3d90ab245aa4c2ea623fa5aea5a5e29f.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 20
 RDS and Oracle 10 g RAC Update Paul Tsien, Oracle
RDS and Oracle 10 g RAC Update Paul Tsien, Oracle
 Agenda Ø Oracle Database 10 g RAC Ø What is RDS (Reliable Datagram Sockets)? Ø Open Source RDS for Linux Ø Beta Customer Experience 2
Agenda Ø Oracle Database 10 g RAC Ø What is RDS (Reliable Datagram Sockets)? Ø Open Source RDS for Linux Ø Beta Customer Experience 2
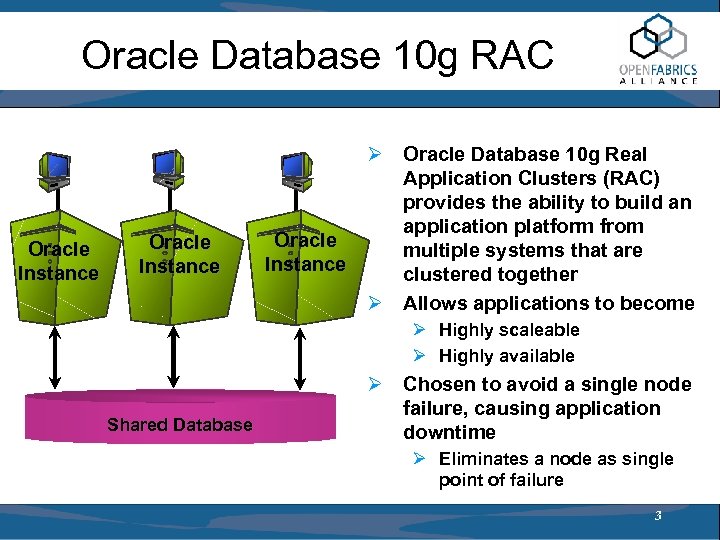 Oracle Database 10 g RAC Oracle Instance Ø Oracle Database 10 g Real Application Clusters (RAC) provides the ability to build an application platform from Oracle multiple systems that are Instance clustered together Ø Allows applications to become Ø Highly scaleable Ø Highly available Shared Database Ø Chosen to avoid a single node failure, causing application downtime Ø Eliminates a node as single point of failure 3
Oracle Database 10 g RAC Oracle Instance Ø Oracle Database 10 g Real Application Clusters (RAC) provides the ability to build an application platform from Oracle multiple systems that are Instance clustered together Ø Allows applications to become Ø Highly scaleable Ø Highly available Shared Database Ø Chosen to avoid a single node failure, causing application downtime Ø Eliminates a node as single point of failure 3
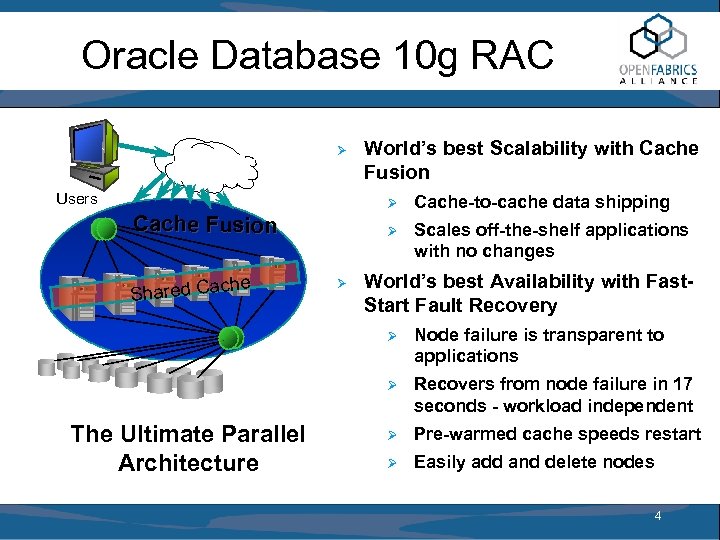 Oracle Database 10 g RAC Ø Users World’s best Scalability with Cache Fusion Ø Ø Cache Fusion he Shared Cac Ø Cache-to-cache data shipping Scales off-the-shelf applications with no changes World’s best Availability with Fast. Start Fault Recovery Ø Ø The Ultimate Parallel Architecture Node failure is transparent to applications Recovers from node failure in 17 seconds - workload independent Ø Pre-warmed cache speeds restart Ø Easily add and delete nodes 4
Oracle Database 10 g RAC Ø Users World’s best Scalability with Cache Fusion Ø Ø Cache Fusion he Shared Cac Ø Cache-to-cache data shipping Scales off-the-shelf applications with no changes World’s best Availability with Fast. Start Fault Recovery Ø Ø The Ultimate Parallel Architecture Node failure is transparent to applications Recovers from node failure in 17 seconds - workload independent Ø Pre-warmed cache speeds restart Ø Easily add and delete nodes 4
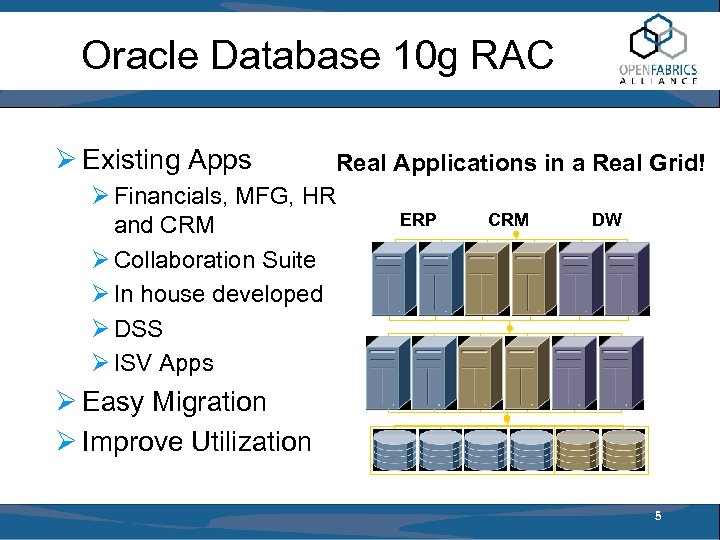 Oracle Database 10 g RAC Ø Existing Apps Real Applications in a Real Grid! Ø Financials, MFG, HR ERP CRM DW and CRM Ø Collaboration Suite Ø In house developed Ø DSS Ø ISV Apps Ø Easy Migration Ø Improve Utilization 5
Oracle Database 10 g RAC Ø Existing Apps Real Applications in a Real Grid! Ø Financials, MFG, HR ERP CRM DW and CRM Ø Collaboration Suite Ø In house developed Ø DSS Ø ISV Apps Ø Easy Migration Ø Improve Utilization 5
 Oracle Database 10 g RAC Ø RAC IPC ØThousands of processes Ø 200 K+ associations (not connections) Ø 64 nodes Ø Oracle IPC Usage ØNew database functionality will significantly increase IPC utilization ØApproach database I/O rates ØVery large messages (8 MB +) 6
Oracle Database 10 g RAC Ø RAC IPC ØThousands of processes Ø 200 K+ associations (not connections) Ø 64 nodes Ø Oracle IPC Usage ØNew database functionality will significantly increase IPC utilization ØApproach database I/O rates ØVery large messages (8 MB +) 6
 What is RDS? ØVision ØA low overhead, low latency, high bandwidth, ultra reliable, supportable, IPC protocol and transport system ØWhich matches Oracles existing IPC models for RAC communication ØOptimized for transfers from 200 bytes to 8 meg 7
What is RDS? ØVision ØA low overhead, low latency, high bandwidth, ultra reliable, supportable, IPC protocol and transport system ØWhich matches Oracles existing IPC models for RAC communication ØOptimized for transfers from 200 bytes to 8 meg 7
 What is RDS? Ø Goal and Objective ØSupport for a reliable datagram IPC in Open. IB ØBased on Socket API ØMinimal code change / testing for Oracle ØFailover inter HCA and intra HCA ports ØRuns over IB, Ether, i. WARP, etc Ø 2 -6 month validation / certification for RAC 8
What is RDS? Ø Goal and Objective ØSupport for a reliable datagram IPC in Open. IB ØBased on Socket API ØMinimal code change / testing for Oracle ØFailover inter HCA and intra HCA ports ØRuns over IB, Ether, i. WARP, etc Ø 2 -6 month validation / certification for RAC 8
 What is RDS? Ø Reliable Datagram IPC ØUDP – Oracle adds reliable delivery via user mode wire protocol engine ØTwo sockets per process, thousands of messages on wire ØSlow sends times (windowing, acks, retrans) ØHolds together but degenerates under CPU load ØWell tested ! 9
What is RDS? Ø Reliable Datagram IPC ØUDP – Oracle adds reliable delivery via user mode wire protocol engine ØTwo sockets per process, thousands of messages on wire ØSlow sends times (windowing, acks, retrans) ØHolds together but degenerates under CPU load ØWell tested ! 9
 What is RDS? Ø Available Options Øu. DAPL / it. API – not supporting ØIPOIB – high CPU overhead, same unreliable delivery (UDP) ØSDP – connection oriented ØWe want to take our existing well tested UDP module, shutoff most of it to run over an O/S provided RD IPC 10
What is RDS? Ø Available Options Øu. DAPL / it. API – not supporting ØIPOIB – high CPU overhead, same unreliable delivery (UDP) ØSDP – connection oriented ØWe want to take our existing well tested UDP module, shutoff most of it to run over an O/S provided RD IPC 10
 What is RDS? Ø RD – Reliable Datagram IPC over IB Ø 50% less CPU than IPOIB, UDP Ø ½ Latency of UDP (no user-mode acks) Ø Within 5% of u. DAPL thru-put using Oracle Ø Minimal code change – reduced our UDP module by 70% - removed windowing, acks, retransmissions, etc. Ø RDS driver ~ = 1 k C lines (b-copy) Ø Decoupled from user-mode CPU loading Ø Passes all Oracle regression tests in < 2 wks !!!! Ø Supports fail-over across and within HCAs 11
What is RDS? Ø RD – Reliable Datagram IPC over IB Ø 50% less CPU than IPOIB, UDP Ø ½ Latency of UDP (no user-mode acks) Ø Within 5% of u. DAPL thru-put using Oracle Ø Minimal code change – reduced our UDP module by 70% - removed windowing, acks, retransmissions, etc. Ø RDS driver ~ = 1 k C lines (b-copy) Ø Decoupled from user-mode CPU loading Ø Passes all Oracle regression tests in < 2 wks !!!! Ø Supports fail-over across and within HCAs 11
 What is RDS? Ø RDS IPC over IB ØUses IB reliable connection (RC) ØNode to Node level connection ØUser mode sockets share small pool of node to node RCs. ØFormed either dynamically at send or at system startup 12
What is RDS? Ø RDS IPC over IB ØUses IB reliable connection (RC) ØNode to Node level connection ØUser mode sockets share small pool of node to node RCs. ØFormed either dynamically at send or at system startup 12
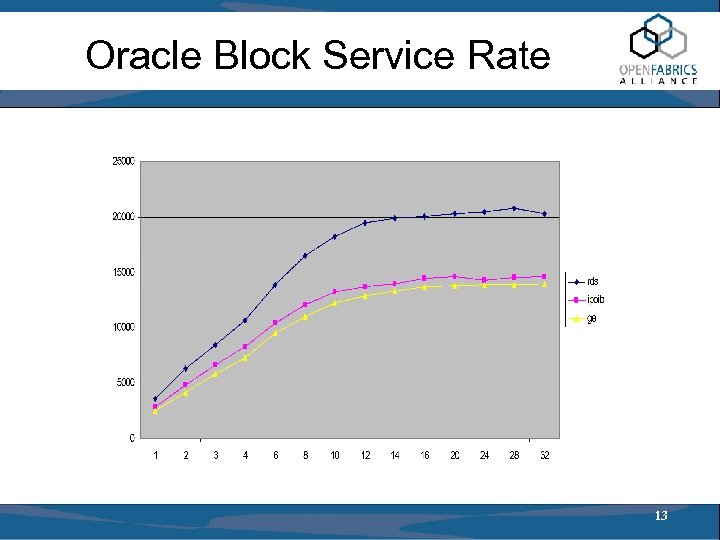 Oracle Block Service Rate 13
Oracle Block Service Rate 13
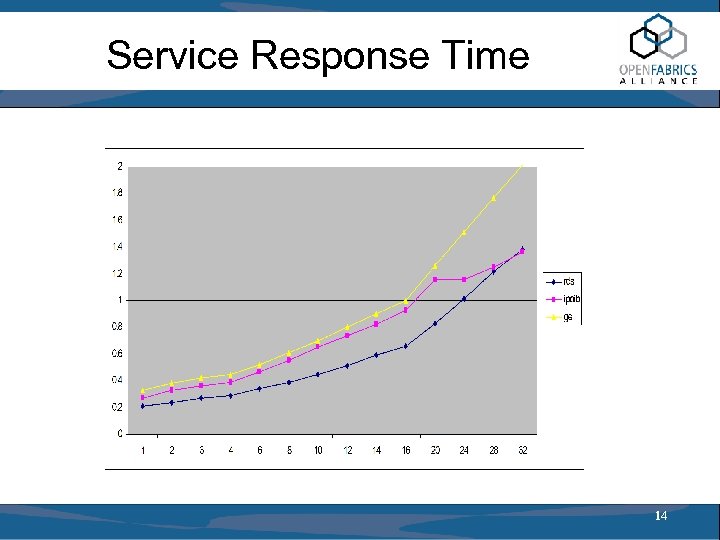 Service Response Time 14
Service Response Time 14
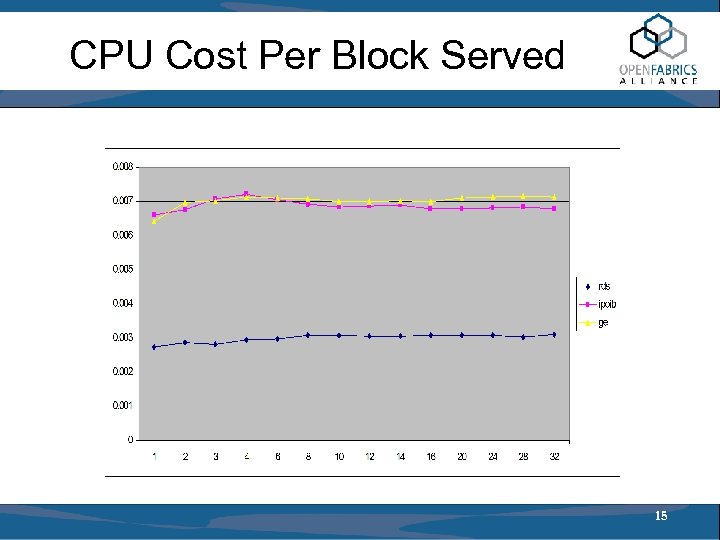 CPU Cost Per Block Served 15
CPU Cost Per Block Served 15
 Open Source RDS for Linux Ø Open Source RDS ØOracle is building Open Source RDS for Linux http: //oss. oracle. com/projects/rds/ ØOracle will support RDS on Linux ØOracle RDS will be pulled into OFED ØOracle RDS will support Gig. E, simple NICs and RDMA NICs (IB/i. WARP) 16
Open Source RDS for Linux Ø Open Source RDS ØOracle is building Open Source RDS for Linux http: //oss. oracle. com/projects/rds/ ØOracle will support RDS on Linux ØOracle RDS will be pulled into OFED ØOracle RDS will support Gig. E, simple NICs and RDMA NICs (IB/i. WARP) 16
 Open Source RDS for Linux Ø Status ØOracle is testing Open Source RDS on Gig. E ØRDS on IB is in development ØBeta testing with customers using Silver. Storm RDS/IB stack ØVery stable ØVery good performance ØRDS is supported by major tier one system vendors 17
Open Source RDS for Linux Ø Status ØOracle is testing Open Source RDS on Gig. E ØRDS on IB is in development ØBeta testing with customers using Silver. Storm RDS/IB stack ØVery stable ØVery good performance ØRDS is supported by major tier one system vendors 17
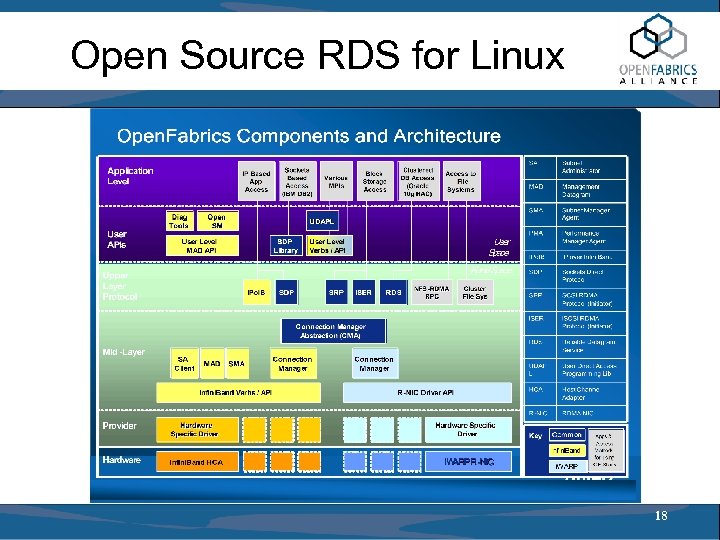 Open Source RDS for Linux 18
Open Source RDS for Linux 18
 Beta Customer Experience ØCustomer Requirements ØImprove application performance (throughput, latency, etc. ) ØMaintain data availability ØLower TCO through commodity hardware without sacrificing performance or scalability ØWant to implement Grid and Utility computing 19
Beta Customer Experience ØCustomer Requirements ØImprove application performance (throughput, latency, etc. ) ØMaintain data availability ØLower TCO through commodity hardware without sacrificing performance or scalability ØWant to implement Grid and Utility computing 19
 Beta Customer Experience Ø Results Ø RDS/IB shows significant real world application performance gains for certain workloads: DSS and mixed DSS/OLTP workloads Ø Throughput and latency Ø Customers are interested in unified fabric for cost and manageability reasons Ø Reservation/Qo. S is a concern Ø Joint customer Oracle World presentation on RDS (Session S 281216, 10/23/2006 11 AM) 20
Beta Customer Experience Ø Results Ø RDS/IB shows significant real world application performance gains for certain workloads: DSS and mixed DSS/OLTP workloads Ø Throughput and latency Ø Customers are interested in unified fabric for cost and manageability reasons Ø Reservation/Qo. S is a concern Ø Joint customer Oracle World presentation on RDS (Session S 281216, 10/23/2006 11 AM) 20


