620f042724a6b8e0869076323f724c75.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 69
 R F I D RADIO FREQUENCY IDENTIFICATION Presented by: Allison Tippett Charlotte Claeys Donald Sengur Teresa Fong Tolu Gamu 1
R F I D RADIO FREQUENCY IDENTIFICATION Presented by: Allison Tippett Charlotte Claeys Donald Sengur Teresa Fong Tolu Gamu 1
 R F I D WHAT YOU WILL LEARN AFTER THIS CLASS: 1) WHY IS RFID IMPORTANT? 2) WHAT IS RFID? 3) BUSINESS APPLICATIONS 4) POTENTIAL CHALLENGES TO MANAGE 5) MANAGERIAL IMPLICATION 6) THE FUTURE OF RFID 2 Tu
R F I D WHAT YOU WILL LEARN AFTER THIS CLASS: 1) WHY IS RFID IMPORTANT? 2) WHAT IS RFID? 3) BUSINESS APPLICATIONS 4) POTENTIAL CHALLENGES TO MANAGE 5) MANAGERIAL IMPLICATION 6) THE FUTURE OF RFID 2 Tu
 R F I D WHY IS RFID IMPORTANT? 3 Tu
R F I D WHY IS RFID IMPORTANT? 3 Tu
 R F I D PROMISED BUSINESS BENEFITS • RFID is a rapidly evolving technology that can dramatically improve operational efficiencies and customer service; • RFID will fundamentally transform the way information about products, equipment, animals and even people is gathered analyzed in real time, providing new business opportunities across all industries. Tu Alan D. Smith (2005), “Exploring radio frequency identification technology and its impact on business systems, ” Information Management & Computer Security, Vol. 13, No. 1 4
R F I D PROMISED BUSINESS BENEFITS • RFID is a rapidly evolving technology that can dramatically improve operational efficiencies and customer service; • RFID will fundamentally transform the way information about products, equipment, animals and even people is gathered analyzed in real time, providing new business opportunities across all industries. Tu Alan D. Smith (2005), “Exploring radio frequency identification technology and its impact on business systems, ” Information Management & Computer Security, Vol. 13, No. 1 4
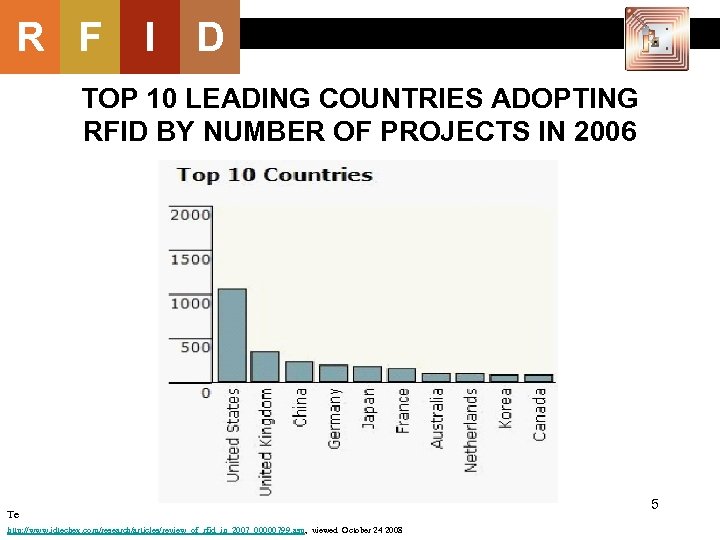 R F I D TOP 10 LEADING COUNTRIES ADOPTING RFID BY NUMBER OF PROJECTS IN 2006 Te http: //www. idtechex. com/research/articles/review_of_rfid_in_2007_00000799. asp, viewed October 24 2008 5
R F I D TOP 10 LEADING COUNTRIES ADOPTING RFID BY NUMBER OF PROJECTS IN 2006 Te http: //www. idtechex. com/research/articles/review_of_rfid_in_2007_00000799. asp, viewed October 24 2008 5
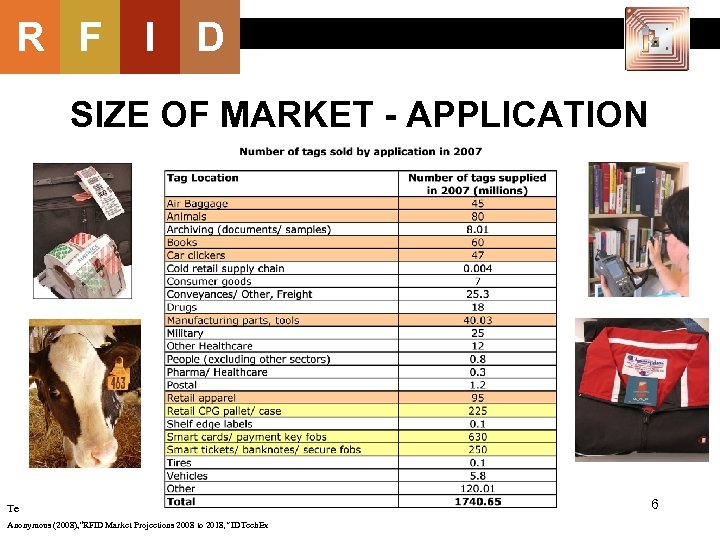 R F I D SIZE OF MARKET - APPLICATION Te Anonymous (2008), “RFID Market Projections 2008 to 2018, ” IDTech. Ex 6
R F I D SIZE OF MARKET - APPLICATION Te Anonymous (2008), “RFID Market Projections 2008 to 2018, ” IDTech. Ex 6
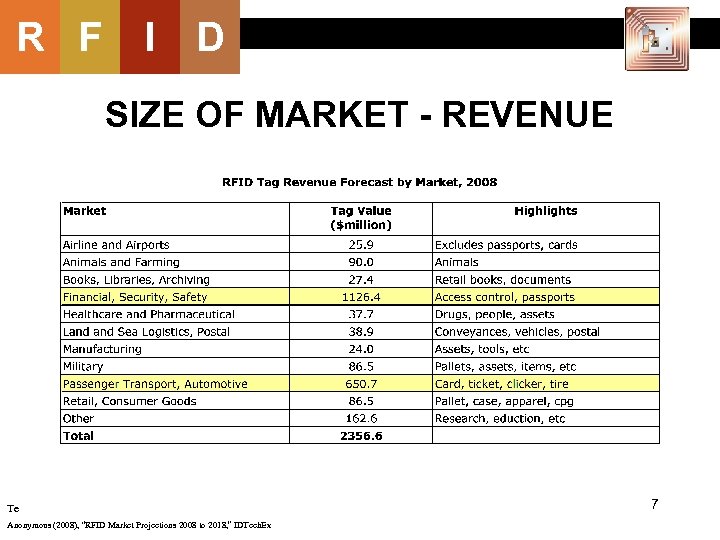 R F I D SIZE OF MARKET - REVENUE Te Anonymous (2008), “RFID Market Projections 2008 to 2018, ” IDTech. Ex 7
R F I D SIZE OF MARKET - REVENUE Te Anonymous (2008), “RFID Market Projections 2008 to 2018, ” IDTech. Ex 7
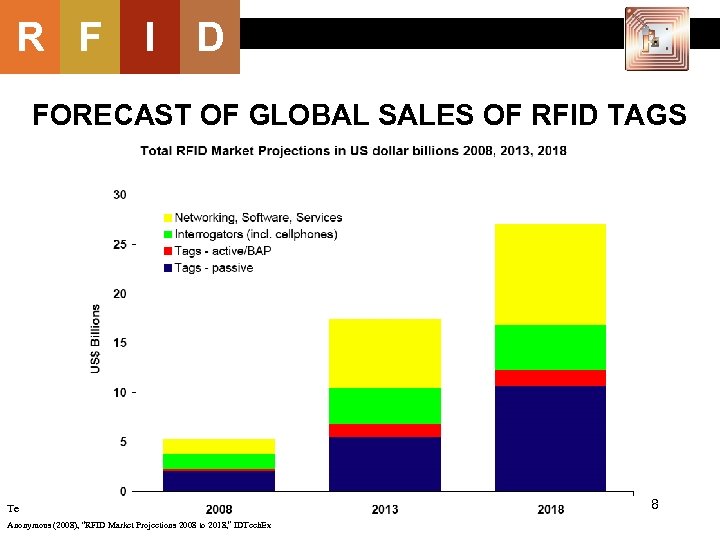 R F I D FORECAST OF GLOBAL SALES OF RFID TAGS Te Anonymous (2008), “RFID Market Projections 2008 to 2018, ” IDTech. Ex 8
R F I D FORECAST OF GLOBAL SALES OF RFID TAGS Te Anonymous (2008), “RFID Market Projections 2008 to 2018, ” IDTech. Ex 8
 R F I D TECHNOLOGY 9 Tu
R F I D TECHNOLOGY 9 Tu
 R F I D WHAT IS RFID? • Radio Frequency Identification describes technologies that use radio waves to mechanically recognize people or objects. Tu http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/RFID, viewed October 24, 2008 10
R F I D WHAT IS RFID? • Radio Frequency Identification describes technologies that use radio waves to mechanically recognize people or objects. Tu http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/RFID, viewed October 24, 2008 10
 R F I D HISTORY OF RFID • “RFID was founded in 1946, by the Soviet Union, which retransmitted incident radio waves with audio information; ” • “The device was a passive listening device not an identification tag as it has been attributed as a predecessor to RFID technology. ” Tu http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/RFID, viewed October 24, 2008 11
R F I D HISTORY OF RFID • “RFID was founded in 1946, by the Soviet Union, which retransmitted incident radio waves with audio information; ” • “The device was a passive listening device not an identification tag as it has been attributed as a predecessor to RFID technology. ” Tu http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/RFID, viewed October 24, 2008 11
 R F I D FOUNDER OF RFID • Mario Cardullo is the father of RFID; • He was the corporate planning officer to the chairman of the Communications Satellite Corporation (Comsat); • After leaving Comsat, he put together a business proposal to develop the EKG terminal and his new idea, the RFID tag. Many people were interested in his ideas and gave him the necessary funds. With these funds he started the company Com. Serv; • Mario Cardullo received the first patent for a read-write RFID tag a passive radio transponder with memory. Tu , http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/RFID, viewed October 24, 2008 12
R F I D FOUNDER OF RFID • Mario Cardullo is the father of RFID; • He was the corporate planning officer to the chairman of the Communications Satellite Corporation (Comsat); • After leaving Comsat, he put together a business proposal to develop the EKG terminal and his new idea, the RFID tag. Many people were interested in his ideas and gave him the necessary funds. With these funds he started the company Com. Serv; • Mario Cardullo received the first patent for a read-write RFID tag a passive radio transponder with memory. Tu , http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/RFID, viewed October 24, 2008 12
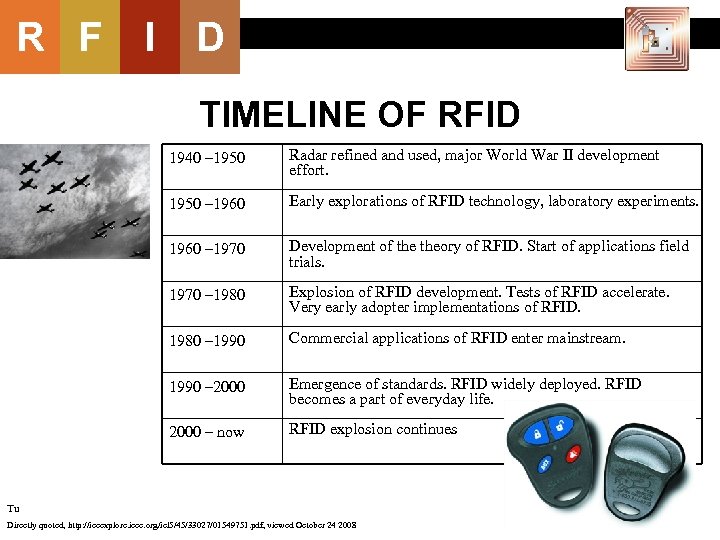 R F I D TIMELINE OF RFID 1940 – 1950 Radar refined and used, major World War II development effort. 1950 – 1960 Early explorations of RFID technology, laboratory experiments. 1960 – 1970 Development of theory of RFID. Start of applications field trials. 1970 – 1980 Explosion of RFID development. Tests of RFID accelerate. Very early adopter implementations of RFID. 1980 – 1990 Commercial applications of RFID enter mainstream. 1990 – 2000 Emergence of standards. RFID widely deployed. RFID becomes a part of everyday life. 2000 – now RFID explosion continues Tu Directly quoted, http: //ieeexplore. ieee. org/iel 5/45/33027/01549751. pdf, viewed October 24 2008 13
R F I D TIMELINE OF RFID 1940 – 1950 Radar refined and used, major World War II development effort. 1950 – 1960 Early explorations of RFID technology, laboratory experiments. 1960 – 1970 Development of theory of RFID. Start of applications field trials. 1970 – 1980 Explosion of RFID development. Tests of RFID accelerate. Very early adopter implementations of RFID. 1980 – 1990 Commercial applications of RFID enter mainstream. 1990 – 2000 Emergence of standards. RFID widely deployed. RFID becomes a part of everyday life. 2000 – now RFID explosion continues Tu Directly quoted, http: //ieeexplore. ieee. org/iel 5/45/33027/01549751. pdf, viewed October 24 2008 13
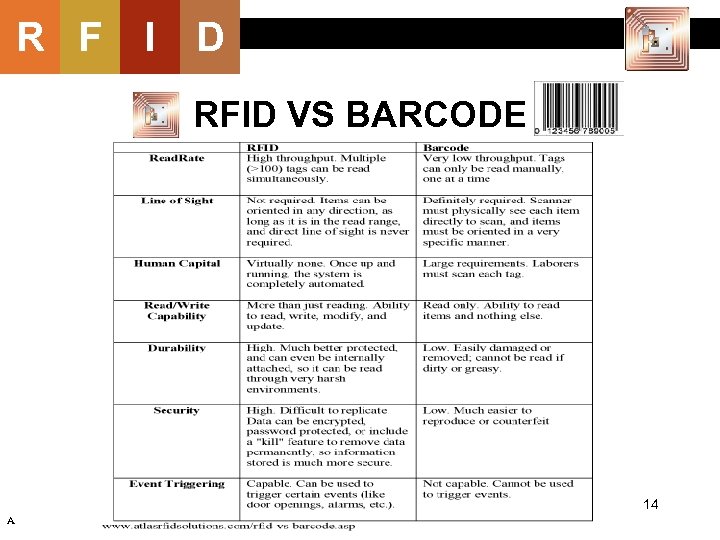 R F I D RFID VS BARCODE 14 A
R F I D RFID VS BARCODE 14 A
 R F I D PARTS OF RFID TECHNOLOGY Tags Readers /Writers Softwares Antennas 15 D
R F I D PARTS OF RFID TECHNOLOGY Tags Readers /Writers Softwares Antennas 15 D
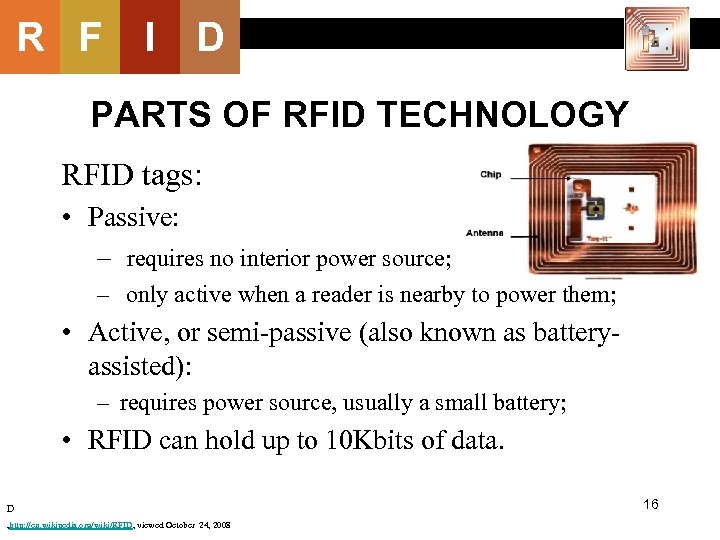 R F I D PARTS OF RFID TECHNOLOGY RFID tags: • Passive: – requires no interior power source; – only active when a reader is nearby to power them; • Active, or semi-passive (also known as batteryassisted): – requires power source, usually a small battery; • RFID can hold up to 10 Kbits of data. D , http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/RFID, viewed October 24, 2008 16
R F I D PARTS OF RFID TECHNOLOGY RFID tags: • Passive: – requires no interior power source; – only active when a reader is nearby to power them; • Active, or semi-passive (also known as batteryassisted): – requires power source, usually a small battery; • RFID can hold up to 10 Kbits of data. D , http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/RFID, viewed October 24, 2008 16
 R F I D PARTS OF RFID TECHNOLOGY Reader: • Read all the tags within reach in sequence; • Active tags send signals to readers; • Readers send signal to passive tags and read the data broadcast by the tags; Writer: • A reader/writer could read and write information on reusable tags. D , http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/RFID, viewed October 24, 2008 17
R F I D PARTS OF RFID TECHNOLOGY Reader: • Read all the tags within reach in sequence; • Active tags send signals to readers; • Readers send signal to passive tags and read the data broadcast by the tags; Writer: • A reader/writer could read and write information on reusable tags. D , http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/RFID, viewed October 24, 2008 17
 R F I D PARTS OF RFID TECHNOLOGY Antennas: • Placed on the tags; • To emit and receive the signals from the readers. D , http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/RFID, viewed October 24, 2008 18
R F I D PARTS OF RFID TECHNOLOGY Antennas: • Placed on the tags; • To emit and receive the signals from the readers. D , http: //en. wikipedia. org/wiki/RFID, viewed October 24, 2008 18
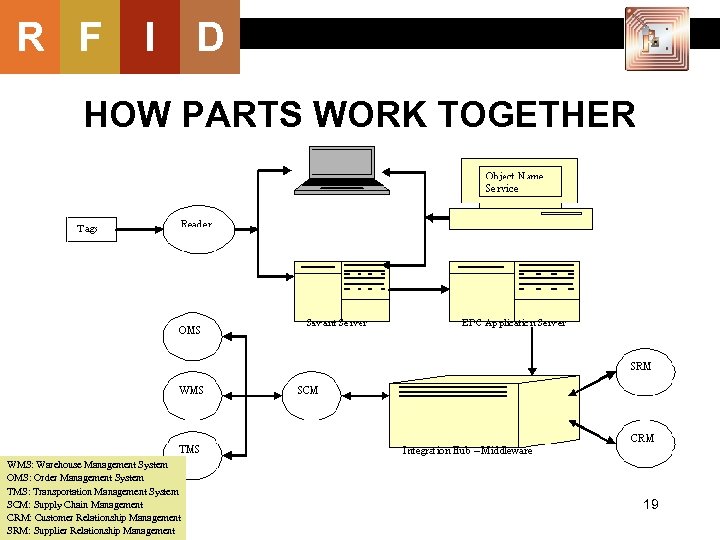 R F I D HOW PARTS WORK TOGETHER WMS: Warehouse Management System OMS: Order Management System TMS: Transportation Management System SCM: Supply Chain Management CRM: Customer Relationship Management SRM: Supplier Relationship Management 19
R F I D HOW PARTS WORK TOGETHER WMS: Warehouse Management System OMS: Order Management System TMS: Transportation Management System SCM: Supply Chain Management CRM: Customer Relationship Management SRM: Supplier Relationship Management 19
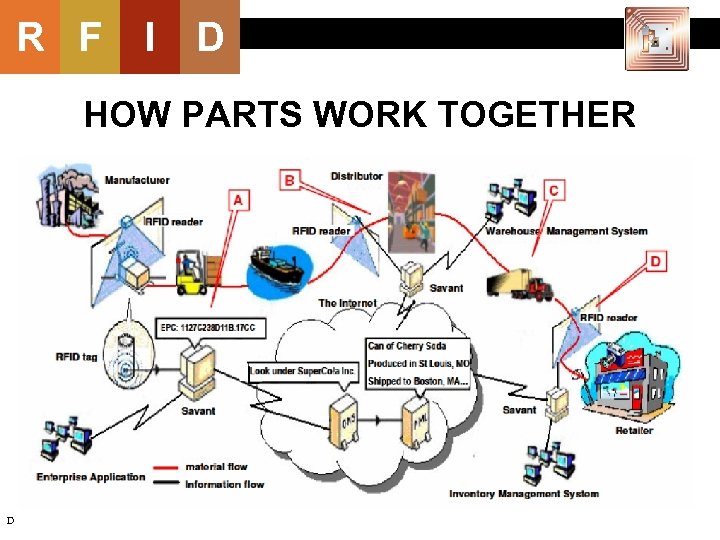 R F I D HOW PARTS WORK TOGETHER 20 D
R F I D HOW PARTS WORK TOGETHER 20 D
 R F I D BUSINESS APPLICATION - CASE STUDY: 21 A
R F I D BUSINESS APPLICATION - CASE STUDY: 21 A
 R F I D RFID IMPLEMENTATION HISTORY • April 30, 2004 – pilot testing; – 8 manufacturing participants; – 28 volunteers; • January 2005 – Mandate: top 100 suppliers. A Anonymous (2004), “Wal-Mart’s January Deadline, ” Greenhouse Grower, Vol. 22, No. 10, pg. 34; John S. Mc. Clenahen (2005), “Wal-Mart’s Big Gamble, ” Industry Week/IW, Vol. 254, No. 4, pp. 42 -49. 22
R F I D RFID IMPLEMENTATION HISTORY • April 30, 2004 – pilot testing; – 8 manufacturing participants; – 28 volunteers; • January 2005 – Mandate: top 100 suppliers. A Anonymous (2004), “Wal-Mart’s January Deadline, ” Greenhouse Grower, Vol. 22, No. 10, pg. 34; John S. Mc. Clenahen (2005), “Wal-Mart’s Big Gamble, ” Industry Week/IW, Vol. 254, No. 4, pp. 42 -49. 22
 R F I D RFID EXPANSION • June 2005: – another 200 suppliers joined the effort; • End of 2006: – All domestic suppliers participated; • 2006: – Expected international roll out. A Carol Sliwa (2004), “Wal-Mart Revises ‘ 05 RFID Expectations, ” Computerworld, Vol. 38, No. 21, pg. 14 23
R F I D RFID EXPANSION • June 2005: – another 200 suppliers joined the effort; • End of 2006: – All domestic suppliers participated; • 2006: – Expected international roll out. A Carol Sliwa (2004), “Wal-Mart Revises ‘ 05 RFID Expectations, ” Computerworld, Vol. 38, No. 21, pg. 14 23
 R F I D WAL-MART’S ROI • Will not disclose any information on how much money is being saved using RFID; • According to an estimate published in Fortune Magazine, Wal-Mart will receive a return of 21. 5% on capital with the use of RFID. A Christine Y. Chen (2004), “Wal-Mart Drives a New Tech Boom, ” Fortune, Vol. 149, No. 13, pg. 202 24
R F I D WAL-MART’S ROI • Will not disclose any information on how much money is being saved using RFID; • According to an estimate published in Fortune Magazine, Wal-Mart will receive a return of 21. 5% on capital with the use of RFID. A Christine Y. Chen (2004), “Wal-Mart Drives a New Tech Boom, ” Fortune, Vol. 149, No. 13, pg. 202 24
 R F I D SUPPLIERS’ ROI • Short-term – the cost of RFID overshadows any trickledown effect received through increased sales; • Long-term – increased visibility of the supply chain will help suppliers better production scheduling and inventory management. A John S. Mc. Clenahen (2005), “Wal-Mart’s Big Gamble, ” Industry Week/IW, Vol. 254, No. 4, pp. 42 -49; David Blanchard (2008), “Wal-Mart Lays Down the law on RFID, ” Industry Week/IW, Vol. 257, No. 5, pp. 72 -74. 25
R F I D SUPPLIERS’ ROI • Short-term – the cost of RFID overshadows any trickledown effect received through increased sales; • Long-term – increased visibility of the supply chain will help suppliers better production scheduling and inventory management. A John S. Mc. Clenahen (2005), “Wal-Mart’s Big Gamble, ” Industry Week/IW, Vol. 254, No. 4, pp. 42 -49; David Blanchard (2008), “Wal-Mart Lays Down the law on RFID, ” Industry Week/IW, Vol. 257, No. 5, pp. 72 -74. 25
 R F I D SUPPLIERS’ INCENTIVE • Do not want to lose Wal-Mart as a distributor because of it’s size, power, and reach. A John S. Mc. Clenahen (2005), “Wal-Mart’s Big Gamble, ” Industry Week/IW, Vol. 254, No. 4, pp. 42 -49 26
R F I D SUPPLIERS’ INCENTIVE • Do not want to lose Wal-Mart as a distributor because of it’s size, power, and reach. A John S. Mc. Clenahen (2005), “Wal-Mart’s Big Gamble, ” Industry Week/IW, Vol. 254, No. 4, pp. 42 -49 26
 R F I D RFID RESEARCH • Wal-Mart sponsored research at the University of Arkansas; • Purpose: to validate the usefulness and effectiveness of RFID technology. Te David Blanchard (2008), “Wal-Mart Lays Down the law on RFID, ” Industry Week/IW, Vol. 257, No. 5, pp. 72 -74 27
R F I D RFID RESEARCH • Wal-Mart sponsored research at the University of Arkansas; • Purpose: to validate the usefulness and effectiveness of RFID technology. Te David Blanchard (2008), “Wal-Mart Lays Down the law on RFID, ” Industry Week/IW, Vol. 257, No. 5, pp. 72 -74 27
 R F I D RESEARCH ANALYSIS • “Analysis at the university’s RFID Research Center indicates in test scores that an automated RFIDenabled inventory system improves accuracy by 13%; ” • This finding is important because inventory inaccuracy can lead to a 10% loss of profit; • With reports of inventory inaccuracy being as high as 65%, the 13% improvement rate demonstrates how RFID can significantly improve this problem. Te Directly Sourced: David Blanchard (2008), “Wal-Mart Lays Down the law on RFID, ” Industry Week/IW, Vol. 257, No. 5, pp. 72 -74 28
R F I D RESEARCH ANALYSIS • “Analysis at the university’s RFID Research Center indicates in test scores that an automated RFIDenabled inventory system improves accuracy by 13%; ” • This finding is important because inventory inaccuracy can lead to a 10% loss of profit; • With reports of inventory inaccuracy being as high as 65%, the 13% improvement rate demonstrates how RFID can significantly improve this problem. Te Directly Sourced: David Blanchard (2008), “Wal-Mart Lays Down the law on RFID, ” Industry Week/IW, Vol. 257, No. 5, pp. 72 -74 28
 R F I D KEY ISSUES FOR SUPPLIERS • Cost; • Standards; • Technology infrastructure. 29 A
R F I D KEY ISSUES FOR SUPPLIERS • Cost; • Standards; • Technology infrastructure. 29 A
 R F I D KEY ISSUES - COST • Wal-Mart pushes the cost of RFID onto its suppliers; • AMR Research estimated that the Wal-Mart suppliers as a whole have spent over $250 million on RFID technology and implementation; • Factors affecting cost are the number of tags needed, complexity of tags, types of products, and the distribution environment. A John S. Mc. Clenahen (2005), “Wal-Mart’s Big Gamble, ” Industry Week/IW, Vol. 254, No. 4, pp. 42 -49 30
R F I D KEY ISSUES - COST • Wal-Mart pushes the cost of RFID onto its suppliers; • AMR Research estimated that the Wal-Mart suppliers as a whole have spent over $250 million on RFID technology and implementation; • Factors affecting cost are the number of tags needed, complexity of tags, types of products, and the distribution environment. A John S. Mc. Clenahen (2005), “Wal-Mart’s Big Gamble, ” Industry Week/IW, Vol. 254, No. 4, pp. 42 -49 30
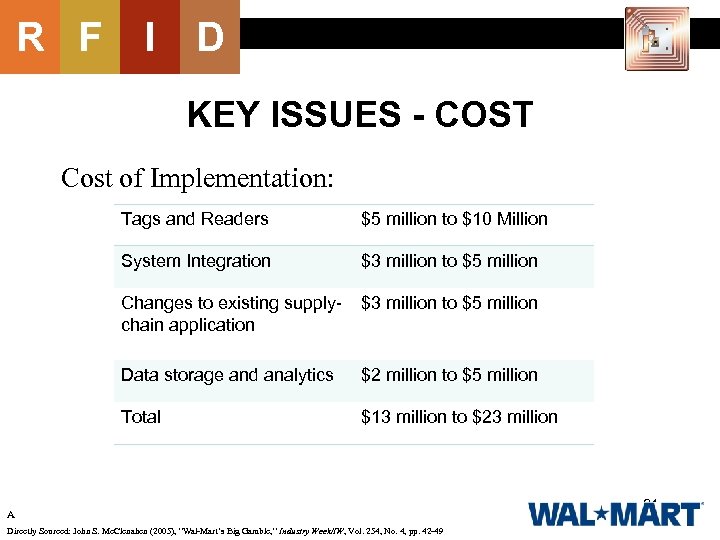 R F I D KEY ISSUES - COST Cost of Implementation: Tags and Readers $5 million to $10 Million System Integration $3 million to $5 million Changes to existing supplychain application $3 million to $5 million Data storage and analytics $2 million to $5 million Total $13 million to $23 million A Directly Sourced: John S. Mc. Clenahen (2005), “Wal-Mart’s Big Gamble, ” Industry Week/IW, Vol. 254, No. 4, pp. 42 -49 31
R F I D KEY ISSUES - COST Cost of Implementation: Tags and Readers $5 million to $10 Million System Integration $3 million to $5 million Changes to existing supplychain application $3 million to $5 million Data storage and analytics $2 million to $5 million Total $13 million to $23 million A Directly Sourced: John S. Mc. Clenahen (2005), “Wal-Mart’s Big Gamble, ” Industry Week/IW, Vol. 254, No. 4, pp. 42 -49 31
 R F I D KEY ISSUES - STANDARD • There are several RFID tag classes and there has not been an official standard which complicates the application and use of RFID. A http: //knowledge. wharton. upenn. edu/article. cfm? articleid=1005, viewed October 8, 2008 32
R F I D KEY ISSUES - STANDARD • There are several RFID tag classes and there has not been an official standard which complicates the application and use of RFID. A http: //knowledge. wharton. upenn. edu/article. cfm? articleid=1005, viewed October 8, 2008 32
 R F I D KEY ISSUES - TECHNOLOGY INFRASTRUCTURE • Suppliers are realizing that the information being collected through RFID cannot be stored or used properly with existing databases; • Updates are needed to filter information especially in areas of business intelligence tools, data mining, & the use of standard data definitions across the corporation; • The biggest obstacle of making RFID work is the managing of information. A http: //knowledge. wharton. upenn. edu/article. cfm? articleid=1005, viewed October 8, 2008 33
R F I D KEY ISSUES - TECHNOLOGY INFRASTRUCTURE • Suppliers are realizing that the information being collected through RFID cannot be stored or used properly with existing databases; • Updates are needed to filter information especially in areas of business intelligence tools, data mining, & the use of standard data definitions across the corporation; • The biggest obstacle of making RFID work is the managing of information. A http: //knowledge. wharton. upenn. edu/article. cfm? articleid=1005, viewed October 8, 2008 33
 R F I D SCENARIO OF RFID IMPLEMENTATION “A case of product leaves the manufacturer and is tracked and instantly routed when it reaches a Wal-Mart distribution center. There’s no need to rip open a case and inspect the contents because the RFID reader has already identified the item. At the store, the goods are monitored in real-time so there’s no need for inventory. When the shelves are empty, RFID readers alert workers to restock shelves. If Wal-Mart’s inventory is depleted, a replenishment message is automatically sent to the supplier. ” C http: //knowledge. wharton. upenn. edu/article. cfm? articleid=1005, viewed October 8, 2008 34
R F I D SCENARIO OF RFID IMPLEMENTATION “A case of product leaves the manufacturer and is tracked and instantly routed when it reaches a Wal-Mart distribution center. There’s no need to rip open a case and inspect the contents because the RFID reader has already identified the item. At the store, the goods are monitored in real-time so there’s no need for inventory. When the shelves are empty, RFID readers alert workers to restock shelves. If Wal-Mart’s inventory is depleted, a replenishment message is automatically sent to the supplier. ” C http: //knowledge. wharton. upenn. edu/article. cfm? articleid=1005, viewed October 8, 2008 34
 R F I D INDUSTRY IMPACT • Many companies are worried about being left behind; • Target, Albertson’s, and Walgreens have all started pilot programs and implementation. C Christine Y. Chen (2004), “Wal-Mart Drives a New Tech Boom, ” Fortune, Vol. 149, No. 13, pg. 202 35
R F I D INDUSTRY IMPACT • Many companies are worried about being left behind; • Target, Albertson’s, and Walgreens have all started pilot programs and implementation. C Christine Y. Chen (2004), “Wal-Mart Drives a New Tech Boom, ” Fortune, Vol. 149, No. 13, pg. 202 35
 R F I D OTHER BUSINESS APPLICATIONS 36 Te
R F I D OTHER BUSINESS APPLICATIONS 36 Te
 R F I D CONTACTLESS SMART CARDS • Largest RFID by far and business is booming; • Over 800 millions tags sold in 2007; • Identification cards that do not need to make contact with the reader to be read, or swiped in a special slot; • Applications: building access, biometrics, parking, cashless vending/payment, time and attendance, loyalty programs, etc; • Available in: plastic cards, key fobs, watches, documents, mobile phones. Te David C. Wyld (2006), “RFID 101: the next big thing for management, ” Management Research News, Vol. 29, No. 4; Anonymous (2008), “Strong growth of RFID smart cards/ payment key fob, ” IDTech. Ex. 37
R F I D CONTACTLESS SMART CARDS • Largest RFID by far and business is booming; • Over 800 millions tags sold in 2007; • Identification cards that do not need to make contact with the reader to be read, or swiped in a special slot; • Applications: building access, biometrics, parking, cashless vending/payment, time and attendance, loyalty programs, etc; • Available in: plastic cards, key fobs, watches, documents, mobile phones. Te David C. Wyld (2006), “RFID 101: the next big thing for management, ” Management Research News, Vol. 29, No. 4; Anonymous (2008), “Strong growth of RFID smart cards/ payment key fob, ” IDTech. Ex. 37
 R F I D CONTACTLESS SMART PAYMENT Master. Card Paypass • “Tap n’ Go; ” • As of Nov 2007, over 20 million Master. Card Pay. Pass cards and devices issued globally; • Approximately 80, 000 merchant locations around the world: Mc. Donald's, 7 -Eleven, CVS, Duane Reade, Sheetz and Regal Entertainment Group. Te Anonymous (2007), “Master. Card Says 20 Million Pay. Pass Contactless Cards Issued, ” Contactless Payment Systems, Dec 10; http: //www. mastercard. com/us/personal/en/aboutourcards/paypass/, viewed October 24, 2008. 38
R F I D CONTACTLESS SMART PAYMENT Master. Card Paypass • “Tap n’ Go; ” • As of Nov 2007, over 20 million Master. Card Pay. Pass cards and devices issued globally; • Approximately 80, 000 merchant locations around the world: Mc. Donald's, 7 -Eleven, CVS, Duane Reade, Sheetz and Regal Entertainment Group. Te Anonymous (2007), “Master. Card Says 20 Million Pay. Pass Contactless Cards Issued, ” Contactless Payment Systems, Dec 10; http: //www. mastercard. com/us/personal/en/aboutourcards/paypass/, viewed October 24, 2008. 38
 R F I D CONTACTLESS SMART PHONE Mc. Donald’s & SK Telecom • Shinchon branch near Yonsei University, Western Seoul, Korea; • First world “Touch Order” menu at a restaurant; • How it works: – Customer downloads “Order” program to their mobile phones; – RFID reader and menu at each table; – Customer plug the reader into their mobile phones and point at food items; – Bill is charged through the mobile phone; – When meal is ready, short message is sent to the phone so customer can pick up at the designated counter. Te Gautam (2007), “Avoid long queues for ordering your favorite burger with RFID, ” Contactless Payment Systems, Sep 12 39
R F I D CONTACTLESS SMART PHONE Mc. Donald’s & SK Telecom • Shinchon branch near Yonsei University, Western Seoul, Korea; • First world “Touch Order” menu at a restaurant; • How it works: – Customer downloads “Order” program to their mobile phones; – RFID reader and menu at each table; – Customer plug the reader into their mobile phones and point at food items; – Bill is charged through the mobile phone; – When meal is ready, short message is sent to the phone so customer can pick up at the designated counter. Te Gautam (2007), “Avoid long queues for ordering your favorite burger with RFID, ” Contactless Payment Systems, Sep 12 39
 R F I D CONTACTLESS SMART TICKET 2008 Beijing Olympics Games • Prevent counterfeiting: – Ticket: Embedded 13. 56 -MHz chip stores a unique serial number to ensure authenticity; – RFID readers that control doors and cameras throughout the facilities. Te Laurie Sullivan (2006), “Olympics technology: RFID’s the ticket for secure games, ” EE Times, Aug 4 40
R F I D CONTACTLESS SMART TICKET 2008 Beijing Olympics Games • Prevent counterfeiting: – Ticket: Embedded 13. 56 -MHz chip stores a unique serial number to ensure authenticity; – RFID readers that control doors and cameras throughout the facilities. Te Laurie Sullivan (2006), “Olympics technology: RFID’s the ticket for secure games, ” EE Times, Aug 4 40
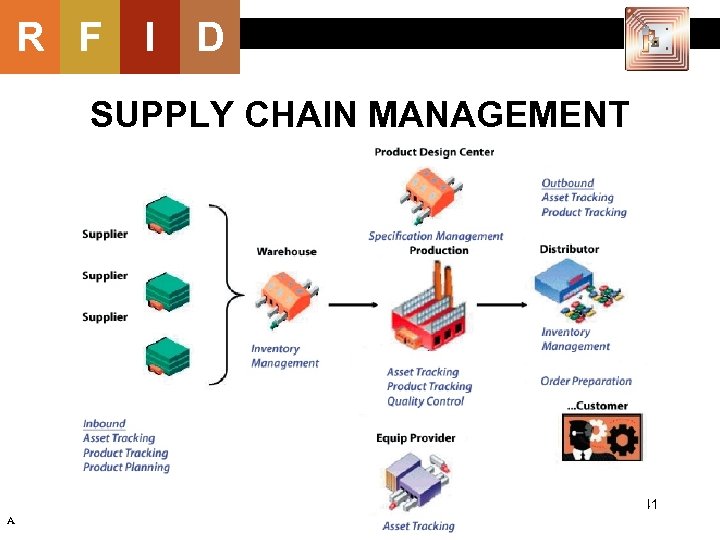 R F I D SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT 41 A
R F I D SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT 41 A
 R F I D SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT U. S. Department of Defense: • Mandate RFID for the military’s worldwide supply chain; • Applied to cases, pallets, packages of supplies; • Anything from uniforms to motor oil. A Elizabeth Wasserman (2007), “RFID Takes Root in Washington, ” RFID Journal, May/June; Anonymous (2003), “Military Edict: Use RFID by 2005, ” RFID Journal, Oct 3. 42
R F I D SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT U. S. Department of Defense: • Mandate RFID for the military’s worldwide supply chain; • Applied to cases, pallets, packages of supplies; • Anything from uniforms to motor oil. A Elizabeth Wasserman (2007), “RFID Takes Root in Washington, ” RFID Journal, May/June; Anonymous (2003), “Military Edict: Use RFID by 2005, ” RFID Journal, Oct 3. 42
 R F I D SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT Shipping: • Combined with environmental sensors to monitor temperature, light, humidity, shock, positioning, etc. A David C. Wyld (2006), “RFID 101: the next big thing for management, ” Management Research News, Vol. 29, No. 4; http: //www. freshpatents. com/Container-security-seal-with-destructible-rfid-tag-dt 20080522 ptan 20080117058. php, viewed October 28, 2008 43
R F I D SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT Shipping: • Combined with environmental sensors to monitor temperature, light, humidity, shock, positioning, etc. A David C. Wyld (2006), “RFID 101: the next big thing for management, ” Management Research News, Vol. 29, No. 4; http: //www. freshpatents. com/Container-security-seal-with-destructible-rfid-tag-dt 20080522 ptan 20080117058. php, viewed October 28, 2008 43
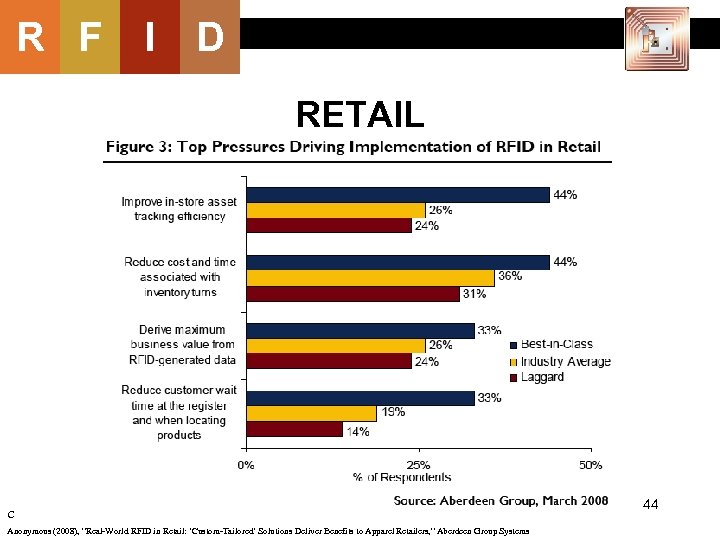 R F I D RETAIL C Anonymous (2008), “Real-World RFID in Retail: ‘Custom-Tailored’ Solutions Deliver Benefits to Apparel Retailers, ” Aberdeen Group Systems 44
R F I D RETAIL C Anonymous (2008), “Real-World RFID in Retail: ‘Custom-Tailored’ Solutions Deliver Benefits to Apparel Retailers, ” Aberdeen Group Systems 44
 R F I D RETAIL • Nokia Retail Store, Arraya Center, Kuwait – http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=LZylfbdu_1 k 45 C
R F I D RETAIL • Nokia Retail Store, Arraya Center, Kuwait – http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=LZylfbdu_1 k 45 C
 R F I D ASSET TRACKING & AUTO ID • Asset Tracking: – Instantly determine the general location of tagged assets; • Auto ID: – Identify items and gather data on objects, humans, or animals without human intervention of data entry. Te David C. Wyld (2006), “RFID 101: the next big thing for management, ” Management Research News, Vol. 29, No. 4 46
R F I D ASSET TRACKING & AUTO ID • Asset Tracking: – Instantly determine the general location of tagged assets; • Auto ID: – Identify items and gather data on objects, humans, or animals without human intervention of data entry. Te David C. Wyld (2006), “RFID 101: the next big thing for management, ” Management Research News, Vol. 29, No. 4 46
 R F I D ASSET TRACKING & AUTO ID • Auto ID: – Animals, Food, & Farming • • Livestock disease control; Improve traceability; Condition monitoring; Crime reduction. Te Elizabeth Wasserman (2007), “RFID Takes Root in Washington, ” RFID Journal, May/June; http: //www. electrocom. au/rfid_animalid. htm, viewed October 28, 2008 47
R F I D ASSET TRACKING & AUTO ID • Auto ID: – Animals, Food, & Farming • • Livestock disease control; Improve traceability; Condition monitoring; Crime reduction. Te Elizabeth Wasserman (2007), “RFID Takes Root in Washington, ” RFID Journal, May/June; http: //www. electrocom. au/rfid_animalid. htm, viewed October 28, 2008 47
 R F I D ASSET TRACKING & AUTO ID • Auto ID: – Identification and Access control • Employee ID badges; • E-passports. Te Elizabeth Wasserman (2007), “RFID Takes Root in Washington, ” RFID Journal, May/June 48
R F I D ASSET TRACKING & AUTO ID • Auto ID: – Identification and Access control • Employee ID badges; • E-passports. Te Elizabeth Wasserman (2007), “RFID Takes Root in Washington, ” RFID Journal, May/June 48
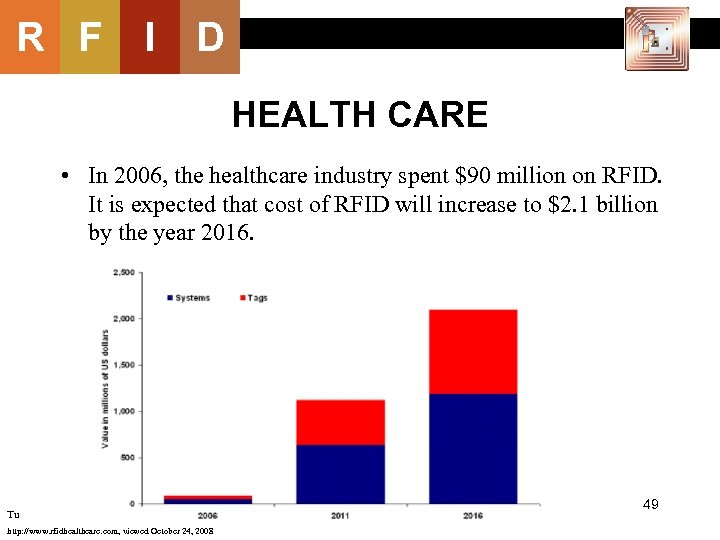 R F I D HEALTH CARE • In 2006, the healthcare industry spent $90 million on RFID. It is expected that cost of RFID will increase to $2. 1 billion by the year 2016. Tu http: //www. rfidhealthcare. com, viewed October 24, 2008 49
R F I D HEALTH CARE • In 2006, the healthcare industry spent $90 million on RFID. It is expected that cost of RFID will increase to $2. 1 billion by the year 2016. Tu http: //www. rfidhealthcare. com, viewed October 24, 2008 49
 R F I D HEALTH CARE Asset Management: • Locate movable assets. Tu http: //www. rfidhealthcare. com, viewed October 24, 2008 50
R F I D HEALTH CARE Asset Management: • Locate movable assets. Tu http: //www. rfidhealthcare. com, viewed October 24, 2008 50
 R F I D HEALTH CARE Patient Care • Track and identify a patient correctly. Tu http: //www. rfidhealthcare. com, viewed October 24, 2008 51
R F I D HEALTH CARE Patient Care • Track and identify a patient correctly. Tu http: //www. rfidhealthcare. com, viewed October 24, 2008 51
 R F I D HEALTH CARE Inventory Management • Identify inventory & prevent out of stock; • Fight counterfeit and theft – CVS: one of nine participating in a pilot designed to establish an RFID operating and adoption model for the drug industry in 2004. Tu Elena Malykhina (2004), “RFID Tests Are Positive For CVS And Pharmaceuticals, ” Information Week, September 30; http: //www. rfidhealthcare. com, viewed October 24, 2008. 52
R F I D HEALTH CARE Inventory Management • Identify inventory & prevent out of stock; • Fight counterfeit and theft – CVS: one of nine participating in a pilot designed to establish an RFID operating and adoption model for the drug industry in 2004. Tu Elena Malykhina (2004), “RFID Tests Are Positive For CVS And Pharmaceuticals, ” Information Week, September 30; http: //www. rfidhealthcare. com, viewed October 24, 2008. 52
 R F I D RFID SUPPLIERS 53 Tu
R F I D RFID SUPPLIERS 53 Tu
 R F I D POTENTIAL CHALLENGES TO MANAGE 54 C
R F I D POTENTIAL CHALLENGES TO MANAGE 54 C
 R F I D CONTROVERSIES • • • High RFID Costs; No global standard; Technological immaturity; Lack of robustness; Information management; Privacy concerns; – Video: http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=FVm. D 4 i. TXRLE • Ethical problems; • Terrorism, blue jacked. C Daniel V. Hunt, Albert Puglia, & Mike Puglia, (2007), “RFID: A Guide to Radio Frequency Identification, ” Wiley; Simson Garfinkel, & Beth Rosenberg (2006), “RFID: Applications, Security, and Privacy”, Addison-Wesley. 55
R F I D CONTROVERSIES • • • High RFID Costs; No global standard; Technological immaturity; Lack of robustness; Information management; Privacy concerns; – Video: http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=FVm. D 4 i. TXRLE • Ethical problems; • Terrorism, blue jacked. C Daniel V. Hunt, Albert Puglia, & Mike Puglia, (2007), “RFID: A Guide to Radio Frequency Identification, ” Wiley; Simson Garfinkel, & Beth Rosenberg (2006), “RFID: Applications, Security, and Privacy”, Addison-Wesley. 55
 R F I D MANAGERIAL IMPLICATION 56 D
R F I D MANAGERIAL IMPLICATION 56 D
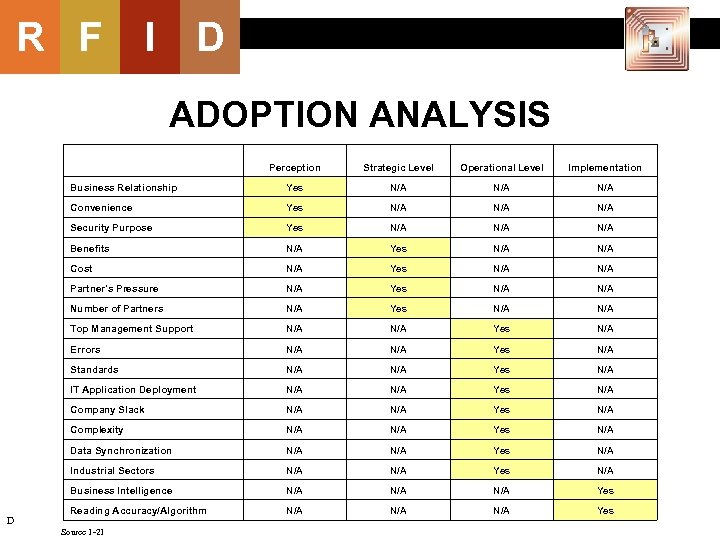 R F I D ADOPTION ANALYSIS Strategic Level Operational Level Implementation Business Relationship Yes N/A N/A Convenience Yes N/A N/A Security Purpose Yes N/A N/A Benefits N/A Yes N/A Cost N/A Yes N/A Partner's Pressure N/A Yes N/A Number of Partners N/A Yes N/A Top Management Support N/A Yes N/A Errors N/A Yes N/A Standards N/A Yes N/A IT Application Deployment N/A Yes N/A Company Slack N/A Yes N/A Complexity N/A Yes N/A Data Synchronization N/A Yes N/A Industrial Sectors N/A Yes N/A Business Intelligence D Perception N/A N/A Yes Reading Accuracy/Algorithm N/A N/A Yes Source 1 -21 57
R F I D ADOPTION ANALYSIS Strategic Level Operational Level Implementation Business Relationship Yes N/A N/A Convenience Yes N/A N/A Security Purpose Yes N/A N/A Benefits N/A Yes N/A Cost N/A Yes N/A Partner's Pressure N/A Yes N/A Number of Partners N/A Yes N/A Top Management Support N/A Yes N/A Errors N/A Yes N/A Standards N/A Yes N/A IT Application Deployment N/A Yes N/A Company Slack N/A Yes N/A Complexity N/A Yes N/A Data Synchronization N/A Yes N/A Industrial Sectors N/A Yes N/A Business Intelligence D Perception N/A N/A Yes Reading Accuracy/Algorithm N/A N/A Yes Source 1 -21 57
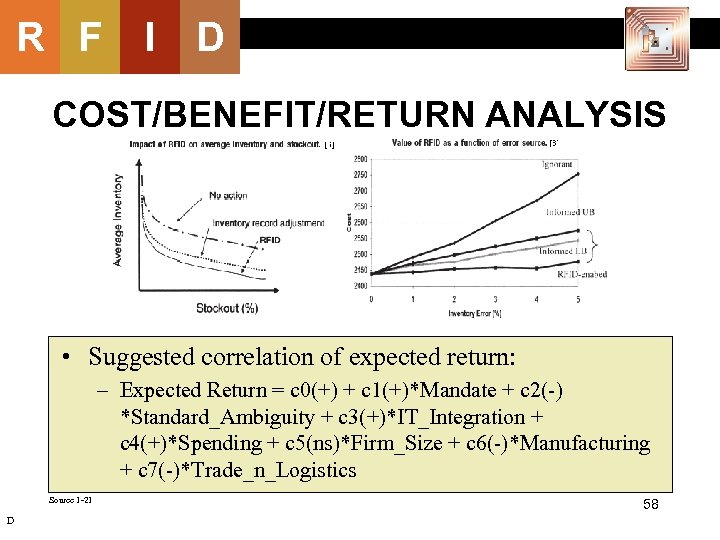 R F I D COST/BENEFIT/RETURN ANALYSIS • Suggested correlation of expected return: – Expected Return = c 0(+) + c 1(+)*Mandate + c 2(-) *Standard_Ambiguity + c 3(+)*IT_Integration + c 4(+)*Spending + c 5(ns)*Firm_Size + c 6(-)*Manufacturing + c 7(-)*Trade_n_Logistics Source 1 -21 D 58
R F I D COST/BENEFIT/RETURN ANALYSIS • Suggested correlation of expected return: – Expected Return = c 0(+) + c 1(+)*Mandate + c 2(-) *Standard_Ambiguity + c 3(+)*IT_Integration + c 4(+)*Spending + c 5(ns)*Firm_Size + c 6(-)*Manufacturing + c 7(-)*Trade_n_Logistics Source 1 -21 D 58
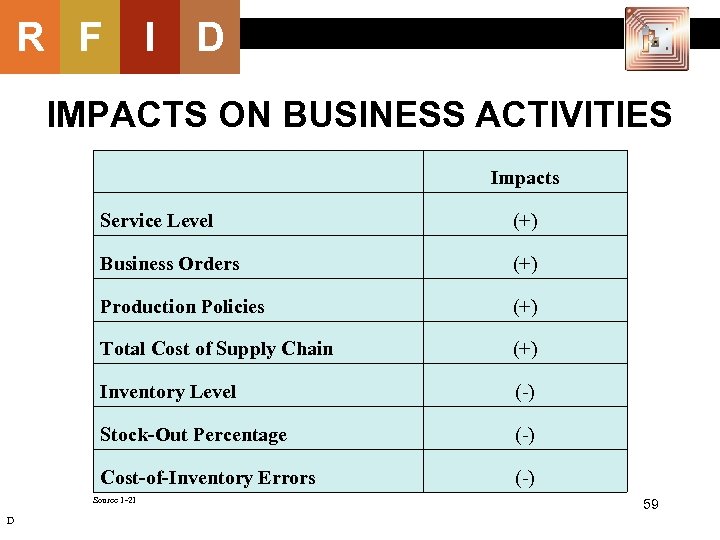 R F I D IMPACTS ON BUSINESS ACTIVITIES Impacts Service Level (+) Business Orders (+) Production Policies (+) Total Cost of Supply Chain (+) Inventory Level (-) Stock-Out Percentage (-) Cost-of-Inventory Errors (-) Source 1 -21 D 59
R F I D IMPACTS ON BUSINESS ACTIVITIES Impacts Service Level (+) Business Orders (+) Production Policies (+) Total Cost of Supply Chain (+) Inventory Level (-) Stock-Out Percentage (-) Cost-of-Inventory Errors (-) Source 1 -21 D 59
 R F I D RFID: THE FUTURE 60 C
R F I D RFID: THE FUTURE 60 C
 R F I D THE FUTURE OF RFID • A Future Supermarket – Video: http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=eob 532 i. Epqk 61 C
R F I D THE FUTURE OF RFID • A Future Supermarket – Video: http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=eob 532 i. Epqk 61 C
 R F I D POTENTIAL USES • • • Item-level Tags; Replacing barcodes; Combination with others technologies; Future improvement of RFID; Future benefits of RFID. C Daniel V. Hunt, Albert Puglia, & Mike Puglia, (2007), “RFID: A Guide to Radio Frequency Identification, ” Wiley; http: //www. wordquests. info/RFID. html, viewed October 21, 2008; http: //www. smso. net/RFID#History, viewed October 21, 2008 62
R F I D POTENTIAL USES • • • Item-level Tags; Replacing barcodes; Combination with others technologies; Future improvement of RFID; Future benefits of RFID. C Daniel V. Hunt, Albert Puglia, & Mike Puglia, (2007), “RFID: A Guide to Radio Frequency Identification, ” Wiley; http: //www. wordquests. info/RFID. html, viewed October 21, 2008; http: //www. smso. net/RFID#History, viewed October 21, 2008 62
 R F I D ITEM-LEVEL TAGS Commercial use: • Wal-Mart: tags on each pallets and cases; • Variety of companies engaged in item-level tagging: American Apparel; • Today: Reserved to luxury goods; • Tomorrow: any goods; • Examples: Italian manufacturer, Japanese students. C Daniel V. Hunt, Albert Puglia, & Mike Puglia, (2007), “RFID: A Guide to Radio Frequency Identification, ” Wiley; Simson Garfinkel, & Beth Rosenberg (2006), “RFID: Applications, Security, and Privacy”, Addison-Wesley. 63
R F I D ITEM-LEVEL TAGS Commercial use: • Wal-Mart: tags on each pallets and cases; • Variety of companies engaged in item-level tagging: American Apparel; • Today: Reserved to luxury goods; • Tomorrow: any goods; • Examples: Italian manufacturer, Japanese students. C Daniel V. Hunt, Albert Puglia, & Mike Puglia, (2007), “RFID: A Guide to Radio Frequency Identification, ” Wiley; Simson Garfinkel, & Beth Rosenberg (2006), “RFID: Applications, Security, and Privacy”, Addison-Wesley. 63
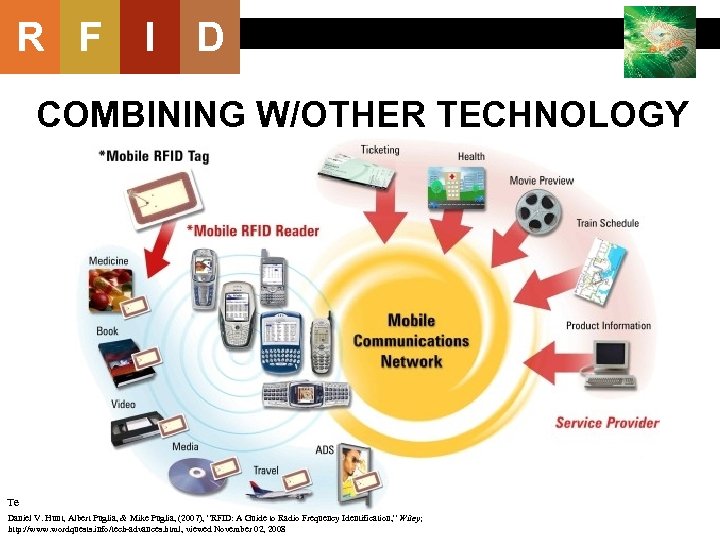 R F I D COMBINING W/OTHER TECHNOLOGY Te Daniel V. Hunt, Albert Puglia, & Mike Puglia, (2007), “RFID: A Guide to Radio Frequency Identification, ” Wiley; http: //www. wordquests. info/tech-advances. html, viewed November 02, 2008 64
R F I D COMBINING W/OTHER TECHNOLOGY Te Daniel V. Hunt, Albert Puglia, & Mike Puglia, (2007), “RFID: A Guide to Radio Frequency Identification, ” Wiley; http: //www. wordquests. info/tech-advances. html, viewed November 02, 2008 64
 R F I D EXAMPLES • Find your keys at home; • Find your car; • Human implant; • Your fridge keeps track of its contents. 65 C
R F I D EXAMPLES • Find your keys at home; • Find your car; • Human implant; • Your fridge keeps track of its contents. 65 C
 R F I D FUTURE IMPROVEMENT OF RFID • • • Process Optimization; Decrease in cost; Decrease in size; Better Memory, better power; Technological developments: – Real-time information of business process; – Improve business performance; – Improve privacy and security. C Daniel V. Hunt, Albert Puglia, & Mike Puglia, (2007), “RFID: A Guide to Radio Frequency Identification, ” Wiley; Simson Garfinkel, & Beth Rosenberg (2006), “RFID: Applications, Security, and Privacy”, Addison-Wesley. 66
R F I D FUTURE IMPROVEMENT OF RFID • • • Process Optimization; Decrease in cost; Decrease in size; Better Memory, better power; Technological developments: – Real-time information of business process; – Improve business performance; – Improve privacy and security. C Daniel V. Hunt, Albert Puglia, & Mike Puglia, (2007), “RFID: A Guide to Radio Frequency Identification, ” Wiley; Simson Garfinkel, & Beth Rosenberg (2006), “RFID: Applications, Security, and Privacy”, Addison-Wesley. 66
 R F I D References: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Zaheeruddin Asif, Munir Mandviwalia (2005), “Integrating the Supply Chain with RFID: A Technical and Business Analysis, ” Communication of the Association for Information Systems, Vol. 15, Article 24, March; Yu-Ju Tu & Selwyn Piramuthu (2008), “Reducing False Reads in RFID-Embedded Supply Chains, ” Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research, Vol. 3, Issue 2, pp. 60 -70; S. K. Hargrove Sr, R. Queen Jr, B. Olubando & A. La. Rochelle, “Developing a Low Cost RFID (Radio Frequency Identifiers) Middleware for Small Business Applications, ” Department of Industrial, Manufacturing and information Engineering, Clarence M. Mitchell, Jr. School of Engineering, Morgan State University, Baltimore, USA; Mark Vandenbosch & Niraj Dawar (2002), “Beyond Better Products: Capturing Value in Customer Interactions”, MIT Sloan Management Review; Hau Lee & Ozalp Ozer (2007), “Unlocking the Value of RFID, ” Production and Operation Management, Vol. 16, No. 1, Jan-Feb; Jonathan Whitaker, Sunil Mithas & M. S. Krishnan (2007), “A Field Study of RFID Deployment and Return Expectations, ” Production and Operation Management, Vol. 16, No. 5, Sep-Oct; Henning Baars, Hans-Georg Kemper, Heiner Lasi & Marc Siegel (2008), “Combining RFID Technology and Business Intelligence for Supply Chain Optimization – Scenarios for Retail Logistics, ” Proceedings of the 41 st Hawaii International Conference in System Sciences; Claudia Loebbecke & Claudio Heyskens (2006), “Weaving the RFID Yarn in the Fashion Industry: The Kaufhof Case, ” MIS Quarterly Executive, Vol. 5 No. 4, Dec; David H. Nguyen, Alfred Kobsa & Gillian Hayes (2008), “An Empirical Investigation of Concerns of Everyday Tracking and Recording Technologies, ” ACM; 67
R F I D References: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Zaheeruddin Asif, Munir Mandviwalia (2005), “Integrating the Supply Chain with RFID: A Technical and Business Analysis, ” Communication of the Association for Information Systems, Vol. 15, Article 24, March; Yu-Ju Tu & Selwyn Piramuthu (2008), “Reducing False Reads in RFID-Embedded Supply Chains, ” Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research, Vol. 3, Issue 2, pp. 60 -70; S. K. Hargrove Sr, R. Queen Jr, B. Olubando & A. La. Rochelle, “Developing a Low Cost RFID (Radio Frequency Identifiers) Middleware for Small Business Applications, ” Department of Industrial, Manufacturing and information Engineering, Clarence M. Mitchell, Jr. School of Engineering, Morgan State University, Baltimore, USA; Mark Vandenbosch & Niraj Dawar (2002), “Beyond Better Products: Capturing Value in Customer Interactions”, MIT Sloan Management Review; Hau Lee & Ozalp Ozer (2007), “Unlocking the Value of RFID, ” Production and Operation Management, Vol. 16, No. 1, Jan-Feb; Jonathan Whitaker, Sunil Mithas & M. S. Krishnan (2007), “A Field Study of RFID Deployment and Return Expectations, ” Production and Operation Management, Vol. 16, No. 5, Sep-Oct; Henning Baars, Hans-Georg Kemper, Heiner Lasi & Marc Siegel (2008), “Combining RFID Technology and Business Intelligence for Supply Chain Optimization – Scenarios for Retail Logistics, ” Proceedings of the 41 st Hawaii International Conference in System Sciences; Claudia Loebbecke & Claudio Heyskens (2006), “Weaving the RFID Yarn in the Fashion Industry: The Kaufhof Case, ” MIS Quarterly Executive, Vol. 5 No. 4, Dec; David H. Nguyen, Alfred Kobsa & Gillian Hayes (2008), “An Empirical Investigation of Concerns of Everyday Tracking and Recording Technologies, ” ACM; 67
 R F I D References: 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. Aditva Sharma, Alex Citurs & Benn Konsynski (2007), “Strategic and Institutional Perspective in the Adoption and Early Integration of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), ” Proceedings of the 40 th Annual Hawaii International Conference in System Sciences; Anne Quaadgras, “Who Joins the Platform? The Case of the RFID Business Econsystem (2005), ” Proceedings of the 38 th Annual Hawaii International Conference in System Sciences; Geng Yang & Sirkka L. Jarvenpaa (2005), “Trust and Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) Adoption within an Alliance, ” Proceedings of the 38 th Annual Hawaii International Conference in System Sciences; Michael A. Jones, David C. Wyld & Jeff W. Totten, “The Adoption of RFID Technology in the Retail Supply Chain, ” The Coastal Business Journal, Vol. 4, No. 1; Charlie Fine, Natalie Klym, Dirk Trossen & Milind Tavshikar (2006), “The Evolution of RFID Networks: The Potential for Disruptive Innovation, ” MIT Center for Business; Uta Knebel, Jan Marco Leimeister & Helmut Krcmar (2006), “Strategic Importance of RFID – The Perspective of IT Decision Maker in Italy, ” Journal of Information Technology Management, Vol. XVII, Nov 4; Vic Matta & Chris Moberg (2007), “Defining the Antecedents for Adoption of RFID in the Supply Chain, ” Issues in Information Systems, Vol. VIII, No. 2; Liping Liu & Bindiganavale S. Vijayaraman, “Information Integration: A Review of Emerging E-Business Technologies, ” College of Business Administration, The University of Akron; Christine Perakslis, Christine & Robert Wolk (2005), “Social Acceptance of RFID as a Biometric Security Method, ” IEEE; Thomas Diekmann, Adam Melski & Matthias Schumann, “Analyzing Impacts of RFID in Supply Chains Using Joint Economic Lot Size Models, ” University of Göttingen, Institute for Information Systems; http: //www. rfidjournal. com; H Jung, F. F. Chen & B. Jeong (2007), “Trends in Supply Chain Design and Management -Technologies and Methodologies, ” ISBN: 978 -1 -84628 -606 -3. 68
R F I D References: 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. Aditva Sharma, Alex Citurs & Benn Konsynski (2007), “Strategic and Institutional Perspective in the Adoption and Early Integration of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), ” Proceedings of the 40 th Annual Hawaii International Conference in System Sciences; Anne Quaadgras, “Who Joins the Platform? The Case of the RFID Business Econsystem (2005), ” Proceedings of the 38 th Annual Hawaii International Conference in System Sciences; Geng Yang & Sirkka L. Jarvenpaa (2005), “Trust and Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) Adoption within an Alliance, ” Proceedings of the 38 th Annual Hawaii International Conference in System Sciences; Michael A. Jones, David C. Wyld & Jeff W. Totten, “The Adoption of RFID Technology in the Retail Supply Chain, ” The Coastal Business Journal, Vol. 4, No. 1; Charlie Fine, Natalie Klym, Dirk Trossen & Milind Tavshikar (2006), “The Evolution of RFID Networks: The Potential for Disruptive Innovation, ” MIT Center for Business; Uta Knebel, Jan Marco Leimeister & Helmut Krcmar (2006), “Strategic Importance of RFID – The Perspective of IT Decision Maker in Italy, ” Journal of Information Technology Management, Vol. XVII, Nov 4; Vic Matta & Chris Moberg (2007), “Defining the Antecedents for Adoption of RFID in the Supply Chain, ” Issues in Information Systems, Vol. VIII, No. 2; Liping Liu & Bindiganavale S. Vijayaraman, “Information Integration: A Review of Emerging E-Business Technologies, ” College of Business Administration, The University of Akron; Christine Perakslis, Christine & Robert Wolk (2005), “Social Acceptance of RFID as a Biometric Security Method, ” IEEE; Thomas Diekmann, Adam Melski & Matthias Schumann, “Analyzing Impacts of RFID in Supply Chains Using Joint Economic Lot Size Models, ” University of Göttingen, Institute for Information Systems; http: //www. rfidjournal. com; H Jung, F. F. Chen & B. Jeong (2007), “Trends in Supply Chain Design and Management -Technologies and Methodologies, ” ISBN: 978 -1 -84628 -606 -3. 68
 R F I D QUESTIONS? 69
R F I D QUESTIONS? 69


