1ef65c6e3d5745e75b7be4dd2d5b54a7.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 59

Rapid Hardening Systems By R. C. Greener

Which Would You Rather Buy? A or B

Benefits of Quick Hardening • Better Freshness and Quality • Smoother Ice Cream Texture • Less Carton Damage in Storage and Distribution Process • Less Chance of Product Skinning • Better Ice Cream Consistency Regardless of Package Size or Shape • Lower Labor and Handling Costs • Inventory reduction - Ship directly from Hardener

Costs to Harden Rapidly • More energy • Higher Capital Investment • Increased product shrinkage if design improper
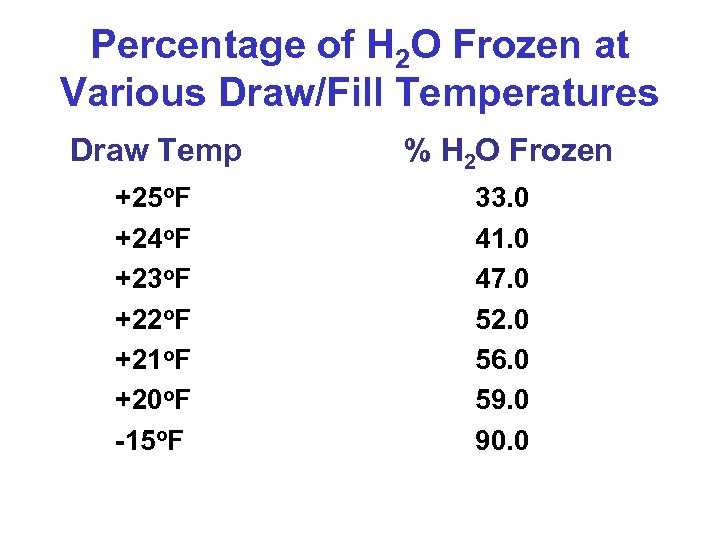
Percentage of H 2 O Frozen at Various Draw/Fill Temperatures Draw Temp % H 2 O Frozen +25 o. F +24 o. F +23 o. F +22 o. F +21 o. F +20 o. F -15 o. F 33. 0 41. 0 47. 0 52. 0 56. 0 59. 0 90. 0
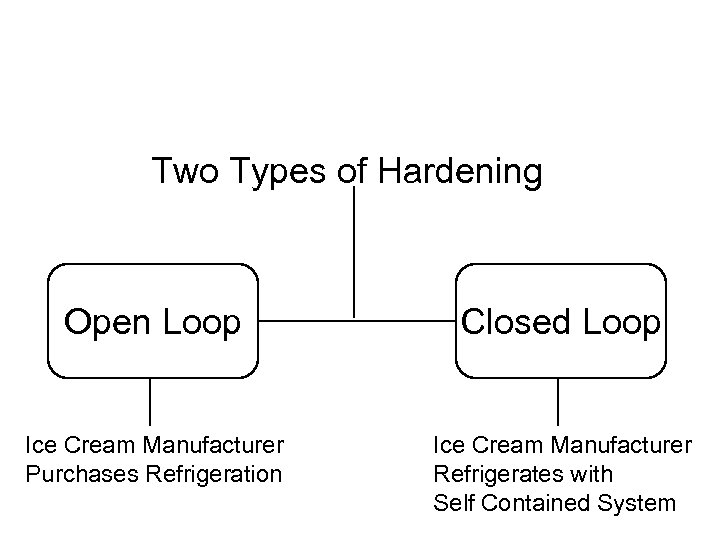
Two Types of Hardening Open Loop Closed Loop Ice Cream Manufacturer Purchases Refrigeration Ice Cream Manufacturer Refrigerates with Self Contained System
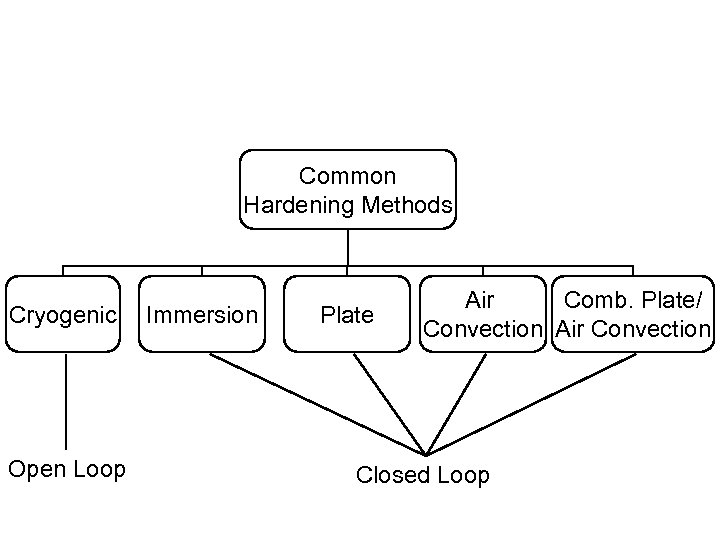
Common Hardening Methods Cryogenic Open Loop Immersion Plate Air Comb. Plate/ Convection Air Convection Closed Loop


Advantages of Cryogenic Hardening • Lowest retention time for ice cream novelties & cakes • Excellent ice cream texture • Allows surface setting of novelty item prior to wrapping • Superior overall quality for cake items
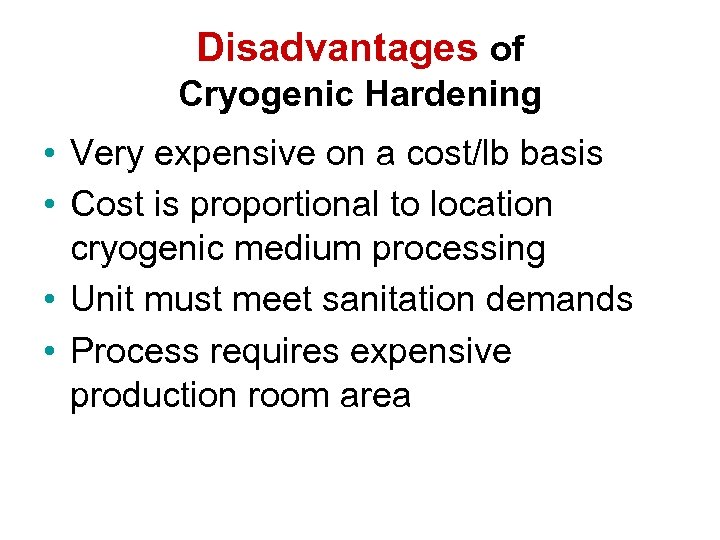
Disadvantages of Cryogenic Hardening • Very expensive on a cost/lb basis • Cost is proportional to location cryogenic medium processing • Unit must meet sanitation demands • Process requires expensive production room area
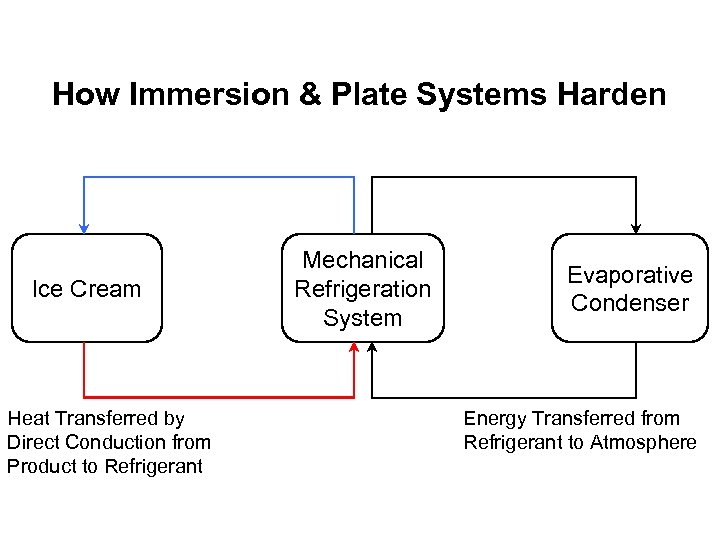
How Immersion & Plate Systems Harden Ice Cream Heat Transferred by Direct Conduction from Product to Refrigerant Mechanical Refrigeration System Evaporative Condenser Energy Transferred from Refrigerant to Atmosphere
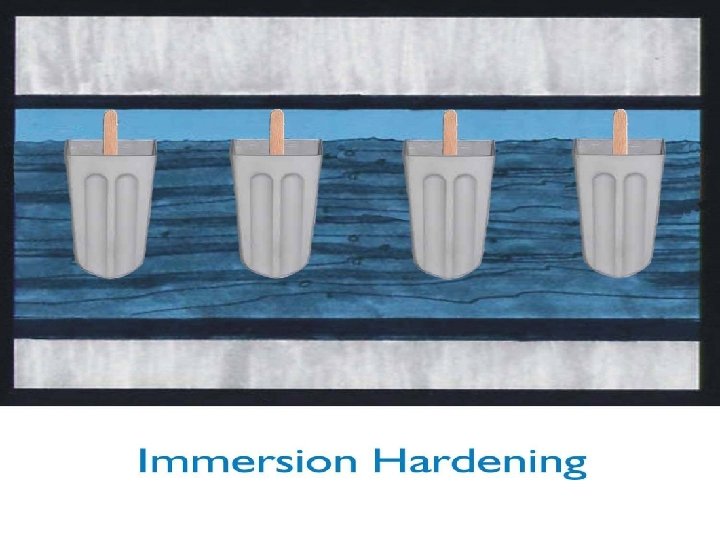
Advantages of Immersion Hardening • Best method to harden stick novelties • Rapid hardening with resultant minimum retention times • Automation allows high production rates • High product quality • Efficient heat removal process

Disadvantages of Immersion Hardening • • • Single item process Requires expensive production room area Must meet sanitation requirements Some units subject to high waste water demands Product shrinkage through process is relatively high • High capital expense for single item manufacture
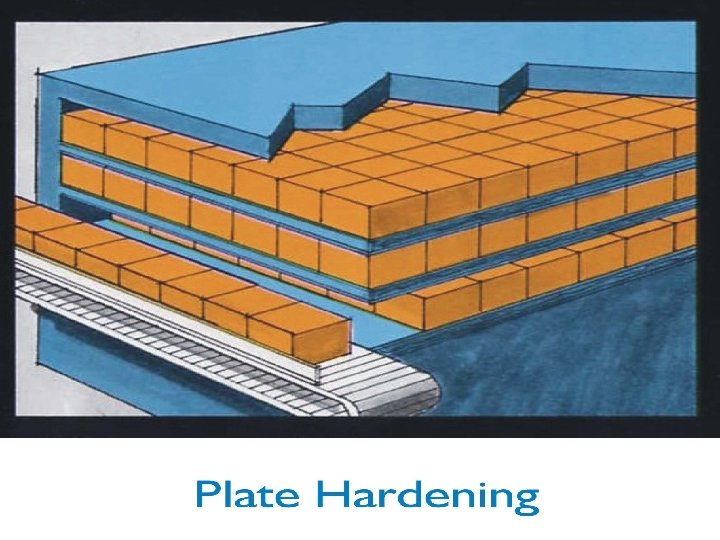

Advantages of Plate Hardener • Makes near perfect squares and rectangles on 95% of production • Rapid hardening with resultant minimum retention times • Heat removal via conduction is very efficient • Requires minimal space in low cost ambient warehouse environment • Low production shrinkage through hardening process
Disadvantages of Plate Hardener • Very limited item utility • Approximately 5% of product has shape irregularities • High capital cost in plants where all volume can not be hardened by plate process • Safety issue because refrigerant is in moving hollow plate • Requires low refrigerant temperature
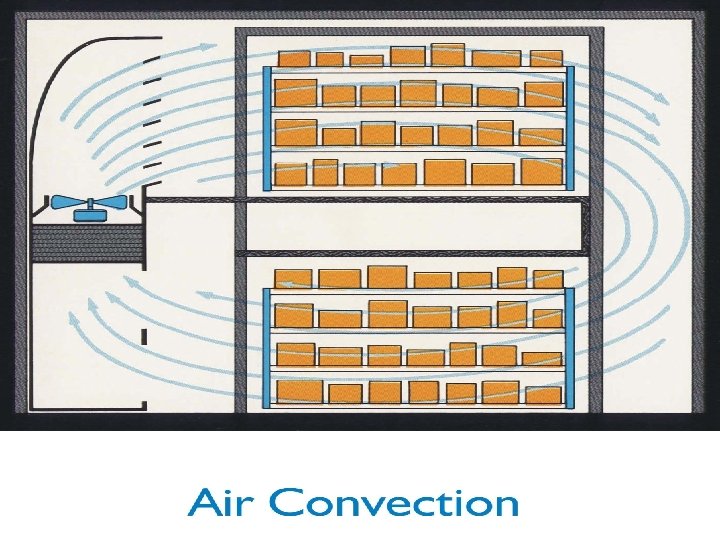
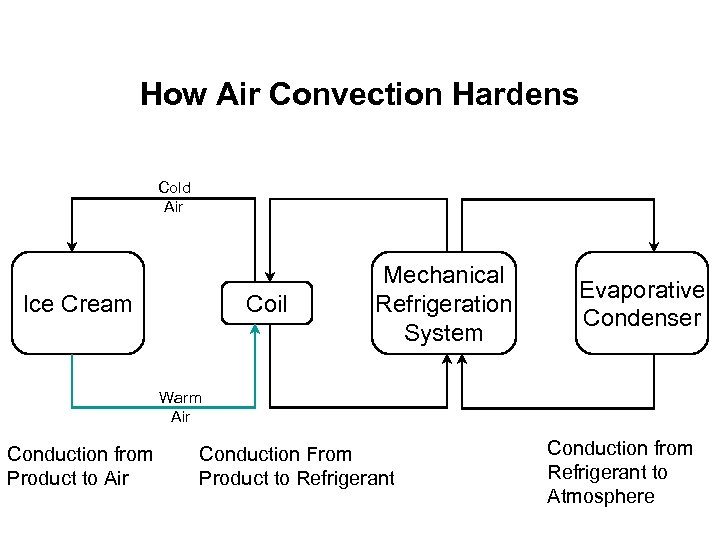
How Air Convection Hardens Cold Air Coil Ice Cream Mechanical Refrigeration System Evaporative Condenser Warm Air Conduction from Product to Air Conduction From Product to Refrigerant Conduction from Refrigerant to Atmosphere

Air Convection Significance • Used for Hardening over 85% of Ice Cream in US. • Used by over 95% of Ice Cream Manufacturers in US
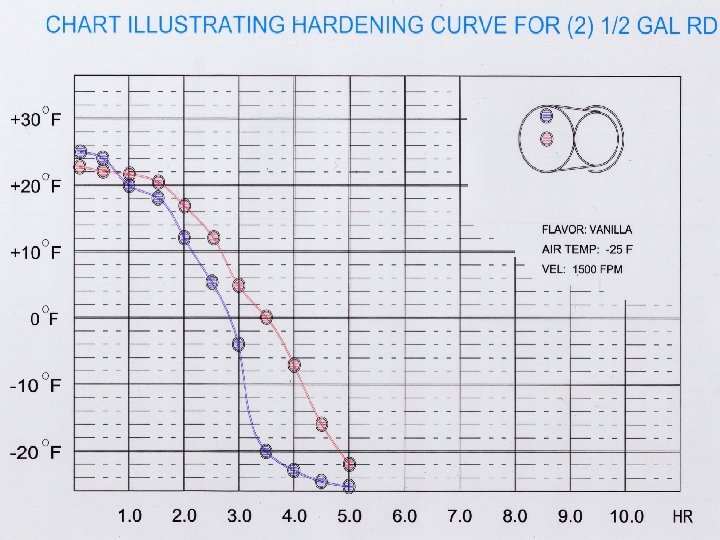
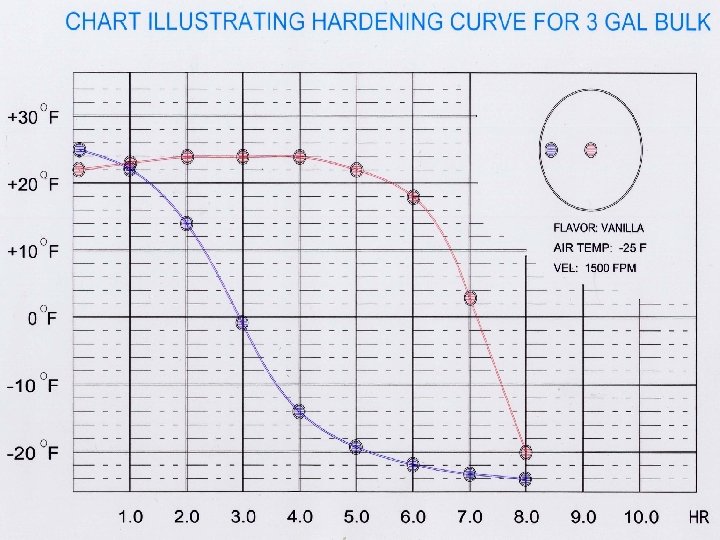

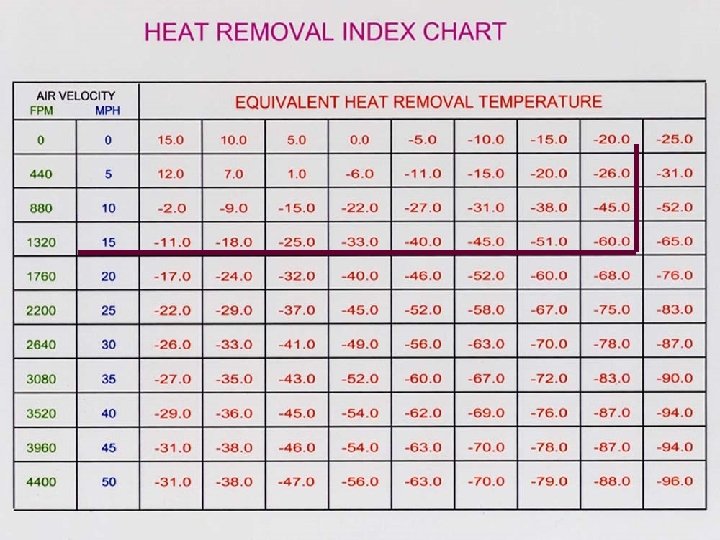
Important Facts about Convection Hardening • Product Draw or Fill Temperature • Package Orientation during Hardening Process. • Laminar Air Flow Vs. Turbulent air flow • Air Vs. Heat Removal Index Temperature • Product Spacing
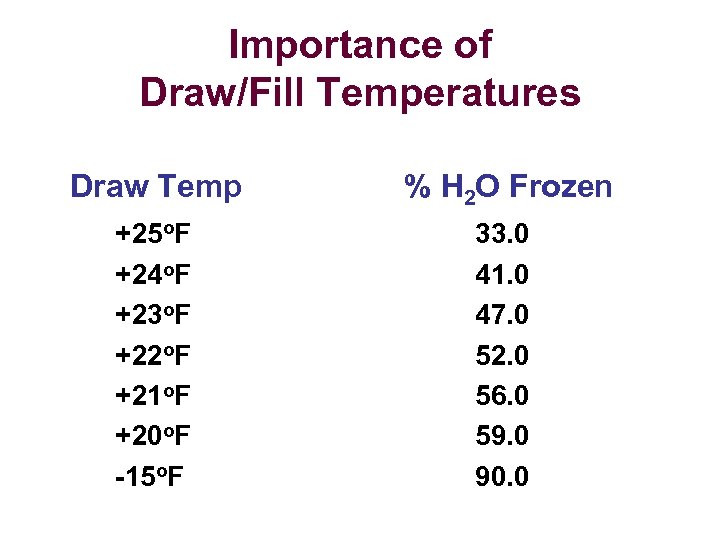
Importance of Draw/Fill Temperatures Draw Temp % H 2 O Frozen +25 o. F +24 o. F +23 o. F +22 o. F +21 o. F +20 o. F -15 o. F 33. 0 41. 0 47. 0 52. 0 56. 0 59. 0 90. 0
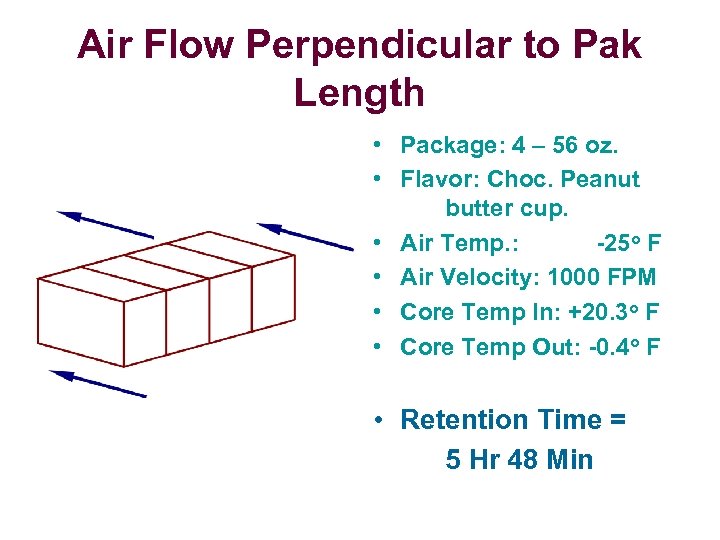
Air Flow Perpendicular to Pak Length • Package: 4 – 56 oz. • Flavor: Choc. Peanut butter cup. • Air Temp. : -25 o F • Air Velocity: 1000 FPM • Core Temp In: +20. 3 o F • Core Temp Out: -0. 4 o F • Retention Time = 5 Hr 48 Min
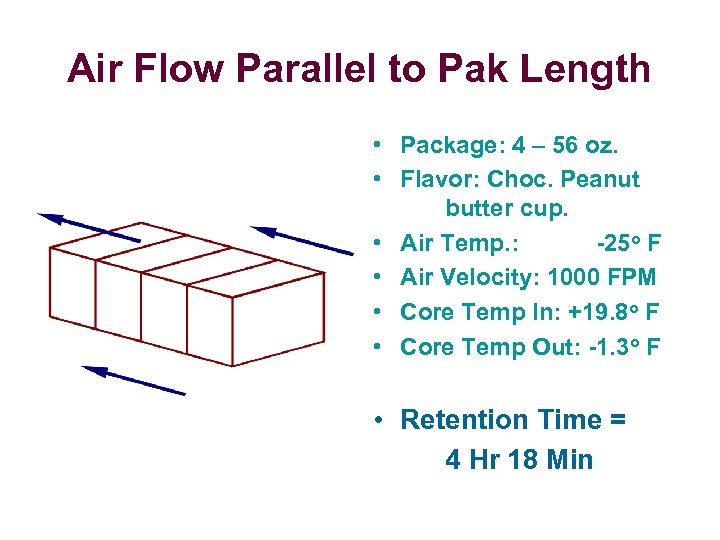
Air Flow Parallel to Pak Length • Package: 4 – 56 oz. • Flavor: Choc. Peanut butter cup. • Air Temp. : -25 o F • Air Velocity: 1000 FPM • Core Temp In: +19. 8 o F • Core Temp Out: -1. 3 o F • Retention Time = 4 Hr 18 Min

Draw Temp vs. Hardening Times • • • Package: 4 – 56 oz. Sq. Rd Flavor: Pumpkin Crème Air Temp. : -23 o F Air Velocity: 1000 FPM Core Temp In: +23. 2 o F Core Temp Out: -0. 1 o F • Retention Time = 5 Hr 28 Min • • • Package: 4 – 56 oz. Sq. Rd Flavor: Pumpkin Crème Air Temp. : -23 o F Air Velocity: 1000 FPM Core Temp In: +19. 3 o F Core Temp Out: -0. 2 o F • Retention Time = 4 Hr 4 Min

Laminar vs Turbulent Air Flow Definitions: Laminar Flow = Streamline flow in a viscous fluid near a solid boundary. Turbulent Flow = Fluid flow in which the velocity at a given point varies erratically in magnitude and direction.

The requirement for an efficient air distribution system is Conversion from Turbulent Flow to Laminar Flow
What Causes Turbulent Flow? 1. 2. 3. Fans and other mechanical methods of moving air. Obstructions to normal air flow. Merging air patterns. Advantages: • Can provide excellent heat removal when hardening. Disadvantages: • Consumes greater amount energy (Fan BHP). • Increases static pressure resulting in reduced air flow (CFM) with existing equipment.

Package Spacing Package Rows should have a minimum of 2. 00 inch space between rows for air flow.
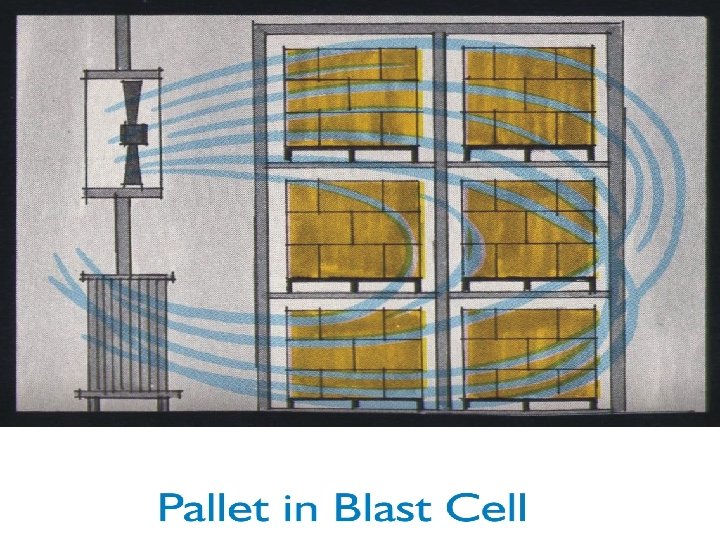
Advantages of Pallet Hardener • More mechanical simplicity than all other air convection hardeners • Low capital investment • Hardens multiple package sizes • Low maintenance costs

Disadvantages of Pallet Hardener • Mediocre to poor hardening results • Requires conscientious operator to insure product quality • High labor costs • High product shrinkage • Can result in unattractive packaging
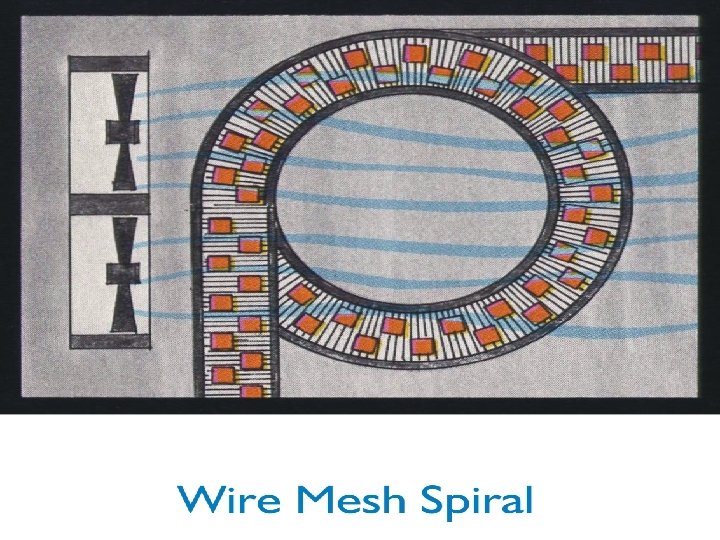

Advantages of Spiral Belt Hardener • Highest degree of mechanical simplicity of automated air convection hardeners • Good hardening when operated within design parameters • Low to moderate capital investment • Hardens multiple package sizes simultaneously • Low production shrinkage through hardening process • Available in system sizes from 250 GPH
Disadvantages of Spiral Belt Hardener • Belt loading limited to 10 lbs/ft of belt for good belt life • High fan horsepower results in high energy demands and cost • Requires low refrigerant temperatures • Very difficult to automate package handling in high output plants • High maintenance costs (belt cost represents 35% of typical system cost)
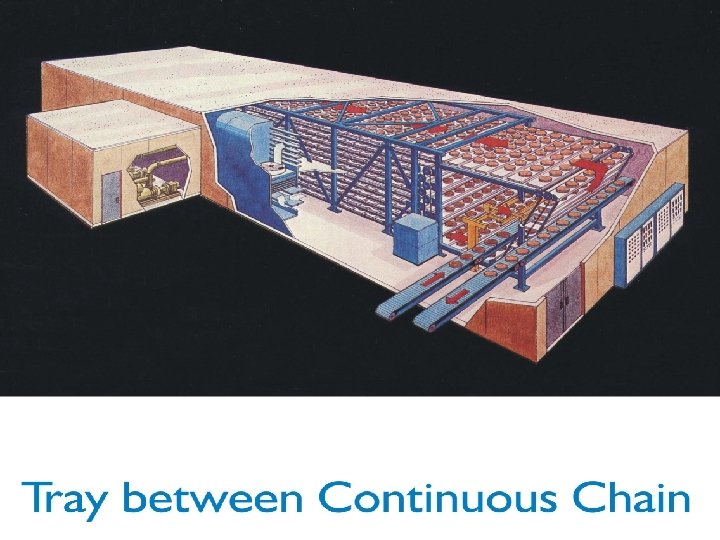

Advantages of Tray between Continuous Chain • Highest degree of mechanical simplicity of automated tray type air convection hardeners • Double pass air system insures very good hardening • Moderate capital investment • Hardens multiple package sizes simultaneously • Low production shrinkage through hardening process • Very good package orientation adapts to automation • Efficient air system reduces energy requirement and cost • Available in systems as small as 250 GPH
Disadvantages of Tray between Continuous Chain • Feed rates less than 2500 GPH • Not very suitable for simultaneous multiple line productions • Higher maintenance costs than tray/transport type systems
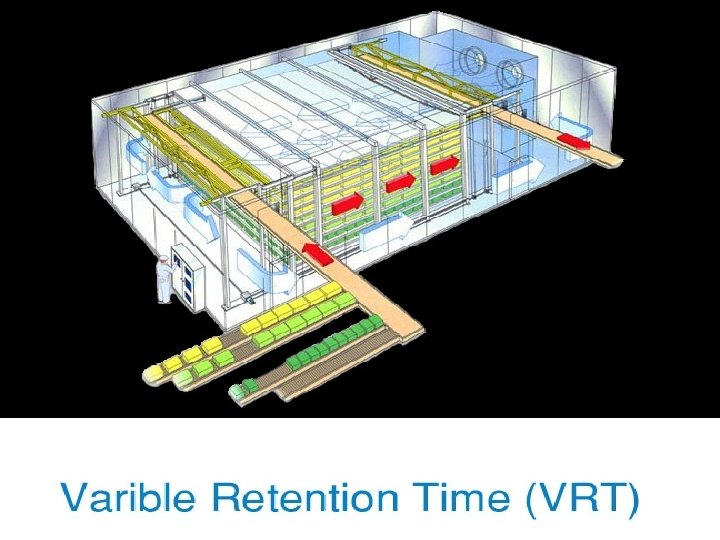

Advantages of Variable Retention Time (VRT) Hardener • Allows variable retention time for different size items • Easily adapts to line automation • Maintains package orientation through the hardening process • Hardens multiple package sizes simultaneously • Handles high production rates (up to 10, 000 GPH)

Disadvantages of Variable Retention Time (VRT) Hardener • • Highest cost hardener Complex program and operation Higher product shrinkage through system High static pressures require higher HP and energy requirements & longer retention times • Inherent design results in higher maintenance costs • Minimum size system is approx 1500 GPH
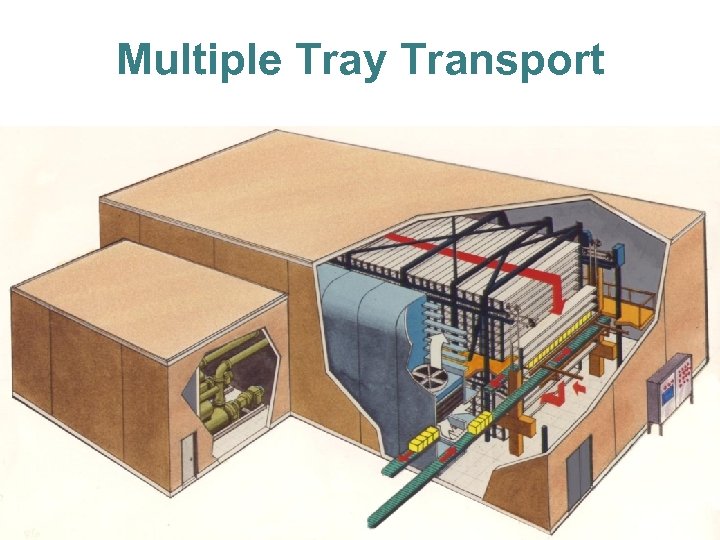
Multiple Tray Transport
Heart of the Multiple Tray Transport The Transport
Advantages of Multiple Tray Transport • Double pass air system insures very good hardening • Hardens multiple package sizes simultaneously • Very low production shrinkage through hardening process w/ good design • Moderate mechanical simplicity of automated tray type air convection hardeners • Moderate capital investment • Very low maintenance cost with long service life (40 + years) • Very good package orientation adapts to automation • Efficient air system reduces energy requirement and cost • Available in sizes to 10, 000 GPH
Disadvantages of Multiple Tray Transport • • No multiple retention time in standard form Minimum size system is 750 GPH More complex than spiral belt system Higher product shrinkage w/ poor design

Advantages of Fusion Cell • Combination conduction/convection system hardens faster than any air convection system • Most efficient air hardening system -- rivals that of plate hardener • Hardens multiple package sizes simultaneously • Very low production shrinkage through hardening process • Moderate mechanical simplicity of automated tray type air convection hardeners • Overall capital investment lower than most air systems • Very low maintenance cost with long service life (30 + years) • Very good package orientation adapts to automation • Available in sizes to 10, 000 GPH • Most compact of air convection hardeners • Allows same refrigerant suction temp for both freezer and hardener

Disadvantages of Fusion Cell • • No multiple retention time in standard form Minimum size system is 750 GPH More complex than spiral belt system Higher floor loadings than other air convection types
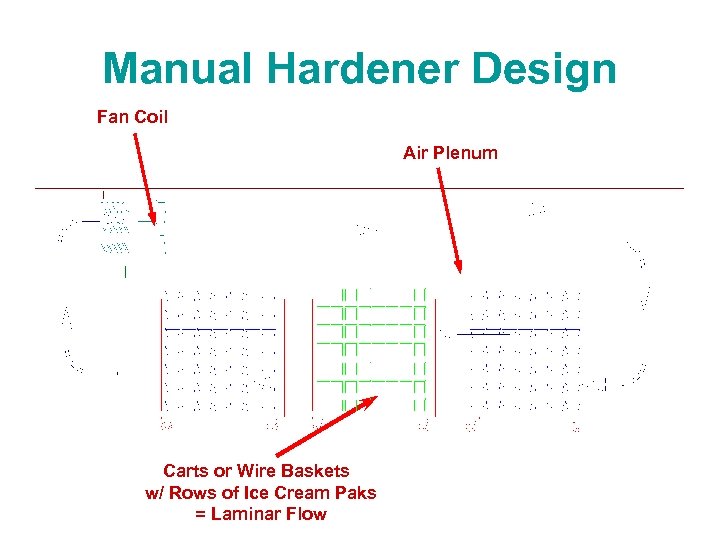
Manual Hardener Design Fan Coil Air Plenum Carts or Wire Baskets w/ Rows of Ice Cream Paks = Laminar Flow

Energy Consumption in Average Ice Cream Plant • Mix Processing = 5% • Freezing = 35% • Hardening = 45% • Storage = 15% = 100% Total

Real Energy Costs • 1. 0 HP motor w/ 16 Hr on/8 Hr off Cycle • 8 Hr off =. 746 x. 08 x 8 Hr x 250 da = $ 119. 36 • 115 off day =. 746 x. 08 x 24 Hr x 115 da = $ 164. 72 • Total Annual Energy Waste = $ 284. 08 • Total Waste for 25 Motors = $ 7, 102. 00 • Does not include: refrigeration losses

Individual Carton vs Over Wrapped Package
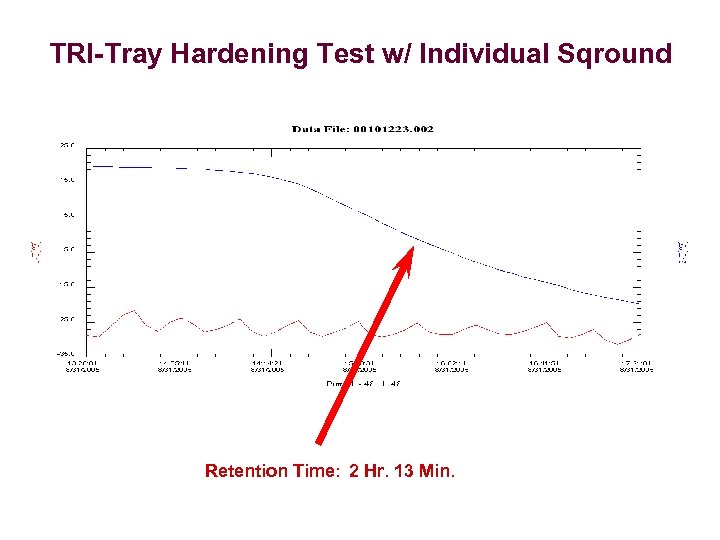
TRI-Tray Hardening Test w/ Individual Sqround Retention Time: 2 Hr. 13 Min.
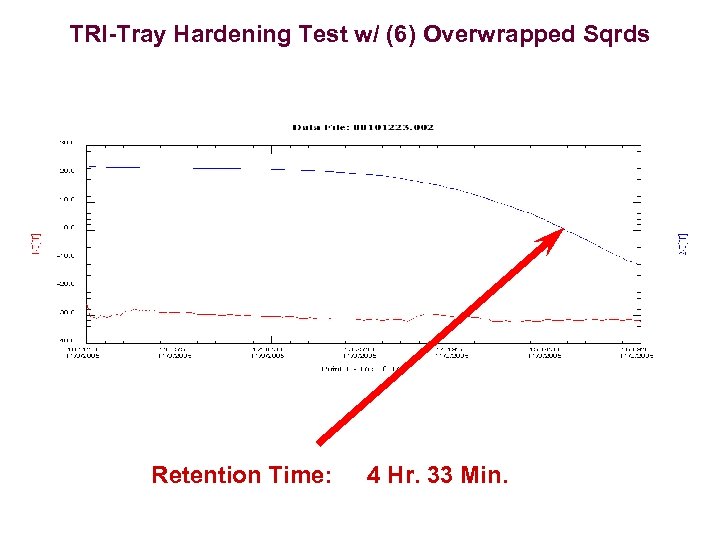
TRI-Tray Hardening Test w/ (6) Overwrapped Sqrds Retention Time: 4 Hr. 33 Min.

Design Objectives of Fast Hardener • Rapid hardening to achieve uniform ice crystallization and improve quality. • Improve package quality. • Ability to adapt to future packaging/marketing changes. • Lowest possible product shrinkage thru hardening process. • Low energy demand. • Low power (kwh) requirement. • Low direct labor. • Low maintenance cost. • Adaptability to Automation. • Capital cost commensurate with operational savings.

Any Question? Thank You! If you have any future question, please contact: dgreener@freestech. com
1ef65c6e3d5745e75b7be4dd2d5b54a7.ppt