1471e64d09df31052a493775760447c7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 13

Ratification Matters: The Domestic Fate of Bilateral Investment Treaties Yoram Z. Haftel U. of Illinois-Chicago yhaftel@uic. edu Alexander Thompson Ohio State University Thompson. 1191@osu. edu The annual national conference of the International Political Economy Society Philadelphia, November 14 -15, 2008

Question • Why are some treaties signed and then ratified quickly, while others languish at the domestic level or are never ratified at all? • What explains variation in the time between signature and mutual ratification of bilateral investment treaties (BITs)

Why Ratification Matters • A key but overlooked stage of cooperation • Unique strategic problems at nexus of domestic and international levels • Signature and ratification perform distinct functions, legally and politically

Hypotheses • Formal Legislative Hurdles – Greater legal hurdles lengthen time to ratification • Domestic Political Constraints – Greater constraints on executive lengthen time to ratification • Rational Anticipation – Ratification obstacles anticipated before or during negotiation stage – Constraints have no bearing on ratification or may even decrease time to ratification

BITs’ Entry into Force • 1, 745 BITs from 1959 to 1999 • 1, 233 (70%) in force by 1999 – Mean time to mutual ratification: 1. 76 years • 512 BITs not in force by 1999 – Mean time since conclusion: 2. 53 years

Data and Research Design • Event history (Cox Proportional Hazard) • DV: spell of mutual ratification • IVs: – Legislative hurdles (Hathaway 2008) – Political constraints – Democracy – Common law • Control variables (Elkins et al. 2006)
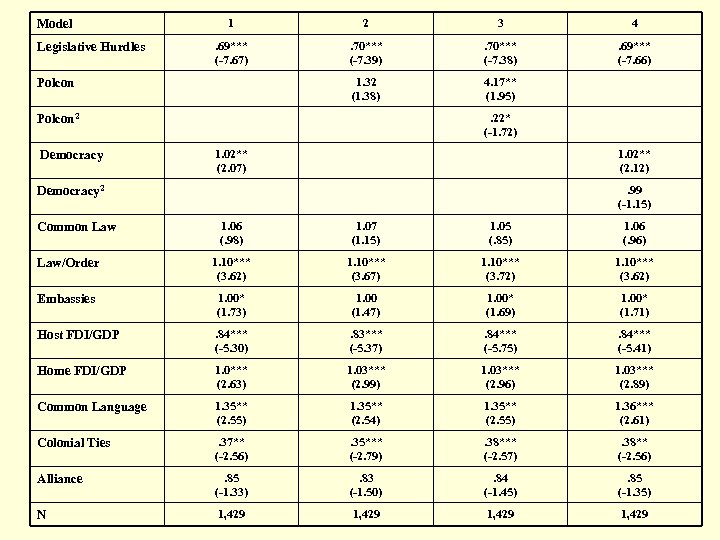
Model Legislative Hurdles 1 2 3 4 . 69*** (-7. 67) . 70*** (-7. 39) . 70*** (-7. 38) . 69*** (-7. 66) 1. 32 (1. 38) 4. 17** (1. 95) Polcon . 22* (-1. 72) Polcon 2 Democracy 1. 02** (2. 07) 1. 02** (2. 12). 99 (-1. 15) Democracy 2 1. 06 (. 98) 1. 07 (1. 15) 1. 05 (. 85) 1. 06 (. 96) Law/Order 1. 10*** (3. 62) 1. 10*** (3. 67) 1. 10*** (3. 72) 1. 10*** (3. 62) Embassies 1. 00* (1. 73) 1. 00 (1. 47) 1. 00* (1. 69) 1. 00* (1. 71) Host FDI/GDP . 84*** (-5. 30) . 83*** (-5. 37) . 84*** (-5. 75) . 84*** (-5. 41) Home FDI/GDP 1. 0*** (2. 63) 1. 03*** (2. 99) 1. 03*** (2. 96) 1. 03*** (2. 89) Common Language 1. 35** (2. 55) 1. 35** (2. 54) 1. 35** (2. 55) 1. 36*** (2. 61) Colonial Ties . 37** (-2. 56) . 35*** (-2. 79) . 38*** (-2. 57) . 38** (-2. 56) Alliance . 85 (-1. 33) . 83 (-1. 50) . 84 (-1. 45) . 85 (-1. 35) N 1, 429 Common Law
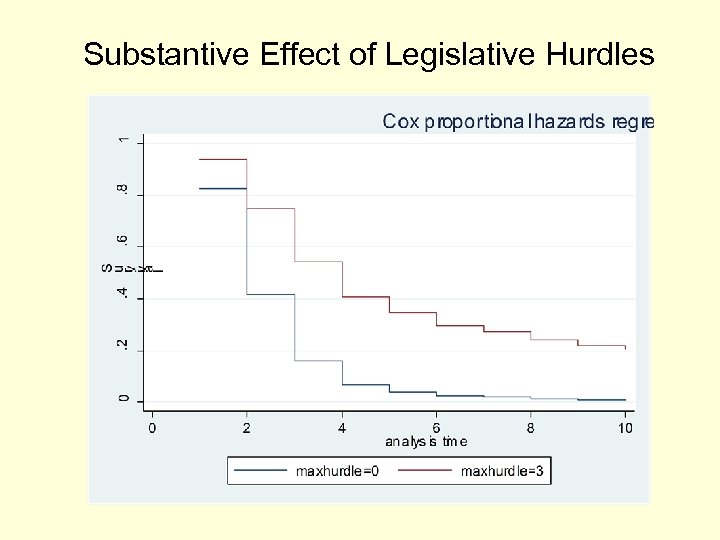
Substantive Effect of Legislative Hurdles

Conclusion • Formal legal hurdles clearly matter • Mixed findings on domestic political constraints; democracy may even speed ratification • Rational anticipation: Transparent countries with high capacity effectively anticipate and address ratification obstacles • Much work remains – National ratification dates – Role of treaty design (sovereignty costs, scope)
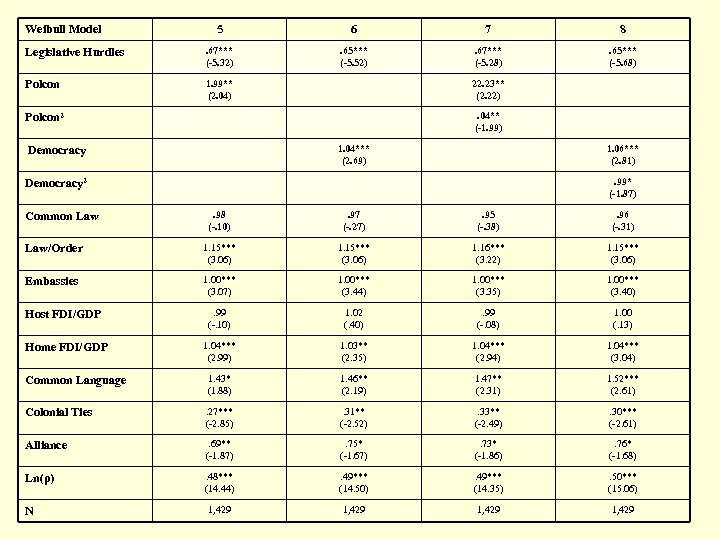
Weibull Model 5 6 7 8 Legislative Hurdles . 67*** (-5. 32) . 65*** (-5. 52) . 67*** (-5. 28) . 65*** (-5. 68) Polcon 1. 99** (2. 04) 22. 23** (2. 22). 04** (-1. 99) Polcon 2 1. 04*** (2. 69) Democracy 1. 06*** (2. 81). 99* (-1. 87) Democracy 2. 98 (-. 10) . 97 (-. 27) . 95 (-. 38) . 96 (-. 31) Law/Order 1. 15*** (3. 06) 1. 16*** (3. 22) 1. 15*** (3. 06) Embassies 1. 00*** (3. 07) 1. 00*** (3. 44) 1. 00*** (3. 35) 1. 00*** (3. 40) . 99 (-. 10) 1. 02 (. 40) . 99 (-. 08) 1. 00 (. 13) 1. 04*** (2. 99) 1. 03** (2. 35) 1. 04*** (2. 94) 1. 04*** (3. 04) Common Language 1. 43* (1. 88) 1. 46** (2. 19) 1. 47** (2. 31) 1. 52*** (2. 61) Colonial Ties . 27*** (-2. 85) . 31** (-2. 52) . 33** (-2. 49) . 30*** (-2. 61) Alliance . 69** (-1. 87) . 75* (-1. 67) . 73* (-1. 86) . 76* (-1. 68) Ln(ρ) . 48*** (14. 44) . 49*** (14. 50) . 49*** (14. 35) . 50*** (15. 06) 1, 429 Common Law Host FDI/GDP Home FDI/GDP N
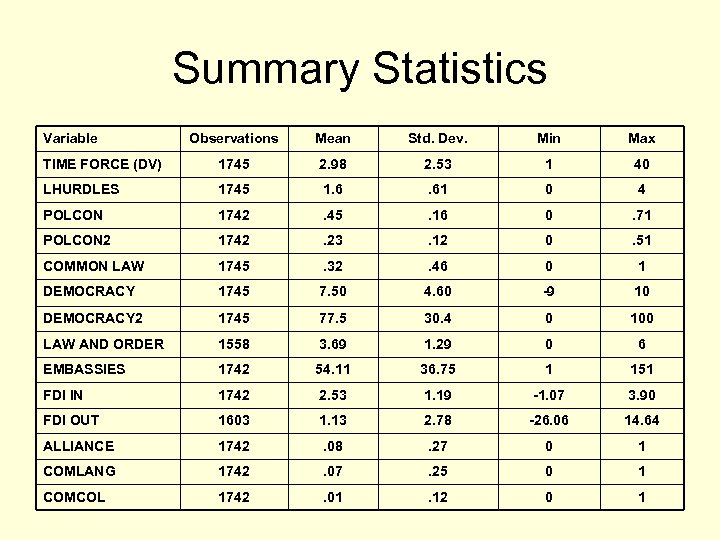
Summary Statistics Variable Observations Mean Std. Dev. Min Max TIME FORCE (DV) 1745 2. 98 2. 53 1 40 LHURDLES 1745 1. 6 . 61 0 4 POLCON 1742 . 45 . 16 0 . 71 POLCON 2 1742 . 23 . 12 0 . 51 COMMON LAW 1745 . 32 . 46 0 1 DEMOCRACY 1745 7. 50 4. 60 -9 10 DEMOCRACY 2 1745 77. 5 30. 4 0 100 LAW AND ORDER 1558 3. 69 1. 29 0 6 EMBASSIES 1742 54. 11 36. 75 1 151 FDI IN 1742 2. 53 1. 19 -1. 07 3. 90 FDI OUT 1603 1. 13 2. 78 -26. 06 14. 64 ALLIANCE 1742 . 08 . 27 0 1 COMLANG 1742 . 07 . 25 0 1 COMCOL 1742 . 01 . 12 0 1
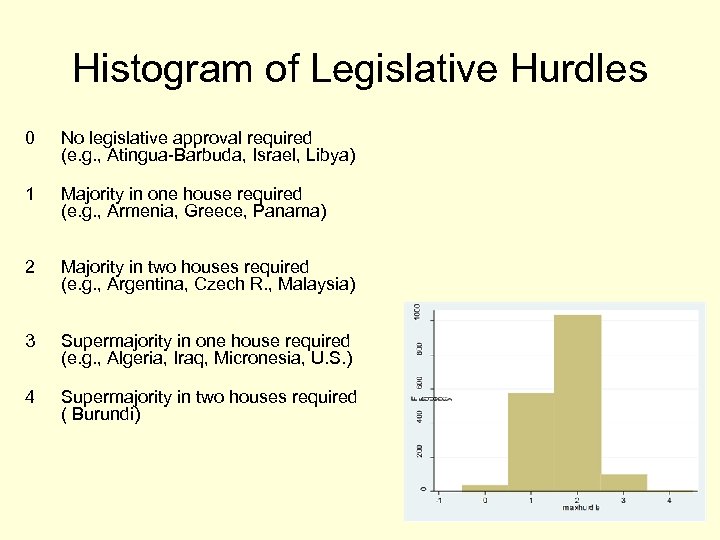
Histogram of Legislative Hurdles 0 No legislative approval required (e. g. , Atingua-Barbuda, Israel, Libya) 1 Majority in one house required (e. g. , Armenia, Greece, Panama) 2 Majority in two houses required (e. g. , Argentina, Czech R. , Malaysia) 3 Supermajority in one house required (e. g. , Algeria, Iraq, Micronesia, U. S. ) 4 Supermajority in two houses required ( Burundi)
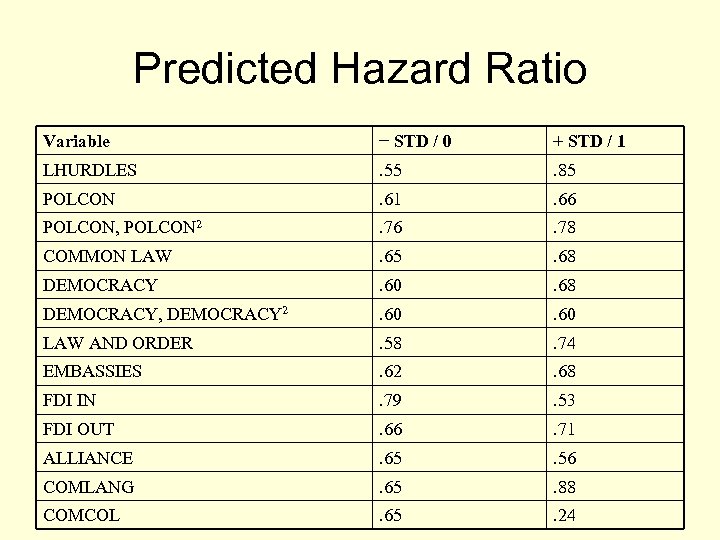
Predicted Hazard Ratio Variable − STD / 0 + STD / 1 LHURDLES . 55 . 85 POLCON . 61 . 66 POLCON, POLCON 2 . 76 . 78 COMMON LAW . 65 . 68 DEMOCRACY . 60 . 68 DEMOCRACY, DEMOCRACY 2 . 60 LAW AND ORDER . 58 . 74 EMBASSIES . 62 . 68 FDI IN . 79 . 53 FDI OUT . 66 . 71 ALLIANCE . 65 . 56 COMLANG . 65 . 88 COMCOL . 65 . 24
1471e64d09df31052a493775760447c7.ppt