qwerty_corrected.pptx
- Количество слайдов: 8
 qwerty p -----“Take it easy” Case #1: Unilever Antipina Tatyana – International management, GSOM Serikova Tatyana – International management, GSOM Tarasova Yana – International management, GSOM Treskunov Igor – Public administration, GSOM
qwerty p -----“Take it easy” Case #1: Unilever Antipina Tatyana – International management, GSOM Serikova Tatyana – International management, GSOM Tarasova Yana – International management, GSOM Treskunov Igor – Public administration, GSOM
 Draft Overview of Unilever strategy and leadership Biggest Ice cream producer Leader in FMCG in Russia One of the world leaders in FMCG Strategic goal of Unilever is to be a leader everywhere Ice cream market specify High dependence on climate and weather Seasonal Need in special condition for storage nd transportation Russian ice cream market specify Huge size of the country => Long - distance delivery Different seasonal peaks in different parts of the country (Как лучще сказать про то, что в питере в три раза сезонность, на юге в 20) Tendency to extremely hot summers (due to global warming? ) Facts: Unilever is Tea - #1 Source: official site of Unilever company (Unilever. com), Case “Delivering Ice to every house”, Deodorants - #1
Draft Overview of Unilever strategy and leadership Biggest Ice cream producer Leader in FMCG in Russia One of the world leaders in FMCG Strategic goal of Unilever is to be a leader everywhere Ice cream market specify High dependence on climate and weather Seasonal Need in special condition for storage nd transportation Russian ice cream market specify Huge size of the country => Long - distance delivery Different seasonal peaks in different parts of the country (Как лучще сказать про то, что в питере в три раза сезонность, на юге в 20) Tendency to extremely hot summers (due to global warming? ) Facts: Unilever is Tea - #1 Source: official site of Unilever company (Unilever. com), Case “Delivering Ice to every house”, Deodorants - #1
 To ensure leadership distributional net should reflect the specificity of the market Market peculiarity Ø Monopolistic competition Ø Seasonality Ø Value shares, % (2011) 22. 4 High dependence on 36. 2 Unilever Nestle Iceberry Russki Holod Talosto Other Seasonality 10 5 0 Jan Fe b. M rc a h. Ap r. M a y Ju n e Ju ly Au g. S e pt O c t. N o v. D e c weather and climate conditions 20 Demand, % 15 Delivery-to-every-house chain: Direct orders; Factory Thought retailers: Factory Through Distribution centers: Factory House Retailers Distribution center House Retailers House Logistics peculiarity: Ø Lack of equipped warehouses Ø Quality of roads Ø Ø Possible costs Storage Huge size of the country => Long - distance delivery Rent Own Transportation High variation of seasonality (from 3 to 20 times) Unilever’s strategic goal – “to be #1 in every market” Source: official site of Unilever company (Unilever. com), Case “Delivering Ice to every house”,
To ensure leadership distributional net should reflect the specificity of the market Market peculiarity Ø Monopolistic competition Ø Seasonality Ø Value shares, % (2011) 22. 4 High dependence on 36. 2 Unilever Nestle Iceberry Russki Holod Talosto Other Seasonality 10 5 0 Jan Fe b. M rc a h. Ap r. M a y Ju n e Ju ly Au g. S e pt O c t. N o v. D e c weather and climate conditions 20 Demand, % 15 Delivery-to-every-house chain: Direct orders; Factory Thought retailers: Factory Through Distribution centers: Factory House Retailers Distribution center House Retailers House Logistics peculiarity: Ø Lack of equipped warehouses Ø Quality of roads Ø Ø Possible costs Storage Huge size of the country => Long - distance delivery Rent Own Transportation High variation of seasonality (from 3 to 20 times) Unilever’s strategic goal – “to be #1 in every market” Source: official site of Unilever company (Unilever. com), Case “Delivering Ice to every house”,
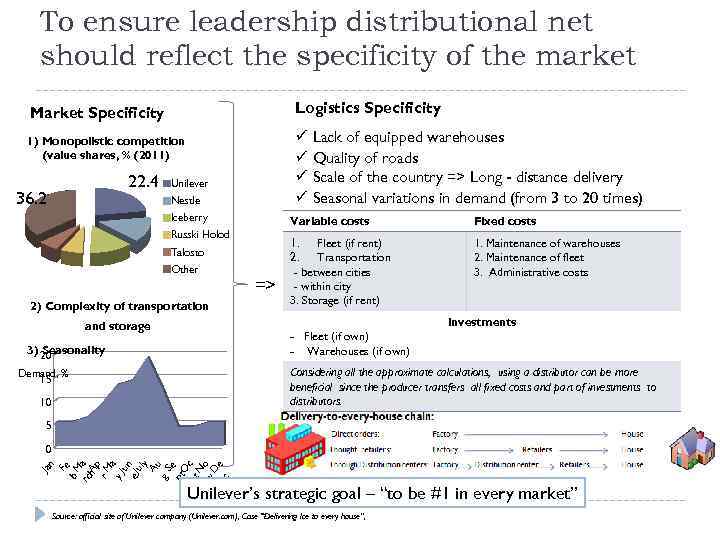 To ensure leadership distributional net should reflect the specificity of the market Logistics Specificity Market Specificity ü Lack of equipped warehouses ü Quality of roads ü Scale of the country => Long - distance delivery ü Seasonal variations in demand (from 3 to 20 times) 1) Monopolistic competition (value shares, % (2011) 22. 4 36. 2 Unilever Nestle Iceberry Variable costs Russki Holod Talosto Other 2) Complexity of transportation => Fixed costs 1. Fleet (if rent) 2. Transportation - between cities - within city 3. Storage (if rent) 1. Maintenance of warehouses 2. Maintenance of fleet 3. Administrative costs Investments and storage - Fleet (if own) - Warehouses (if own) 3) 20 Seasonality Considering all the approximate calculations, using a distributor can be more beneficial since the producer transfers all fixed costs and part of investments to distributors. Demand, % 15 10 5 Jan Fe b. M rc a h. Ap r. M a y Ju n e Ju ly Au g. S e pt O c t. N o v. D e c 0 Unilever’s strategic goal – “to be #1 in every market” Source: official site of Unilever company (Unilever. com), Case “Delivering Ice to every house”,
To ensure leadership distributional net should reflect the specificity of the market Logistics Specificity Market Specificity ü Lack of equipped warehouses ü Quality of roads ü Scale of the country => Long - distance delivery ü Seasonal variations in demand (from 3 to 20 times) 1) Monopolistic competition (value shares, % (2011) 22. 4 36. 2 Unilever Nestle Iceberry Variable costs Russki Holod Talosto Other 2) Complexity of transportation => Fixed costs 1. Fleet (if rent) 2. Transportation - between cities - within city 3. Storage (if rent) 1. Maintenance of warehouses 2. Maintenance of fleet 3. Administrative costs Investments and storage - Fleet (if own) - Warehouses (if own) 3) 20 Seasonality Considering all the approximate calculations, using a distributor can be more beneficial since the producer transfers all fixed costs and part of investments to distributors. Demand, % 15 10 5 Jan Fe b. M rc a h. Ap r. M a y Ju n e Ju ly Au g. S e pt O c t. N o v. D e c 0 Unilever’s strategic goal – “to be #1 in every market” Source: official site of Unilever company (Unilever. com), Case “Delivering Ice to every house”,
 2) Карта "своя сеть-дистрибьюторы/локальныерегиональные-почтифедеральные" + что-то умное о рынке, может Портер Моя карта с фабриками(Яна)
2) Карта "своя сеть-дистрибьюторы/локальныерегиональные-почтифедеральные" + что-то умное о рынке, может Портер Моя карта с фабриками(Яна)
 Current distributional net doesn’t suit company’s goals* 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) No common strategy (distribution methods vary even in neighbor areas) Company’s representatives are only in Moscow and Tula In most prospective areas (South, St. Petersburg) services of competitors are used Delivery quality/price ratio varies among distributors Doesn’t cover completely segment’s territory 1) => 2) 3) 4) Potential demand is not completely covered Segment of “key accounts” can suffer Lack of control on net Company probably didn’t get all information about demand its fluctuation Factory Distribution Center Underdeveloped area Own Network Logistics Distributors’ Regional Distributional Regional Centers Center Key Account’s Distr. Center Key Accounts * More detailed data you can see in app. 1 Modern/Traditional trade
Current distributional net doesn’t suit company’s goals* 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) No common strategy (distribution methods vary even in neighbor areas) Company’s representatives are only in Moscow and Tula In most prospective areas (South, St. Petersburg) services of competitors are used Delivery quality/price ratio varies among distributors Doesn’t cover completely segment’s territory 1) => 2) 3) 4) Potential demand is not completely covered Segment of “key accounts” can suffer Lack of control on net Company probably didn’t get all information about demand its fluctuation Factory Distribution Center Underdeveloped area Own Network Logistics Distributors’ Regional Distributional Regional Centers Center Key Account’s Distr. Center Key Accounts * More detailed data you can see in app. 1 Modern/Traditional trade
 Theoretical framework of the desired supply chain • Elimination of the “bullwhip effect” => no need in 3 PL (third party logistics) Multiagent approach More dynamic logistics model Local performance measurement (LPM) Consumer behaviour: driving the value chain Vendor chain: automated sales • Collaborative warehousing approach • Information sharing: driving the collaborative supply chain, transparency Current KPI s Sustainability KPI s Availability to consumer (percent in-stock) Cost reduction Financial KPI s Return on investment (ROI) Gross Margin Return on “X” (GMROX) Return on brand equity Inventory Traceability Energy consumption CO 2 emissions (greenhouse gases) Traffic congestion Water consumption Security compliance Infrastructure simplification
Theoretical framework of the desired supply chain • Elimination of the “bullwhip effect” => no need in 3 PL (third party logistics) Multiagent approach More dynamic logistics model Local performance measurement (LPM) Consumer behaviour: driving the value chain Vendor chain: automated sales • Collaborative warehousing approach • Information sharing: driving the collaborative supply chain, transparency Current KPI s Sustainability KPI s Availability to consumer (percent in-stock) Cost reduction Financial KPI s Return on investment (ROI) Gross Margin Return on “X” (GMROX) Return on brand equity Inventory Traceability Energy consumption CO 2 emissions (greenhouse gases) Traffic congestion Water consumption Security compliance Infrastructure simplification
 5) Что должно быть - выводы и рекоммендации
5) Что должно быть - выводы и рекоммендации


