624c4ccd5c23e89fdb612b59cbcbb604.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 28
 Ratio Analysis and Valuation n Valuation theory n n n ROE disaggregation into RNOA and financial returns n n n Discounted free cash flows Residual income ROE - Identifying and Computing Operating Working Capital and Operating Assets exercise ROE Disaggregation (P&G) exercise Pfizer (PFE) valuation exercise Margin and Turnover EVA © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
Ratio Analysis and Valuation n Valuation theory n n n ROE disaggregation into RNOA and financial returns n n n Discounted free cash flows Residual income ROE - Identifying and Computing Operating Working Capital and Operating Assets exercise ROE Disaggregation (P&G) exercise Pfizer (PFE) valuation exercise Margin and Turnover EVA © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
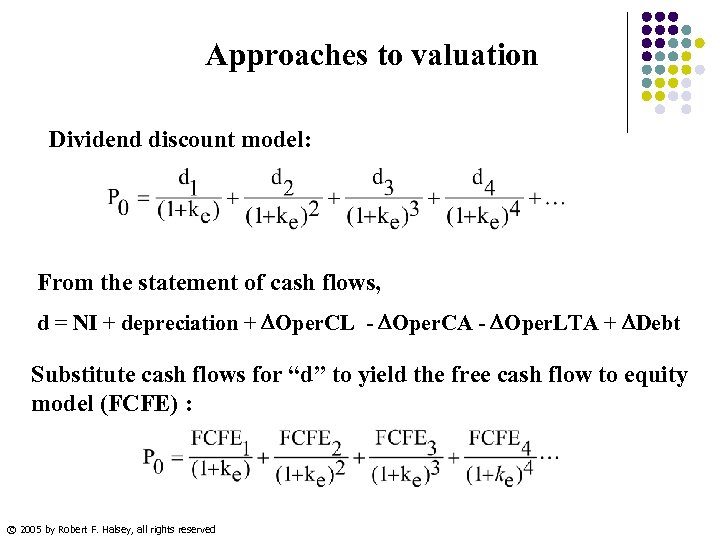 Approaches to valuation Dividend discount model: From the statement of cash flows, d = NI + depreciation + Oper. CL - Oper. CA - Oper. LTA + Debt Substitute cash flows for “d” to yield the free cash flow to equity model (FCFE) : © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
Approaches to valuation Dividend discount model: From the statement of cash flows, d = NI + depreciation + Oper. CL - Oper. CA - Oper. LTA + Debt Substitute cash flows for “d” to yield the free cash flow to equity model (FCFE) : © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
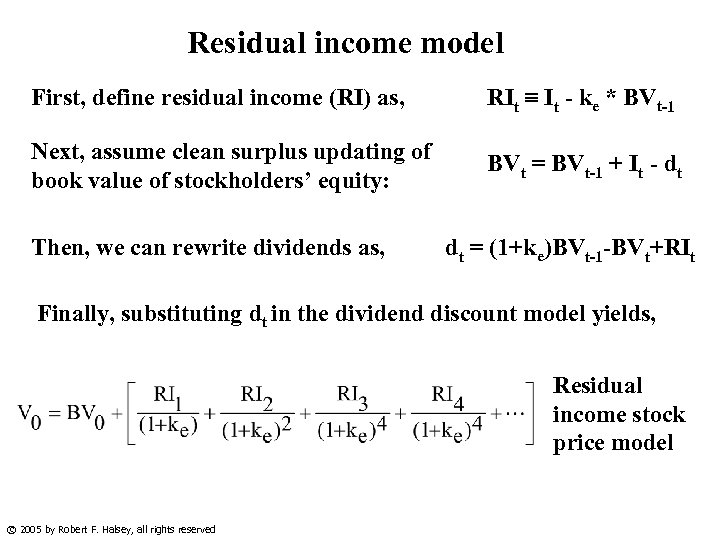 Residual income model First, define residual income (RI) as, RIt It - ke * BVt-1 Next, assume clean surplus updating of book value of stockholders’ equity: BVt = BVt-1 + It - dt Then, we can rewrite dividends as, dt = (1+ke)BVt-1 -BVt+RIt Finally, substituting dt in the dividend discount model yields, Residual income stock price model © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
Residual income model First, define residual income (RI) as, RIt It - ke * BVt-1 Next, assume clean surplus updating of book value of stockholders’ equity: BVt = BVt-1 + It - dt Then, we can rewrite dividends as, dt = (1+ke)BVt-1 -BVt+RIt Finally, substituting dt in the dividend discount model yields, Residual income stock price model © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
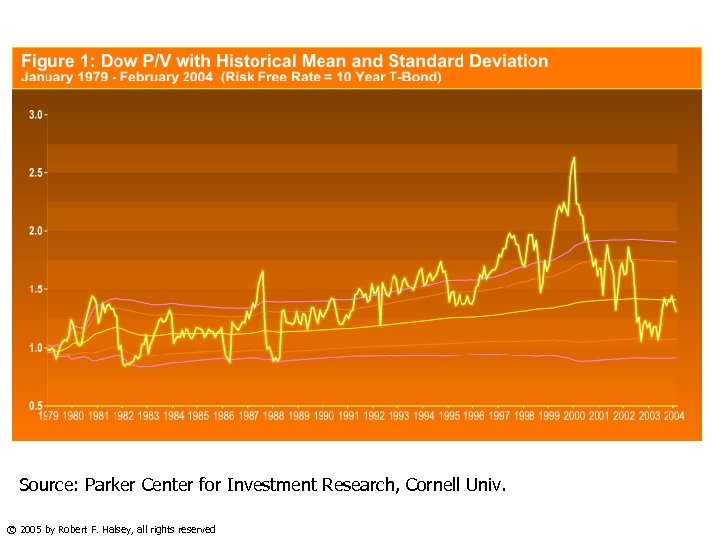 Source: Parker Center for Investment Research, Cornell Univ. © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
Source: Parker Center for Investment Research, Cornell Univ. © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
 FCF and RI models n n The FCF and RI models are theoretically equivalent since both are derived from the dividend discount model. They will, therefore, yield the same valuation in a steady state (constant RNOA) FCF defines value in terms of cash flows. RI defines value in terms of accrual accounting (earnings and book values) © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
FCF and RI models n n The FCF and RI models are theoretically equivalent since both are derived from the dividend discount model. They will, therefore, yield the same valuation in a steady state (constant RNOA) FCF defines value in terms of cash flows. RI defines value in terms of accrual accounting (earnings and book values) © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
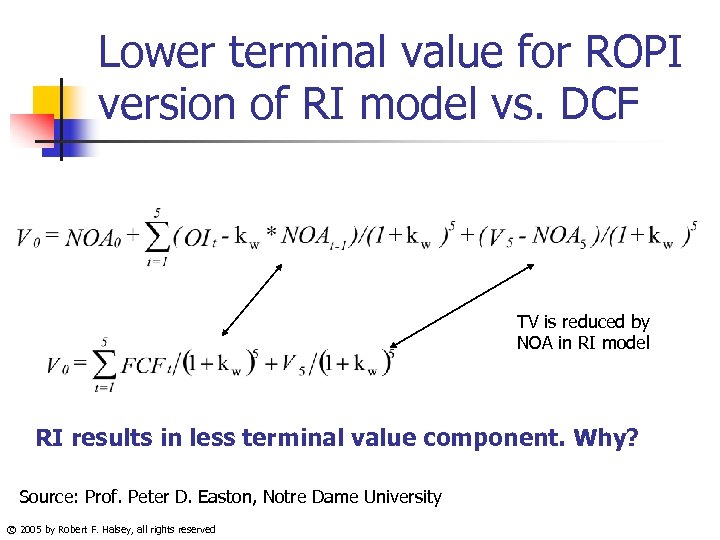 Lower terminal value for ROPI version of RI model vs. DCF TV is reduced by NOA in RI model RI results in less terminal value component. Why? Source: Prof. Peter D. Easton, Notre Dame University © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
Lower terminal value for ROPI version of RI model vs. DCF TV is reduced by NOA in RI model RI results in less terminal value component. Why? Source: Prof. Peter D. Easton, Notre Dame University © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
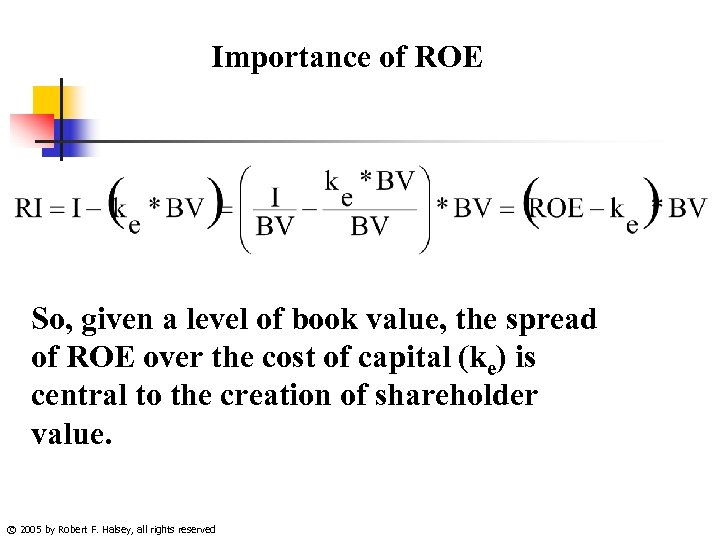 Importance of ROE So, given a level of book value, the spread of ROE over the cost of capital (ke) is central to the creation of shareholder value. © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
Importance of ROE So, given a level of book value, the spread of ROE over the cost of capital (ke) is central to the creation of shareholder value. © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
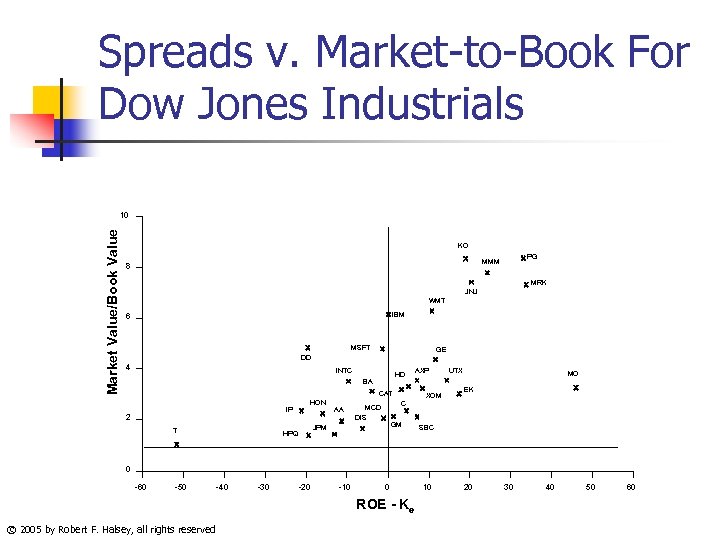 Spreads v. Market-to-Book For Dow Jones Industrials Market Value/Book Value 10 KO PG MMM 8 MRK JNJ WMT IBM 6 MSFT GE DD 4 INTC HD BA CAT IP 2 HON AA C MCD DIS T GM JPM HPQ AXP XOM UTX MO EK SBC 0 -60 -50 -40 -30 -20 -10 0 ROE - Ke © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved 10 20 30 40 50 60
Spreads v. Market-to-Book For Dow Jones Industrials Market Value/Book Value 10 KO PG MMM 8 MRK JNJ WMT IBM 6 MSFT GE DD 4 INTC HD BA CAT IP 2 HON AA C MCD DIS T GM JPM HPQ AXP XOM UTX MO EK SBC 0 -60 -50 -40 -30 -20 -10 0 ROE - Ke © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved 10 20 30 40 50 60
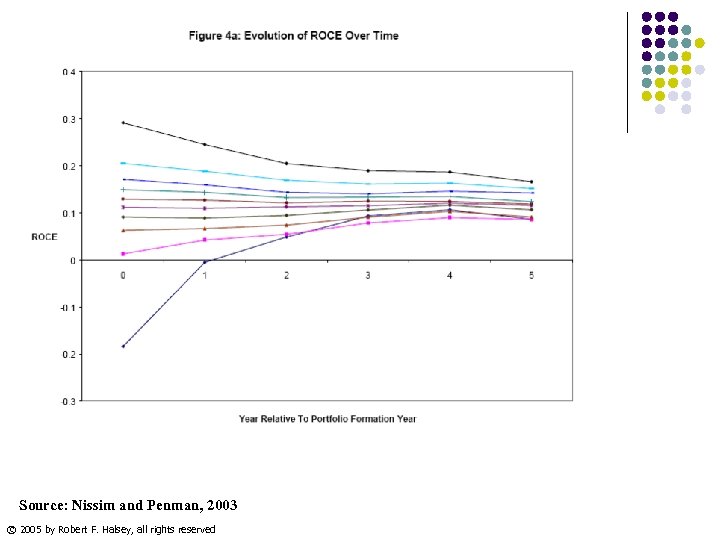 Source: Nissim and Penman, 2003 © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
Source: Nissim and Penman, 2003 © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
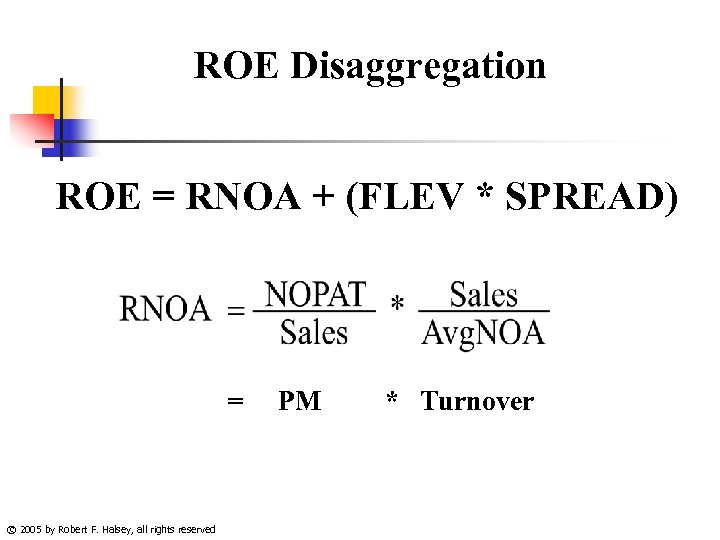 ROE Disaggregation ROE = RNOA + (FLEV * SPREAD) = © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved PM * Turnover
ROE Disaggregation ROE = RNOA + (FLEV * SPREAD) = © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved PM * Turnover
 Exercises ROE - Identifying and Computing Operating Working Capital and Operating Assets exercise ROE Disaggregation (P&G) exercise Pfizer (PFE) valuation exercise © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
Exercises ROE - Identifying and Computing Operating Working Capital and Operating Assets exercise ROE Disaggregation (P&G) exercise Pfizer (PFE) valuation exercise © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
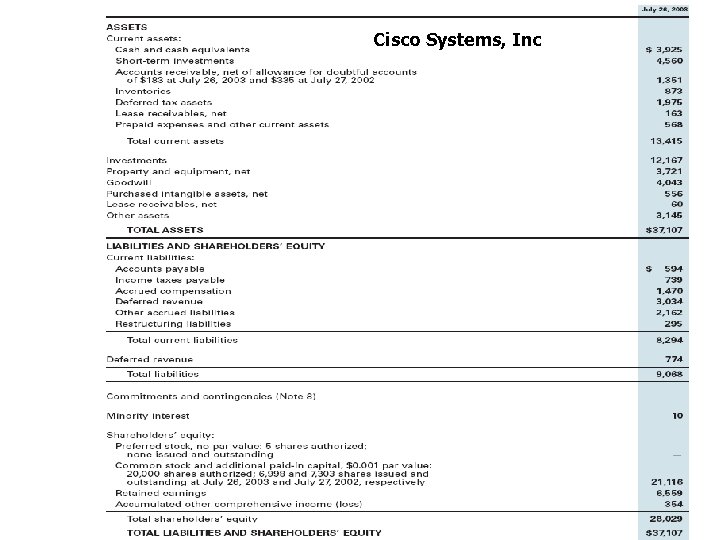 Cisco Systems, Inc
Cisco Systems, Inc
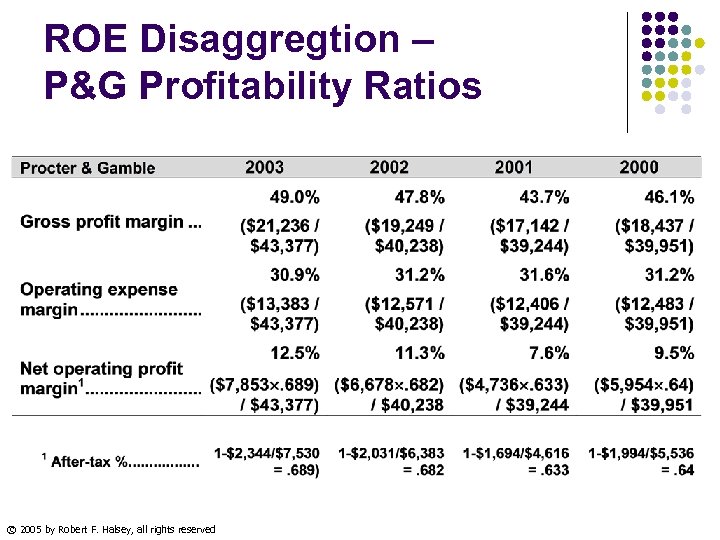 ROE Disaggregtion – P&G Profitability Ratios © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
ROE Disaggregtion – P&G Profitability Ratios © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
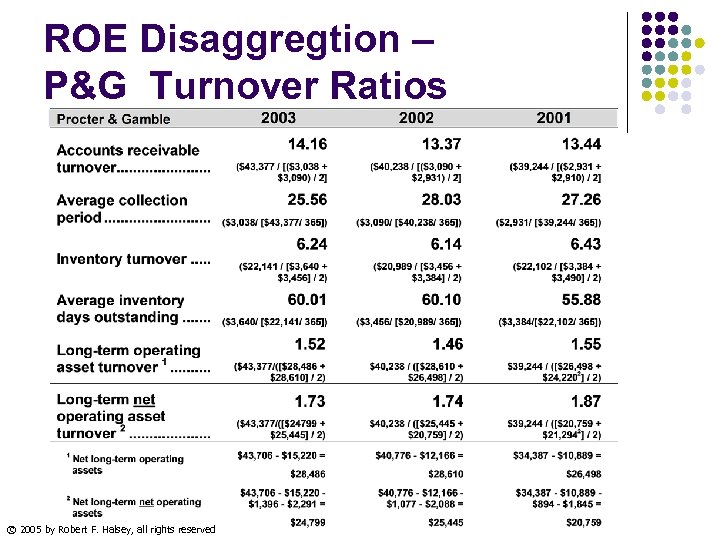 ROE Disaggregtion – P&G Turnover Ratios © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
ROE Disaggregtion – P&G Turnover Ratios © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
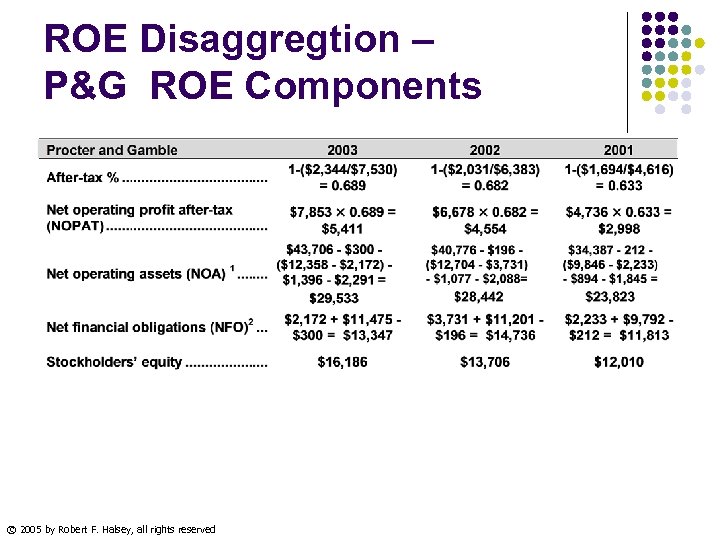 ROE Disaggregtion – P&G ROE Components © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
ROE Disaggregtion – P&G ROE Components © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
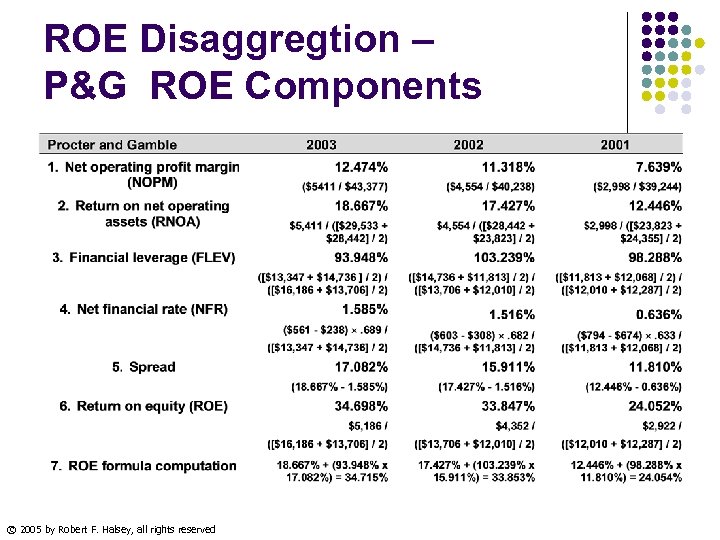 ROE Disaggregtion – P&G ROE Components © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
ROE Disaggregtion – P&G ROE Components © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
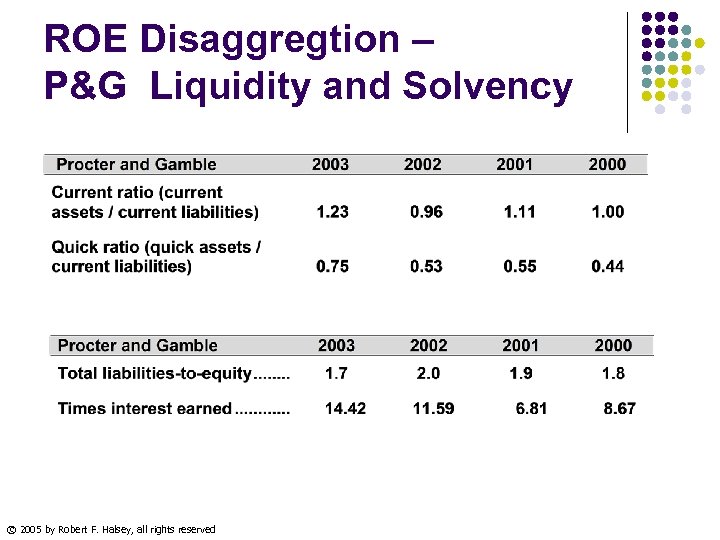 ROE Disaggregtion – P&G Liquidity and Solvency © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
ROE Disaggregtion – P&G Liquidity and Solvency © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
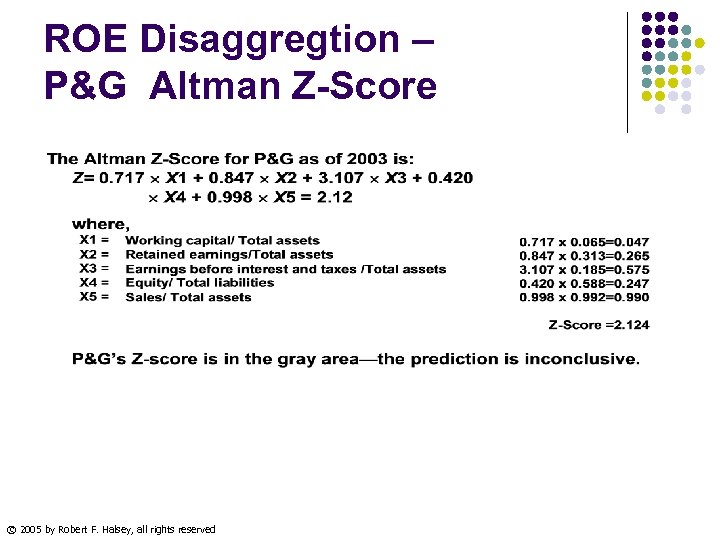 ROE Disaggregtion – P&G Altman Z-Score © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
ROE Disaggregtion – P&G Altman Z-Score © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
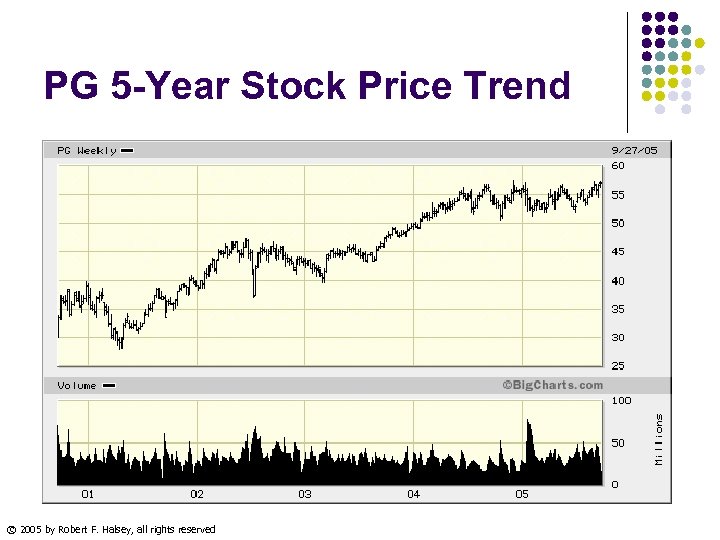 PG 5 -Year Stock Price Trend © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
PG 5 -Year Stock Price Trend © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
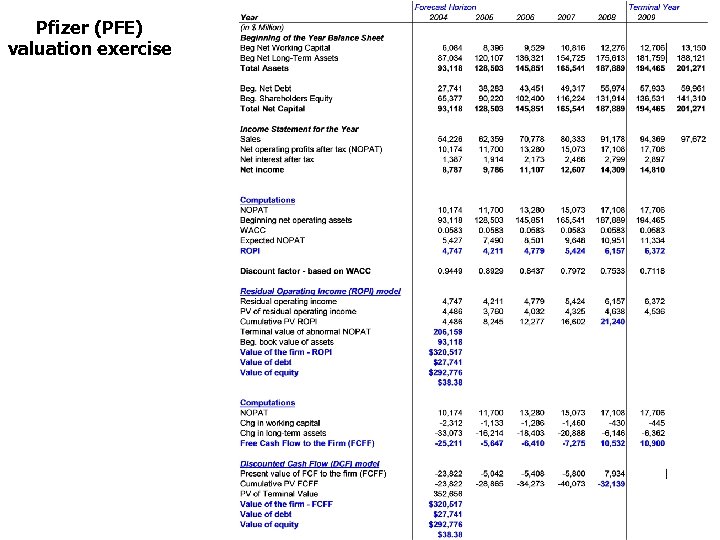 Pfizer (PFE) valuation exercise
Pfizer (PFE) valuation exercise
 ROE Disaggregation Empirical Findings Definition: ROE = RNOA + LEV × Spread Median 12. 2% ≈ 10. 3% + 0. 40 × 3. 3% n n Companies are, on average, conservatively financed (LEV<1. 0). They earn, on average, a positive spread on borrowed monies. RNOA is, on average, approximately 84% of reported ROE. All industries that survive must earn a combination of operating and financial returns that meet shareholder expectations. © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
ROE Disaggregation Empirical Findings Definition: ROE = RNOA + LEV × Spread Median 12. 2% ≈ 10. 3% + 0. 40 × 3. 3% n n Companies are, on average, conservatively financed (LEV<1. 0). They earn, on average, a positive spread on borrowed monies. RNOA is, on average, approximately 84% of reported ROE. All industries that survive must earn a combination of operating and financial returns that meet shareholder expectations. © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
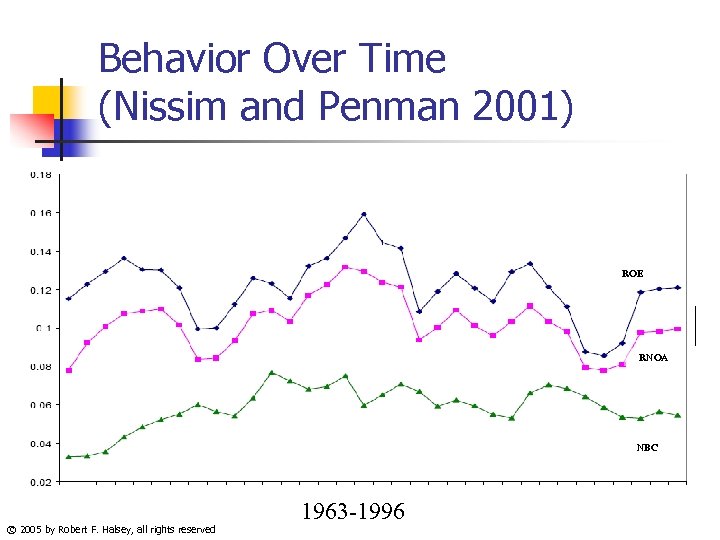 Behavior Over Time (Nissim and Penman 2001) ROE RNOA NBC © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved 1963 -1996
Behavior Over Time (Nissim and Penman 2001) ROE RNOA NBC © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved 1963 -1996
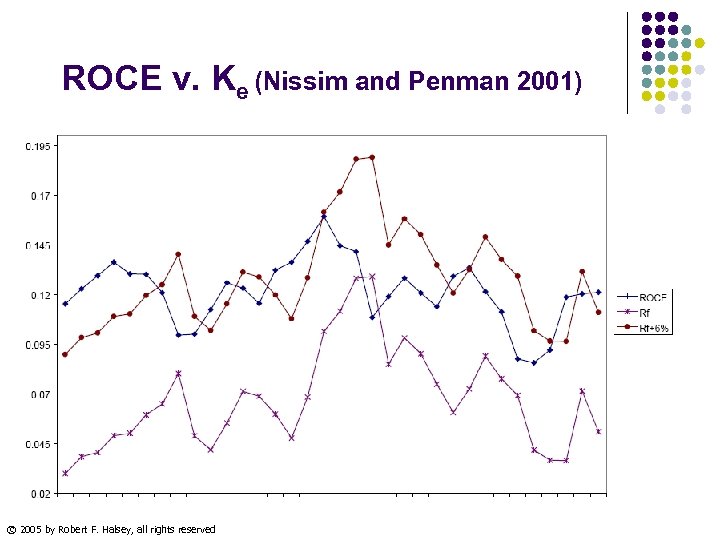 ROCE v. Ke (Nissim and Penman 2001) © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
ROCE v. Ke (Nissim and Penman 2001) © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
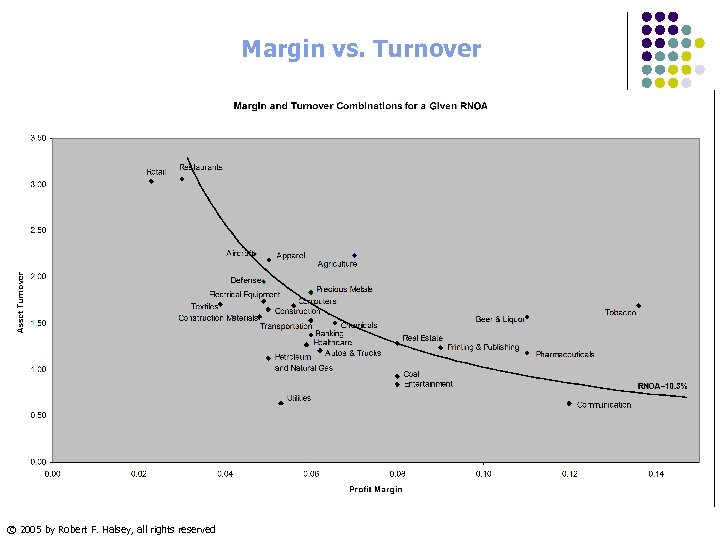 Margin vs. Turnover © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
Margin vs. Turnover © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
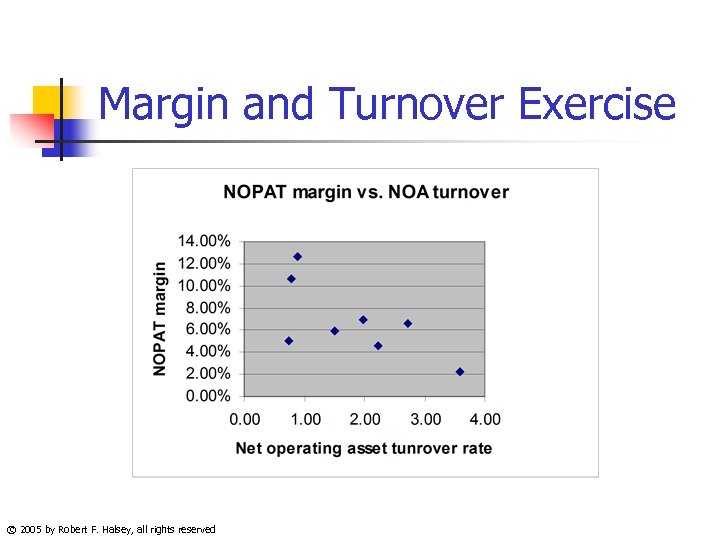 Margin and Turnover Exercise © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
Margin and Turnover Exercise © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
 Compare RI with Economic Value Added TM (“EVA”) Under EVA, MV = capital + PV of future EVA, where EVA 1 = NOPAT 1 - kwacc*capital 0 © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
Compare RI with Economic Value Added TM (“EVA”) Under EVA, MV = capital + PV of future EVA, where EVA 1 = NOPAT 1 - kwacc*capital 0 © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
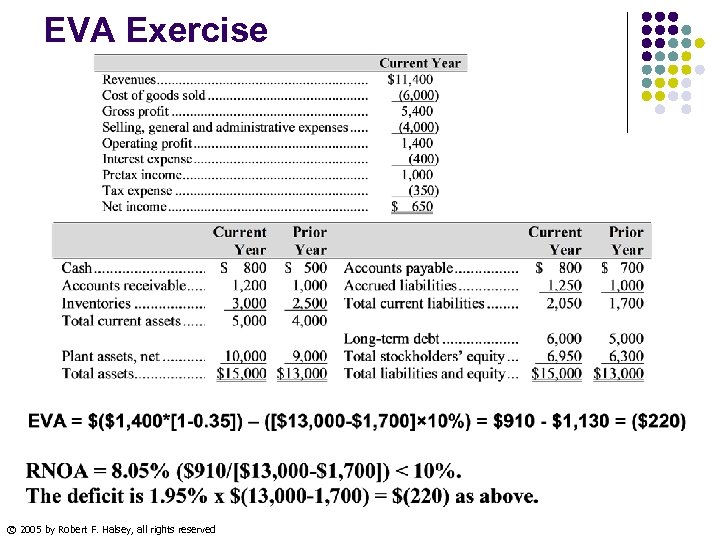 EVA Exercise © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
EVA Exercise © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
 EVA Exercise – Areas for Improvement © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved
EVA Exercise – Areas for Improvement © 2005 by Robert F. Halsey, all rights reserved


