d7d1c113a43ab61b65ae570bf34325c4.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 30
 Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Module 4: Disciplines II
Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Module 4: Disciplines II
 Objectives w Understand discipline concepts for: § Analysis & Design § Test § Implementation § Deployment § Configuration & Change Management Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 2
Objectives w Understand discipline concepts for: § Analysis & Design § Test § Implementation § Deployment § Configuration & Change Management Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 2
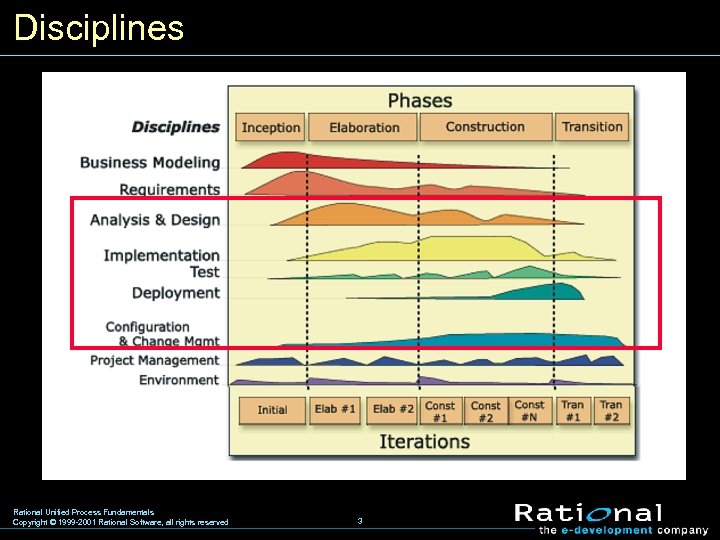 Disciplines Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 3
Disciplines Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 3
 Discipline: Analysis & Design w Purpose: § To transform the requirements into a design of the system-to-be § To evolve a robust architecture for the system § To adapt the design to match the nonfunctional requirements and the implementation environment w Design is a refinement of analysis w Primary artifact is Design Model Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 4
Discipline: Analysis & Design w Purpose: § To transform the requirements into a design of the system-to-be § To evolve a robust architecture for the system § To adapt the design to match the nonfunctional requirements and the implementation environment w Design is a refinement of analysis w Primary artifact is Design Model Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 4
 The Design Model Artifact: w Consists of a collection of models that collaborate to describe the structure and behavior of the system. w Is an object model describing the realization of use cases. w Serves as an abstraction of the implementation model and its source code. w Is used as essential input to activities in implementation and test. Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 5
The Design Model Artifact: w Consists of a collection of models that collaborate to describe the structure and behavior of the system. w Is an object model describing the realization of use cases. w Serves as an abstraction of the implementation model and its source code. w Is used as essential input to activities in implementation and test. Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 5
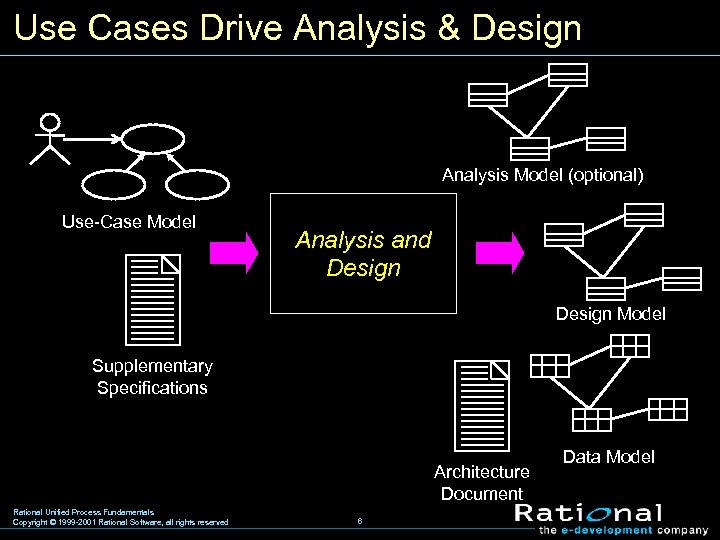 Use Cases Drive Analysis & Design Analysis Model (optional) Use-Case Model Analysis and Design Model Supplementary Specifications Architecture Document Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 6 Data Model
Use Cases Drive Analysis & Design Analysis Model (optional) Use-Case Model Analysis and Design Model Supplementary Specifications Architecture Document Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 6 Data Model
 Analysis & Design Considerations w Transform requirements into classes and subsystems w Adhere to constraints of § Nonfunctional requirements § Implementation environment w Design the database § Mapping the design model to a data model w Identify components § Subsystems and interfaces Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 7
Analysis & Design Considerations w Transform requirements into classes and subsystems w Adhere to constraints of § Nonfunctional requirements § Implementation environment w Design the database § Mapping the design model to a data model w Identify components § Subsystems and interfaces Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 7
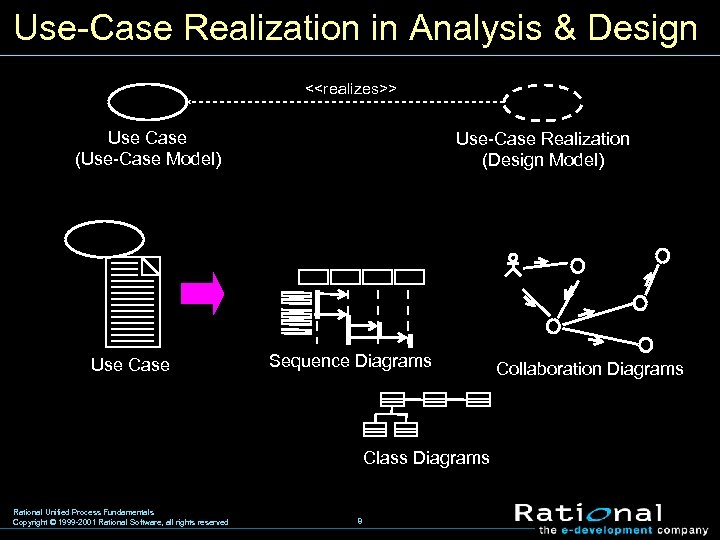 Use-Case Realization in Analysis & Design <
Use-Case Realization in Analysis & Design <
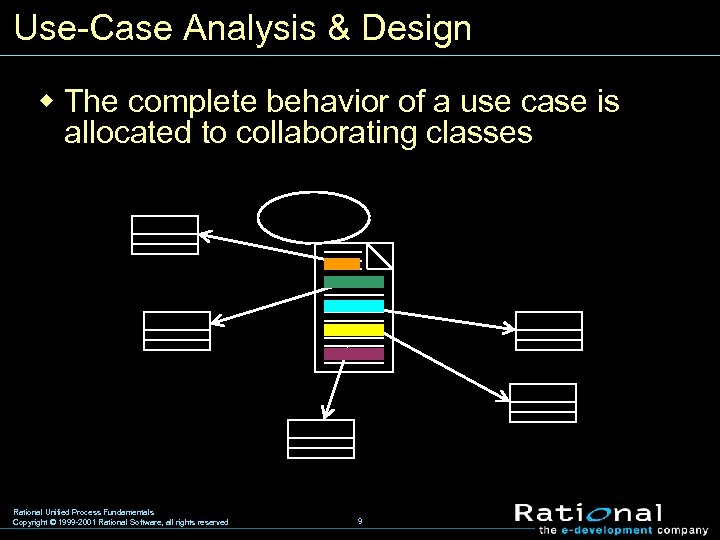 Use-Case Analysis & Design w The complete behavior of a use case is allocated to collaborating classes Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 9
Use-Case Analysis & Design w The complete behavior of a use case is allocated to collaborating classes Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 9
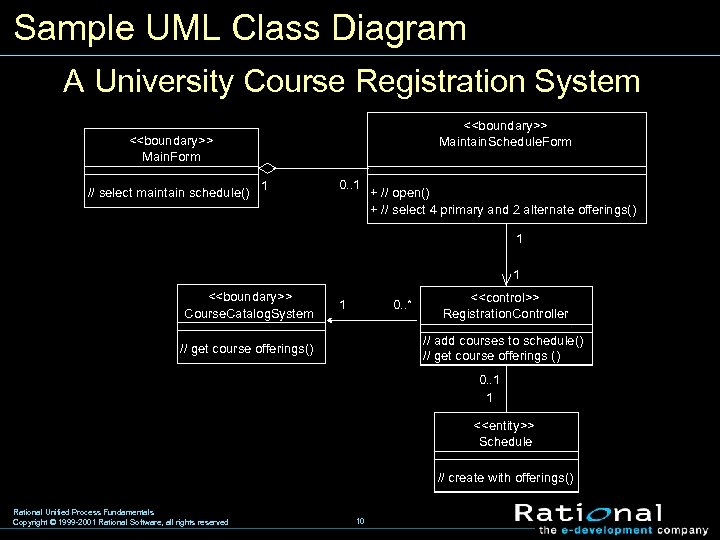 Sample UML Class Diagram A University Course Registration System <
Sample UML Class Diagram A University Course Registration System <
 Purposes of Architecture w Intellectual control w Basis for reuse w Basis for project management Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 11
Purposes of Architecture w Intellectual control w Basis for reuse w Basis for project management Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 11
 Architecture: Intellectual Control w Architecture is used for different things by various stakeholders § Customer: visualize what they are buying § Project manager: scheduling and resource allocation § System analyst: organize requirements § Developer: understand boundaries of their chunk of the project § Software architect: reason about evolution or reuse w Multidimensional reality (i. e. multiple views) § Multiple views: functional, implementation, dynamic, structural, spatial (physical distribution), etc. Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 12
Architecture: Intellectual Control w Architecture is used for different things by various stakeholders § Customer: visualize what they are buying § Project manager: scheduling and resource allocation § System analyst: organize requirements § Developer: understand boundaries of their chunk of the project § Software architect: reason about evolution or reuse w Multidimensional reality (i. e. multiple views) § Multiple views: functional, implementation, dynamic, structural, spatial (physical distribution), etc. Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 12
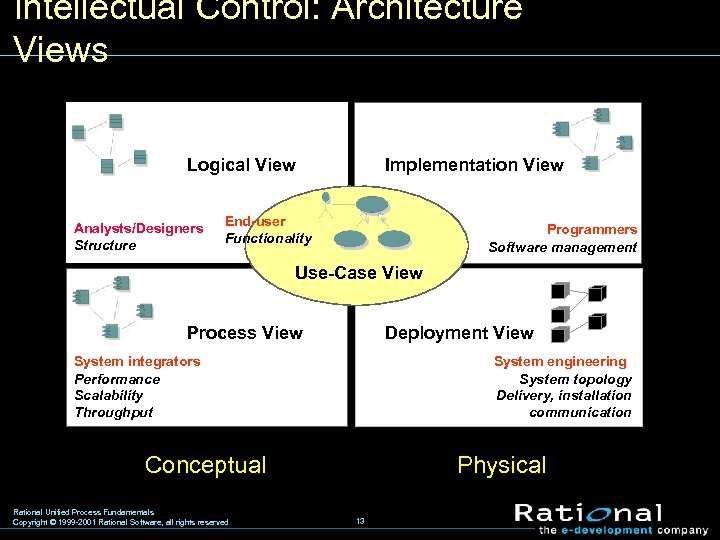 Intellectual Control: Architecture Views Logical View Analysts/Designers Structure Implementation View End-user Functionality Programmers Software management Use-Case View Process View Deployment View System integrators Performance Scalability Throughput System engineering System topology Delivery, installation communication Conceptual Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved Physical 13
Intellectual Control: Architecture Views Logical View Analysts/Designers Structure Implementation View End-user Functionality Programmers Software management Use-Case View Process View Deployment View System integrators Performance Scalability Throughput System engineering System topology Delivery, installation communication Conceptual Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved Physical 13
 Architecture: Basis for Reuse w The structural elements and interfaces which compose the system w The behavior seen in the collaboration of these elements w The composition of these elements into progressively larger subsystems Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 14
Architecture: Basis for Reuse w The structural elements and interfaces which compose the system w The behavior seen in the collaboration of these elements w The composition of these elements into progressively larger subsystems Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 14
 Architecturally Significant Elements w Not all design is architecture w Main business classes w Important mechanisms w Processors and processes w Layers and subsystems w Architectural views = slices through models Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 15
Architecturally Significant Elements w Not all design is architecture w Main business classes w Important mechanisms w Processors and processes w Layers and subsystems w Architectural views = slices through models Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 15
 Architecture: Basis for Project Management w Architecture Milestone in Elaboration phase is the Lifecyle Architecture milestone w Architecture primarily results from Analysis & Design w Architecture in phases and iterations: § It drives the risk mitigation of iterations § Architecture baseline is an exit criterion for Elaboration Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 16
Architecture: Basis for Project Management w Architecture Milestone in Elaboration phase is the Lifecyle Architecture milestone w Architecture primarily results from Analysis & Design w Architecture in phases and iterations: § It drives the risk mitigation of iterations § Architecture baseline is an exit criterion for Elaboration Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 16
 Discipline: Test w Purpose: Testing focuses primarily on the evaluation or assessment of quality realized through a number of core practices: § Finding and documenting defects in software quality. § Generally advising about perceived software quality. § Proving the validity of the assumptions made in design and requirement specifications through concrete demonstration. § Validating the software product functions as designed. § Validating that the requirements have been implemented appropriately. w Test discipline acts in many respects as a service provider to the other disciplines. Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 17
Discipline: Test w Purpose: Testing focuses primarily on the evaluation or assessment of quality realized through a number of core practices: § Finding and documenting defects in software quality. § Generally advising about perceived software quality. § Proving the validity of the assumptions made in design and requirement specifications through concrete demonstration. § Validating the software product functions as designed. § Validating that the requirements have been implemented appropriately. w Test discipline acts in many respects as a service provider to the other disciplines. Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 17
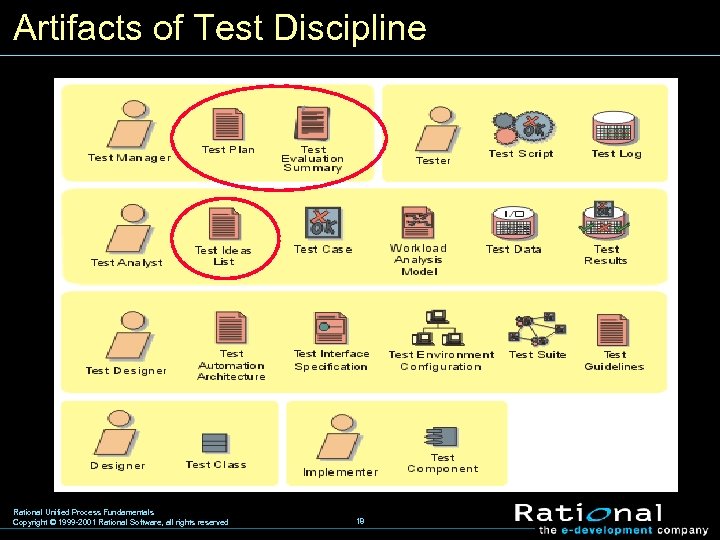 Artifacts of Test Discipline Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 18
Artifacts of Test Discipline Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 18
 Workflow Detail: Define Evaluation Mission Roles responsible for related activities: §Test Manager (mainly) §Test Analyst §Test Designer For each Iteration: § Identify the objectives for and deliverables of the testing effort § Identify a good utilization strategy for test resources § Define the scope and boundaries for the test effort § Outline the approach that will be used Define Evaluation Mission Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved § Define how progress will be monitored and assessed 19
Workflow Detail: Define Evaluation Mission Roles responsible for related activities: §Test Manager (mainly) §Test Analyst §Test Designer For each Iteration: § Identify the objectives for and deliverables of the testing effort § Identify a good utilization strategy for test resources § Define the scope and boundaries for the test effort § Outline the approach that will be used Define Evaluation Mission Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved § Define how progress will be monitored and assessed 19
 Concept: Test Automation and Tools w Data acquisition tools w Static measurement tools w Dynamic measurement tools w Simulators or Drivers w Test management tools Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 20
Concept: Test Automation and Tools w Data acquisition tools w Static measurement tools w Dynamic measurement tools w Simulators or Drivers w Test management tools Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 20
 Discipline: Implementation w The purposes of Implementation are: § To implement classes and objects in terms of components § To define the organization of the components in terms of implementation subsystems § To test the developed components as units § To create an executable system w Implementation results in an Implementation Model Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 21
Discipline: Implementation w The purposes of Implementation are: § To implement classes and objects in terms of components § To define the organization of the components in terms of implementation subsystems § To test the developed components as units § To create an executable system w Implementation results in an Implementation Model Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 21
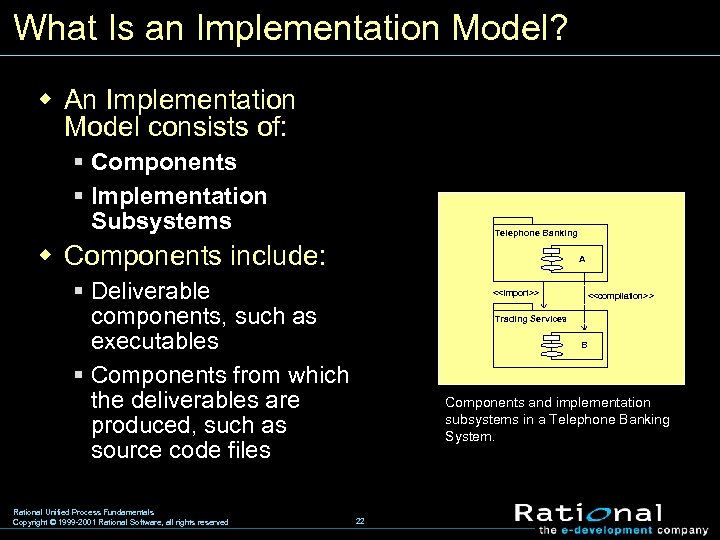 What Is an Implementation Model? w An Implementation Model consists of: § Components § Implementation Subsystems Telephone Banking w Components include: A § Deliverable components, such as executables § Components from which the deliverables are produced, such as source code files Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved <
What Is an Implementation Model? w An Implementation Model consists of: § Components § Implementation Subsystems Telephone Banking w Components include: A § Deliverable components, such as executables § Components from which the deliverables are produced, such as source code files Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved <
 Concept: Build w Operational version of a system or part of a system w Demonstrates a subset of the capabilities provided in the final product w Integral part of the iterative lifecycle w Provides review points w Helps uncover integration problems as soon as they are introduced Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 23
Concept: Build w Operational version of a system or part of a system w Demonstrates a subset of the capabilities provided in the final product w Integral part of the iterative lifecycle w Provides review points w Helps uncover integration problems as soon as they are introduced Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 23
 Discipline: Deployment w Purpose: Manage the activities associated with ensuring that the software product is available for its end users, such as: § Product deployment § Testing at the installation and target sites § Beta testing § Creating end-user support material § Creating user training material § Releasing to customer (in the form of shrinkwrapped package, download site, etc. ) Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 24
Discipline: Deployment w Purpose: Manage the activities associated with ensuring that the software product is available for its end users, such as: § Product deployment § Testing at the installation and target sites § Beta testing § Creating end-user support material § Creating user training material § Releasing to customer (in the form of shrinkwrapped package, download site, etc. ) Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 24
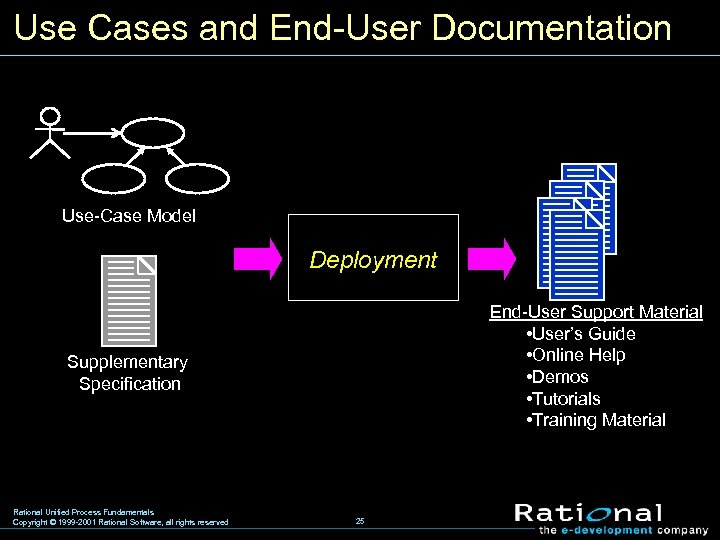 Use Cases and End-User Documentation Use-Case Model Deployment End-User Support Material • User’s Guide • Online Help • Demos • Tutorials • Training Material Supplementary Specification Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 25
Use Cases and End-User Documentation Use-Case Model Deployment End-User Support Material • User’s Guide • Online Help • Demos • Tutorials • Training Material Supplementary Specification Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 25
 Discipline: Configuration & Change Management w Purpose: Track and maintain integrity of project artifacts § Change control § Configuration identification and management § Configuration status accounting § Change tracking § Version selection § Software manufacture § Workspace management Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 26
Discipline: Configuration & Change Management w Purpose: Track and maintain integrity of project artifacts § Change control § Configuration identification and management § Configuration status accounting § Change tracking § Version selection § Software manufacture § Workspace management Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 26
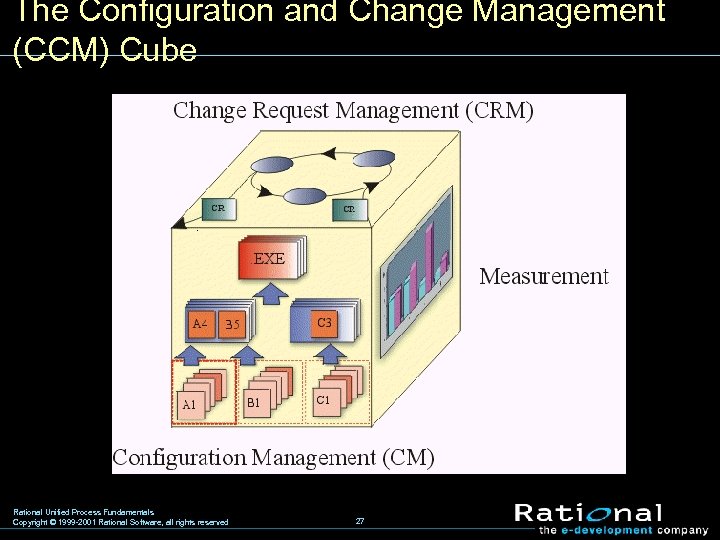 The Configuration and Change Management (CCM) Cube Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 27
The Configuration and Change Management (CCM) Cube Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 27
 Configuration Management (CM) w Describes the product structure (logically correct configurations) w Identifies which artifacts are to be tracked w Identifies dependencies among artifacts w Maintaining traceability between artifacts w Isolate individual and team workspaces Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 28
Configuration Management (CM) w Describes the product structure (logically correct configurations) w Identifies which artifacts are to be tracked w Identifies dependencies among artifacts w Maintaining traceability between artifacts w Isolate individual and team workspaces Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 28
 Change Request Management (CRM) Addresses: w The capture and management of requested changes to one or more artifacts by various stakeholders. § A change request has a lifecycle: new, logged, approved, assigned and complete. § Not all change requests are acted on. The potential impact of a proposed change determines if it will be acted on. Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 29
Change Request Management (CRM) Addresses: w The capture and management of requested changes to one or more artifacts by various stakeholders. § A change request has a lifecycle: new, logged, approved, assigned and complete. § Not all change requests are acted on. The potential impact of a proposed change determines if it will be acted on. Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 29
 Configuration Status Accounting w This type of accounting describes the state of the product based on the type, number, rate, and severity of defects found and fixed during the course of product development. w Metrics derived under this aspect, either through audits or raw data, are useful in determining the overall completeness status of the project. w Problem areas that require attention Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 30
Configuration Status Accounting w This type of accounting describes the state of the product based on the type, number, rate, and severity of defects found and fixed during the course of product development. w Metrics derived under this aspect, either through audits or raw data, are useful in determining the overall completeness status of the project. w Problem areas that require attention Rational Unified Process Fundamentals Copyright © 1999 -2001 Rational Software, all rights reserved 30


