dc10faf185be2e2fd198c110f1a2e198.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 25
 r 13 apte Ch GENE Y NOLOG TECH
r 13 apte Ch GENE Y NOLOG TECH
 Section 1: DNA TECHNOLOGY-Tools of DNA Positive ID at a crime scene Improvement of food crops Human predisposition for disease Research treatments for genetic diseases
Section 1: DNA TECHNOLOGY-Tools of DNA Positive ID at a crime scene Improvement of food crops Human predisposition for disease Research treatments for genetic diseases
 DNA Identification No two human beings are identical genetically – except identical twins Human beings have pretty much the same DNA except for 0. 1% Because of this difference, we can compare samples of humans for paternity, providing evidence, tracing human origins, identifying remains
DNA Identification No two human beings are identical genetically – except identical twins Human beings have pretty much the same DNA except for 0. 1% Because of this difference, we can compare samples of humans for paternity, providing evidence, tracing human origins, identifying remains
 Noncoding DNA We only use about 2% of our DNA The remaining 98% is called noncoding DNA This DNA contains many long, repeating varying nucleotide sequences called variable number tandem repeats – VNTR CACACA CACACA
Noncoding DNA We only use about 2% of our DNA The remaining 98% is called noncoding DNA This DNA contains many long, repeating varying nucleotide sequences called variable number tandem repeats – VNTR CACACA CACACA
 Noncoding DNA, cont. The pattern of repeating nucleotides varies tremendously in the human population and can be used to make up a DNA profile
Noncoding DNA, cont. The pattern of repeating nucleotides varies tremendously in the human population and can be used to make up a DNA profile
 Steps in DNA Identification DNA Extraction (isolation) PCR – polymerase chain reaction – the molecular photocopying process http: //learn. genetics. utah. edu/content/labs/pcr/
Steps in DNA Identification DNA Extraction (isolation) PCR – polymerase chain reaction – the molecular photocopying process http: //learn. genetics. utah. edu/content/labs/pcr/
 Steps, cont. – RE’s Restriction enzymes – the molecular scissors Enzymes that can cut (hydrolyze) DNA at specific sites. Current DNA technology is totally dependent on restriction enzymes. Restriction enzymes are endonucleases – they cut within the DNA
Steps, cont. – RE’s Restriction enzymes – the molecular scissors Enzymes that can cut (hydrolyze) DNA at specific sites. Current DNA technology is totally dependent on restriction enzymes. Restriction enzymes are endonucleases – they cut within the DNA
 Steps, cont. Bacterial enzymes – used to cut bacteriophage DNA (viruses that invade bacteria) – why? Different bacterial strains produce different restriction enzymes The names of restriction enzymes are derived from the name of the bacterial strain they are isolated from
Steps, cont. Bacterial enzymes – used to cut bacteriophage DNA (viruses that invade bacteria) – why? Different bacterial strains produce different restriction enzymes The names of restriction enzymes are derived from the name of the bacterial strain they are isolated from
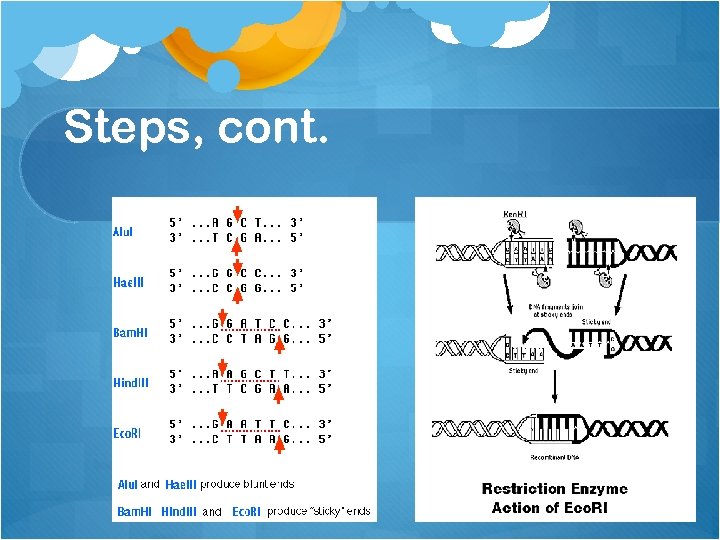
 Steps, cont. Titles of restriction enzymes are derived from the first letter of the genus + the first two letters of the species of organism from which they were isolated. Eco. RI - from Escherichia coli Bam. HI - from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Hind. III - from Haemophilus influenzae
Steps, cont. Titles of restriction enzymes are derived from the first letter of the genus + the first two letters of the species of organism from which they were isolated. Eco. RI - from Escherichia coli Bam. HI - from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Hind. III - from Haemophilus influenzae
 Steps, cont.
Steps, cont.
 Steps, cont. Using this piece of DNA, cut it with Eco RI G/AATTC GACCG/AATTCAGTTAATTCG/AATTC
Steps, cont. Using this piece of DNA, cut it with Eco RI G/AATTC GACCG/AATTCAGTTAATTCG/AATTC
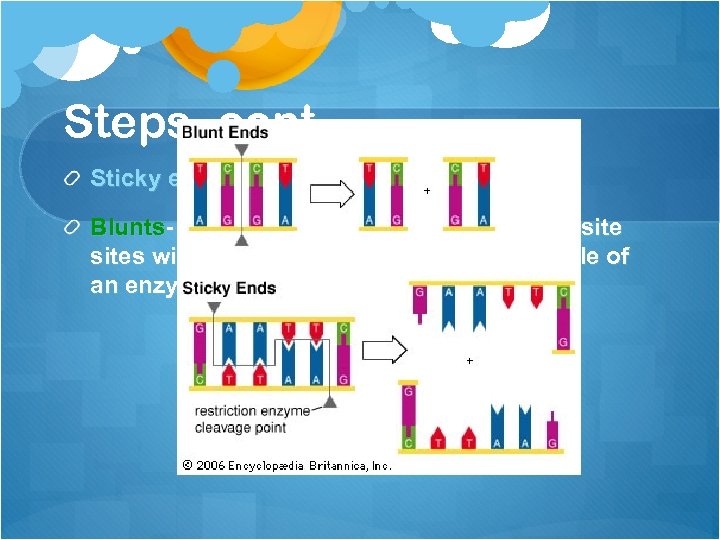 Steps, cont. Sticky ends – Creates an overhang. Bam. H 1 Blunts- Enzymes that cut at precisely opposites without overhangs. Sma. I is an example of an enzyme that generates blunt ends
Steps, cont. Sticky ends – Creates an overhang. Bam. H 1 Blunts- Enzymes that cut at precisely opposites without overhangs. Sma. I is an example of an enzyme that generates blunt ends
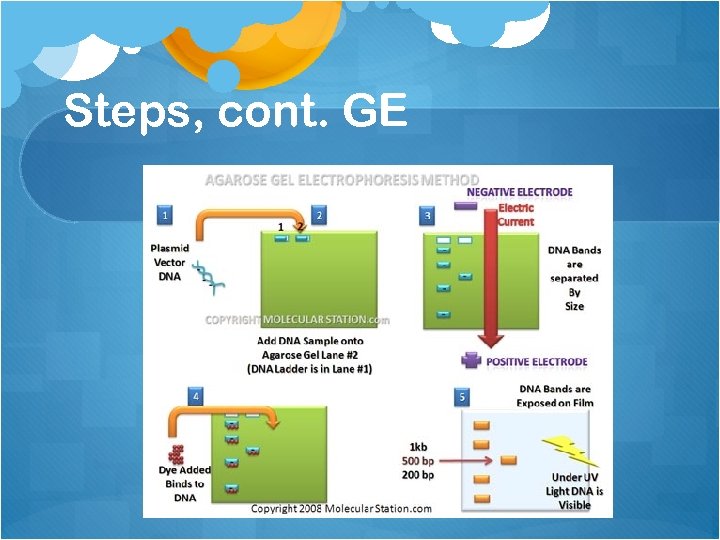
 Steps, cont. GE Gel Electrophoresis – the molecular sieve Separates nucleic acids or proteins based on size and charge DNA fingerprinting – Banding pattern of the fragments of cut DNA on a special gel medium (agarose)
Steps, cont. GE Gel Electrophoresis – the molecular sieve Separates nucleic acids or proteins based on size and charge DNA fingerprinting – Banding pattern of the fragments of cut DNA on a special gel medium (agarose)
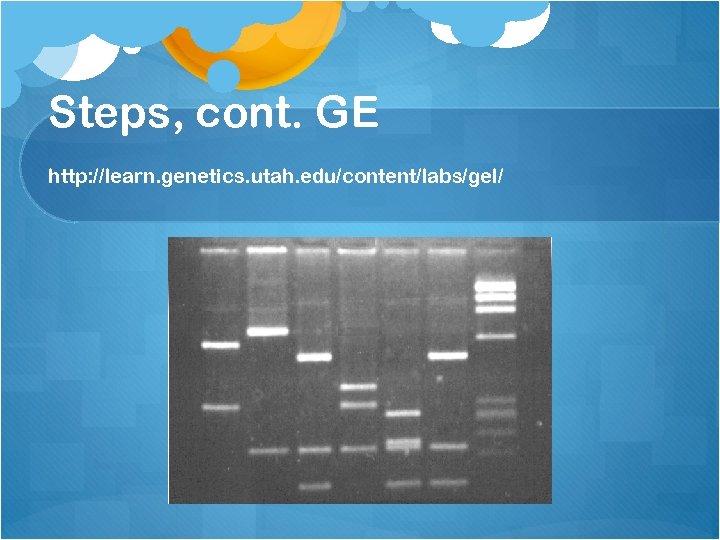 Steps, cont. GE http: //learn. genetics. utah. edu/content/labs/gel/
Steps, cont. GE http: //learn. genetics. utah. edu/content/labs/gel/
 Steps, cont. GE
Steps, cont. GE
 DNA Fingerprinting A powerful tool to analyze VNTR Odds are 1/100, 000, 000 that any two people will have the same genetic fingerprint!!!
DNA Fingerprinting A powerful tool to analyze VNTR Odds are 1/100, 000, 000 that any two people will have the same genetic fingerprint!!!
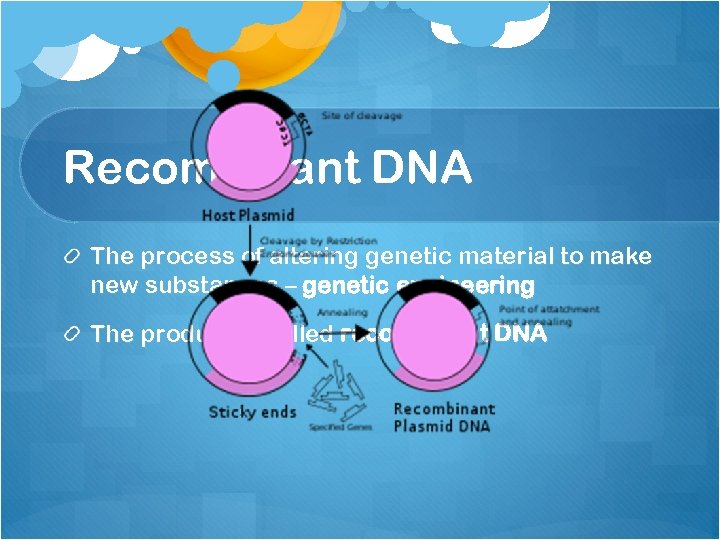 Recombinant DNA The process of altering genetic material to make new substances – genetic engineering The product is called recombinant DNA
Recombinant DNA The process of altering genetic material to make new substances – genetic engineering The product is called recombinant DNA
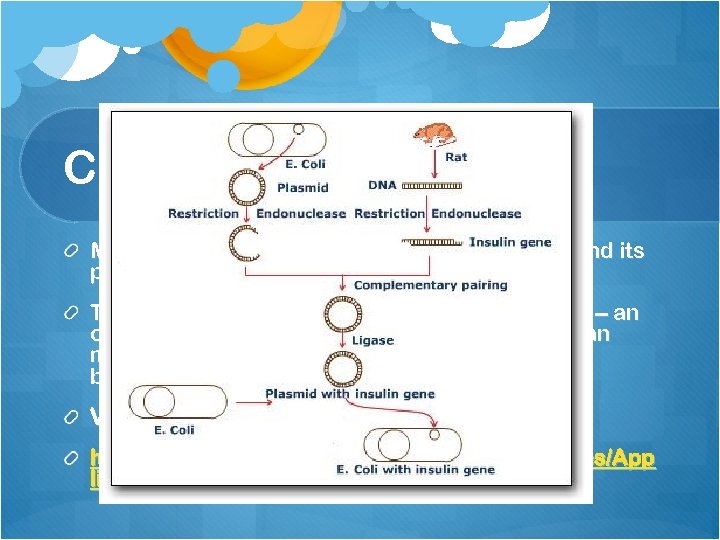 Cloning Vectors Many copies of a desired gene can be cloned and its product harvested This is accomplished by using a cloning vector – an organism that contains the desired gene and can multiply rapidly – this organism is usually a bacterium Vector = carrier http: //www. bioteach. ubc. ca/Teaching. Resources/App lications/GMOpkg. JKlose. GLampard 2. swf
Cloning Vectors Many copies of a desired gene can be cloned and its product harvested This is accomplished by using a cloning vector – an organism that contains the desired gene and can multiply rapidly – this organism is usually a bacterium Vector = carrier http: //www. bioteach. ubc. ca/Teaching. Resources/App lications/GMOpkg. JKlose. GLampard 2. swf
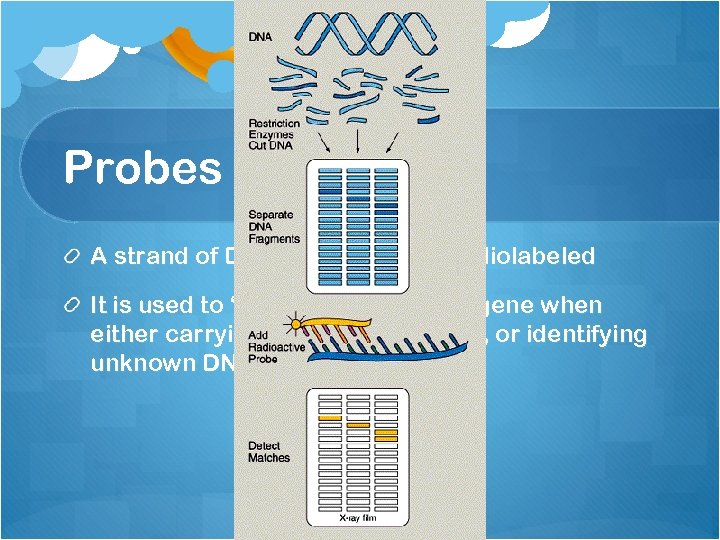 Probes A strand of DNA or RNA that is radiolabeled It is used to “fish” for the desired gene when either carrying out recombination, or identifying unknown DNA
Probes A strand of DNA or RNA that is radiolabeled It is used to “fish” for the desired gene when either carrying out recombination, or identifying unknown DNA
 Section 2: The Human Genome Huge research project, conducted over 13 years, sequenced and identified 20 -25, 000 human genes Findings include: 2% coding DNA, RNA useful in regulating gene expression, transposons shuffle to make new genetic combinations
Section 2: The Human Genome Huge research project, conducted over 13 years, sequenced and identified 20 -25, 000 human genes Findings include: 2% coding DNA, RNA useful in regulating gene expression, transposons shuffle to make new genetic combinations
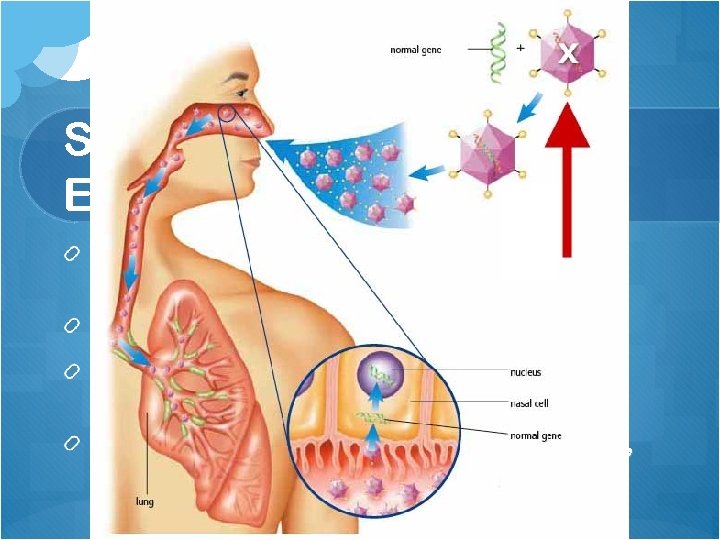 Section 3: Genetic Engineering Gene therapy – treat a genetic disorder by inserting a functional gene CFTR gene in cystic fibrosis, a temporary fix Gene inserted into a nonpathogenic virus and introduced into nasal spray Not completely successful; lung tissue is deep, cells slough off, rejection responses
Section 3: Genetic Engineering Gene therapy – treat a genetic disorder by inserting a functional gene CFTR gene in cystic fibrosis, a temporary fix Gene inserted into a nonpathogenic virus and introduced into nasal spray Not completely successful; lung tissue is deep, cells slough off, rejection responses
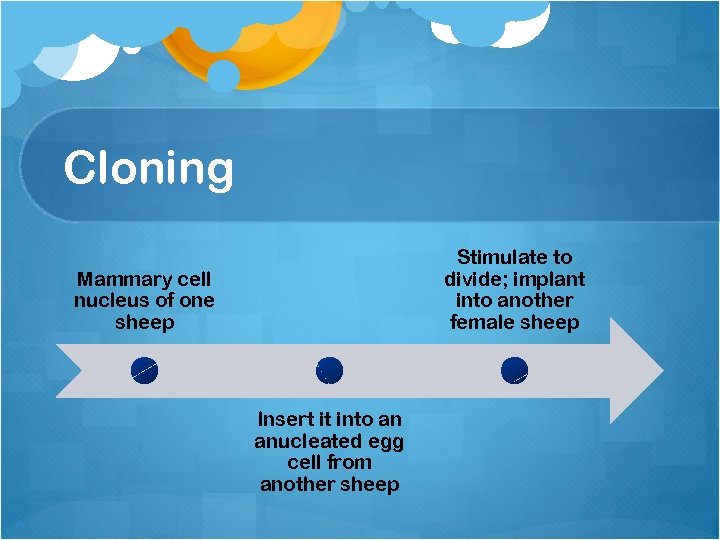 Cloning Stimulate to divide; implant into another female sheep Mammary cell nucleus of one sheep Insert it into an anucleated egg cell from another sheep
Cloning Stimulate to divide; implant into another female sheep Mammary cell nucleus of one sheep Insert it into an anucleated egg cell from another sheep
 HELLO DOLLY!!! Dolly died prematurely as she had short telomeres = ends of chromosomes – like aglets! Currently animals can be cloned to grow up organs for human transplants
HELLO DOLLY!!! Dolly died prematurely as she had short telomeres = ends of chromosomes – like aglets! Currently animals can be cloned to grow up organs for human transplants
 Other applications GMOs – genetically modified organisms, crops Increase yield, make crops weather and pest resistant, increase nutritional value Controversy related to genetically modified (GM) food : risk of harm from GM food, whether GM food should be labeled, the role of government regulators, the effect of GM crops on the environment, the impact of GM crops for farmers, the role of GM crops in feeding the growing world population
Other applications GMOs – genetically modified organisms, crops Increase yield, make crops weather and pest resistant, increase nutritional value Controversy related to genetically modified (GM) food : risk of harm from GM food, whether GM food should be labeled, the role of government regulators, the effect of GM crops on the environment, the impact of GM crops for farmers, the role of GM crops in feeding the growing world population
 GM foods, cont. Soy, corn, dairy Buy organic, 100% grass fed beef Buy local PLU codes – 5 numbers beginning with a 9 = organic; 4 numbers = conventional; 5 numbers beginning with an 8 = GM
GM foods, cont. Soy, corn, dairy Buy organic, 100% grass fed beef Buy local PLU codes – 5 numbers beginning with a 9 = organic; 4 numbers = conventional; 5 numbers beginning with an 8 = GM


