fa973a8e2f9f2273815ba45445df6a4b.ppt
- Количество слайдов: 40
 ¡Quiz Returned ¡Law of Supply ¡Homework ¡Supply and Demand ¡Worksheet ¡Homework n. Read Naked Economics, Chapter 1 n. Review Powerpoint for next class (online) n. Read “Current Reading Assignment” (online)
¡Quiz Returned ¡Law of Supply ¡Homework ¡Supply and Demand ¡Worksheet ¡Homework n. Read Naked Economics, Chapter 1 n. Review Powerpoint for next class (online) n. Read “Current Reading Assignment” (online)
 QUIZ RETURNED
QUIZ RETURNED
 Law of Supply n n n When price increase, the quantity supplied increases. When price decreases, the quantity supplied decreases. P Qs , P Qs A direct relationship.
Law of Supply n n n When price increase, the quantity supplied increases. When price decreases, the quantity supplied decreases. P Qs , P Qs A direct relationship.
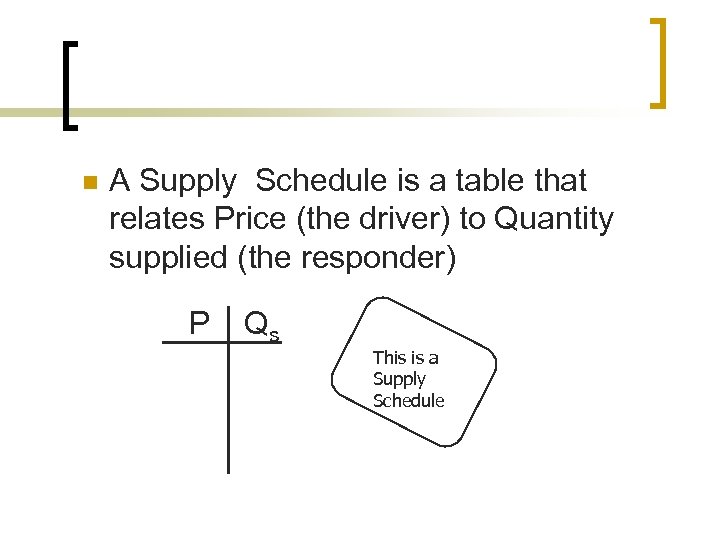 n A Supply Schedule is a table that relates Price (the driver) to Quantity supplied (the responder) P Qs This is a Supply Schedule
n A Supply Schedule is a table that relates Price (the driver) to Quantity supplied (the responder) P Qs This is a Supply Schedule
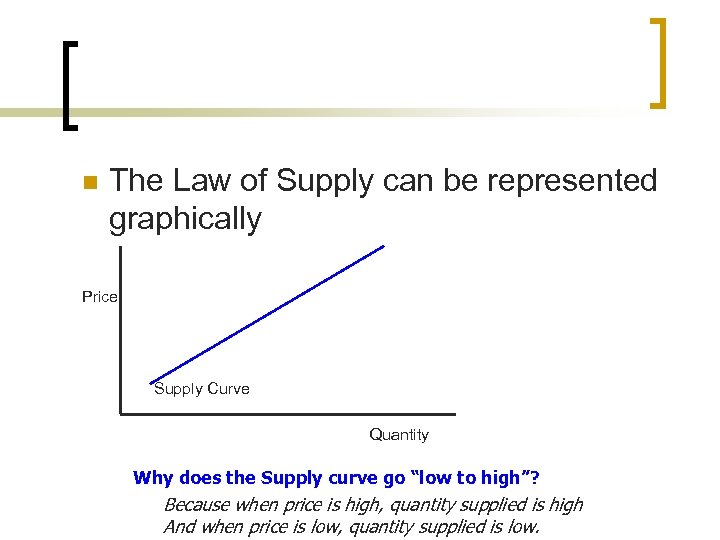 n The Law of Supply can be represented graphically Price Supply Curve Quantity Why does the Supply curve go “low to high”? Because when price is high, quantity supplied is high And when price is low, quantity supplied is low.
n The Law of Supply can be represented graphically Price Supply Curve Quantity Why does the Supply curve go “low to high”? Because when price is high, quantity supplied is high And when price is low, quantity supplied is low.
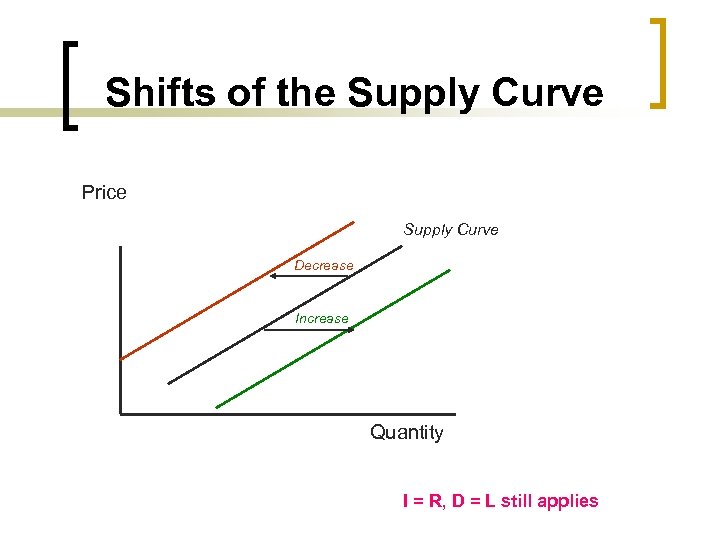 Shifts of the Supply Curve Price Supply Curve Decrease Increase Quantity I = R, D = L still applies
Shifts of the Supply Curve Price Supply Curve Decrease Increase Quantity I = R, D = L still applies
 ELASTICITY OF SUPPLY n How sensitive are suppliers to a change in price n P Qs = Elastic Supply n P Qs = Inelastic Supply Remember…Law of Supply still applies
ELASTICITY OF SUPPLY n How sensitive are suppliers to a change in price n P Qs = Elastic Supply n P Qs = Inelastic Supply Remember…Law of Supply still applies
 Length of time to produce the good or service is the main determinant of the elasticity of supply The longer it takes to produce the good or service, the more inelastic. Helpful Hint…Inelastic is the long word and that takes a long time to produce
Length of time to produce the good or service is the main determinant of the elasticity of supply The longer it takes to produce the good or service, the more inelastic. Helpful Hint…Inelastic is the long word and that takes a long time to produce
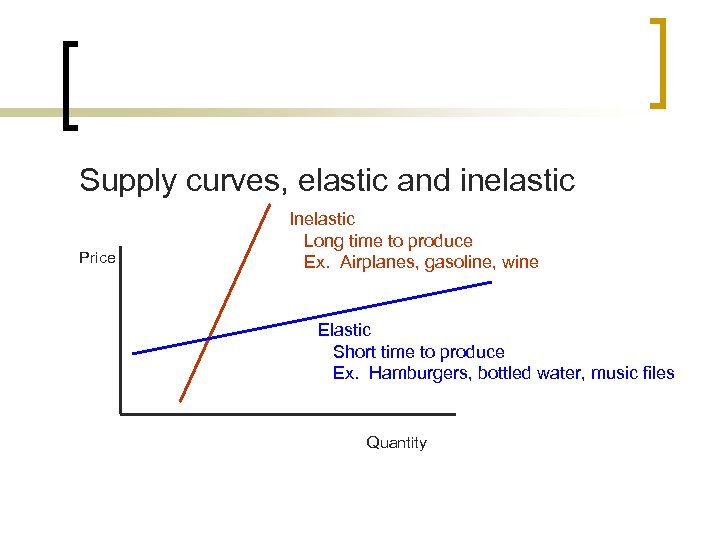 Supply curves, elastic and inelastic Price Inelastic Long time to produce Ex. Airplanes, gasoline, wine Elastic Short time to produce Ex. Hamburgers, bottled water, music files Quantity
Supply curves, elastic and inelastic Price Inelastic Long time to produce Ex. Airplanes, gasoline, wine Elastic Short time to produce Ex. Hamburgers, bottled water, music files Quantity
 Questions on supply 1. What is the law of supply? (a) the lower the price, the larger the quantity supplied (b) the higher the price, the larger the quantity supplied (c) the higher the price, the smaller the quantity supplied (d) the lower the price, the more manufacturers will produce the good 2. What happens when the price of a good down? (a) existing producers will expand some new producers will enter the market (b) some producers will produce less and others will drop out of the market (c) existing firms will continue their usual output but will earn less (d) new firms will enter the market as older ones drop out
Questions on supply 1. What is the law of supply? (a) the lower the price, the larger the quantity supplied (b) the higher the price, the larger the quantity supplied (c) the higher the price, the smaller the quantity supplied (d) the lower the price, the more manufacturers will produce the good 2. What happens when the price of a good down? (a) existing producers will expand some new producers will enter the market (b) some producers will produce less and others will drop out of the market (c) existing firms will continue their usual output but will earn less (d) new firms will enter the market as older ones drop out
 Government Influences on Supply By raising or lowering the cost of producing goods, the government can encourage or discourage an entrepreneur or industry. Subsidies A subsidy is a government payment that supports a business or market. Subsidies cause the supply of a good to increase. Taxes The government can reduce the supply of some goods by placing an excise tax on them. An excise tax is a tax on the production or sale of a good. Regulation occurs when the government steps into a market to affect the price, quantity, or quality of a good. Regulation usually raises costs.
Government Influences on Supply By raising or lowering the cost of producing goods, the government can encourage or discourage an entrepreneur or industry. Subsidies A subsidy is a government payment that supports a business or market. Subsidies cause the supply of a good to increase. Taxes The government can reduce the supply of some goods by placing an excise tax on them. An excise tax is a tax on the production or sale of a good. Regulation occurs when the government steps into a market to affect the price, quantity, or quality of a good. Regulation usually raises costs.
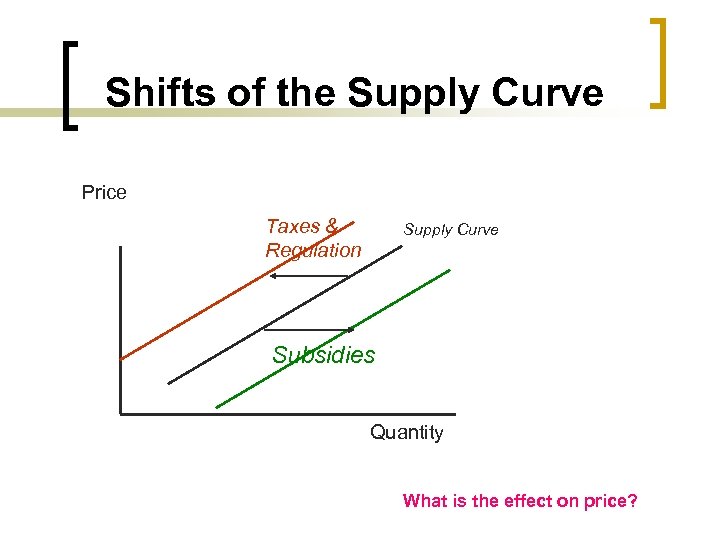 Shifts of the Supply Curve Price Taxes & Regulation Supply Curve Subsidies Quantity What is the effect on price?
Shifts of the Supply Curve Price Taxes & Regulation Supply Curve Subsidies Quantity What is the effect on price?
 Government Influences on Supply EXAMPLES? Subsidies Taxes Regulation
Government Influences on Supply EXAMPLES? Subsidies Taxes Regulation
 Government Influences on Supply EXAMPLES? Subsidies…Electric Cars, College education, “green industries” Taxes…Cigarettes, alcohol, green house gases Regulation…. Cars, Housing OTHERS?
Government Influences on Supply EXAMPLES? Subsidies…Electric Cars, College education, “green industries” Taxes…Cigarettes, alcohol, green house gases Regulation…. Cars, Housing OTHERS?
 THREE MINUTE BREAK http: //www. online-stopwatch. com/bombcountdown/
THREE MINUTE BREAK http: //www. online-stopwatch. com/bombcountdown/
 Supply and Demand Putting Supply and Demand together Take out a piece of paper
Supply and Demand Putting Supply and Demand together Take out a piece of paper
 Supply and Demand Putting Supply and Demand together Price Quantity
Supply and Demand Putting Supply and Demand together Price Quantity
 Supply and Demand Draw a Demand Curve Price Quantity
Supply and Demand Draw a Demand Curve Price Quantity
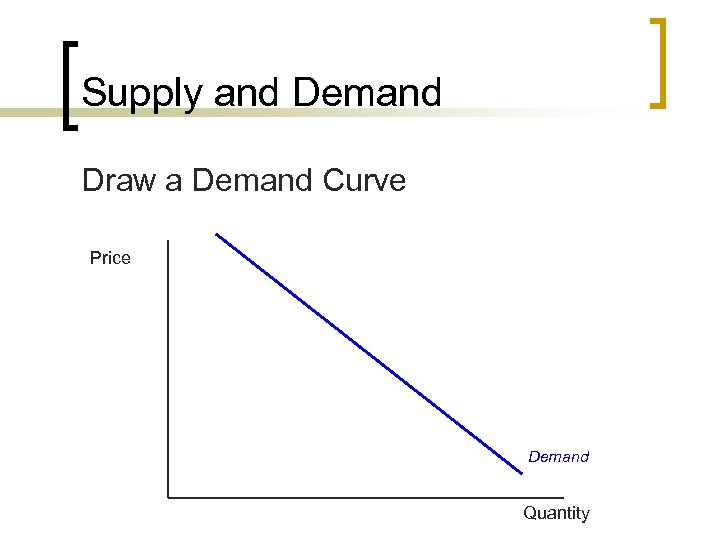 Supply and Demand Draw a Demand Curve Price Demand Quantity
Supply and Demand Draw a Demand Curve Price Demand Quantity
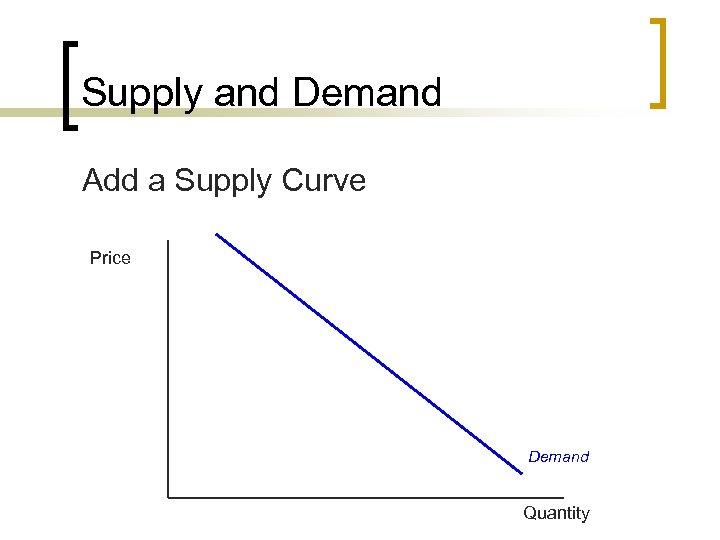 Supply and Demand Add a Supply Curve Price Demand Quantity
Supply and Demand Add a Supply Curve Price Demand Quantity
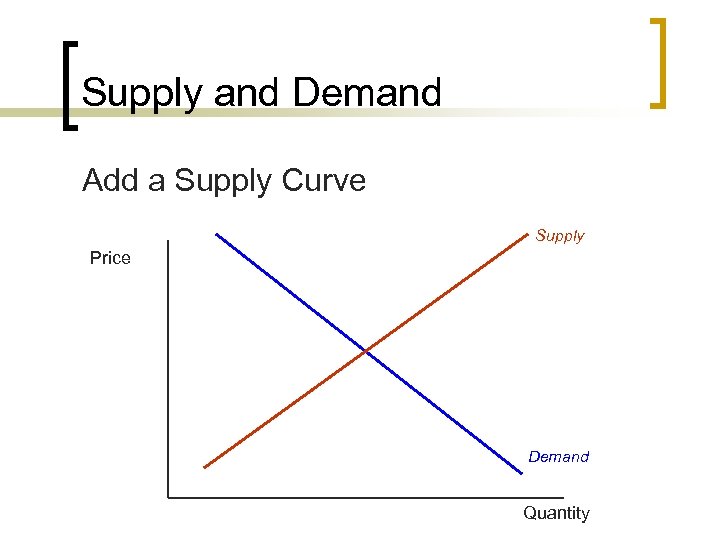 Supply and Demand Add a Supply Curve Supply Price Demand Quantity
Supply and Demand Add a Supply Curve Supply Price Demand Quantity
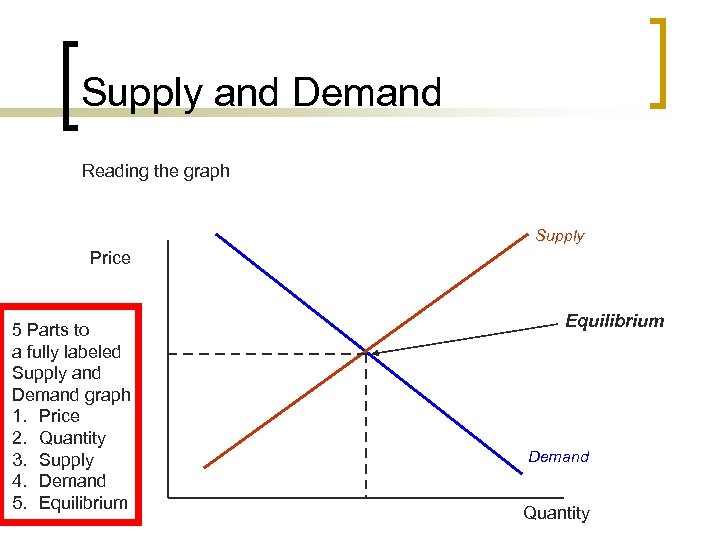 Supply and Demand Reading the graph Supply Price 5 Parts to a fully labeled Supply and Demand graph 1. Price 2. Quantity 3. Supply 4. Demand 5. Equilibrium Demand Quantity
Supply and Demand Reading the graph Supply Price 5 Parts to a fully labeled Supply and Demand graph 1. Price 2. Quantity 3. Supply 4. Demand 5. Equilibrium Demand Quantity
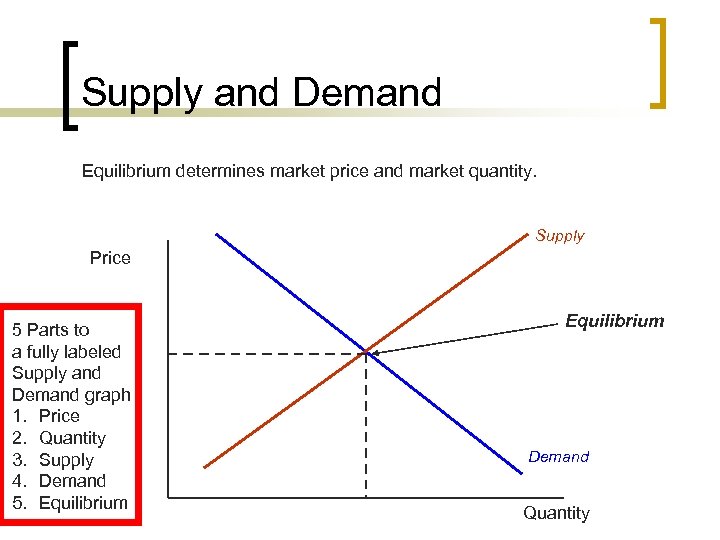 Supply and Demand Equilibrium determines market price and market quantity. Supply Price 5 Parts to a fully labeled Supply and Demand graph 1. Price 2. Quantity 3. Supply 4. Demand 5. Equilibrium Demand Quantity
Supply and Demand Equilibrium determines market price and market quantity. Supply Price 5 Parts to a fully labeled Supply and Demand graph 1. Price 2. Quantity 3. Supply 4. Demand 5. Equilibrium Demand Quantity
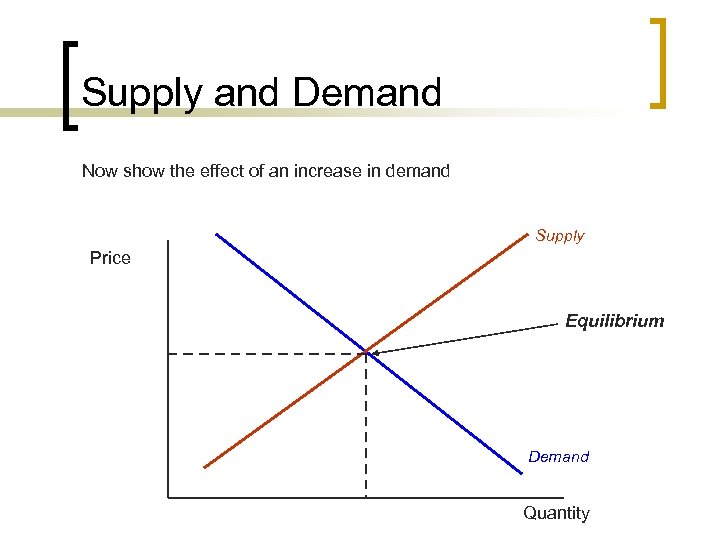 Supply and Demand Now show the effect of an increase in demand Supply Price Equilibrium Demand Quantity
Supply and Demand Now show the effect of an increase in demand Supply Price Equilibrium Demand Quantity
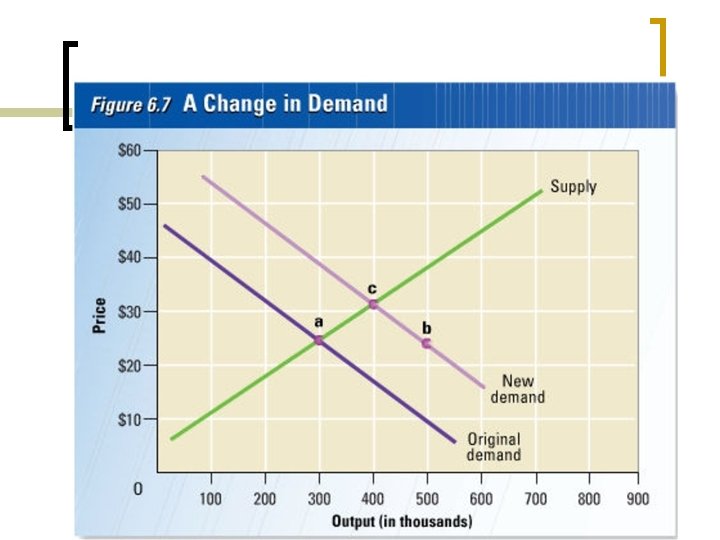
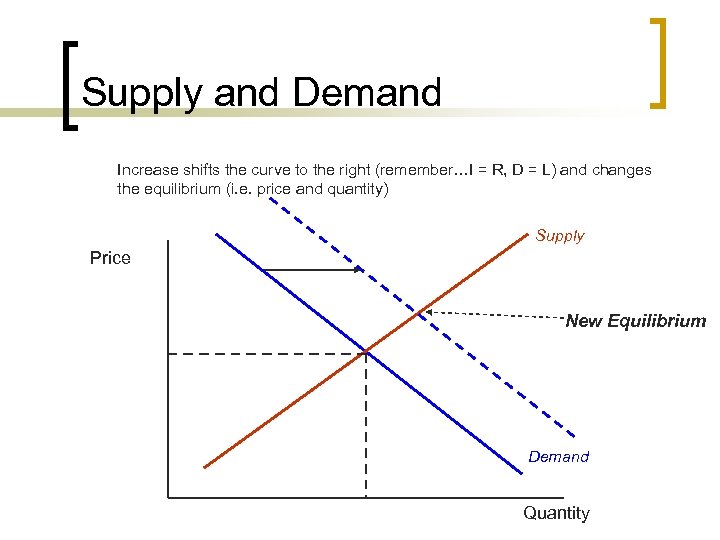 Supply and Demand Increase shifts the curve to the right (remember…I = R, D = L) and changes the equilibrium (i. e. price and quantity) Supply Price New Equilibrium Demand Quantity
Supply and Demand Increase shifts the curve to the right (remember…I = R, D = L) and changes the equilibrium (i. e. price and quantity) Supply Price New Equilibrium Demand Quantity
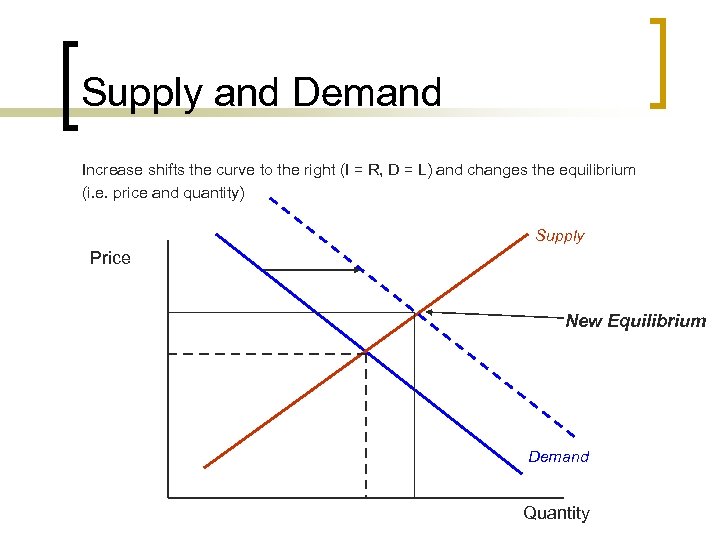 Supply and Demand Increase shifts the curve to the right (I = R, D = L) and changes the equilibrium (i. e. price and quantity) Supply Price New Equilibrium Demand Quantity
Supply and Demand Increase shifts the curve to the right (I = R, D = L) and changes the equilibrium (i. e. price and quantity) Supply Price New Equilibrium Demand Quantity
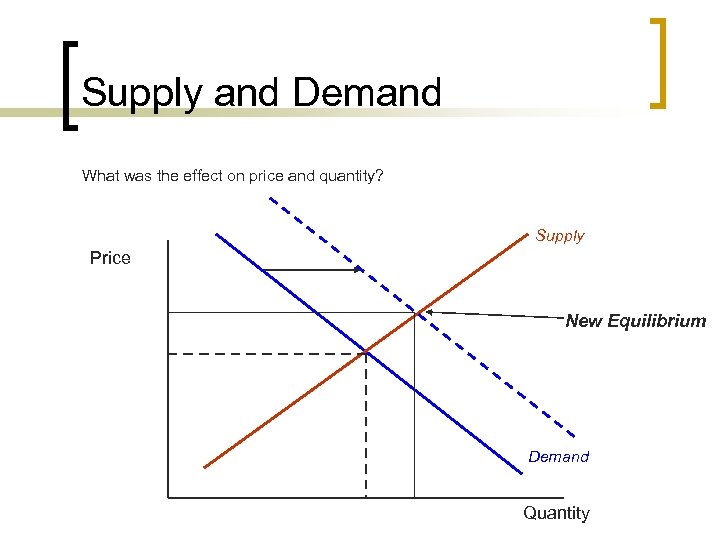 Supply and Demand What was the effect on price and quantity? Supply Price New Equilibrium Demand Quantity
Supply and Demand What was the effect on price and quantity? Supply Price New Equilibrium Demand Quantity
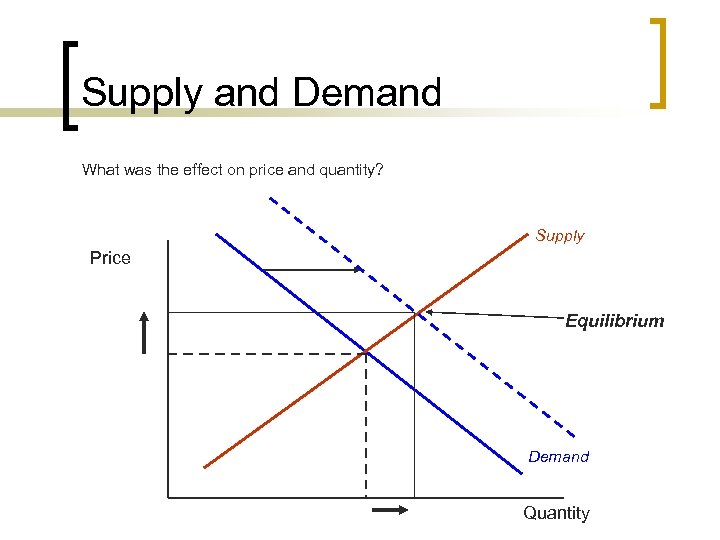 Supply and Demand What was the effect on price and quantity? Supply Price Equilibrium Demand Quantity
Supply and Demand What was the effect on price and quantity? Supply Price Equilibrium Demand Quantity
 Student Video http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=x. GRm. F 8 jd. Atw
Student Video http: //www. youtube. com/watch? v=x. GRm. F 8 jd. Atw
 worksheet
worksheet
 Taxes and subsidies What’s the public benefit that justifies the Government’s action (the tax)? What are the unintended consequences of the Government’s action? What are other alternatives for the Government to achieve the goal?
Taxes and subsidies What’s the public benefit that justifies the Government’s action (the tax)? What are the unintended consequences of the Government’s action? What are other alternatives for the Government to achieve the goal?
 Let’s see if we got it… http: //www. wnyc. org/story/101889 morning-coffee-costs-more/ draw a fully labelled (five parts) supply and demand curve explaining what’s going on
Let’s see if we got it… http: //www. wnyc. org/story/101889 morning-coffee-costs-more/ draw a fully labelled (five parts) supply and demand curve explaining what’s going on
 Supply and Demand Curve
Supply and Demand Curve
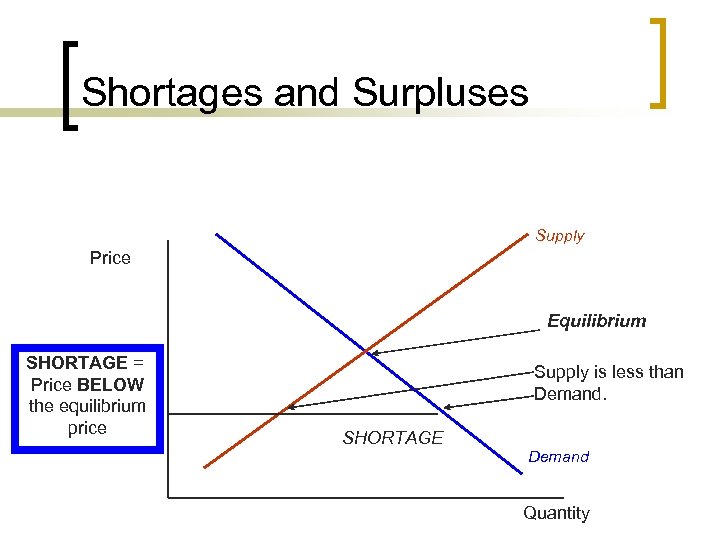 Shortages and Surpluses Supply Price Equilibrium SHORTAGE = Price BELOW the equilibrium price Supply is less than Demand. SHORTAGE Demand Quantity
Shortages and Surpluses Supply Price Equilibrium SHORTAGE = Price BELOW the equilibrium price Supply is less than Demand. SHORTAGE Demand Quantity
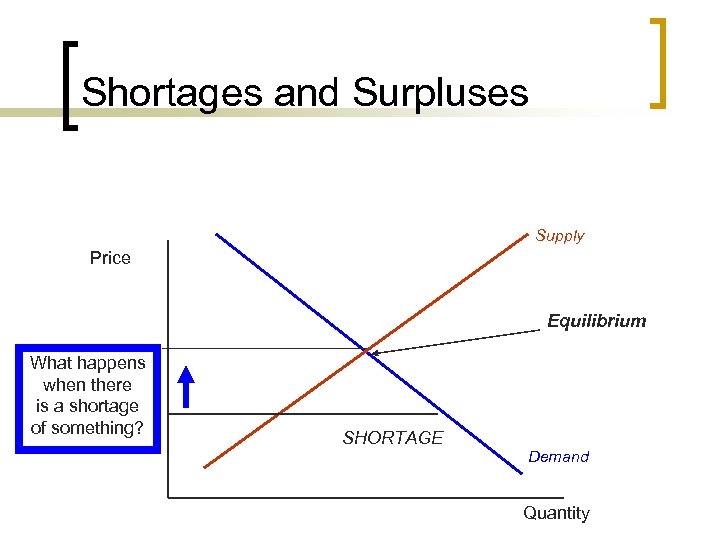 Shortages and Surpluses Supply Price Equilibrium What happens when there is a shortage of something? SHORTAGE Demand Quantity
Shortages and Surpluses Supply Price Equilibrium What happens when there is a shortage of something? SHORTAGE Demand Quantity
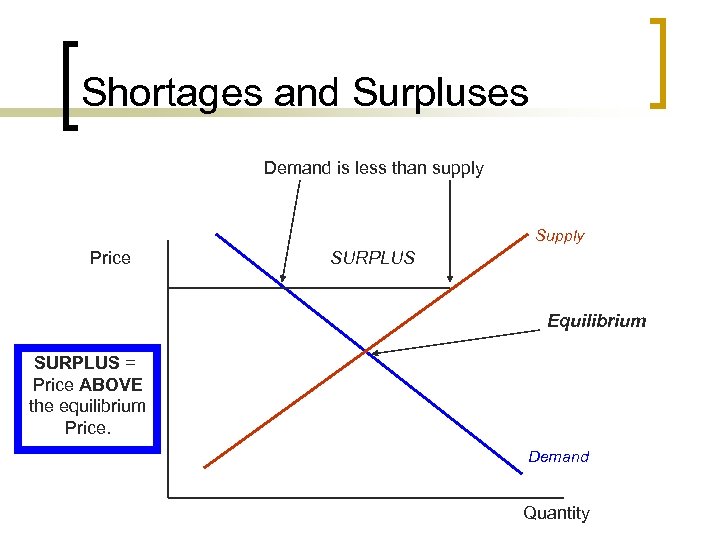 Shortages and Surpluses Demand is less than supply Supply Price SURPLUS Equilibrium SURPLUS = Price ABOVE the equilibrium Price. Demand Quantity
Shortages and Surpluses Demand is less than supply Supply Price SURPLUS Equilibrium SURPLUS = Price ABOVE the equilibrium Price. Demand Quantity
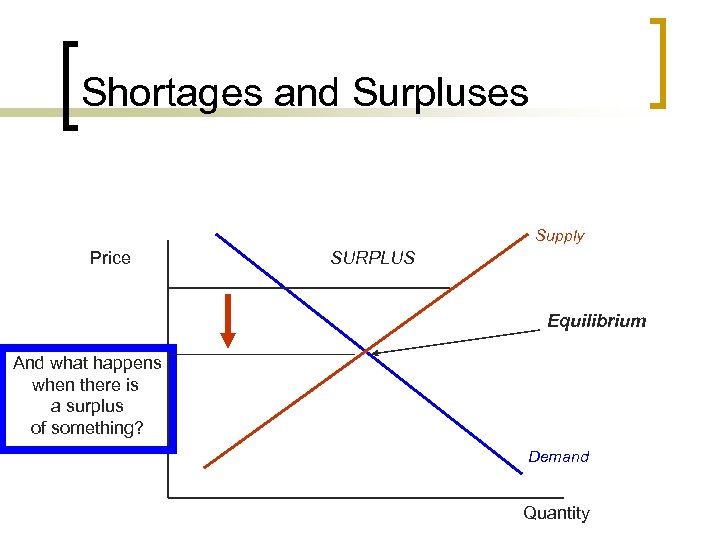 Shortages and Surpluses Supply Price SURPLUS Equilibrium And what happens when there is a surplus of something? Demand Quantity
Shortages and Surpluses Supply Price SURPLUS Equilibrium And what happens when there is a surplus of something? Demand Quantity
 Homework Review Powerpoint for next class (online) Read “Current Reading Assignment” (online) Read Naked Economics, Chapter 1…“Who Feeds Paris? ” Helpful Hint…as you read Chapter One of Naked Economics, ask yourself “How does it relate to Supply and Demand? ”
Homework Review Powerpoint for next class (online) Read “Current Reading Assignment” (online) Read Naked Economics, Chapter 1…“Who Feeds Paris? ” Helpful Hint…as you read Chapter One of Naked Economics, ask yourself “How does it relate to Supply and Demand? ”
 Homework Read Naked Economics, Chapter One Helpful Hint…as you read Chapter One, how does it relate to Supply and Demand?
Homework Read Naked Economics, Chapter One Helpful Hint…as you read Chapter One, how does it relate to Supply and Demand?


