6999e7821f06cd86c461521b7645d7d0.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 14
Rapid Prototyping
Team Members 08 MCD 002 D V SYAMALA GAYATRI 08 MCD 003 HARIPRANEETH E 08 MCD 004 HARSHA K 08 MCD 005 JAGADISHKUMAR R 08 MCD 008 JEEVA P A 08 MCD 009 KALLURI JAYA PRAKASH 08 MCD 010 LOGESH M
Introduction • Rapid Prototyping (RP) techniques are methods that allow designers to produce physical prototypes quickly. • It consists of various manufacturing processes by which a solid physical model of part is made directly from 3 D CAD model data without any special tooling. • The first commercial rapid prototyping process was brought on the market in 1987. • Nowadays, more than 30 different processes (not all commercialized) with high accuracy and a large choice of materials exist. • These processes are classified in different ways: by materials used, by energy used, by lighting of photopolymers, or by typical application range. 08 MCD 005
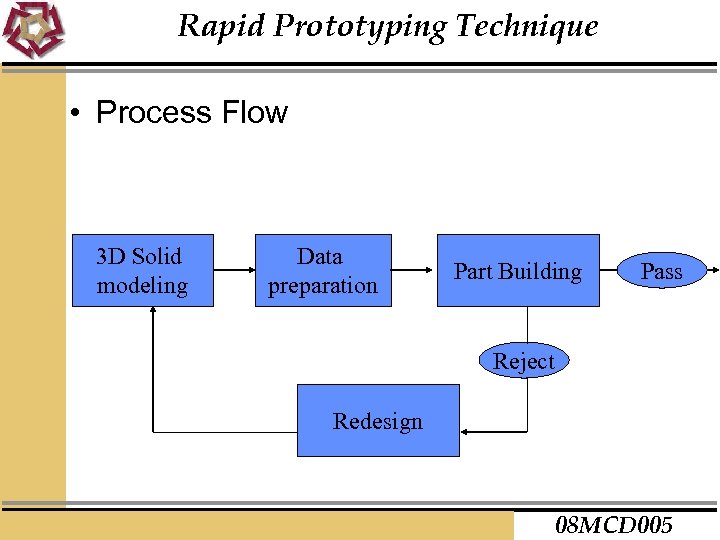
Rapid Prototyping Technique • Process Flow 3 D Solid modeling Data preparation Part Building Pass Reject Redesign 08 MCD 005
Prototyping- What is it ? . Physical Model of the product. Degrees of Prototyping. Full Complete scale Model - functional model. Scaled Model - functional/ simulated material. Geometrical configuration 08 MCD 008
Prototyping- Why? Ù Visualization Ù Design Change Ù Complex Object Fabrication Ù Testing Fit/ Packaging Ù Cost, Time, and Resource estimation Ù Process Planning Ù First to Market -- Critical for today’s industry Ù JIT concept (0 Inventory) Ù Rapid tooling / no tooling -- trend in technology 08 MCD 008
Rapid Prototyping Processes Ù SLS --- Selective Laser Sintering Ù SLA --- Stereolithography Ù LOM --- Laminated Object Manufacturing Ù FDM --- Fused Deposition Modeling Ù Others 08 MCD 008
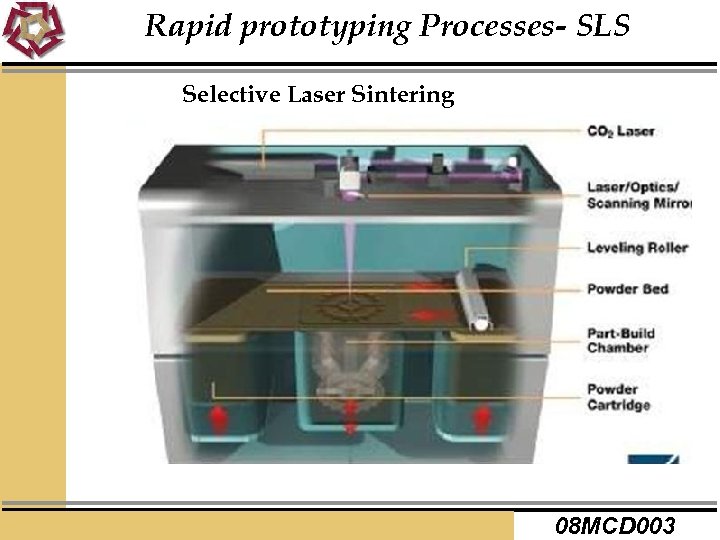
Rapid prototyping Processes- SLS Selective Laser Sintering 08 MCD 003
Rapid prototyping Processes- SLS Application Range Ø Visual Representation models Ø Functional and tough prototypes Ø cast metal parts Advantages Ø Flexibility of materials used Ø No need to create a structure to support the part Ø Parts do not require any post curing except when ceramic is used. Disadvantages Ø During solidification, additional powder may be hardened at the border line. Ø The roughness is most visible when parts contain sloping (stepped) surfaces. 08 MCD 009
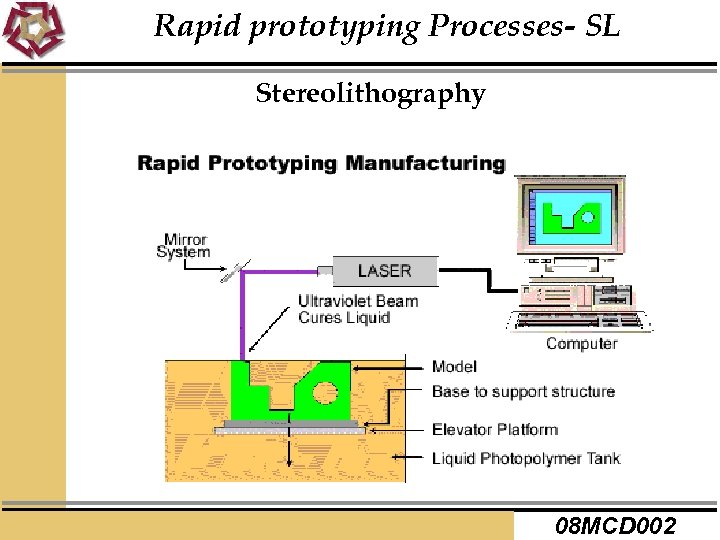
Rapid prototyping Processes- SL Stereolithography 08 MCD 002
Rapid prototyping Processes- SL Application Range Ø Parts used for functional tests Ø Manufacturing of medical models Ø Form –fit functions for assembly tests Advantages Ø Possibility of manufacturing parts which are impossible to be produced conventionally in a single process Ø Can be fully atomized and no supervision is required. Ø High Resolution Ø No geometric limitations Disadvantages Ø Necessity to have a support structure Ø Require labor for post processing and cleaning 08 MCD 010
Rapid prototyping Processes • Other Processes • Ballistic Particle Manufacturing (BPM) • This process uses a 3 D solid model data to direct streams of material at a target. • 3 D Printing • It creates parts by layered printing process. The layers are produced by adding a layer of powder to the top of a piston and cylinder containing a powder bed and the part is being fabricated. • Model Maker • It uses ink jet printer technology with 2 heads. One deposits building material, and the other deposits supporting wax. 08 MCD 004
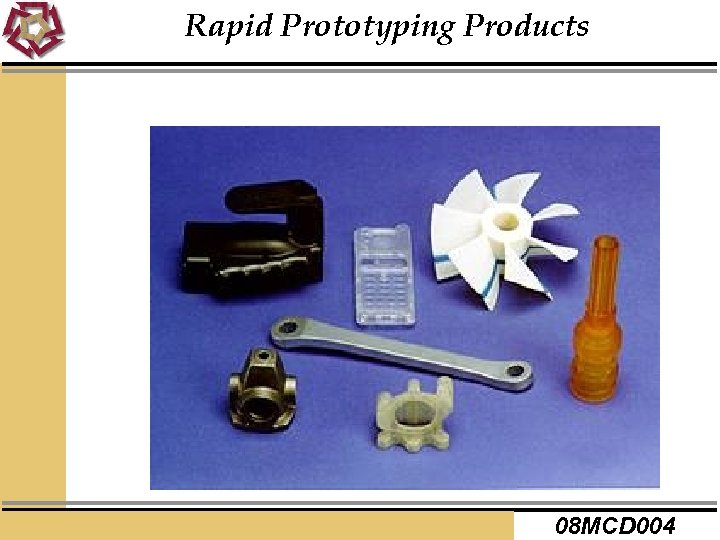

Rapid Prototyping Products 08 MCD 004

6999e7821f06cd86c461521b7645d7d0.ppt