28fb27416684d450480aed9ec02a0c66.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 27
 RE@Cting to MATHS i. MOVIE HD elluminate session Drift Media © 2008 www. driftmedia. com. au
RE@Cting to MATHS i. MOVIE HD elluminate session Drift Media © 2008 www. driftmedia. com. au
 Capturing/Digitising In order to work with the raw footage, it needs to be converted into a digital file. There are 2 main ways to capture: 1. 2. Firewire/ USB- digital file- transfer loss- less File transfer ie Flip cameras either as a native transfer or via Flipshare.
Capturing/Digitising In order to work with the raw footage, it needs to be converted into a digital file. There are 2 main ways to capture: 1. 2. Firewire/ USB- digital file- transfer loss- less File transfer ie Flip cameras either as a native transfer or via Flipshare.
 Role of the Editor The editor is the person that helps the director tell the story buy putting it into order The editor uses sound and pictures to tell the story The editor uses tools like computers, sound and image software and playback decks to tell the story The editor is a good communicator
Role of the Editor The editor is the person that helps the director tell the story buy putting it into order The editor uses sound and pictures to tell the story The editor uses tools like computers, sound and image software and playback decks to tell the story The editor is a good communicator
 Role of the Editor The editor helps the director by checking the shots are working The editor “cuts” the film together The editor corrects problems with “continuity” and “poor shot selection” The editor is not a magician…. if the shot is rubbish going into the system, it will be rubbish going out. . .
Role of the Editor The editor helps the director by checking the shots are working The editor “cuts” the film together The editor corrects problems with “continuity” and “poor shot selection” The editor is not a magician…. if the shot is rubbish going into the system, it will be rubbish going out. . .
 Housekeeping Before you start, create 4 folders “MASTERS”- your i. Movie project file goes in here “KEEP”- put your go takes in here “THROW” – put content you don’t need in here “BLOOPERS” – put any outtakes or bloopers here Before you start to edit, put your footage in one of the 3 folders.
Housekeeping Before you start, create 4 folders “MASTERS”- your i. Movie project file goes in here “KEEP”- put your go takes in here “THROW” – put content you don’t need in here “BLOOPERS” – put any outtakes or bloopers here Before you start to edit, put your footage in one of the 3 folders.
 Paper Edit Costs nothing Doesn’t involve any equipment Allows the Director to work through their raw footage Can be pictures on post it notes (eg a storyboard) Can be a list of timecodes (called an Edit Decision List or EDL).
Paper Edit Costs nothing Doesn’t involve any equipment Allows the Director to work through their raw footage Can be pictures on post it notes (eg a storyboard) Can be a list of timecodes (called an Edit Decision List or EDL).
 Before you start- a question. . i. Movie. HD is formatted to start with the American format- 29. 97 frames per second. In Australia what do we use? ? ? Drift Media © 2008 www. driftmedia. com. au
Before you start- a question. . i. Movie. HD is formatted to start with the American format- 29. 97 frames per second. In Australia what do we use? ? ? Drift Media © 2008 www. driftmedia. com. au
 To check the format on i. Movie Go to i. Movie. HD-Preferences Make sure the section that says “New Project Framerate” says 25. Close i. Movie. HD and re open it Recheck your Preferences to make sure it still says 25 fps Drift Media © 2008 www. driftmedia. com. au
To check the format on i. Movie Go to i. Movie. HD-Preferences Make sure the section that says “New Project Framerate” says 25. Close i. Movie. HD and re open it Recheck your Preferences to make sure it still says 25 fps Drift Media © 2008 www. driftmedia. com. au
 Create a new project Go to File- New Name your project after your group or program title, NOT “My Great Movie” Save your project to the folder you created called MASTERS For most of your productions (and if you use a Flip) the standard setting for Video Format is “DV”. If you have a 16: 9 camera select widescreen Drift Media © 2008 www. driftmedia. com. au
Create a new project Go to File- New Name your project after your group or program title, NOT “My Great Movie” Save your project to the folder you created called MASTERS For most of your productions (and if you use a Flip) the standard setting for Video Format is “DV”. If you have a 16: 9 camera select widescreen Drift Media © 2008 www. driftmedia. com. au
 Import your files Go to File- Import Select the files in your “KEEP” folder Hit OK Drift Media © 2008 www. driftmedia. com. au
Import your files Go to File- Import Select the files in your “KEEP” folder Hit OK Drift Media © 2008 www. driftmedia. com. au
 Non linear editing basics Non linear editing Non destructive- working with reference files not with actual media All NLE systems have the same basic elements: Clip Browser Timeline Preview Window
Non linear editing basics Non linear editing Non destructive- working with reference files not with actual media All NLE systems have the same basic elements: Clip Browser Timeline Preview Window
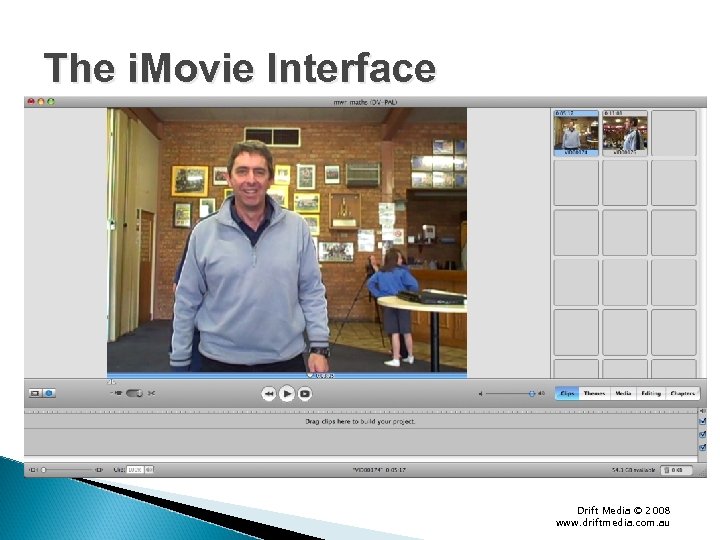 The i. Movie Interface Drift Media © 2008 www. driftmedia. com. au
The i. Movie Interface Drift Media © 2008 www. driftmedia. com. au
 Non linear editing basics The only keys you need to know as an editor APPLE + Z
Non linear editing basics The only keys you need to know as an editor APPLE + Z
 Offline Edit Also called a “rough cut”. Clips are roughly put together in sequence. No or limited effects.
Offline Edit Also called a “rough cut”. Clips are roughly put together in sequence. No or limited effects.
 Trimming the Edit Select Timeline Mode Depending on the format of your camera, you can either: ◦ Crop by clicking on your file and using the yellow triangles below the Preview window to show the where you want the clip to start and end. This is called Marking In and Out. ◦ Split the clip by placing the Playhead at the point where you want to remove content. Go to Edit- Split Video at Playhead or Apple + T Drift Media © 2008 www. driftmedia. com. au
Trimming the Edit Select Timeline Mode Depending on the format of your camera, you can either: ◦ Crop by clicking on your file and using the yellow triangles below the Preview window to show the where you want the clip to start and end. This is called Marking In and Out. ◦ Split the clip by placing the Playhead at the point where you want to remove content. Go to Edit- Split Video at Playhead or Apple + T Drift Media © 2008 www. driftmedia. com. au
 Types of Basic Edits Enter and Exit Frame Cut on the move
Types of Basic Edits Enter and Exit Frame Cut on the move
 Cut on the Move If you have movement in your shots, and different scenes you can make your editing invisible. In Timeline view, find the point where the motion starts Drift Media © 2008 www. driftmedia. com. au
Cut on the Move If you have movement in your shots, and different scenes you can make your editing invisible. In Timeline view, find the point where the motion starts Drift Media © 2008 www. driftmedia. com. au
 Cut on the Move Go to Edit- Split. The file will now be cut on the Timeline. Remove the smaller clip (the bit after the object starts to move) Import your next clip Drift Media © 2008 www. driftmedia. com. au
Cut on the Move Go to Edit- Split. The file will now be cut on the Timeline. Remove the smaller clip (the bit after the object starts to move) Import your next clip Drift Media © 2008 www. driftmedia. com. au
 Cut on the Move Find the spot where the object is moving and split the clip. This time delete the small file before the movement Drift Media © 2008 www. driftmedia. com. au
Cut on the Move Find the spot where the object is moving and split the clip. This time delete the small file before the movement Drift Media © 2008 www. driftmedia. com. au
 Example When you get it right the edit should not be visible. The moment your audience sees your edit they forget about the story. Drift Media © 2008 www. driftmedia. com. au
Example When you get it right the edit should not be visible. The moment your audience sees your edit they forget about the story. Drift Media © 2008 www. driftmedia. com. au
 Types of Edits (Advanced) Jump cut Down the line cut Effect cut
Types of Edits (Advanced) Jump cut Down the line cut Effect cut
 Online Edit Also called a “fine cut”. Clips are trimmed to running length 1. 2. 3. Special Effects added Audio Effects added Titles/ Graphics added
Online Edit Also called a “fine cut”. Clips are trimmed to running length 1. 2. 3. Special Effects added Audio Effects added Titles/ Graphics added
 Adding Graphics and Pics Graphics, titles and backgrounds can add another dimension to your project. They can be constructed using the following packages: Paint Powerpoint Photoshop Still images can be edited and manipulated in image viewing software or Photoshop and imported into your editing software
Adding Graphics and Pics Graphics, titles and backgrounds can add another dimension to your project. They can be constructed using the following packages: Paint Powerpoint Photoshop Still images can be edited and manipulated in image viewing software or Photoshop and imported into your editing software
 Audio- Soundscape The soundscape is the overall sound aspect of your production and includes: the sting the dialogue or hook additional background or “spot” sounds
Audio- Soundscape The soundscape is the overall sound aspect of your production and includes: the sting the dialogue or hook additional background or “spot” sounds
 Audio Sweetening Audio levels for entire program checked (each individual clip) Scenes with voice may be EQ’d or effected Transitional “pops” between clips may be smoothed over with 2 frame dissolves.
Audio Sweetening Audio levels for entire program checked (each individual clip) Scenes with voice may be EQ’d or effected Transitional “pops” between clips may be smoothed over with 2 frame dissolves.
 Exporting a QT file from movie. HD GO to SHARE. Then Quicktime Select “Expert Settings” Name your file. Group nand topic_MASTER. Make note of where the file is being saved Select Movie to Quicktime Movie in the Export Window Drift Media © 2008 www. driftmedia. com. au
Exporting a QT file from movie. HD GO to SHARE. Then Quicktime Select “Expert Settings” Name your file. Group nand topic_MASTER. Make note of where the file is being saved Select Movie to Quicktime Movie in the Export Window Drift Media © 2008 www. driftmedia. com. au
 Exporting a File (cont) Under the Options Menu, check your Settings Video Settings should be: Compression- DV PAL Quality: Best Frame rate: 25 Scan Mode: Interlaced Aspect ratio: 4: 3 Dimensions: 720 X 576 (768 X 576) (Compressor Native) Sound Settings Format: Integer (Big Endian) Sample rate: 48. 000 khz Sample Size: 16 bit Channels: Stereo (L-R) Hit “OK” Drift Media © 2008 www. driftmedia. com. au
Exporting a File (cont) Under the Options Menu, check your Settings Video Settings should be: Compression- DV PAL Quality: Best Frame rate: 25 Scan Mode: Interlaced Aspect ratio: 4: 3 Dimensions: 720 X 576 (768 X 576) (Compressor Native) Sound Settings Format: Integer (Big Endian) Sample rate: 48. 000 khz Sample Size: 16 bit Channels: Stereo (L-R) Hit “OK” Drift Media © 2008 www. driftmedia. com. au


