6c5ef8d4514413b4468f2ff510503359.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 19

r Performance Metrics for a Wholesaler / Distributor Michael Kody VP, Supply Chain Solutions April 2007

Introduction r Michael Kody, Vice President of Supply Chain solutions at Amerisource. Bergen Corporation. We are a roughly $70 B company that delivers pharmaceuticals and medical supplies to thousands of retail and institutional pharmacy customers on a just-in-time basis. We also provide consulting services to help healthcare providers improve their businesses and focus on their strengths.

Industry Overview r • $300 B in pharmaceuticals distributed across the United States • 80% through Wholesalers/Distributors (10% to mail order services/government, 10% Large Chains, 1% to hospitals) • To Patients – (22% hospitals; 15% independents; 41% chains; 22% mail order; government, doctors, other) • 80% of hospital pharmaceuticals received through Wholesalers/Distributors
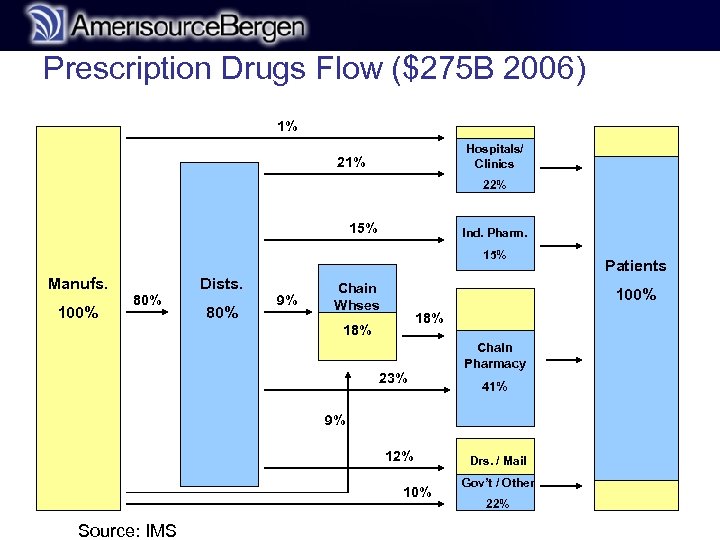
Prescription Drugs Flow ($275 B 2006) r 1% Hospitals/ Clinics 21% 22% 15% Ind. Pharm. 15% Manufs. 100% Dists. 80% 9% Chain Whses 100% 18% 23% Chain Pharmacy 41% 9% 12% 10% Source: IMS Patients Drs. / Mail Gov’t / Other 22%

Wholesaler Coverage of US Population r • ABC provides next day service to the entire United States • Our 26 distribution centers are distributed around population centers while ensuring coverage to remote locations • More than 90% of the US population is within 100 miles of a distribution center • Only the most remote areas are more than a 10 hour drive from a distribution center • Physical proximity to people and logistical networks are the drivers for leveraging Wholesalers in a flexible value chain

Inventory and Sales Considerations • Typical on hand / on order quantities as well as demand variability • Inventory is based upon customers’ expected demand • Generally only maintain a few weeks of supply in inventory • Demand often fluctuates (we may see orders triple) • Events drive customers orders variability r
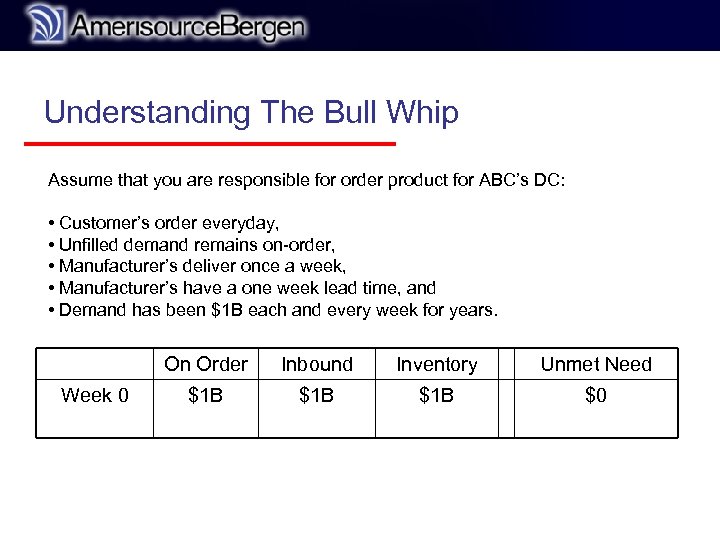
r Understanding The Bull Whip Assume that you are responsible for order product for ABC’s DC: • Customer’s order everyday, • Unfilled demand remains on-order, • Manufacturer’s deliver once a week, • Manufacturer’s have a one week lead time, and • Demand has been $1 B each and every week for years. On Order Week 0 Inbound Inventory Unmet Need $1 B $1 B $0

r Understanding The Bull Whip Assume that your company picks up a new customer and Customer Orders are now $1. 5 B per week (every week). On Order Inbound Inventory Unmet Need $1 B $1 B $0 Week 0 What do you do?

r Understanding The Bull Whip Assume that your company picks up a new customer and Customer Orders are now $1. 5 B per week (every week). On Order Inbound Inventory Unmet Need Week 1 $1. 5 B $1 B $. 5 B Week 2 $1. 5 B $1 B $1. 0 B Week 3 $1. 5 B Future $1. 5 B
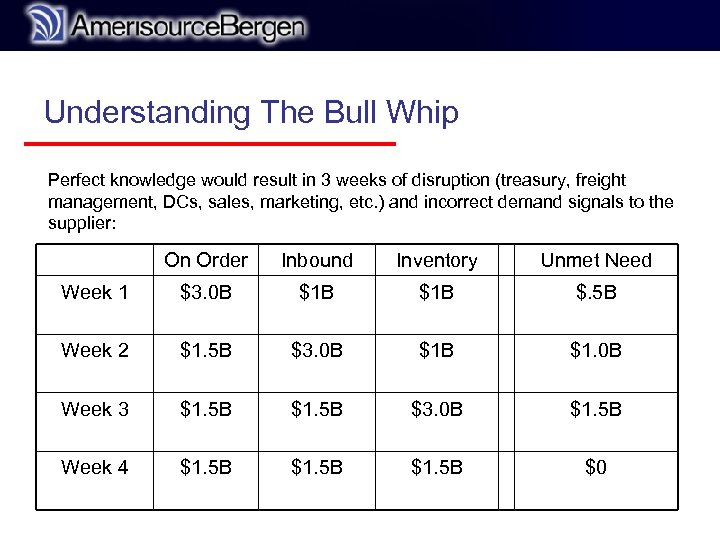
r Understanding The Bull Whip Perfect knowledge would result in 3 weeks of disruption (treasury, freight management, DCs, sales, marketing, etc. ) and incorrect demand signals to the supplier: On Order Inbound Inventory Unmet Need Week 1 $3. 0 B $1 B $. 5 B Week 2 $1. 5 B $3. 0 B $1. 0 B Week 3 $1. 5 B $3. 0 B $1. 5 B Week 4 $1. 5 B $0

r A significant change occurred in 2004/2005 in the U. S. Pharmaceutical supply chain with the implementation of the Fee-for. Service model. The traditional role of the “wholesaler” transitioned into a role of a supplier of “distribution services” to both upstream manufacturers and downstream dispensing customers.
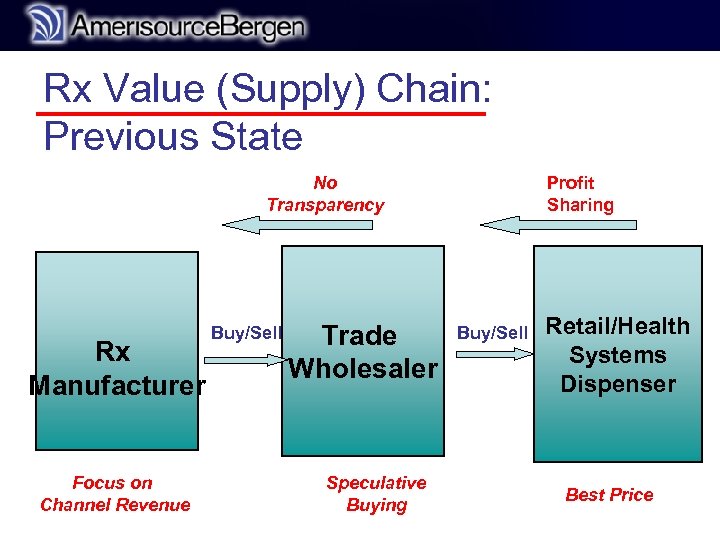
r Rx Value (Supply) Chain: Previous State No Transparency Rx Manufacturer Focus on Channel Revenue Buy/Sell Trade Wholesaler Speculative Buying Profit Sharing Buy/Sell Retail/Health Systems Dispenser Best Price
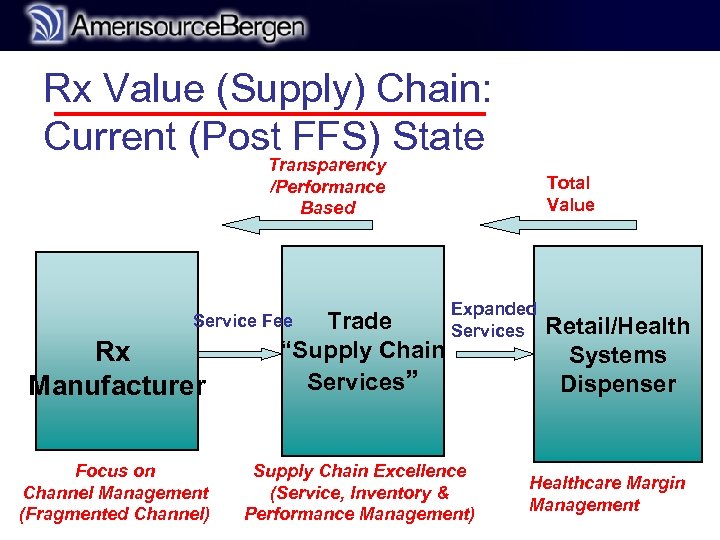
r Rx Value (Supply) Chain: Current (Post FFS) State Transparency /Performance Based Total Value Expanded Services Rx Manufacturer Trade “Supply Chain Services” Focus on Channel Management (Fragmented Channel) Supply Chain Excellence (Service, Inventory & Performance Management) Service Fee Retail/Health Systems Dispenser Healthcare Margin Management
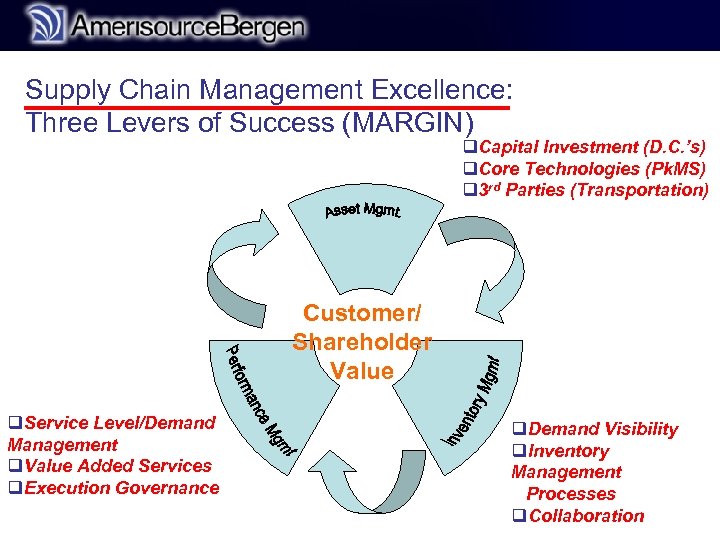
r Supply Chain Management Excellence: Three Levers of Success (MARGIN) q. Capital Investment (D. C. ’s) q. Core Technologies (Pk. MS) q 3 rd Parties (Transportation) Customer/ Shareholder Value q. Service Level/Demand Management q. Value Added Services q. Execution Governance q. Demand Visibility q. Inventory Management Processes q. Collaboration

r Themes for Success Ü Strong Customer Orientation (Internal/External) Ü Drive for Internal/External Collaboration Ü Effective/Efficient Use of Resources Ü Evolving/Learning Together

Typical Performance Goals • Perfect Order Fill Rate • Perfect Transaction Processing • No Returns or Waste • Minimal Inventory • Perfect Demand Information • Minimal Lead Time • Product Handling / Quality Assurance r

Typical Performance Metrics • Service Level Tiers • Days on Hand Tiers • Demand Management Incentives • Incentives / Penalties Related to Deductions • Return Management Incentives • etc. r

Opportunities r • Mutual Understanding of Business Challenges and Opportunities • Collaborative Decisions Based Upon Increased Value in the Supply Chain • Performance Metrics that are Simple and Motivate Value Added Behavior • Knowledge Sharing and SOP • Performance Incentives for Value Added Collaborative Projects

r Questions?
6c5ef8d4514413b4468f2ff510503359.ppt