84fd5748cbda4d7c894ee83ea6a97aac.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 24

Rain Water Harvesting Systems Prabhat R. Ojasvi projasvi@yahoo. com 135 -2757213 Indian Institute of Soil and Water Conservation Dehradun
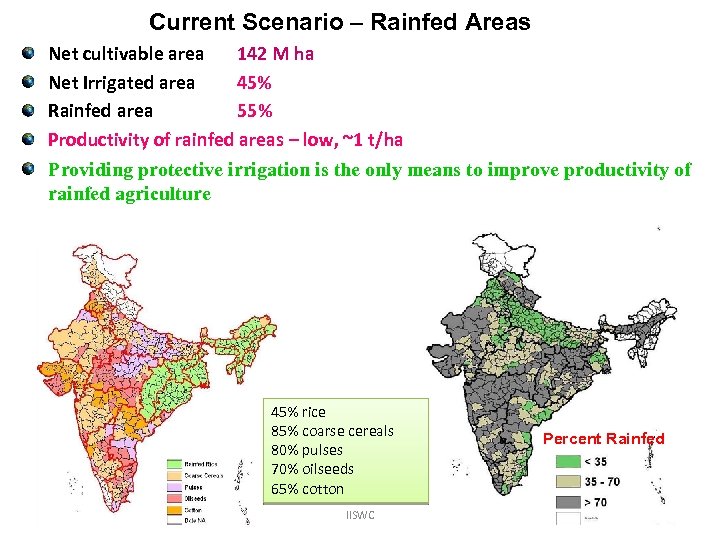
Current Scenario – Rainfed Areas Net cultivable area 142 M ha Net Irrigated area 45% Rainfed area 55% Productivity of rainfed areas – low, ~1 t/ha Providing protective irrigation is the only means to improve productivity of rainfed agriculture 45% rice 85% coarse cereals 80% pulses 70% oilseeds 65% cotton IISWC Percent Rainfed

PMKSY : major interventions • AIBP- major and medium projects • Repair, restoration and creation of water sources • Improve irrigation potential and distribution networks of on going schemes • Ground water recharge and development : moisture conservation and ‘run-off’ control measures , • Precision agriculture, micro-irrigation • Watershed management, MNREGS
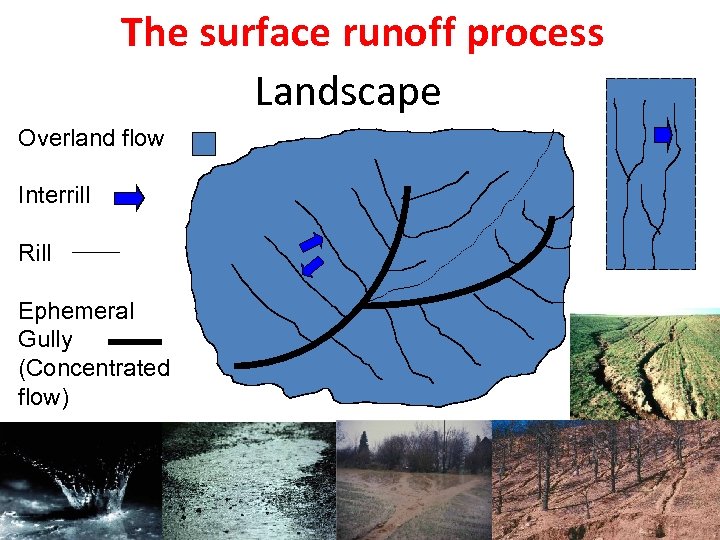
The surface runoff process Landscape Overland flow Interrill Rill Ephemeral Gully (Concentrated flow)
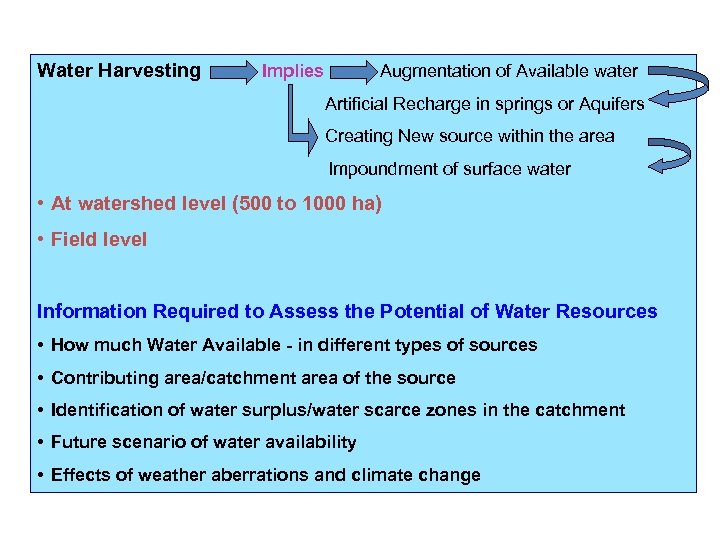
Water Harvesting Implies Augmentation of Available water Artificial Recharge in springs or Aquifers Creating New source within the area Impoundment of surface water • At watershed level (500 to 1000 ha) • Field level Information Required to Assess the Potential of Water Resources • How much Water Available - in different types of sources • Contributing area/catchment area of the source • Identification of water surplus/water scarce zones in the catchment • Future scenario of water availability • Effects of weather aberrations and climate change
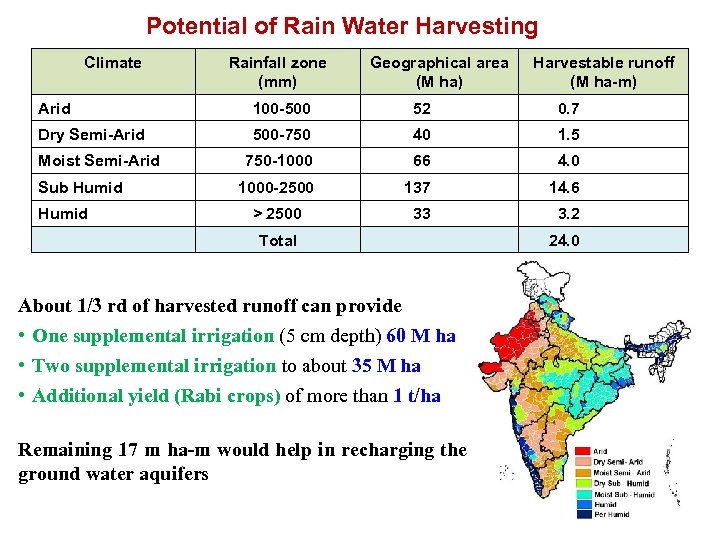
Potential of Rain Water Harvesting Climate Rainfall zone (mm) Geographical area (M ha) Harvestable runoff (M ha-m) Arid 100 -500 52 0. 7 Dry Semi-Arid 500 -750 40 1. 5 750 -1000 66 4. 0 1000 -2500 137 14. 6 > 2500 33 3. 2 Moist Semi-Arid Sub Humid Total About 1/3 rd of harvested runoff can provide • One supplemental irrigation (5 cm depth) 60 M ha • Two supplemental irrigation to about 35 M ha • Additional yield (Rabi crops) of more than 1 t/ha Remaining 17 m ha-m would help in recharging the ground water aquifers 24. 0
Impact of Rain Water Harvesting Experimental Watersheds in different agro-ecological regions • Creation of water storage capacity - 12 to 158 ha-m in a period of 6 years increased irrigated area - 65 to 585% • Reduced runoff from the watersheds by 9 to 24% and soil loss • Increased groundwater table by 1 to 2 m Large Scale Adoption of RWHS – Gujarat Experience • Over 5. 5 lakh water harvesting structures created in by 2008 • check dams, boribandhs and khet talavadis • Decentralized rain water harvesting resulted in artificial recharge to ground water in the Saurashtra and Kachchh regions About 2. 13 M ha treated under watersheds during 2009 - 2012 with water harvesting structures resulted 90% of watersheds -- increase in ground water (more than 1 meter) 88% of watersheds -- reduction in soil loss (more than 25%) 85% of watersheds -- more than 100% increase in cropping intensity 60% watersheds -- increase in cereal yield (more than 50%) 93% watersheds -- increase in employment as labour days IISWC

Rainwater Harvesting and Utilization Techniques Arid Regions Water harvesting- Tanka, Nadi, Khadin Rainfall (mm) Catchment (m) Runoff (m 3) 200 400 30 200 50 200 750 100 Cost ~ Rs 300 -1000 per cu m IISWC

Rainwater Harvesting and Utilization Techniques for Semi -arid Regions Dugout Water harvesting ponds LDPE lined pond at Vejalpura-Rampura Watershed Æ Æ Pond Capacity 500 m 3 Catchment area 2 ha Irrigation by 5 hp diesel engine Command area : one irrigation of cotton crop during post monsoon season in 0. 25 ha Æ The cotton yields increased by 28 % Recommended Domain Sandy to sandy loam soil of semi-arid areas IISWC

Rainwater Harvesting and Utilization Techniques for Semi -arid Regions Embankment type water harvesting pond Vejalpura-Rampura Watershed Æ Æ Æ Pond Capacity 1200 m 3 Catchment area is 20 ha Irrigation by 5 hp diesel engine Command area : two irrigation of cotton crop during post monsoon season in 4 ha The cotton yields increased by 40 % Recommended Domain In clay loam soil of semi-arid areas IISWC

Rainwater Harvesting and Utilization Techniques for Semi -arid Regions Water harvesting- Dugout Pond The surface runoff generated from sloping lands during rainy season is harvested and stored into a dug out pond Æ Æ Yield of soybean increased by 40% with one supplemental irrigation Yield of toria increased by 180% with one supplemental irrigation Yield of mustard increased by 130 and 400% with two supplemental irrigation Cost: benefit ratio- 1: 2. 3 Recommended Domain Seasonal streams, Red soils of Bundelkhand region IISWC

Rainwater Harvesting and Utilization Techniques for Semi -arid Regions Water harvesting- Dugout Pond Farm ponds with a design capacity of 1800 cum can be constructed for every 10 ha of catchment receiving annual rainfall 600 -650 mm , from which 3600 cum of runoff can be expected. Æ Æ Æ Farm pond capacity- 2145 cu m (cost 1. 15 lakh) Catchment area- 24 ha High density orchard- 2. 40 ha Irrigation by a drip system with pump set using power from a tractor (1. 2 L) Yield increase- 55 -99% in crop yields with supplemental irrigation Recommended Domain Black soils and low rainfall regions of Southern India Farm pond (2145 cu m storage capacity) with a stilling basin on the upstream Drip irrigation set-up, Bengal gram grown as an intercrop is rainfed IISWC Pomegranate plants raised under drip irrigation in rainfed Vertisols using stored run off water

Water Harvesting and Micro Irrigation System for Small Farmers Middle Himalayan Hilly Region Water harvesting- Perennial stream flow/ Low discharge springs Water is diverted from perennial streams or springs stored in a low-cost pond and utilized through gravity-fed micro irrigation system to grow vegetable crops in hilly terraces Small low cost water harvesting pond for gravity fed micro irrigation Low-cost water harvesting pond Æ Capacity : 10 m 3 (cost Rs. 16000) Æ Lining material: Silpaulin sheet (200 GSM) Drip irrigation system Æ Inline drip tape, Mainline, Screen Filter Domain: Terrace cultivation of high value vegetable crops A view of tomato with gravity-fed drip irrigation Low cost drip irrigation for sloping broad based terraces IISWC

Participatory Water Resource Development Water harvesting- High discharge springs Water conveyance system- Underground pipe line with risers Tanks capacity Length of pipeline Risers (Nos. ) Discharge Number of beneficiaries Command area (ha) Total cost 70, 000 & 50, 000 Litres 5. 3 km 45 12 (litr/sec) 44 25 Rs. 19, 20, 000 IISWC

Watershed based Participatory Water Harvesting Water harvesting- Large ponds Catchment area of pond 4. 32 ha Capacity of pond 2 ha-m Area being irrigated at present 10. 0 ha Gravity irrigation 6. 0 ha Lift irrigation 4. 0 ha Crop Yields 3 -4 times as Compared to Rainfed area Recommended Domain Shiwalik region of Himachal Pradesh, Haryana and Punjab IISWC

Water Harvesting – Subsurface Dam IISWC

Ridge and furrow method

Mulching for moisture conservation

LASER ASSISTED LAND LEVELING • Uniform water application 25% of irrigation water can be saved • Larger plot size and better water use efficiency • Better crop stand lesser weeds RAISED BED PLANTING • 30 -40% saving in irrigation water • in-situ rainwater conservation.
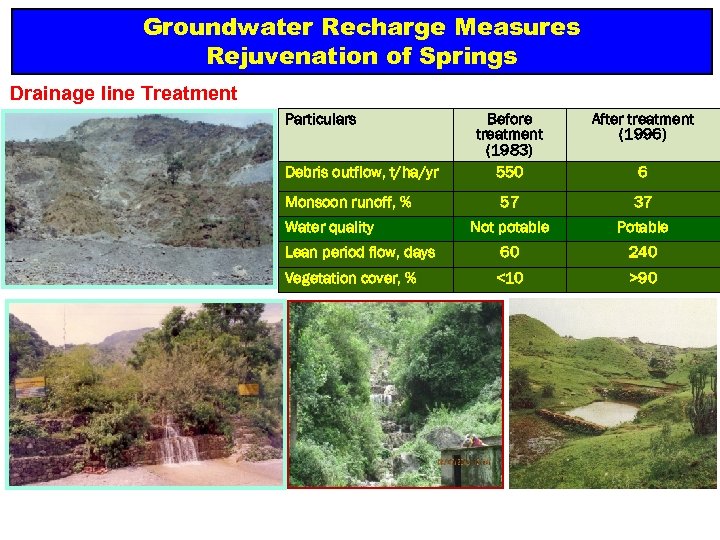
Groundwater Recharge Measures Rejuvenation of Springs Drainage line Treatment Particulars Before treatment (1983) 550 After treatment (1996) 57 37 Not potable Potable Lean period flow, days 60 240 Vegetation cover, % <10 >90 Debris outflow, t/ha/yr Monsoon runoff, % Water quality 6

Groundwater Recharge Measures Check dams and Percolation Ponds Check dam Percolation Tank • Ground water recharge in 1 to 2 km downstream • 28– 82 mm rainfall ->1 mm potential recharge • Rise in water table 3 m Open well 1. 6 -2. 4 m Bore well (WHS) • Natural recharge 5– 10%

Groundwater Recharge Measures Countour trenching • Runoff management and Plantation on sloping land • Decrease runoff - ground water recharge

Thank you IISWC
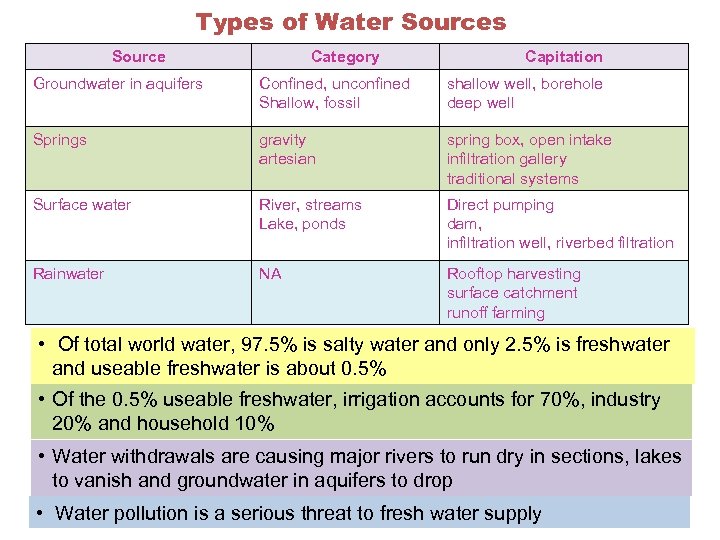
Types of Water Sources Source Category Capitation Groundwater in aquifers Confined, unconfined Shallow, fossil shallow well, borehole deep well Springs gravity artesian spring box, open intake infiltration gallery traditional systems Surface water River, streams Lake, ponds Direct pumping dam, infiltration well, riverbed filtration Rainwater NA Rooftop harvesting surface catchment runoff farming • Of total world water, 97. 5% is salty water and only 2. 5% is freshwater and useable freshwater is about 0. 5% • Of the 0. 5% useable freshwater, irrigation accounts for 70%, industry 20% and household 10% • Water withdrawals are causing major rivers to run dry in sections, lakes to vanish and groundwater in aquifers to drop • Water pollution is a serious threat to fresh water supply
84fd5748cbda4d7c894ee83ea6a97aac.ppt