 Rank Size Rule and Primate City The Rank Size Rule notes the relationship between the ranks of cities and their populations. It was advanced by Zipf in 1941. This is only used as a probability model.
Rank Size Rule and Primate City The Rank Size Rule notes the relationship between the ranks of cities and their populations. It was advanced by Zipf in 1941. This is only used as a probability model.
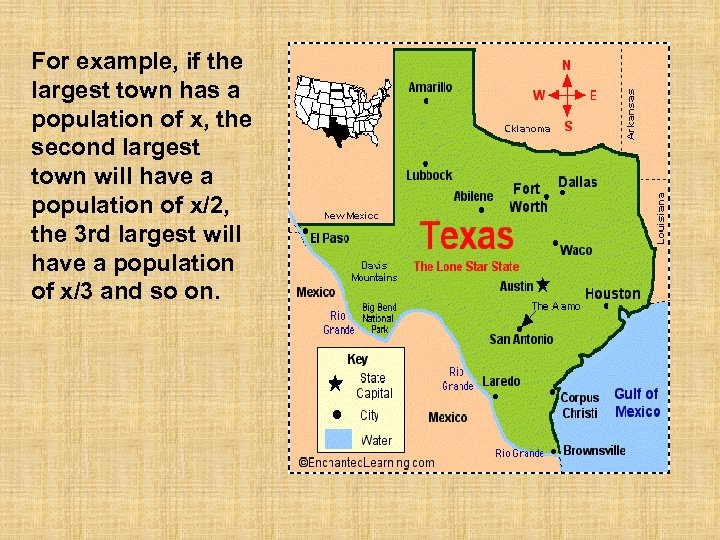 For example, if the largest town has a population of x, the second largest town will have a population of x/2, the 3 rd largest will have a population of x/3 and so on.
For example, if the largest town has a population of x, the second largest town will have a population of x/2, the 3 rd largest will have a population of x/3 and so on.
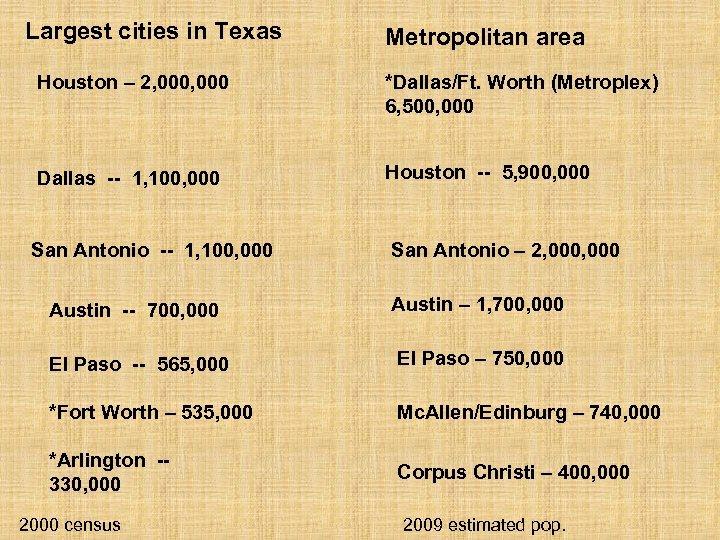 Largest cities in Texas Metropolitan area Houston – 2, 000 *Dallas/Ft. Worth (Metroplex) 6, 500, 000 Dallas -- 1, 100, 000 Houston -- 5, 900, 000 San Antonio -- 1, 100, 000 San Antonio – 2, 000 Austin -- 700, 000 Austin – 1, 700, 000 El Paso -- 565, 000 El Paso – 750, 000 *Fort Worth – 535, 000 Mc. Allen/Edinburg – 740, 000 *Arlington -330, 000 Corpus Christi – 400, 000 2000 census 2009 estimated pop.
Largest cities in Texas Metropolitan area Houston – 2, 000 *Dallas/Ft. Worth (Metroplex) 6, 500, 000 Dallas -- 1, 100, 000 Houston -- 5, 900, 000 San Antonio -- 1, 100, 000 San Antonio – 2, 000 Austin -- 700, 000 Austin – 1, 700, 000 El Paso -- 565, 000 El Paso – 750, 000 *Fort Worth – 535, 000 Mc. Allen/Edinburg – 740, 000 *Arlington -330, 000 Corpus Christi – 400, 000 2000 census 2009 estimated pop.
 The Law of the Primate City The primate city is the largest most dominant city in a region. The degree of primacy refers to the dominance of the largest city over the rest of the country. Write the largest city in: China Egypt Mexico Australia
The Law of the Primate City The primate city is the largest most dominant city in a region. The degree of primacy refers to the dominance of the largest city over the rest of the country. Write the largest city in: China Egypt Mexico Australia
 Factors that affect a Primate City Having an underdeveloped economy Having an agriculturally dominant economy A rapidly expanding population.
Factors that affect a Primate City Having an underdeveloped economy Having an agriculturally dominant economy A rapidly expanding population.
 Advantages of a Primate City Agglomeration of economic activities Large market for goods and services Centralized transportation system
Advantages of a Primate City Agglomeration of economic activities Large market for goods and services Centralized transportation system
 Disadvantages of a Primate City Unequal economic distribution “spoke and hub” transportation system prevents equal access to all regions Negative environment – slums, pollution, traffic congestion
Disadvantages of a Primate City Unequal economic distribution “spoke and hub” transportation system prevents equal access to all regions Negative environment – slums, pollution, traffic congestion
 Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso
Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso
 Most LDCs have a high degree of primacy while most MDCs have a low degree of primacy. Exceptions?
Most LDCs have a high degree of primacy while most MDCs have a low degree of primacy. Exceptions?
 Rank the top three cities (include population) of each country below. Goodes page 259 Look up your country and find the three largest cities. Do they show up on page 259? The legend (key) is at the bottom of the first page of each unit. 1. Europe 3. Middle East Poland Saudi Arabia Spain Iraq Greece Israel 2. East Asia 4. Africa South Korea South Africa Japan Libya Vietnam Nigeria 11 lesson
Rank the top three cities (include population) of each country below. Goodes page 259 Look up your country and find the three largest cities. Do they show up on page 259? The legend (key) is at the bottom of the first page of each unit. 1. Europe 3. Middle East Poland Saudi Arabia Spain Iraq Greece Israel 2. East Asia 4. Africa South Korea South Africa Japan Libya Vietnam Nigeria 11 lesson
 RANK SIZE AND PRIMATE CITIES 1. Make two columns. 2. Group cities by countries. 3. Locate five examples of countries that match “Rank size” and “Primate Cities. ” 4. List the country and top four cities in population 5. Determine which countries fit the criteria for Rank Size or Primate. 6. Look for patterns within each category between countries (peds/pings, population, industry, agriculture, location etc…) 7. What generalizations can you make about the Rank Size and Primate cities on your list? (at least two)
RANK SIZE AND PRIMATE CITIES 1. Make two columns. 2. Group cities by countries. 3. Locate five examples of countries that match “Rank size” and “Primate Cities. ” 4. List the country and top four cities in population 5. Determine which countries fit the criteria for Rank Size or Primate. 6. Look for patterns within each category between countries (peds/pings, population, industry, agriculture, location etc…) 7. What generalizations can you make about the Rank Size and Primate cities on your list? (at least two)