2ec53e57336f0755df51b68fedc40190.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 139
 Radiology Differential Diagnosis Richard D. Lackman, MD Director Orthopaedic Oncology Center Cooper University Hospital
Radiology Differential Diagnosis Richard D. Lackman, MD Director Orthopaedic Oncology Center Cooper University Hospital
 Bone Forming Tumors • • • Osteoid Osteoma Osteoblastoma Osteochondroma Osteosarcoma Blastic Mets Paget’s Cartilage Forming Tumors • • • Enchondroma Osteochondroma Chondromyxoid fibroma Chondroblastoma Chondrosarcoma 3 rd List • • • Infection Mets, myeloma Fibrous dysplasia Nonossifying fibroma LC Histiocytosis GCT ABC Simple Cyst Stress fx Round Cell Tumor Metabolic condition
Bone Forming Tumors • • • Osteoid Osteoma Osteoblastoma Osteochondroma Osteosarcoma Blastic Mets Paget’s Cartilage Forming Tumors • • • Enchondroma Osteochondroma Chondromyxoid fibroma Chondroblastoma Chondrosarcoma 3 rd List • • • Infection Mets, myeloma Fibrous dysplasia Nonossifying fibroma LC Histiocytosis GCT ABC Simple Cyst Stress fx Round Cell Tumor Metabolic condition
 Matrix Formation • None ( Lytic ) • Calcified Matrix – Cartilage – Bone – Other
Matrix Formation • None ( Lytic ) • Calcified Matrix – Cartilage – Bone – Other
 Margin – width of interface with adjacent medullary bone. Geographic 1 mm. Motheaten 2 -4 mm. Permeative 1 -4 cm.
Margin – width of interface with adjacent medullary bone. Geographic 1 mm. Motheaten 2 -4 mm. Permeative 1 -4 cm.
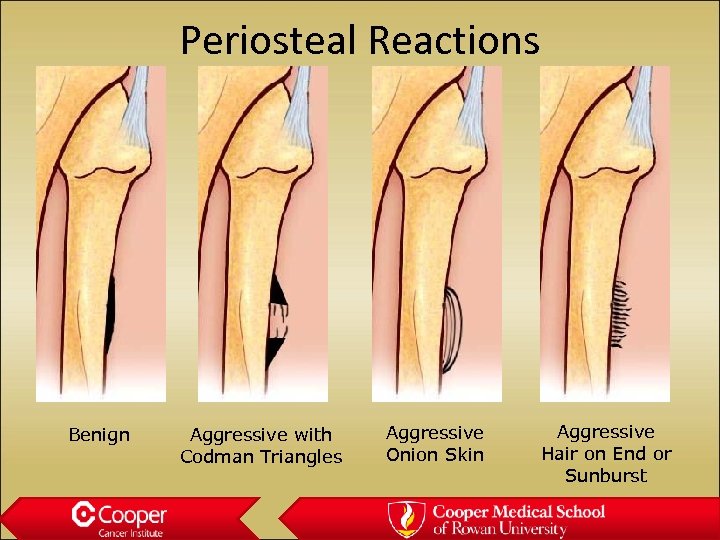 Periosteal Reactions Benign Aggressive with Codman Triangles Aggressive Onion Skin Aggressive Hair on End or Sunburst
Periosteal Reactions Benign Aggressive with Codman Triangles Aggressive Onion Skin Aggressive Hair on End or Sunburst
 Periosteal Reaction • Does Not Occur If: – The tumor is not out in the periosteum • Giant Cell Tumor – The periosteum does not recognize the tumor cells as foreign • Lymphoma
Periosteal Reaction • Does Not Occur If: – The tumor is not out in the periosteum • Giant Cell Tumor – The periosteum does not recognize the tumor cells as foreign • Lymphoma
 Osteoid Osteoma • Small lytic nidus with surrounding sclerosis, constant pain relieved by NSAIDS • Prostaglandin secretion • MRI-edema, Best seen on CT scan
Osteoid Osteoma • Small lytic nidus with surrounding sclerosis, constant pain relieved by NSAIDS • Prostaglandin secretion • MRI-edema, Best seen on CT scan
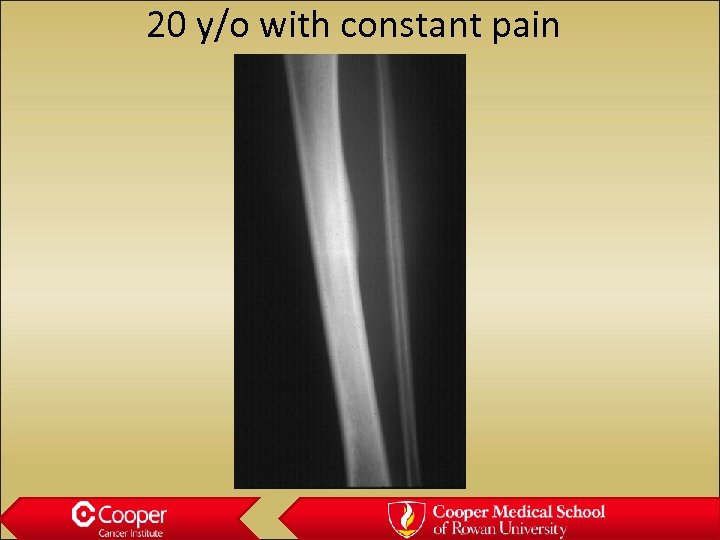 20 y/o with constant pain
20 y/o with constant pain
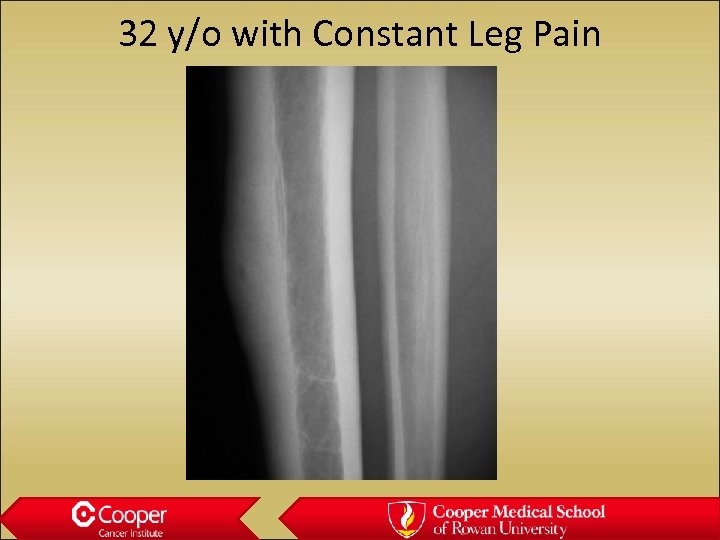 32 y/o with Constant Leg Pain
32 y/o with Constant Leg Pain
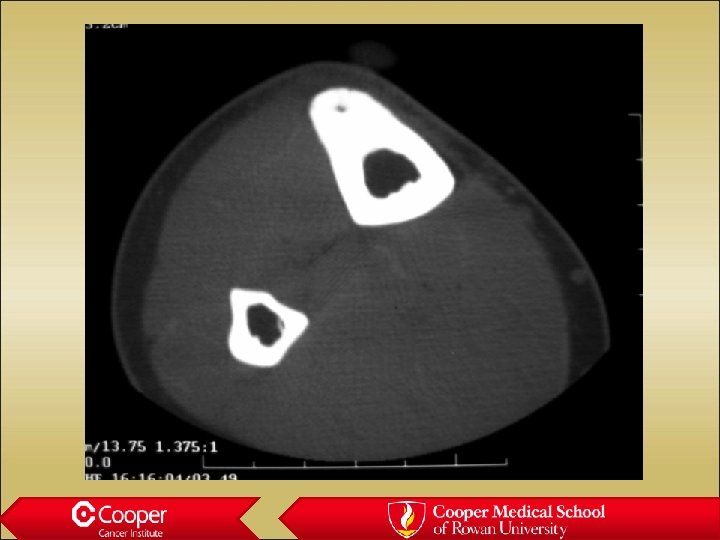
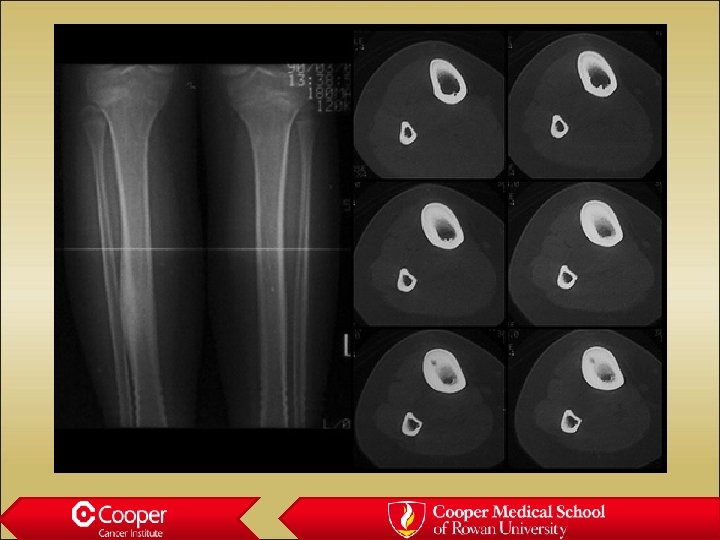
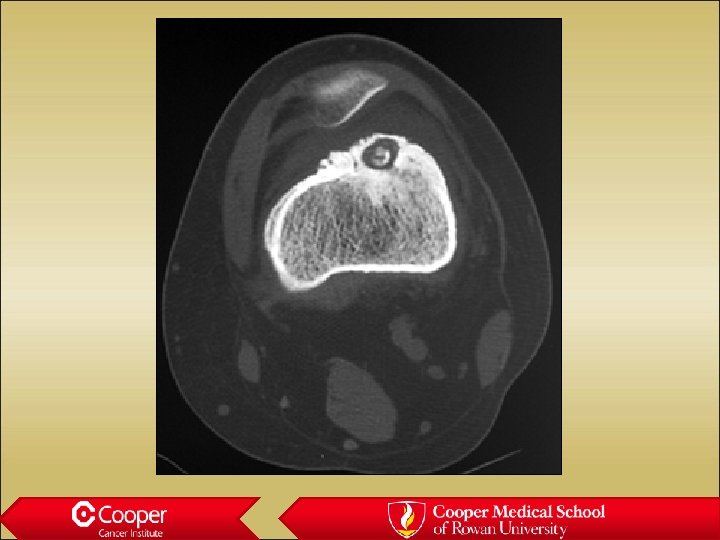
 Osteoblastoma • Lytic lesion • Painful • Posterior elements of the spine
Osteoblastoma • Lytic lesion • Painful • Posterior elements of the spine
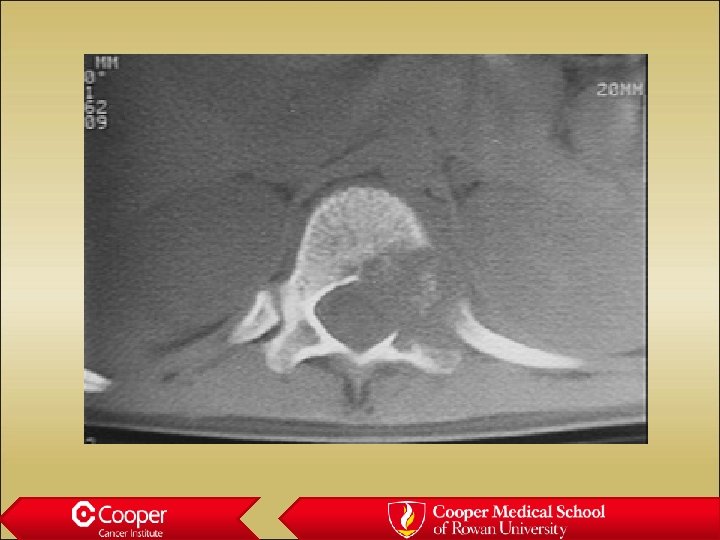
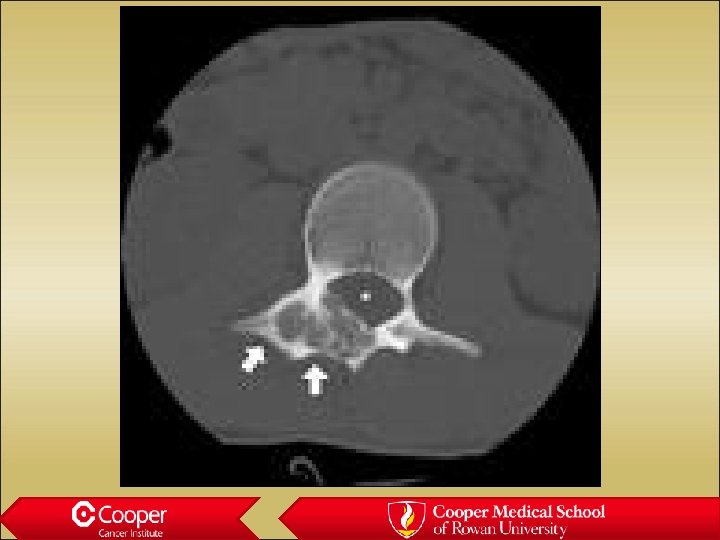
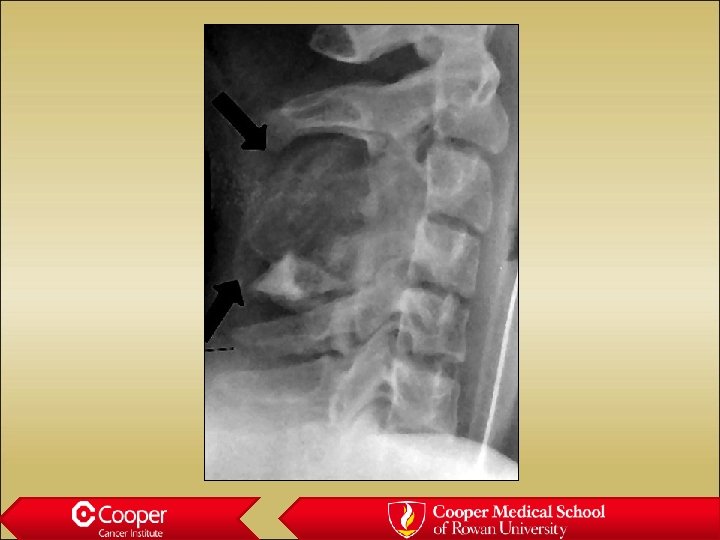
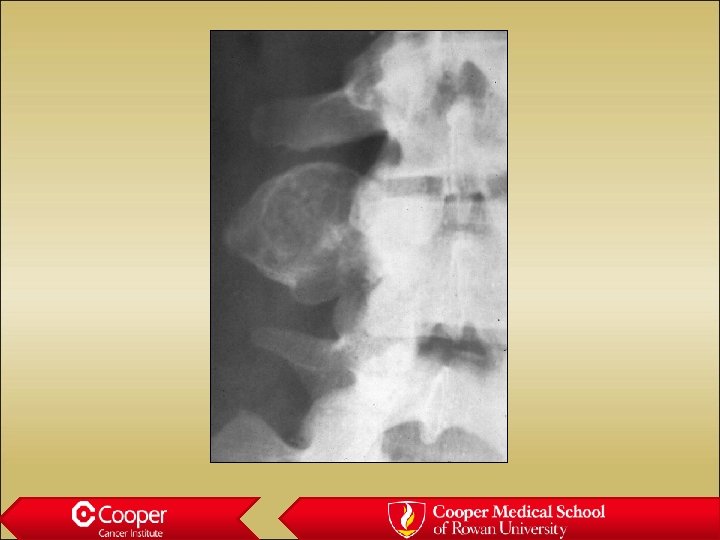
 Osteochondroma • Grows out from the medullary canal • Cortex of the bone becomes cortex of the lesion • Never sits on an intact cortex • Malignant if cartilage cap is thicker than 2. 5 cm in aduts
Osteochondroma • Grows out from the medullary canal • Cortex of the bone becomes cortex of the lesion • Never sits on an intact cortex • Malignant if cartilage cap is thicker than 2. 5 cm in aduts
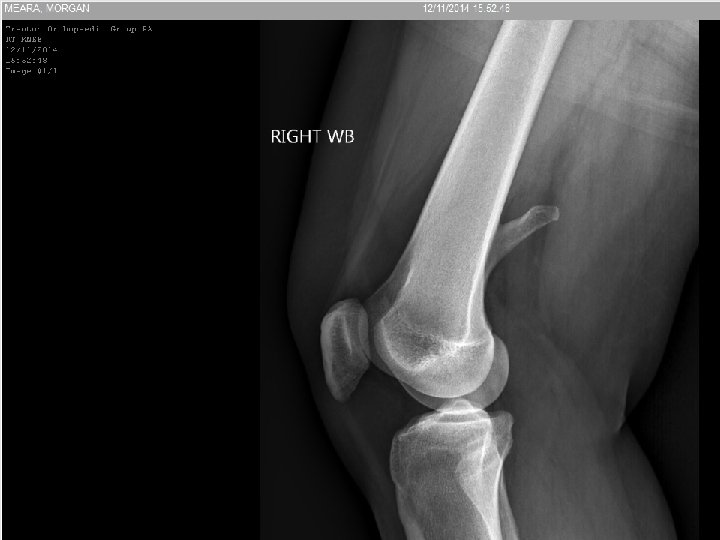
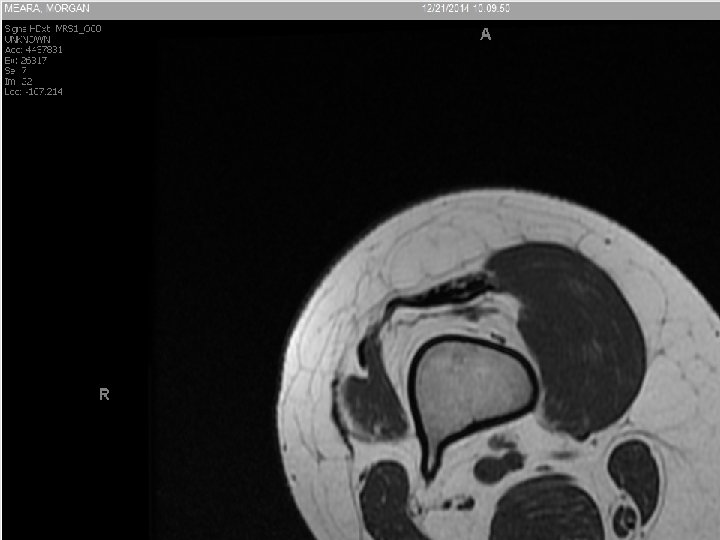
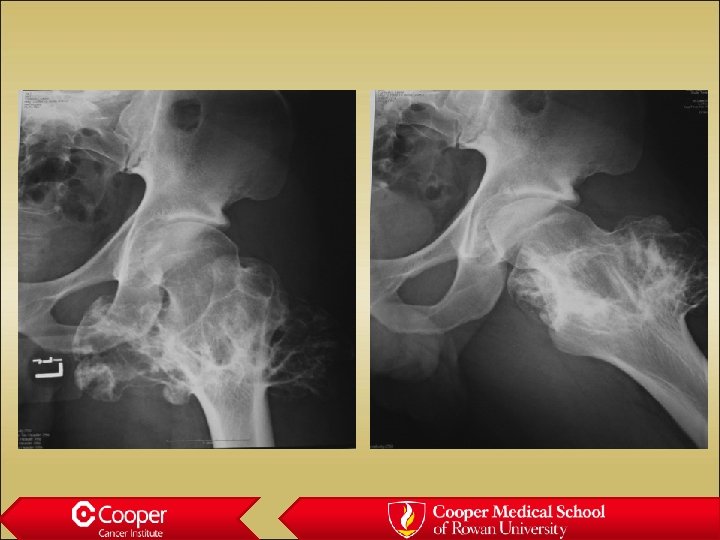
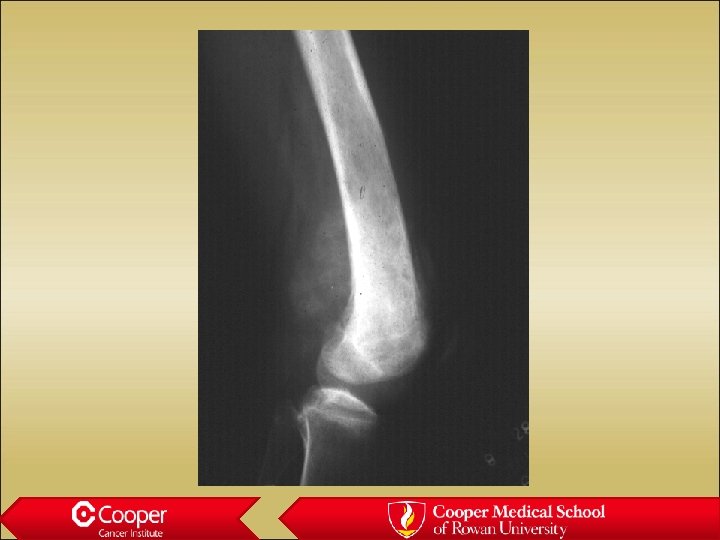
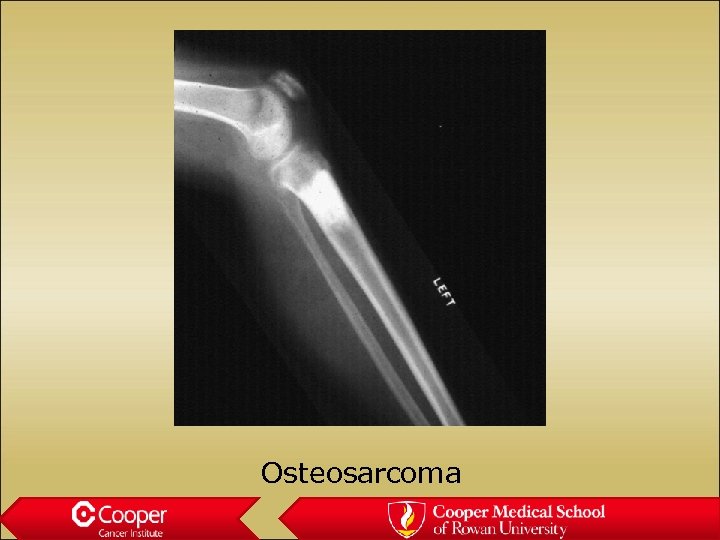
 Osteosaroma • Age 10 to 30, second peak in Paget’s • Usually metaphyseal • Permeative margin with cortical destruction and soft tissue extension • Osteoblastic, chondroblastic, fibroblastic, telanectatic (secondary ABC)
Osteosaroma • Age 10 to 30, second peak in Paget’s • Usually metaphyseal • Permeative margin with cortical destruction and soft tissue extension • Osteoblastic, chondroblastic, fibroblastic, telanectatic (secondary ABC)
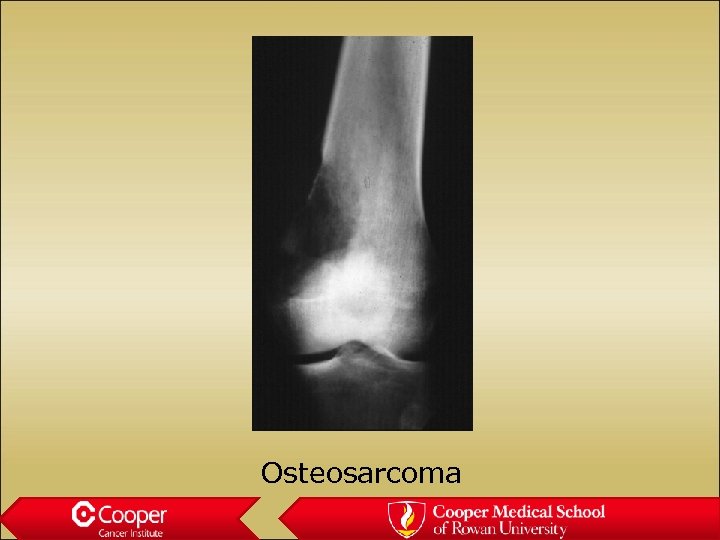 Osteosarcoma
Osteosarcoma
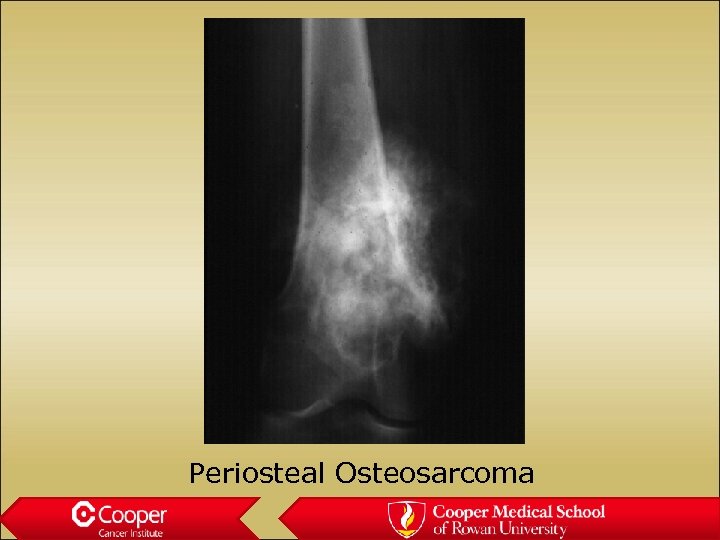 Periosteal Osteosarcoma
Periosteal Osteosarcoma
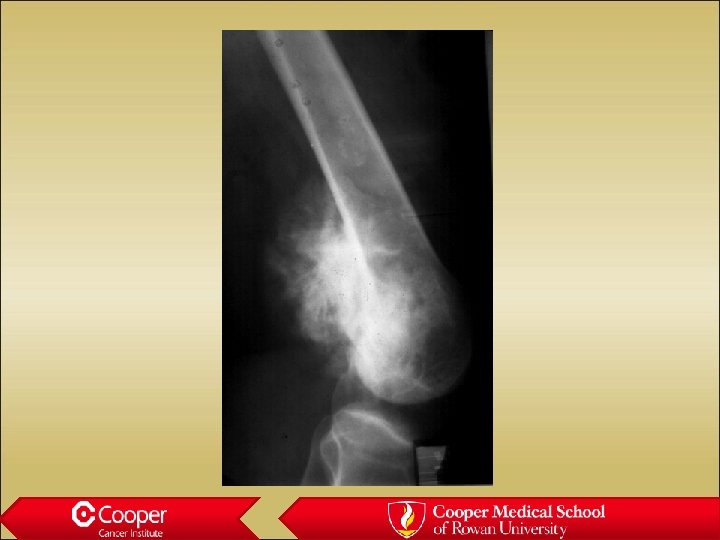
 Osteosarcoma
Osteosarcoma
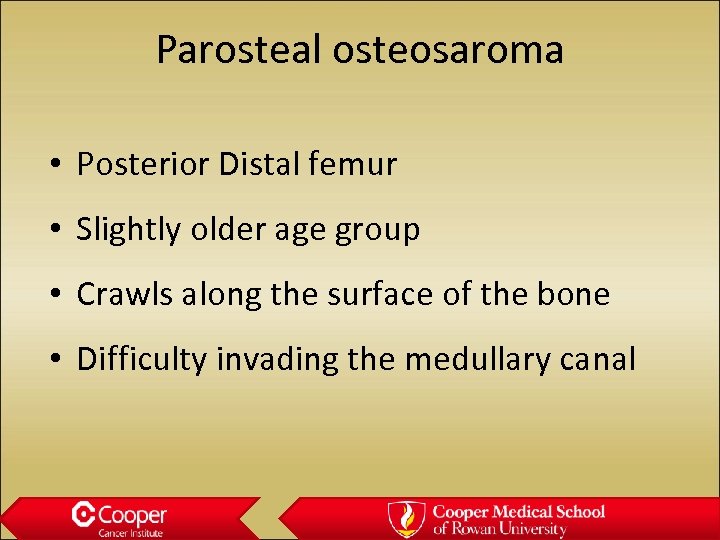 Parosteal osteosaroma • Posterior Distal femur • Slightly older age group • Crawls along the surface of the bone • Difficulty invading the medullary canal
Parosteal osteosaroma • Posterior Distal femur • Slightly older age group • Crawls along the surface of the bone • Difficulty invading the medullary canal
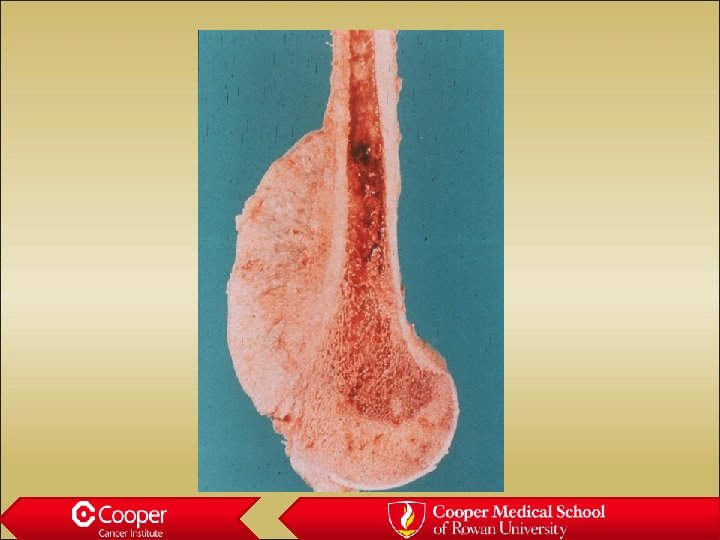
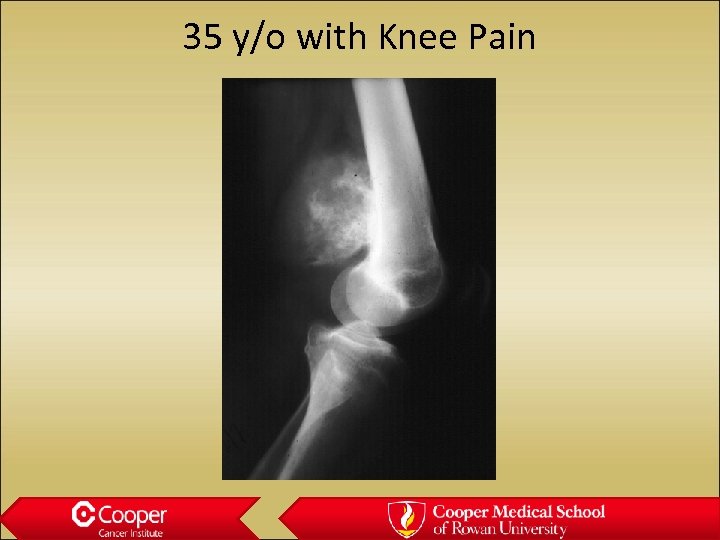 35 y/o with Knee Pain
35 y/o with Knee Pain
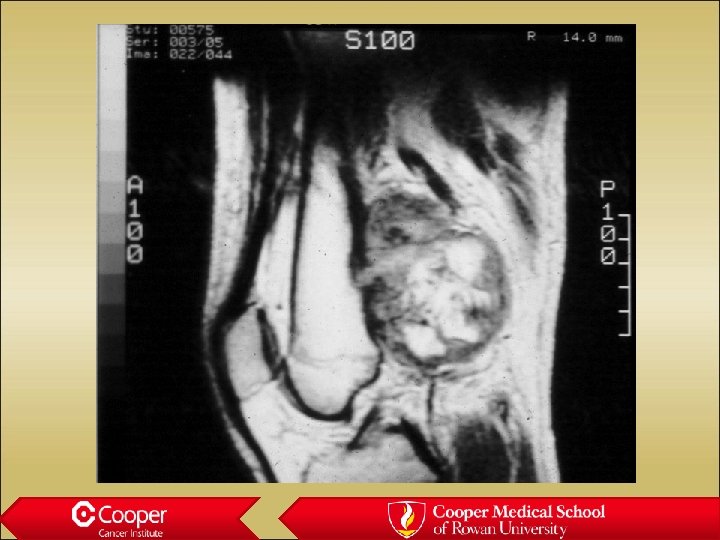
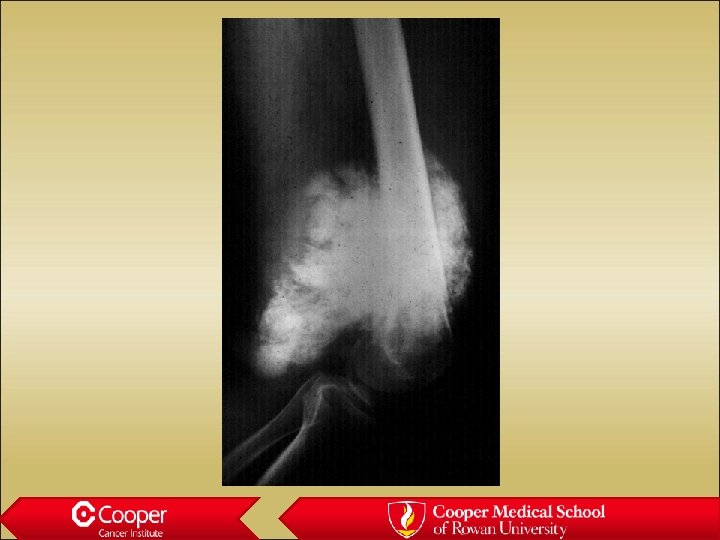
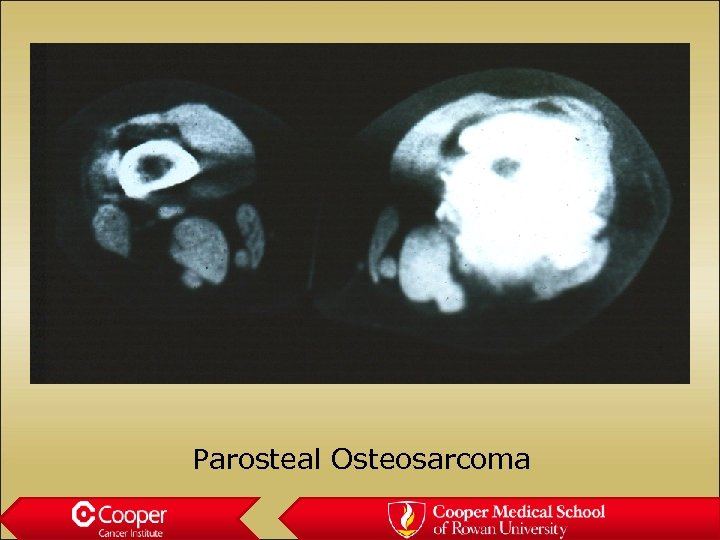 Parosteal Osteosarcoma
Parosteal Osteosarcoma
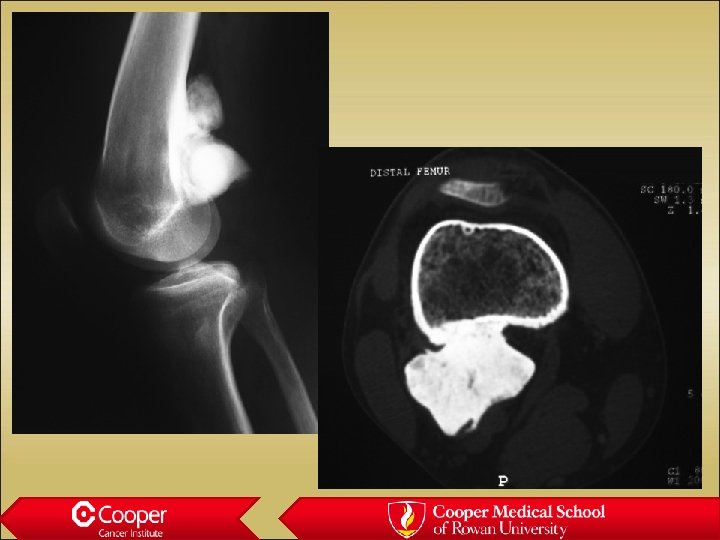
 Blastic Mets • 90% of prostate mets are blastic • LS Spine via Batson’s plexus • Breast may be mixed
Blastic Mets • 90% of prostate mets are blastic • LS Spine via Batson’s plexus • Breast may be mixed
 Pagets Disease • Uncoupled resorption-formation • Spectrum of associated radiographic findings • Pain: stress fracture vs. malignant transformation
Pagets Disease • Uncoupled resorption-formation • Spectrum of associated radiographic findings • Pain: stress fracture vs. malignant transformation
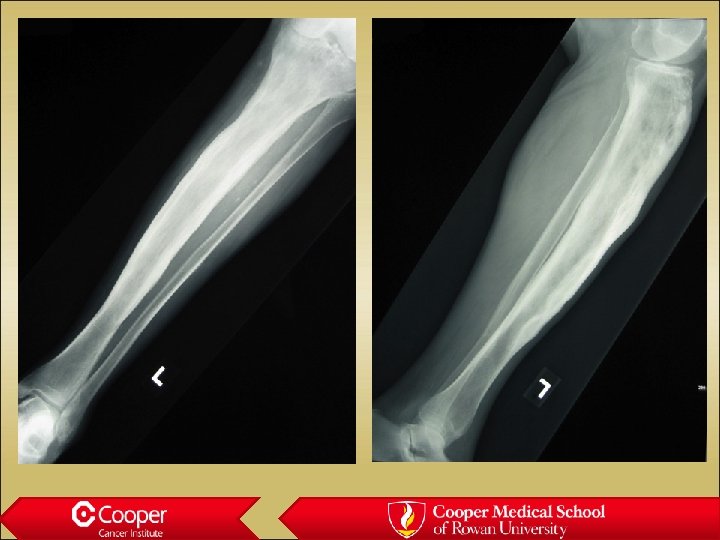
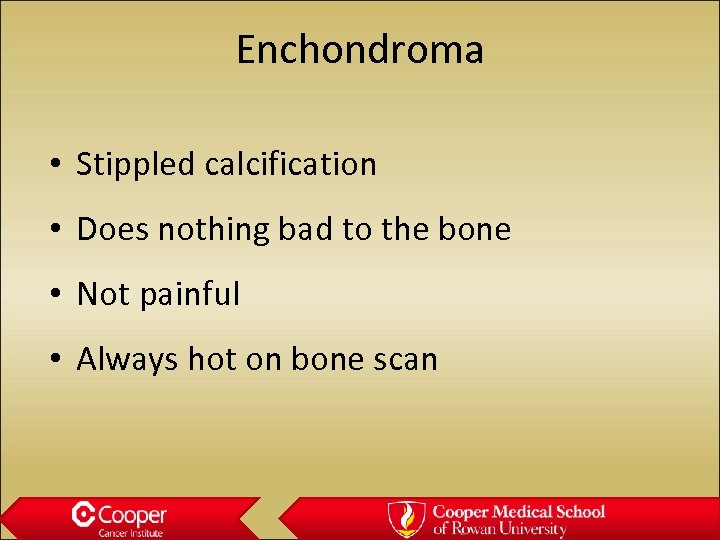 Enchondroma • Stippled calcification • Does nothing bad to the bone • Not painful • Always hot on bone scan
Enchondroma • Stippled calcification • Does nothing bad to the bone • Not painful • Always hot on bone scan
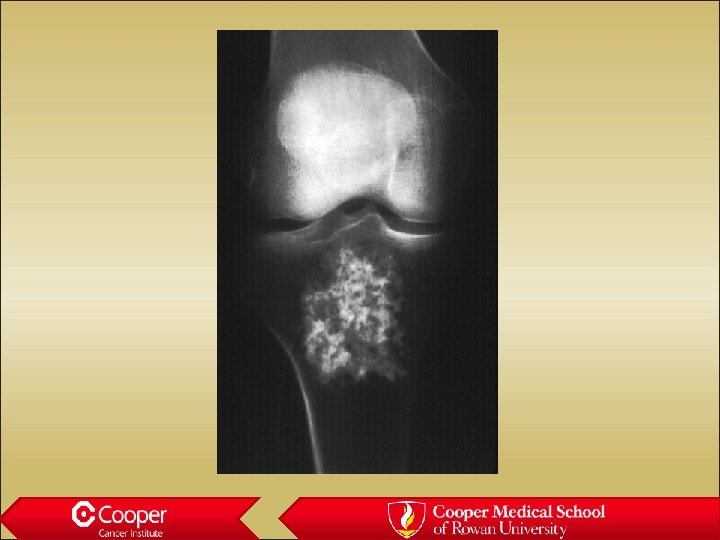
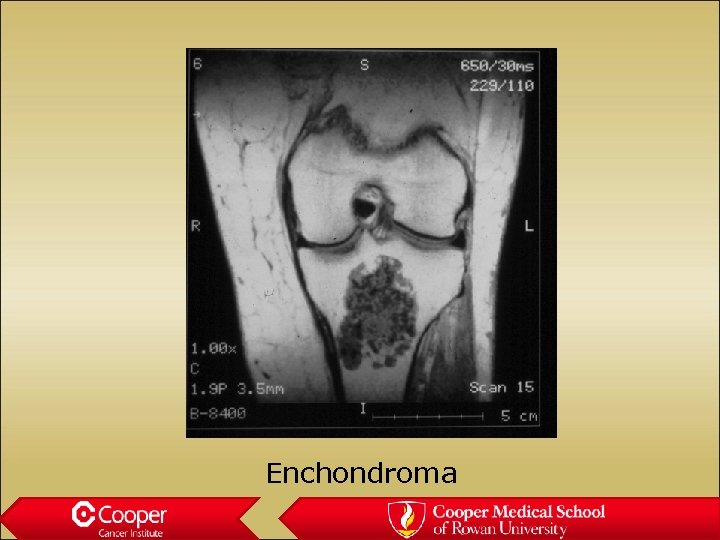 Enchondroma
Enchondroma
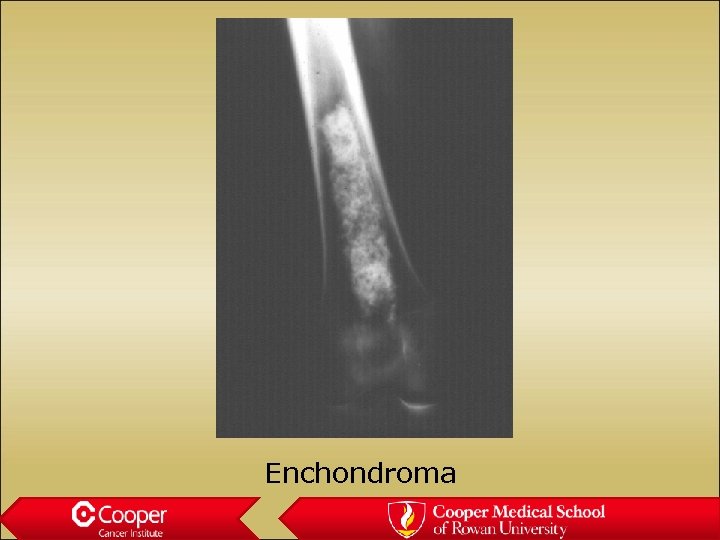 Enchondroma
Enchondroma
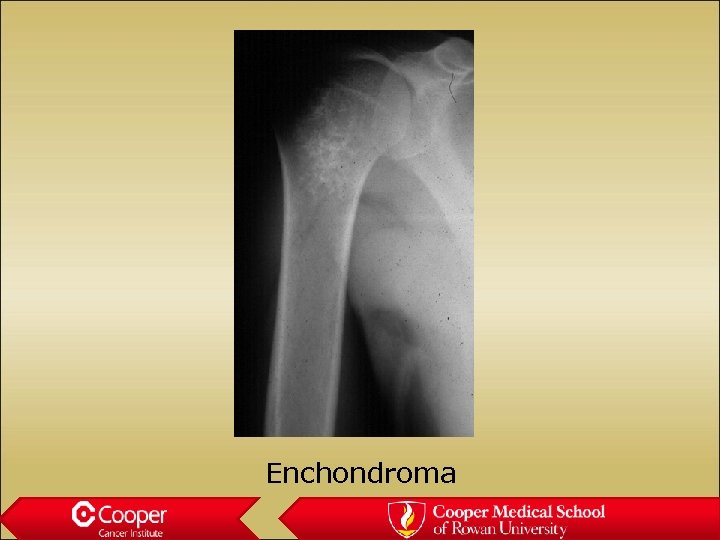 Enchondroma
Enchondroma
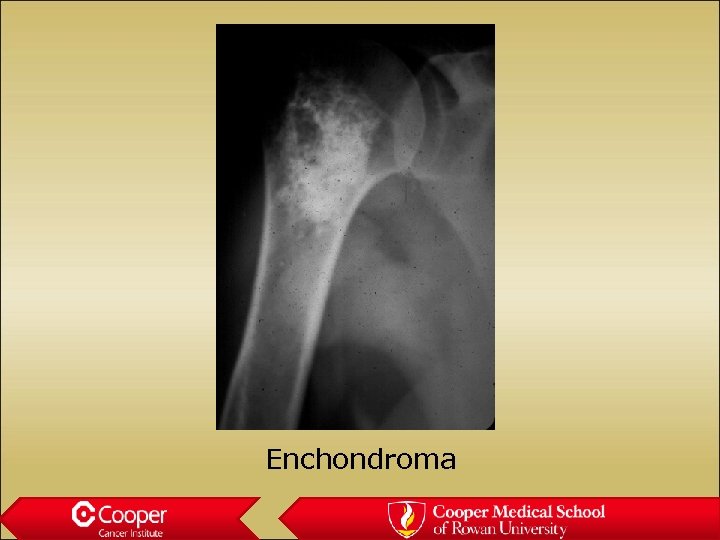 Enchondroma
Enchondroma
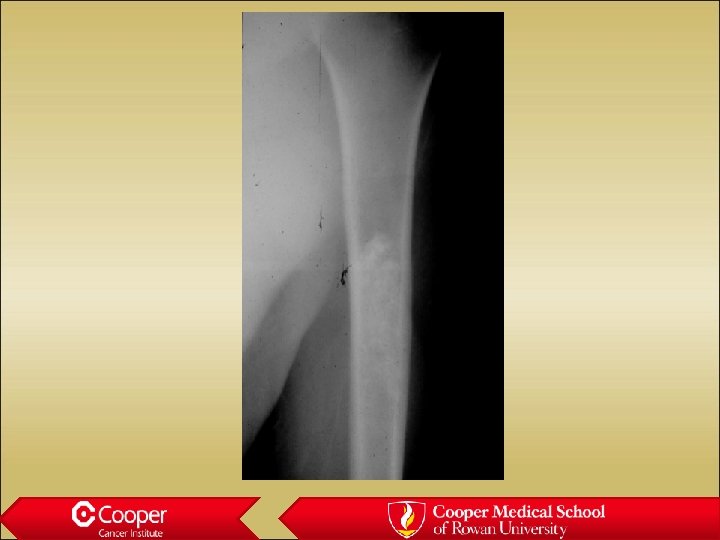
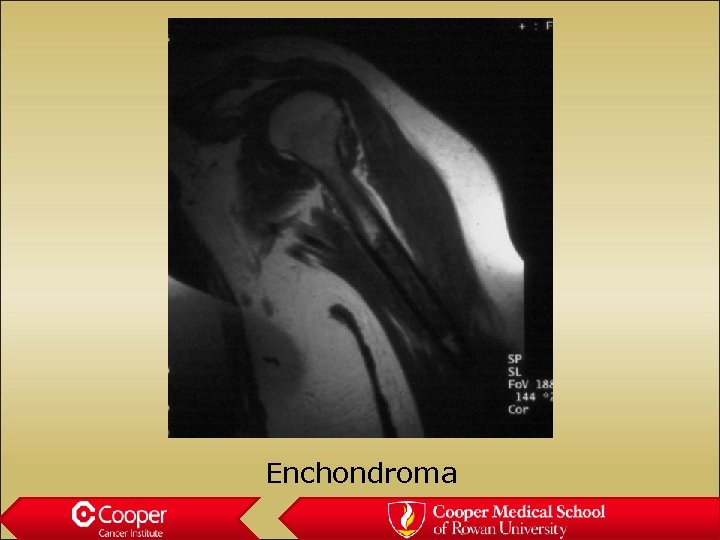 Enchondroma
Enchondroma
 Chondrosarcoma • Intralesional lysis • Endosteal scalloping • Cortical thinning/expansion • pain
Chondrosarcoma • Intralesional lysis • Endosteal scalloping • Cortical thinning/expansion • pain
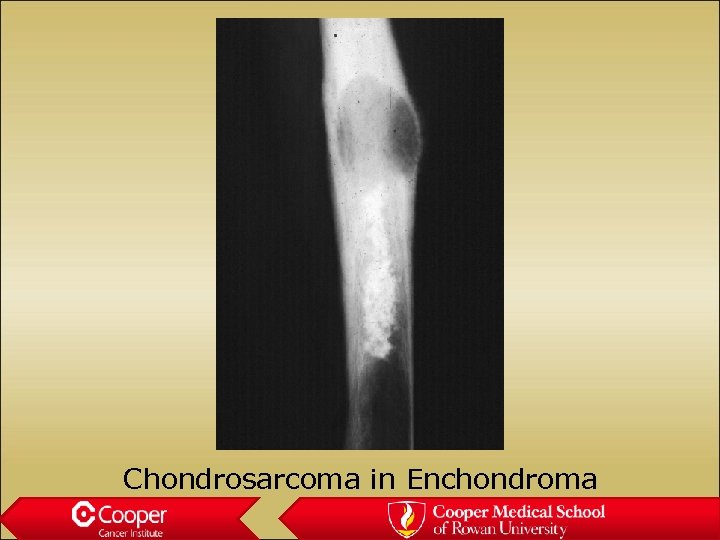 Chondrosarcoma in Enchondroma
Chondrosarcoma in Enchondroma
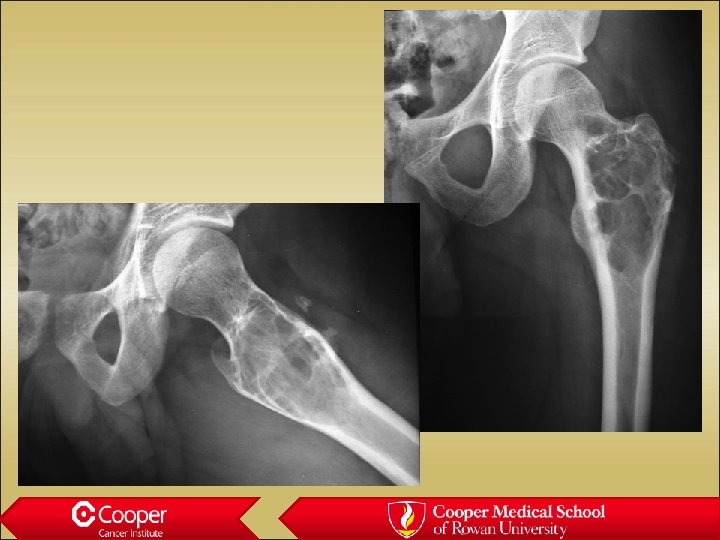
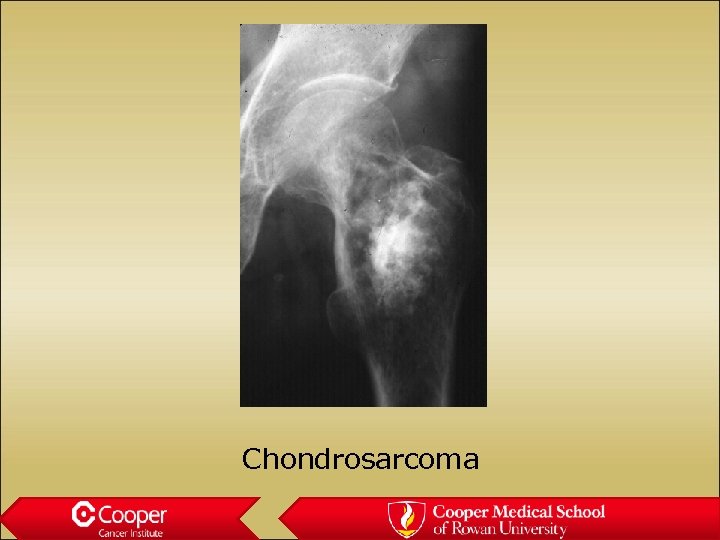 Chondrosarcoma
Chondrosarcoma
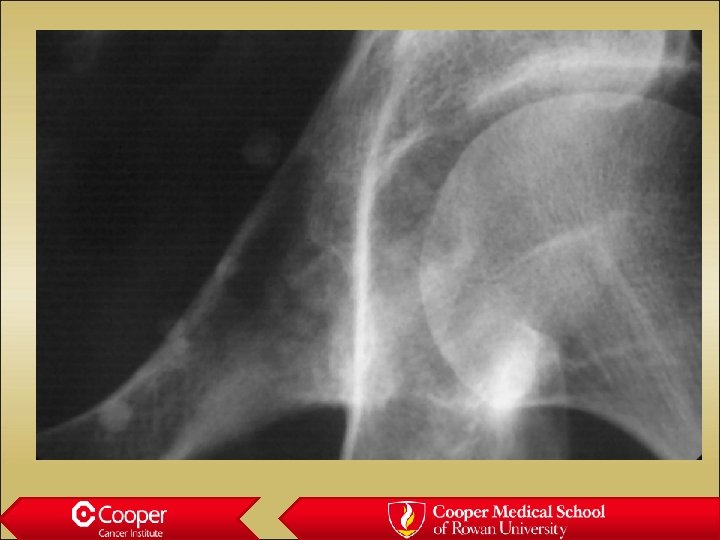
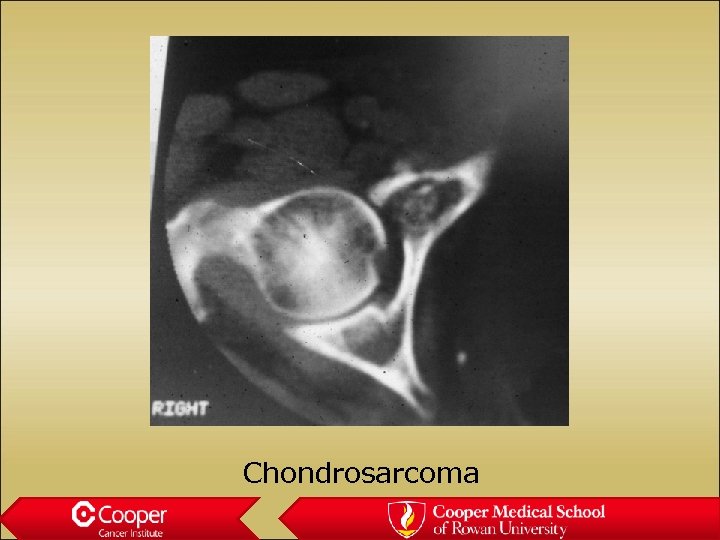 Chondrosarcoma
Chondrosarcoma
 Chondromyxoid fibroma • Large benign looking lytic lesion • Proximal tibia • Young adults (20 -40) • Painful
Chondromyxoid fibroma • Large benign looking lytic lesion • Proximal tibia • Young adults (20 -40) • Painful
 13 y/o with Knee Pain
13 y/o with Knee Pain
 Periosteal chondroma • Benign cartilage tumor on the surface • Periosteal scalloping • May be painful
Periosteal chondroma • Benign cartilage tumor on the surface • Periosteal scalloping • May be painful
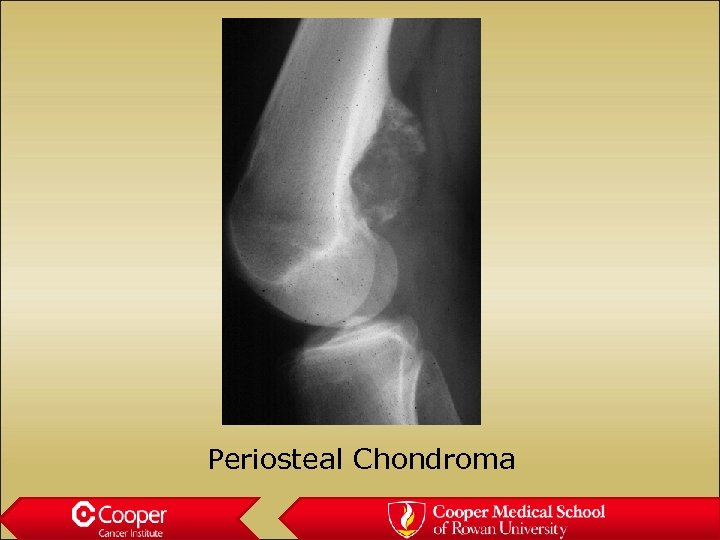 Periosteal Chondroma
Periosteal Chondroma
 Chondroblastoma • Lytic lesion in the epiphysis of a child • Painful • Significant surrounding edema • Mimics infection
Chondroblastoma • Lytic lesion in the epiphysis of a child • Painful • Significant surrounding edema • Mimics infection
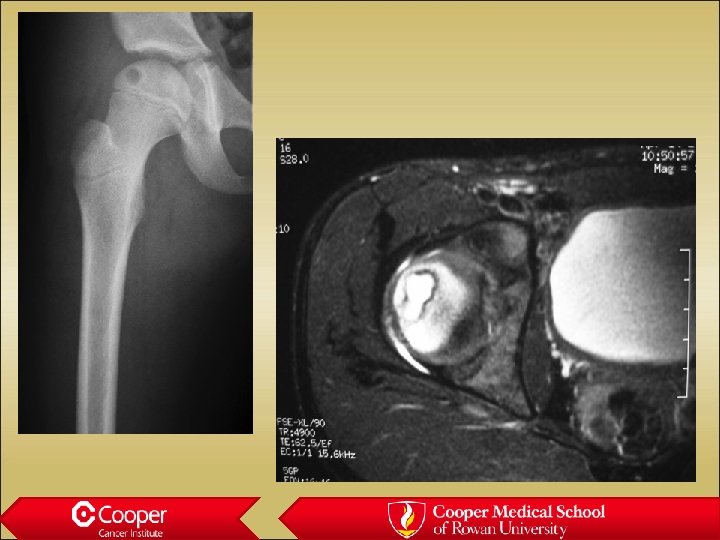
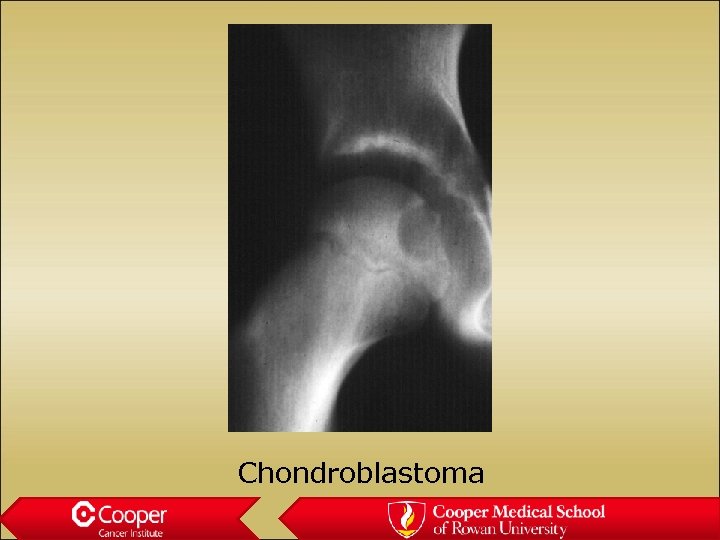 Chondroblastoma
Chondroblastoma
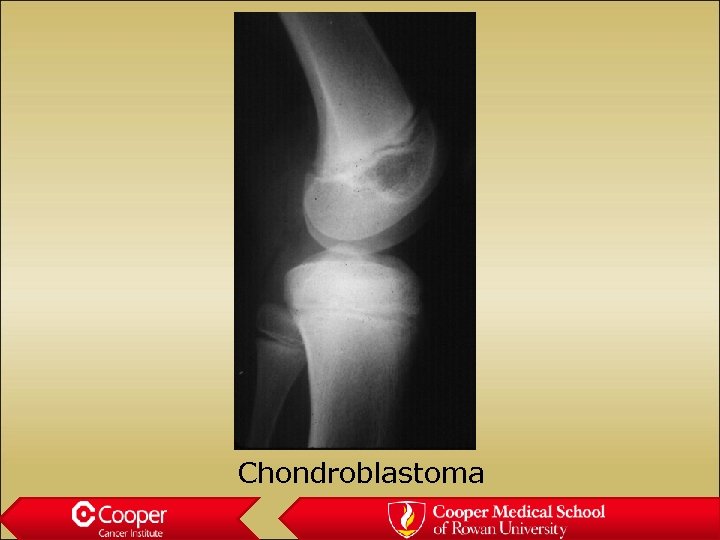 Chondroblastoma
Chondroblastoma
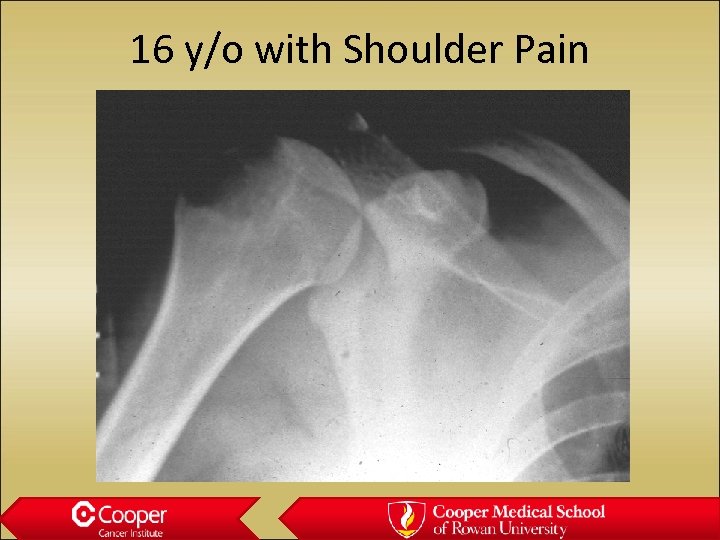 16 y/o with Shoulder Pain
16 y/o with Shoulder Pain
 Infection • Mimics everything • Poorly marginated • Significant edema
Infection • Mimics everything • Poorly marginated • Significant edema

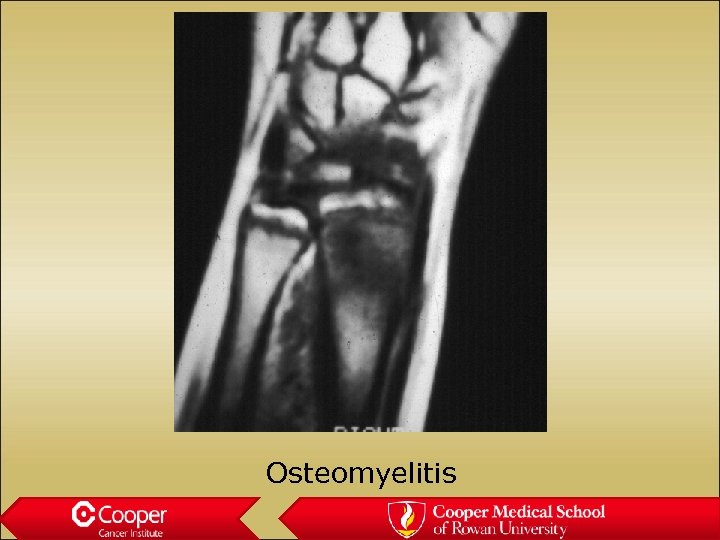 Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis
 Lytic Mets • Most common aggressive lesion in older adults • Soft issue mass suggests sarcoma but occurs with kidney, lung • Usually multiple
Lytic Mets • Most common aggressive lesion in older adults • Soft issue mass suggests sarcoma but occurs with kidney, lung • Usually multiple
 Plasmacytoma/myeloma • Punched out lytic lesions in bone • May mimic osteoporosis • Very lytic within the lesion
Plasmacytoma/myeloma • Punched out lytic lesions in bone • May mimic osteoporosis • Very lytic within the lesion
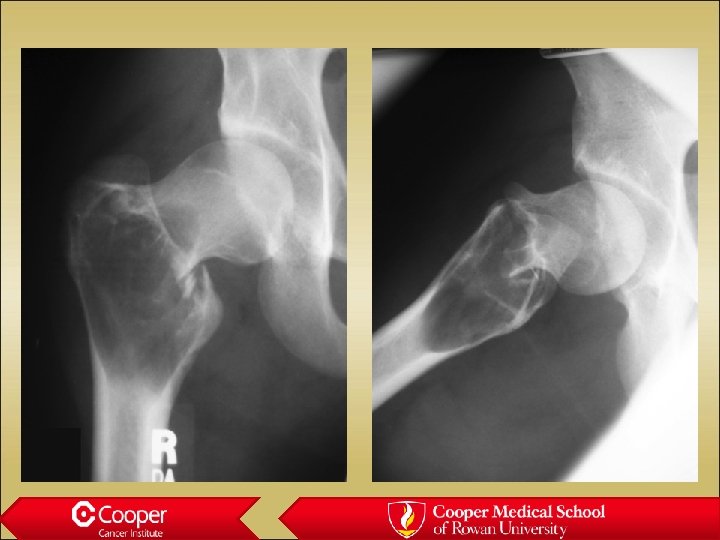
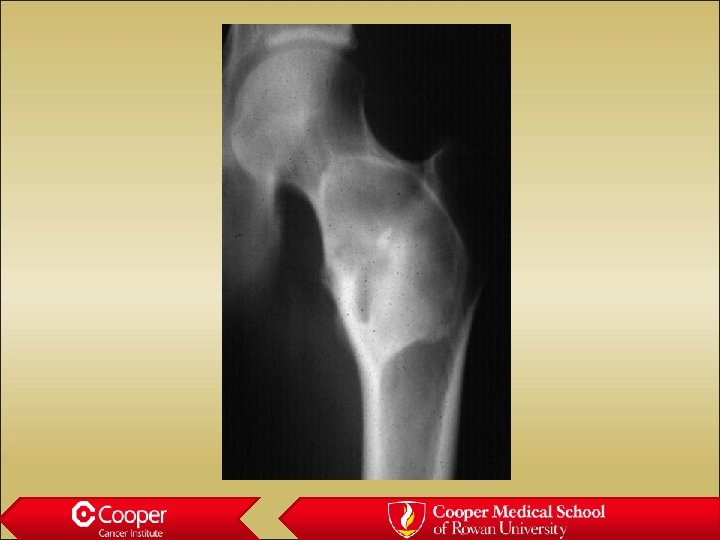
 Fibrous dysplasia • In the diff dx of every benign lesion • Long lesion in a long bone • Ground glass deformity • May be polyostotic • May be small and mimic NOF
Fibrous dysplasia • In the diff dx of every benign lesion • Long lesion in a long bone • Ground glass deformity • May be polyostotic • May be small and mimic NOF
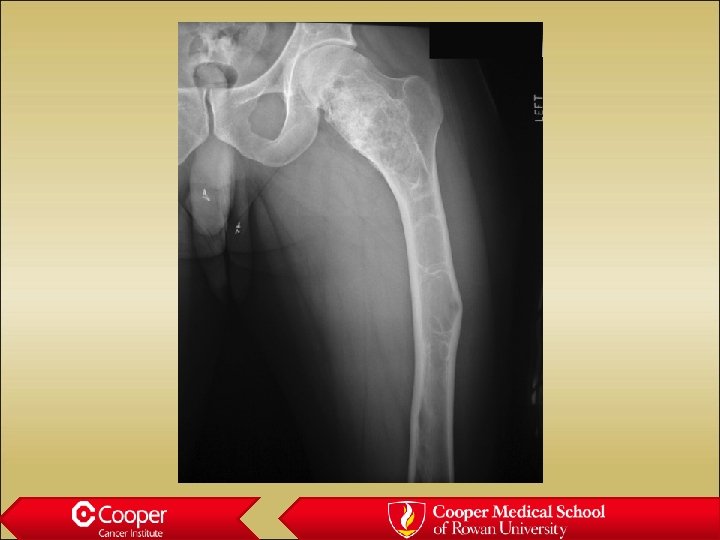
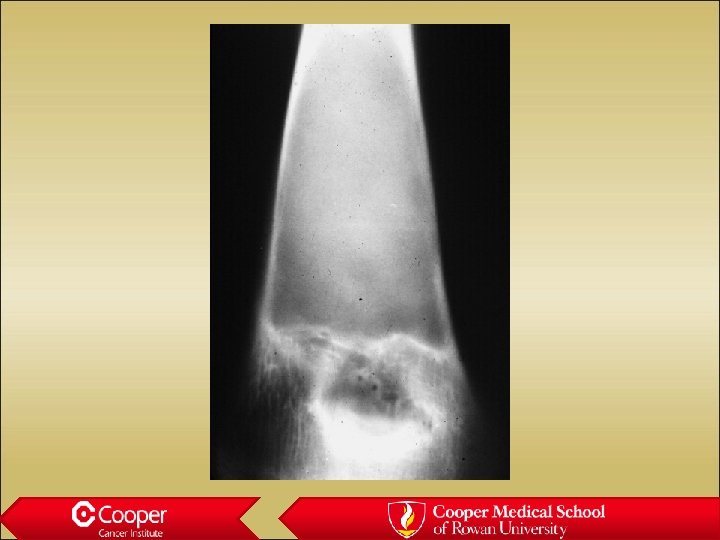
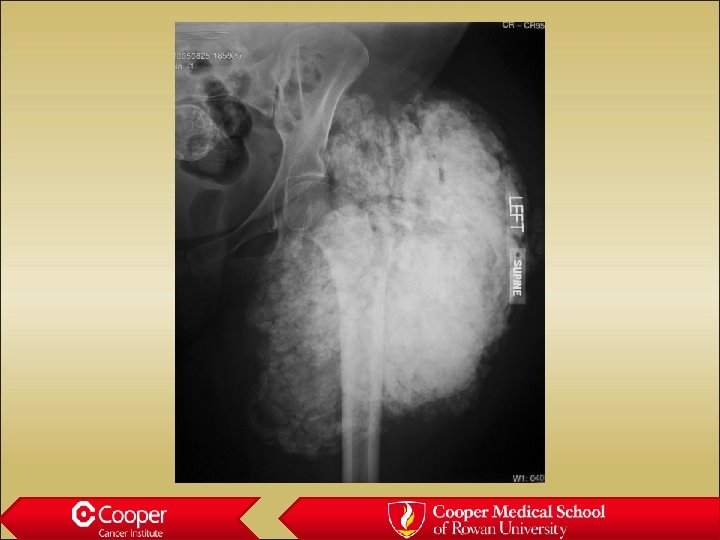
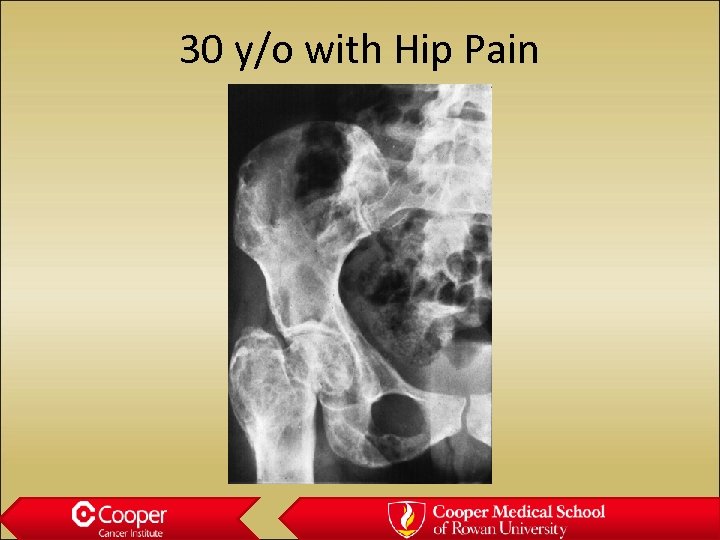 30 y/o with Hip Pain
30 y/o with Hip Pain
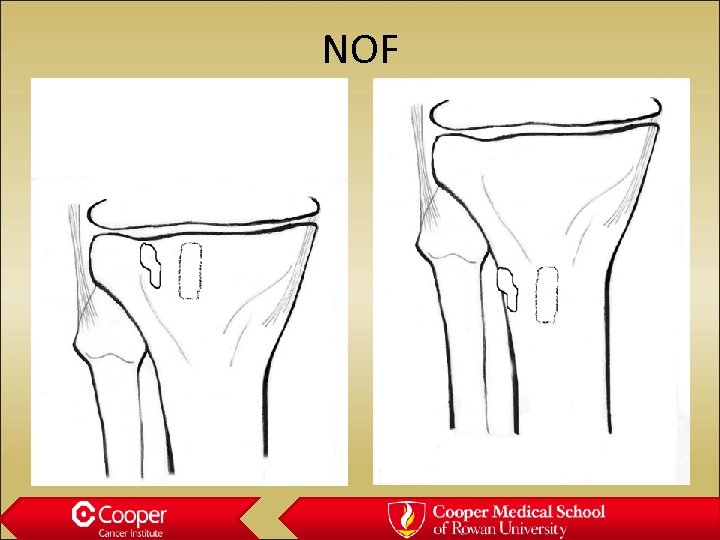 NOF
NOF
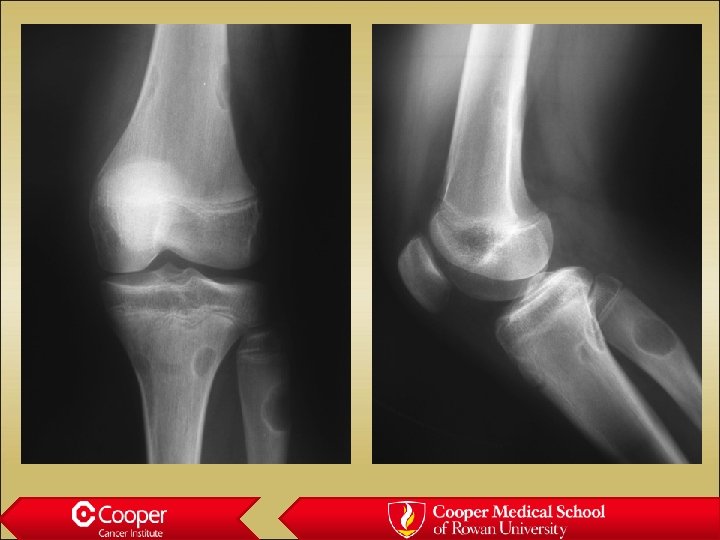
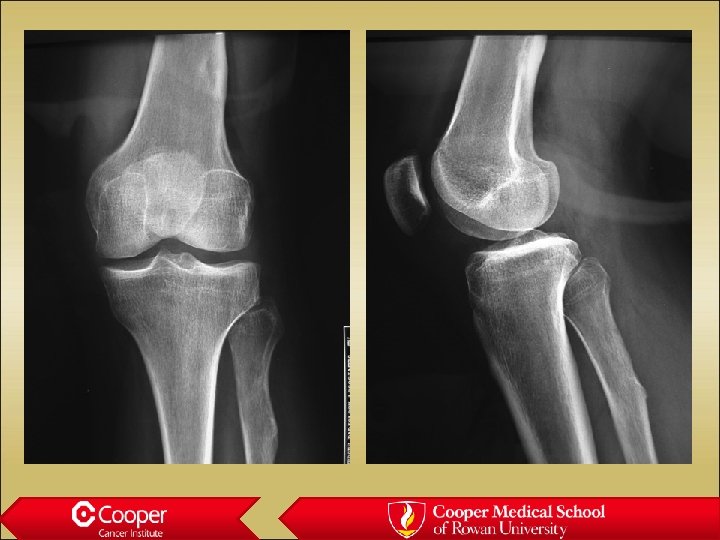
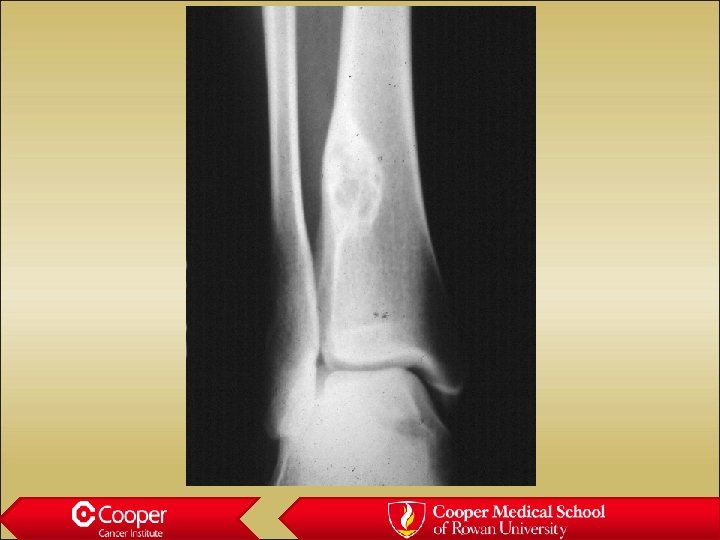
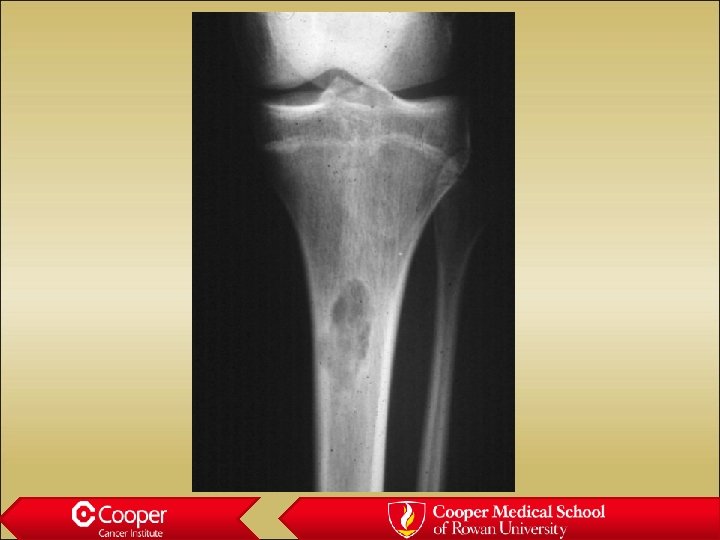
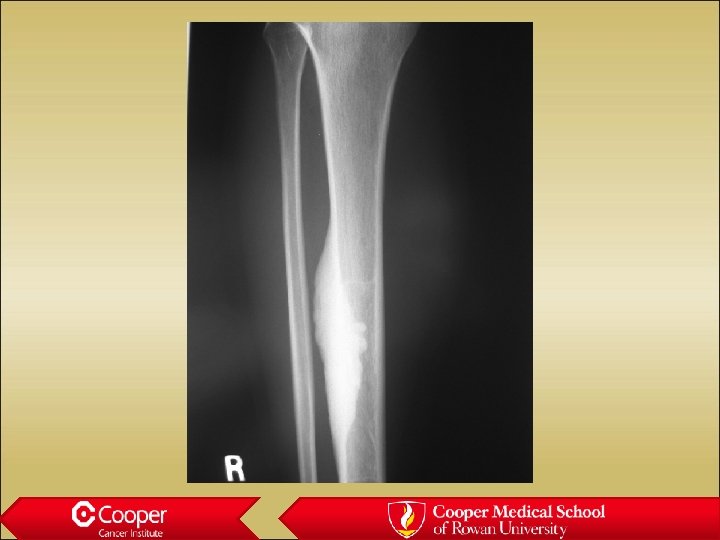
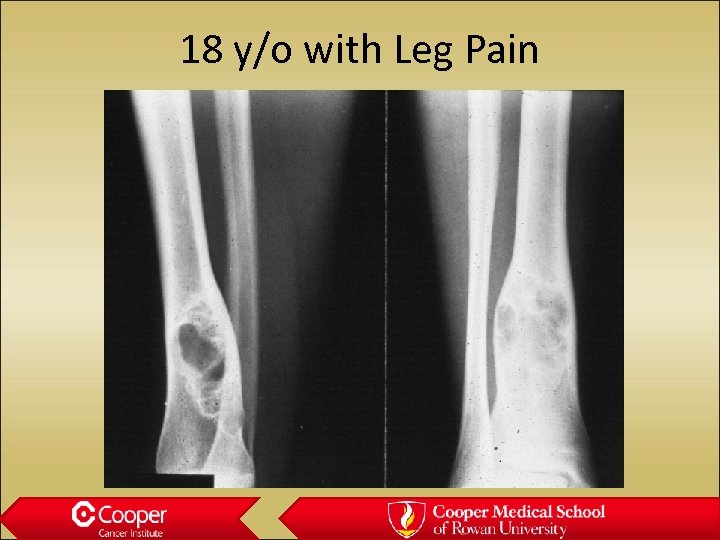 18 y/o with Leg Pain
18 y/o with Leg Pain
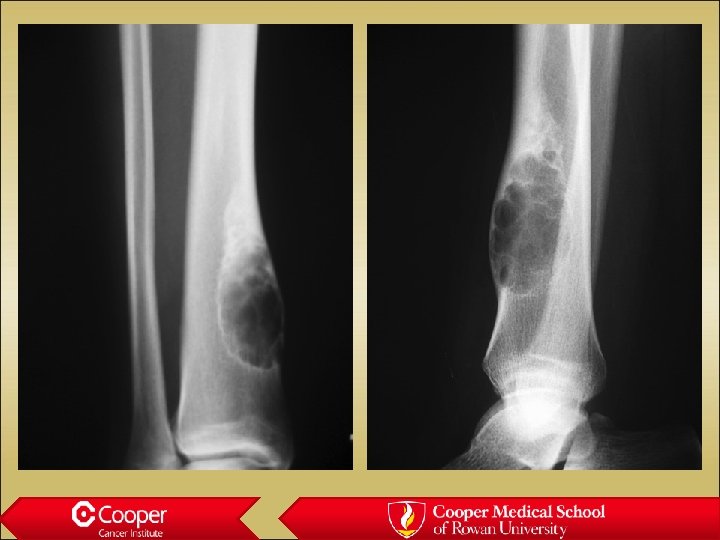
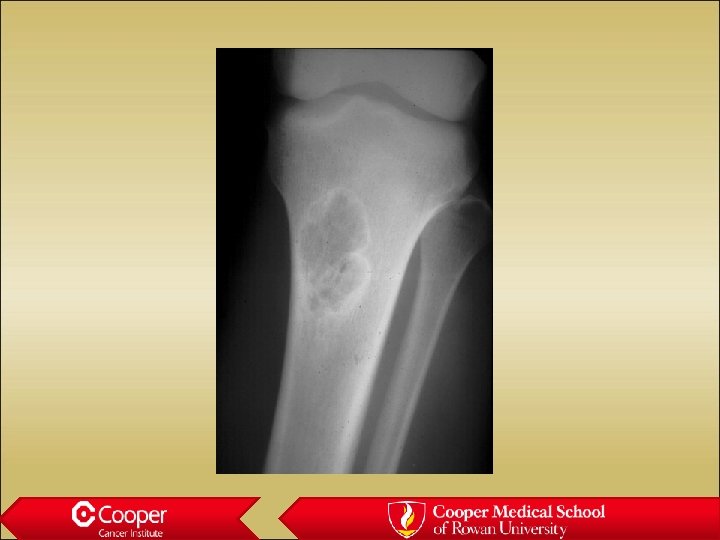
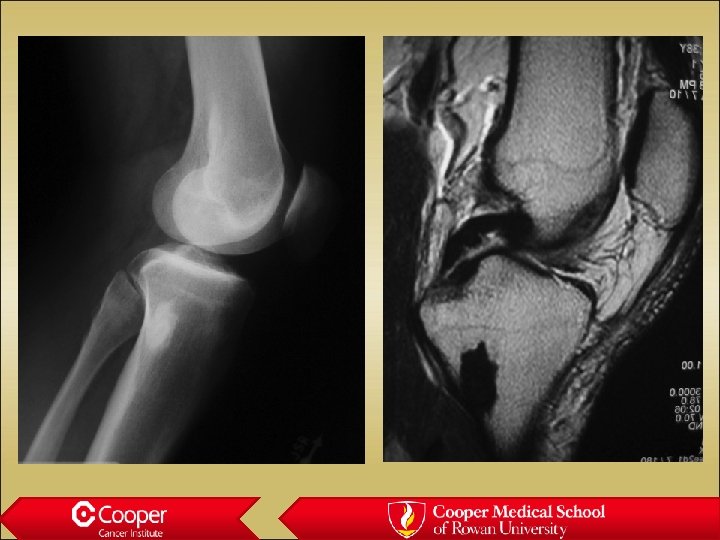
 LC Histiocytosis • Intra-medullary lytic lesion in a child • Poorly marginated • Periosteal reaction • Very inflammatory • Painful
LC Histiocytosis • Intra-medullary lytic lesion in a child • Poorly marginated • Periosteal reaction • Very inflammatory • Painful
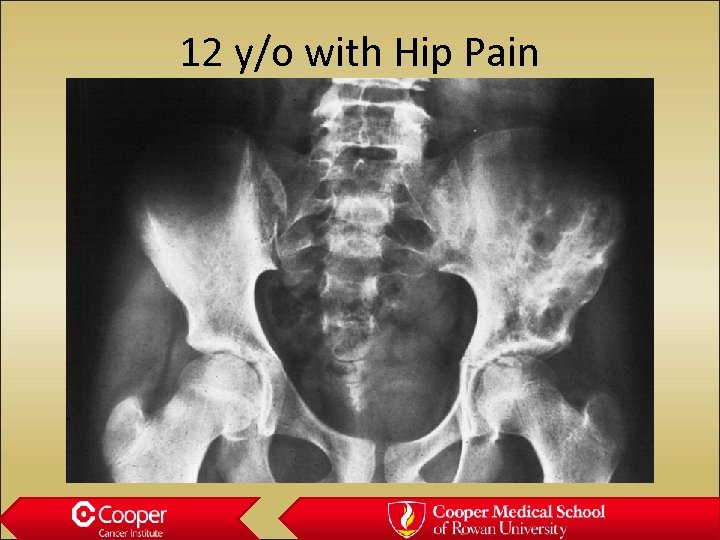 12 y/o with Hip Pain
12 y/o with Hip Pain
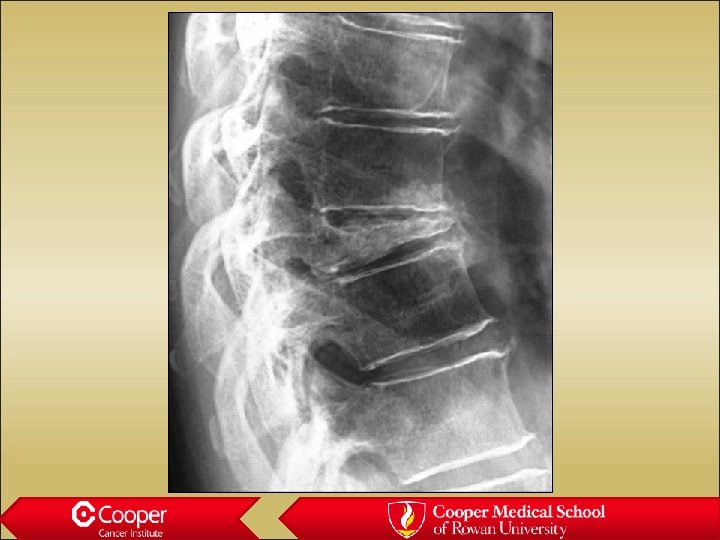
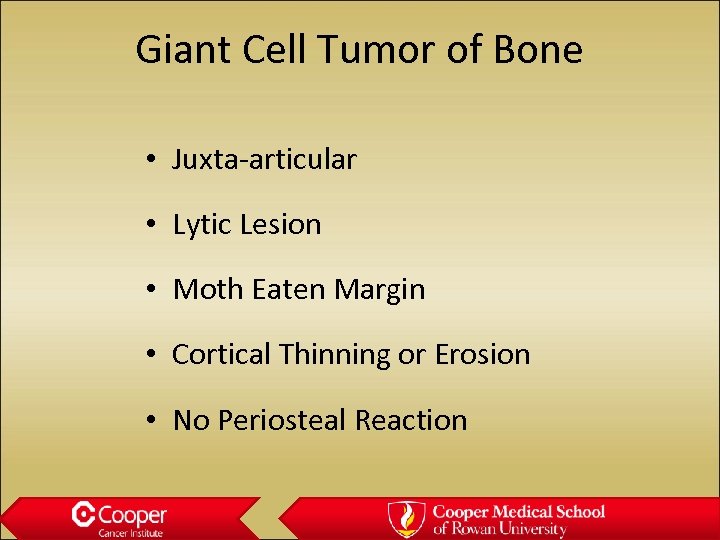 Giant Cell Tumor of Bone • Juxta-articular • Lytic Lesion • Moth Eaten Margin • Cortical Thinning or Erosion • No Periosteal Reaction
Giant Cell Tumor of Bone • Juxta-articular • Lytic Lesion • Moth Eaten Margin • Cortical Thinning or Erosion • No Periosteal Reaction
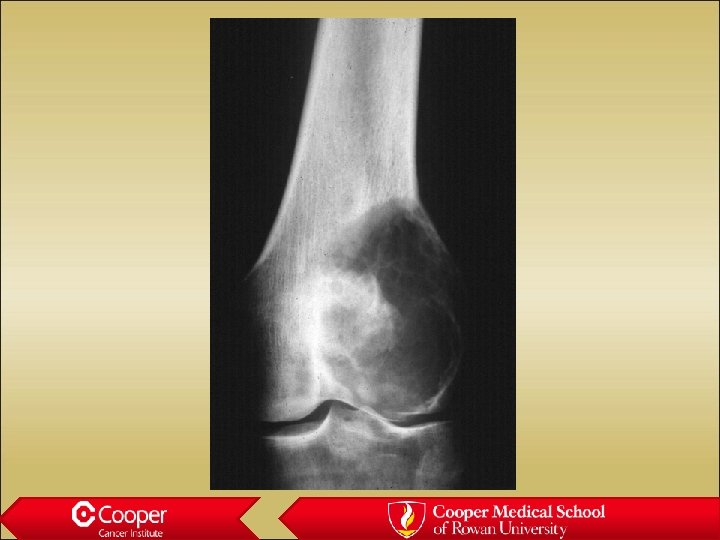
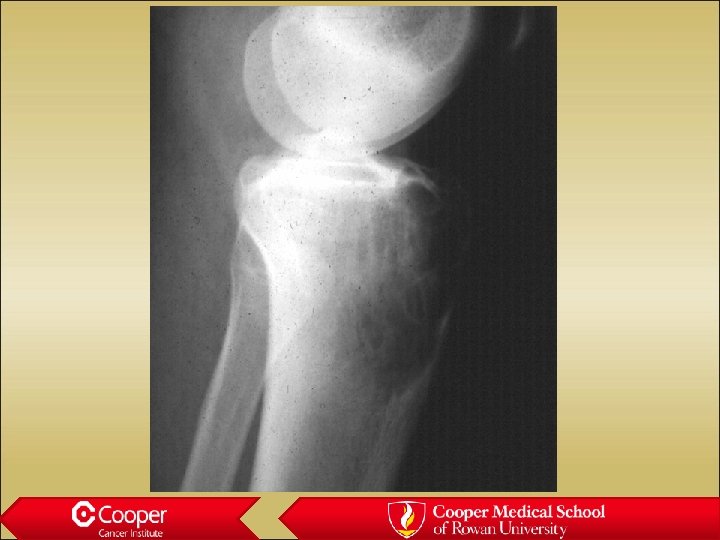
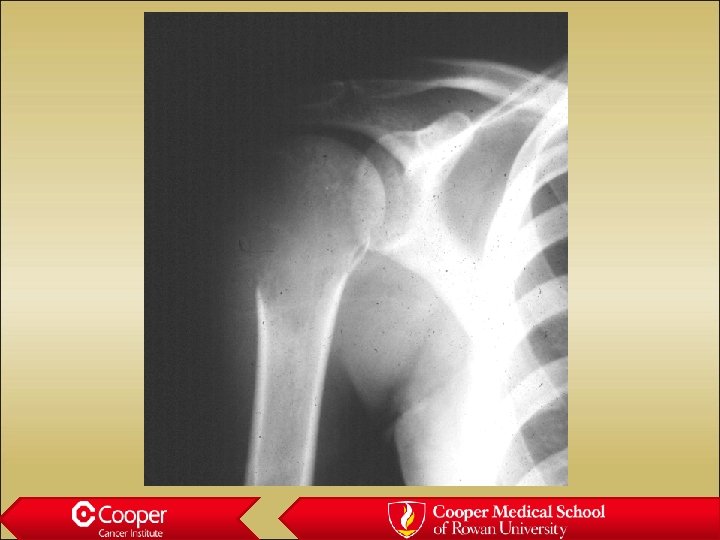
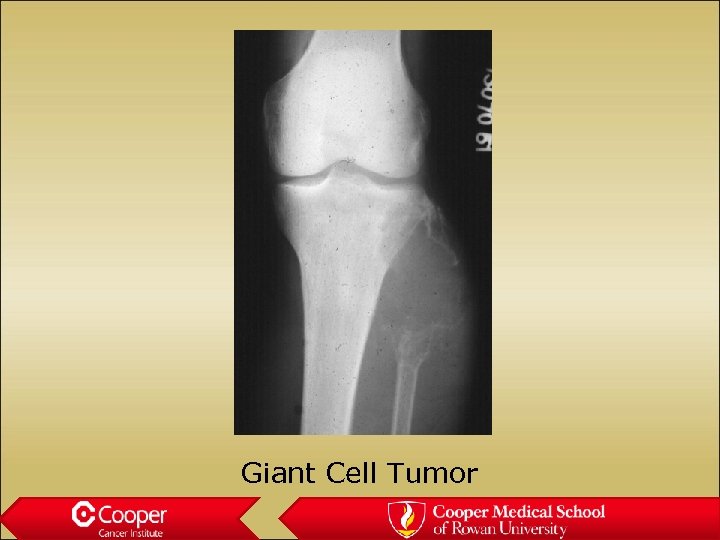 Giant Cell Tumor
Giant Cell Tumor
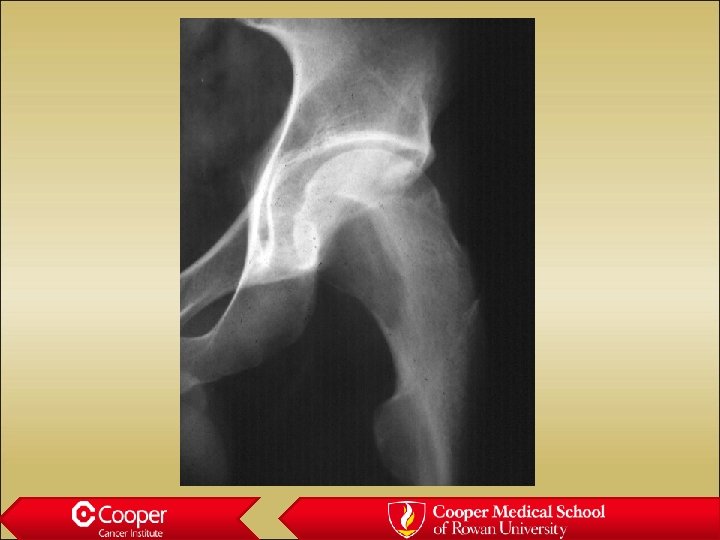
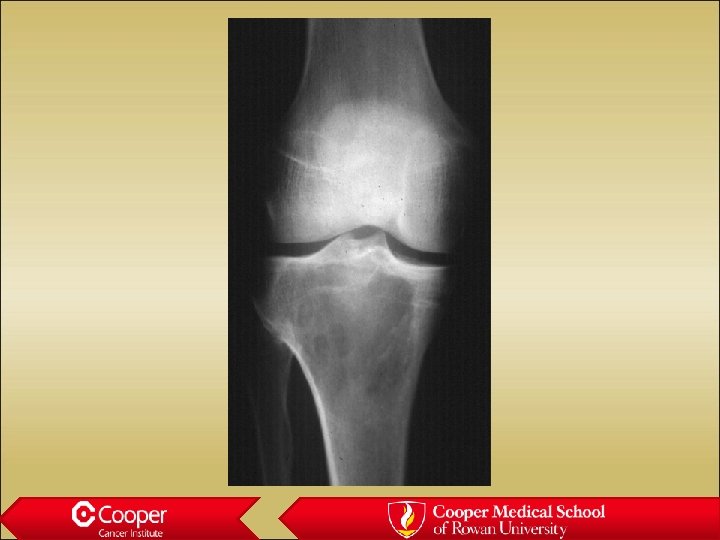
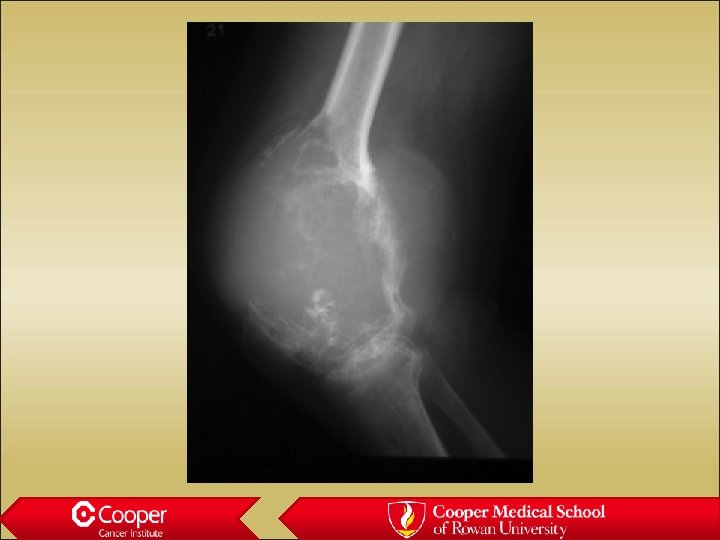
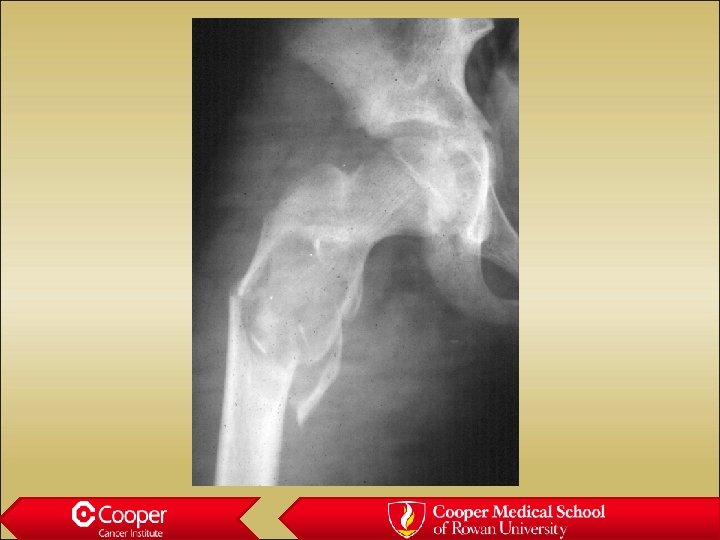
 Unicameral bone cyst • Full width lytic lesion • Cortical thinning • No periosteal reaction • Slight expansion • Proximal Humerus
Unicameral bone cyst • Full width lytic lesion • Cortical thinning • No periosteal reaction • Slight expansion • Proximal Humerus
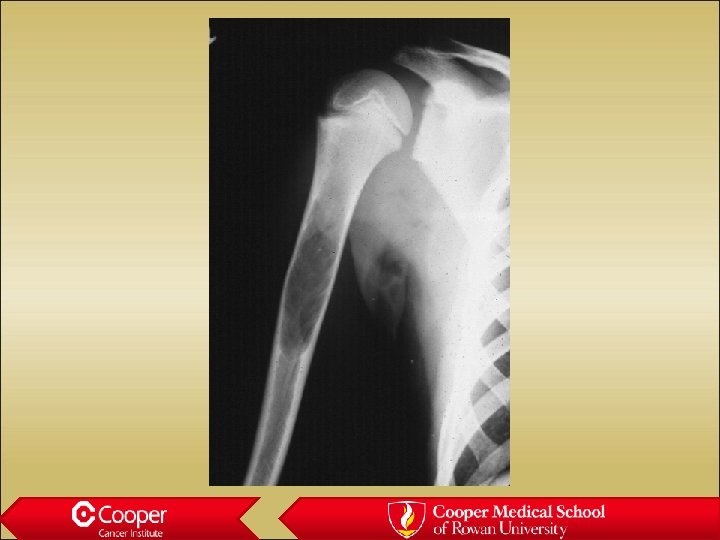
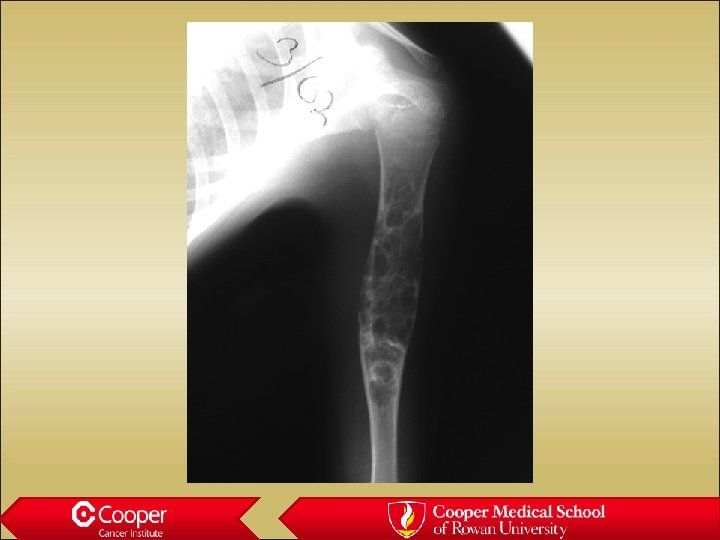
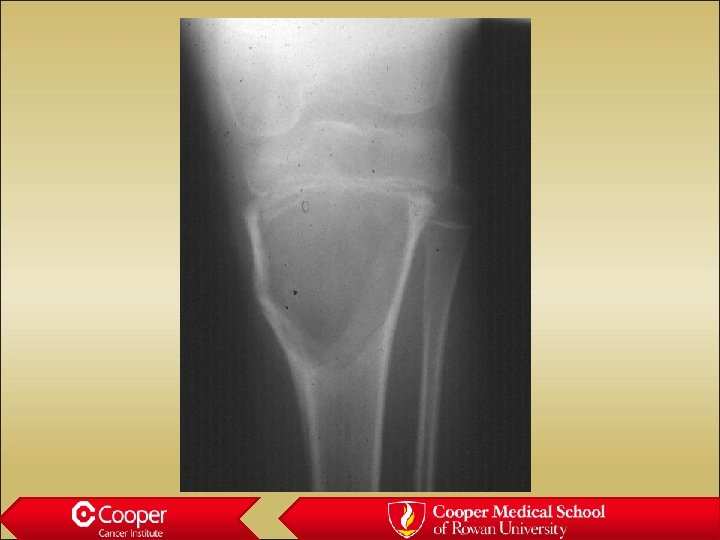
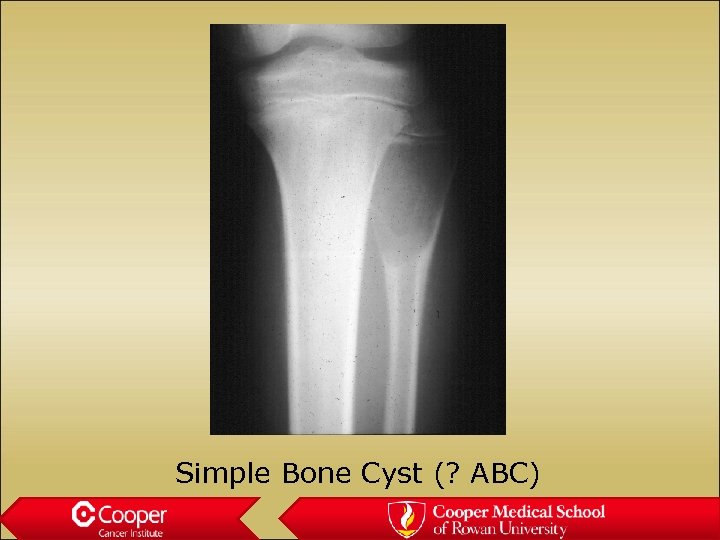 Simple Bone Cyst (? ABC)
Simple Bone Cyst (? ABC)
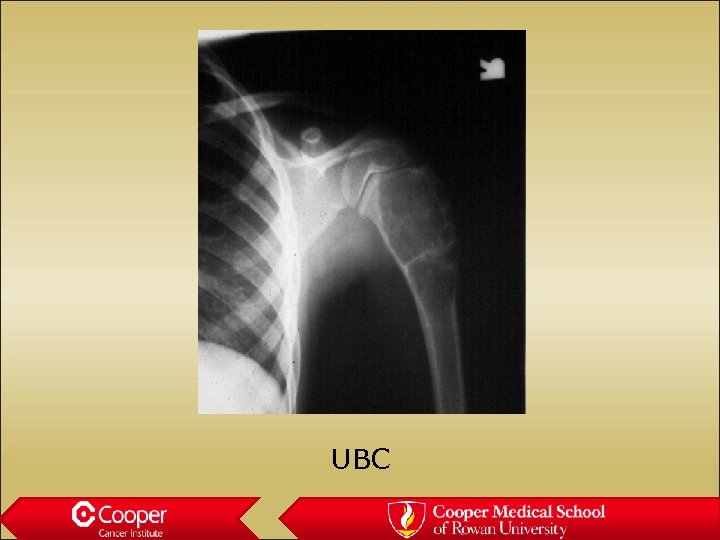 UBC
UBC
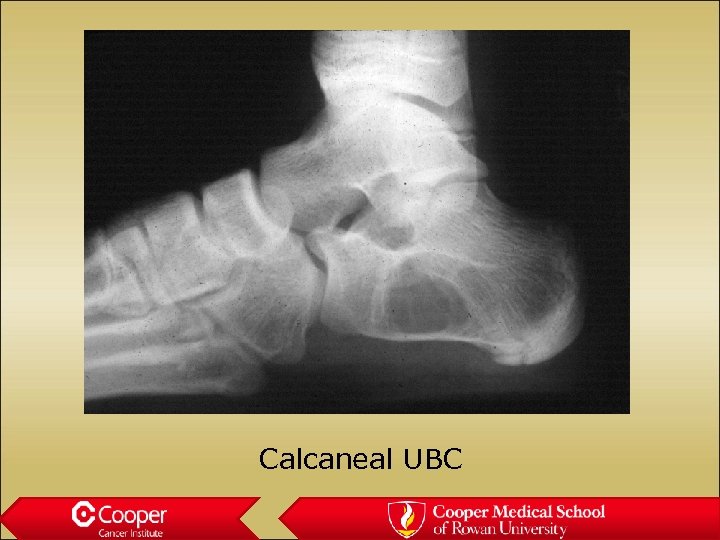 Calcaneal UBC
Calcaneal UBC
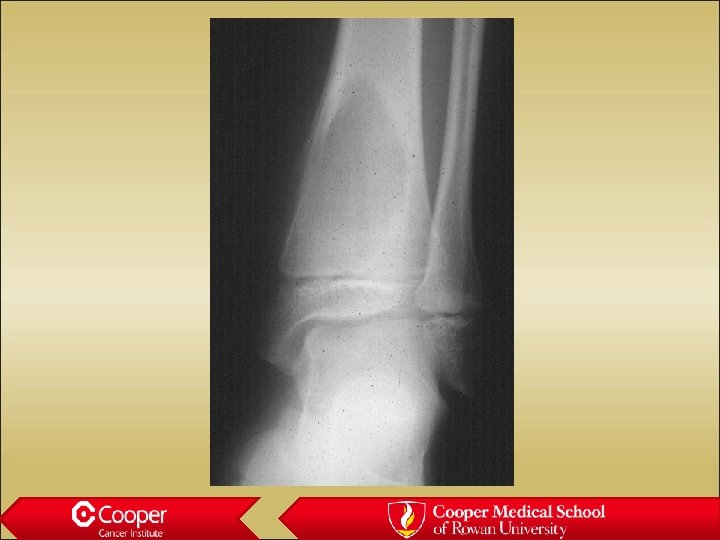
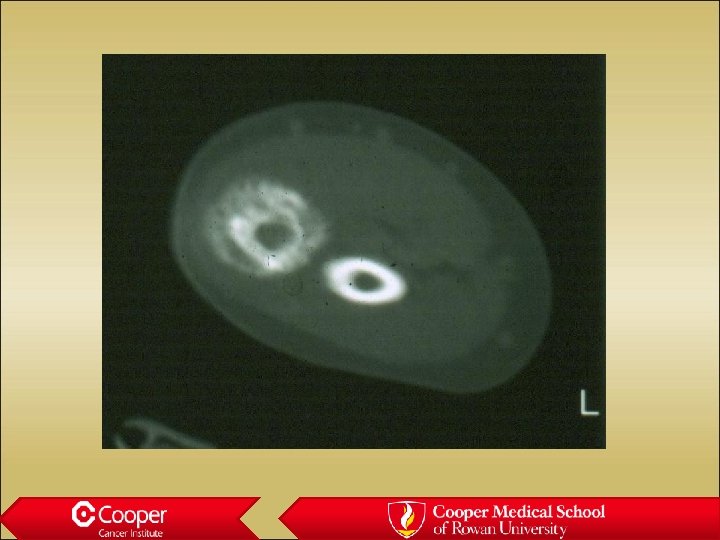
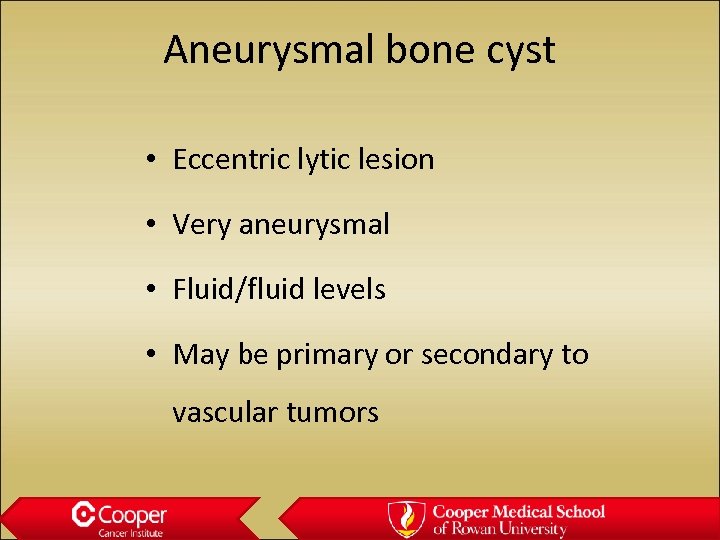 Aneurysmal bone cyst • Eccentric lytic lesion • Very aneurysmal • Fluid/fluid levels • May be primary or secondary to vascular tumors
Aneurysmal bone cyst • Eccentric lytic lesion • Very aneurysmal • Fluid/fluid levels • May be primary or secondary to vascular tumors
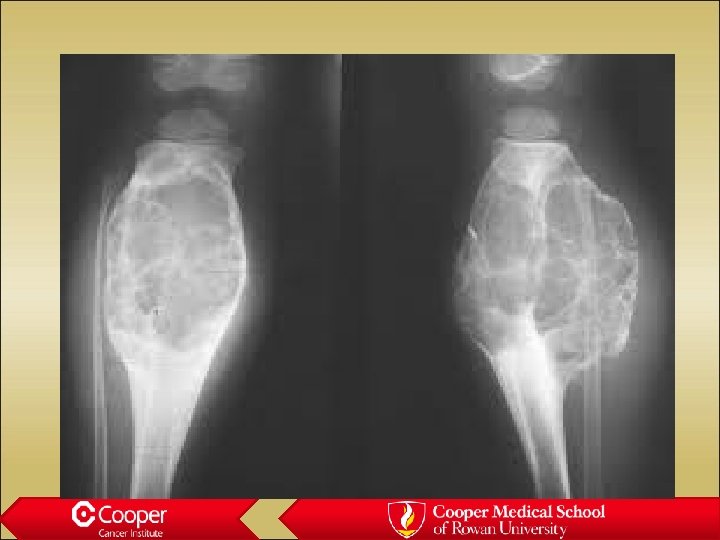
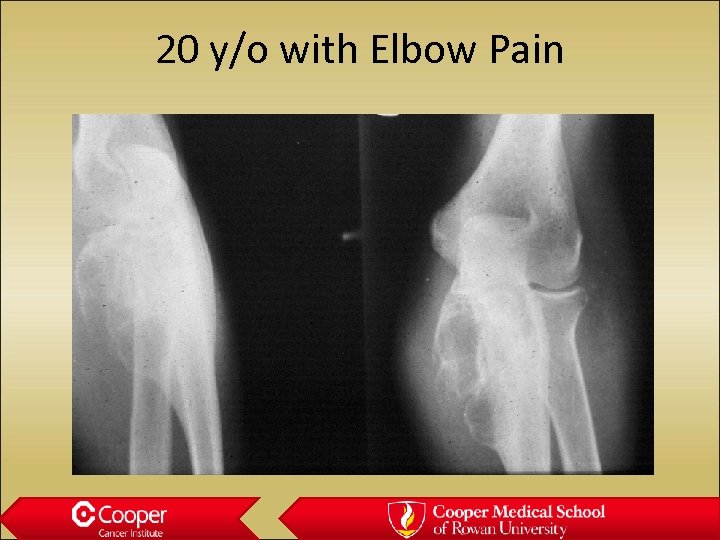 20 y/o with Elbow Pain
20 y/o with Elbow Pain
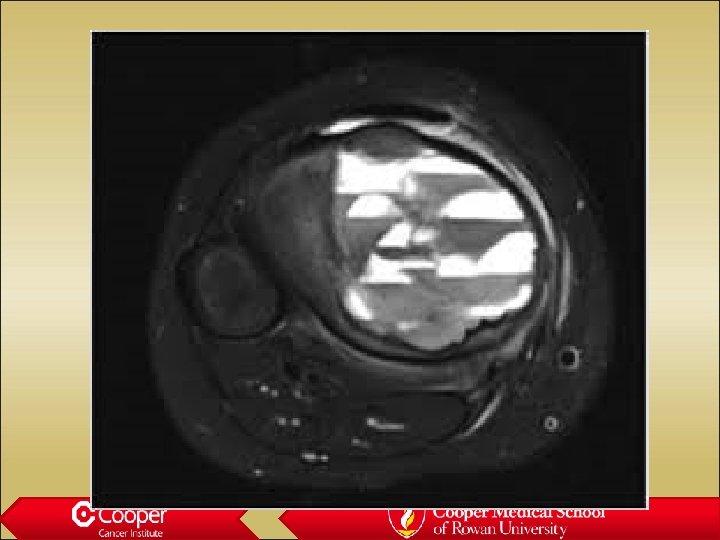
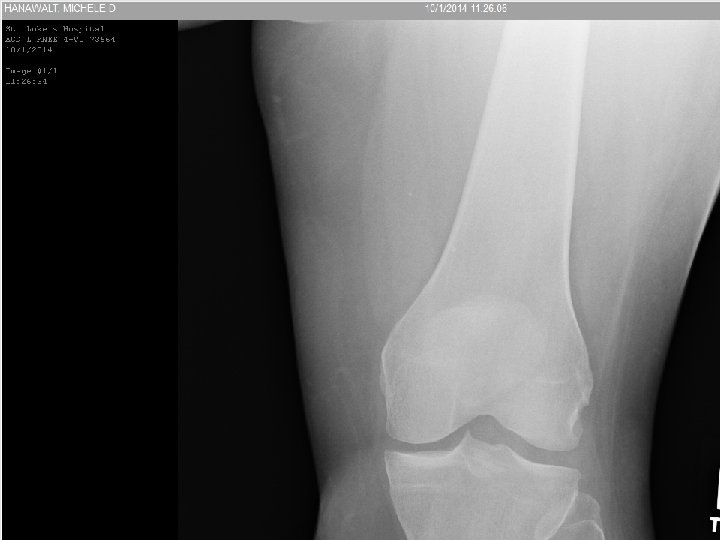
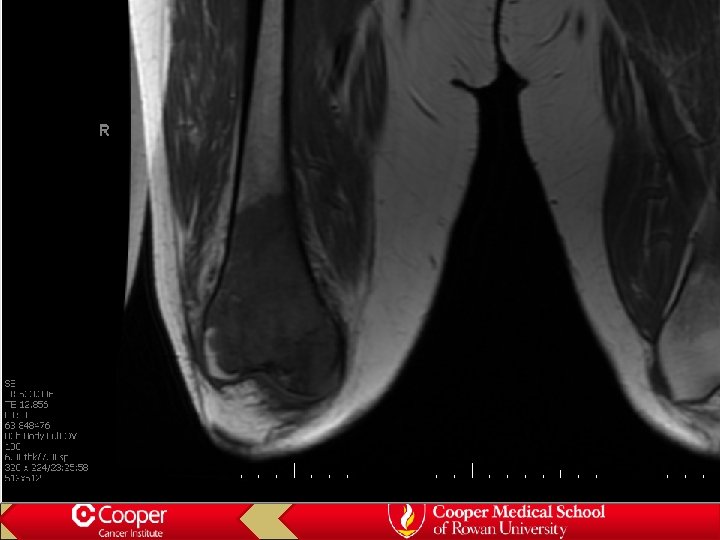
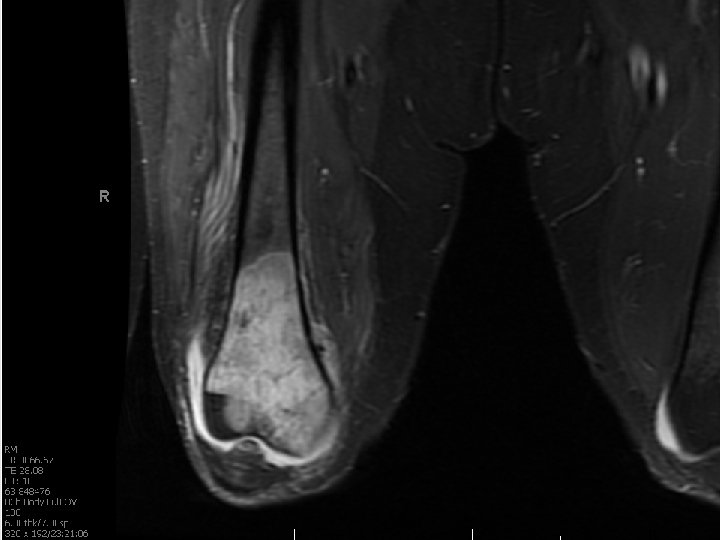
 Lymphoma • Marrow replacement • Permeative, not destructive • Minimal bone changes • Late soft tissue extension • Minimal periosteal reaction
Lymphoma • Marrow replacement • Permeative, not destructive • Minimal bone changes • Late soft tissue extension • Minimal periosteal reaction
 Ewing’s Sarcoma • Children and young adults • Diaphyseal • Onion skin periosteal reaction • Large soft tissue mass • 11/22, CD 99, Ews-fli
Ewing’s Sarcoma • Children and young adults • Diaphyseal • Onion skin periosteal reaction • Large soft tissue mass • 11/22, CD 99, Ews-fli
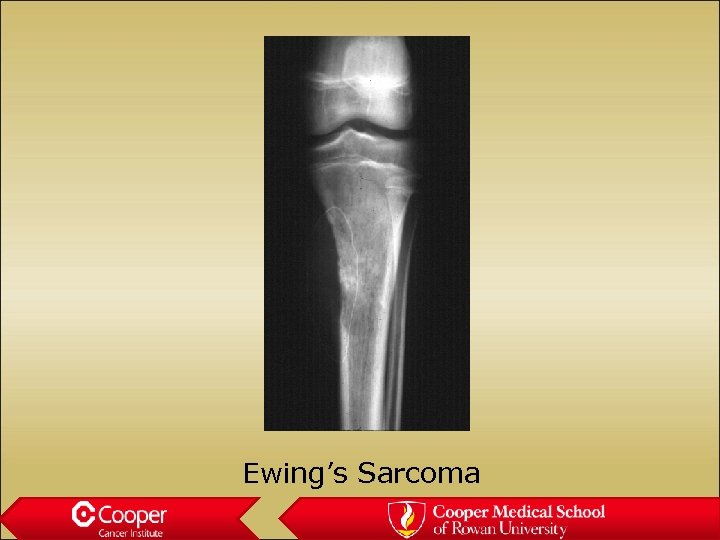 Ewing’s Sarcoma
Ewing’s Sarcoma
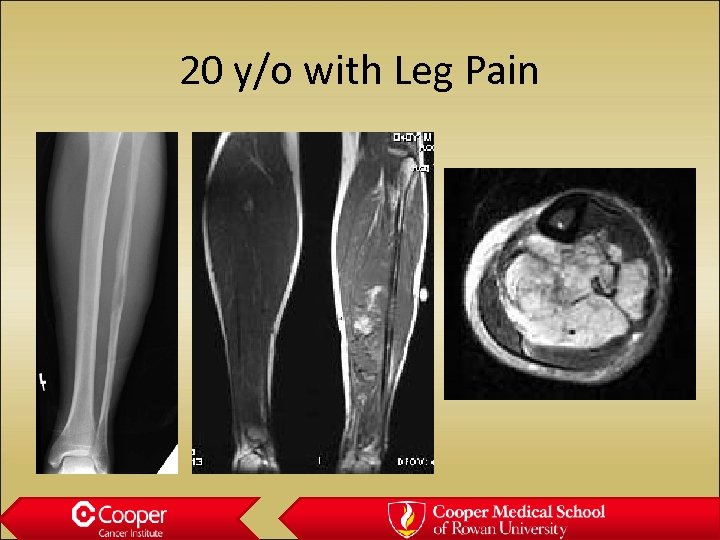 20 y/o with Leg Pain
20 y/o with Leg Pain
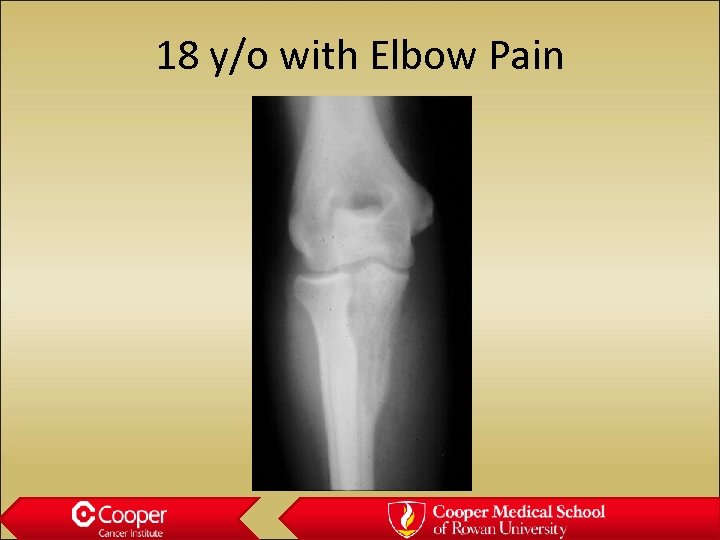 18 y/o with Elbow Pain
18 y/o with Elbow Pain
 Adamantinoma • Young adults • Soap bubble sclerotic lesion of the anterior cortex of the shaft of the tibia • Biphasic (epithelial/mesenchymal)
Adamantinoma • Young adults • Soap bubble sclerotic lesion of the anterior cortex of the shaft of the tibia • Biphasic (epithelial/mesenchymal)
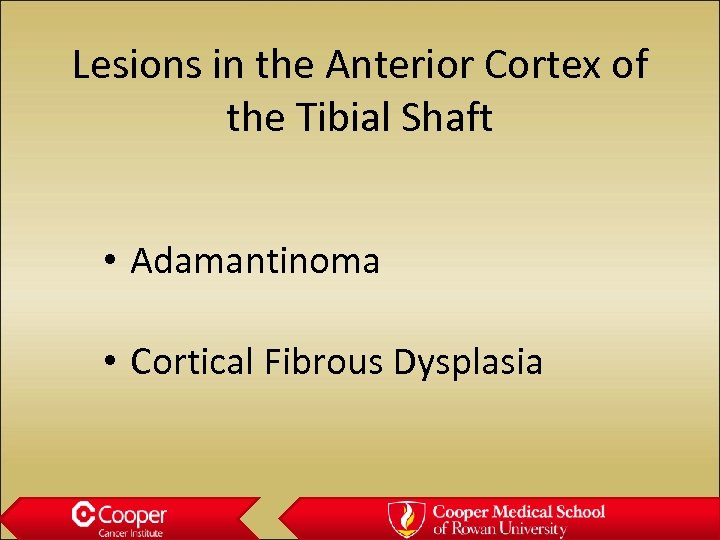 Lesions in the Anterior Cortex of the Tibial Shaft • Adamantinoma • Cortical Fibrous Dysplasia
Lesions in the Anterior Cortex of the Tibial Shaft • Adamantinoma • Cortical Fibrous Dysplasia
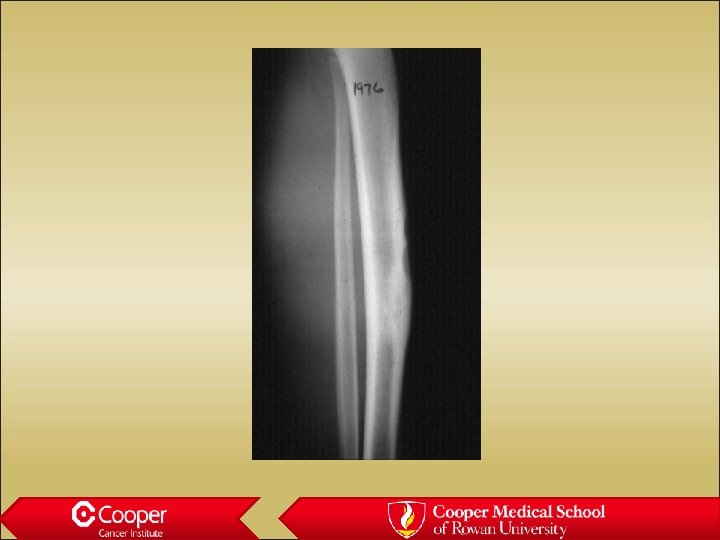
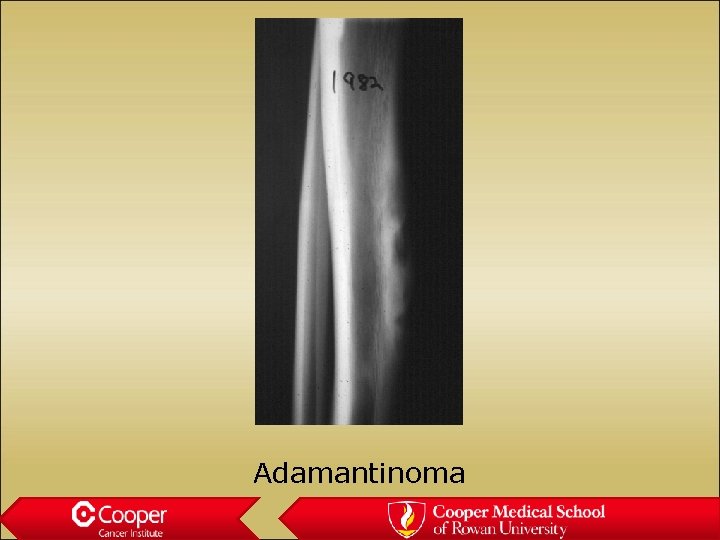 Adamantinoma
Adamantinoma
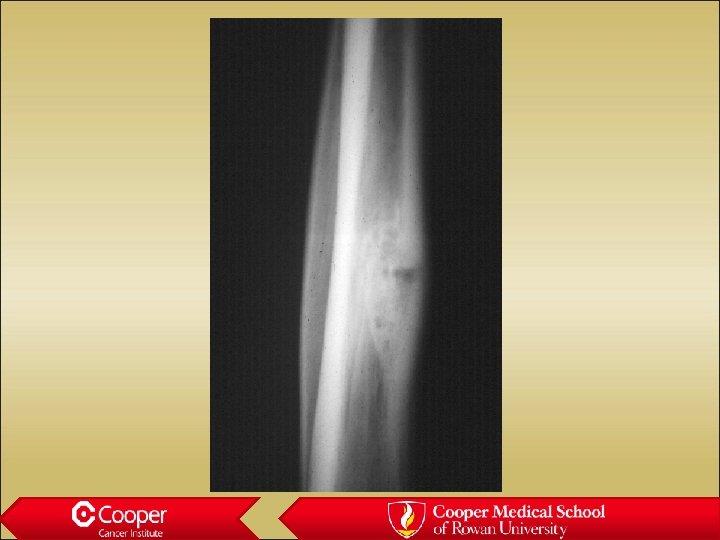
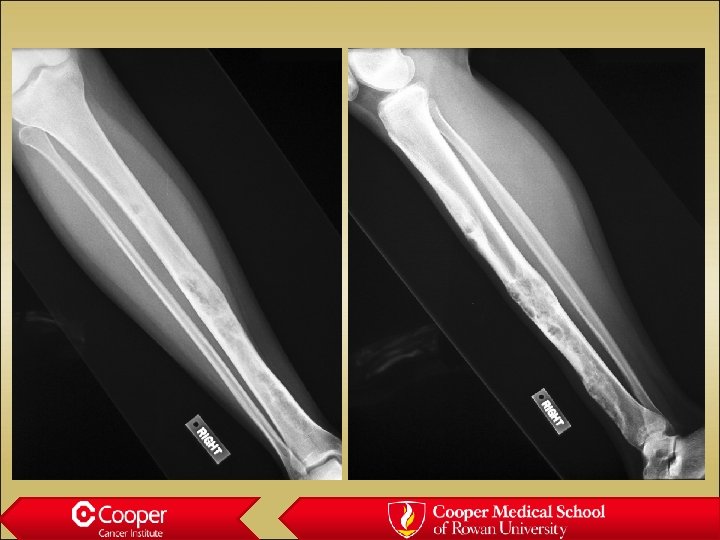
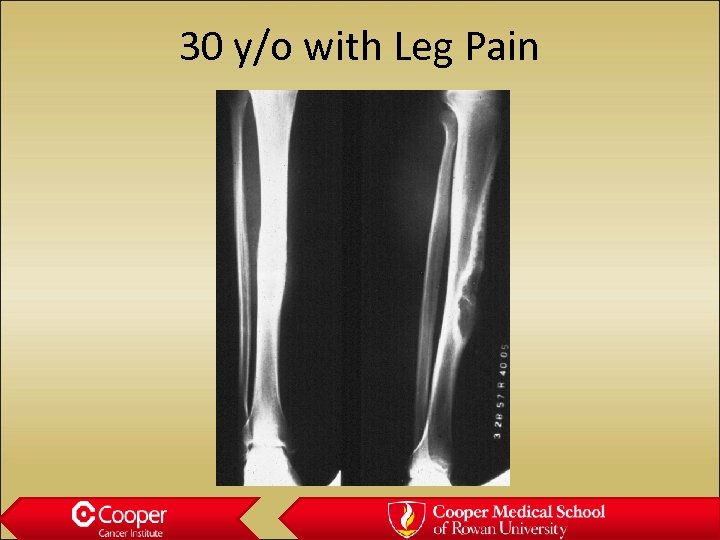 30 y/o with Leg Pain
30 y/o with Leg Pain
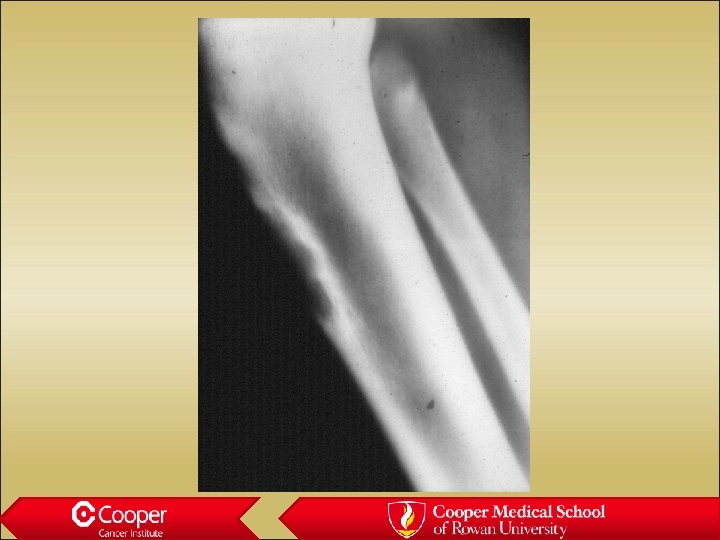
 Chordoma • Notochord remnant tumor • Midline • Sacrum and O/C junction • Anterior extension
Chordoma • Notochord remnant tumor • Midline • Sacrum and O/C junction • Anterior extension
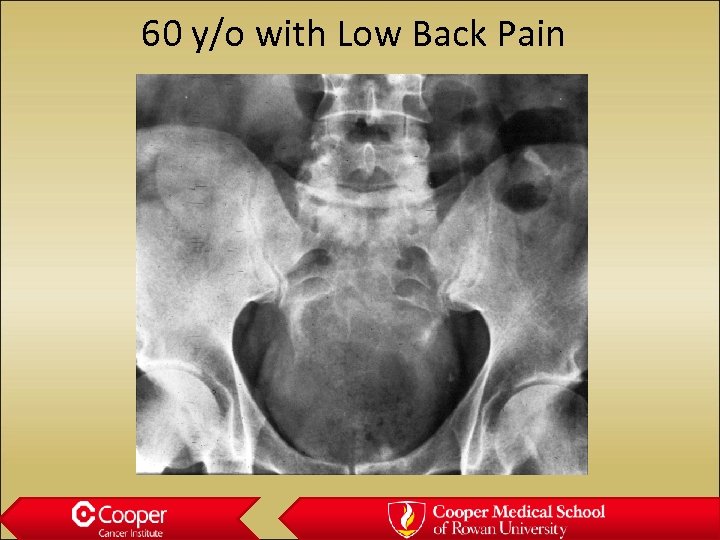 60 y/o with Low Back Pain
60 y/o with Low Back Pain
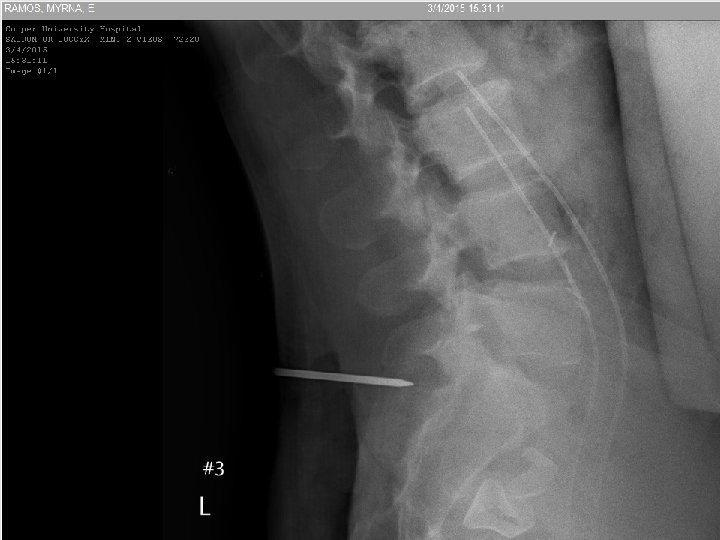
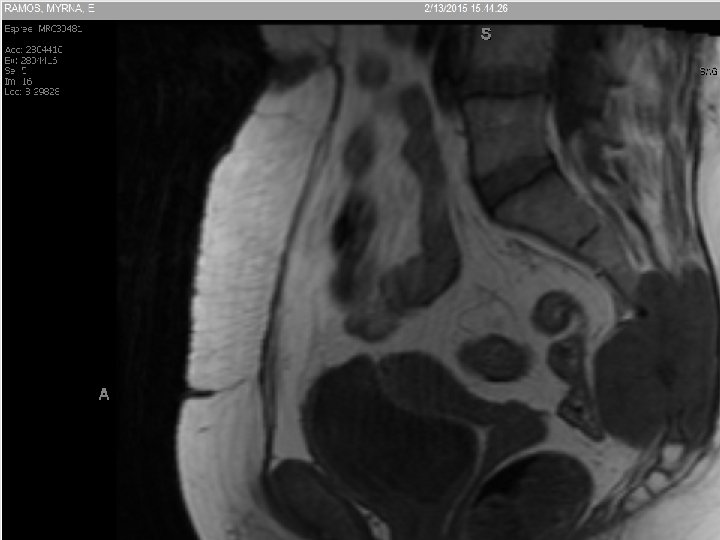
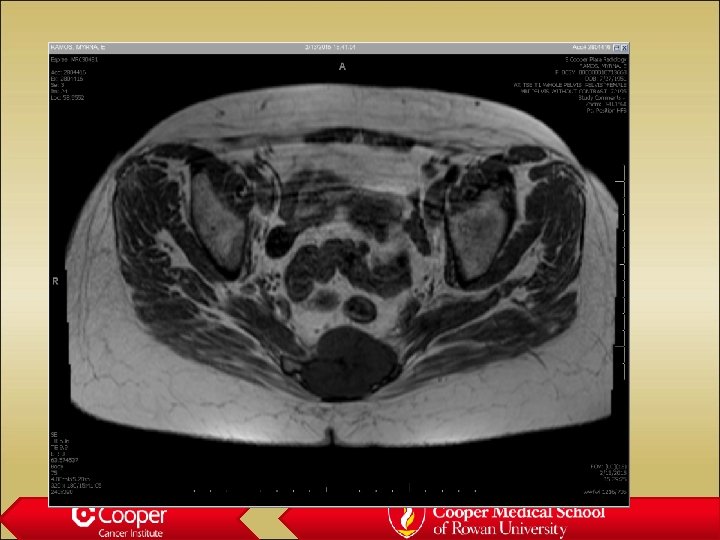
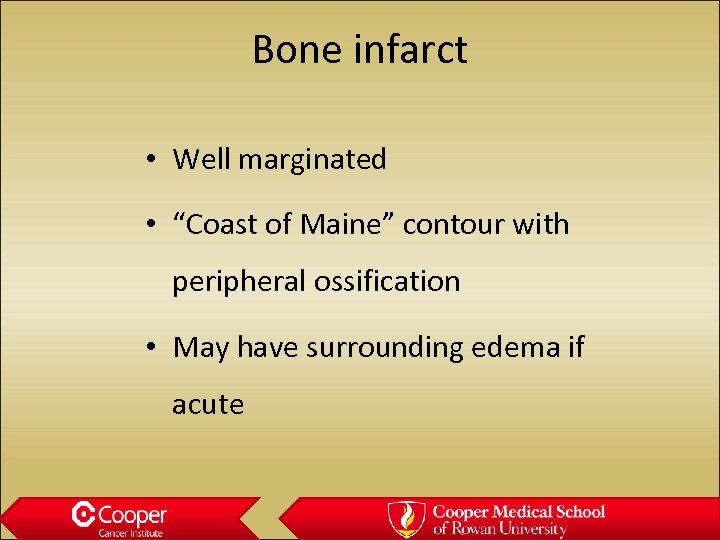 Bone infarct • Well marginated • “Coast of Maine” contour with peripheral ossification • May have surrounding edema if acute
Bone infarct • Well marginated • “Coast of Maine” contour with peripheral ossification • May have surrounding edema if acute
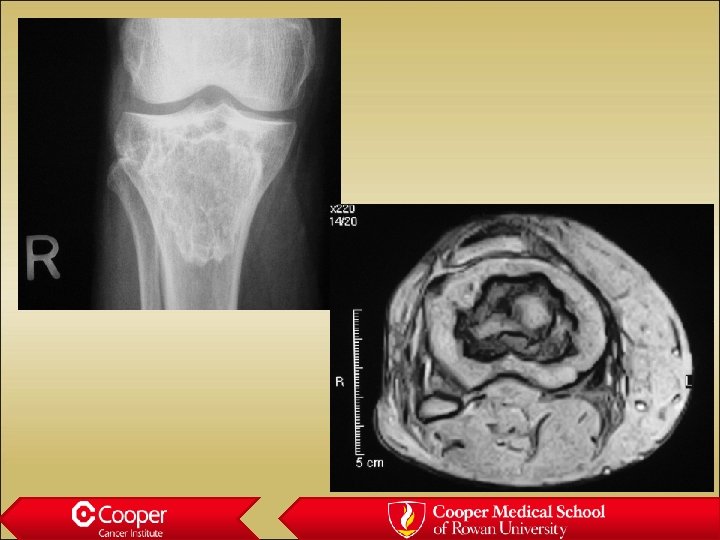
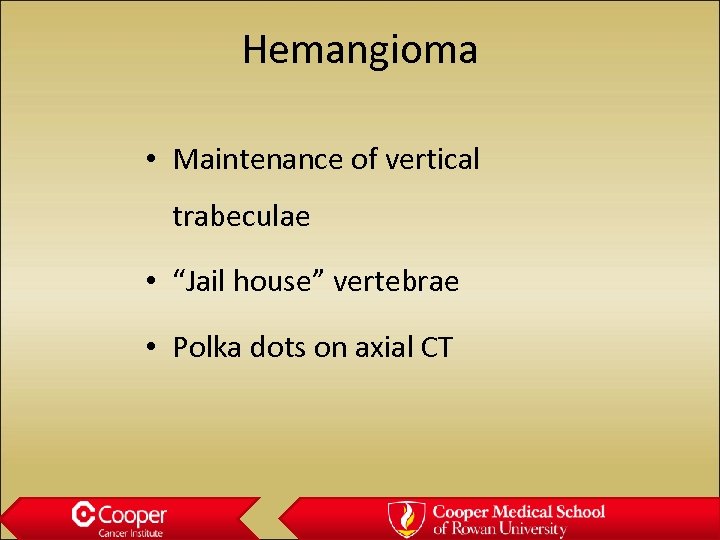 Hemangioma • Maintenance of vertical trabeculae • “Jail house” vertebrae • Polka dots on axial CT
Hemangioma • Maintenance of vertical trabeculae • “Jail house” vertebrae • Polka dots on axial CT
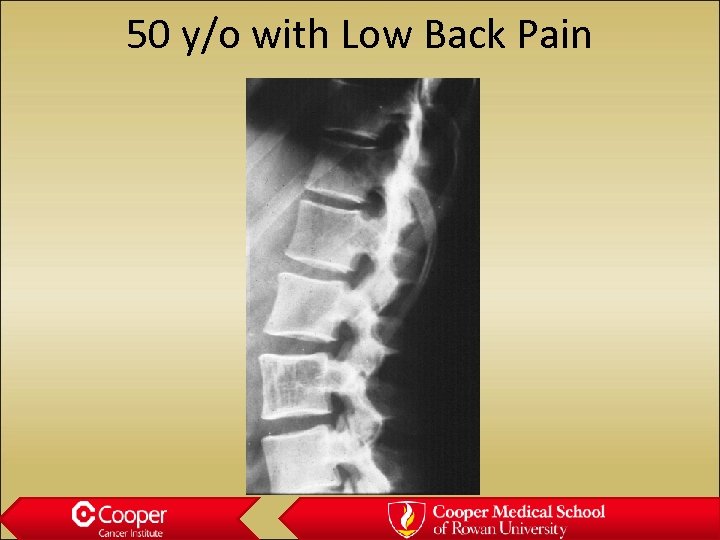 50 y/o with Low Back Pain
50 y/o with Low Back Pain
 Intraosseous Lipoma • Sclerotic border • Fat density asymptomatic incidental finding
Intraosseous Lipoma • Sclerotic border • Fat density asymptomatic incidental finding
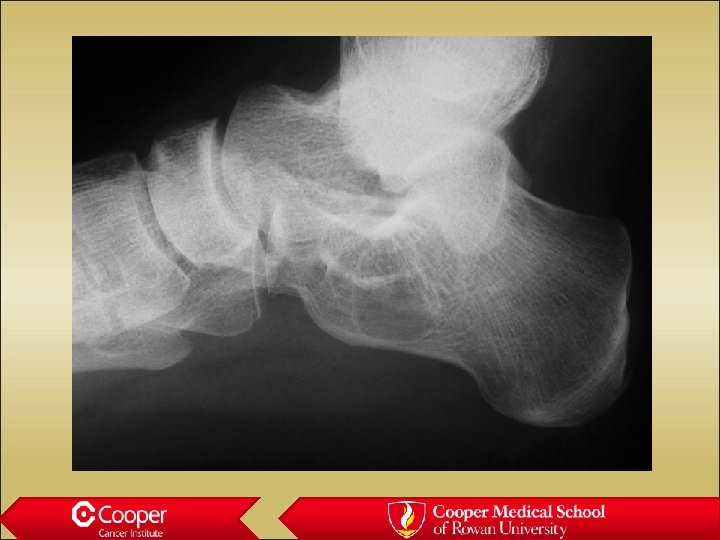
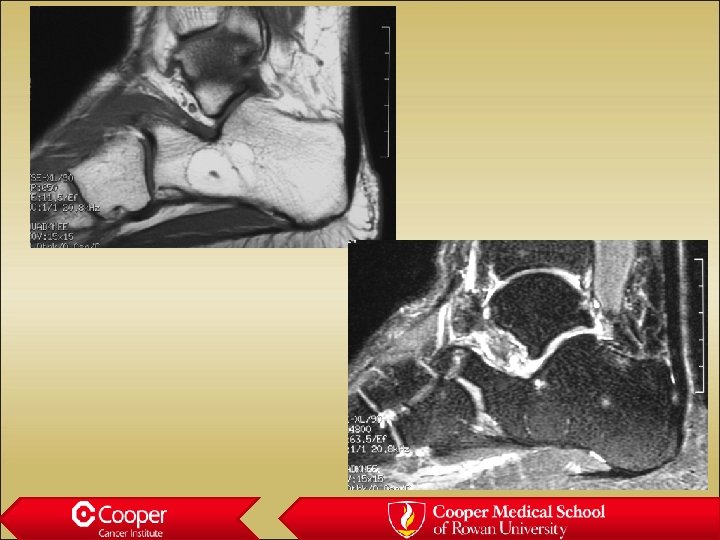
 Bone Island • Cortical bone in the medullary canal • Well marginated
Bone Island • Cortical bone in the medullary canal • Well marginated
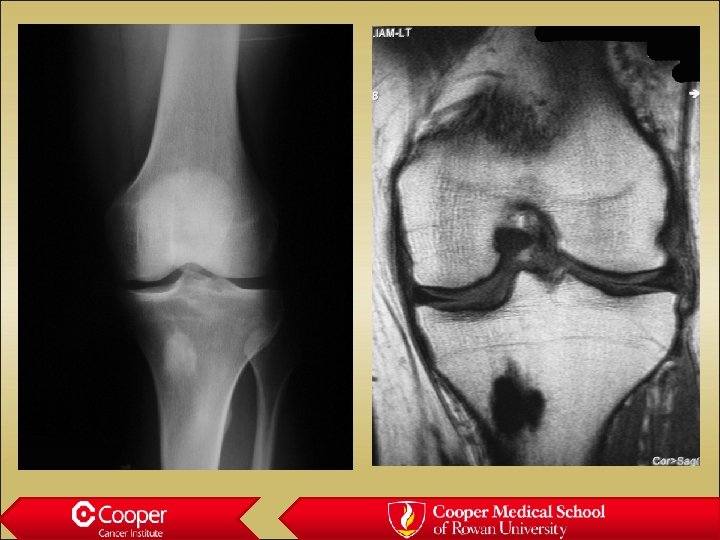
 Tumoral calcinosis • Amorphous calcium in soft tissues • Associated with renal failure
Tumoral calcinosis • Amorphous calcium in soft tissues • Associated with renal failure
 Thank You
Thank You


