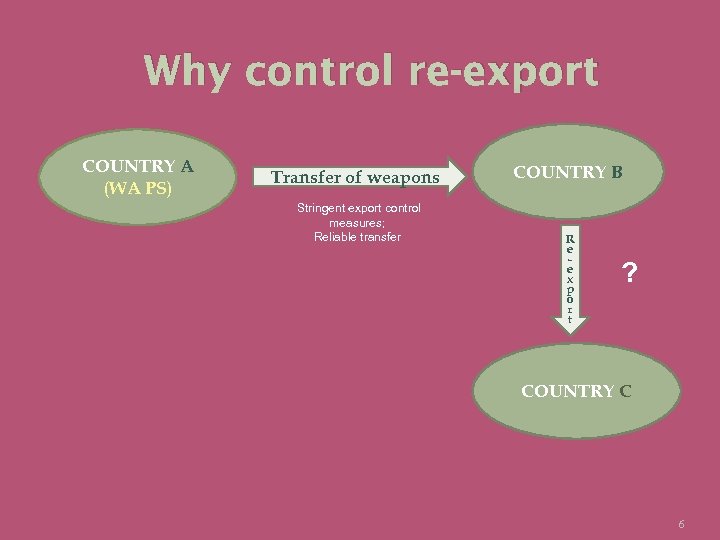
Why control re-export COUNTRY A (WA PS) Transfer of weapons Stringent export control measures; Reliable transfer COUNTRY B R e e x p o r t ? COUNTRY C 6
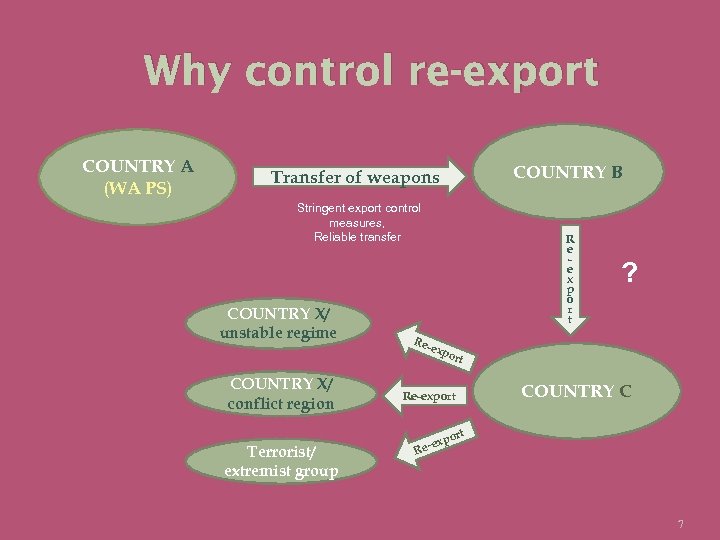
Why control re-export COUNTRY A (WA PS) COUNTRY B Transfer of weapons Stringent export control measures, Reliable transfer COUNTRY X/ unstable regime COUNTRY X/ conflict region Terrorist/ extremist group R e e x p o r t Re- ? exp o rt Re-export COUNTRY C t por ex Re- 7
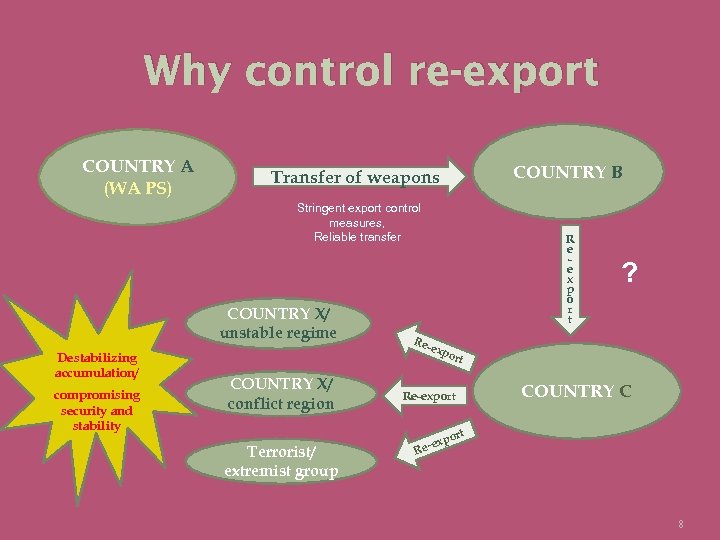
Why control re-export COUNTRY A (WA PS) COUNTRY B Transfer of weapons Stringent export control measures, Reliable transfer COUNTRY X/ unstable regime Destabilizing accumulation/ compromising security and stability COUNTRY X/ conflict region Terrorist/ extremist group R e e x p o r t Re- ? exp o rt Re-export COUNTRY C t por ex Re- 8
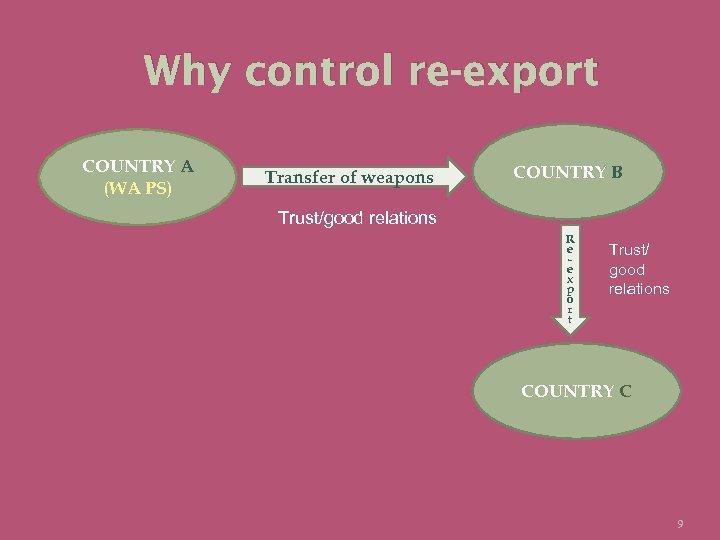
Why control re-export COUNTRY A (WA PS) Transfer of weapons COUNTRY B Trust/good relations R e e x p o r t Trust/ good relations COUNTRY C 9
Why control re-export COUNTRY A (WA PS) Transfer of weapons COUNTRY B Trust/good relations No tru st? Ba dr ela tio ns? R e e x p o r t Trust/ good relations COUNTRY C 10

How to control re-export BEST PRACTICE GUIDELINES on Subsequent Transfer (Re-export) Controls for Conventional Weapons Systems contained in Appendix 3 of the Initial Elements (2011) Battle tanks Armoured Combat Vehicles Large Calibre Artillery Systems Military Aircraft/UAVs Military and Attack Helicopters Warships Missiles or Missile Systems SALW/MANPADS 11

WA Best Practice Guidelines on Re-Export Controls Complete systems SCOPE Exported technology Weapons produced under license 12

WA Best Practice Guidelines on Re-Export Controls • Greater responsibility in transfers of conventional arms Objective s • Prevention of destabilizing accumulations of such arms • Need to prevent the acquisition of conventional arms by terrorist groups and organizations, as well as by individual terrorists 13

WA Best Practice Guidelines on Re-Export Controls GOVERNMENTTOGOVERNMENT AGREEMENTS END-USE/USER ASSURANCES EXPORT LICENSES Subsequent Transfers (Re-export) of conventional weapons systems and their production technology to third governments will be made in accordance with the terms of these documents Importing government will provide the appropriate assurances 14

WA Best Practice Guidelines on Re-Export Controls END-USE/USER ASSURANCES: • not allow re-export without prior authorization of the original exporting government • not use goods for undeclared purposes • not transfer goods to an unauthorized internal end-user 15

WA Best Practice Guidelines on Re-Export Controls Aspects to consider in the review of requests for Subsequent Transfers/Re-export National security and policy concerns Legitimacy of the End-Use/User Legitimate defence requirements of the importing country Effect on Regional Stability Effectiveness of the importer’s export control system 16

WA Best Practice Guidelines on Re-Export Controls Additional requirements: To disclose reasons for denial of re-export permission To ensure that re-export of goods produced under license is consistent with the provisions of all documents pursuant to which the production technology was transferred To exercise restraint so as to avoid re-export to entities not authorized by states directly involved in the transaction Take measures to limit the number of brokers involved in reexport of conventional arms 17

Re-export control in Russia LEGISLATION: Federal Law #114 “On military and technical cooperation with foreign states” dated 19 July 1998 Presidential Decree #1062 dated 10 September 2005 on military and technical cooperation of the Russian Federation with foreign states” Regulation on implementation of military and technical cooperation between the Russian Federation and foreign states Etc. ! Specific provisions on re-export ! 18

Re-export control in Russia DECISIONS on export and RE-EXPORT are taken by: PRESIDENT of the Russian Federation GOVERNMENT of the Russian Federation Federal Service for Military and Technical Cooperation ( see paragraph 13 of the Regulation on implementation of military and technical cooperation between the Russian Federation and foreign states: “Decisions on re-export or transfer to third countries of military goods supplied to foreign customers, as well as on transfer to third countries of military goods produced under Russian licenses, are taken by the President of the Russian Federation. . . by the Government of the Russian Federation… by the Federal Service for Military and Technical Cooperation…”) 19

Re-export control in Russia AUTHORIZED AGENCY: Federal Service for Military and Technical Cooperation AUTHORIZED BROKER: Rosoboronexport KEY ELEMENTS OF CONTROL: Re-export provisions are included in intergovernmental treaties and agreements on export of conventional arms Re-export provisions are included in follow-on contracts between authorized Russian and foreign entities on transfer of arms (legally binding guarantees not to re-export military goods without prior written consent of the Russian Federation) End-user controls 20

Re-export control in Russia END-USER CONTROLS Limited range of end-users Governments Agencies and bodies designated by Governments (e. g. military, law-enforcement, etc. ) Checking legal powers of a customer Authorization from the Government License granting the right to be engaged in arms trade Authorization for signing the contract Consular legalization of documents 21

Re-export control in Russia END-USER CONTROLS Content of end-user certificates: Description of military items Information on the end-use Full and credible information about end-user Assurances by an authorized body that military items will be used only by the designated end-user and only for declared end -use Assurances by an authorized body that re-export of military items may only take place by the prior written consent of the Russian Federation 22

Re-export control in Russia REVIEW OF REQUESTS FOR RE-EXPORT Criteria listed in Article 3 of the Best Practice Guidelines for re-export Legal assurances that items will only be used for declared purposes Legal assurances that further re-export will require written consent of the Russian Federation 23

Thanks for your attention! 24
aefb55f60515462b25de2529e0111b3f.ppt